Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
EDITOR'S CHOICE
EDITORIAL
Introducing the Global Health and Equity section in the British Journal of Dermatology
- Pages: 201-202
- First Published: February 2022
COMMENTARIES
How to manage patients with Gorlin syndrome
- Page: 203
- First Published: 22 November 2021
Linked Article: Verkouteren et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:215–226.
Atopic dermatitis, hypertension and cardiovascular disease
- Pages: 203-204
- First Published: 02 November 2021
Linked Article: Yousaf et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:227–235.
Are antimicrobial peptides a double-edged sword in hidradenitis suppurativa pathophysiology?
- Pages: 204-205
- First Published: 17 November 2021
Linked Article: Yao et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:236–244.
Adaptive designs for clinical trials have potential advantages, but statistical challenges lurk!
- Pages: 205-206
- First Published: 22 November 2021
Linked Article: Cro et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:245–256.
Alopecia areata: progress, but who pays?
- Pages: 206-207
- First Published: 07 October 2021
Linked Article: Harries et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:257–265.
Personal ultraviolet radiation exposure can be determined through a simple modelling approach
- Pages: 207-208
- First Published: 24 November 2021
Linked Article: Soueid et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:266–273.
Challenges of multidimensional atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 208-209
- First Published: 24 November 2021
Linked Article: Nakamura et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:274–284.
Targeting CD56 with an antibody–drug conjugate in Merkel cell carcinoma
- Pages: 209-210
- First Published: 24 November 2021
Linked Article: Esnault et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:295–306.
Genome-wide scan for structural variation underlying psoriasis
- Pages: 210-211
- First Published: 22 November 2021
Linked Article: Zhen et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:307–317.
Autophagy protects from photoageing in skin fibroblasts
- Pages: 211-212
- First Published: 15 November 2021
Linked Article: Xie et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:318–333.
Time for a change
- Pages: 212-213
- First Published: 24 November 2021
Linked Article: Ulriksdotter et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:334–340.
Recognizing psoriasis in children and adolescents: the DIPSOC study
- Pages: 213-214
- First Published: 22 November 2021
Linked Article: Burden-Teh et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:341–351.
Evidence-Based Dermatology
GUIDELINES
A guideline for the clinical management of basal cell naevus syndrome (Gorlin–Goltz syndrome)
- Pages: 215-226
- First Published: 10 August 2021
Linked Comment: E. Epstein. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:203.
Plain language summary available online
Systematic Review
Association between atopic dermatitis and hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 227-235
- First Published: 28 July 2021
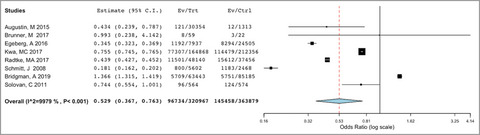
What is already known about this topic?
- Previous studies have showed conflicting results regarding the association between atopic dermatitis (AD) and hypertension.
What does this study add?
- This systematic review and meta-analysis found that AD, particularly moderate-to-severe disease, is associated with increased odds of hypertension compared with healthy controls, especially among the US population.
Linked Comment: H. Ben Abdallah and C. Vestergaard. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:203–204.
Plain language summary available online
Antimicrobial peptides in hidradenitis suppurativa: a systematic review
- Pages: 236-244
- First Published: 09 September 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Various studies have investigated the level of antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) in hidradenitis suppurativa (HS).
What does this study add?
- The data presented in this systematic review point to a dysregulation of AMPs in both lesional and nonlesional skin in HS.
Linked Comment: S.L. Schell and A.M. Nelson. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:204–205.
Plain language summary available online
Original Articles
CLINICAL TRIAL
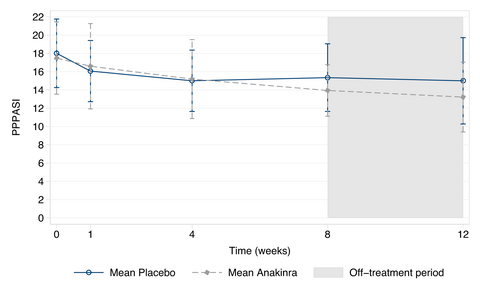
Anakinra for palmoplantar pustulosis: results from a randomized, double-blind, multicentre, two-staged, adaptive placebo-controlled trial (APRICOT)
- Pages: 245-256
- First Published: 19 August 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Treatment options for palmoplantar pustulosis include superpotent corticosteroids, phototherapy, acitretin, methotrexate and ciclosporin. However, these have poor evidence for benefit and there is a risk of toxicity with long-term use.
- Anakinra is a recombinant interleukin (IL)-1 receptor antagonist that blocks the activity of IL-1α and IL-1β, two cytokines repeatedly linked to neutrophil activation and extravasation.
- A therapeutic benefit of anakinra has been shown in neutrophilic dermatoses and conditions that manifest with skin pustulation.
What does this study add?
- Anakinra was not significantly superior to placebo at 8 weeks in objective investigator-assessed and patient-reported measures.
- A greater proportion of participants in the anakinra group strongly agreed that the treatment was worthwhile.
- The safety profile of anakinra was consistent with previous studies.
- This is one of the largest randomized controlled trials for this rare condition, providing important data on its natural history and change in disease severity over time.
Linked Comment: S.N. Lo and J.F. Thompson. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:205–206.
Plain language summary available online
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The epidemiology of alopecia areata: a population-based cohort study in UK primary care
- Pages: 257-265
- First Published: 06 July 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Alopecia areata (AA) is a common cause of nonscarring hair loss associated with psychological morbidity.
- Large-scale population-based information on the disease burden and clinical management of AA is lacking.
What does this study add?
- In the largest population-based study of AA to date, comprising 4·16 million people, we estimate that new-onset AA peaks at age 25–29 years.
- People of Asian ethnicity, and from socially deprived and urban areas, are more likely to present with AA.
- After diagnosis, one in four people with AA are referred for specialist dermatology review. Specialist referral rates are lower in people from more socially deprived areas.
Linked Comment: R. Sinclair. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:206–207.
Plain language summary available online
Estimating personal solar ultraviolet radiation exposure through time spent outdoors, ambient levels and modelling approaches
- Pages: 266-273
- First Published: 17 August 2021

What is already known about this topic?
- Most studies evaluating health effects of solar ultraviolet radiation (UVR) have relied on surrogates to assess personal UVR exposure.
- However, the available evidence validating these surrogates is scarce.
What does this study add?
- In the present study, we evaluated and compared the validity of three approaches to estimate personal UVR exposure (objectively measured using a personal dosimeter), including (i) ambient UVR levels, (ii) time spent outdoors and (iii) a modelling approach, during different seasons among indoor and outdoor workers.
- Modelled UVR exposure and time outdoors could predict more than three-quarters of the variation in the objectively measured personal UVR (and are therefore of value to be applied in epidemiological studies of the health effects of UVR), whereas ambient UVR could predict only around one-fifth.
- Our findings support a major role of personal behaviour in determining personal UVR exposure.
Linked Comment: P. O’Mahoney. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:207–208.
Plain language summary available online
Modelling trajectories of parentally reported and physician-confirmed atopic dermatitis in a birth cohort study
- Pages: 274-284
- First Published: 26 September 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Atopic dermatitis (AD) is heterogeneous, but there is no general consensus on what the different subtypes are.
- Techniques such as latent class analysis (LCA) have been used to disentangle the long-term course of AD.
- AD phenotypes assigned the same name in different studies often differ in the age of onset, temporal trajectory, distributions within a population and associated risk factors, which makes comparisons difficult and clinical application uncertain.
What does this study add?
- We report that the use of different data sources and definitions of AD has a major influence on the number and type of AD phenotypes identified by longitudinal LCA, in addition to the phenotype membership among individual children.
- Although AD latent classes, at a population level, appeared similar when different definitions were used, almost half of the children changed class allocation in different models.
- The association with oral food challenge-confirmed peanut allergy across all models was similar, with a striking nine- to 11-fold increase among children in the persistent AD class.
Linked Comment: S-P. Sinikumpu and L. Huilaja. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:208–209.
Plain language summary available online
QUALITATIVE AND OUTCOMES RESEARCH
Psychometric validation and responder definition of the sleep disturbance numerical rating scale in moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 285-294
- First Published: 05 October 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Sleep disturbance (SD) is a dynamic, multidimensional concept resulting in daytime fatigue and subsequent changes in physical and mental health that vary from day to day.
- SD is an important part of the burden of atopic dermatitis, but ways of effectively and reliably measuring it from the patient perspective have been lacking.
- A self-reported, daily, 11-point SD numerical rating scale (NRS) was recently developed for assessing SD in patients with moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis, and its content validity was previously established.
What does this study add?
- The study showed that the SD NRS is reliable, valid and responsive and can measure day-to-day fluctuations in SD related to atopic dermatitis.
- The study also established an initial responder definition (i.e. meaningful interpatient change) for the SD NRS score.
What are the clinical implications of this work?
- The SD NRS is a brief, simple, easy-to-interpret and validated patient-reported global measure for the daily assessment of SD related to atopic dermatitis.
- The SD NRS can be used in clinical trials and clinical practice to assess changes in sleep quality in patients with atopic dermatitis.
Plain language summary available online
TRANSLATIONAL RESEARCH
Adcitmer®, a new CD56-targeting monomethyl auristatin E-conjugated antibody, is a potential therapeutic approach in Merkel cell carcinoma
- Pages: 295-306
- First Published: 28 September 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) is an aggressive skin cancer.
- While immune checkpoint inhibitors constitute a major advance in treating patients with MCC with advanced disease, new therapeutic options are still urgently required.
- CD56, which is expressed by most MCC tumours, might constitute a therapeutic target for the development of antibody–drug conjugate therapies.
What does this study add?
- We generated a CD56-targeting monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) bioconjugate antibody (Adcitmer®) and demonstrated its optimal biochemical properties, specific binding and cytotoxicity in vitro in MCC cell lines, and its capacity to reduce tumour growth in vivo in a MCC mouse model.
What is the translational message?
- Adcitmer®, a new CD56-targeting MMAE bioconjugate antibody, may represent a potential therapeutic option to be investigated as an alternative approach or in combination with immune checkpoint inhibitors in patients with inoperable MCC.
Linked Comment: L. Leiendecker et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:209–210.
Plain language summary available online
Three novel structural variations at the major histocompatibility complex and IL12B predispose to psoriasis
- Pages: 307-317
- First Published: 09 September 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Single-nucleotide polymorphism-based association studies have uncovered hundreds of genetic variants associated with psoriasis.
- However, the missing heritability and unclear underlying pathogenesis of psoriasis still exist.
- Several structural variations (SVs) associated with psoriasis have been reported, but they only cover a small proportion of the missing heritability and the recruited sample size was limited.
What does this study add?
- We report the most comprehensive SV map of psoriasis so far, with a large sample size.
- We undertook a genome-wide screen of SVs in five independent Han Chinese cohorts with a total of 45 386 participants.
- We identified two novel SVs at the major histocompatibility complex, one novel SV at IL12B and confirmed one previously reported SV at the late cornified envelope gene cluster for psoriasis.
What is the translational message?
- A full understanding of the mechanisms contributing to psoriasis risk at established susceptibility loci should take SVs into account.
- The associated SVs identified will provide novel targets for diagnosis and treatment.
Linked Comment: N. Dand. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:210–211.
Plain language summary available online
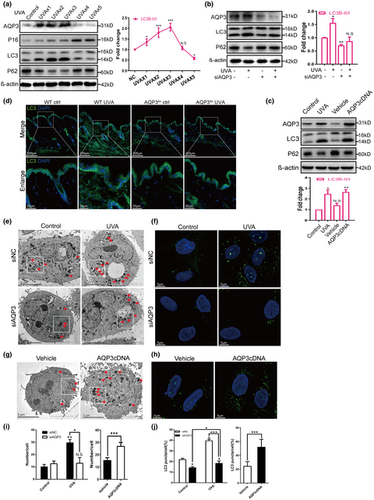
Autophagy induction regulates aquaporin 3-mediated skin fibroblast ageing
- Pages: 318-333
- First Published: 28 July 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Ultraviolet (UV) exposure is one of the leading causes of skin ageing and disease.
- Autophagy is an essential catabolic pathway that clears damaged cytoplasmic components and abnormal particles.
- Autophagy is linked to various diseases including skin ageing, but its relationship with UV in premature skin ageing remains controversial.
- Aquaporin 3 (AQP3) is the predominant aquaporin expressed in the skin and was recently found to be associated with autophagy in cancer cells.
What does this study add?
- We observed a different response of autophagy and senescence in human dermal fibroblasts to short- or long-term UVA exposure.
- Short-term UVA irradiation induced autophagy and upregulated AQP3 but not senescence, whereas long-term UVA irradiation inhibited autophagy, AQP3 and trigger senescence in vitro and in vivo.
- Autophagy induced by AQP3 overexpression robustly prevented UVA-induced senescence in vitro and in vivo.
What is the translational message?
- UV-triggered cutaneous ageing severely compromises youthful appearance.
- Besides its function as a channel, AQP3 controls skin photoageing by regulating autophagy through direct interactions with DEDD/Beclin1.
- The sophisticated regulating mechanism of AQP3 may be one explanation for the diverse responses of skin cells to different doses of UV stimulation.
- AQP3 represents a potential target for future interventions against skin ageing.
Linked Comment: D. Bergamaschi. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:211–212.
Plain language summary available online
MEDICAL DERMATOLOGY
Allergic contact dermatitis caused by dipropylene glycol diacrylate in the Omnipod® insulin pump
- Pages: 334-340
- First Published: 12 September 2021
What is already known about this topic?
- Contact allergy to medical devices (MDs) is a growing clinical problem.
- Isobornyl acrylate is a culprit allergen found in several different MDs in recent years.
What does this study add?
- Dipropylene glycol diacrylate has now for the first time been identified in an MD.
- There is evidence of alteration in device contents between batches, risking polysensitization among users.
Linked Comment: T. Agner and A. Goossens. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:212–213.
Plain language summary available online
PAEDIATRIC DERMATOLOGY
Identifying the best predictive diagnostic criteria for psoriasis in children (< 18 years): a UK multicentre case–control diagnostic accuracy study (DIPSOC study)
- Pages: 341-351
- First Published: 03 September 2021
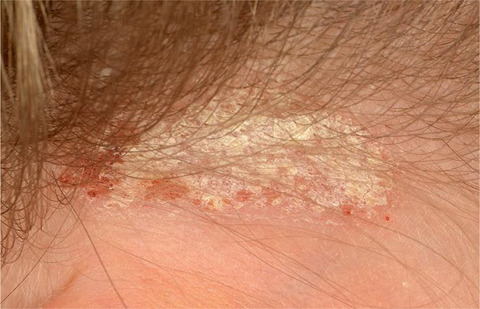
What is already known about this topic?
- A diagnosis of psoriasis may be delayed in children and young people, and psoriasis may be misdiagnosed in primary and secondary care.
- Diagnostic criteria for psoriasis in adults and children have been lacking.
- The development of criteria will aid recognition and clinical diagnosis of psoriasis, and provide a disease definition for clinical trials and epidemiological studies.
- Studies to develop diagnostic criteria should aim to minimize bias in the study design.
What does this study add?
- The consensus-agreed 16 diagnostic criteria and proposed scoring system demonstrated good diagnostic accuracy.
- Using statistical modelling, a shortlist of the seven best predictive diagnostic criteria was identified. The presence of two or more of these criteria had a sensitivity and specificity of over 70%.
- The criteria provide a reminder to clinicians that psoriasis in children can often develop in skin covered by hair and clothing.
Linked Comment: R.J.G. Chalmers. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:213–214.
Plain language summary available online
Correspondence
PERSPECTIVES
Standardized clinical photography considerations in patients across skin tones
- Pages: 352-354
- First Published: 26 September 2021
Management of mild hidradenitis suppurativa: our greatest challenge yet
- Pages: 355-356
- First Published: 05 October 2021
RESEARCH LETTERS
Underreporting of race and ethnicity in paediatric atopic dermatitis clinical trials: a cross-sectional analysis of demographic reporting and representation
- Pages: 357-359
- First Published: 04 September 2021
Cause-specific mortality in people with bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 359-361
- First Published: 12 September 2021
Combined carboplatin and paclitaxel therapy improves overall survival in patients with nivolumab-resistant acral and mucosal melanoma
- Pages: 361-363
- First Published: 12 September 2021
Single-centre experience of using pegylated liposomal doxorubicin as maintenance treatment in mycosis fungoides
- Pages: 363-365
- First Published: 16 September 2021
Exploring the lived experience of women with rosacea: visible difference and psychological impact
- Pages: 366-367
- First Published: 28 September 2021
A summary of the updated report on the incidence and epidemiological trends of keratinocyte cancers in the UK 2013–2018
- Pages: 367-369
- First Published: 26 September 2021
The effect of surgical-site infections on patient-reported cosmetic outcomes of scars in dermatological surgery
- Pages: 369-371
- First Published: 01 October 2021
Eligibility criteria for programmed death receptor 1 inhibitors vs. real-world advice: a retrospective analysis of 69 patients with advanced cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck
- Pages: 371-372
- First Published: 01 October 2021
Lupus erythematosus and epidermal necrolysis: a case series of 16 patients
- Pages: 372-374
- First Published: 01 October 2021
Occupational dermatoses during the second wave of the COVID-19 pandemic: a UK prospective study of 805 healthcare workers
- Pages: 374-376
- First Published: 05 October 2021
Eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with dupilumab therapy
- Pages: 376-377
- First Published: 05 October 2021
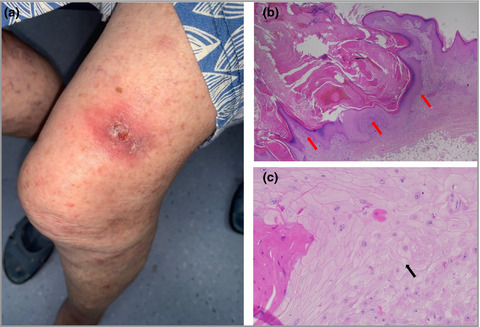
We would like to present the case of eruptive keratoacanthomas associated with dupilumab therapy, which occurred in an 85-year-old woman receiving biologic therapy for the treatment of atopic dermatitis. With the increasing prevalence of Dupilumab usage, this is an important potential complication of which clinicians should be aware.
Citric acid treatment of infected venous eczema refractory to conventional treatment: a novel approach
- Pages: 377-379
- First Published: 05 October 2021
Real-world effectiveness of brentuximab vedotin in the treatment of CD30-positive cutaneous T-cell lymphoma: a single-centre retrospective review
- Pages: 379-381
- First Published: 05 October 2021
CORRESPONDENCE: IMAGE GALLERY
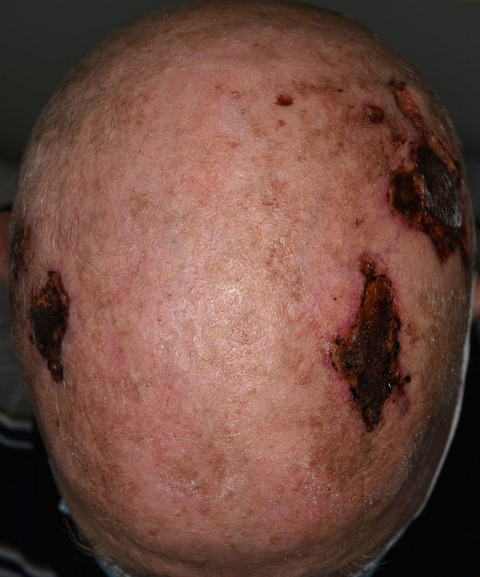
Bilateral giant cell arteritis with skin necrosis following SARS-CoV-2 vaccination
- Page: e83
- First Published: 02 November 2021
PLAIN LANGUAGE SUMMARIES
Different ways of estimating the amount of individual sun exposure
- Page: e84
- First Published: February 2022
Linked article: Souedi et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:266–273.
Is aquaporin linked to skin ageing?
- Page: e85
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Xie et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:318–333.
A guideline for the clinical management of patients with basal cell naevus syndrome (Gorlin syndrome)
- Page: e86
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Verkouteren et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:215–226.
A new sleep disturbance questionnaire for people with atopic dermatitis
- Page: e87
- First Published: February 2022
Linked article: Puelles et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:285–294.
The association between atopic dermatitis and high blood pressure
- Page: e88
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Yousaf et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:227–235.
Adcitmer® is a potential treatment for Merkel cell carcinoma
- Page: e89
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Esnault et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:295–306.
Improved understanding of psoriasis genetics and structural variations
- Page: e90
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Zhen et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:307–317.
Diagnostic criteria for psoriasis in children and young people
- Page: e91
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Burden-Teh et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:341–351.
Predicting the long-term course of atopic dermatitis in childhood
- Page: e92
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Nakamura et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:274–284.
Anakinra use did not offer benefit for the treatment of palmoplantar pustulosis
- Page: e93
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Cro et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:245–256.
Alopecia areata: findings from a study of UK general practice records
- Page: e94
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Harries et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:257–265.
Contact allergy to insulin pumps
- Page: e95
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Ulriksdotter et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:334–340.
The role of inhibitory peptides, locally produced in the skin, in hidradenitis suppurativa
- Page: e96
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Yao et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:236–244.
估计个体日晒量的不同方法
- Page: e97
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Souedi et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:266–273.
水通道蛋白是否与皮肤老化有关?
- Page: e98
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Xie et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:318–333.
基底细胞痣综合征(Gorlin 综合征)患者临床管理指南
- Page: e99
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Verkouteren et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:215–226.
针对特应性皮炎患者的新睡眠障碍问卷
- Page: e100
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Puelles et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:285–294.
特应性皮炎与高血压之间的关联
- Page: e101
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Yousaf et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:227–235.
Adcitmer® 是 Merkel 细胞癌的潜在治疗方法
- Page: e102
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Esnault et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:295–306.
提高对银屑病遗传学和结构变异的理解
- Page: e103
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Zhen et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:307–317.
儿童和青少年银屑病诊断标准
- Page: e104
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Burden-The et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:341–351.
预测儿童期特应性皮炎的长期病程
- Page: e105
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Nakamura et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:274–284.
使用阿那白滞素对治疗掌跖脓疱病没有益处
- Page: e106
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Cro et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:245–256.
斑秃:一项英国全科诊所记录研究的结果
- Page: e107
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Harries et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:257–265.
接触性胰岛素泵过敏
- Page: e108
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Ulriksdotter et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:334–340.
皮肤局部产生的抑制肽在化脓性汗腺炎中的作用
- Page: e109
- First Published: February 2022
Linked Article: Yao et al. Br J Dermatol 2022; 186:236–244.











2690-442X.cover.png)