Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITOR’S PICKS
COMMENTARY
Illuminating nail disorders: A comprehensive overview of advanced imaging techniques
- Pages: 709-710
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Evidenced-based approach facilitates choosing between different topical compounds in acne vulgaris
- Pages: 711-712
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Low-dose isotretinoin for difficult-to-treat rosacea: Enough evidence to be convinced—What's next?
- Pages: 713-714
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Will targeted microbiome modulation in the skin be the future of acne vulgaris treatment?
- Pages: 715-716
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Antipsychotics in dermatology: Optimal choice of drugs for the treatment of delusional infestation and other potential uses for skin conditions
- Pages: 717-718
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Advancing biomarker-based prognostication in melanoma
- Pages: 719-720
- First Published: 25 March 2025
On the importance of assessing stigma in dermatological research
- Pages: 721-722
- First Published: 25 March 2025
Diagnostic workup in paradoxical urticaria induced by H1-antihistamines
- Pages: 723-724
- First Published: 25 March 2025
HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVE
Ambassadors in Dermatology and Venereology: An interview with Professor Fabio Ayala
- Pages: 725-729
- First Published: 25 March 2025
POSITION STATEMENT
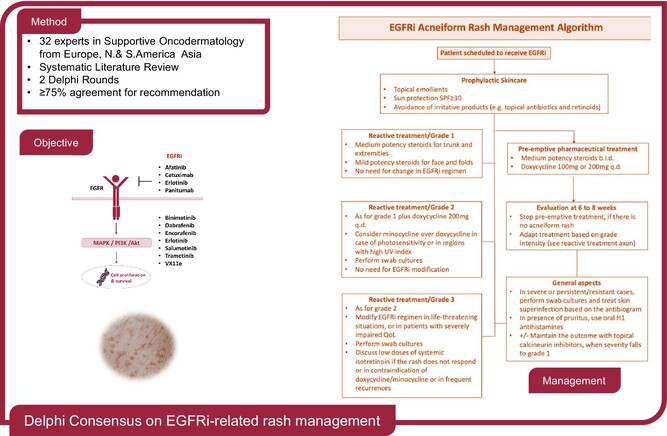
Management of human epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors-related acneiform rash: A position paper based on the first Europe/USA Delphi consensus process
- Pages: 730-741
- First Published: 26 October 2024
GUIDELINES
2024 European guidelines for the management of genital herpes
- Pages: 742-758
- First Published: 02 December 2024
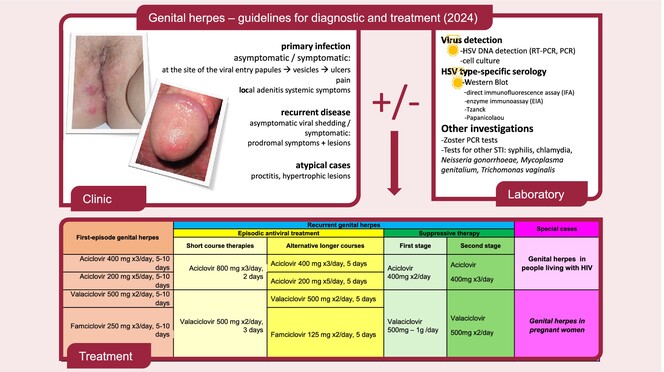
Genital herpes—guidelines for diagnostic and treatment (2024): strategies for diagnosis, management and follow-up of the most common sexually transmitted infection. The guidelines covers common clinical scenarios (including recurrent genital herpes), infection during pregnancy and coinfection with human immunodeficiency virus.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Advances in image-based diagnosis of nail disorders
- Pages: 759-774
- First Published: 04 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES AND SYSTEMATIC REVIEWS
ACNE AND ROSACEA
Efficacy of topical treatments for mild-to-moderate acne: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized control trials
- Pages: 775-784
- First Published: 29 June 2024
Low-dose isotretinoin for the management of rosacea: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 785-792
- First Published: 06 September 2024
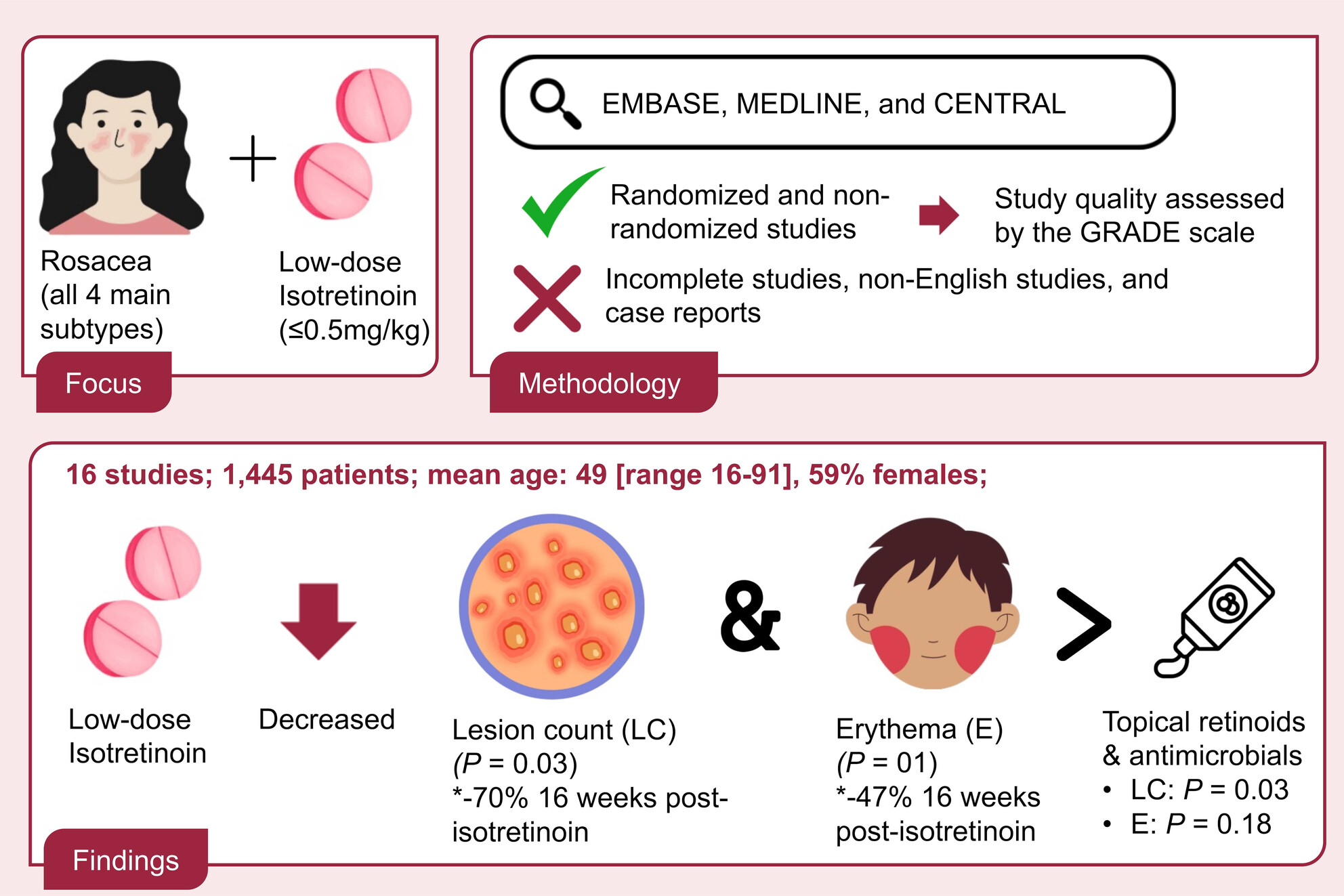
Isotretinoin, a vitamin A derivative primarily known for treating acne vulgaris, has been investigated for rosacea despite its off-label use. This systematic review and meta-analysis of 16 studies involving 1445 patients examined low-dose isotretinoin (defined as ≤0.5 mg/kg/day) for the four main types of rosacea. This study found significant reduction in lesion count (p = 0.03) and erythema (p = 0.01), with low-dose isotretinoin outperforming topical retinoids and antimicrobials in reducing lesion count (p = 0.03). Its effect on erythema in rosacea however, did not meet statistical significant (p = 0.18). Improvements persisted 16 weeks post-treatment, with a relapse rate of 35% at 5.5 months. Study design heterogeneity limited comprehensive comparisons. Overall, low-dose isotretinoin appears to be an effective, well-tolerated, and safe treatment for rosacea.
Acne and the cutaneous microbiome: A systematic review of mechanisms and implications for treatments
- Pages: 793-805
- First Published: 13 September 2024
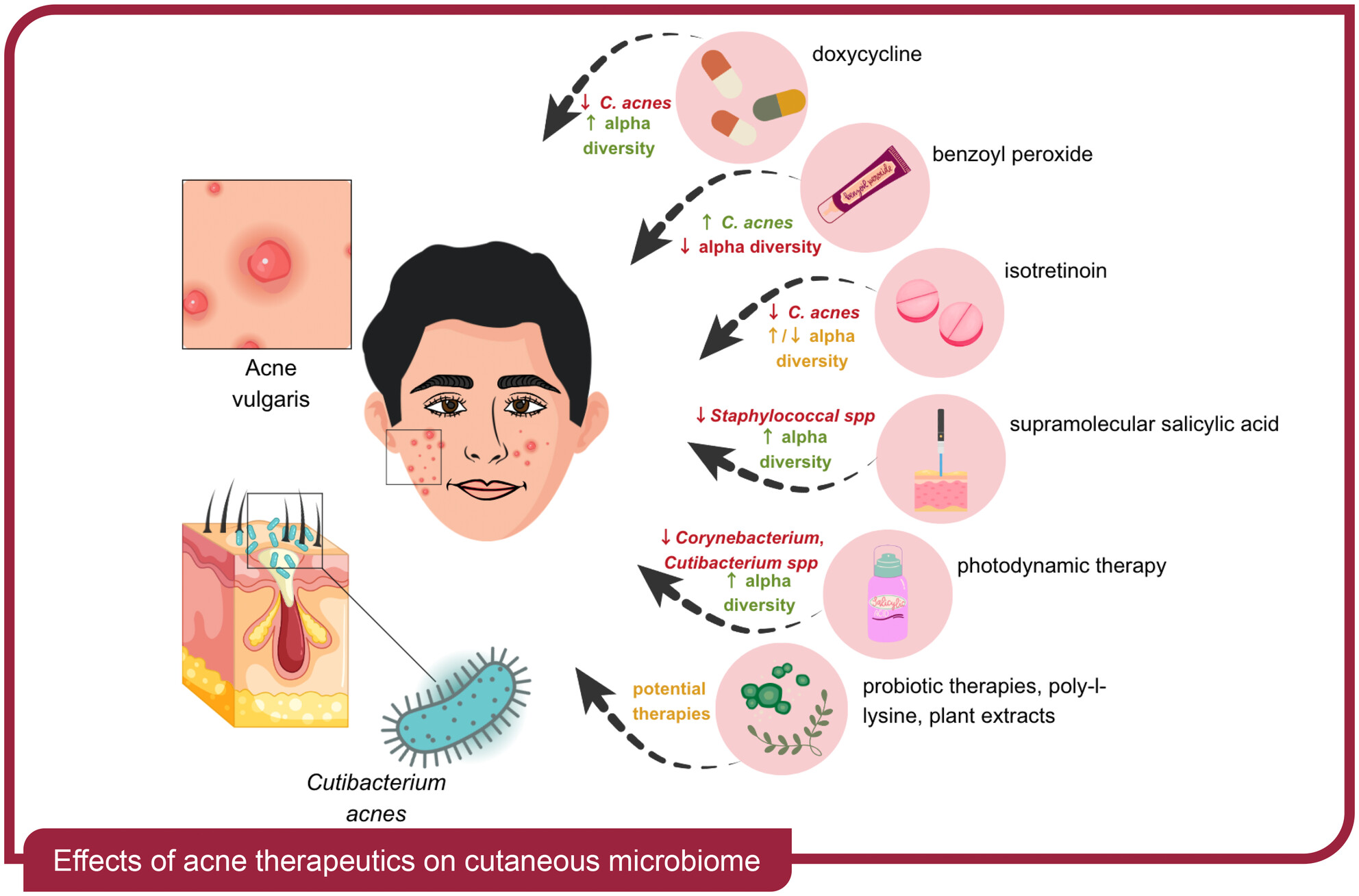
Impact of Acne Therapies on the Skin Microbiome: This graphical abstract illustrates how various acne treatments affect the cutaneous microbiome, particularly focusing on Cutibacterium acnes and overall microbial diversity. Common treatments like doxycycline and benzoyl peroxide generally decrease C. acnes and reduce alpha diversity, while isotretinoin has variable effects. Newer therapies, including probiotics and plant extracts, are highlighted for their potential to restore microbial balance, suggesting a shift towards microbiome-focused treatment strategies.
Compliance with the pregnancy prevention program among women initiating isotretinoin treatment between 2014 and 2021: A nationwide cohort study on the French Health Data System (SNDS)
- Pages: 806-814
- First Published: 19 May 2024
PATIENT EXPERIENCE
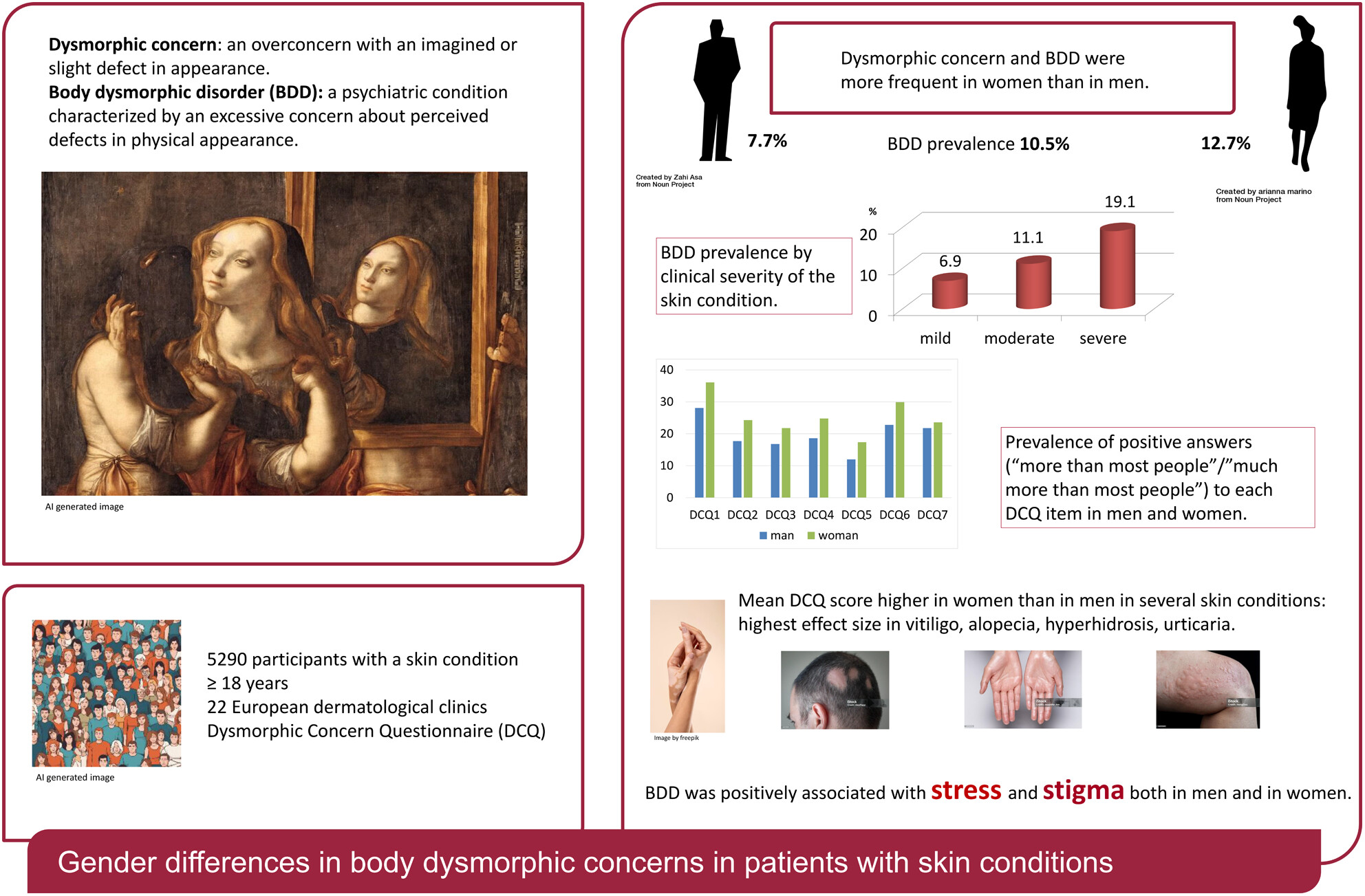
A cross-sectional study on gender differences in body dysmorphic concerns in patients with skin conditions in relation to sociodemographic, clinical and psychological variables
- Pages: 823-832
- First Published: 25 July 2024
Health-related quality of life in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: A post hoc analysis of a phase 3 trial in mycosis fungoides and Sézary syndrome
- Pages: 833-845
- First Published: 24 September 2024
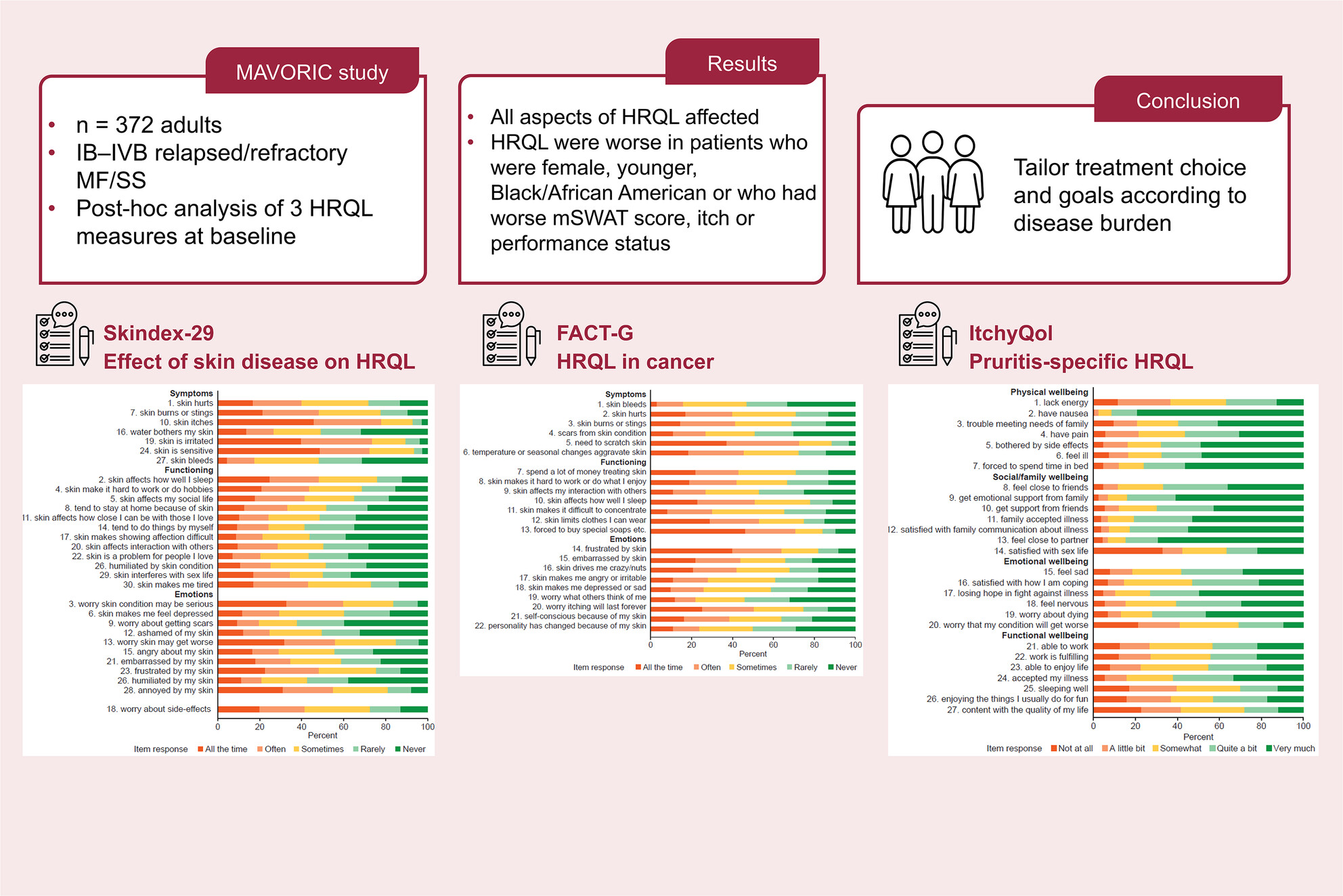
This study found that all aspects of HRQL were compromised in patients with relapsed/refractory stage IB–IVB MF/SS. Different aspects of HRQL were worse in patients who were female, younger, Black/African American or who had worse mSWAT score, itch or performance status. Understanding of the individual's symptom burden, including patient-reported measures, should be used to inform treatment goals and therapeutic choice.
Psychometric properties of the revised internalized skin bias questionnaire
- Pages: 846-854
- First Published: 09 October 2024
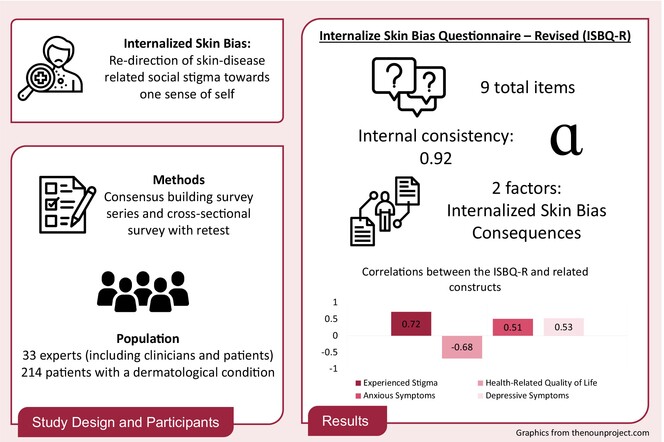
This two-part study included consensus-building surveys and a cross-sectional survey among participants with self-reported dermatological conditions to assess instrument psychometric properties of the revised Internalized Skin Bias Questionnaire (ISBQ-R). Overall, 33 experts participated including 22 (66.7%) dermatologists or dermatology researchers and 11 (33.3%) patients. The revised survey was completed by 214 participants with various dermatological conditions. Adding and modifying new items (9 in total) resulted in an instrument with stronger internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha = 0.92) and a stronger correlation with other existing stigma measures (ρ = 0.72) as well as health-related quality of life (ρ = −0.68), anxious (ρ = 0.51) and depressive (0.53) symptoms. Additionally, the study further expanded upon previous research by exploring a two-factor structure, suggesting that the ISBQ-R could be used as a single or dual factor instrument depending on investigator goals.
SKIN CANCER
Histological deep margins in cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the scalp and risk of recurrence
- Pages: 855-864
- First Published: 22 July 2024
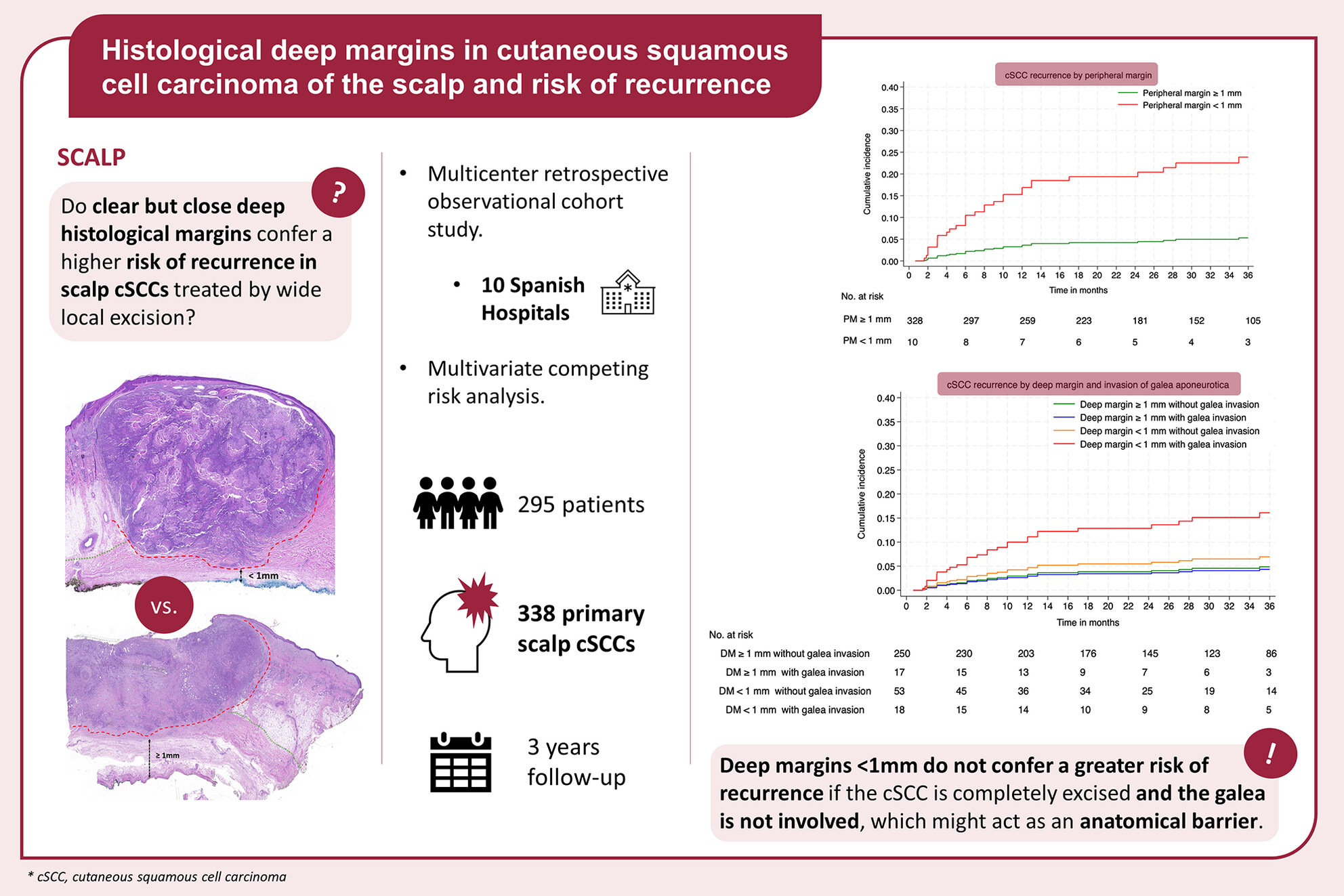
Deep histological margins <1 mm do not confer a greater recurrence risk in scalp cSCC as long as the tumour is completely excised and the galea is not involved. However, peripheral margins <1 mm associate a higher risk of recurrence. Thus, surgical excision of cSCCs of the scalp should include the galea, which might act as an anatomical barrier.
BAUSSS biomarker improves melanoma survival risk assessment
- Pages: 865-870
- First Published: 31 August 2024
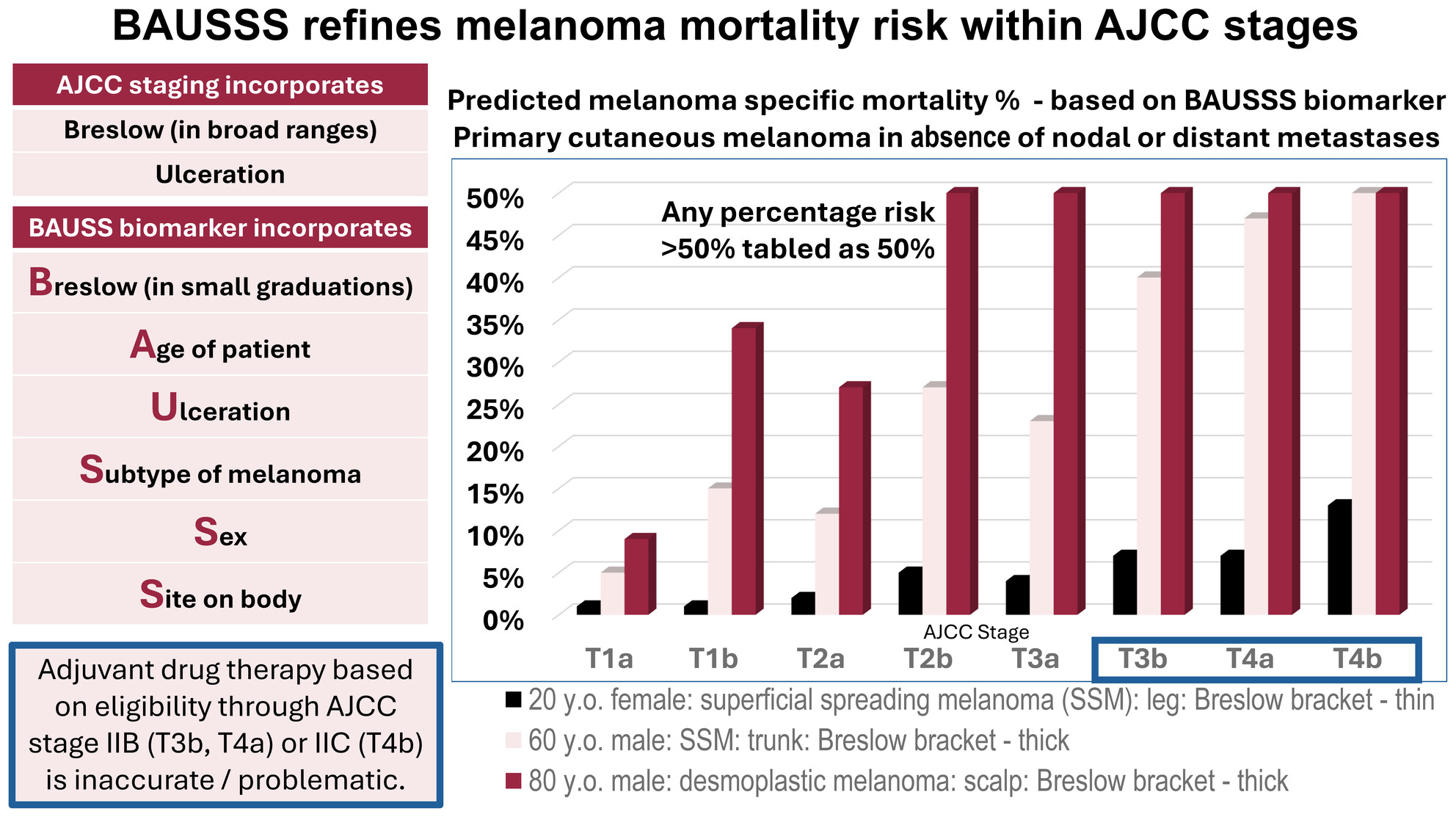
The range of mortality risk within individual AJCC staging brackets is very wide. Administering adjuvant drug therapy based solely on AJCC T3b, T4a and T4b staging will result in many high-risk patients over 60 years of age being denied such drugs while other patients under young patients will be offered drug therapy despite having a relatively low risk primary tumour.
ANNOUNCEMENT
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Coexistence of oligoclonal and polyclonal HTLV-1-positive T cells with presentation of acute-type adult T-cell leukaemia-lymphoma successfully treated by ultraviolet B phototherapy and etretinate
- Pages: e297-e299
- First Published: 08 August 2024
Dupilumab may break the “itch-scratch cycle” in chronic prurigo and induce remission in a subset of patients
- Pages: e300-e302
- First Published: 09 August 2024
Doxycycline-induced fixed drug eruption: The new epidemic?
- Pages: e303-e305
- First Published: 09 August 2024
Transcriptomic analysis of one patient with lupus skin lesions treated with anifrolumab
- Pages: e306-e309
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Cutaneous leishmaniasis as immune reconstitution syndrome: A clinical and histopathological case series
- Pages: e310-e312
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Factors associated with long-term complete remission in pemphigus patients receiving rituximab therapy
- Pages: e313-e316
- First Published: 16 August 2024
A randomized single-blinded prospective study comparing simulated daylight photodynamic therapy with natural daylight photodynamic therapy for multiple actinic keratoses
- Pages: e317-e319
- First Published: 21 August 2024
Prolonged complete remission of a lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma of the skin with bone metastases induced by pembrolizumab
- Pages: e320-e322
- First Published: 21 August 2024
Recalcitrant erosive palms and soles eccrine syringofibroadenoma successfully treated with radiotherapy
- Pages: e323-e325
- First Published: 21 August 2024
Melanosis and isolated follicular vitiligo during checkpoint inhibitors for metastatic melanoma
- Pages: e326-e328
- First Published: 22 August 2024
Familial Mediterranean fever and MEFV gene variants in hidradenitis suppurativa: A systematic review
- Pages: e329-e332
- First Published: 27 August 2024
Assessing outcomes of cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma with large-calibre nerve invasion as solitary high-risk factor: A single-institution cohort study
- Pages: e333-e335
- First Published: 10 September 2024
Extracorporeal photophoresis in treatment of corticosteroid refractory colitis induced by combined immunotherapy for metastatic melanoma
- Pages: e342-e343
- First Published: 11 September 2024
Abrocitinib for prurigo nodularis: Clinical efficacy and safety profile
- Pages: e344-e346
- First Published: 12 September 2024
Concurrent intrathecal nivolumab and targeted therapy in a patient with melanoma-associated leptomeningeal disease
- Pages: e347-e349
- First Published: 12 September 2024
The development and validation of an investigator global assessment score for keratosis pilaris
- Pages: e350-e352
- First Published: 13 September 2024
Efficacy of dupilumab against pruritus in dystrophic epidermolysis bullosa: Real-life data from a retrospective bicentric study
- Pages: e353-e355
- First Published: 13 September 2024
Advanced age and dermoscopic streaks increase the likelihood of a diagnostic upgrade of ambiguous melanocytic tumours after clinicopathological correlation
- Pages: e356-e358
- First Published: 13 September 2024
ChatGPT and acne: Accuracy and reliability of the information provided—The AI-check study
- Pages: e359-e362
- First Published: 16 September 2024
Evidence of early coronary atherosclerotic plaque in hidradenitis suppurativa compared to the background population is indicative of myocardial infarction risk
- Pages: e363-e365
- First Published: 16 September 2024
The effect of age on the severity of psoriasis
- Pages: e366-e368
- First Published: 16 September 2024
Low-dose oral minoxidil for the treatment of monilethrix: A retrospective review
- Pages: e369-e371
- First Published: 18 September 2024
B-type natriuretic peptide levels are associated with chronic itch: A case–control study
- Pages: e372-e374
- First Published: 20 September 2024
Combining an anti-IL-4Rα biologic with a JAK1 inhibitor leads to a higher treatment response in resistant atopic dermatitis versus monotherapy alone: A case series
- Pages: e375-e377
- First Published: 25 September 2024
Incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer in patients with vitiligo who applied ruxolitinib cream
- Pages: e378-e380
- First Published: 17 October 2024
Reply to ‘Incidence of nonmelanoma skin cancer in patients with vitiligo who applied ruxolitinib cream’
- Pages: e381-e382
- First Published: 08 November 2024
Comment on ‘Low-dose isotretinoin for the management of rosacea: A systematic review and meta-analysis’
- Pages: e383-e384
- First Published: 03 November 2024