Reflectance confocal microscopy for margin mapping of melanoma of the lentigo maligna type: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Protocol registration: PROSPERO, CRD42023415120.
Abstract
Background
Melanoma of the lentigo maligna (LM) type and its invasive counterpart, lentigo maligna melanoma (LMM), occur in chronically sun-damaged skin and tend to have subclinical extension that makes presurgical margin mapping challenging. Reflectance confocal microscopy (RCM) is a non-invasive imaging modality that enables in vivo visualization of the skin at the cellular level, allowing for adequate estimation of LM/LMM margins.
Objectives
We aimed to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis evaluating RCM's performance compared with histopathology in margin mapping of LM/LMM.
Methods
We searched MEDLINE, Embase, Cochrane, and Clinicaltrials.gov for studies published until July 2023, assessing RCM diagnostic accuracy for presurgical LM/LMM margin delineation. Negative predictive value (NPV; number of true negatives confirmed by histopathology out of all negatives found on RCM) was our primary outcome. Secondary outcomes were proportion of agreement between RCM and histopathology, mean number of stages to clear lesion, sensitivity, and specificity.
Results
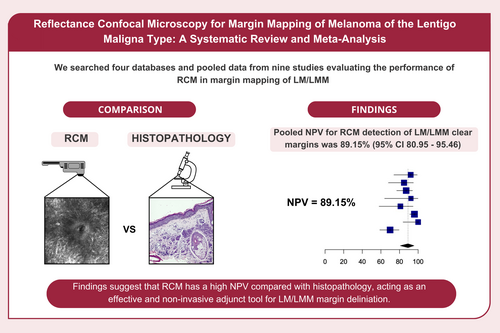
Of the 955 search results, nine studies (329 participants) were included. Pooled NPV for RCM detection of LM/LMM clear margins was 89.15% (95% CI 80.95–95.46; I2 = 80%). The RCM and histopathology agreement rate was 92.09% (95% CI 84.71–96.07; I2 = 57%). Mean number of stages needed to clear the lesion using RCM was 1.16 (95% CI 1.08–1.23; I2 = 0). Compared with histopathology, RCM sensitivity and specificity were 91.4% (95% CI 82.2–96.1; I2 = 0%) and 95.7% (95% CI 90.7–98; I2 = 68%), respectively.
Conclusions
These results support that RCM has a high concordance rate with the gold standard histopathology for presurgical LM/LMM margin mapping, constituting a valuable tool for its management.
Graphical Abstract
When compared with the gold standard histopathologic examination, the non-invasive RCM imaging technique has a negative predictive value (true negative margins confirmed by histopathology among all negative margins analysed by RCM) of 89.15%, highlighting its efficacy for margin mapping of melanoma of the lentigo maligna type.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
K.N. declares the following positions of leadership: Board of Directors—American College of Mohs Surgery (unpaid); Board of Directors—American Society for Dermatologic Surgery (unpaid); Board of Directors—Dermatology Foundation (unpaid). Y.M., I.R.M., I.P.C., S.A.C., A.G., I.L., R.d.M.-S., J.H., M.V. and C.N-D. declare no competing interests.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
This meta-analysis is based on data extracted from previously published research that belongs to the public domain. The authors do not have access to individual study's patient-level data and encourage readers interested in these types of data to contact the corresponding author from each of the studies here included.