Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITOR’S PICKS
COMMENTARY
Darier disease: Golden era of discovery and global collaborations
- Pages: 883-884
- First Published: 25 April 2025
Topical minocycline foam: A new option for acne treatment?
- Pages: 885-886
- First Published: 25 April 2025
Interdisciplinary care in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases with skin manifestations within the WHO's people-centred healthcare framework
- Pages: 887-888
- First Published: 25 April 2025
Clonal disorders of clinical significance. A concept with important therapeutic implications
- Pages: 891-892
- First Published: 25 April 2025
Epidermolytic ichthyosis: New insights and ongoing challenges
- Pages: 893-894
- First Published: 25 April 2025
Er:YAG laser ablation: Possibly a valuable tool in the management of refractory Hailey–Hailey disease
- Pages: 895-896
- First Published: 25 April 2025
Who treats matters: Elevating LGBTQI dermatology
- Pages: 897-898
- First Published: 25 April 2025
GUIDELINES
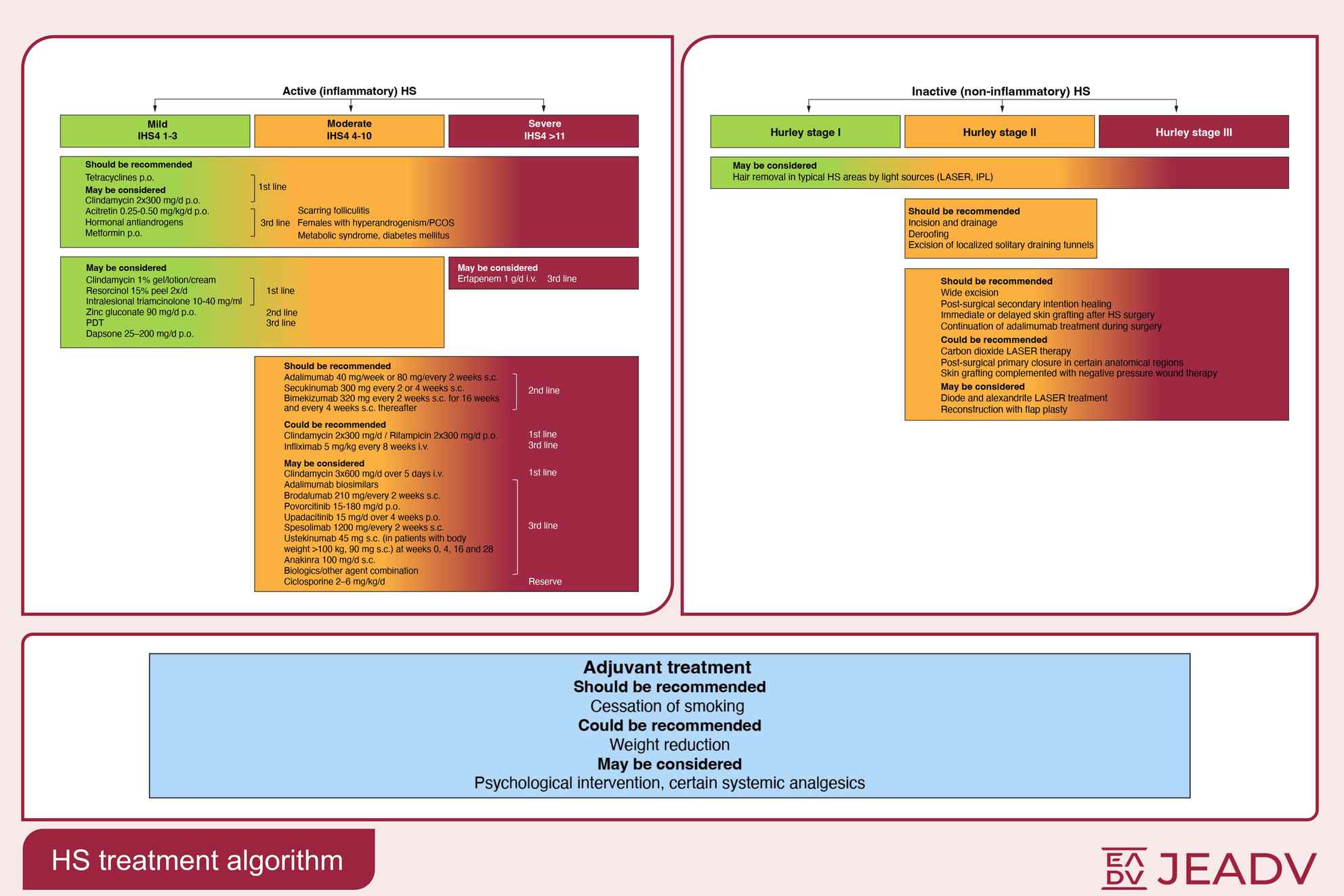
European S2k guidelines for hidradenitis suppurativa/acne inversa part 2: Treatment
- Pages: 899-941
- First Published: 19 December 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Darier disease: Current insights and challenges in pathogenesis and management
- Pages: 942-951
- First Published: 28 November 2024
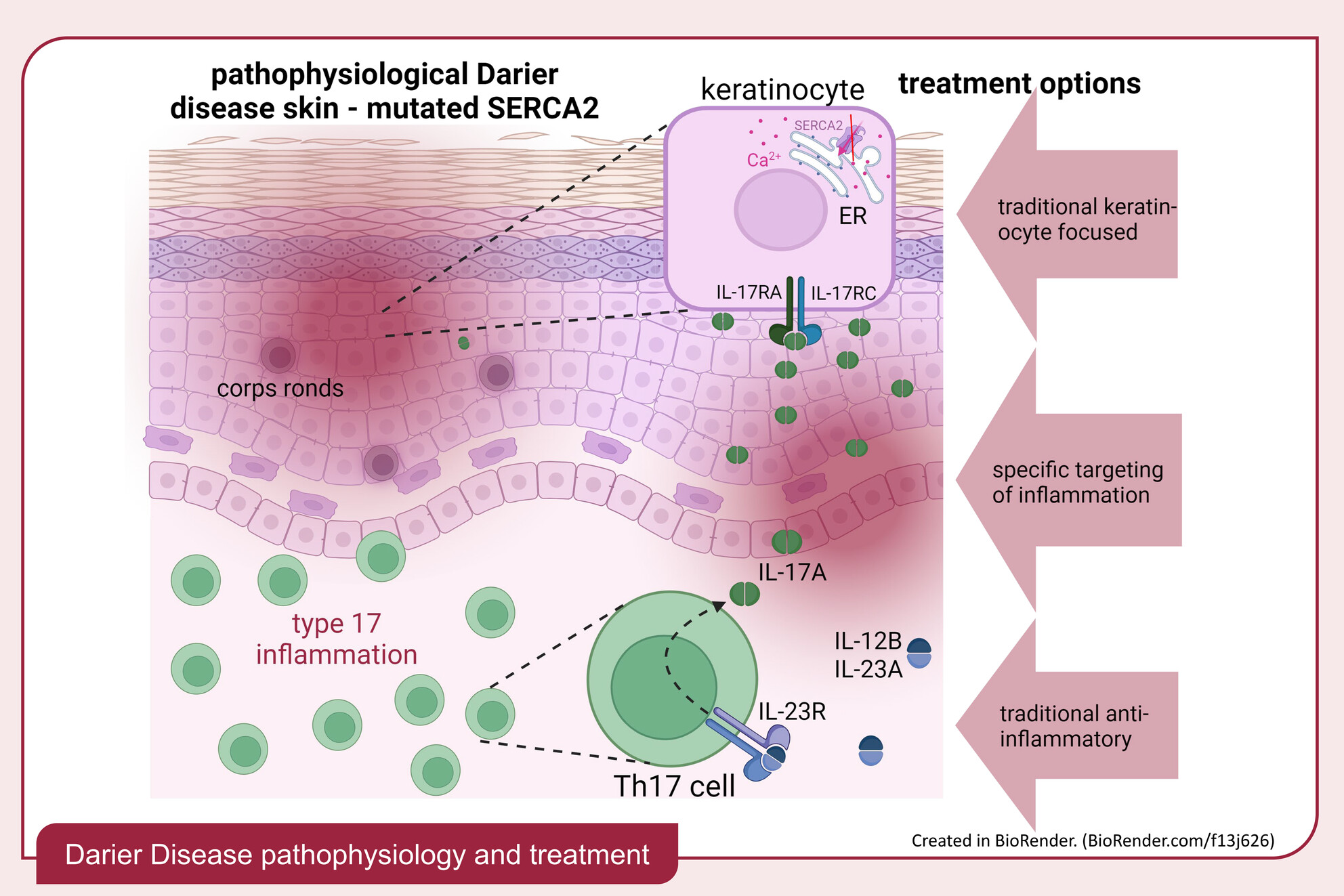
Darier disease (DD) is characterized by the following: Disrupted Ca2+ gradients, impaired desmosomes, impaired keratinocyte differentiation, type 17 inflammation, DC and LC ↓, Th17 cells ↑. DD treatment: First line: keratinocyte focused and/or anti-inflammatory. Second line: experimental approaches like specific targeting of the inflammatory infiltrate.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AND SYSTEMATIC REVIEW
ACNE
International expert consensus recommendations for the use of dermocosmetics in acne
- Pages: 952-966
- First Published: 15 June 2024
INTERNAL MEDICINE AND SKIN
Dermatologic manifestations of hereditary hemochromatosis: A systematic review
- Pages: 976-986
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Experience of patients and healthcare practitioners with interdisciplinary care in immune-mediated inflammatory diseases with skin manifestations: A systematic scoping review
- Pages: 987-1000
- First Published: 07 December 2024
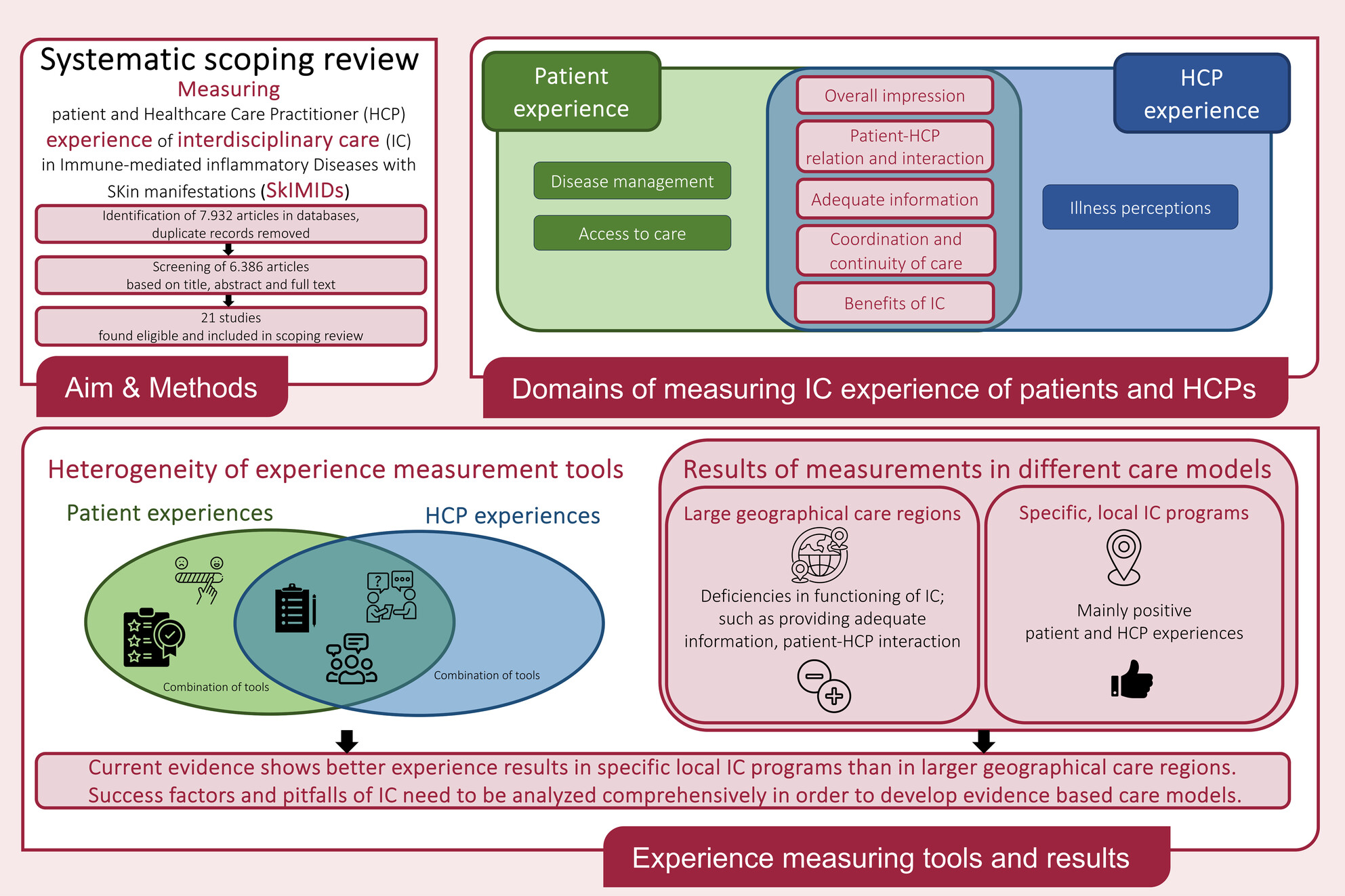
This scoping review gathers evidence on patient- and HCP perceptions on interdisciplinary care (IC) for Immune-mediated inflammatory Diseases with Skin manifestations (skIMID) and state-of-the-art of measurement. IC experience is captured very heterogeneously and strongly depends on the context of the care provider. Experience seems to be better in local programmes than systems rolled out in larger geographical regions. Future need is to develop a standardized core IC outcome set, including medical-, process- and financial indicators, patient and HCP care experience measures. Such data will support benchmarking and identification of improvement areas in quality of care.
Dermatological emergencies and determinants of hospitalization in Switzerland: A retrospective study
- Pages: 1001-1010
- First Published: 22 June 2024
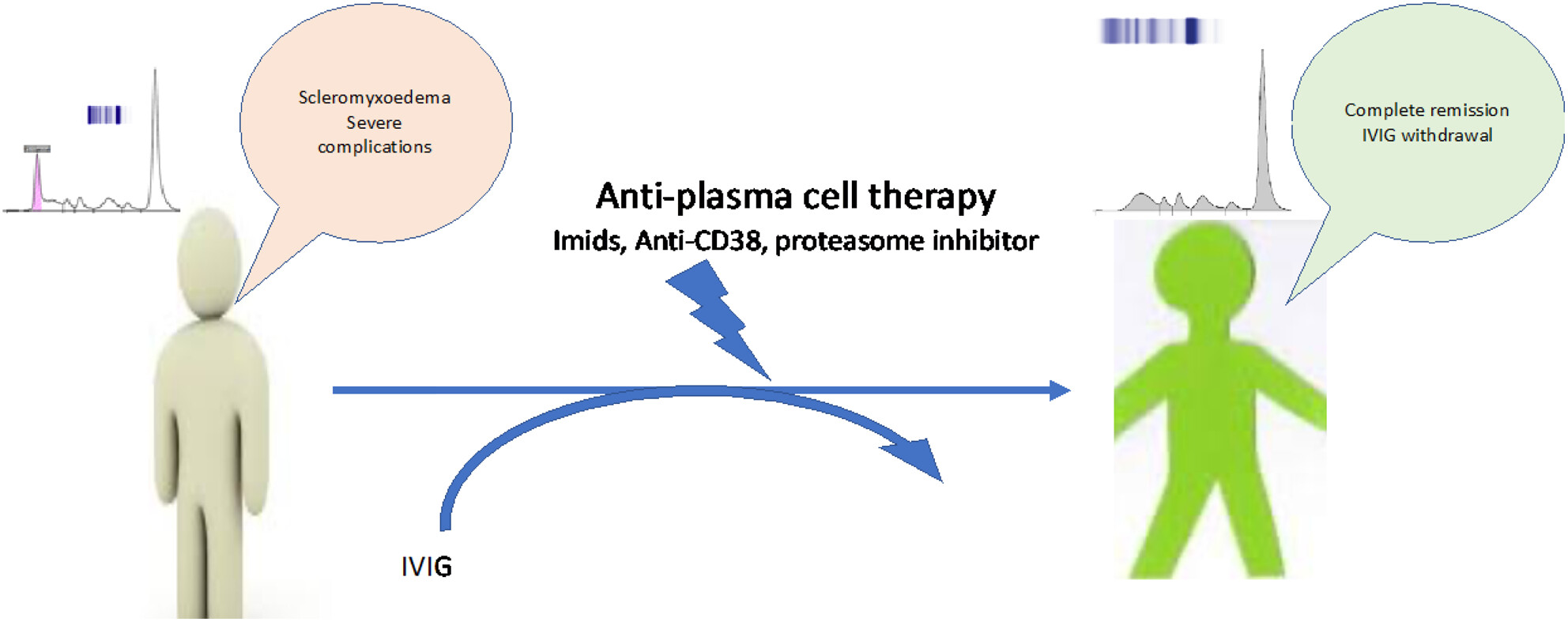
Plasma cell-directed therapies induce profound clinical and durable responses in patients with severe or relapsed/refractory scleromyxedema
- Pages: 1011-1016
- First Published: 31 July 2024
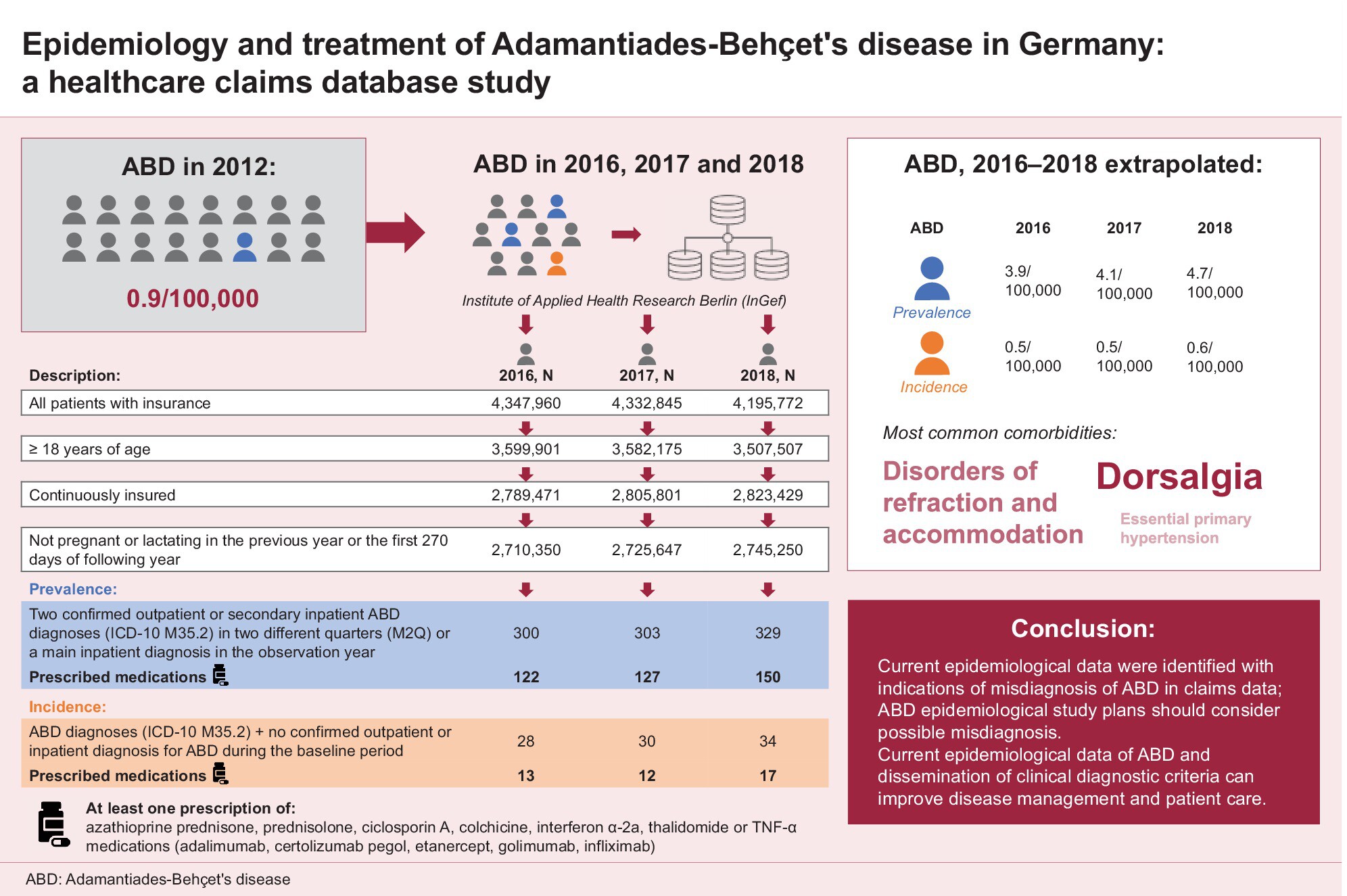
Epidemiology and treatment of Adamantiades–Behçet's disease in Germany: A healthcare claims database study
- Pages: 1017-1027
- First Published: 12 December 2024
RARE SKIN DISEASES
Epidermolytic ichthyosis: Clinical spectrum and burden of disease in a large German cohort
- Pages: 1028-1037
- First Published: 13 May 2024
Long-term remission of Hailey–Hailey disease by Er:YAG ablative laser therapy
- Pages: 1038-1045
- First Published: 01 October 2024
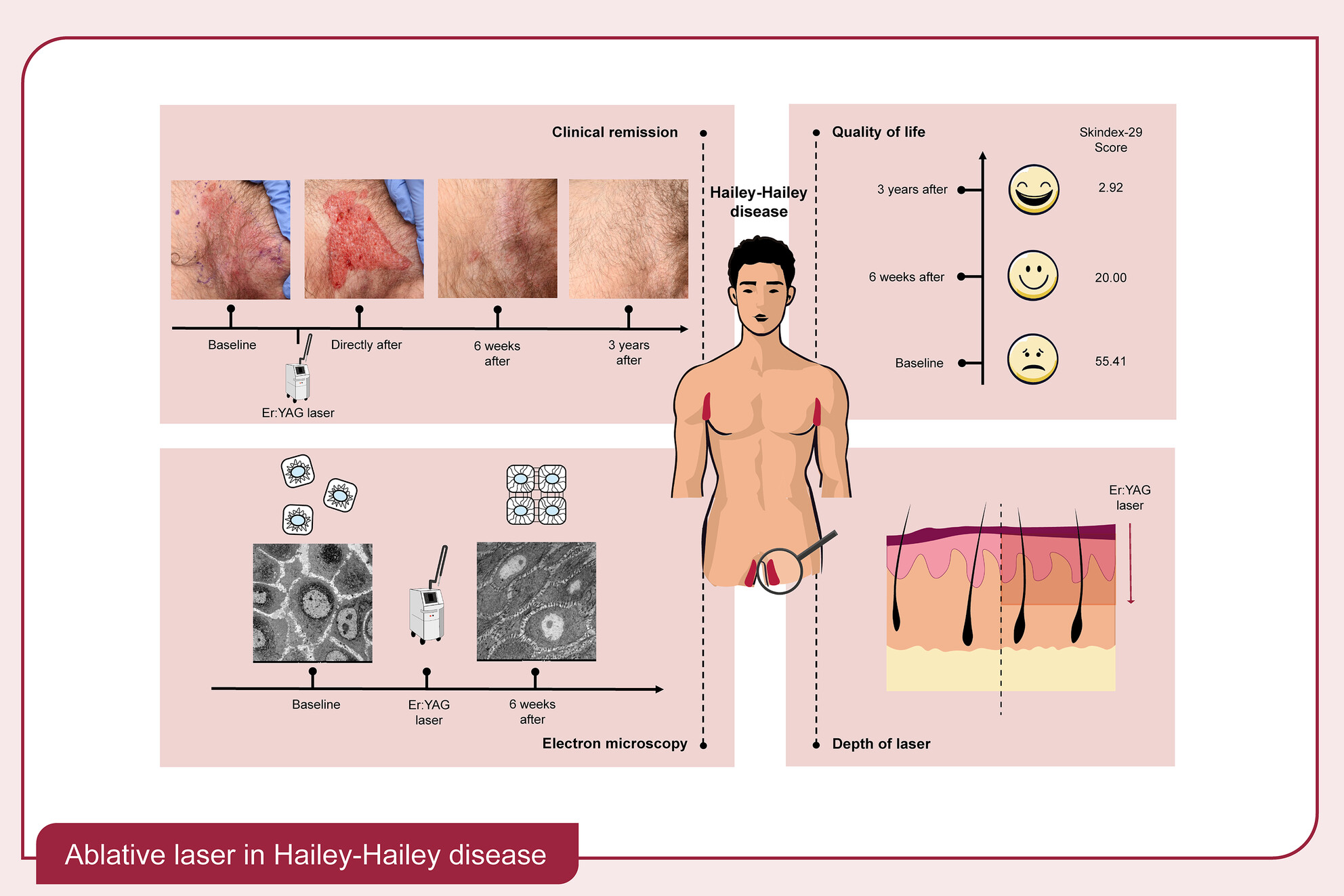
Upper left panel: Hailey–Hailey lesion at baseline, directly after, 6 weeks and 3 years after a single Er:YAG laser ablation. Long-term remission was noted in 75/77 Hailey–Hailey plaques after a median follow-up of 38 months. Upper right panel: Median quality of life scores at baseline, 6 weeks and 3 years after laser ablation with a significant improvement at 6 weeks and 3 years after laser ablation. Bottom left panel: Electron microscopy of keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum at baseline and 6 weeks after laser ablation. Laser-treated skin showed an increased number of desmosomes, decreased intercellular distance and decreased perinuclear retraction of keratin filaments. Bottom right panel: Cross-section of the skin on the right side showing the depth of laser ablation. Laser ablation up to mid-dermis induced long-term remission of Hailey–Hailey disease.
Long-term effects of sirolimus treatment for slow-flow vascular malformations: Real-world evidence from the French observational multicentre SIROLO study
- Pages: 1046-1054
- First Published: 25 November 2024
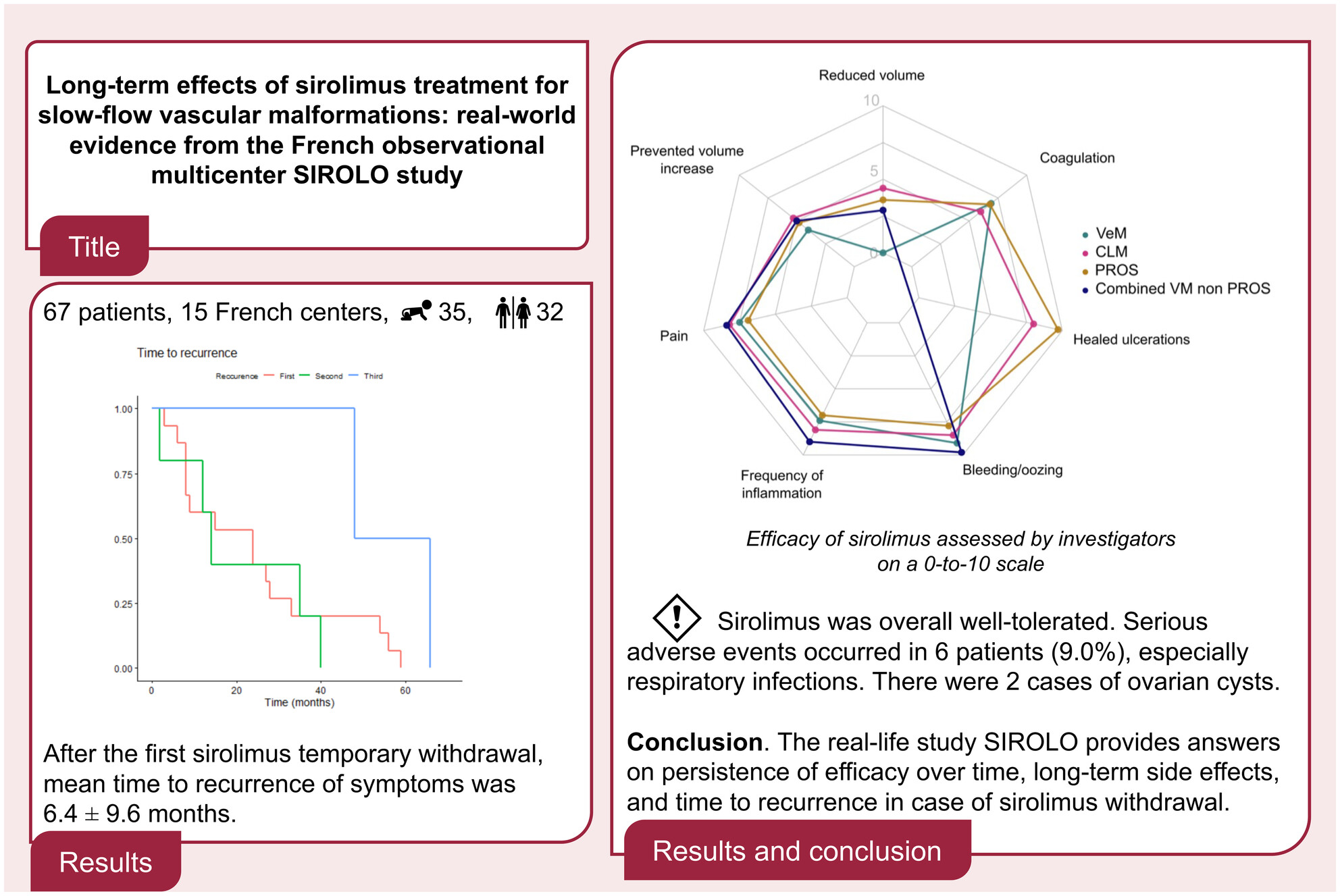
Overall, 67 patients were included from 15 French centres (35 children and 32 adults). After the first sirolimus temporary withdrawal, mean time to recurrence of symptoms was 6.4 ± 9.6 months (survival curve). Sirolimus was overall well-tolerated (radar chart). Serious adverse events occurred in six patients (9.0%), especially respiratory infections. There were two cases of ovarian cysts. Conclusion. The real-life study SIROLO provides answers on persistence of efficacy over time, long-term side effects and time to recurrence in case of sirolimus withdrawal.
ANNOUNCEMENT
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Excellent response to cemiplimab and radiotherapy in advanced metastatic porocarcinoma
- Pages: e385-e387
- First Published: 22 August 2024
Erectile dysfunction in patients with seborrhoeic dermatitis
- Pages: e388-e390
- First Published: 22 August 2024
A cluster of early syphilis cases with ocular manifestations on the island of Crete
- Pages: e391-e393
- First Published: 18 September 2024
Improvements in patient-reported outcomes with oral roflumilast for psoriasis: Results from a randomized controlled trial (PSORRO)
- Pages: e394-e397
- First Published: 19 September 2024
Tangential biopsy of the nail bed and matrix, with plate evaluation, for diagnosis of lichen planus
- Pages: e398-e400
- First Published: 20 September 2024
Oesophageal lichen planus: Clinical, endoscopic and fibroscopic characteristics
- Pages: e401-e403
- First Published: 26 September 2024
Mycophenolate mofetil as a steroid-sparing agent in oral mucous membrane pemphigoid: A retrospective review
- Pages: e404-e406
- First Published: 26 September 2024
Epidemiological analysis of mycosis fungoides (MF) in children and young adult patient populations: A population-based analysis of the nationwide surveillance, epidemiology and end results (SEER) database
- Pages: e407-e409
- First Published: 12 October 2024
Effectiveness and safety of risankizumab dose optimization in adult patients with plaque psoriasis: An international multicentre retrospective cohort study
- Pages: e410-e412
- First Published: 15 October 2024
The effect of cigarette smoking on Behcet's disease outcomes: A multicentre study
- Pages: e413-e416
- First Published: 21 October 2024
Clearance of Darier disease lesions in a patient with concomitant atopic dermatitis treated with abrocitinib
- Pages: e417-e419
- First Published: 22 October 2024
Assessing dermatologists-venereologists' awareness, vigilance and attitude towards LGBT individuals: A cross-sectional study in Greece
- Pages: e420-e423
- First Published: 23 October 2024
ApreScalp: A Phase 4 multicentre, randomized, placebo-controlled study evaluating the effect of apremilast on pruritus and quality of life of patients with moderate-to-severe scalp psoriasis
- Pages: e424-e426
- First Published: 24 October 2024
Nail clipping may not be sufficient to corroborate the diagnosis of psoriasis
- Pages: e427-e429
- First Published: 05 November 2024
Cardiovascular events in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with JAK/TYK inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: e430-e435
- First Published: 07 November 2024
Effects of comorbidities on delayed wound healing in patients with pyoderma gangrenosum
- Pages: e436-e438
- First Published: 26 November 2024
Robustness of automated acne lesion detection across various imaging conditions: A comparative analysis with dermatologists
- Pages: e439-e441
- First Published: 04 December 2024
Upadacitinib for orofacial granulomatosis associated with Crohn's disease
- Pages: e442-e443
- First Published: 07 December 2024
Systemic anti-inflammatory therapy in congenital ichthyosis: Real-world experience in a series of 22 cases
- Pages: e444-e447
- First Published: 11 December 2024
Dapagliflozin-associated chronic balanitis due to Streptococcus agalactiae
- Pages: e448-e450
- First Published: 13 December 2024
Enhancing multimodal deep learning for improved precision and efficiency in medical diagnostics
- Pages: e451-e452
- First Published: 29 May 2024
Response to ‘Enhancing multimodal deep learning for improved precision and efficiency in medical diagnostics’
- Pages: e453-e455
- First Published: 20 September 2024
Effective and safe use of benzyl benzoate in young children at the same concentrations as adults: A matter of vehicle?
- Pages: e456-e457
- First Published: 29 July 2024
Reply to ‘Burnout and professional quality of life in dermatologists’
- Pages: e458-e459
- First Published: 04 October 2024
Enhancing HFUS accuracy in melanoma assessment: The role of artificial intelligence and statistical precision
- Pages: e460-e461
- First Published: 05 November 2024
Response—Letter to the Editor: High-frequency ultrasound accuracy in preoperative cutaneous melanoma assessment
- Pages: e462-e463
- First Published: 07 January 2025