Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Masthead
Contents
Research Article
Optimization of Synthesis of Cassava Starch Phosphates by Response Surface Methodology and Characterization of the Modified Starches
- First Published: 06 February 2024
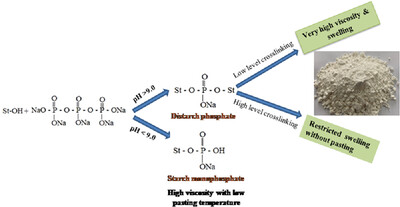
Reaction of cassava starch with sodium tripolyphosphate/sodium trimetaphosphate at different concentrations and pH results in monostarch phosphate or crosslinked distarch phosphates, depending on the reaction conditions used. At lower levels of crosslinking, modified starches with remarkably high paste viscosity and swelling power are formed, whereas at the higher levels of crosslinking, thermostable starch phosphates with restricted swelling and non-pasting properties are obtained.
Lily Polysaccharide Nano-Selenium Promotes A549 Cells Apoptosis through Cell Cycle Inhibition
- First Published: 08 March 2024
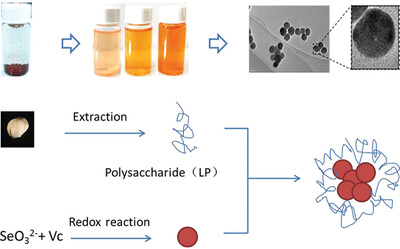
The polysaccharide extracted from Lanzhou Lily has the function of dispering and stabilizing nano-selenium, which is prepared by sodium selenite and vitamin C through REDOX reaction. The nano-selenium prepared by Lanzhou Lily polysaccharide is a uniform and stable solution. It is also proved that nano-selenium polysaccharide could inhibit the cell cycle of A549 and promete its apoptosis.
Preparation of 1,3-Diglyceride Microcapsules with Low Glycemic Index
- First Published: 19 March 2024
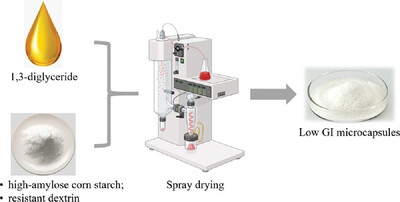
This research used high-amylose corn starch and resistant dextrina as wall material, making the microcapsules are low GI product that suit for diabetic patients. They used 1,3-diglyceride as core material, so that the prepared microcapsules are friendly to obese people and other patients with metabolic diseases.
Determination of Physicochemical and Functional Properties of Cross-Linked, Hydroxypropylated, and Dual Modified Corn Starch and Investigation of Its Use as Gelling Agent in Soft Confectionery
- First Published: 12 August 2023
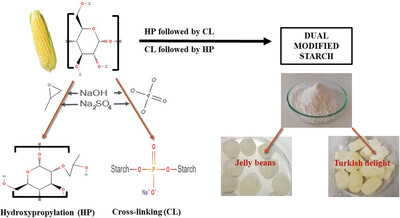
Dual-modified corn starches are prepared by hydroxypropylation and cross-linking and they result in more favorable properties than single-modified ones. Gelatinization and retrogradation properties of dual modified starches are affected by the reaction sequence. Cross-linking of hydroxypropylated starch results in non-retrograde and low viscosity profile. First hydroxypropylated then cross-linked starch is promising thickening agent as gelatin substitute for jelly confectionaries.
Starch/Wood Powder/Glycerol/Lemongrass Essential Oil Composite as Hydro-Degradable Materials for 3D Printing
- First Published: 05 April 2024
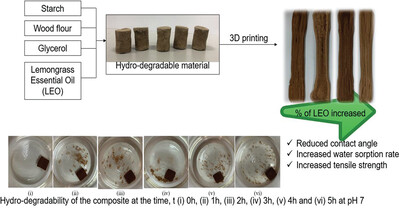
This study explores the use of hydro-degradable starch-based composite for 3D printing, aiming to address the issue of global microplastic pollution. Incorporating lemongrass essential oil (LEO) as an additive enhances the strength of the composite by 55%. The resulting material exhibits good hydro-degradability and printability, making it suitable for real-life applications such as photo frames and souvenirs.
Review
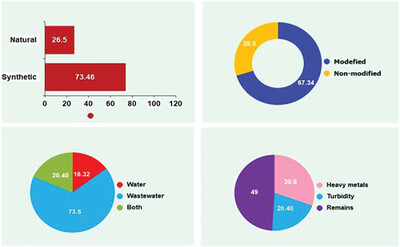
Starch-Based Materials as a Natural Compound's Application in Water and Wastewater Treatment: A Systematic Review
- First Published: 13 February 2024
Research Article
Comparative Study of the Performances of Octenyl Succinic Anhydride-Modified Agriophyllum squarrosum and Quinoa Starches to Stabilize Pickering Emulsions
- First Published: 01 March 2024
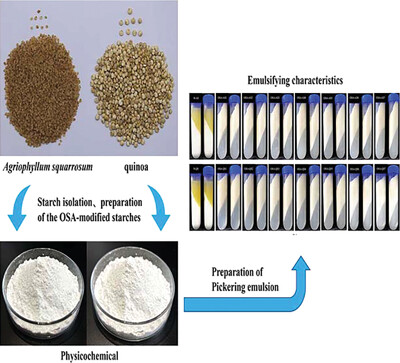
OSA-modified Agriophyllum squarrosum and quinoa very small particle starches are prepared in this study. Compared with OSA-modified quinoa starch, which has been extensively studied, OSA-modified A. squarrosum starch also effectively stabilizes Pickering emulsions and is a potential unstudied starch-based Pickering emulsion stabilizer.
Biocompatible Polysaccharide-Based Wound Dressing Comprising Cellulose Fabric Treated with Gum Tragacanth, Alginate, Bacterial Cellulose, and Chamomile Extracts
- First Published: 24 January 2024
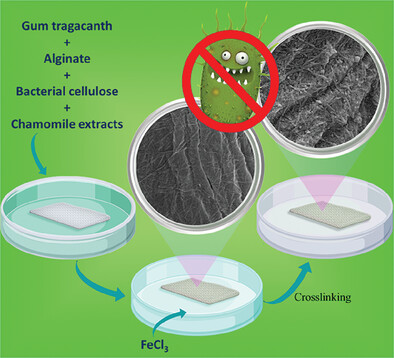
A novel wound dressing with both effective and efficient by combining chamomile and alginate medicinal plants is developed to produce a humid environment owing to the hydrogel nature of the wound dressing. The optimal sample, which contains 0.5 w% gum tragacanth, 0.5 w% alginate, and 0.5 w% bacterial cellulose, has the best antibacterial features while being biocompatible.
Interactions of Native Maize Starch Components with Pectin Using Extrusion
- First Published: 24 January 2024
Starch Gelatinization Behavior: The Impact of Granular Structure
- First Published: 24 January 2024
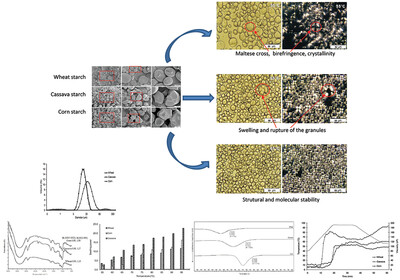
Starches characterization reveals the influence of botanical origin, reflecting the complexity of the molecular and granular structure. Viscosity curves show different gelatinization temperatures to starches from cereal and tuber, with loss of birefringence, swelling and granular rupture are proven by optical microscopy.
Genetic Analysis of Accumulation of Amylose and Resistant Starch in Subtropical Maize Hybrids
- First Published: 08 February 2024
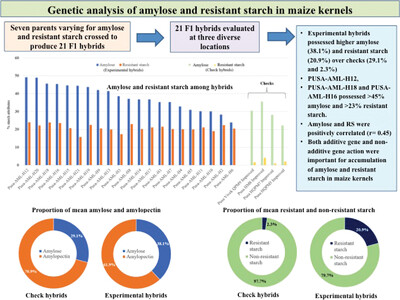
Amylose (22.2%–49.1%) and resistant-starch (RS: 1.02%–23.9%) showed wide-variation. Improved hybrids possessed higher amylose (38.1%) and RS (20.9%) over checks (amylose: 29.1%, RS: 2.3%). PUSA-AML-H12, PUSA-AML-H18, and PUSA-AML-H16 with >45.0% amylose and >23.0% RS are the most promising hybrids. Amylose and RS show positive-correlation (r = 0.45). Both additive and nonadditive variances govern their accumulation.
Effects of the Ethanolic Extract of Onion Peel on the Physicochemical Properties of Wheat Starch
- First Published: 11 March 2024
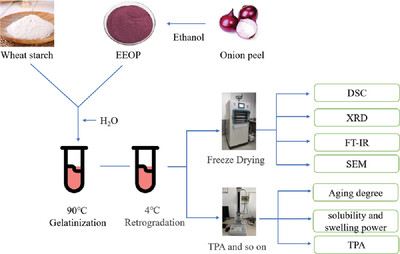
This study is to investigate the interactions between wheat starch (WS) and ethanol extract of onion peel (EEOP) at different concentrations (1.0%, 2.5%, 5.0%, and 10.0%) during gelatinization, as well as the effects of these interactions on the physicochemical and retrogradation properties of wheat starch.
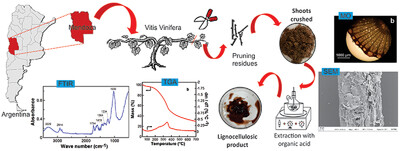
Physicochemical Characterization of Vitis vinifera Pruning Shots from Mendoza, Argentina: Extraction of Lignocellulosic Products
- First Published: 06 February 2024
Enhancing the Formulation of Chemically Modified Starch Bionanoparticles Through Ultrasonic Assisted Emulsification: A Parameter Study
- First Published: 24 January 2024
Minimizing the Health Issues by Potentiating the Sweetness of Sugars Through Mid-Infrared Application
- First Published: 14 February 2024
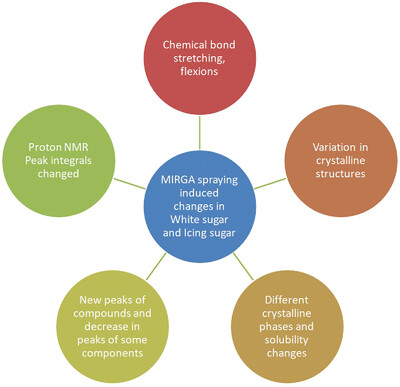
White sugar and icing sugars are commonly used food ingredients and are the underlying cause for many chronic diseases. Mid-infrared in 2–6 µm wavelength range applied in the form of a spray using mid-infrared spraying atomizer (MIRGA) has increased the sweetness of sugars. Various instrumentations have proven the mid-infrared induced changes in the components of sugar at molecular and chemical bond level. Increasing the sweetness leads to 15%–30% reduction of the usual sugar quantity requirement.
Effect of Simultaneous Ultrasonication and Protease Treatment on Wet Milling of High-Amylose Corn
- First Published: 22 March 2024
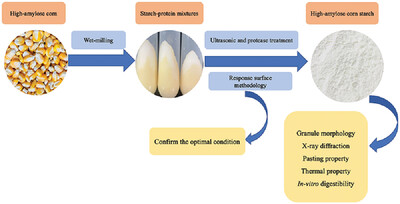
Wet milling of high-amylose corn with simultaneous ultrasonication and protease treatment increases the starch yield and decreases the starch protein content without changing the starch properties. This study provides important technical data for scaling up simultaneous ultrasonication and protease treatment to industrial scale with minor modifications of the conventional wet-milling process.
Nanostructured Composite of Starch/Silica Hybrid Decorated with Titanium Oxide Nanoparticles for Photocatalytic, Sonocatalytic, and Sonophotocatalytic
- First Published: 06 February 2024
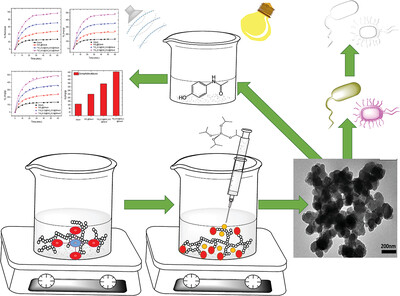
Nanocomposite (TiO2(x)@SiO2(x)@Starch) is synthesized using a sol-gel method. The degradation of paracetamol is investigated in the presence of nanocomposites. The sonophotocatalysis, photocatalysis and sonocatalysis systems separately use. Sonophotocatalysis is more excellent than photocatalysis and sonocatalysis processes. Nanocomposite has antimicrobial activity that increased parallel with the TiO2 percent. TiO2(0.8)@SiO2(0.2)@Starch nanocomposite shown a broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity.
Potential of Hydroxypropylated Corn and Sorghum Starch Extrudates as Simultaneous Fat and Casein Mimetics in Analogue Mozzarella Cheese: Insights from Functional, Rheological, Textural, and Sensory Analysis
- First Published: 02 February 2024
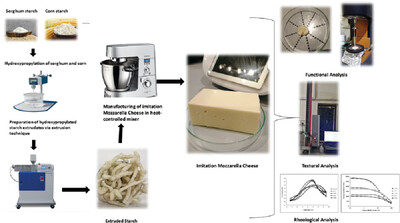
Native and HEx permit instantaneous replacement of casein by 15% and fat by 10% in analogue mozzarella cheese. Incorporation of native and HEx improves the melt and stretch of the analogue mozzarella cheese. Cheese made from HEx exhibits a softer and more elastic texture than native extrudates and control counterparts.
Review
Unveiling the Benefits of Resistant Starch in Legumes: Overview of Current and Future Prospective
- First Published: 05 March 2024
Incorporating legumes into one's daily meals presents a promising strategy for boosting resistant starch consumption and leveraging its potential health-enhancing properties. This review provides a concise overview of resistant starch and the latest developments in controlling the starch biosynthesis pathway by employing RNA interference (RNAi) and CRISPR/Cas9 technologies.
Vinyl Polymers as Key Materials in Contact Lens Design: A Review of Progress and Future Directions
- First Published: 01 March 2024

This review article explores the role of vinyl polymers in the development of contact lenses, shedding light on their unique properties and applications. By summarizing the progress made and outlining future directions, it aims to showcase how vinyl polymers are shaping the future of comfortable and effective vision correction.
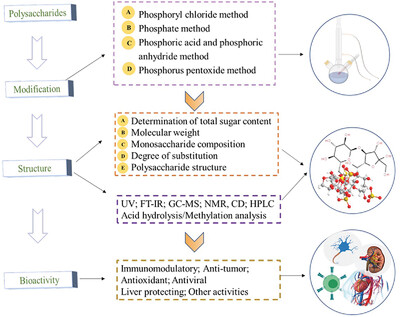
Modification, Structure Identification, and Biological Activities of Phosphorylated Polysaccharides: A Review
- First Published: 05 February 2024
Research Article
Effect of Particle Diameter on Water Sorption by Rice Grains
- First Published: 01 March 2024
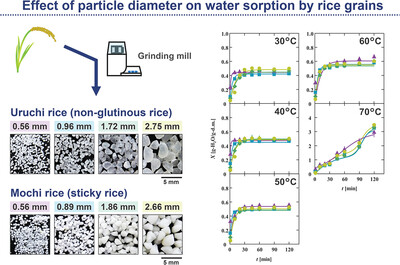
Water sorption of non-glutinous Uruchi and sticky Mochi rice grains of different diameters is kinetically analyzed using linear driving force and autocatalytic models. Water–sorption curves are classified into two types based on their shape and according to the state of rice grains below and above the gelatinization temperature.
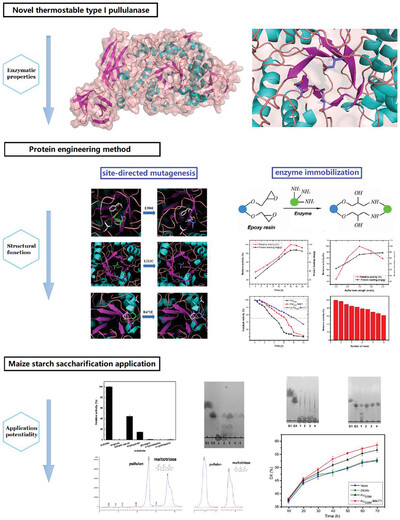
Protein Engineering of Novel Thermostable Pullulanase from Geobacillus stearothermophilus and Starch Saccharification Application
- First Published: 05 April 2024
Review
Exploring the Efficacy of Polysaccharides as Green Corrosion Inhibitors: A Comprehensive Review
- First Published: 06 February 2024
Corrosion remains a pervasive challenge across industries, prompting the exploration of sustainable corrosion prevention strategies. This comprehensive review delves into the world of polysaccharides as green corrosion inhibitors. Natural, biodegradable, and eco-friendly, polysaccharides offer multifaceted protection against material degradation. The study investigates their inhibitive mechanisms, practical applications, and the comparative advantages they hold over traditional inhibitors. Challenges and emerging trends are explored, paving the way for a sustainable future in corrosion prevention. Join us on a journey to explore the efficacy of polysaccharides as eco-conscious guardians against corrosion.
Research Article
Influence of Heat Moisture, Ultrasonication, and Gamma Irradiation on Pasting, Thermal, Morphological, and Physicochemical Properties of Indian Teff (Eragrostis tef) Starch
- First Published: 25 February 2024
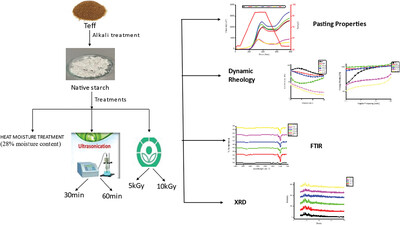
Effect of Heat moisture treatment, Ultrasonication (US) and Gamma Irradiation on Indian Teff starch is studied. US provided high swelling power to Teff starch. Viscosity, Dynamic and thermal attributes are affected by modifications. No significant differences are observed in Morphology and X-ray diffraction patterns compared with native.
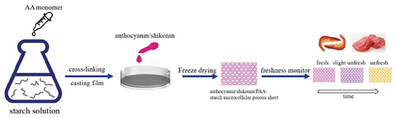
Cross-Linking Interpenetration Polyacrylic Acid-Starch Porous Sheet Combined with Anthocyanin and Shikonin for Freshness Monitoring
- First Published: 12 March 2024
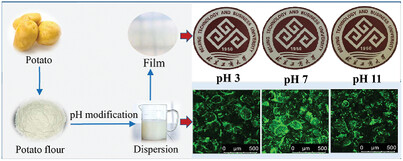
Effect of pH on the Properties of Potato Flour Film-Forming Dispersions and the Resulting Films
- First Published: 24 January 2024
Ultrasound Effect on the Hydrogen Peroxide Oxidation of Corn Starch, Molecular Structure, and Functional Properties of Obtained Starch Derivatives
- First Published: 01 March 2024
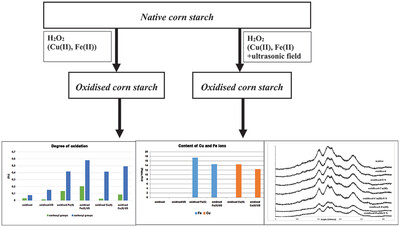
The ultrasonic field influences on effectiveness oxidation starch. The ultrasonic influences on catalysts mobility during oxidation of starch. Structural and functional properties of oxidized starch are related with ultrasonic. Oxidized starch can be used in industries as thickeners and as carriers of metal ions.
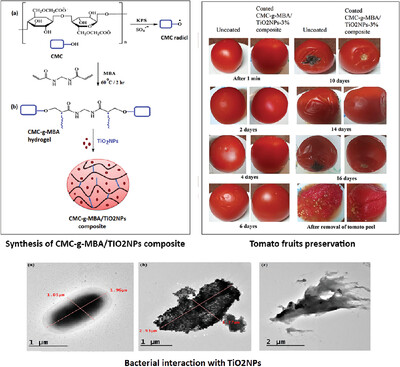
Synthesis of Novel Antimicrobial and Food-Preserving Hydrogel Nanocomposite Films Based on Carboxymethylcellulose
- First Published: 13 February 2024
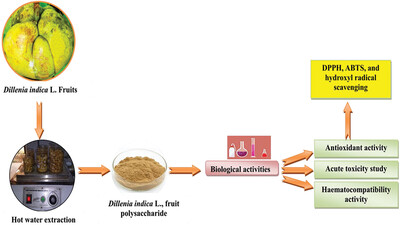
Extraction, Characterization, Biocompatibility, and Antioxidant Activity of Dillenia Indica L. Fruit Polysaccharide
- First Published: 19 February 2024
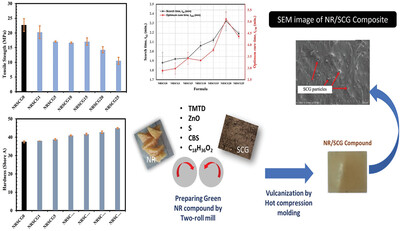
Enhancing Natural Rubber Composites with Spent Coffee Ground: Physical Properties, Odor Absorption, and Processing
- First Published: 14 February 2024