Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Cross-platform comparison of next-generation sequencing and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry for detecting KRAS/NRAS/BRAF/PIK3CA mutations in cfDNA from metastatic colorectal cancer patients
- First Published: 17 August 2021
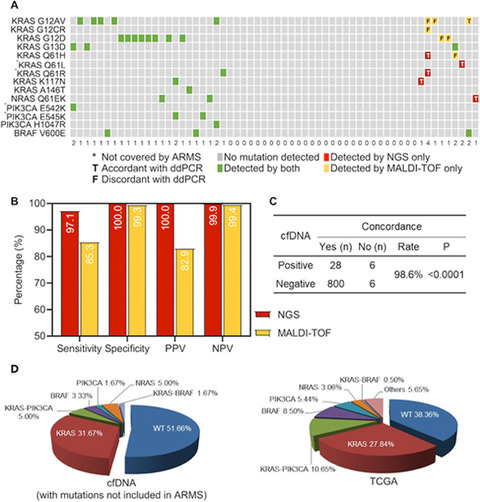
Nowadays, liquid biopsy using plasma cell-free DNA (cfDNA) is a crucial tool in cancer management. But it is still confusing which platform should be used as well as how to use cfDNA. In this study, we conducted a prospective study to compare two broad-coverage profiling platforms, next-generation sequencing (NGS) and matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF), on cfDNA analysis and explore the potential use of cfDNA in metastatic colorectal cancer (mCRC). Our results revealed the advantages of NGS assay over MALDI-TOF assay and indicated how to improve MALDI-TOF assay. Moreover, our results suggested the potential value of cfDNA analysis in monitoring treatment response in mCRC.
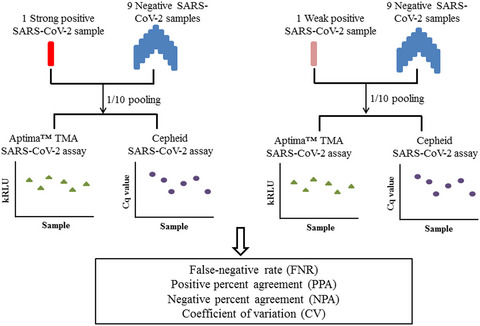
The Hologic Aptima SARS-CoV-2 assay enables high ratio pooling saving reagents and improving turnaround time
- First Published: 02 July 2021
The automated processing algorithm to correct the test result of serum neuron-specific enolase affected by specimen hemolysis
- First Published: 07 July 2021
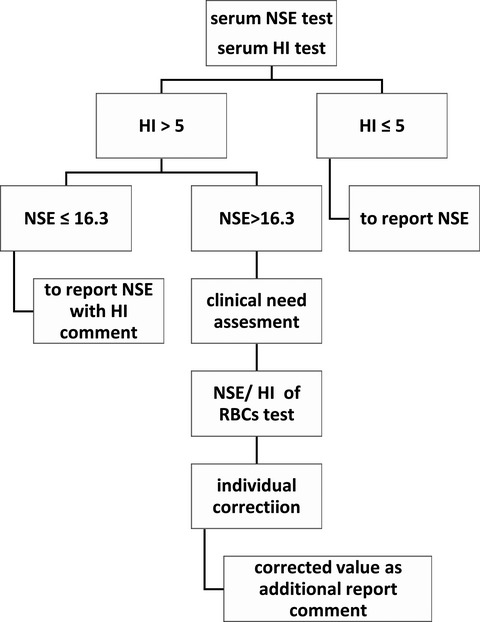
The automated processing algorithm for serum NSE influenced by specimen hemolysis. We recommend estimation for clinical needs when a NSE result is above 16.3 μg/L and is also influenced by specimen hemolysis. If the result is used for tendency supervision of tumor marker, level variation more than 25% compared to last test, which is warning clinical importance, will reminder the need of the individual corrected equation. And so it is if the result is used for auxiliary diagnosis of SCLC or NB.
Age- and sex-specific reference intervals for superoxide dismutase enzyme and several minerals in a healthy adult cohort
- First Published: 17 July 2021
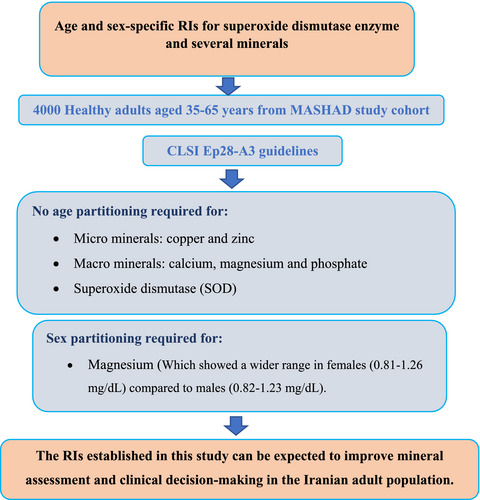
The aim of this study was to establish RIs for clinically important markers including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and serum copper, zinc, calcium, magnesium and phosphate in a cohort of healthy Iranian adults. Sex- and age-specific RIs were then calculated based on CLSI Ep28-A3 guidelines. Age and sex partitioning were not required for all parameters, apart from serum magnesium, which showed a wider range in females (0.81–1.26 mg/dl) compared to males (0.82–1.23 mg/dl).
Clinical value of INSL3 in the diagnosis and development of diabetic nephropathy
- First Published: 07 July 2021
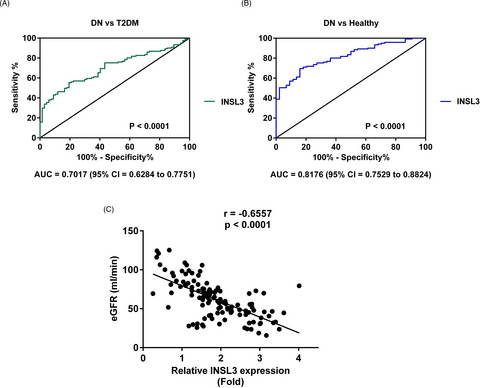
We detected that the expression of INSL3 notably increased in both serum sample and high-glucose-treated SV40-MES-13 cells compared with samples from type 2 diabetic mellitus patients, healthy controls, and normal-glucose-treated SV40-MES-13. The receiver operating characteristic analysis clarified that INSL3 could discriminate DN patients from T2DM patients and healthy controls with the area under the curves (AUC) of INSL3 of 0.7017 (95% CI = 0.6284~0.7751) and 0.8176 (95% CI = 0.7529~0.8824), respectively. Furthermore, the correlation analysis elucidated that INSL3 expression was negatively correlated with DN diagnosis golden criterion eGFR (r = −0.6557, p < 0.0001). Finally, experiments in vitro claimed that the proliferation rate of SV40-MES-13 cells after high-glucose treatment was inhibited after INSL3 knockdown; in the meantime, the apoptosis rate significantly increased deeper suggested the potential of INSL3 in DN diagnosis and development. Collectively, this study demonstrated the clinical significance of INSL3 in diagnosing and developing DN.
Down-regulated IL36RN expression based on peripheral blood mononuclear cells and plasma of periodontitis patients and its clinical significance
- First Published: 17 July 2021
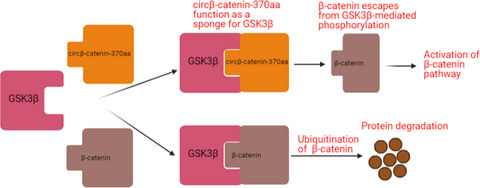
Circular RNA circβ-catenin aggravates the malignant phenotype of non-small-cell lung cancer via encoding a peptide
- First Published: 23 July 2021
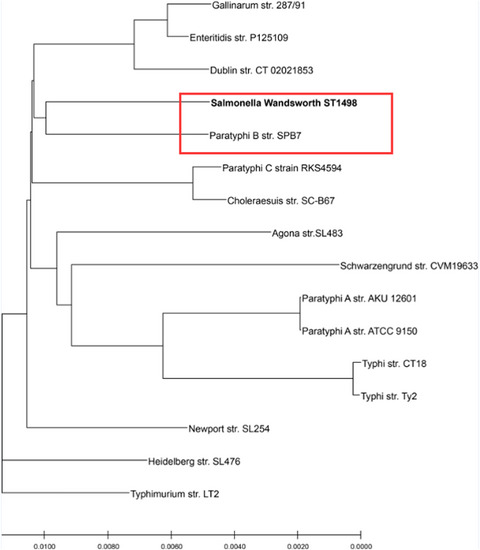
Multilocus sequence typing analysis and second-generation sequencing analysis of Salmonella Wandsworth
- First Published: 10 July 2021
CASE REPORT
A rare case of pulmonary nocardiosis comorbid with Sjogren’s syndrome
- First Published: 21 August 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLES
MALT1 positively correlates with Th1 cells, Th17 cells, and their secreted cytokines and also relates to disease risk, severity, and prognosis of acute ischemic stroke
- First Published: 17 July 2021
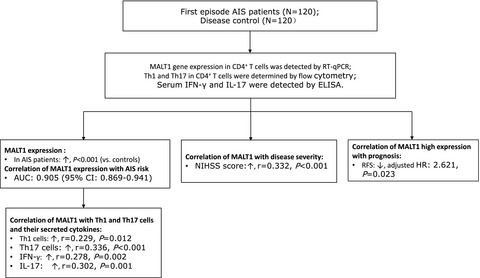
Background: This study aimed to explore the association of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma translocation protein 1 (MALT1) with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) risk and also to explore its association with T helper type 1 (Th1) cells, Th17 cells, disease severity, and prognosis in AIS patients. Methods: One hundred twenty first-episode AIS patients and 120 non-AIS patients with high-stroke-risk factors (as controls) were recruited. Besides, in the cluster of differentiation 4-positive (CD4+) T cells, the MALT1 gene expression was detected by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction; meanwhile, Th1 and T h17 were detected by flow cytometry. Moreover, serum interferon (IFN)-γ and interleukin (IL)-17 were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Results: MALT1 expression was increased in AIS patients compared with controls and also it could differentiate AIS patients from controls, with an area under curve of 0.905 (95% confidence interval: 0.869-0.941). In AIS patients, MALT1 positively correlated with Th1 cells, Th17 cells, IFN-γ, and IL-17. Besides, MALT1 positively correlated with the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale score. Furthermore, the Kaplan-Meier curve and univariate Cox’s regression analyses showed no correlation of MALT1 high expression with recurrence-free survival (RFS) in AIS patients, although after adjustment using multivariant Cox’s regression, high MALT1 expression independently correlated with worse RFS in AIS patients. Conclusion: MALT1 expression is increased and positively correlates with disease severity, Th1 cells, and Th17 cells, whose high expression severs as an independent risk factor for worse RFS in AIS patients.
Elevated serum eotaxin and IP-10 levels as potential biomarkers for the detection of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- First Published: 21 July 2021
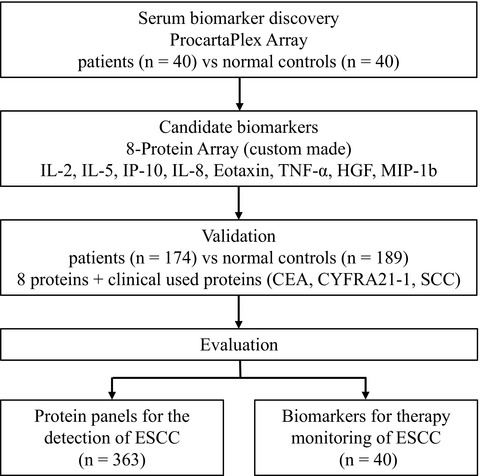
Serum samples from 40 ESCC patients and 40 normal controls were used to screen protein candidates by using ProcartaPlex Array in the biomarker discovery stage. The diagnostic values of the candidate IL-2, IL-5, IP-10, IL-8, eotaxin, TNF-α, HGF, MIP-1b using ELISA were further evaluated in 363 serum samples in the biomarker assessment stage and were finally evaluation value of protein panels for the detection and therapy monitoring of ESCC.
Novel factor VII gene mutations in six families with hereditary coagulation factor VII deficiency
- First Published: 02 August 2021
In this study, we performed coagulation index tests and gene sequencing on 7 hereditary FVII deficiency patients and their family members to explain the pathogenesis of the disease based on the analysis of their genetic information. Also, we compared the structures of newly discovered mutant proteins with the wild type and predicted their pathogenicity. To sum up, this study expands our insight on the pathogenesis of hereditary human coagulation FVII deficiency.
Aberrant expression of five miRNAs in papillary thyroid carcinomas
- First Published: 16 July 2021
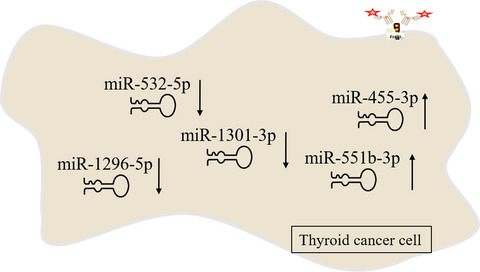
miR-1296-5p, miR-1301-3p and miR-532-5p were significantly downregulated (p = 0.0001, p = 0.0006, p = 0.0024, respectively), while miR-551b-3p and miR-455-3p were significantly upregulated in PTC tissues compared to A-PTC (p = 0.0005, p = 0.0046, respectively). Aberrant expression of miR-1296-5p, miR-532-5p, and miR-455-3p are correlation with clinical-pathological features. ROC cure indicated that those five miRNAs have diagnostic value.
Vitamin D level, lipid profile, and vitamin D receptor and transporter gene variants in sickle cell disease patients from Kurdistan of Iraq
- First Published: 14 July 2021
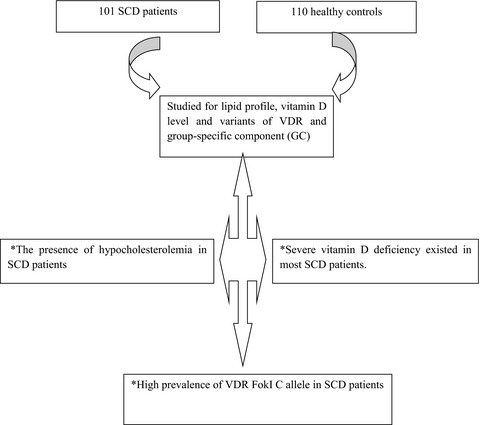
We found positive association between vitamin D level with HDL-C and total cholesterol in studied individuals, induced hypocholesterolemia by hemolytic stress, the presence of severe vitamin D deficiency, and the high prevalence of VDR FokI C allele with an adverse effect on bone mineral density among SCD patients from Kurdistan of Iraq.
Diagnostic value of red blood cell distribution width, platelet distribution width, and red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio in children with hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis
- First Published: 17 July 2021
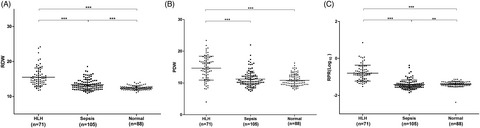
Comparison of laboratory parameters—RDW, PDW, and RPR among different groups. Abbreviations: RDW, red blood cell distribution width; PDW, platelet distribution width; RPR, red blood cell distribution width to platelet ratio; HLH, hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. The data of PRP were shown as log10. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.
PHD finger protein 19 expression in multiple myeloma: Association with clinical features, induction therapy outcome, disease progression, and survival
- First Published: 13 August 2021
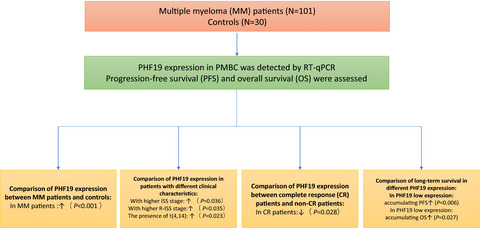
Background: PHD finger protein 19 (PHF19), also known as polycomb-like protein 3 (PCL3), promotes the progression of multiple myeloma (MM) and drug resistance; however, its role in the management of MM remains unclear. Therefore, we aimed to elucidate the correlation between PHF19 expression and treatment response, disease progression, and survival of patients with MM. Methods: Plasma cells derived from the bone marrow of 101 patients with de novo MM were collected prior to induction therapy, as were plasma cells derived from the bone marrow of 30 healthy donors. PHF19 expression in plasma cells was analyzed using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction. Furthermore, the response to induction therapy, progression-free survival (PFS), and overall survival (OS) were assessed. Results: PHF19 expression tends to be upregulated more often in MM patients than in healthy donors (p < 0.001) and can accurately predict MM risk (area under curve [AUC], 0.916; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.869–0.962). Furthermore, elevated PHF19 expression was correlated with higher International Staging System (ISS) (p = 0.036) and revised ISS stages (p = 0.035). In addition, MM patients who achieved complete response (CR) exhibited reduced PHF19 compared to those who did not (p = 0.028). Moreover, increased PHF19 expression was correlated with unfavorable PFS (p = 0.006) and OS (p = 0.027) rates. Furthermore, the results of multivariate Cox analysis also revealed that PHF19 high expression was independently associated with a reduced PFS rate (hazard ratio: 2.025, p = 0.028). Conclusion: Increased PHF19 expression is correlated with poor induction therapy response and unfavorable long-term prognosis of MM.
Diagnostic value of conventional tumor markers in young patients with pulmonary nodules
- First Published: 23 July 2021
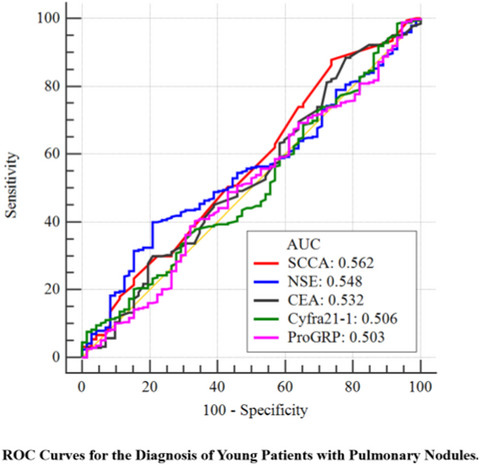
Preoperative diagnosis of pulmonary nodules is mainly based on the combination of imaging and tumor markers. Our study found the expression of the five tumor markers (CYFRA21-1, ProGRP, CEA, NSE, and SCCA) did not differ significantly in young patients with pulmonary nodules. The AUC of tumor markers did not exceed 0.600, whether it was a single tumor marker or a combination of tumor markers.
Comparison of the analytical and clinical performances of two different routine testing protocols for antinuclear antibody screening
- First Published: 04 August 2021
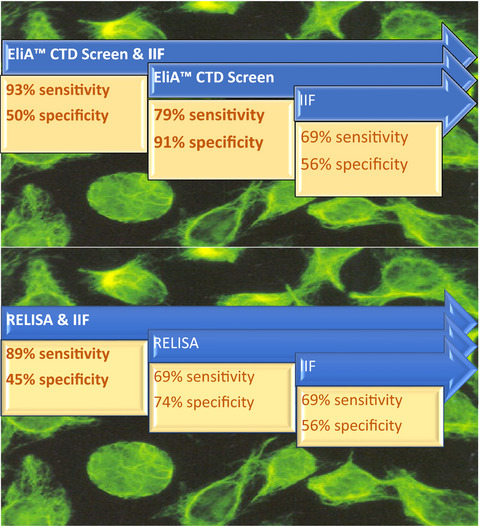
There is still room for improvement in ANA screening testing. Currently there are different methods available for systemic autoimmune rheumathic disease sift, but the optimization of screening protocols does not only rely on the selection of the best method–there is no perfect test- but in the detection of the optimal combination for the specific laboratory routine. In our study we compared the performance of two protocols in our routine samples: solid phase test+IIF and ELISA+IIF. IIF together with EliA CTD Screen (solid phase test) resulted in the highest sensitivity, while EliA CTD Screen showed the best sensitivity/specificity balance.
Preliminary exploration on the serum biomarkers of bloodstream infection with carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae based on mass spectrometry
- First Published: 31 July 2021
Carbapenem-resistant K. pneumoniae (CRKP) bloodstream infections (BSI) must be rapidly identified to improve patient survival rates. To better facilitate the identification of CRKP BSI, we interrogated blood samples using a mass spectrometry profiling approach to identify relevant diagnostic biomarkers. We successfully established a serum peptide-based diagnostic model that distinguished clinical CRKP BSI samples from normal healthy controls. The application of MALDI-TOF MS to measure serum peptides therefore represents a promising approach for early BSI diagnosis of BSI, especially for multidrug-resistant bacteria where identification is urgent. Although the relationships between these biomarkers and drug-resistant bacterial infections are not clear, these findings provide new clues for the search for biomarkers of drug-resistant bacterial infection. We will continue to explore the underlying scientific mechanisms associated between changes in these proteins and CRKP BSIs in our future research.
Chaperonin-containing tailless complex polypeptide 1 subunit 6A correlates with increased World Health Organization grade, less isocitrate dehydrogenase mutation, and deteriorative survival of astrocytoma patients
- First Published: 27 July 2021
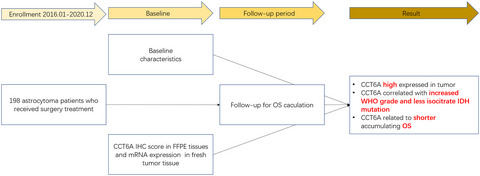
Chaperonin-containing tailless complex polypeptide 1 subunit 6A (CCT6A) is reported to be an efficient prognostic biomarker in various cancers, but it is rarely reported in astrocytoma. Thus, this study aimed to evaluate the expression of CCT6A and its correlation with disease features and prognosis in astrocytoma patients. Totally, 198 astrocytoma patients who received surgery treatment were enrolled. CCT6A protein expression was determined in the tumor tissues fixed in formalin and embedded in paraffin (FFEP) by immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay. In addition, 133 out of 198 astrocytoma patients had fresh tumor tissues frozen in the liquid nitrogen for the determination of CCT6A mRNA expression by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction. Sixty-nine (34.8%), 70 (35.4%), 46 (23.2%), and 13 (6.6%) astrocytoma patients had the CCT6A immunohistochemistry (IHC) score of 0–3, 4–6, 7–9, and 10–12, respectively. CCT6A protein expression was correlated with increased World Health Organization (WHO) grade (P < 0.001) and less isocitrate dehydrogenase (IDH) mutation (P = 0.002); meanwhile, CCT6A mRNA expression was only related to elevated WHO grade (P = 0.001). However, CCT6A protein and mRNA expression were not correlated with other clinical features and subsequent treatment modalities (all P > 0.05). Moreover, CCT6A protein high and CCT6A mRNA high were related to shorter accumulating overall survival (OS; both P < 0.05). CCT6A protein high was an independent factor for predicting the worse OS (hazard ratio: 1.821, P = 0.012). CCT6A correlates with elevated WHO grade and less IDH mutation; besides, CCT6A high expression is independently associated with unfavorable accumulating OS of astrocytoma patients.
Pooled analysis of LAMP assay for the diagnosis of norovirus infection
- First Published: 31 July 2021
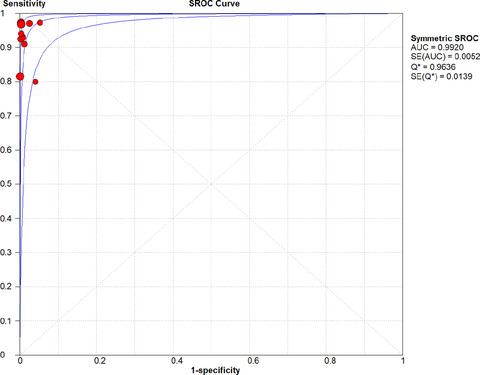
The AUC was 0.9920, and Q* was 0.9636 in SROC; the curve was close to the top left corner. The results proved a higher value, suggesting a greater diagnostic potential of LAMP for norovirus infection. One may conclude that the capacity of LAMP in the early diagnosis of norovirus is considerably high. LAMP may be a practical and reliable method for detecting norovirus infection.
A five-gene panel refines differential diagnosis of thyroid nodules
- First Published: 28 July 2021
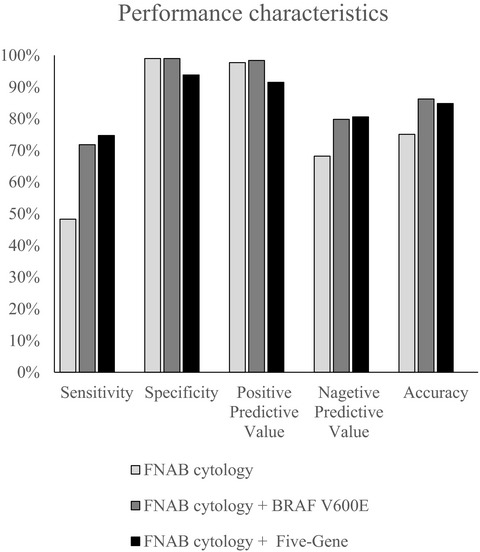
Our study focuses on the feasibility and utility of a five-gene panel containing BRAF/RAS/TERT mutation detection in the improvement of fine-needle aspiration biopsy (FNAB) cytology in differential diagnosis of thyroid nodules in China. Our results demonstrated that BRAF/five-gene mutations detected in FNAB samples can effectively improve the sensitivity, negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy of FNAB cytology, while kept the specificity and positive predictive value (PPV).
Performance evaluation of three automated quantitative immunoassays and their correlation with a surrogate virus neutralization test in coronavirus disease 19 patients and pre-pandemic controls
- First Published: 08 August 2021
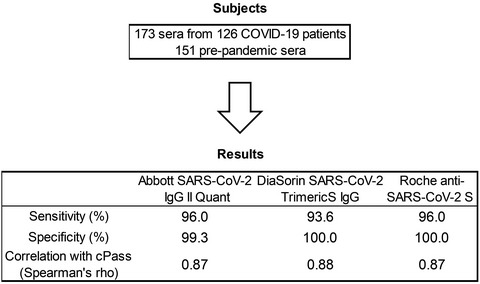
The performances of three automated quantitative immunoassays detecting antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, Abbott SARS-CoV-2 IgG II Quant; DiaSorin LIAISON SARS-CoV-2 TrimericS IgG; Roche Elecsys anti-SARS-CoV-2 S were comparable, with superior sensitivity and specificity. The three immunoassays demonstrated strong correlations with GenScript cPass virus neutralization test.
Immunological characteristics and effect of cyclosporin in patients with immune thrombocytopenia
- First Published: 30 July 2021
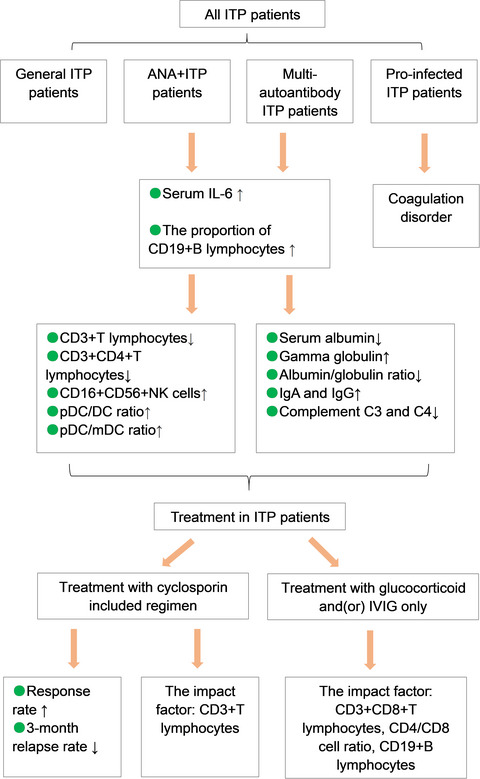
We showed clinical characteristics of four subgroups of ITP patients according to immune indexes and proinfection. The patients with autoantibodies usually combined with imbalance of immune cells. Comparing with glucocorticoid and(or) IVIG only treatment, cyclosporin-included regimen has a higher response rate and lower relapse rate. The number of CD3+T lymphocytes is the independent impact factor that influence the therapeutic effect of cyclosporin.
Risk factors for prolonged virus shedding of respiratory tract and fecal in adults with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 infection
- First Published: 13 August 2021
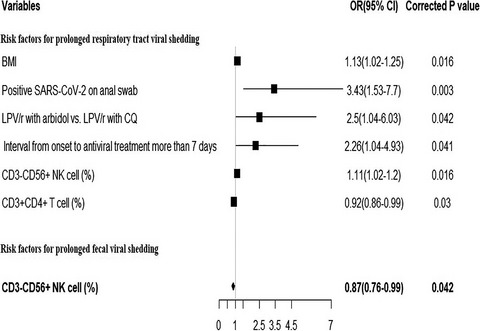
The multivariable logistic regression analysis suggested that BMI (OR, 3.32; 95% CI, 1.08–10.0), positive rectal swab (OR, 3.43; 95% CI, 1.53–7.7), treatment by lopinavir/ritonavir with chloroquine phosphate (OR, 2.5; 95% CI, 1.04–6.03), interval from onset to antiviral treatment more than 7 days (OR, 2.26; 95% CI, 1.04–4.93), lower CD4+ T cell (OR, 0.92; 95% CI, 0.86–0.99) and higher NK cells (OR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.02–1.20) were significantly associated with prolonged respiratory tract viral shedding even after adjustment for age and gender. Additionally, CD3−CD56+ NK cells (OR, 0.87; 95% CI: 0.76–0.99) on admission were linked to prolonged fecal shedding.
APOE gene ɛ4 allele (388C-526C) effects on serum lipids and risk of coronary artery disease in southern Chinese Hakka population
- First Published: 27 July 2021
Apolipoprotein E (ApoE) and solute carrier organic anion transporter family member 1B1 (SLCO1B1) are involved in the regulation of lipid metabolism; however, the relationship between APOE and SLCO1B1 gene polymorphisms and coronary artery disease (CAD) has been controversial. APOE ε4 allele may be associated with susceptibility to CAD in southern Chinese Hakka population. It indicated that the APOE SNPs rs429358 and rs7412 are associated with CAD. This is the first systematic study of the association between CAD and APOE and SLCO1B1 gene polymorphisms in Hakka population. This study provides valuable information for the prediction of the risk of coronary heart disease.
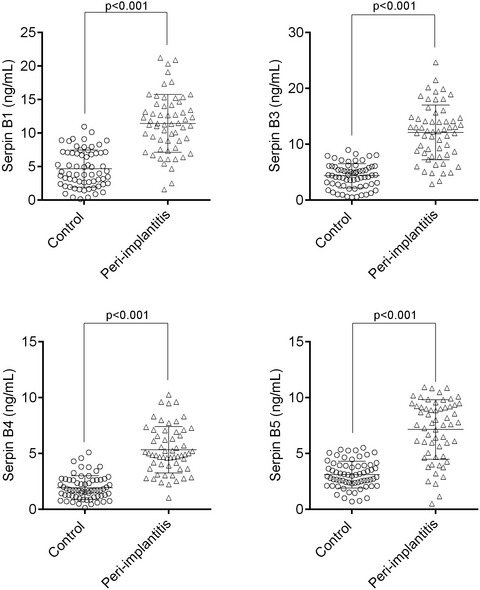
Levels of SERPIN family proteins in peri-implant crevicular fluid in patients with peri-implantitis
- First Published: 04 August 2021
Combined procalcitonin and hemogram parameters contribute to early differential diagnosis of Gram-negative/Gram-positive bloodstream infections
- First Published: 06 August 2021
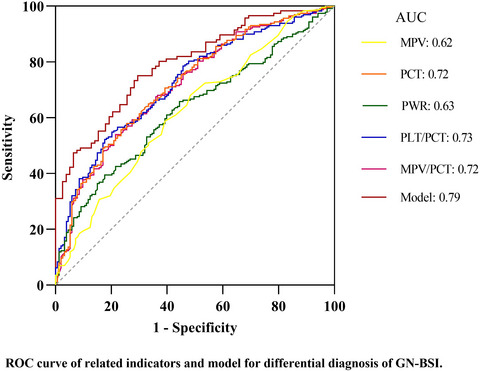
The differential diagnosis of Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-positive bacteria bloodstream infection is mainly based on blood culture pathogens. Our study found that PCT, MPV, PWR, PLT/PCT, and MPV/PCT values obtained from routine blood tests can be used to discriminate Gram-negative bloodstream infections among bloodstream infections to some extent. The combination of MPV, PWR, and PCT is helpful for the clinical diagnosis of GN-BSI, with more effective sensitivity and specificity.
A new method for anti-negative interference of calcium dobesilate in serum creatinine enzymatic analysis
- First Published: 30 July 2021
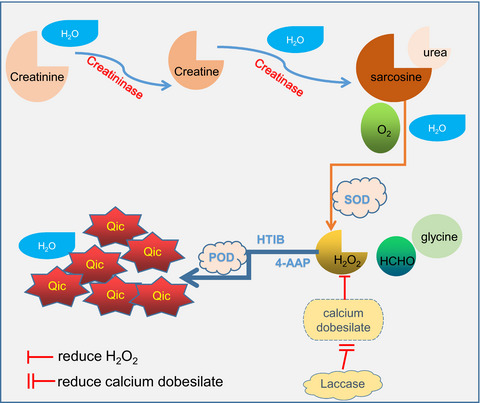
The serum creatinine quantitative method SOE was negatively interfered with by the commonly used drug calcium dobesilate, resulting in lower than the actual value. The new BG reagent laccase was added to prevent the generation of negative interference and make the detection more accurate. Schematic diagram of creatinine detection of the new BG reagent. SOD: sarcosine oxidase. 4-AAP: 4-aminophenazone. POD: peroxidase. HTIB: 2,4,6-triiodo-3-hydroxybenzoic acid. Qic: quinoneimine chromogen. Calcium dobesilate is a strong reducing agent that consumes H2O2 during the reaction, resulting in decreased QIC of the final chromatographic substance. Laccase is a strong oxidant that can oxidize calcium dobesilate in advance before H2O2 is produced so that H2O2 will not be consumed and negative interference can be avoided.
A novel multiplex qPCR method for assessing the comparative lengths of telomeres
- First Published: 04 August 2021
METTL3-mediated m6A methylation of ASPM drives hepatocellular carcinoma cells growth and metastasis
- First Published: 16 August 2021
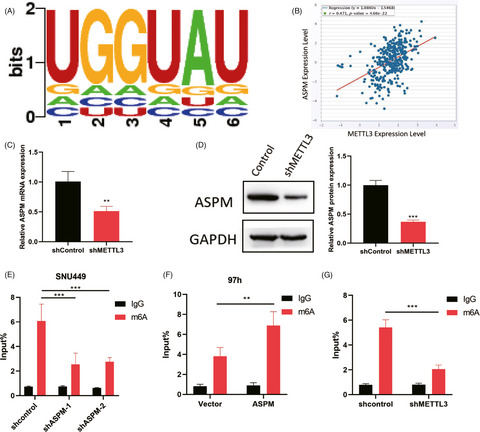
METTL3 mediated m6A modification of ASPM in LIHC.A. SRAMP database was performed to predict m6A sequences motif of METTL3 and ASPM. B. STARbase database was performed to analyze the correlation between the expression of METTL3 and ASPM. For further confirmation, SNU449 cells were stably infected with METTL3 knockdown, and ASPM protein and mRNA expression level were measured by qPCR(C) and Western blotting (D). E. ASPM was silenced in LIHC cells, and MeRIP-qPCR was adopted to test m6A levels of ASPM. F. ASPM was overexpressed in LIHC cells, and MeRIP-qPCR was adopted to test m6A levels of ASPM. G. MeRIP-PCR was utilized to assess the m6A levels of ASPM when METTL3 was knockdown. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. Data represent at least three independent sets of experiment.
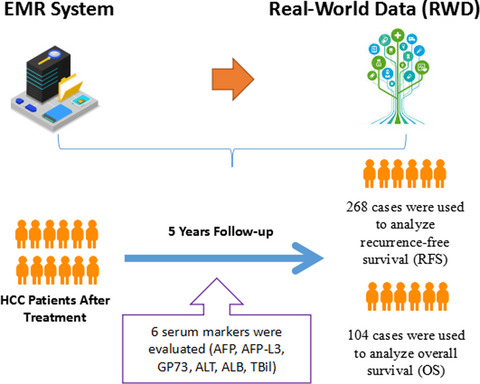
The prognostic values of serum markers in hepatocellular carcinoma after invasive therapies based on real-world data
- First Published: 17 August 2021
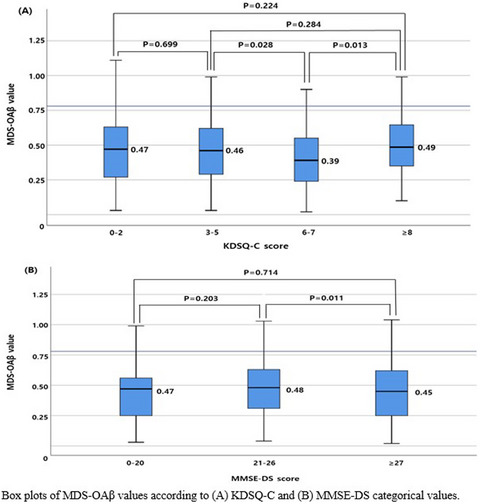
Reference interval and the role of plasma oligomeric beta amyloid in screening of risk groups for cognitive dysfunction at health checkups
- First Published: 03 August 2021
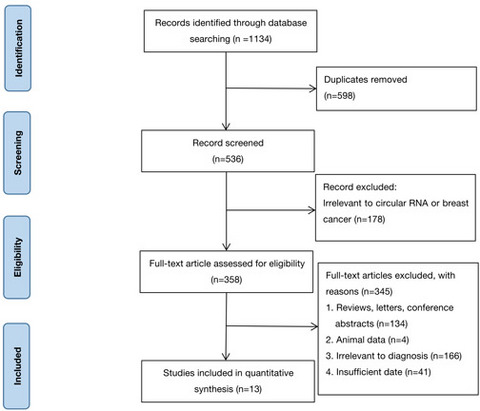
CircRNAs as promising biomarker in diagnosis of breast cancer: An updated meta-analysis
- First Published: 31 July 2021
Distribution and reference interval establishment of neutral-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR), and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) in Chinese healthy adults
- First Published: 13 August 2021
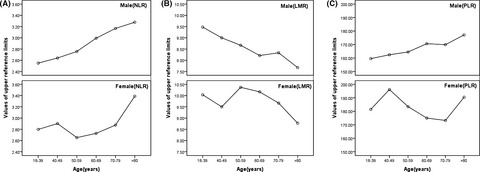
Values of upper reference limits for three indicators in different age partitions. A: Values of upper reference limits for NLR in different age partitions. B: Values of upper reference limits for LMR in different age partitions. C: Values of upper reference limits for PLR in different age partitions. The line chart based on age showed that the reference upper limit of NLR, LMR, and PLR increased with age in male population. In female population, the reference upper limit of NLR in 50–59 group, LMR in >80 group, and PLR in 70–79 group showed a trough; the reference upper limit of NLR in >80 group, LMR in 50–59 group, and PLR in 40–49 group showed peak.
Circulating methylated THBS1 DNAs as a novel marker for predicting peritoneal dissemination in gastric cancer
- First Published: 13 August 2021
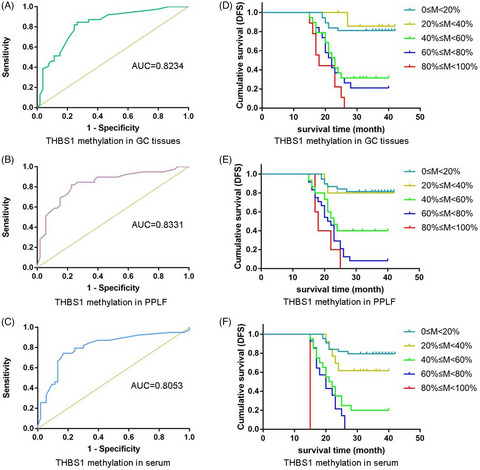
Postoperative recurrence of gastric cancer usually occurs in the peritoneum, and peritoneal dissemination and recurrence are the main causes of poor prognosis. Therefore, it is very necessary to find a biomarker that can predict peritoneal dissemination of gastric cancer cells. Here, we found that THBS1 methylation levels in preoperative serum or peritoneal fluid can accurately predict peritoneal dissemination and suggest a poor prognosis in patients with gastric cancer.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Analysis of COVID-19 vaccines: Types, thoughts, and application
- First Published: 15 August 2021
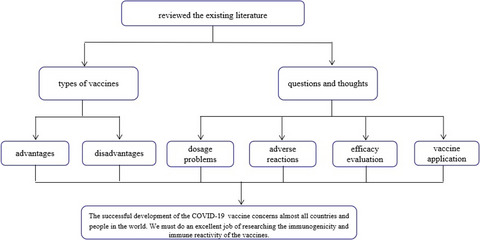
We reviewed the mechanism and types of COVID-19 vaccines through the literature. At the same time, we found some existing problems in vaccines research, such as injection dosage, adverse reactions, efficacy evaluation and vaccine application. An excellent job must be performed to research the immunogenicity and immune reactivity of the COVID-19 vaccines.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Kinetics of platelet adhesion to a fibrinogen-coated surface in whole blood under flow conditions
- First Published: 04 August 2021
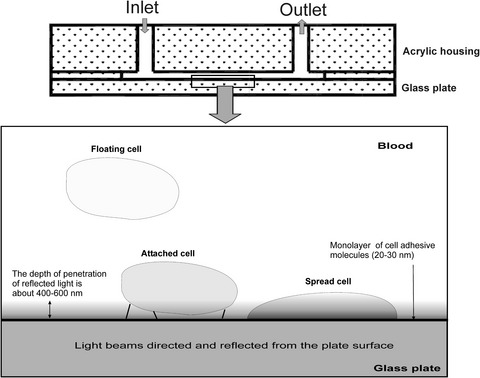
The laser optical system for recording of platelet adhesion to protein-coated surfaces under flow conditions. The illustration of the flow chamber with the flat glass surface coated with a monolayer of cell-adhesive molecules. The glass surface was coated with fibrinogen. The reflected light evanesces into the blood sample beyond the reflection zone to a depth of approximately 400–600 nm. Platelets or other blood cells in the flow do not interact with this laser radiation, which evanesces to such a small depth. The laser light can interact with platelets only when they are strongly attached to or spread onto the glass surface.
The biotin interference within interference suppressed immunoassays
- First Published: 04 August 2021
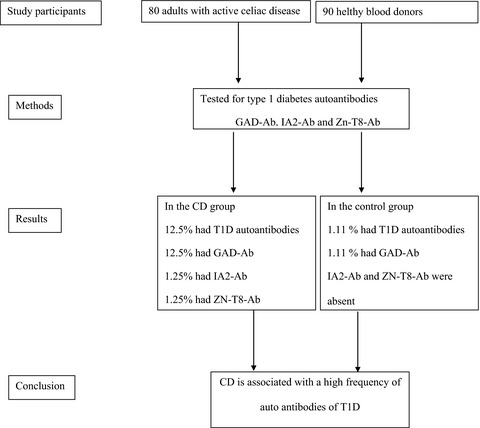
Frequency of auto-antibodies of type 1 diabetes in adult patients with celiac disease
- First Published: 04 August 2021
Effects of m6A RNA methylation regulators on endometrial cancer
- First Published: 04 August 2021
CTR9-mediated JAK2/STAT3 pathway promotes the proliferation, migration, and invasion of human glioma cells
- First Published: 08 August 2021
Lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio combined with CA19-9 for predicting postoperative recurrence of colorectal cancer in patients with diabetes
- First Published: 21 August 2021
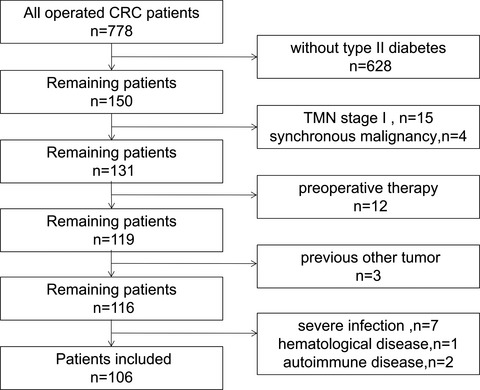
In the present study, a total of 106 patients with CRC and type II diabetes before surgery were included in the analysis, the median follow-up was 60 months, and 38 had a disease recurrence. We found that both LMR and CA19-9 are significantly related to prognosis, and the combination of the above two is expected to become a new index for predicting postoperative recurrence of CRC in patients with diabetes.
Abnormal regulation of microRNAs and related genes in pediatric β-thalassemia
- First Published: 16 August 2021
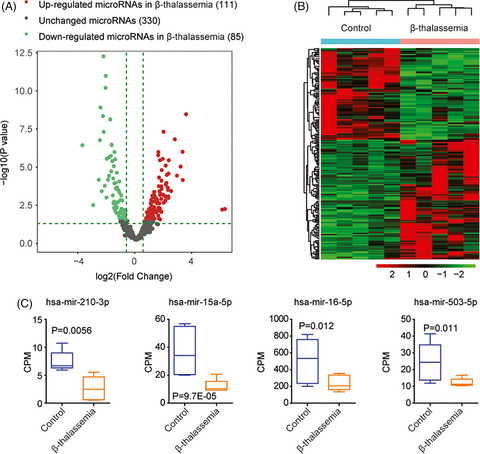
We performed microRNA sequencing to identify the microRNA expression profiling of pediatric β-thalassemia. Totally, 530 microRNAs were identified. Based on criteria of fold change >1.5 and p-value <0.05, 111 microRNAs were upregulated in β-thalassemia patients, while 85 microRNAs were downregulated in β-thalassemia patients. Those microRNAs could clearly distinguish the normal cohorts from the β-thalassemia patients. Hsa-miR-2100-3p, hsa-microRNA-15a-5p, hsa-microRNA-16-5p, and hsa-miR-503-5p were all downregulated in pediatric β-thalassemia patients. We also found five let7 microRNAs hsa-let-7b-5p, hsa-let-7i-5p, hsa-let-7f-5p, hsa-let-7e-5p, and hsa-let-7d-5p and were downregulated in pediatric thalassemia patients.
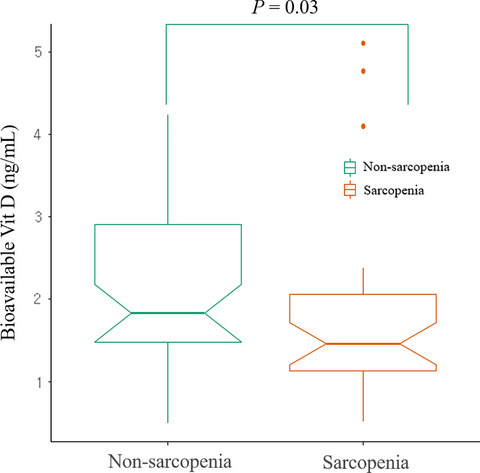
Comparative analysis of the association between various serum vitamin D biomarkers and sarcopenia
- First Published: 05 August 2021
The diagnostic value of the combination of hemoglobin, CA199, CA125, and HE4 in endometriosis
- First Published: 18 August 2021
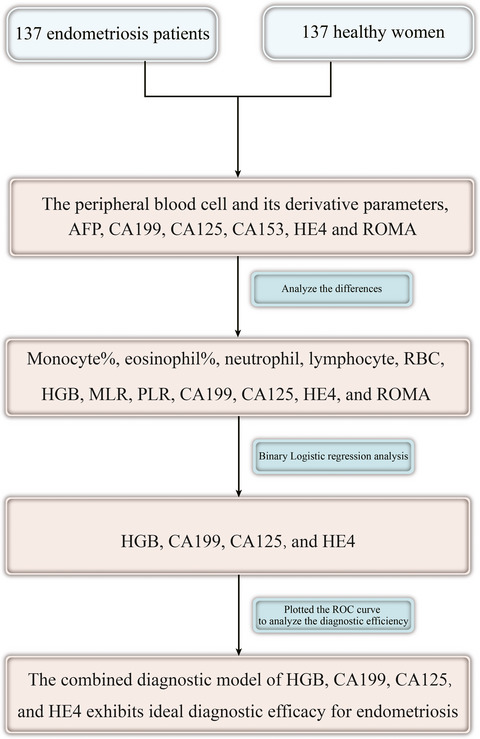
This study retrospectively analyzed the differences in the peripheral blood cells and their derivative parameters and tumor biomarkers between the patients with endometriosis and healthy people, and established a more efficient combined diagnostic model based on HGB, CA199, CA125, and HE4. The combined diagnostic model reached a sensitivity of 85.4%, a specificity of 78.83%, and an area under the curve of 0.900, which may provide a novel approach for the early non-invasive diagnosis of endometriosis.
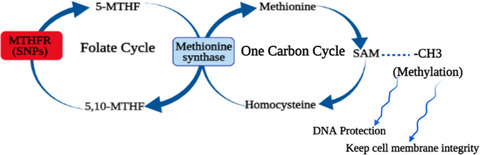
The effect of A1298c polymorphism of the MTHFR gene on anti-Müllerian hormone levels: experimental and Web-based analysis
- First Published: 08 August 2021
AC016405.3 functions as an oncogenic long non-coding RNA by regulating ERBB3 via sponging miR-22-3p in breast cancer
- First Published: 17 August 2021
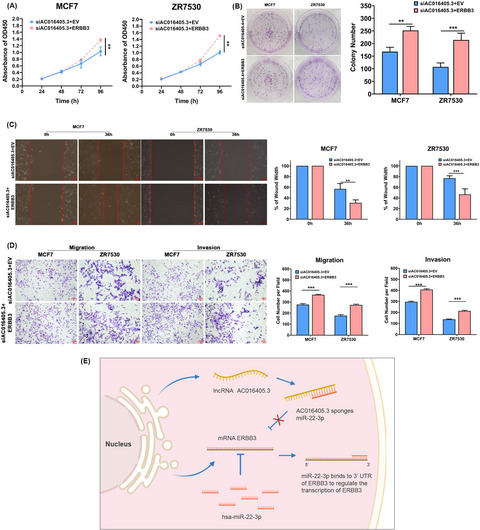
AC016405.3 is involved in BRCA progression by up-regulating ERBB3 expression via miR-22-3p. BRAC cells (MCF7 and ZR7530) were co-transfected si-AC016405.3 with empty vector (EV) or ERBB3 overexpression vector (ERBB3). The proliferation of BRAC cells from different groups was examined by (A) CCK-8 and (B) colony formation assays. (C) Wound-healing assay assessed the migration ability of BRAC cells from different groups. (D) Transwell assay evaluated both the migration and invasion of BRAC cells from different groups. (E) A schematic diagram exhibited the proposed mechanism that cytoplasmic AC016405.3 sponges miR-22-3p to promote ERBB3 expression thus contributes to BRCA progression. Note: **p < 0.01 and ***p < 0.005. Scale bar = 100μm.
Reduced expression of circRNA hsa_circ_001888 in gastric cancer and its clinical significance
- First Published: 16 August 2021
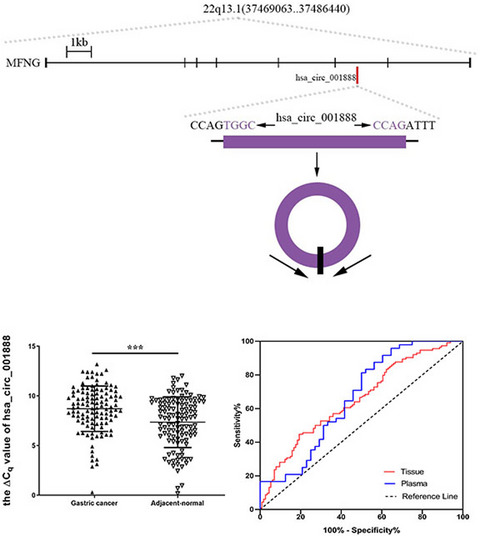
This study aimed to identify the relationship between gastric cancer (GC) and a new circRNA named hsa_circ_001888. The results indicated that hsa_circ_001888 was significantly downregulated in GC cell lines, tissues and plasma samples compared to control samples. Hsa_circ_001888 may serve as a potential biomarker in the diagnosis of GC with high degrees of specificity, sensitivity and accuracy.
Sestrin2 and Beclin1 levels in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
- First Published: 16 August 2021
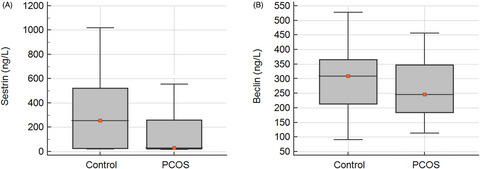
This study attempted to evaluate the plasma concentrations of Sestrin2 and Beclin1 in women with PCOS and healthy controls, and to explore the clinical value of these proteins as novel biomarkers for PCOS. Plasma sestrin2 levels of the subjects with PCOS (40.74 [24.39–257.70]) were significantly lower than that of healthy subjects (255.78 [25.46–528.66]; p-value = 0.040). A cut-off value of 420.5 ng/L had an appropriate sensitivity (83.87%) and specificity (46.88%) for discriminating individuals with and without PCOS. There were no statistically significant differences between the two groups concerning plasma levels of beclin1. Our findings highlight the dysregulation of sestrin2 as a marker of autophagy in PCOS and its usefulness as a novel biomarker for PCOS.
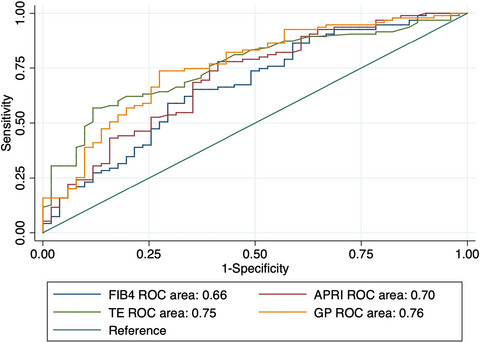
Performance of noninvasive tools for identification of minimal liver fibrosis in patients with hepatitis B virus infection
- First Published: 17 August 2021
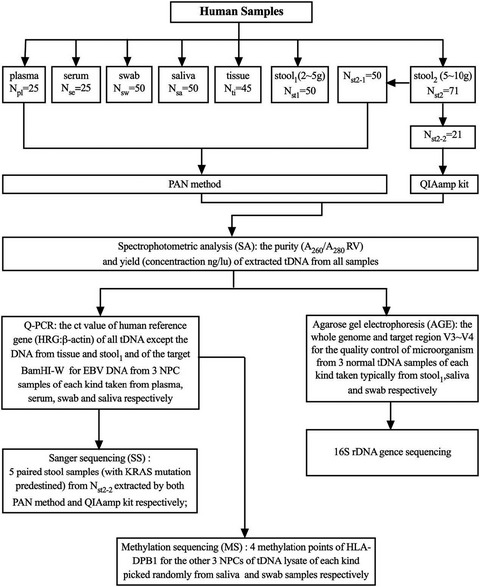
Development and validation of a flexible DNA extraction (PAN) method for liquid biopsy of multiple sample types
- First Published: 16 August 2021
IL-23/IL-17 axis and soluble receptors isoforms sIL-23R and sIL-17RA in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-presenting periodontitis
- First Published: 17 August 2021
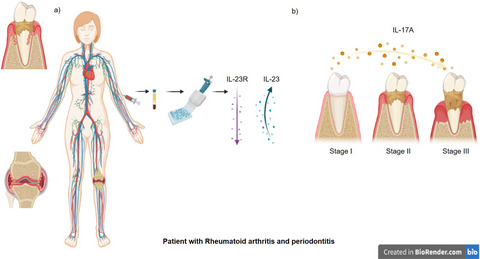
Blood sample was taken to obtain plasma from all study participants. IL-23, IL-23R, IL-17A, and IL-17RA were detected with ELISA technique. Results: (a) The sIL-23R levels were found lower in the RAP group and IL-23 levels were increased. (b) IL-17A was lower in the P and RAP group but not in RA patients. According to the chronicity of periodontitis, RAP group showed a decreased IL-17A levels in advanced stages of the periodontal disease.
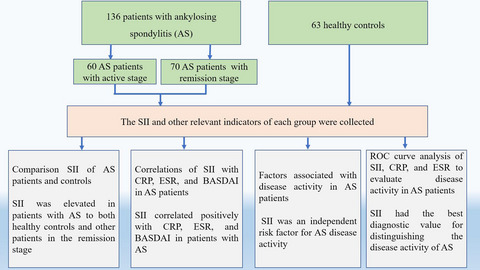
Systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with disease activity in patients with ankylosing spondylitis
- First Published: 21 August 2021
The clinical value of high fluorescent lymphocytes and smudge cells in the diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis
- First Published: 17 August 2021
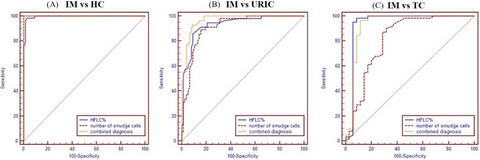
HFLC% can be used for auxiliary diagnosis of IM, thereby saving time and reducing cost of smear and manual classification. HFLC% assists the diagnosis of IM with the following advantages. First, this indicator has high specificity and sensitivity for the diagnosis of IM, which can effectively avoid missed diagnosed. Second, HFLC%, as one of the blood routine indicators, can be obtained directly from the automatic blood analyzer. It does not increase additional economic burdens and manual operations. It has better adaptability and superiority, and can prompt clinical diagnosis and treatment earlier. In addition, when the number of smudge cells in the peripheral blood increases, the doctor should be alert to the possibility of IM.
CASE REPORT
Identification of a novel EXT2 frameshift mutation in a family with hereditary multiple exostoses by whole-exome sequencing
- First Published: 17 August 2021
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Influences of the lncRNA TUG1-miRNA-34a-5p network on fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis through targeting the lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA)
- First Published: 17 August 2021
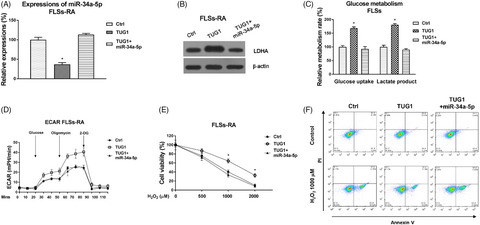
Our conclusions uncover critical roles and molecular mechanisms of the TUG1-mediated glucose metabolism and apoptosis of FLSs-RA through modulating the miR-34a-5p-LDHA pathway in RA patients, suggesting that targeting TUG1 could be an effective therapeutic approach to suppress the proliferation of FLSs for rheumatoid arthritis treatment.