Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image
- Page: i
- First Published: 12 August 2020

The cover image is based on the Research Article Failure analysis of field-failed bypass diodes by Chuanxiao Xiao et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3297.
Cover Image
- Page: ii
- First Published: 12 August 2020

The cover image is based on the Research Article High-performance HTL-free perovskite solar cell: An efficient composition of ZnO NRs, RGO, and CuInS2 QDs, as electron-transporting layer matrix by Reza Taheri-Ledari et al., https://doi.org/10.1002/pip.3306.
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Fabrication and characteristics of high-VOC single-crystalline Cu2ZnSnSe4 solar cells
- Pages: 863-872
- First Published: 04 June 2020

Cu2ZnSnSe4 single crystal solar cells with open-circuit voltages reaching 450 mV are demonstrated. Copper-poor absorbers of two different compositions were evaluated as a function of surface treatment, demonstrating a need for more rigorous chemical treatments at lower Cu content. The decrease in Cu concentration leads to an increase in bandgap from 0.98 to 1.03 eV while having little effect on sub-bandgap absorption and is accompanied by the formation of a low-temperature current barrier.
Simulation of performance differences between offshore and land-based photovoltaic systems
- Pages: 873-886
- First Published: 11 May 2020
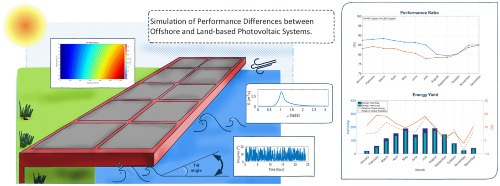
Modeling, simulation, and comparison for the performance of floating and land-based PV systems. The effect of sea waves is considered to compute the irradiation on a varying tilted surface for the FPV system and wind speed is considered for computing the effect of the natural cooling system for both systems. The computed energy yields show that relative annual average output energy is about 12.96% higher at sea.
Environmentally improved CdTe photovoltaic recycling through novel technologies and facility location strategies
- Pages: 887-898
- First Published: 08 June 2020
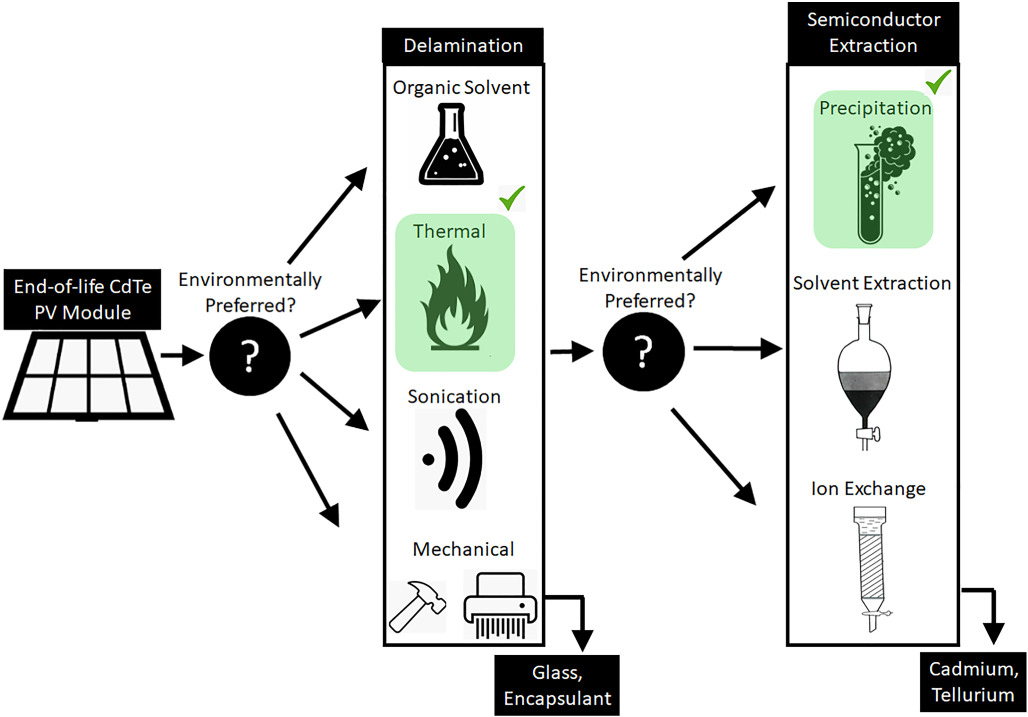
Eight novel CdTe photovoltaic recycling technologies were compared with the incumbent used in industry and a literature-reported technology. Thermal delamination with precipitation of cadmium and tellurium has a 23% lower climate-change impact than the incumbent used in industry. In removing ethylene-vinyl acetate, sonication was ineffective and using organic solvents was environmentally burdensome. A 100-km increment in road transportation necessitates a 6% reduction in inventory at the centralized facility for centralized recycling to have a lower climate-change impact than decentralized recycling.
Interdigitated back-contacted structure: A different approach towards high-efficiency ultrathin copper indium gallium (di)selenide solar cells
- Pages: 899-908
- First Published: 11 June 2020
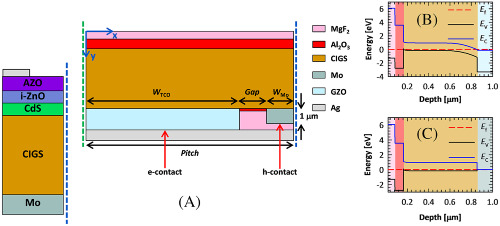
An interdigitated back-contacted (IBC) configuration is proposed and using a modelling platform is opto-electrically optimized for submicron copper indium gallium (di)selenide (CIGS). The results are compared with a reference front/back-contacted (FBC) solar cell with similar absorber thickness and exhibiting 11.9% efficiency. The alumina-assisted chemical and electrical passivation is used for front and rear side. An efficiency of 19.7% is possible with optimum geometry (nearly 90% TCO coverage), engineered bandgap (increasing towards the front side) and high-quality absorber (less defective).
Failure analysis of field-failed bypass diodes
- Pages: 909-918
- First Published: 08 June 2020
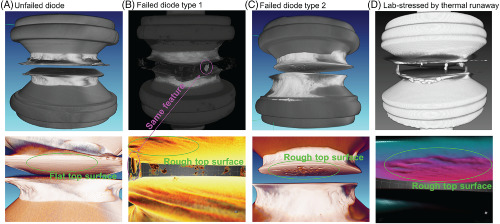
We investigated shunted bypass diodes from a rooftop installation and found defects in the Schottky junction are the origin of shunt failure. Misorientation of the various modules exacerbated the stress on the diodes. The failure shows up as a rough interface of Si/metal in X-ray computed tomography. The commonly observed melted solder metal on the sides of the diode die is not necessarily the origin of failure, but rather, a result of extensive heat caused by failure.
Electrostatic potential fluctuations and light-soaking effects in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells
- Pages: 919-934
- First Published: 18 June 2020
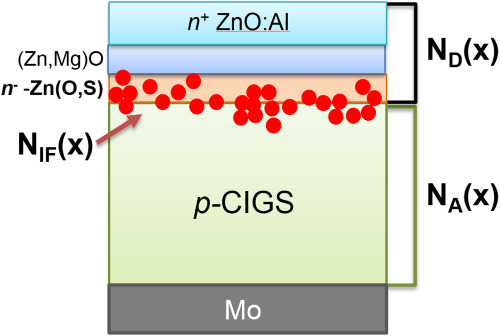
It is shown that the dominant effect of electrostatic potential fluctuations in Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells is linked to the local variations in the doping densities ND and the interface-charge density NIF introduced via the buffer layer deposition or duration of RbF postdeposition treatment. Furthermore, light soaking was found to reduce electrostatic fluctuations in cells with Zn(O,S) buffer. To explain this, we proposed a model based on changes in charge states of defects at the CIGS/buffer interface.
The role of heterointerfaces and subgap energy states on transport mechanisms in silicon heterojunction solar cells
- Pages: 935-945
- First Published: 05 June 2020
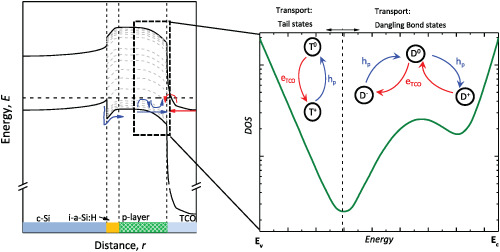
We analyse the mechanisms of charge exchange among SHJ layers with the support of rigorous numerical simulations. This transport depends on the alignment and on the nature of energy states at heterointerfaces. The transport based on direct energy transitions is more efficient than transport based on subgap energy states. Energy states associated to dangling bonds support the charge exchange more efficiently than tail states. With optimal energy alignment, FF>86% and VOC~750mV are concurrently attained in SHJ solar cells.
Organic tandem solar cells under indoor light illumination
- Pages: 946-955
- First Published: 09 June 2020
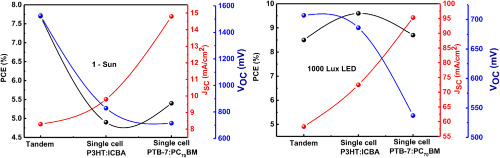
Organic tandem solar cell with the active materials having optimized band gap and thickness is tested under low-intensity indoor light. The current-matching limitation of a tandem photovoltaic structure connected in series limits the highest output current and open-circuit voltage at low-intensity light. Therefore, the tandem solar cell constructed with active materials having optimized band gaps and thicknesses is less efficient than single-celled photovoltaic device for indoor application.
High-performance HTL-free perovskite solar cell: An efficient composition of ZnO NRs, RGO, and CuInS2 QDs, as electron-transporting layer matrix
- Pages: 956-970
- First Published: 21 June 2020
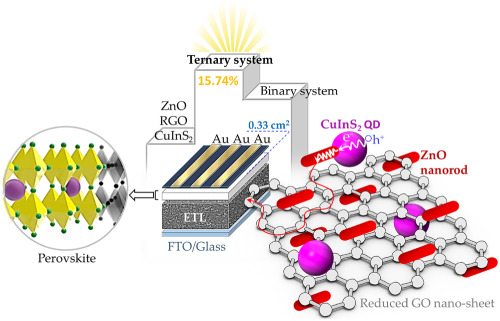
A novel ternary ZnO nanorods, reduced graphene oxide, and CuInS2 quantum dot nanocomposite as an electron-transporting layer (ETL) are prepared for enhancing the efficiency of the perovskite solar cells (PSCs). The photovoltaic and photoelectric properties of the cell are substantially enhanced through using these materials as ETL due to including the band gaps close to each other, which results in reduced electron recombination and great efficiency (15.76%) in less expensive hole-transporting layer (HTL)-free PSCs.
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Impact of bilayer structures on the surface passivation quality of high-rate-sputtered hydrogenated amorphous silicon for silicon heterojunction solar cells
- Pages: 971-976
- First Published: 02 June 2020
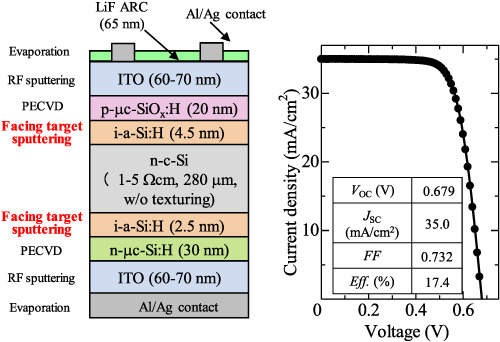
We investigated the crystalline silicon surface passivation effect of intrinsic hydrogenated amorphous silicon (i-a-Si:H) films deposited by facing target sputtering using a two-step deposition technique, which consists in a stack of i-a-Si:H layers deposited with different sputtering powers. 0.5-nm-thick initial i-a-Si:H deposited with a relatively low sputtering power was sufficient to suppress the surface sputtering damage. The highest efficiency for a silicon heterojunction solar cell with a sputtered i-a-Si:H passivation layer was achieved despite the use of a non-textured wafer.




