Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
GNAS gene mutations affecting XLαs and bone health: A long neglected relationship
- Pages: 279-286
- First Published: 30 May 2023
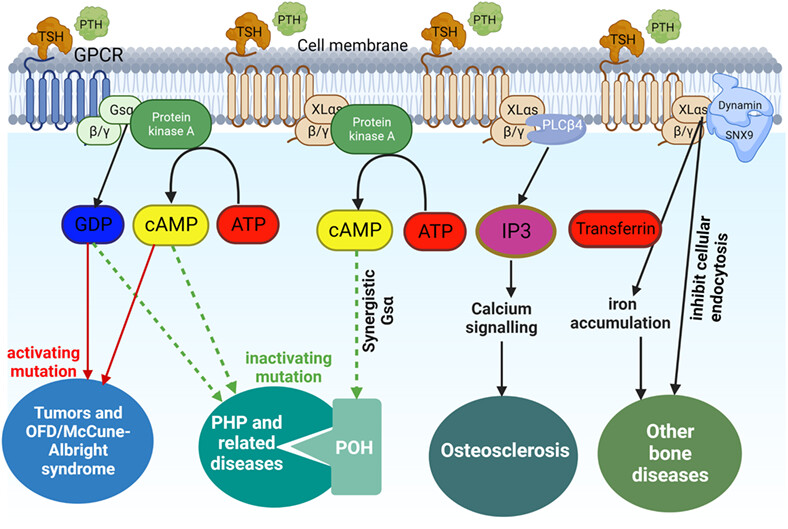
In skeletal health, the importance of other transcriptional products encoded by GNAS genes (e.g., XLαs, extralarge variant of Gsα), in addition to the α-subunit of the activating heterotrimeric G protein (Gsα), cannot be ignored. Abnormal expression of Gsα is associated with certain tumors and Osteofibrous dysplasia (OFD)/McCune-Albright syndrome (activating mutations), pseudohypoparathyroidism(PHP) and related diseases (inactivating mutations). In our review, we found that deletion of XLαs expression can synergize with Gsα to participate in the development of progressive osseous heteroplasia (POH) in PHP-related diseases by regulating the cAMP-PKA signaling pathway, affect bone remodeling through the Phospholipase C β4-inositol triphosphate-Ca2+ pathway and may even act as an inhibitor of clathrin-induced endocytosis in osteocytes.
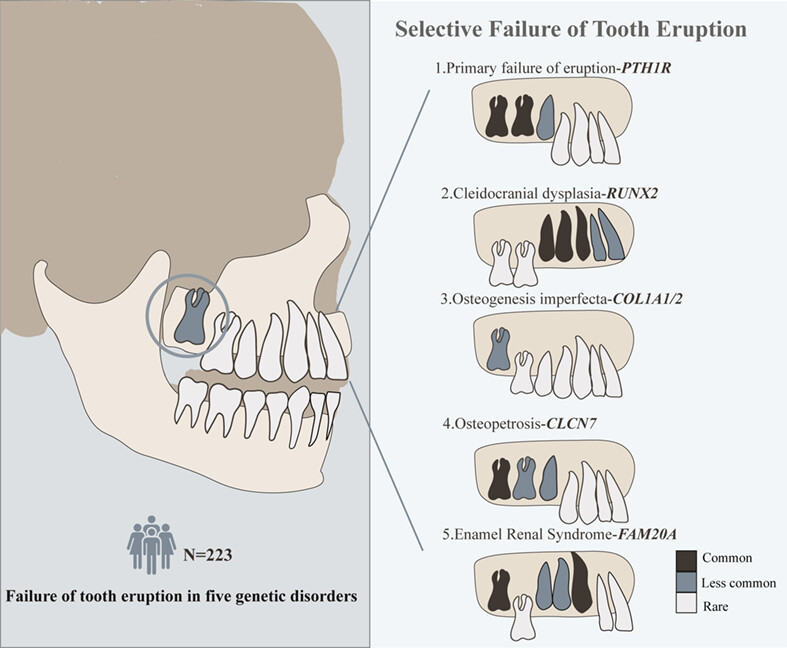
Genotype-phenotype analysis of selective failure of tooth eruption—A systematic review
- Pages: 287-297
- First Published: 13 July 2023
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Genetic diagnosis of kidney disease by whole exome sequencing and its clinical application
- Pages: 298-312
- First Published: 04 June 2023
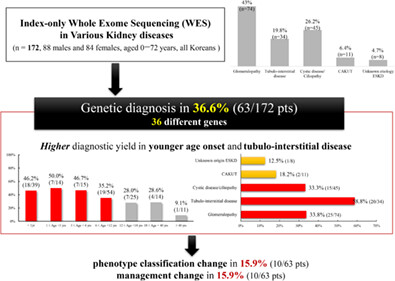
- Among 172 pediatric or adult patients with various kidney diseases, WES diagnosed genetic kidney diseases in 63 (36.6%) patients.
- Higher diagnostic yield was detected in younger age at onset or in tubulo-interstitial disease phenotype.
- Renal phenotypes (16%) reclassified and management (16%) changed after the genetic diagnosis.
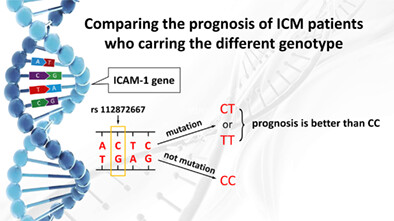
Development and validation of a novel nomogram to predict the impact of the polymorphism of the ICAM-1 gene on the prognosis of ischemic cardiomyopathy
- Pages: 313-323
- First Published: 13 June 2023
A homozygous founder variant in PDE2A causes paroxysmal dyskinesia with intellectual disability
- Pages: 324-333
- First Published: 15 June 2023
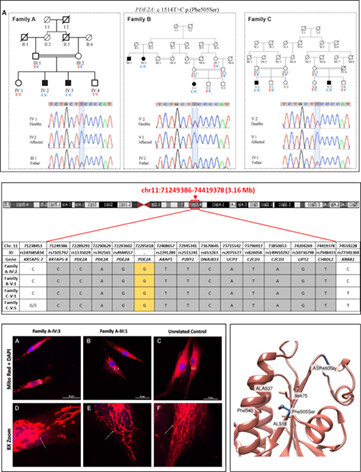
- A homozygous founder variant in PDE2A leads to paroxysmal dyskinesia in three Pakistani families.
- Patient fibroblasts revealed aberrant mitochondrial morphology compared to the controls.
- The identified variant is predicted to result in an empty space in the core of the protein leading to instability of the protein.
Filling the gap: Genetic risk assessment in hypercholesterolemia using LDL-C and LPA genetic scores
- Pages: 334-343
- First Published: 07 July 2023
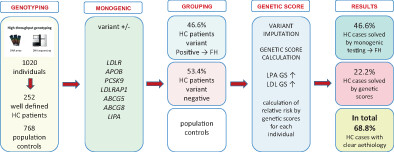
The proposed screening apprach resulted in the predictive identification of at risk individuals in our population cohort with a positive predictive value of 90%. For the clinically diagnosed hypercholesterolemia patients, a more precise diagnosis of the underlying disease etiology is provided by analysing monogenic causes and gentic risk scores associated with increased LDL-C and particularly Lp(a). We found nine novel variants in FH genes and increaded diagnostic yield from 46.6% to 68.8% allowing individualized treatment strategies in the future.
SHORT REPORTS
Novel LSS variants in alopecia and intellectual disability syndrome: New case report and clinical spectrum of LSS-related rare disease traits
- Pages: 344-349
- First Published: 09 May 2023
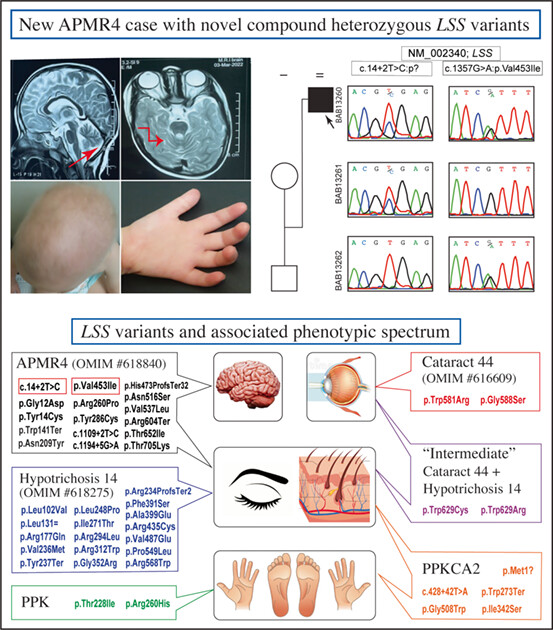
Elbendary et al. report a new Egyptian patient with alopecia-intellectual disability syndrome type 4 (APMR4) and cerebellar involvement due to novel compound heterozygous LSS splice site (c.14+2T>C) and missense (c.1357 G>A; p.V4531) variants. A review of all reported variants to date in 29 families with LSS-related phenotypes showed an emerging genotype–phenotype correlation.
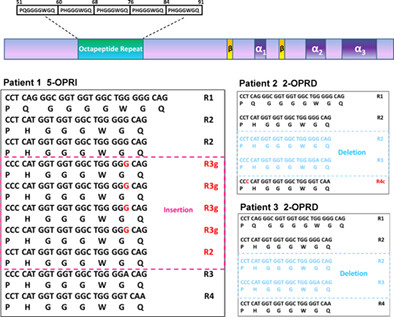
Octapeptide repeat alteration mutations of the prion protein gene in clinically diagnosed Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia
- Pages: 350-355
- First Published: 06 May 2023
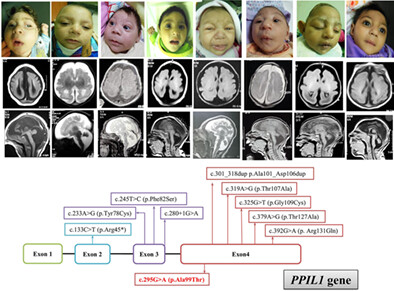
A founder PPIL1 variant underlies a recognizable form of microlissencephaly with pontocerebellar hypoplasia
- Pages: 356-364
- First Published: 15 May 2023
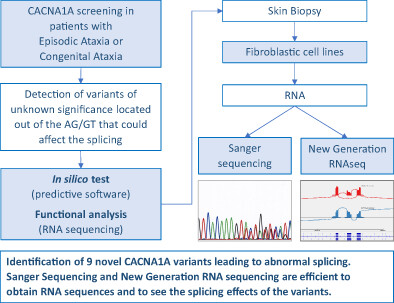
Characterization of novel CACNA1A splice variants by RNA-sequencing in patients with episodic or congenital ataxia
- Pages: 365-370
- First Published: 13 May 2023
Novel biallelic variants expand the phenotype of NAA20-related syndrome
- Pages: 371-376
- First Published: 16 May 2023
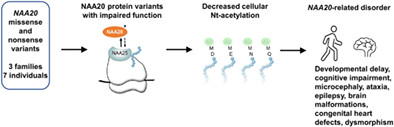
Biallelic pathogenic variants in the NAA20 gene have been described in 7 individuals belonging to 3 separate families. These variants functionally results in a reduced cellular N-acetylation, leading to a phenotypic spectrum that includes developmental delay, cognitive impairment, microcephaly, ataxia, epilepsy, brain malformations, congenital heart defects, and craniofacial dysmorphisms.
Increased diagnostic yield from negative whole genome-slice panels using automated reanalysis
- Pages: 377-383
- First Published: 17 May 2023
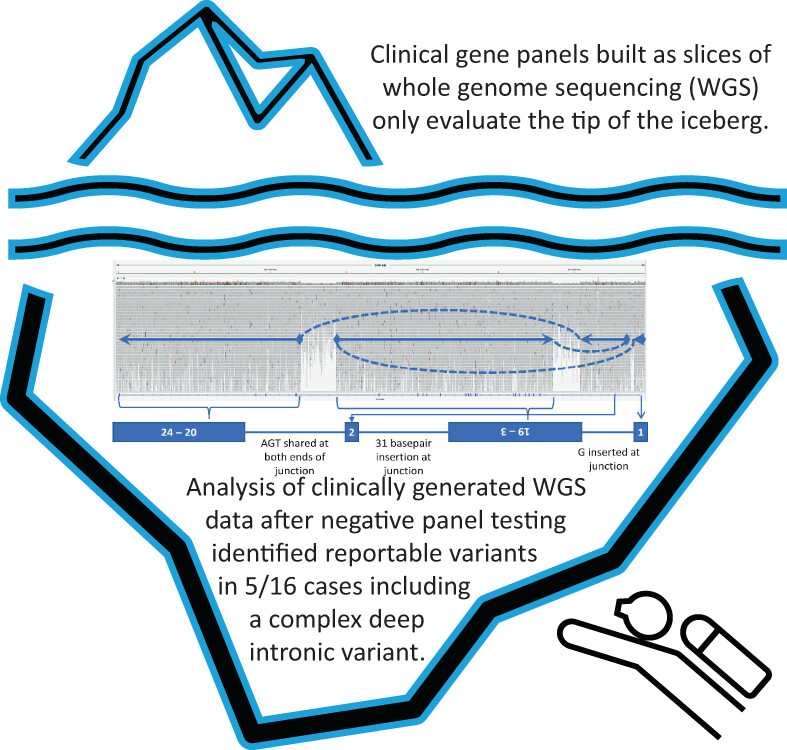
Whole genome sequencing (WGS) data, produced from clinically ordered panels built as bioinformatic slices for 16 clinically diverse, undiagnosed cases, were reanalyzed using a machine-learning-based tool for variant prioritization and yielded additional potentially clinically significant variants in five out of 16 cases including a complex variant not detectable by exome.
RESEARCH LETTERS
Discovering the ANK2-related autism phenotype
- Pages: 384-386
- First Published: 23 April 2023

Interestingly, disease-causing mutations in the ANK2 gene have been identified in patients with autism since 2012, though with no full clinical description. In this Research Letter, for the first time, we describe the detailed characteristics of a patient with autism caused by a new mutation in this gene. Our report is a first step to better understanding ANK2-related autism and will contribute to facilitating its further diagnosis.
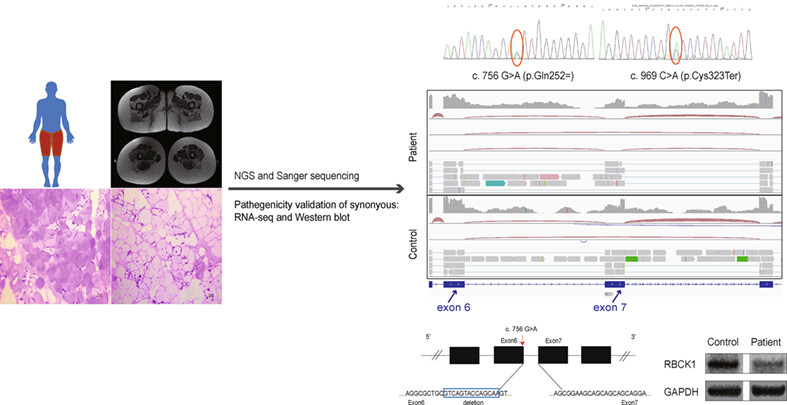
A synonymous codon variant altering splicing of RBCK1 expands the phenotype and genotype spectra of polyglucosan body myopathy 1
- Pages: 387-389
- First Published: 27 April 2023
Genome sequencing identifies KMT2E-disrupting cryptic structural variant in a female with O'Donnell-Luria-Rodan syndrome
- Pages: 390-392
- First Published: 08 May 2023
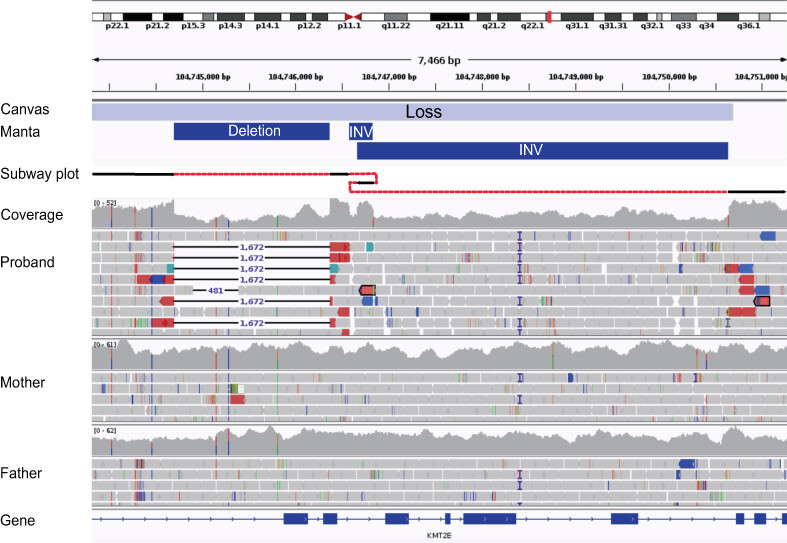
We describe a patient from the 100,000 Genomes Project with a complex de novo structural variant within KMT2E leading to O'Donnell-Luria-Rodan syndrome. This case expands the mutational spectrum for this syndrome and highlights the importance of revisiting unsolved cases using better SV prioritisation tools and updated gene panels.
Pigmentation abnormalities in Coffin-Siris syndrome
- Pages: 393-394
- First Published: 11 May 2023