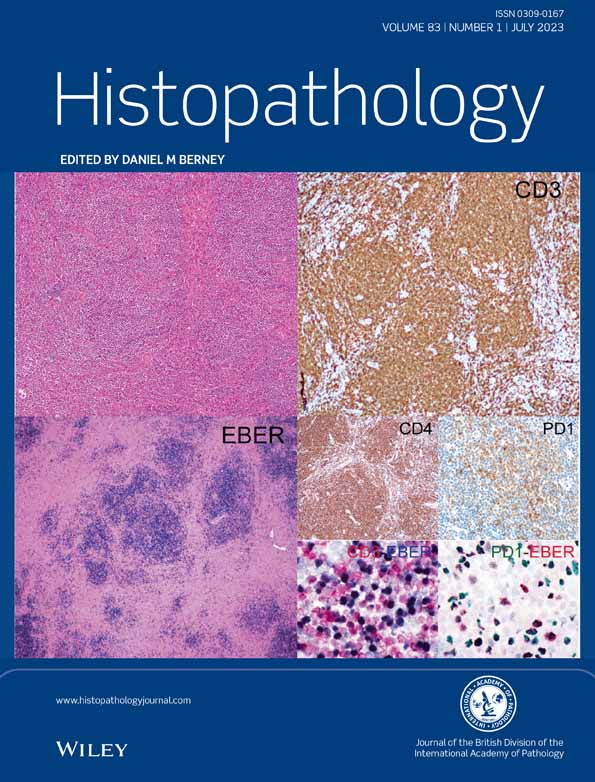
A nodal EBV-positive T cell lymphoma with a T follicular helper cell phenotype
Zhaoxuan Zhang and Wei Wang contributed equally to this study.
Abstract
Aims
Nodal T follicular helper (TFH) cell lymphoma (nTFHL) is a rare type of clinically aggressive T cell lymphoma. With this lymphoma type, Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) infection is frequently detected in non-neoplastic B lymphocytes, but not yet identified in neoplastic T cells. We report two cases of nTFHL showing a classic morphology and immunoprofile, with EBV-encoded small RNAs (EBER) in-situ hybridisation positivity in neoplastic TFH cells.
Methods and results
Clonal T cell receptor (TR) gene rearrangement was detected in both cases. Whole exome sequencing identified TET2, RHOA p. G17V, as well as gene mutations unique to each case. Microdissection analysis showed EBER positivity in tumour cells and in background non-neoplastic T lymphocytes.
Conclusion
These two immunocompetent cases of nTFHL with EBV-positive tumour cells exhibit the featured gene mutation profile and poor prognosis of this disease. This novel finding of EBV positivity in our cases expands the currently recognised spectrum of EBV-positive nodal T cell lymphomas to include rare cases of nTFHL.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the report, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.