Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Image
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 15 June 2023
The cover image is based on the Short Report A nodal EBV-positive T cell lymphoma with a T follicular helper cell phenotype by Zhaoxuan Zhang et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/his.14919.
Issue Information
Review
Diagnostic test accuracy meta-analysis of PRAME in distinguishing primary cutaneous melanomas from benign melanocytic lesions
- Pages: 3-14
- First Published: 21 March 2023
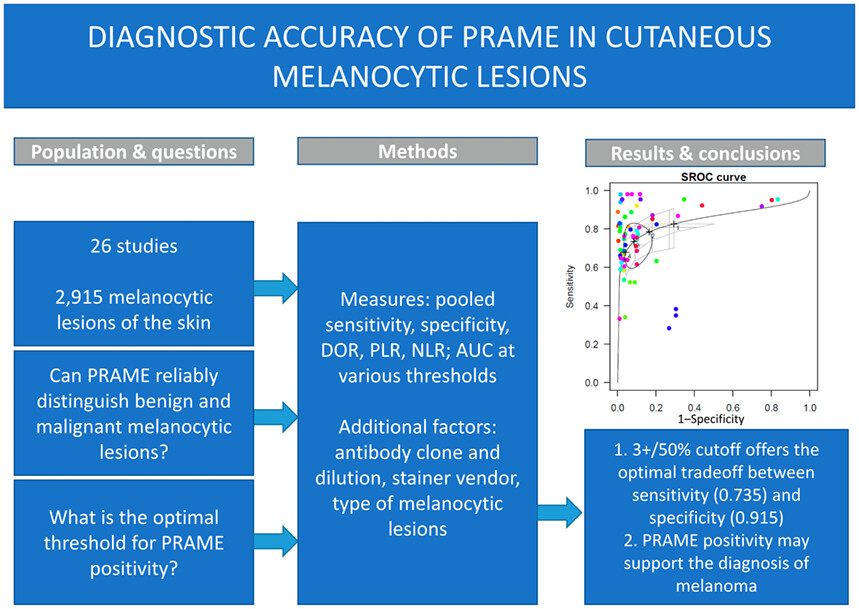
PRAME immunohistochemistry may serve as an ancillary marker to support the diagnosis of melanoma, but its performance is low in spitzoid lesions. The meta-analysis suggests that the 3+/50% threshold might be more useful in practice than the widely recommended 4+/75%, as it shows higher sensitivity with retained satisfactory specificity.
Editorial
What's in a name? The overlap between tumour typing and grading highlighting deficiencies in nomenclature
- Pages: 15-16
- First Published: 15 June 2023
Original Articles
Human papillomavirus and p53 status define three types of vulvar squamous cell carcinomas with distinct clinical, pathological, and prognostic features
- Pages: 17-30
- First Published: 26 April 2023
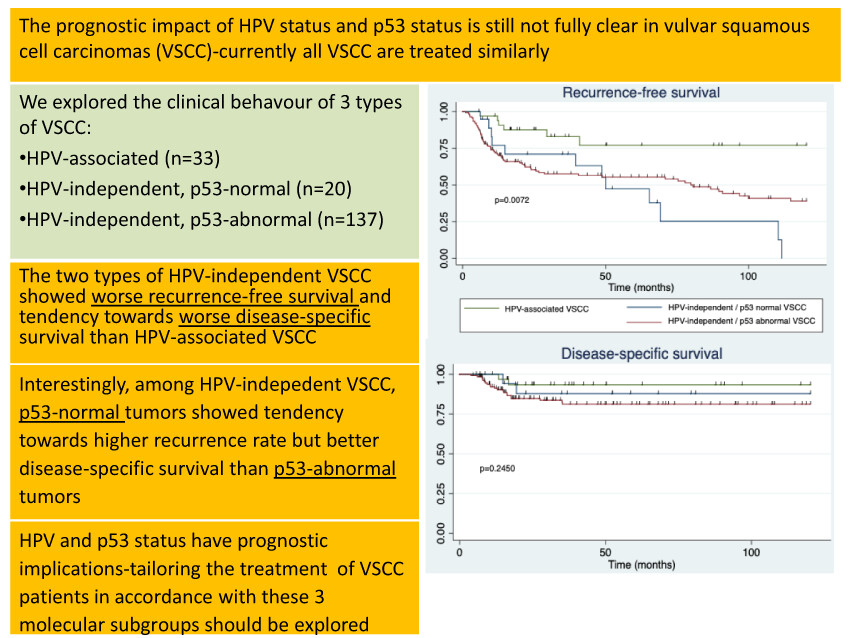
Currently, all VSCC are treated similarly, irrespective of HPV and p53 status. Our findings suggest that in the future, the treatment of VSCC might be tailored in accordance with these molecular subgroups (HPV-associated VSCC, HPV-independent VSCC with wildtype p53, HPV-independent VSCC with mutated p53), given their different prognosis and behaviour.
Metastatic solid tumours to the penis: a clinicopathologic evaluation of 109 cases from an international collaboration
- Pages: 31-39
- First Published: 18 April 2023
We describe the largest and most comprehensive series of metastatic solid tumours to the penis with 109 cases. Penile metastases often occurred in the setting of advanced metastatic disease and were associated with poor prognosis. The most frequent primary site was the genitourinary tract, specifically the prostate.
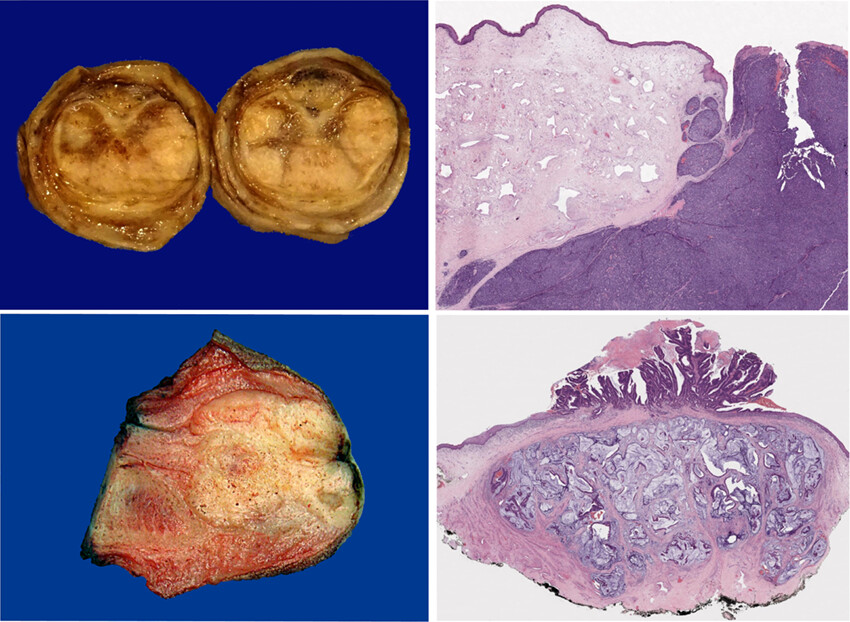
Intraosseous hibernoma: clinicopathologic and imaging analysis of 18 cases
- Pages: 40-48
- First Published: 26 April 2023
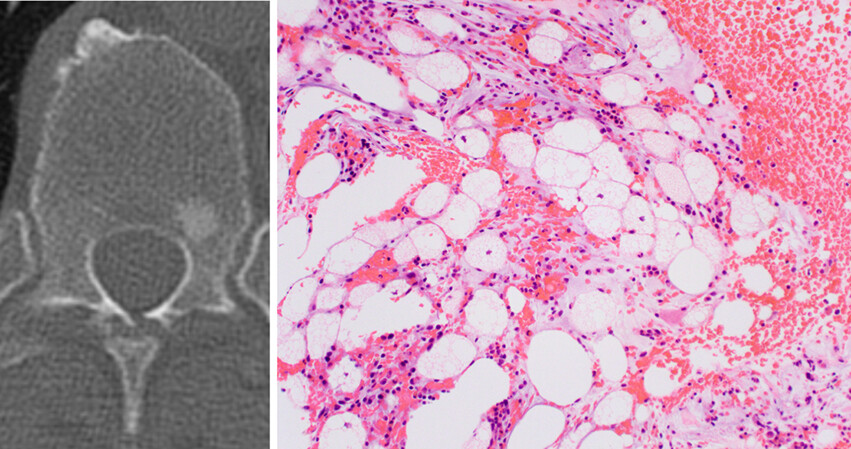
Intraosseous hibernomas are rare benign tumours most frequently detected as small sclerotic lesions in the spine and pelvis of older adults. Clinically and on imaging studies, these tumours frequently raised concern for a metastasis. Accurate classification is needed to prevent unnecessary procedures and assuage fears of an aggressive process.
Diagnostic utility of FOXO1 immunohistochemistry for rhabdomyosarcoma classification
- Pages: 49-56
- First Published: 01 March 2023
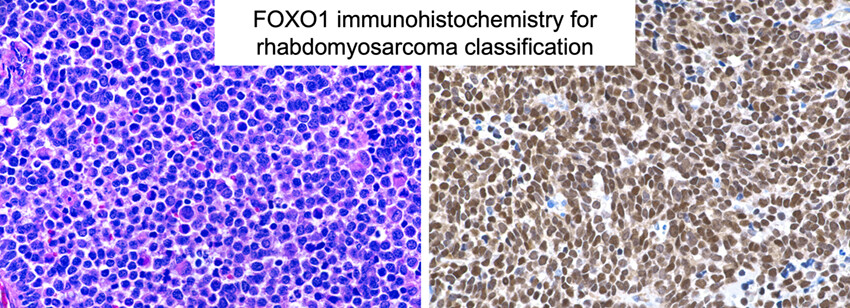
Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma is characterised by an oncogenic translocation involving PAX3 or PAX7 and FOXO1; identification of this translocation is important for diagnostic classification. This study suggests that among rhabdomyosarcomas, FOXO1 immunohistochemistry is a highly sensitive and relatively specific surrogate marker of the PAX3/7::FOXO1 fusion oncoprotein.
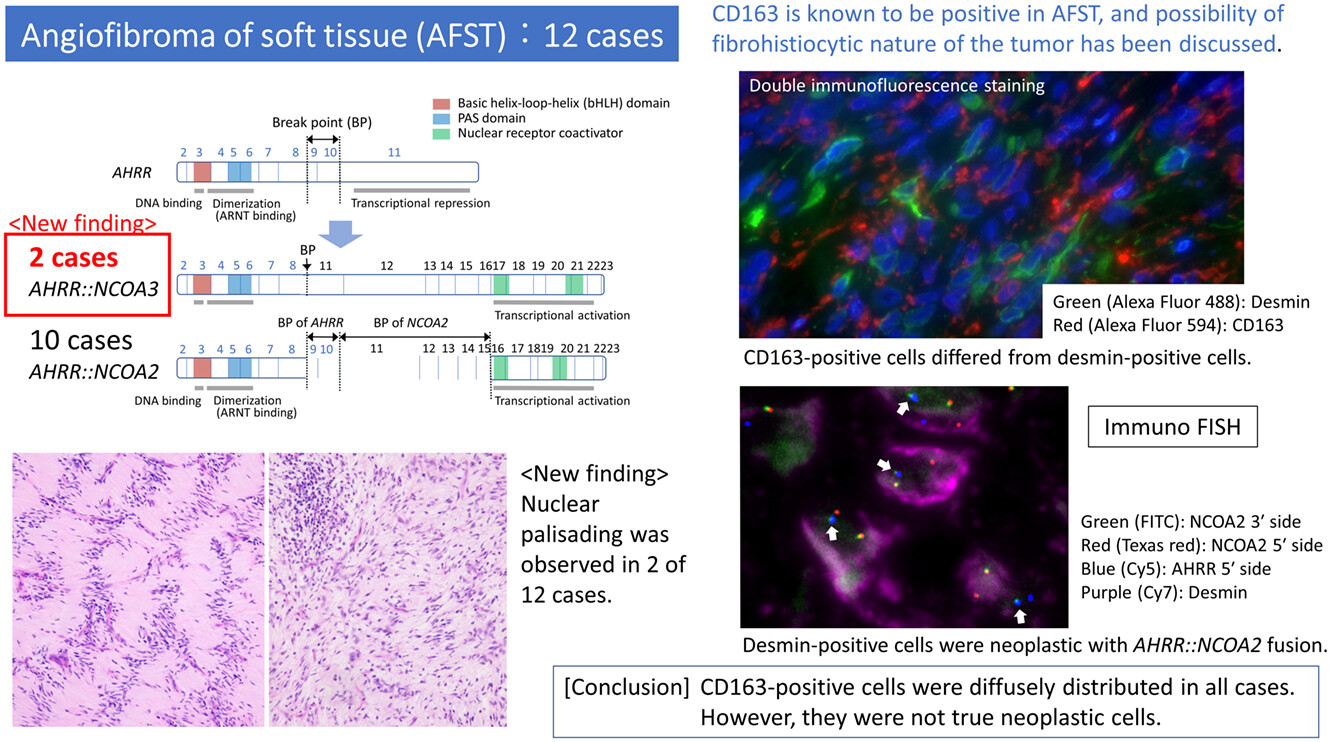
Clinicopathologic and genetic characterization of angiofibroma of soft tissue: a study of 12 cases including two cases with AHRR::NCOA3 gene fusion
- Pages: 57-66
- First Published: 01 March 2023
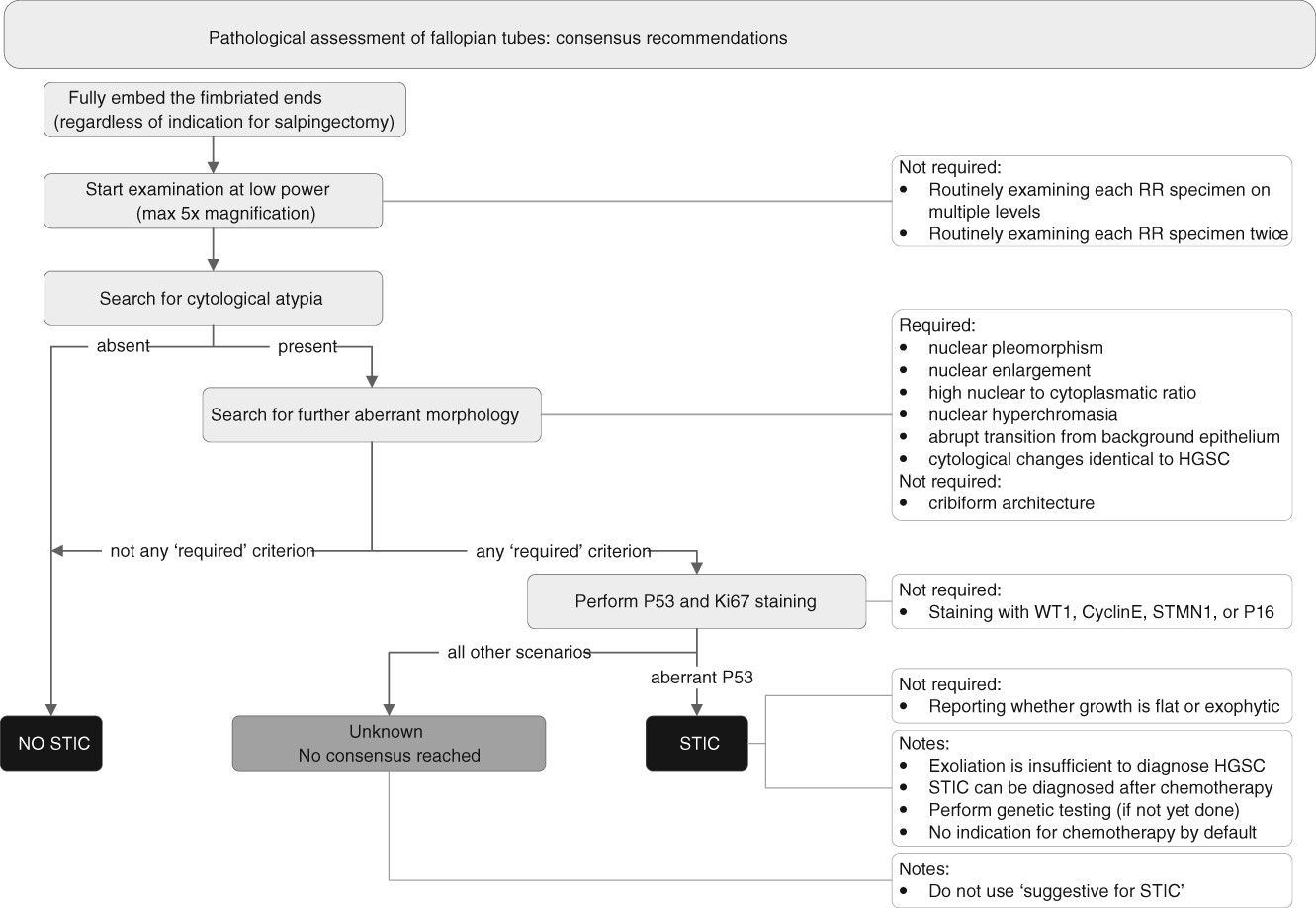
Consensus based recommendations for the diagnosis of serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma: an international Delphi study
- Pages: 67-79
- First Published: 20 March 2023
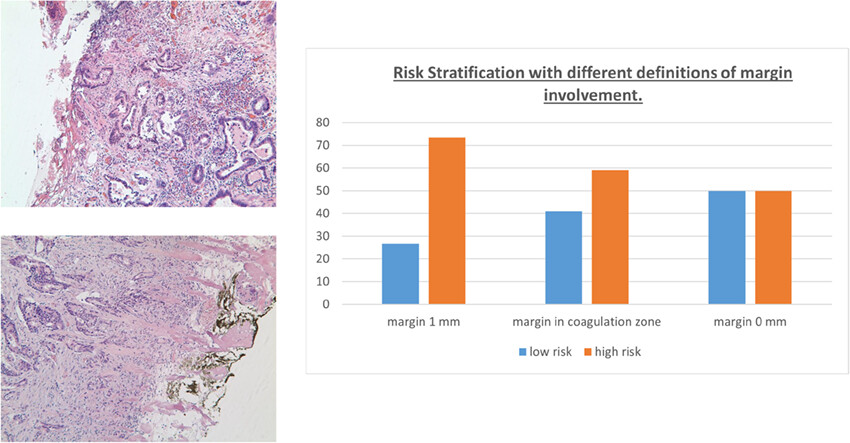
Resection margin involvement after endoscopic excision of malignant colorectal polyps: definition of margin involvement and its impact upon tumour recurrence
- Pages: 80-90
- First Published: 20 March 2023
BRCA1 and BRCA2 carriers with breast, ovarian and prostate cancer demonstrate a different pattern of metastatic disease compared with non-carriers: results from a rapid autopsy programme
- Pages: 91-103
- First Published: 31 March 2023
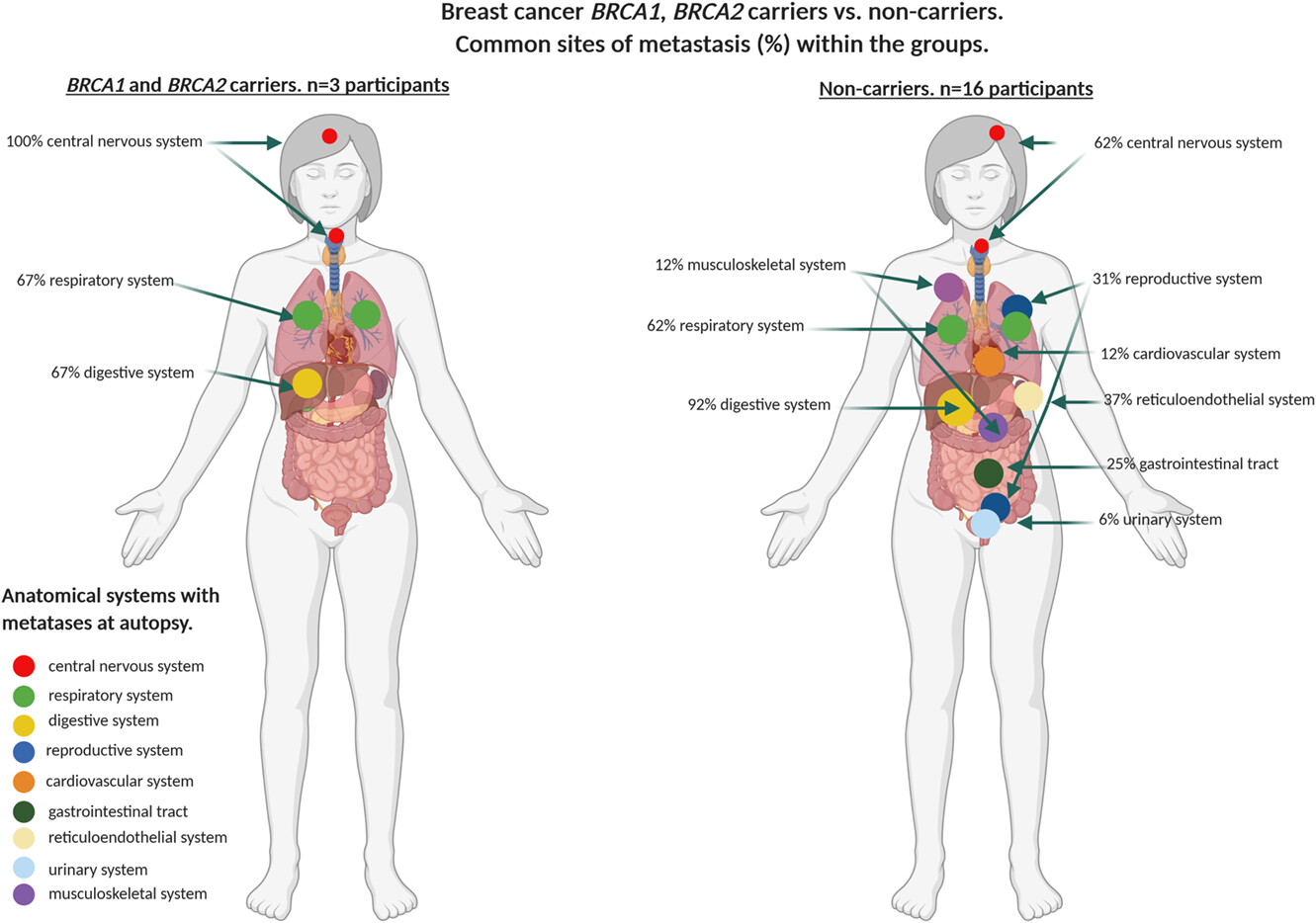
This study catalogued and compared the pattern of metastatic disease in germline BRCA1/2 pathogenic mutation carriers and non-carriers with breast, ovarian and prostate cancer from a rapid autopsy programme. Our findings suggest that metastatic patterns of breast and ovarian cancers maybe impacted by BRCA1/2 carrier status, suggesting that tumours derived from patients with these mutations use different mechanisms of dissemination.
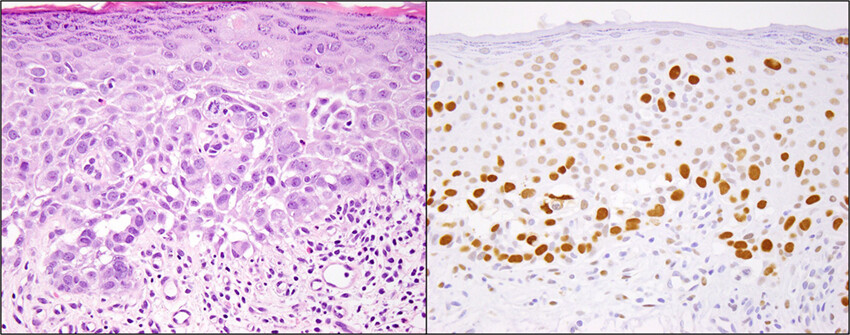
TRPS1 expression is sensitive and specific for primary extramammary Paget disease
- Pages: 104-108
- First Published: 27 March 2023
Spectrum of kinase gene rearrangements in a large series of paediatric inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours
- Pages: 109-115
- First Published: 18 April 2023
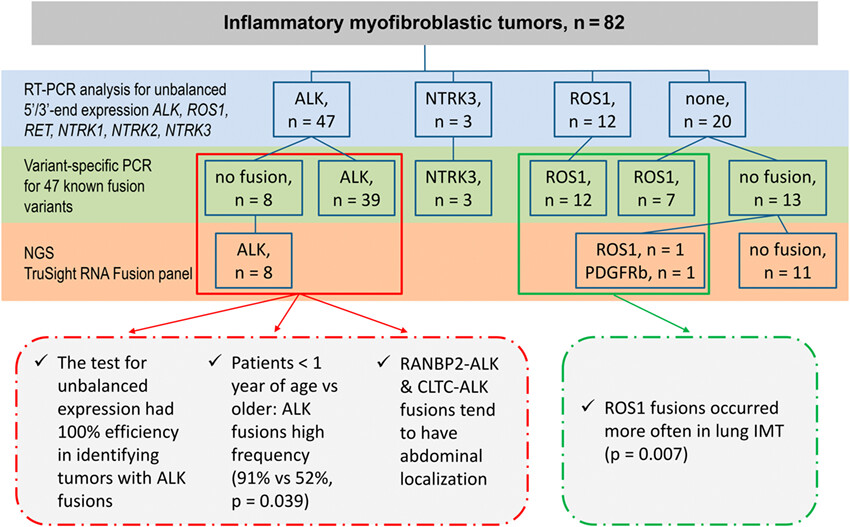
This study presents the largest series of inflammatory myofibroblastic tumours (IMTs), which were subjected to comprehensive analysis of kinase gene rearrangements. A combination of non-expensive PCR test for 5′/3′-end unbalanced gene expression, variant-specific PCR and NGS revealed gene fusions in 71 of 82 (87%) IMTs. Some rearrangements demonstrated age- and organ-dependent distribution.
DNA content abnormality frequently develops in the right/proximal colon in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease and is highly predictive of subsequent detection of dysplasia
- Pages: 116-125
- First Published: 03 April 2023
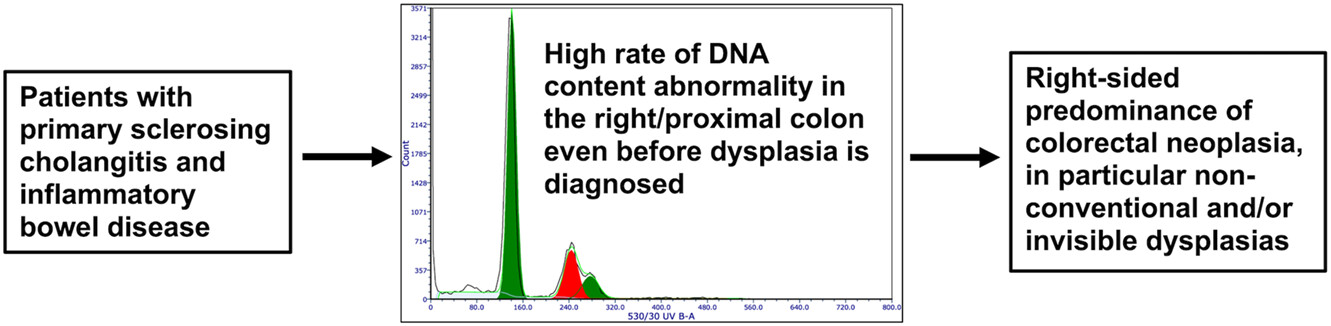
DNA content abnormality is frequently detected in the right/proximal colon in patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis and inflammatory bowel disease even before dysplasia is diagnosed, and is highly predictive of subsequent detection of dysplasia, in particular, nonconventional and/or invisible dysplasias.
Low PD-L1 expression in immune cells predicts the presence of nodal metastasis in early invasive (pT1) colorectal cancer: a novel tool to tailor surgical treatment
- Pages: 126-136
- First Published: 18 April 2023
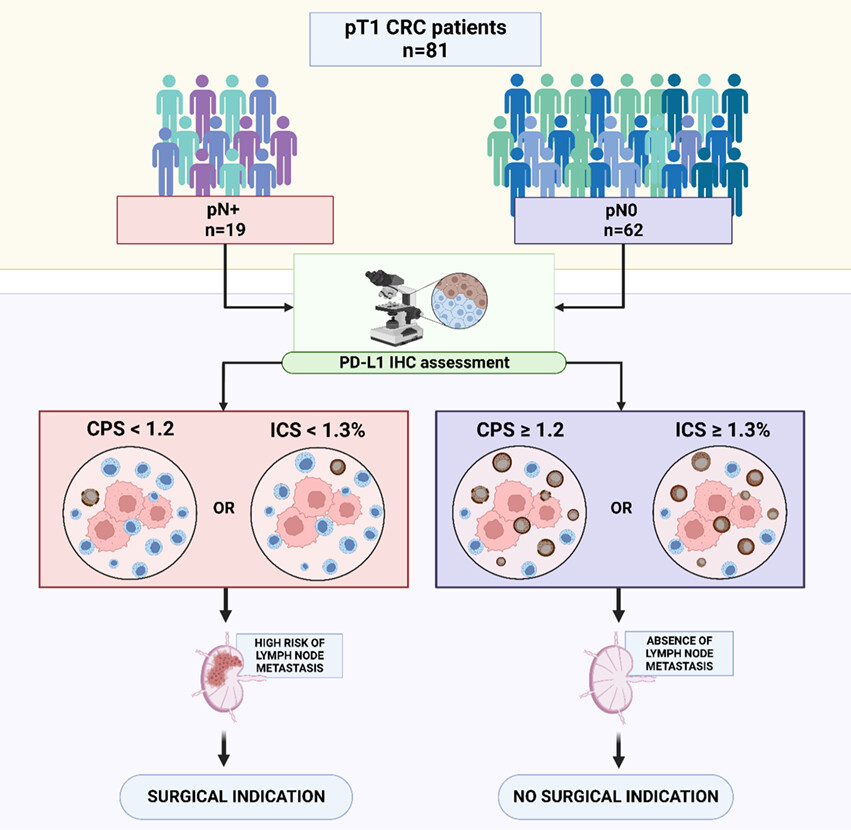
Low PD-L1 expression by immune cells predicts lymph node metastasis in pT1 colorectal carcinoma. PD-L1 CPS < 1.2 and PD-L1 ICS < 1.3% were determined to be the optimal cut-off values, allowing the identification of metastatic patients and thus to potentially avoid a significant rate of unnecessary surgeries.
Short Reports
A nodal EBV-positive T cell lymphoma with a T follicular helper cell phenotype
- Pages: 137-142
- First Published: 18 April 2023
Lesson of the Month
Correspondence
MiR-371a-3p in cystic trophoblastic tumour of the testis: supporting a maturation phenomenon towards teratoma
- Pages: 151-154
- First Published: 26 April 2023
Small-cell carcinoma of the ovary hypercalcaemic type shows a wild-type immunohistochemical staining pattern of p53
- Pages: 154-156
- First Published: 17 April 2023
Collagenous colitis incomplete triggered by SARS-CoV-2 infection
- Pages: 156-159
- First Published: 11 April 2023