Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Contents
Review
Recent Advancements on Barnyard Millet Starch: A Sustainable Alternative to Conventional Starch
- First Published: 05 March 2024
The Effect of Natural Polysaccharides in Treatment of Diabetic Nephropathy: A Review
- First Published: 19 March 2024
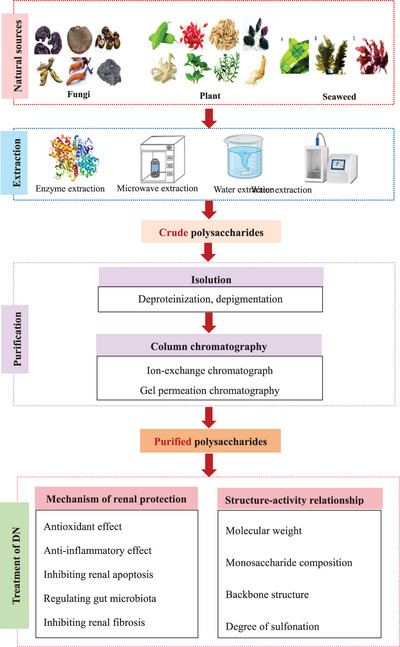
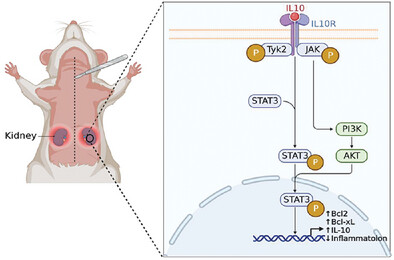
Polysaccharides are extracted from natural plants, fungi and algae by water extraction, ultrasonic extraction, microwave extraction and enzyme extraction, which showed good anti-diabetic nephropathy effect. There is a good structure-activity relationship between structural characteristics (molecular weight, monosaccharide composition, backbone structure, degree of sulfonation) and diabetic nephropathy.
Research Progress on Pharmacological Effects and Mechanism of Polygonatum sibiricum Polysaccharides
- First Published: 24 April 2024
Syntheses, Properties, and Applications of Aminated-Starch: A Review
- First Published: 21 April 2024
Viability of Ecofriendly Ionic Liquids in Starch Plasticization and Modification
- First Published: 21 April 2024
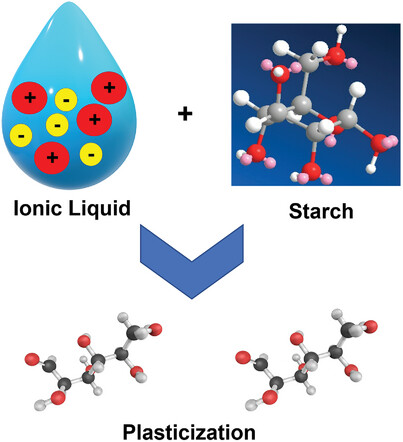
Ionic liquids dissolve starch at lower temperatures without the need for extensive chemical modification, thereby enhancing the solubility and processability of starch. They improve the plasticization efficiency and lead to the creation of biocompatible, biodegradable, and renewable alternatives to traditional plastics and synthetic materials.
Research Article
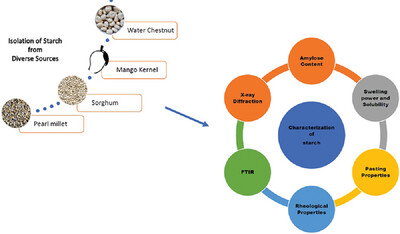
Comprehensive Characterization of Starch from Diverse Sources: Physicochemical, and Functional Properties
- First Published: 01 March 2024
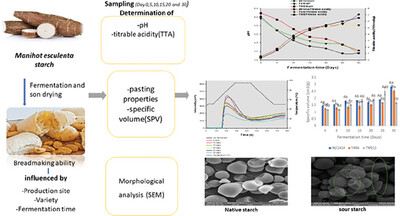
Effect of Fermentation Time and Varietal Difference on the Pasting Properties and Bread-Making Ability of Cassava Starch (Manihot esculenta)
- First Published: 21 March 2024
Impacts of Konjac Glucomannan on the Pasting, Texture, and Rheological Properties of Potato Starch with Different Heat–Moisture Treatments
- First Published: 11 March 2024
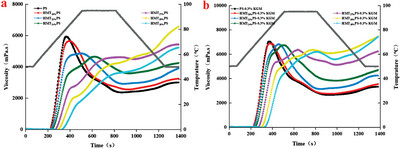
The heat moisture treatment (HMT) results in significant changes in potato starch pasting profiles with decreased peak viscosity and increased final viscosity. The konjac glucomannan addition significantly increases the mixture viscosity, and the impact is more significant with greater change extents on the HMT starches than the original starch.
Calcium Alginate-Sago Starch Particles for Sustained Drug Release: Preparation and In Vitro Characterization
- First Published: 13 March 2024
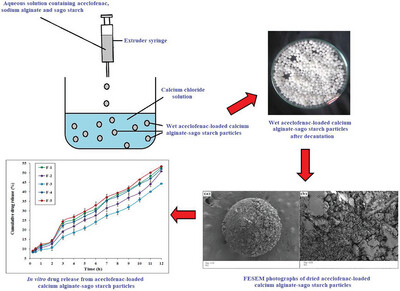
Calcium alginate-sago starch particles are prepared via an ionic gelation process. These particles showed drug encapsulation efficiency of 84.72 ± 1.94% to 94.59 ± 3.53% and sustained In Vitro aceclofenac releasing profile over 12 h. These aceclofenac-loaded particles were characterized by FESEM, FTIR, and P-XRD.
Characterization of Sub-Tropically Adapted Maize Breeding Lines for Loci Governing Kernel Amylose and Resistant Starch
- First Published: 13 March 2024
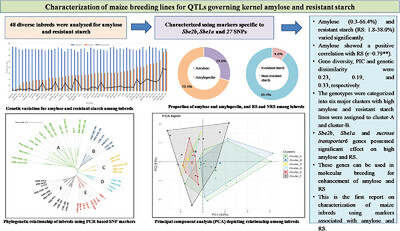
Traditional maize contains low amylose (<35%) and RS (<5%) thus providing less health benefits. Significant variation for amylose (0.3–66.4%) and RS (1.8–38.0%) is observed among 48 inbreds. Sbe2b, Sbe1a, and sucrose transporter6 genes are effective in selection for higher amylose and RS. These genes can be utilized in molecular breeding.
Synthesis and Characterization of Functionalized Starch by Grafting Pyridine for Use in Antimicrobial Applications
- First Published: 09 March 2024
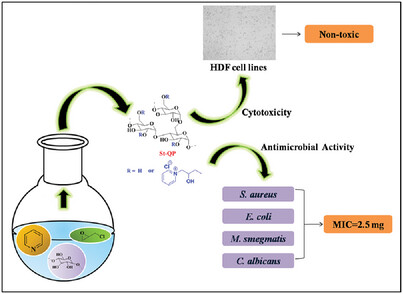
Quaternary pyridine grafted starch (St-QP) is synthesized by a simple one-pot method and their antimicrobial activity is evaluated against four microorganisms. Resulted polymer shows excellent antimicrobial activity and their MIC is found be 2.5 mg. In addition, St-QP coated cotton fabric shows good antimicrobial activity and durability.
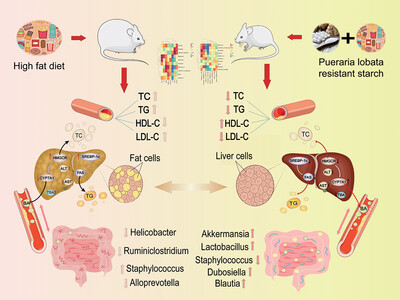
Pueraria lobata Resistant Starch Regulating Lipid Metabolism and Gut Microbiota in High-Fat Diet Mice
- First Published: 15 March 2024
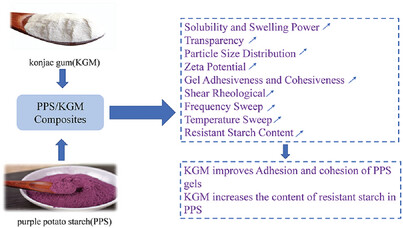
Effects of Konjac Gum on Physicochemical, Rheological, Textural Properties, and In Vitro Digestibility of Purple Potato Starch
- First Published: 19 April 2024
Transformations in Properties of Indian Barnyard Millet Starch as Induced by Ultra-Sonication and Gamma Irradiation
- First Published: 15 March 2024
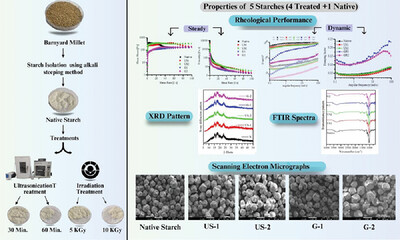
Starch from barnyard millet is effectively modified using ultrasound and gamma irradiation. Rheological, thermal, and micro-structural attributes of starch are studied. The starches exhibit a greater value for storage modulus (G′) as compared to loss modulus (G″), as revealed by their dynamic rheological studies. Thermal attributes indicate an increment in T0, Tp, and Tc for both the modified starches.
Ternary Blend of Chitosan/Polyvinyl Alcohol/Carboxymethylcellulose as an Efficient System for the Release Studies of Metformin Hydrochloride
- First Published: 13 March 2024
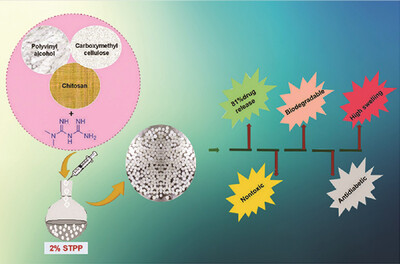
The release of metformin from the ternary blend of chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol, and carboxymethylcellulose is discussed in the study. The antidiabetic activity of the developed beads is assessed. The hydrogel beads made of chitosan/polyvinyl alcohol/carboxymethylcellulose are an excellent vehicle for the antidiabetic drug metformin.
Optimization of Microwave Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polysaccharides from Malus hupehensis and Evaluation Its Antioxidant Activity
- First Published: 15 March 2024
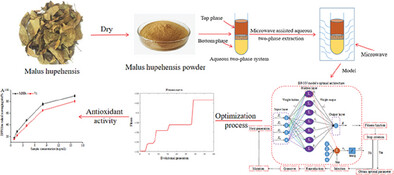
Malus hupehensis contains various active components including polysaccharides, polyphenols, vitamin, phenolic acid, etc. The main purpose of this paper is optimized the microwave assisted aqueous two-phase extraction (MATPE) polysaccharides from M. hupehensis via back propagation neural network coupled genetic algorithm and then evaluated its antioxidant activity through free radicals scavenging experiments.
Effect of Soy Protein Isolate on Pasting, Rheological, and Textural Attributes of Potato Starch
- First Published: 18 March 2024
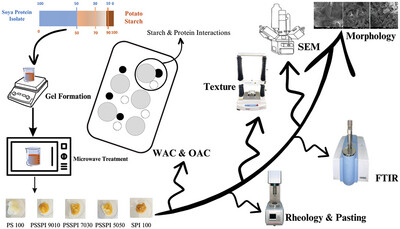
Incorporation soy protein isolate (SPI) at different concentration significantly affects the functional, pasting, rheological, textural, and microstructural properties of potato starch (PS). Peak, final, breakdown and setback viscosity, hardness, springiness, cohesiveness of PS-SPI composite gel decrease with increase in SPI concentration. SPI leads to formation of less compact structure in potato starch.
Physicochemical, Rheological Properties, and In-Vitro Starch Digestibility of Flours and Starches from Pigeon Pea, Cowpea, Pinto Bean, and Navy Bean
- First Published: 13 March 2024
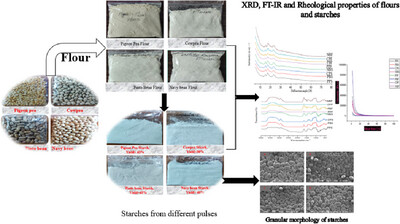
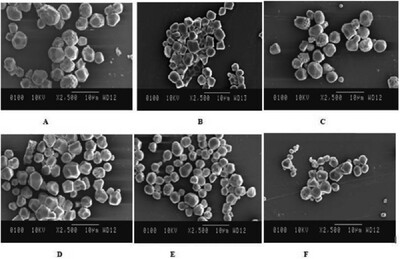
Properties of flours and starches from four different pulses are studied. Significant differences are observed in the properties of flours and starches for the same pulse. Differences are also observed between the different types of pulses. SEM micrographs show smooth granular surfaces with no cracks or holes for all starches. The resistant starch content of starches is higher, but the slowly digestible starch content is lower than that of flours.
Effect of Starch Binders on the Properties of Bioglass Tablets for Bone Tissue Engineering Applications
- First Published: 26 April 2024

The SiO2–CaO–P2O5–Na2O nanofiber bioglass tablets are synthesized using cellulose nanofibers as template and sago starch and xanthan gum as binders. Bindered tablets have higher Ca/P ratio and better hydroxyapatite formation. The tablets produced showed antibacterial properties against Staphylococcus areus and E coli. Different type of binders produced bioactive glass of different crystal structures.
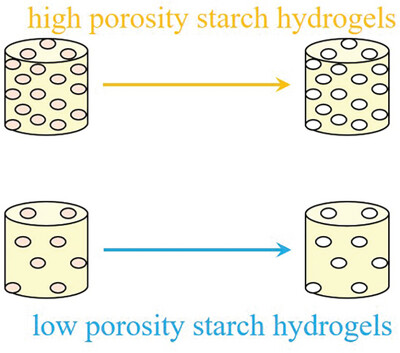
Controlling the Porosity of Starch Hydrogels with Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) (PMMA) Beads
- First Published: 29 March 2024
Effects of Dual Modification of HMT and Cross Linking on Morphological, Thermal, Digestibility, and Structural Properties of Wild Tuber (Amorphophallus abyssinicus) Starch
- First Published: 03 April 2024
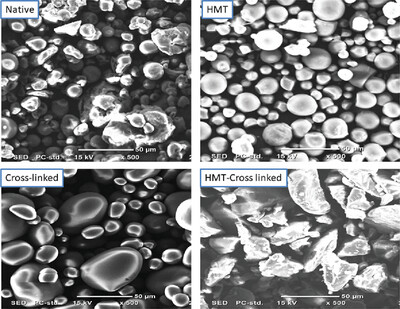
There are few research findings conducted to investigate the modification of Bagana tuber (Amorphophallus abyssinicus) starch through dual modification methods. The research finding reveals that modification improves thermal and digestibility properties of starches which are advantageous for wider industrial applications. SEM images of native, HMT treated, CL, and dual modified (HMT–CL) bagana starch at 500× magnification.
Preparation and Application of Zwitterion Modified Starch Catalyzed by HRP-ACAC Binary System
- First Published: 22 March 2024
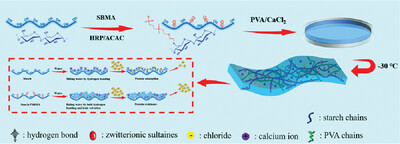
The HRP/ACAC binary enzyme system is first used to catalyze the amphoteric monomer [2-(methylpropenoxy) ethyl] dimethyl -(3-sulfopropyl) grafting of starch. While maintaining the original properties of starch, the hydrophobicity, antibacterial properties, and anti-protein adsorption properties are improved.
Characterization of Physicochemical Properties of Annealed Corn Flour and Starch: A Verification of Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 29 March 2024
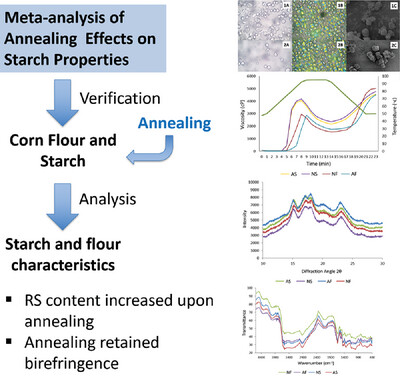
This study reports the properties of corn flour and starch upon annealing treatment, as a verification of meta-analysis. Annealing improves RS yield in corn flour and starch. It also changes their pasting properties, while still retaining their birefringence and type of crystallinity, but alters the regions of amorphous and crystalline.
Ultrasound Assisted Aqueous Two-Phase Extraction of Polysaccharides from Ophiopogon japonicus: Process Optimization, Structure Characterization, and Antioxidant Activity
- First Published: 22 March 2024
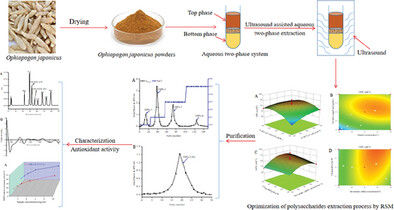
Ultrasound assisted aqueous two-phase extraction (UATPE) is used to extract polysaccharides from Ophiopogon japonicus, optimizes its process by response surface methodology, and then purifies the crude polysaccharides by different column chromatography to obtain a homogenous fraction (OJPs-2-SG), characterizes its structure, and evaluates its antioxidant activity.
Preparation of Starch Coconut Fatty Acid Inclusion Complexes by Twin-Screw Extrusion
- First Published: 01 April 2024
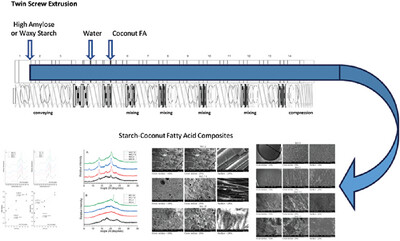
Starch and coconut fatty acids can be processed in an extruder at high solids content produce solid starch–coconut fatty acid composites. Composites prepared using high amylose starch contain 61 V amylose inclusion complexes while waxy starch composites only entrap the fatty acids within a starch matrix and can be used as a carrier for coconut fatty acids.
Structure and Physicochemical Properties of Resistant Starch III with Different Milling Methods
- First Published: 29 March 2024
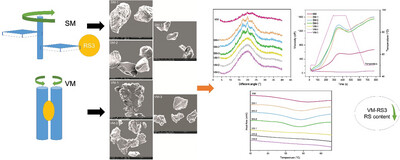
The purpose of this study is to investigate the structural properties, physical properties, and in vitro digestibility of RS3 induced by shear milling (SM) and vibration milling (VM). VM destroys the crystal structure and VM-RS3 is not detected gelatinization properties, and the hydration properties are smaller than SM.
Spray-Drying Assisted 3D Printing to Manufacture Beef Products
- First Published: 29 March 2024
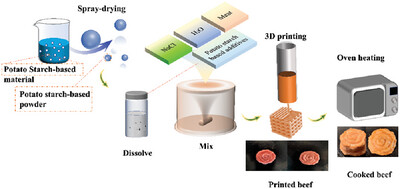
The addition of spray dried powders improves printing accuracy, freeze-thaw stability, moisture content, cooking yield, lightness, and reduced diameter reduction, redness, hardness, cohesiveness, and chewiness. Moreover, the results suggest that P-N, can be classified as potential level 6 diets (soft and bite-sized) according to the IDDSI framework.
Preparation of Multi-Grain Flour with High Content of Resistant Starch and the Mechanism Underlying the Improved Digestion Resistance
- First Published: 28 March 2024
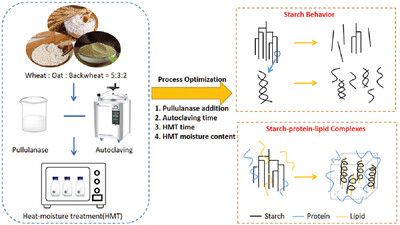
Pullulanase and heat–moisture treatment increase the resistant starch in multi-grain flour. The treatment induces recrystallization of short-chain starch fragments in flour and promotes the formation of starch–protein/lipid complexes in flour. Starch recrystallization and molecular interactions increase digestion resistance.
Physicochemical and Morphological Properties of Litchi Seed Starch Oxidized by Different Levels of Sodium Hypochlorite
- First Published: 04 April 2024

A non-conventional litchi seed starch was extracted and modification was done using sodium hypochlorite (NaOCl) as an oxidizing agent. The effect of the oxidation on the properties of the litchi seed starch was investigated. The carbonyl and carboxyl content of the oxidized starches increased with increase in the concentration of NaOCl. Furthermore, amylose content was reduced and Water and oil absorption capacities, paste clarity, solubility and relative crystallinity improved significantly. Surface erosion was observed at higher NaOCl concentrations and differences were observed in FTIR spectroscopy of the native and oxidized litchi seed starches.
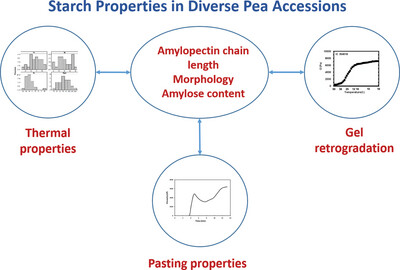
Characterization of Starch Properties in Diverse Pea Accessions: Structural, Morphological, Thermal, Pasting, and Retrogradation Analysis
- First Published: 04 April 2024
The Effects of D-Allulose on the Gelatinization and Recrystallization Properties of Starches from Different Botanical Sources
- First Published: 03 April 2024
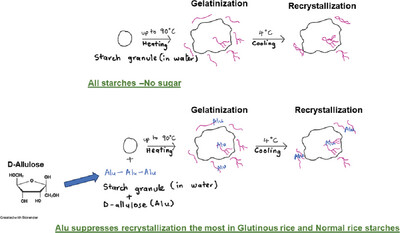
When D-allulose (Alu) is gelatinized with potato, wheat, tapioca, corn, normal rice, and glutinous rice starches, Alu does not significantly increase the gelatinization temperatures of the starches. However, upon cooling and storage at 4 °C, Alu significantly suppresses recrystallization of glutinous rice and normal rice starches.
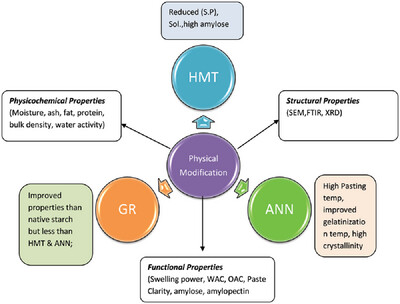
Effect of Heat Moisture Treatment, Annealing, and Gelatinization-Retrogradation Modifications on Physico-Chemical, Functional, and Structural Properties of Starch from Elephant Foot Yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius)
- First Published: 04 April 2024
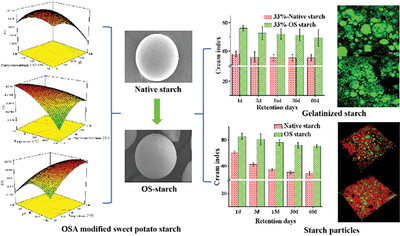
Comparative Study on the Emulsification of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride Modified Sweet Potato Starch: As Macromolecular and Particulate Stabilizers
- First Published: 06 April 2024
Characterization and Drug Release Properties of Curcumin Loaded Native and Nano-Sized Starches of Pigeon Pea (Cajanus cajan) and Bambara Nut (Vigna subterranean)
- First Published: 05 April 2024

Starch nanoparticles of Bambara nut and pigeon pea starches are prepared by nanoprecipitation. Physicochemical and material properties improve with nanoparticles fabrication. There is an improvement in drug release of curcumin due to the use of the starches and starch nanoparticles as carriers for the delivery of the drug.
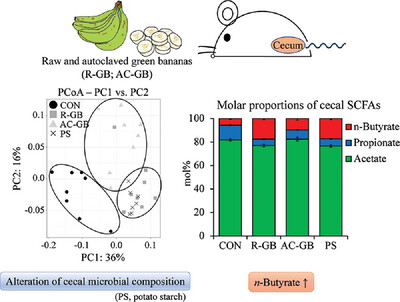
Effect of Raw and Cooked Green Bananas on Cecal Fermentation Characteristics in Rats
- First Published: 12 April 2024
Ultrafine Starch Particles as Pickering Emulsion Stabilizers With Different Interfacial Behaviors
- First Published: 27 April 2024
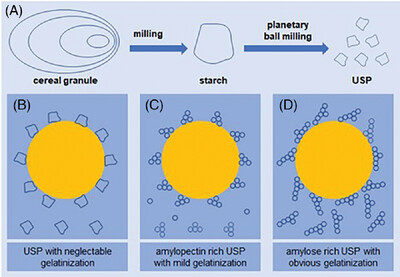
Ultrafine starch particles (USPs) have better emulsifying ability, due to reduced particle size and glutinous USP has the best emulsion stability due to higher emulsion height and no oil phase separation. USP behaves differently at interface and in water phase, due to swelling, crystalline disruption, and gelatinization.
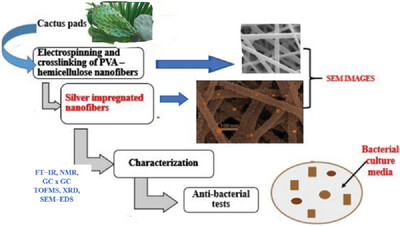
Hemicellulose-Based Nanofibers Decorated In Situ with Silver Nanoparticles for Antibacterial Applications
- First Published: 21 April 2024
Evaluating the Impact of Inulin Addition before Solar Drying on the Characteristics of Sour Cassava Starch as a Food Ingredient
- First Published: 19 April 2024
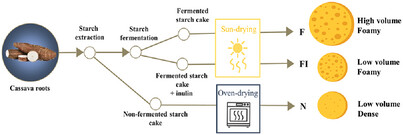
The expansion of sour cassava starch during baking depends on the sun-drying step. Adding inulin before sun-drying reduces starch oxidation. Inulin is oxidized and formed a coating around the granules, which reduces their water absorption. Snacks made from inulin-added starch show lower expansion during baking than those from sour cassava starch, but exhibit a foamy structure similar to the latter.