Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 1277-1279
- First Published: 17 May 2018

Cover of this issue. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 (IDO-1), a negative immune-regulatory molecule, is predominantly expressed in tumor endothelial cells of ccRCC specimens. See also Seeber et al. (pp. 1583–1591 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
In this Issue: Volume 109, Issue 5, May 2018
- Pages: 1280-1281
- First Published: 17 May 2018
REVIEW ARTICLES
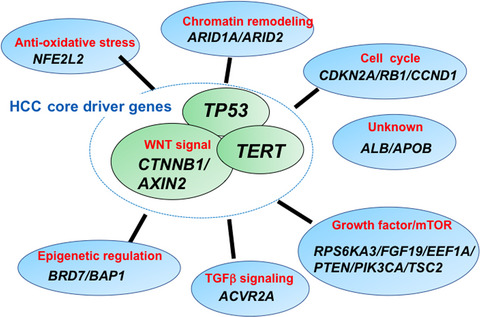
Molecular genomic landscapes of hepatobiliary cancer
- Pages: 1282-1291
- First Published: 23 March 2018
Podoplanin: An emerging cancer biomarker and therapeutic target
- Pages: 1292-1299
- First Published: 25 March 2018
Podoplanin (PDPN) is a transmembrane receptor glycoprotein that is upregulated on transformed cells, cancer associated fibroblasts (CAFs), and inflammatory macrophages that contribute to cancer progression. This review describes recent advances in how PDPN may be used as a biomarker and therapeutic target for many types of cancer including glioma, squamous cell carcinoma, mesothelioma, and melanoma.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Anti-human SIRPα antibody is a new tool for cancer immunotherapy
- Pages: 1300-1308
- First Published: 23 February 2018
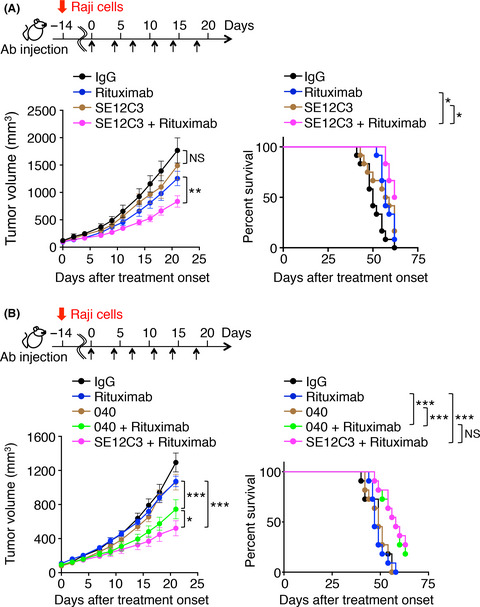
A blocking mAb to human SIRPα significantly enhanced the inhibitory effect of rituximab on the growth of tumors formed by Burkitt's lymphoma Raji cells in immunodeficient mice engineered to express human SIRPα.The survival of tumor-bearing mice treated with both the mAb and rituximab was also markedly prolonged in comparison with that of those treated with either Ab alone. Our results thus suggest that the combination of Abs to human SIRPα with therapeutic Abs specific for tumor antigens warrants further investigation for potential application to cancer immunotherapy.
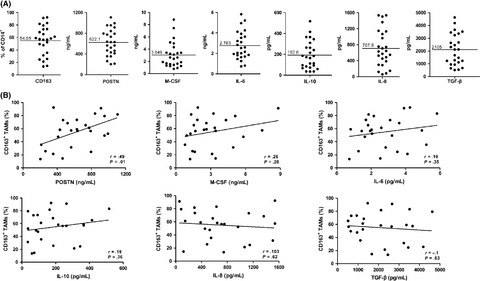
Cross-talk between ovarian cancer cells and macrophages through periostin promotes macrophage recruitment
- Pages: 1309-1318
- First Published: 12 March 2018
Development of a vaccine based on bacteria-mimicking tumor cells coated with novel engineered toll-like receptor 2 ligands
- Pages: 1319-1329
- First Published: 25 March 2018
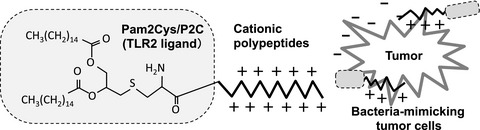
We designed two novel lipopeptides as anti-tumor immunoadjuvants that can coat tumor cell surfaces. Tumor cells coated with these engineered lipopeptides (called bacteria-mimicking tumor cells) promoted DC phagocytosis and antigen cross-presentation via TLR2 and induced the strong anti-tumor effect.
Sonodynamic therapy-assisted immunotherapy: A novel modality for cancer treatment
- Pages: 1330-1345
- First Published: 25 March 2018
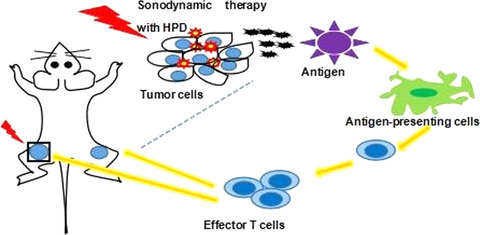
HiPorfin (HPD)-induced SDT killed tumor cells, promoted calreticulin expression on the cell surface and provoked immune responses. Meanwhile, we observed functional antitumor vaccination and the abscopal effect as a result of SDT in H22 tumor-bearing mice. Furthermore, this strategy conferred an immunological memory, which could protect against tumor recurrence after elimination of the initial tumor.
CARCINOGENESIS
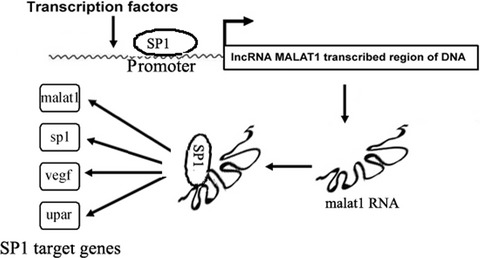
Long non-coding RNA metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 promotes lung adenocarcinoma by directly interacting with specificity protein 1
- Pages: 1346-1356
- First Published: 25 March 2018
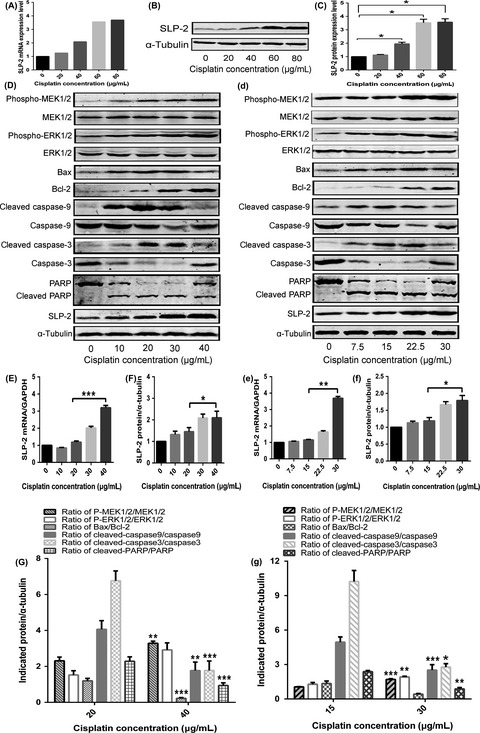
Stomatin-like protein 2 inhibits cisplatin-induced apoptosis through MEK/ERK signaling and the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway in cervical cancer cells
- Pages: 1357-1368
- First Published: 08 March 2018
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
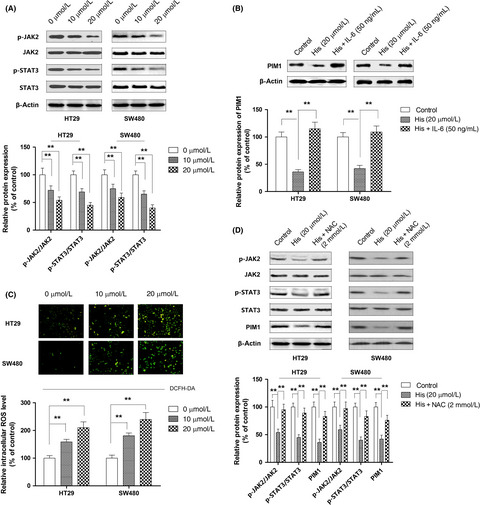
Retracted: Hispidulin suppresses cell growth and metastasis by targeting PIM1 through JAK2/STAT3 signaling in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 1369-1381
- First Published: 25 March 2018
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
CARCINOGENESIS
LKB1 obliterates Snail stability and inhibits pancreatic cancer metastasis in response to metformin treatment
- Pages: 1382-1392
- First Published: 30 March 2018
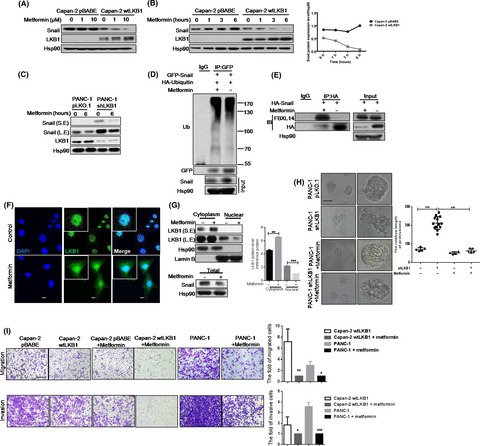
LKB1 is negatively correlated with Snail at protein level in pancreatic cancer (PC). Loss of LKB1 promotes PC's metastasis via elevating Snail protein in AMPK-independent pathway. LKB1 enhances E3 ligase FBXL14 to interact with Snail protein, leading to increasing ubiquitin-mediated Snail degradation Metformin inhibits metastasis through LKB1-mediated Snail ubiquitination in PC cells.
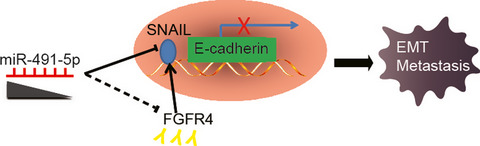
Downregulation of miR-491-5p promotes gastric cancer metastasis by regulating SNAIL and FGFR4
- Pages: 1393-1403
- First Published: 23 March 2018
MicroRNA-708-3p mediates metastasis and chemoresistance through inhibition of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer
- Pages: 1404-1413
- First Published: 25 March 2018
PRMT9 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis via activating PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signaling
- Pages: 1414-1427
- First Published: 30 March 2018
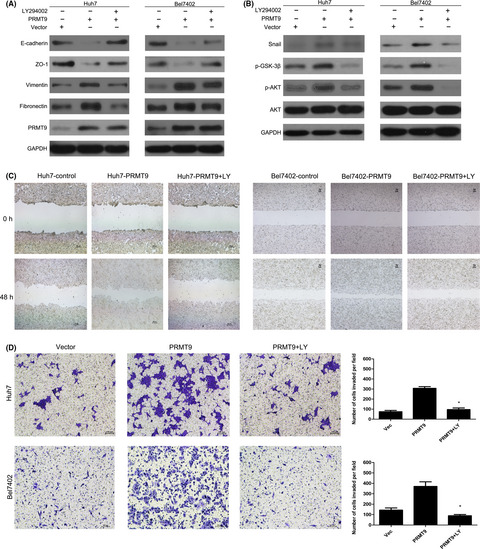
This study is the first to demonstrated that PRMT9 is an oncogene that plays an important role in HCC invasion and metastasis through EMT by regulating Snail expression via activation of the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β/Snail signalling pathway. Thus, PRMT9 may serve as a candidate prognostic biomarker and a potential therapeutic target.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
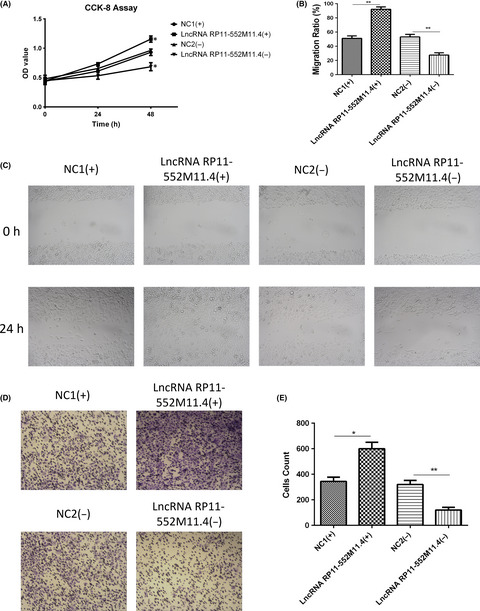
Long non-coding RNA RP11-552M11.4 promotes cells proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting BRCA2 in ovarian cancer
- Pages: 1428-1446
- First Published: 25 February 2018
Periostin antisense oligonucleotide suppresses bleomycin-induced formation of a lung premetastatic niche for melanoma
- Pages: 1447-1454
- First Published: 02 March 2018
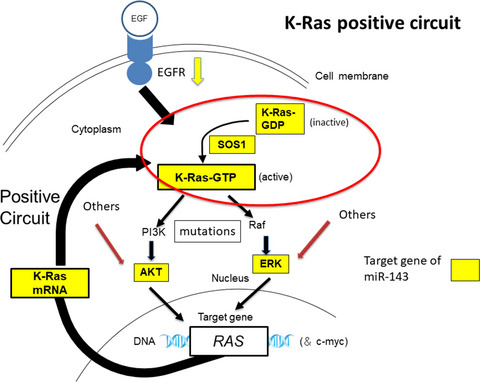
Impairment of K-Ras signaling networks and increased efficacy of epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors by a novel synthetic miR-143
- Pages: 1455-1467
- First Published: 02 March 2018
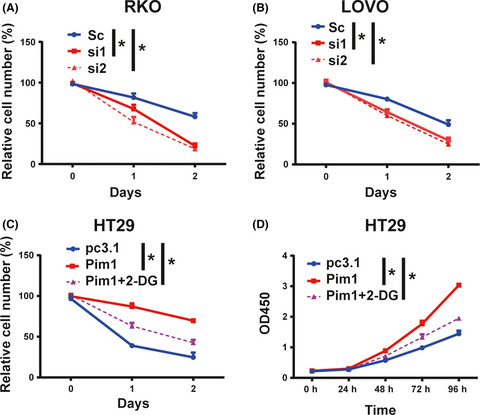
Pim1 supports human colorectal cancer growth during glucose deprivation by enhancing the Warburg effect
- Pages: 1468-1479
- First Published: 08 March 2018
Established gastric cancer cell lines transplantable into C57BL/6 mice show fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 promotion of tumor growth
- Pages: 1480-1492
- First Published: 13 March 2018
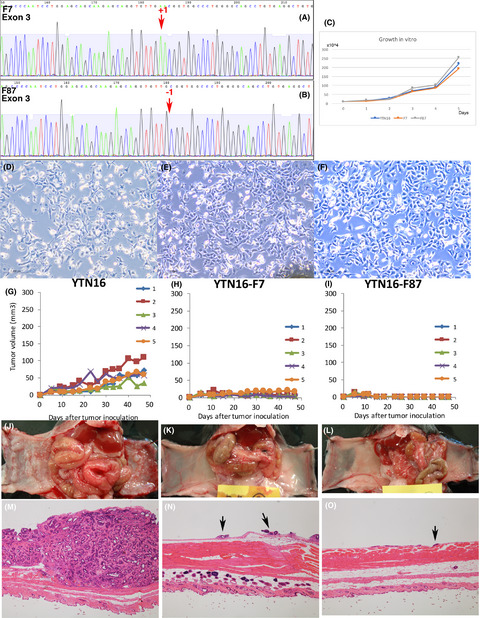
C57BL/6 mouse transplantable C57BL/6 mouse gastric cancer cell lines were established. These cell lines would be useful for analysis of the molecular function of trans-gene or knockout in a C57BL/6 mouse background, and gastric cancer immune therapy. Identification of the efficacy of FGFR4 blockade is a pertinent example of how these mouse cancer lines can be used for analyzing the effectiveness of cancer therapy.
Therapeutic strategies for afatinib-resistant lung cancer harboring HER2 alterations
- Pages: 1493-1502
- First Published: 13 March 2018
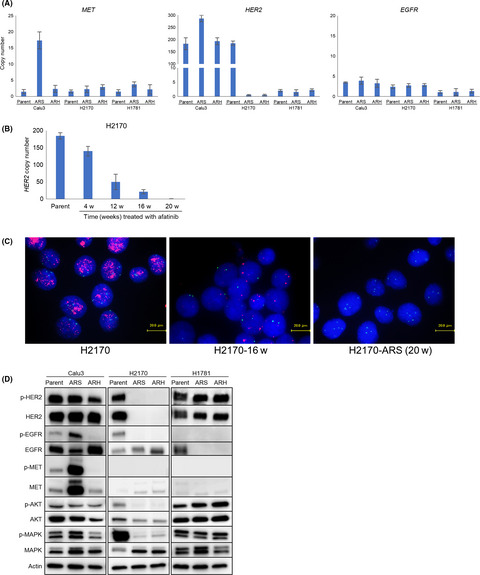
This is the first report in which afatinib-resistant cell lines were experimentally established using HER2-altered NSCLC cell lines, and their resistance mechanisms were thoroughly investigated. As a result, the afatinib-resistant NSCLC cell lines displayed various resistant mechanisms such as MET amplification, loss of HER2 amplification, and epithelial to mesenchymal transition or cancer stem cell-like features, with specific sensitivity to various drugs such as MET-tyrosine kinase inhibitor crizotinib.
Ribosome display and selection of single-chain variable fragments effectively inhibit growth and progression of microspheres in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 1503-1512
- First Published: 25 March 2018
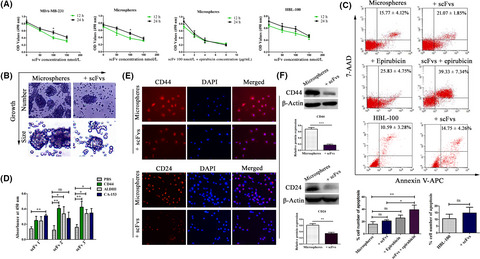
This study demonstrated that the scFvs from dynamic screening by ribosome display in a natural state could result in high-affinity evolution to recognize the microspheres. The scFvs could effectively inhibit the microspheres’ collective growth and invasion through targets that might be CD44+/CD24+. When combined with chemotherapy, the scFvs exhibited enhancement of their high-affinity efficiency in inhibiting the proliferation and invasion of microspheres in vitro and in vivo.
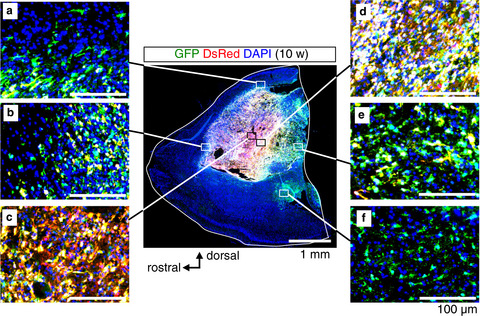
Spontaneous development of intratumoral heterogeneity in a transposon-induced mouse model of glioma
- Pages: 1513-1523
- First Published: 25 March 2018
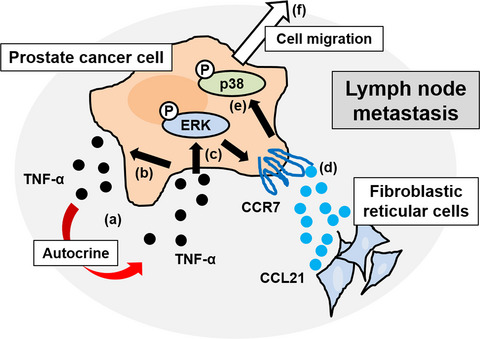
Tumor necrosis factor-α induces prostate cancer cell migration in lymphatic metastasis through CCR7 upregulation
- Pages: 1524-1531
- First Published: 25 March 2018
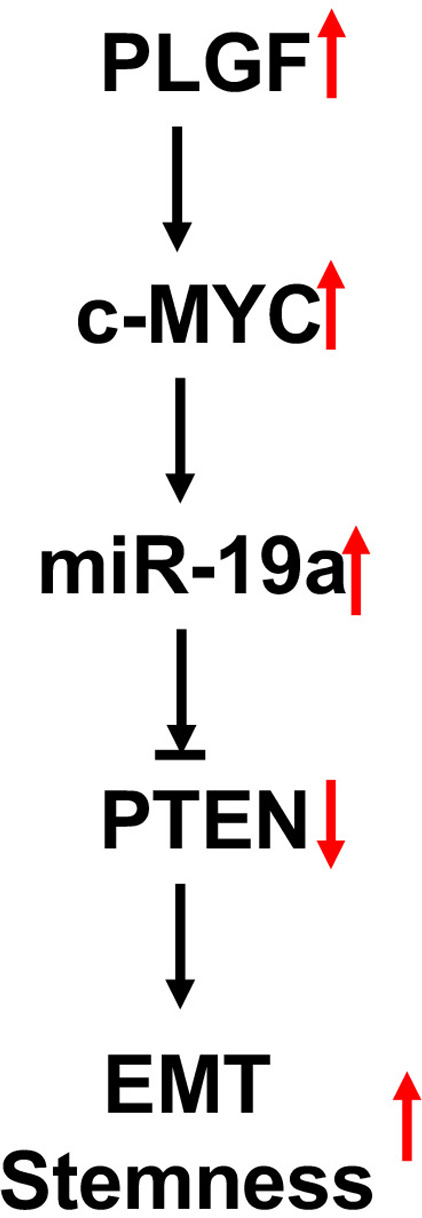
The PLGF/c-MYC/miR-19a axis promotes metastasis and stemness in gallbladder cancer
- Pages: 1532-1544
- First Published: 25 March 2018
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to peptide vaccination predicts survival in stage III colorectal cancer
- Pages: 1545-1551
- First Published: 23 February 2018

Vaccination-induced immune response could improve prognosis of HLA-A* 2402-positive patients and immune responses that occur shortly after initiating therapy could be used to predict the therapeutic effect. In addition, an HLA-A status double-blind biologically randomized study, what we call “HLA key open method”, could have some limitations due to potential cross-reactivity of the peptides to other serotypes.
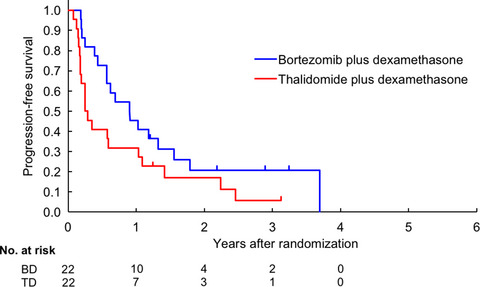
Bortezomib plus dexamethasone vs thalidomide plus dexamethasone for relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma
- Pages: 1552-1561
- First Published: 25 February 2018
Feasibility of carbon-ion radiotherapy for re-irradiation of locoregionally recurrent, metastatic, or secondary lung tumors
- Pages: 1562-1569
- First Published: 02 March 2018
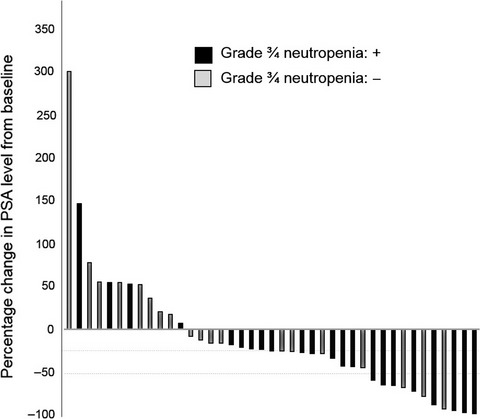
Prognostic significance of grade 3/4 neutropenia in Japanese prostate cancer patients treated with cabazitaxel
- Pages: 1570-1575
- First Published: 01 March 2018
A retrospective multicenter study of carbon-ion radiotherapy for major salivary gland carcinomas: Subanalysis of J-CROS 1402 HN
- Pages: 1576-1582
- First Published: 01 March 2018
High IDO-1 expression in tumor endothelial cells is associated with response to immunotherapy in metastatic renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1583-1591
- First Published: 02 March 2018
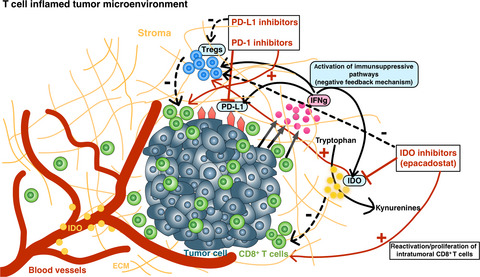
In this retrospective study, we analyzed the predictive value ot the expression of IDO1 on tumor tissue of renal cell carcinoma patients undergoing checkpoint inhibition. A signifcanty correlation between the overexpression of IDO1 in tumor endothelial cells and response to nivolumab therapy could be found for the first time.
Phase I study of taselisib in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumors or hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer
- Pages: 1592-1601
- First Published: 03 March 2018

This article reports the first study of taselisib administration in Japanese patients with solid tumors or hormone receptor (HR)-positive advanced or recurrent breast cancer. In this phase I, multicenter study, taselisib was well tolerated, with no dose-limiting toxicities or deaths reported. All patients who achieved partial response were positive for PIK3CA gene mutations.
Phase II study of adjuvant chemotherapy with paclitaxel and nedaplatin for uterine cervical cancer with lymph node metastasis
- Pages: 1602-1608
- First Published: 25 March 2018
Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor therapy concurrently with induction chemotherapy in locoregionally advanced nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 1609-1616
- First Published: 25 March 2018
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Non-invasive estimation of 10B-4-borono-L-phenylalanine-derived boron concentration in tumors by PET using 4-borono-2-18F-fluoro-phenylalanine
- Pages: 1617-1626
- First Published: 02 March 2018
Activation of AMPK by simvastatin inhibited breast tumor angiogenesis via impeding HIF-1α-induced pro-angiogenic factor
- Pages: 1627-1637
- First Published: 13 March 2018
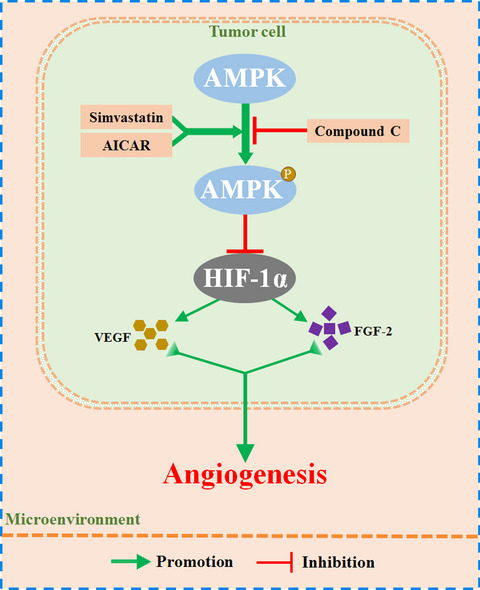
Simvastatin significantly suppressed tumor angiogenesis promoted by HIF-1α-induced pro-angiogenic factors in 4T1 tumor cells. Further inhibition of AMPK phosphorylation by compound C almost completely abrogated simvastatin-induced anti-angiogenesis, which was accompanied by the reduction of protein levels of HIF-1α and its downstream pro-angiogenic factors.
Fluorescence tumor imaging by i.v. administered indocyanine green in a mouse model of colitis-associated colon cancer
- Pages: 1638-1647
- First Published: 09 March 2018
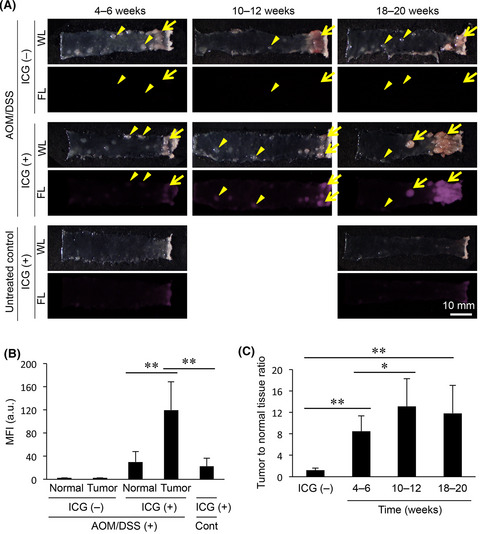
The present study demonstrated that fluorescence contrast-enhanced imaging following intravenously administered indocyanine green (ICG), a fluorescent contrast agent, can be applied to the detection of colon tumors in a mouse colitis-associated colon cancer model. The tumor tissue preference of ICG in the present model can be attributed to the enhanced vascular leakage of ICG involving inflammatory mediators, such as COX-2 and iNOS, in conjunction with increased tumor vascularity.
c-Src inhibitor selectively inhibits triple-negative breast cancer overexpressed Vimentin in vitro and in vivo
- Pages: 1648-1659
- First Published: 25 March 2018
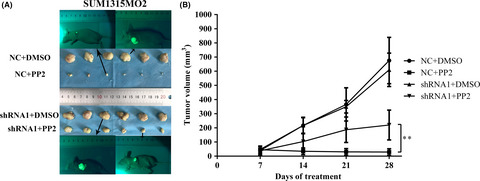
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is the most intractable subgroup as, so far, there are no effective targeted drugs. Studies indicated that TNBC has shown high sensitivity to c-Src inhibitor in vitro but is of limited benefit in clinical tests. Our study showed that vimentin is a crucial molecule to affect the therapeutic effects of the c-Src inhibitor in TNBC, and it provides an important rationale for the clinic to precisely select TNBC patients who would benefit from c-Src inhibitor treatment.
Synthetic α-mangostin dilaurate strongly suppresses wide-spectrum organ metastasis in a mouse model of mammary cancer
- Pages: 1660-1671
- First Published: 30 March 2018
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND PREVENTION
Metabolome analysis for pancreatic cancer risk in nested case-control study: Japan Public Health Center-based prospective Study
- Pages: 1672-1681
- First Published: 25 March 2018
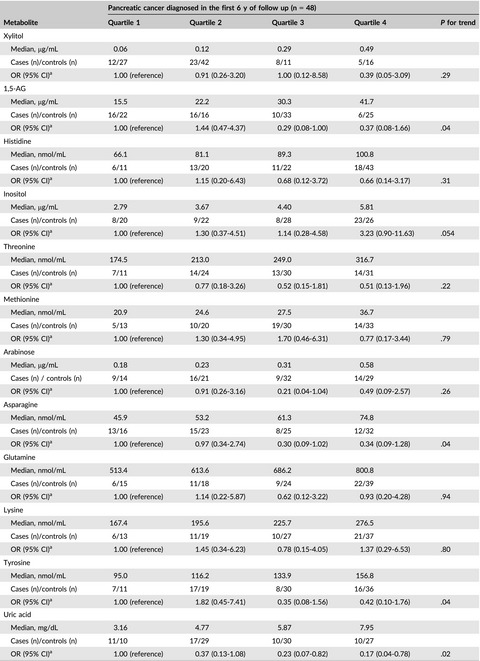
We analyzed targeted blood metabolites quantitatively by gas chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry in a nested case-control study including 170 pancreatic cancer cases and 340 matched controls. We found that some metabolites are useful for early detection of pancreatic cancer but are not associated with the risk of pancreatic cancer.
GENETICS, GENOMICS, AND PROTEOMICS
Droplet digital polymerase chain reaction assay and peptide nucleic acid-locked nucleic acid clamp method for RHOA mutation detection in angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 1682-1689
- First Published: 01 March 2018

Angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma (AITL) is a distinct subtype of nodal peripheral T-cell lymphoma (PTCL). Somatic RHOA mutations, (most frequently c.G50T, p.G17V RHOA mutation) are a genetic hallmark of AITL. Our results showed that a combination of NGS, ddPCR and PNA-LNA clamp methods increased the detection rate of RHOA mutations at the p.G17 position.
Novel method for DNA methylation analysis using high-performance liquid chromatography and its clinical application
- Pages: 1690-1700
- First Published: 09 March 2018
Circulating exosomes contain protein biomarkers of metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 1701-1709
- First Published: 23 March 2018
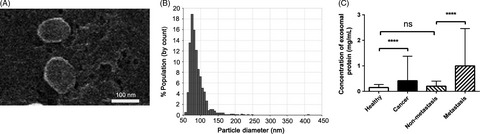
This is the first study using the proteomics technique to find a diagnostic marker for metastatic NSCLC. It provides an objective basis for the early diagnosis, early treatment and prognosis of metastatic NSCLC, and provides a key point for the diagnosis of other cancerous solid tumors. It also provides a new idea for non-invasive biomarkers for other metastatic cancers, and the clinical application of exosomes will have better prospects.
INFLAMMATION AND VIROLOGY
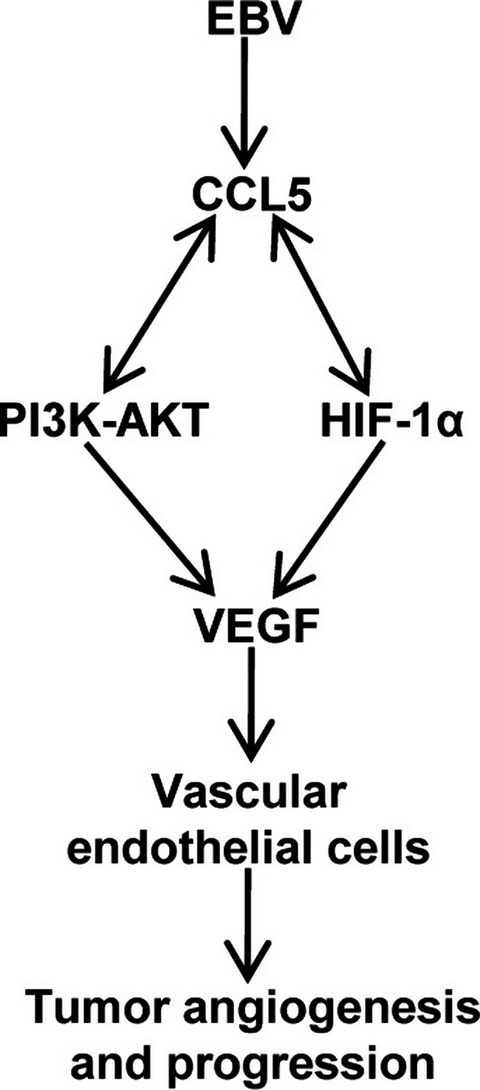
Induction of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 5 by Epstein–Barr virus infection enhances tumor angiogenesis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- Pages: 1710-1722
- First Published: 23 March 2018
PATHOLOGY
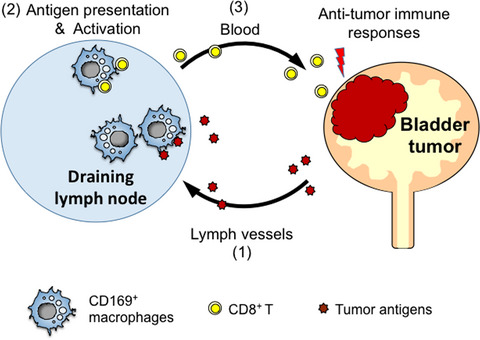
CD169-positive sinus macrophages in the lymph nodes determine bladder cancer prognosis
- Pages: 1723-1730
- First Published: 09 March 2018
REPORT
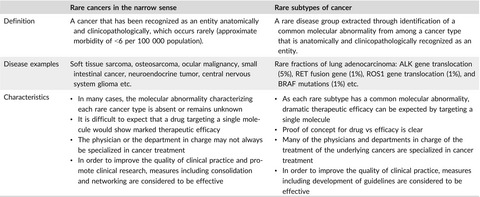
Current state of therapeutic development for rare cancers in Japan, and proposals for improvement
- Pages: 1731-1737
- First Published: 17 May 2018