Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information
- Pages: 543-545
- First Published: 26 April 2017

Cover of this issue. Mosaic expression of SMARCB1/INI1 in schwannomatosis. See also Kohashi et al. (pages 547–552 of this issue).
IN THIS ISSUE
REVIEW ARTICLES
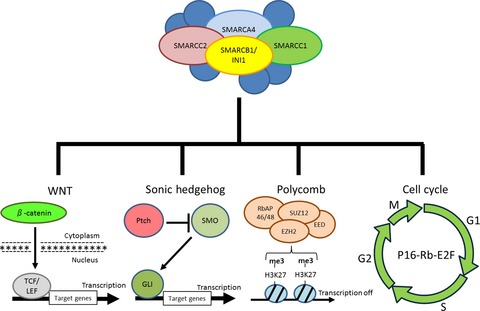
Oncogenic roles of SMARCB1/INI1 and its deficient tumors
- Pages: 547-552
- First Published: 21 January 2017
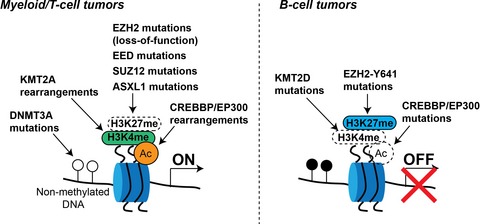
Epigenetics in normal and malignant hematopoiesis: An overview and update 2017
- Pages: 553-562
- First Published: 18 January 2017
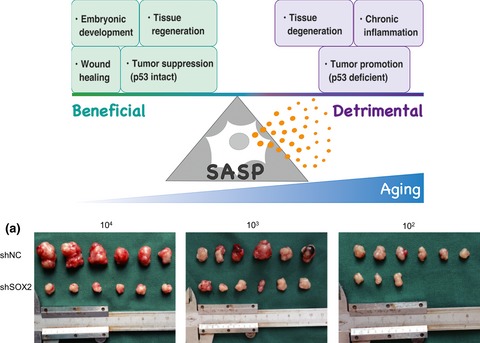
Impact of senescence-associated secretory phenotype and its potential as a therapeutic target for senescence-associated diseases
- Pages: 563-569
- First Published: 06 February 2017
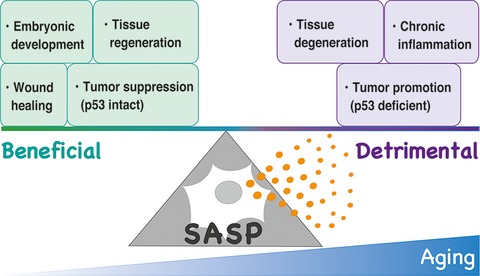
We provide the latest insight into the impact of senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) on age-related diseases by reviewing and discussing its functional and regulatory mechanisms. SASP could have beneficial or detrimental outcomes in physiological and pathological processes during aging, and emerging therapeutic strategies targeting senescent cells and SASP are promising for future clinical translation controlling aging and aging-associated diseases, including cancer.
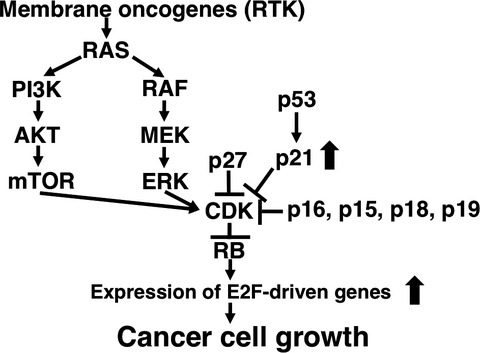
Molecular-targeting therapies against quantitative abnormalities in gene expression with malignant tumors
- Pages: 570-573
- First Published: 08 February 2017
Suppressors of cytokine signaling: Potential immune checkpoint molecules for cancer immunotherapy
- Pages: 574-580
- First Published: 11 February 2017
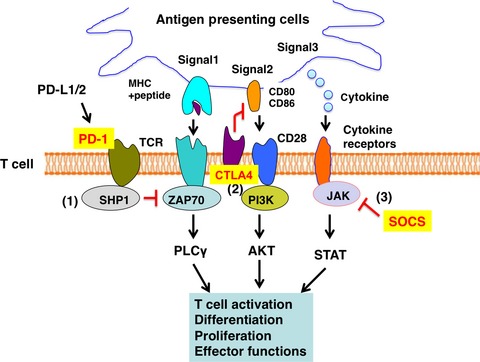
Inhibition of immune-checkpoint molecules, PD-1 and CTLA4, has been shown to be a promising cancer treatment. SOCS proteins are the third immune-checkpoint molecules that inhibit cytokine signaling. This review is focusing on the mechanism of inhibition of cytokine signaling by CIS, SOCS1 and SOCS3, and their relationship to T cell biology and anti-tumor immunity.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
BASIC AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY
Novel pegylated interferon-β as strong suppressor of the malignant ascites in a peritoneal metastasis model of human cancer
- Pages: 581-589
- First Published: 27 January 2017
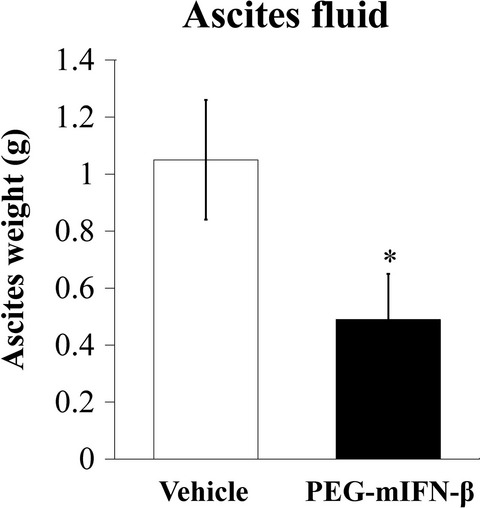
Malignant ascites manifests as an end-stage event during the progression of a number of cancers and is associated with significant morbidity. In this study, we report on the development of a novel, long-acting formulation of human and mouse interferon-β (IFN-β). Pegylated IFN-β contains the site-specific conjugation of polyethylene glycol residue to IFN-β. We demonstrated that PEG-mIFN-β, but not PEG-hIFN-β, significantly suppressed the accumulation of ascites fluid in this model. These findings reveal a new facet of the long-acting PEG-hIFN-β and provide a therapeutic rationale for evaluating long-acting PEG-IFN-β in the treatment of malignant ascites.
Programmed death-ligand 1 is prognostic factor in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and is associated with epidermal growth factor receptor
- Pages: 590-597
- First Published: 13 February 2017
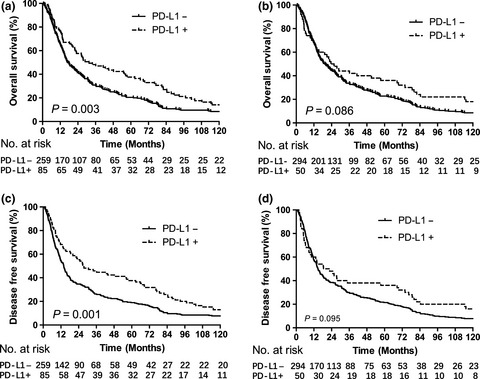
Our study indicates that tumor-infiltrating immune cell PD-L1 expression is an independent prognostic factor for ESCC, and the association between EGFR and PD-L1 is vital to determining survival. It is important to consider radiotherapy-induced imbalance of pro-tumor and anti-tumor immune response. A combination of radiotherapy and PD-L1-targeted therapies could be a promising therapeutic strategy for ESCC patients.
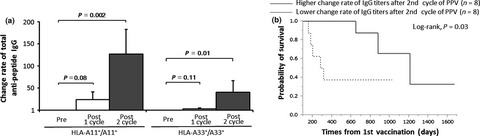
Immunological evaluation of peptide vaccination for cancer patients with the HLA -A11+ or -A33+ allele
- Pages: 598-603
- First Published: 08 February 2017
CARCINOGENESIS
Downregulation of delta-aminolevulinate dehydratase is associated with poor prognosis in patients with breast cancer
- Pages: 604-611
- First Published: 03 February 2017
Identification of FERM domain-containing protein 5 as a novel target of β-catenin/TCF7L2 complex
- Pages: 612-619
- First Published: 24 January 2017
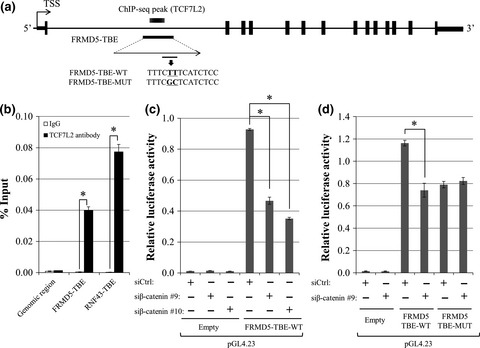
Deregulation of the canonical Wnt signaling pathway plays an important role in human tumorigenesis. In this study, we identified FRMD5 as a novel Wnt signaling target gene in colorectal cancer cells. Gene set enrichment analysis revealed that FRMD5 is associated with cell cycle and cell-extracellular interaction.
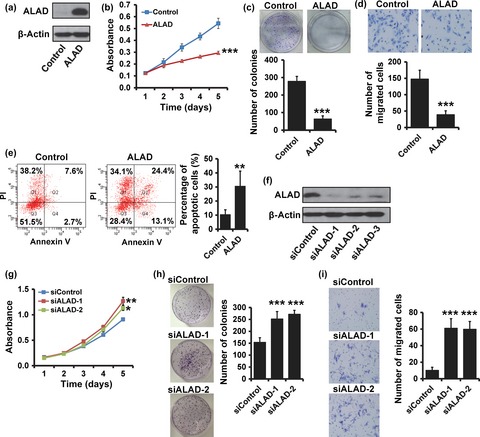
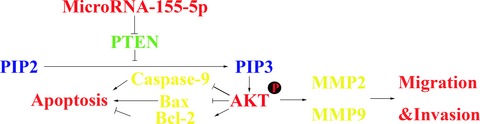
MicroRNA-155-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by suppressing PTEN through the PI3K/Akt pathway
- Pages: 620-631
- First Published: 28 January 2017
Sox2-dependent inhibition of p21 is associated with poor prognosis of endometrial cancer
- Pages: 632-640
- First Published: 11 February 2017
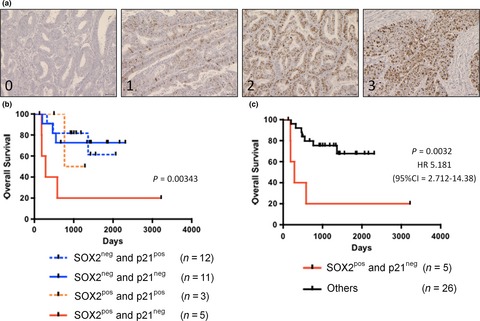
SOX2 is required for endometrial cancer cell growth. Expressions of SOX2 in endometrial cancer patients is significantly correlated with histological grade and poor prognosis. Low p21 together with high SOX2 expressions in advanced endometrial cancer patients are associated with the most unfavorable outcomes of patients.
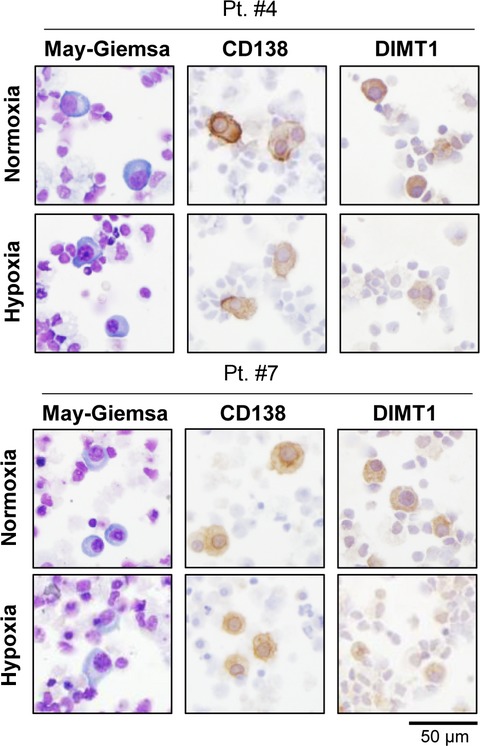
Hypoxia-inducible microRNA-210 regulates the DIMT1-IRF4 oncogenic axis in multiple myeloma
- Pages: 641-652
- First Published: 06 February 2017
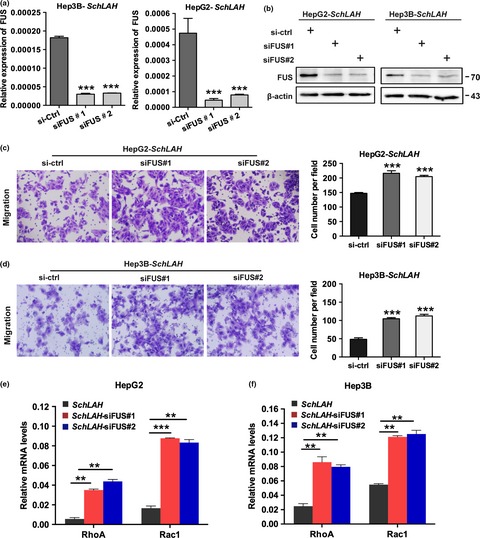
Long noncoding RNA SchLAH suppresses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma through interacting with fused in sarcoma
- Pages: 653-662
- First Published: 14 February 2017
CLINICAL RESEARCH
Predictive and prognostic role of serum neopterin and tryptophan breakdown in prostate cancer
- Pages: 663-670
- First Published: 20 January 2017
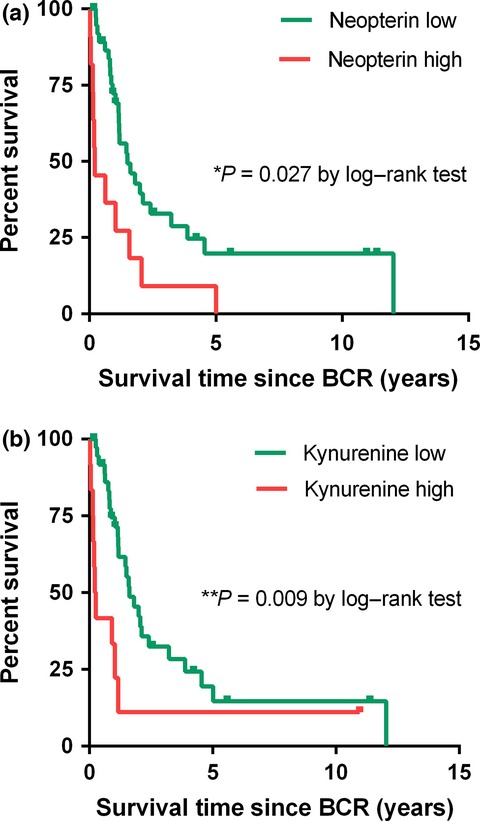
Accelerated neopterin and tryptophan breakdown seems to play an important role regarding prostate carcinogenesis, with the highest levels in patients with biochemical recurrence after radical prostatectomy. Neopterin was the only independent prognostic factor for cancer-specific survival after biochemical recurrence. These data may support the recommendation of neopterin measurement in making decision for further oncologic treatment strategies and in monitoring patients during therapy following biochemical recurrence.
HER2 somatic mutations are associated with poor survival in HER2-negative breast cancers
- Pages: 671-677
- First Published: 06 February 2017
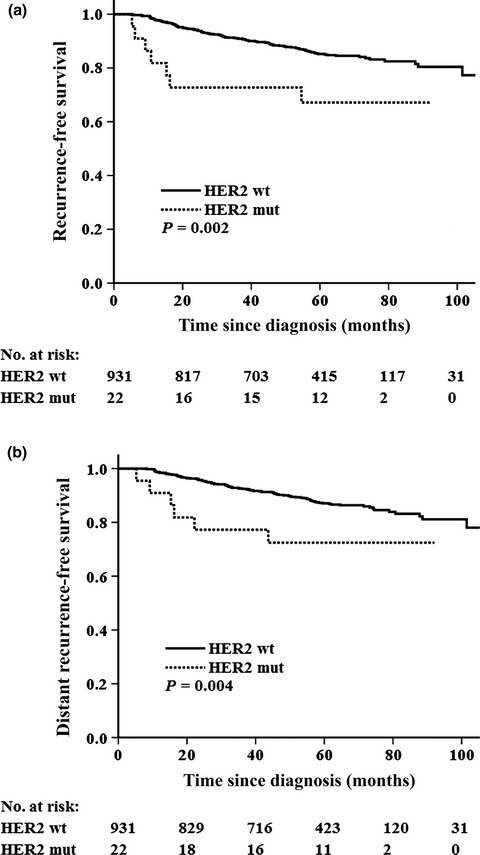
We identified HER2 somatic mutations in tumors from 1348 unselected breast cancer patients by sequencing the entire HER2 coding region. Here, we are first to report that HER2-negative breast cancer patients with HER2 somatic mutation have an unfavorable survival. Therefore, HER2-negative patients with HER2 somatic mutation are potentially good candidates for HER2-targeted therapy or for recruitment into ongoing clinical trials.
CELL, MOLECULAR, AND STEM CELL BIOLOGY
Cluster microRNAs miR-194 and miR-215 suppress the tumorigenicity of intestinal tumor organoids
- Pages: 678-684
- First Published: 16 January 2017
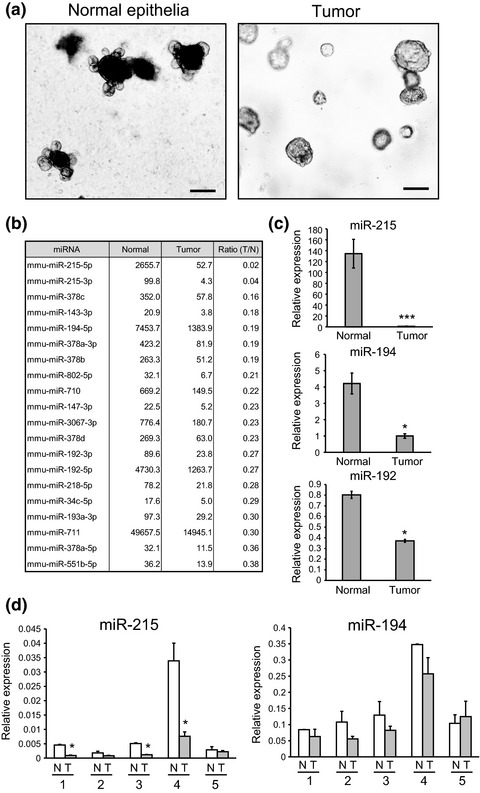
Here we established organoids derived from intestinal tumors of Min mice. Expression of the cluster miRNAs, miR-194 and miR-215, was markedly suppressed in intestinal tumor organoids in comparison with organoids derived from normal intestinal epithelia. Enforced expression of miR-194 and miR-215 suppresses intestinal tumor organoids.
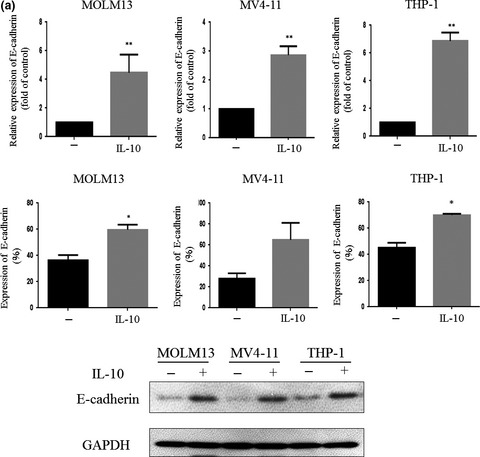
MicroRNA-9 plays a role in interleukin-10-mediated expression of E-cadherin in acute myelogenous leukemia cells
- Pages: 685-695
- First Published: 20 January 2017
Podoplanin promotes progression of malignant pleural mesothelioma by regulating motility and focus formation
- Pages: 696-703
- First Published: 09 February 2017
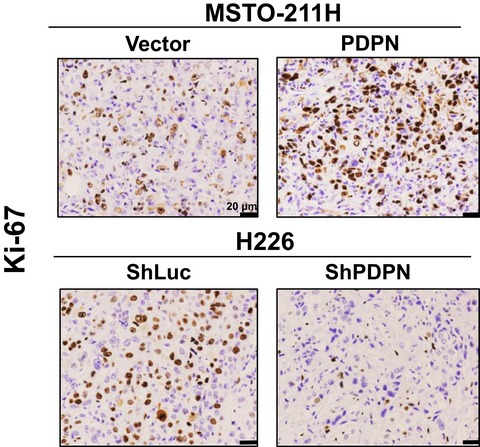
Podoplanin (PDPN) is an established diagnostic marker for malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM), but the function of PDPN in MPM is not fully understood. In the present study, we demonstrated that PDPN plays a major role in the progression of MPM by stimulating cell motility via RhoA/ROCK pathway activation and by blocking contact inhibition associated with decreased E-cadherin expression and YAP1 activation.Collectively, our findings indicate that PDPN is an ideal target for treatment of patients with MPM.
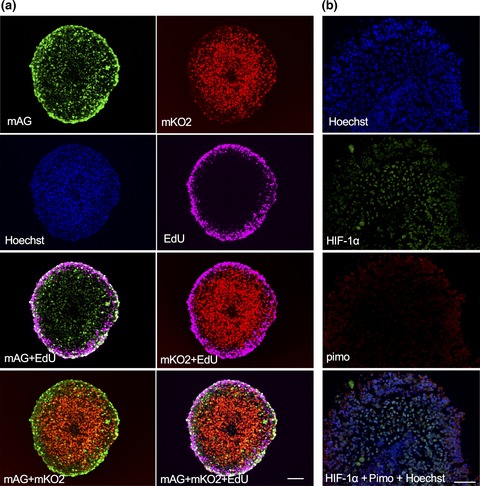
Radiosensitivity of quiescent and proliferating cells grown as multicellular tumor spheroids
- Pages: 704-712
- First Published: 30 January 2017
Protein-arginine deiminase 2 suppresses proliferation of colon cancer cells through protein citrullination
- Pages: 713-718
- First Published: 03 February 2017
SOX2 is required to maintain cancer stem cells in ovarian cancer
- Pages: 719-731
- First Published: 06 February 2017
Identification of proteasomal catalytic subunit PSMA6 as a therapeutic target for lung cancer
- Pages: 732-743
- First Published: 06 February 2017
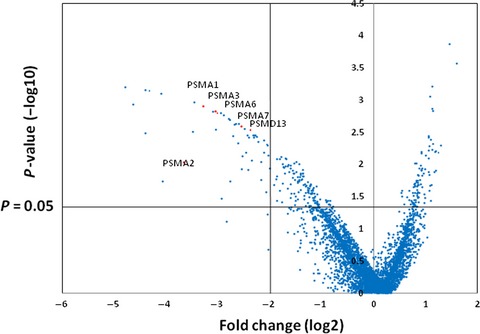
By doing an integrative analysis we have identified PSMA6, a subunit of the proteasome complex, as one of the most promising targets for lung cancer. We showed that PSMA6 knockdown suppressed the viability of cancer cells through the induction of apoptosis or cell cycle arrest at G2/M, with only a minimal effect on normal lung epithelial cells. Our data suggested that targeting PSMA6 for lung cancer may be an attractive novel therapeutic strategy.
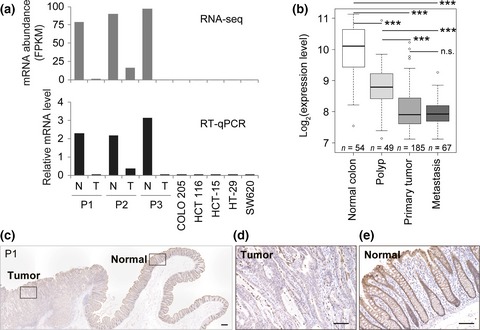
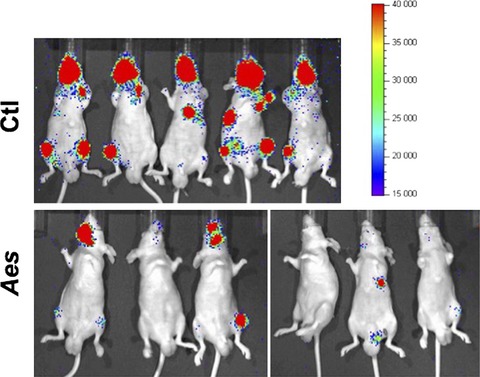
Amino-terminal enhancer of split gene AES encodes a tumor and metastasis suppressor of prostate cancer
- Pages: 744-752
- First Published: 08 February 2017
Effect of a hypoxic microenvironment after radiofrequency ablation on residual hepatocellular cell migration and invasion
- Pages: 753-762
- First Published: 09 February 2017
DRUG DISCOVERY AND DELIVERY
Targeting of tumor growth and angiogenesis underlies the enhanced antitumor activity of lenvatinib in combination with everolimus
- Pages: 763-771
- First Published: 20 January 2017
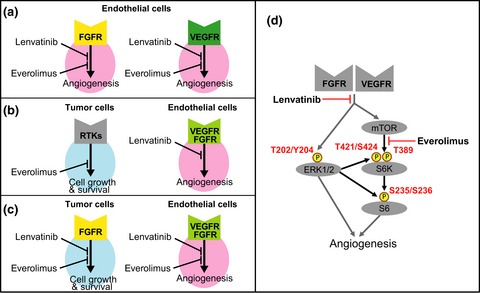
Lenvatinib is a multiple receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that selectively inhibits VEGFR, FGFR, and other proangiogenic and oncogenic pathway-related RTKs. Here we show that simultaneous targeting of tumor cell growth and angiogenesis by lenvatinib plus everolimus, and enhanced inhibition of VEGF- and FGF-driven angiogenesis through greater inhibition of the mTOR–S6K–S6 signaling pathway underlie the antitumor activity conferred by the combination of lenvatinib plus everolimus in preclinical RCC models.
Mitochondrial uncoupler exerts a synthetic lethal effect against β-catenin mutant tumor cells
- Pages: 772-784
- First Published: 20 January 2017
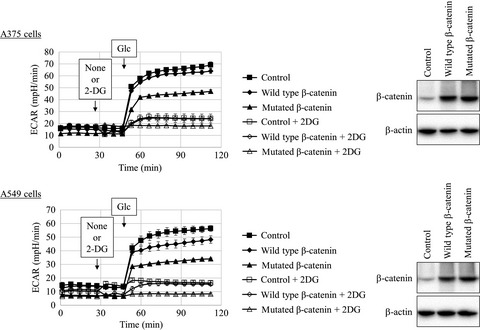
We screened an in-house natural product library for compounds that exhibited synthetic lethality towards beta-catenin mutations and isolated nonactin, an antibiotic mitochondrial uncoupler, as a hit compound. Nonactin, as well as other mitochondrial uncouplers, induced apoptosis selectively in beta-catenin mutated tumor cells in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, we found that expression of an active mutant form of beta-catenin induced a decrease in the glycolysis rate.
Protein kinase A inhibition facilitates the antitumor activity of xanthohumol, a valosin-containing protein inhibitor
- Pages: 785-794
- First Published: 25 January 2017
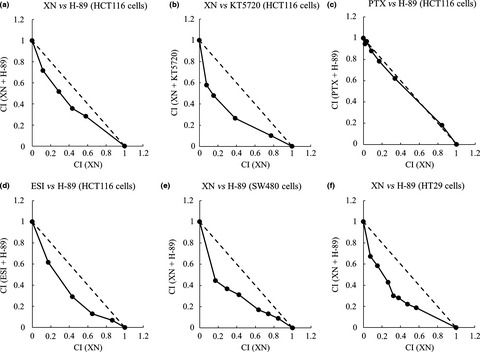
The inhibition of protein kinase A (PKA), a downstream kinase of adenylate cyclase (AC) pathway, enhanced the apoptosis-inducing activity of xanthohumol (XN). It indicated that the AC/PKA pathway could contribute to preventing apoptosis induced by XN and that the activity of AC/PKA pathway in tumor cells could determine sensitivity to XN.
Immune-complex level of cofilin-1 in sera is associated with cancer progression and poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 795-803
- First Published: 04 February 2017
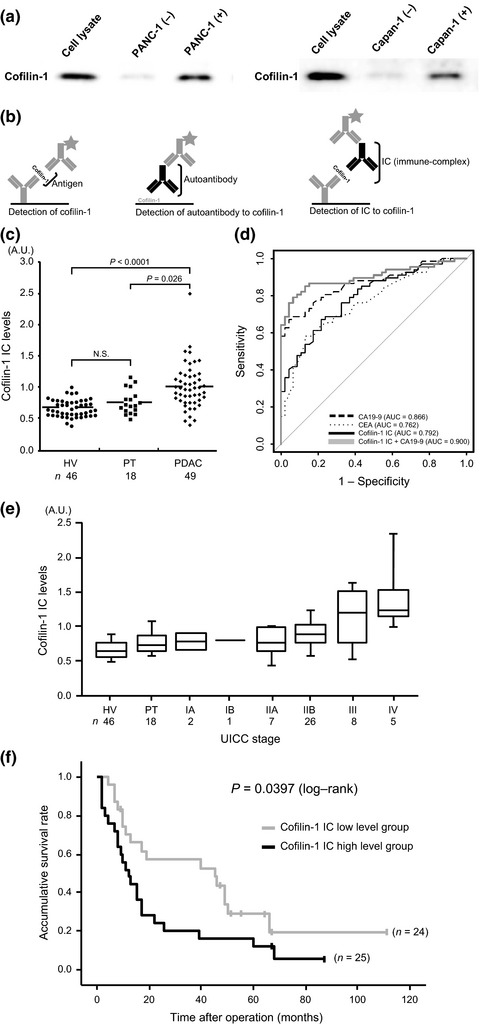
High cofilin-1 expression is associated with hematogenous dissemination in recurrence forms of pancreatic cancer (PDAC) patients. The immune-complex (IC) levels of cofilin-1 in sera of PDAC patients were higher than those in sera of healthy volunteers and patients with pancreatitis. The IC levels of cofilin-1 showed a stepwise increase during PDAC progression, and high IC levels of cofilin-1 indicated poor prognosis of patients after surgery.