Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITOR’S PICKS
EDITORIAL
Biologics targeting interleukin (IL)-23 and the risk of cardiovascular events: Where are we?
- Pages: 447-448
- First Published: 25 February 2025
COMMENTARY
Closing the gap between possibilities and reality in psoriasis management
- Pages: 449-450
- First Published: 25 February 2025
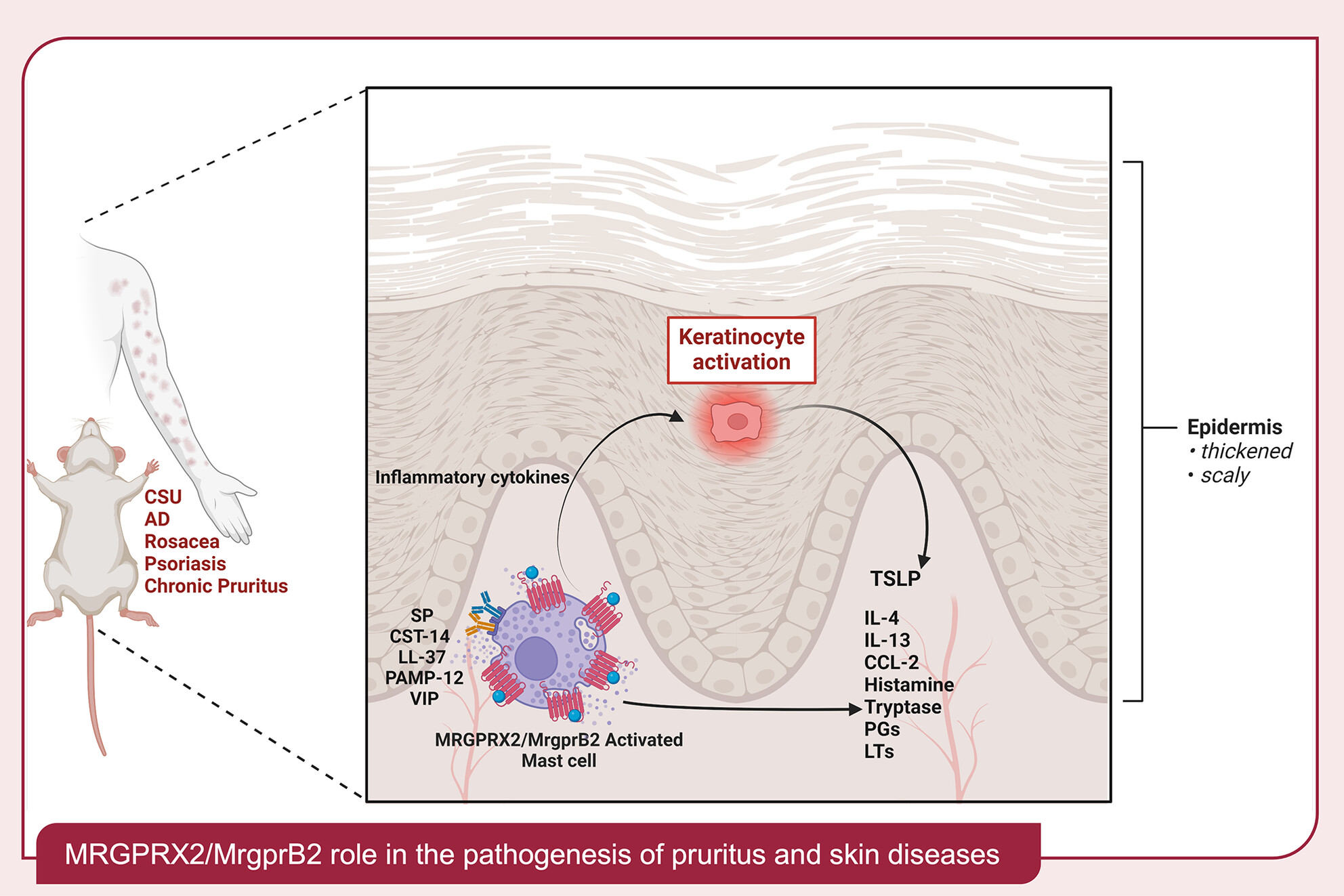
No allergy, but mast cells are involved: MRGPRX2 in chronic inflammatory skin diseases
- Pages: 451-452
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Beyond the surface: Integrating sex and gender in dermatologic therapy
- Pages: 453-454
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Shifting the focus: Exploring happiness as a health outcome in dermatology
- Pages: 455-456
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Preventing penile cancer and poor outcomes
- Pages: 457-458
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Reflectance confocal microscopy: Presurgical margin assessment improves lentigo maligna and lentigo maligna melanoma management
- Pages: 459-460
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Bridging the gap: From clinical intuition to structured cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma classification
- Pages: 461-462
- First Published: 25 February 2025
Towards greener conferences: Addressing the sustainability of cosmeceutical samples
- Pages: 463-464
- First Published: 25 February 2025
GUIDELINES
Belgian recommendations for managing psoriasis in a changing treatment landscape
- Pages: 465-475
- First Published: 12 October 2024
REVIEW ARTICLE
Beyond the classic players: Mas-related G protein-coupled receptor member X2 role in pruritus and skin diseases
- Pages: 476-486
- First Published: 23 July 2024
Considerations for defining and diagnosing generalized pustular psoriasis
- Pages: 487-497
- First Published: 06 September 2024
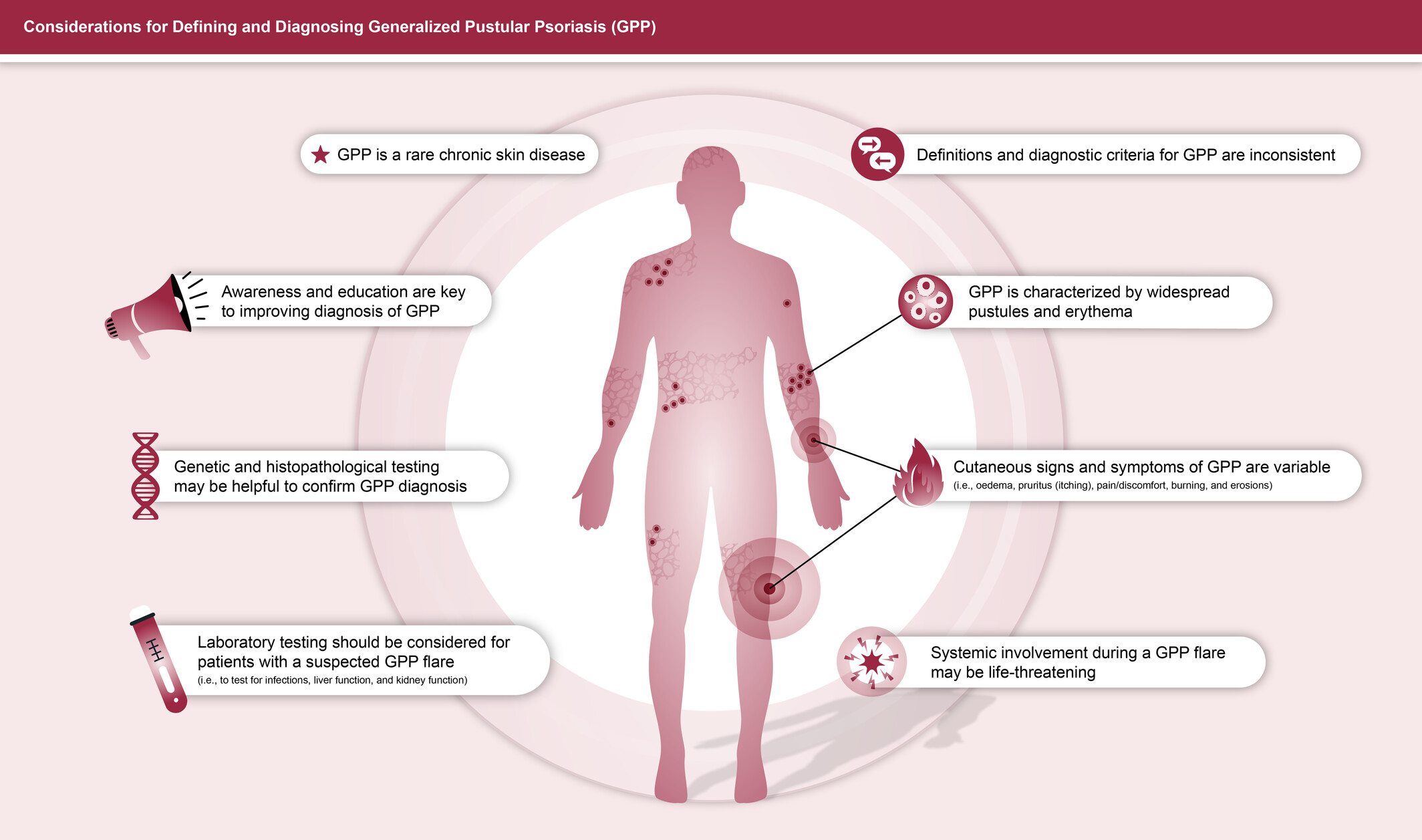
Generalized pustular psoriasis (GPP) is a rare chronic skin disease with inconsistent definitions and diagnostic criteria. It is characterized by widespread pustules and erythema, which are often accompanied by other signs and symptoms. Cases of suspected GPP may benefit from laboratory testing to assess organ function as well as genetic and histopathological testing to support a diagnosis. Increased awareness and education of this rare and highly variable disease will improve diagnosis and timely treatment.
Hair regrowth in alopecia areata and re-pigmentation in vitiligo in response to treatment: Commonalities and differences
- Pages: 498-511
- First Published: 11 September 2024
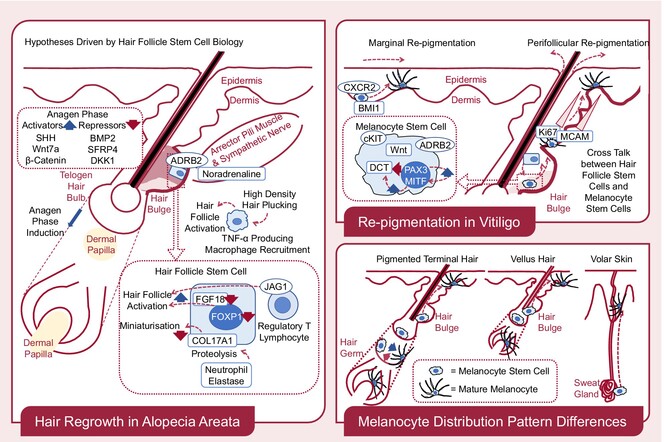
Hair Regrowth in Alopecia Areata. This scheme summarizes recent findings in hair follicle stem cell biology and their implication to regrow hair in alopecia areata. Hair follicle stem cells reside in hair bulge abundantly. Anagen drivers are enhanced and suppressed expression levels of activators and repressors at telogen, respectively. Noradrenaline secreted from niche activates hair follicle regeneration via ADRB2, FOXP1 and FGF18. Hair plucking at high density regenerate hair follicles via TNF-α. JAG1 + regulatory T lymphocytes regenerate hair follicles. Loss of COL17A1 results in hair follicle miniaturization. Burgundy and navy arrows indicate downregulation and upregulation, respectively. ADRB2, adrenergic receptor B2; BMP2, bone morphogenic protein 2; COL17A1, collagen XVII; DKK1, dickkopf 1; FGF18, fibroblast growth factor 18; FOXP1, forkhead box P1; JAG1, jagged 1; SFRP4, secreted frizzled-related protein 4; SHH, sonic hedgehog; TNFα, tumour necrosis factor-α. Re-pigmentation in Vitiligo. This scheme summarizes recent findings in melanocyte stem cell biology and their implication to re-pigment vitiligo skin. Melanocyte stem cells reside in lower portion of hair bulge and hair germ at telogen phase and contribute to perifollicular re-pigmentation. Amplifying melanocytes tend to lose proliferation and migration potential. BMI + CXCR2 + melanocyte stem cells exist in interfollicular epidermis and may contribute to marginal re-pigmentation. Hair follicle stem cells regulate melanocyte stem cells via cKIT, Wnt and other signals. PAX3 activates MITF, followed by DCT activation, whereas PAX3 directly downregulates DCT and maintains stemness. Noradrenaline induces melanocyte stem cell differentiation and migration via ADRB2. BMI1, B lymphoma Mo-MLV insertion region 1; cKIT, receptor tyrosine kinase for stem cell factor; CXCR2, chemokine C-X-C motif receptor 2; DCT, dopachrome tautomerase; MCAM, melanoma cell adhesion molecule; MITF, microphthalmia associated transcription factor; PAX3, paired box gene 3. Melanocyte Distribution Pattern Differences. The distribution pattern of melanocyte stem cells is different depending on the density of pigmented terminal hair and that of vellus hair. As compared with hair follicle stem cells, melanocyte stem cells are sparsely distributed. Volar melanocyte stem cells reside in eccrine sweat gland and require a long travel to distribute melanocytes in the epidermis. Volar melanocytes is sparse, as compared with melanocytes in hairy skin.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE AND SHORT REPORT
PSORIASIS
A systematic review of sex and gender differences in treatment outcome of inflammatory skin diseases: Is it time for new guidelines?
- Pages: 512-528
- First Published: 30 July 2024
Happiness across the borders—A cross-sectional study among patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis in Europe
- Pages: 529-542
- First Published: 14 August 2024
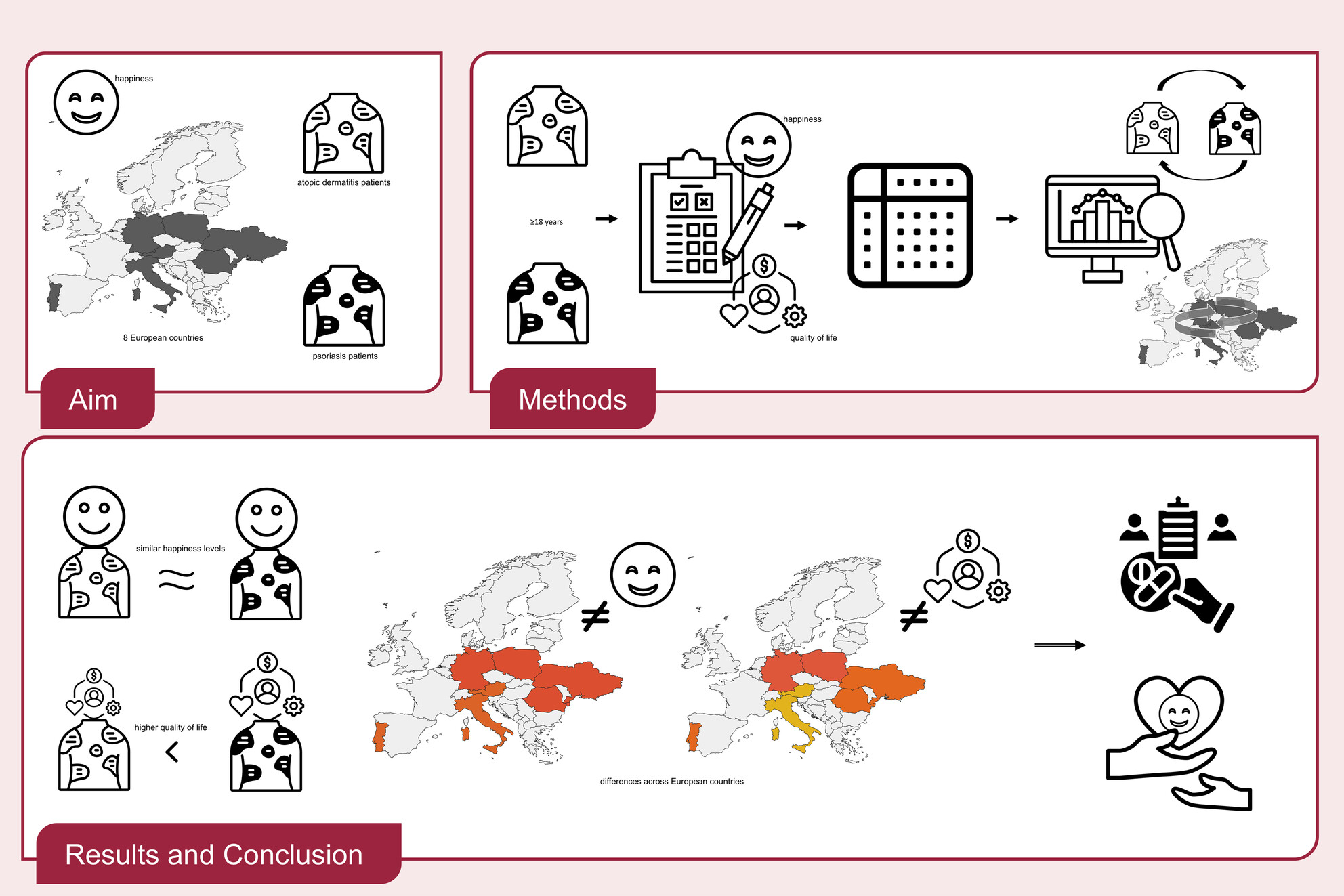
The study aimed to assess happiness among psoriasis and atopic dermatitis patients from 8 European countries. Patients ≥18 years of age were asked to complete a questionnaire on happiness and quality of life. Differences between psoriasis and atopic dermatitis patients and between the European countries were analysed. Psoriasis and atopic dermatitis patients showed similar levels of happiness, while patients with psoriasis showed higher quality of life. Both happiness and quality of life varied between European countries, with Austrian patients displaying the highest happiness levels. Equality in treatment access is imperative, alongside the development of targeted positive psychological interventions to enhance happiness.
SKIN CANCER
Efficacy of interventions for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen's disease): A systematic review and meta-analysis of proportions
- Pages: 543-554
- First Published: 16 August 2024
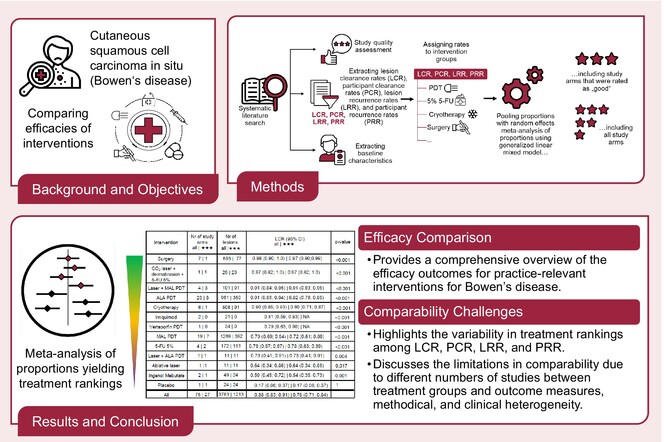
Graphical abstract of the study on cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in situ, commonly known as Bowen's disease, with the primary objective of comparing the efficacies of different treatment interventions. The top right corner section depicts the methods used herein: the study begins with a systematic literature search to identify relevant studies. Subsequently, a quality assessment of the studies is conducted. Data extraction focuses on several key metrics: lesion clearance ates (LCR), participant clearance rates (PCR), lesion recurrence rates (LRR), participant recurrence rates (PRR) and baseline characteristics. The extracted data are then used to group the various interventions, including PDT, 5% 5-FU, cryotherapy and surgery, among others. Two meta-analyses of proportions are conducted for each outcome using a generalized linear mixed model: one focusing exclusively on high-quality studies, and another encompassing all study arms to ensure comprehensive results. At the bottom left, the meta-analysis process using forest plots is illustrated. The treatment efficacies are presented in descending order in treatment rankings, exemplified with a ranking of LCR. At the bottom right, the conclusions are stated: the efficacy comparison provides a thorough overview of the efficacy outcomes for practice-relevant interventions in treating Bowen's disease. Additionally, the study addresses the challenges in comparability, highlighting the variability in treatment rankings across LCR, PCR, LRR and PRR. It also discusses the limitations in comparability due to the different numbers of studies between treatment groups and outcome measures, as well as methodical and clinical heterogeneity.
In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy role for early to advanced lentigo maligna melanoma spectrum: A systematic review and pooled analysis
- Pages: 555-565
- First Published: 13 November 2024
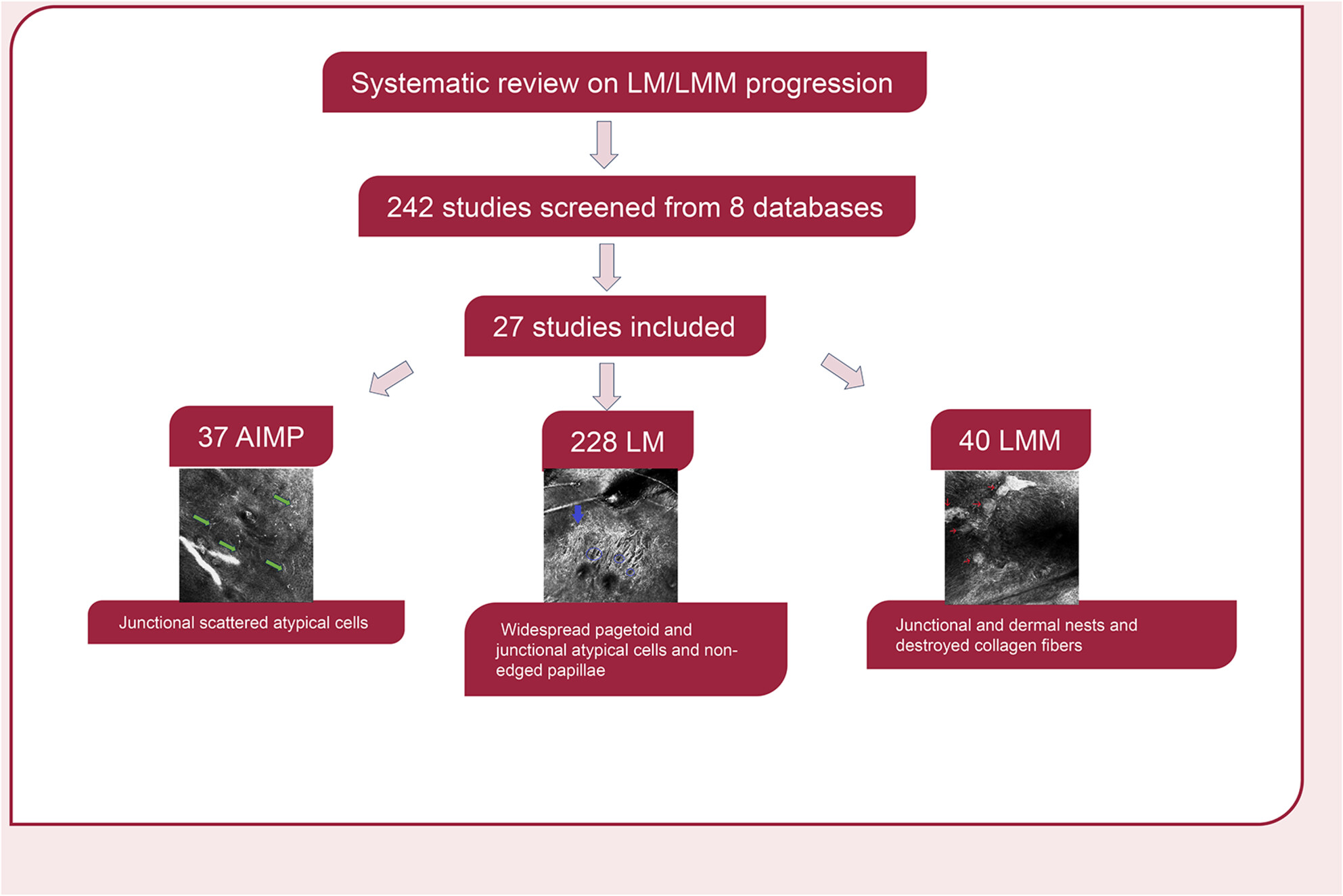
Key confocal features in LM/LMM progression: Architecture: AIMP: Preserved; LM: Non-edged papillae; LMM: Epidermal/junctional disarray, collagen fibre destruction. Cellular distribution: AIMP: Junctional scattered atypical cells; LM: Widespread pagetoid and junctional atypical cells with junctional nests; LMM: Widespread pagetoid and junctional atypical cells with junctional and dermal nests. Cell Types: AIMP: Dendritic cells with mild atypia; LM/LMM: Dendritic cells with mild atypia, round nucleated cells with marked atypia.
Reflectance confocal microscopy for margin mapping of melanoma of the lentigo maligna type: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 566-575
- First Published: 15 November 2024
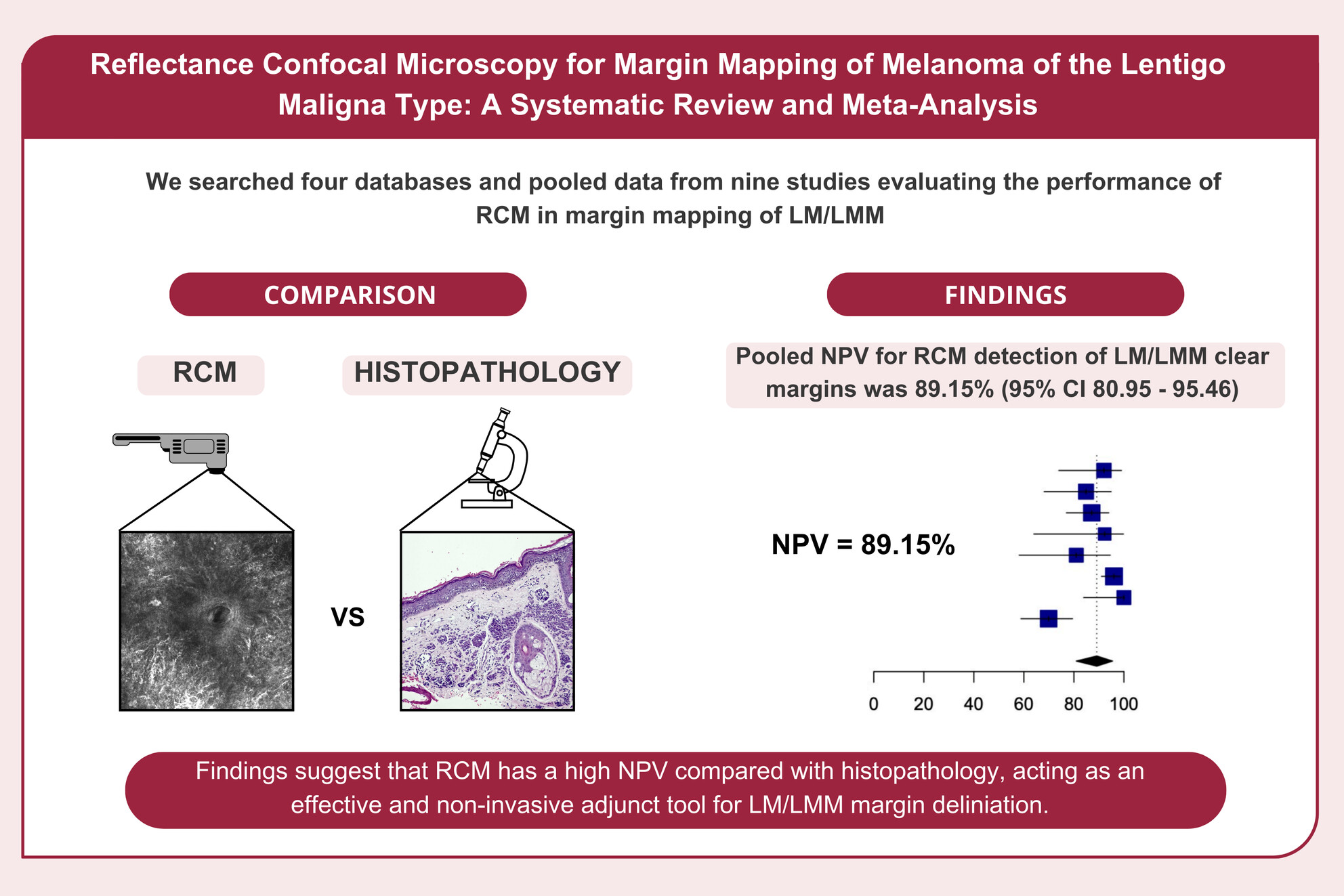
When compared with the gold standard histopathologic examination, the non-invasive RCM imaging technique has a negative predictive value (true negative margins confirmed by histopathology among all negative margins analysed by RCM) of 89.15%, highlighting its efficacy for margin mapping of melanoma of the lentigo maligna type.
Factors predictive of recurrence, metastasis and death in node-negative penile squamous cell carcinoma: A retrospective multicentre cohort study
- Pages: 576-585
- First Published: 06 June 2024
Radiotherapy and prognostic factors in adnexal carcinomas: A retrospective study of 657 patients from the French CARADERM network
- Pages: 586-593
- First Published: 12 June 2024
Predictors of malignancy in melanocytic lesions presenting as new lesions compared to baseline total body photography: A case–control study
- Pages: 594-603
- First Published: 25 June 2024
Successful implementation of handheld reflectance confocal microscopy as the standard of care in the (surgical) management of lentigo maligna (melanoma)
- Pages: 604-611
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Operational classification of cutaneous squamous cell carcinomas based on unsupervised clustering of real cases by experts
- Pages: 612-621
- First Published: 03 July 2024
PATIENT EXPERIENCE
Predictors and mechanisms of self-stigma in five chronic skin diseases: A systematic review
- Pages: 622-630
- First Published: 09 September 2024
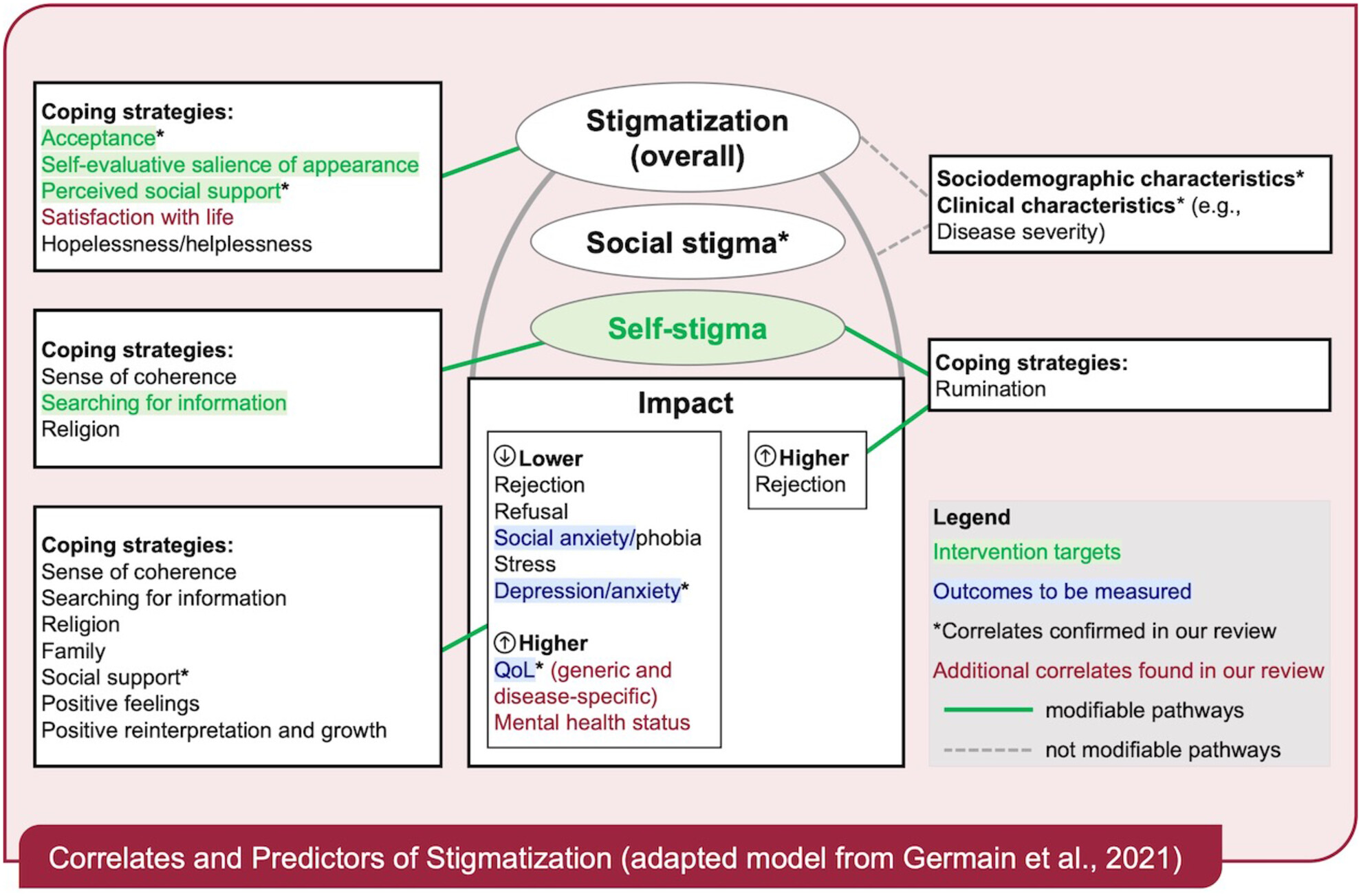
Along with experiencing stigmatization in social contexts, individuals with visible chronic skin disease often deal with self-stigma. The graphical abstract depicts an adapted model from Germain and colleagues (2021) and highlights correlates, predictors and outcomes associated with self-stigma for people with atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, vitiligo, alopecia areata or hidradenitis suppurativa according to the present systematic literature review of 27 included studies. Study quality ratings were good although majority of the reviewed studies were cross-sectional and causal inferences could not be made. Psychosocial correlates to self-stigmatization with supporting evidence in both Germain and colleagues' (2021) model and the current review were noted with an asterisk (*), whereas additional correlates found in our review were emphasized in red text. Several psychosocial correlates were considered modifiable, such as social stigma, coping strategies and social support, and therefore potential targets for psychosocial interventions (highlighted in green and pathways depicted with solid green lines), while others were not (depicted with dashed grey lines). The figure also identifies measurable outcomes (highlighted in blue) for future interventions.
The Dermatology Life Quality Index (DLQI) used as the benchmark in validation of 101 quality-of-life instruments: A systematic review
- Pages: 631-679
- First Published: 13 September 2024
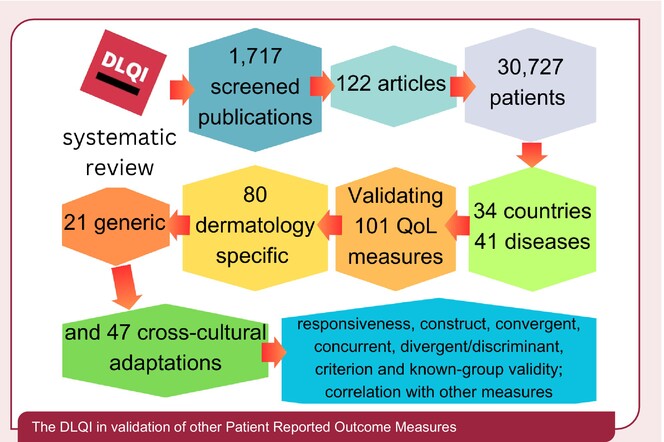
This study systematically analysed peer-reviewed publications describing use of the DLQI in validation of other PRO and QoL measures and identified widespread use of the DLQI as a benchmark in validation of other dermatology PRO/QoL measures. It confirms the central role DLQI plays in the development of novel instruments and validation across dermatology and beyond.
Patient-reported outcome measurements in facial skin surgery and a comparison between Mohs micrographic surgery and conventional excisions
- Pages: 680-687
- First Published: 22 April 2024
Psychosocial and mental impact of alopecia areata: Analysis of the Danish Skin Cohort
- Pages: 688-697
- First Published: 28 June 2024
ANNOUNCEMENT
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
The doctor will see you now, in 4 months: A Belgian perspective on waiting times for dermatologic care
- Pages: e204-e205
- First Published: 10 June 2024
Financial impact on social security of the incorporation of adalimumab for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa: An analysis of the 61-million-contributor Brazilian Social Security System (INSS)
- Pages: e206-e208
- First Published: 29 June 2024
Skin pain and sleep quality numeric rating scales for children aged 6 months to 5 years with atopic dermatitis
- Pages: e209-e212
- First Published: 29 June 2024
Evaluation of antipruritic effects of serlopitant, a neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist, in patients with epidermolysis bullosa: A phase 2 randomized controlled trial
- Pages: e215-e217
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Effectiveness, safety and drug survival of oral roflumilast for hidradenitis suppurativa
- Pages: e218-e221
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Pemphigus foliaceus successfully treated with upadacitinib
- Pages: e222-e224
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Surgical margin reduction in excision of cutaneous melanoma: A retrospective analysis
- Pages: e225-e227
- First Published: 02 July 2024
Large-scale international study on scalp seborrheic dermatitis: Prevalence, demographics, healthcare trends and quality of life
- Pages: e228-e231
- First Published: 02 July 2024
Reflection on the environmental sustainability of cosmeceutical samples received by delegates at the EADV Congress 2023
- Pages: e232-e233
- First Published: 02 July 2024
Cutaneous peri-ocular involvement in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: e234-e236
- First Published: 03 July 2024
Efficacy of virtual reality on pain and anxiety management in dermatological procedures
- Pages: e237-e238
- First Published: 09 July 2024
Hidradenitis suppurativa: A prospective epidemiologic study in Albania
- Pages: e239-e241
- First Published: 12 July 2024
Capillary malformation types are a marker of venous malformation severity
- Pages: e242-e243
- First Published: 12 July 2024
Evaluation of combination therapy with ofatumumab and systemic corticosteroids for pemphigus: A multi-centre cohort study
- Pages: e244-e247
- First Published: 12 July 2024
The risk of developing Kaposi sarcoma after a primary malignancy: A surveillance, epidemiology and end results-based analysis
- Pages: e248-e250
- First Published: 13 July 2024
Repigmentation by body region in patients with vitiligo treated with ruxolitinib cream over 52 weeks
- Pages: e251-e254
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Line-field confocal optical coherence tomography (LC-OCT) for the assessment of flat pigmented lesions of the face
- Pages: e255-e257
- First Published: 20 July 2024
Punch grafting can be used as a supplementary treatment for perilesional halo after melanocyte grafting for vitiligo
- Pages: e258-e260
- First Published: 20 July 2024
Conventional PDT versus one PDT session plus 3% diclofenac gel for severe skin field cancerization of the face and scalp: Randomized controlled trial assessing clinical and histological response
- Pages: e263-e265
- First Published: 29 July 2024
Distinct signatures of cutaneous microbiome associated with disease severity in Hailey–Hailey disease
- Pages: e266-e268
- First Published: 29 July 2024
Drug survival of abrocitinib compared to dupilumab in adult patients with atopic dermatitis
- Pages: e269-e270
- First Published: 29 July 2024
Dermatologic immune-related adverse events: It is time for a game change!
- Pages: e271-e272
- First Published: 02 August 2024
The efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin for the treatment of pyoderma gangrenosum: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: e273-e275
- First Published: 05 August 2024
Sweat volume quantification in paediatric population
- Pages: e276-e277
- First Published: 06 August 2024
The potential role of derma-venereologists in prescribing and managing pre-exposure prophylaxis in Italy
- Pages: e278-e279
- First Published: 06 August 2024
Interactions between dupilumab and vitiligo: A scoping review
- Pages: e280-e282
- First Published: 06 August 2024
Clinical benefit from palbociclib, letrozole and goserelin combination therapy for sweat gland carcinoma with neuroendocrine differentiation (SCAND)
- Pages: e283-e286
- First Published: 08 August 2024
Risankizumab efficacy and safety in psoriatic patients with latent tuberculosis infection: A multicentric real-world study
- Pages: e287-e289
- First Published: 13 September 2024
Anti-IL-23 therapy for the treatment of moderate-to-severe inverse psoriasis: A 52-week multicenter study
- Pages: e290-e292
- First Published: 13 September 2024
Comment on ‘Efficacy of interventions for cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma in situ (Bowen's disease): A systematic review and meta-analysis of proportions’
- Pages: e293-e294
- First Published: 23 September 2024
Reply to ‘Effectiveness, safety and drug survival of oral roflumilast for hidradenitis suppurativa’ by Holgersen et al.
- Pages: e295-e296
- First Published: 20 November 2024