Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Exploring the Ionic Mechanochemical Coupling Effects in the Swelling Behavior of Hydrogels Based on the Interaction Parameter
- First Published: 09 March 2025
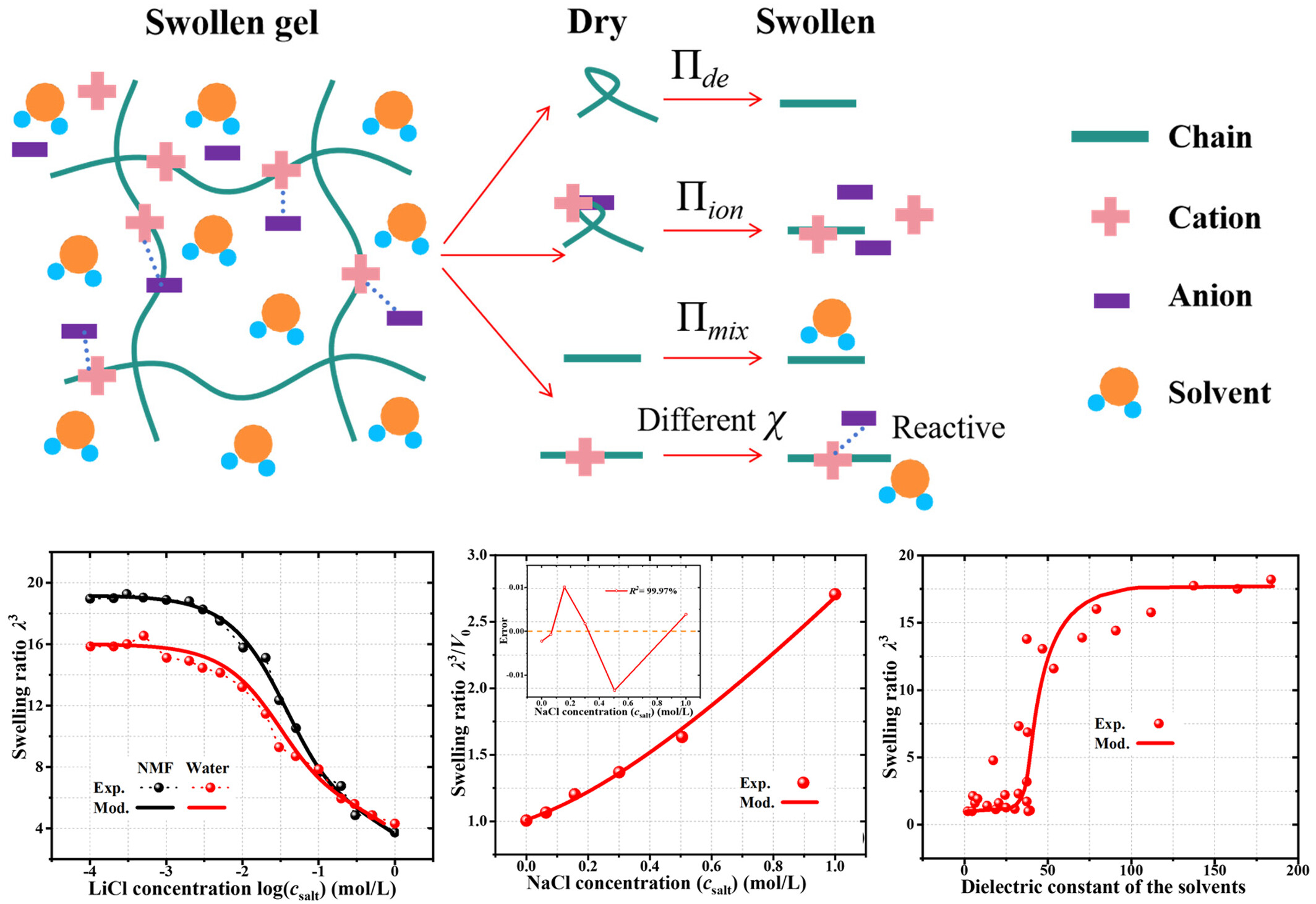
The swelling of hydrogels was initially composed of the polymer network deformation energy and the mixing free energy suggested by Flory and Rehner. Based on the classical Flory-Rehner theoretical framework, recent studies have shown that hydrogels in salt solutions also need to analyze the role of ions. In this study, an extended Flory-Rehner model is formulated to describe the ionic mechanochemical coupling effects in the free swelling of hydrogels, of which the chains and ions reactions are controlled by reaction kinetics. The free energy of swelling hydrogels is considered to include network deformation energy, mixing energy, and ion energy. The effect of ion concentration and reaction on the free swelling of hydrogels is considered to be an ionic mechanochemical coupling effect, which significantly changes the Flory-Huggins interaction parameters.
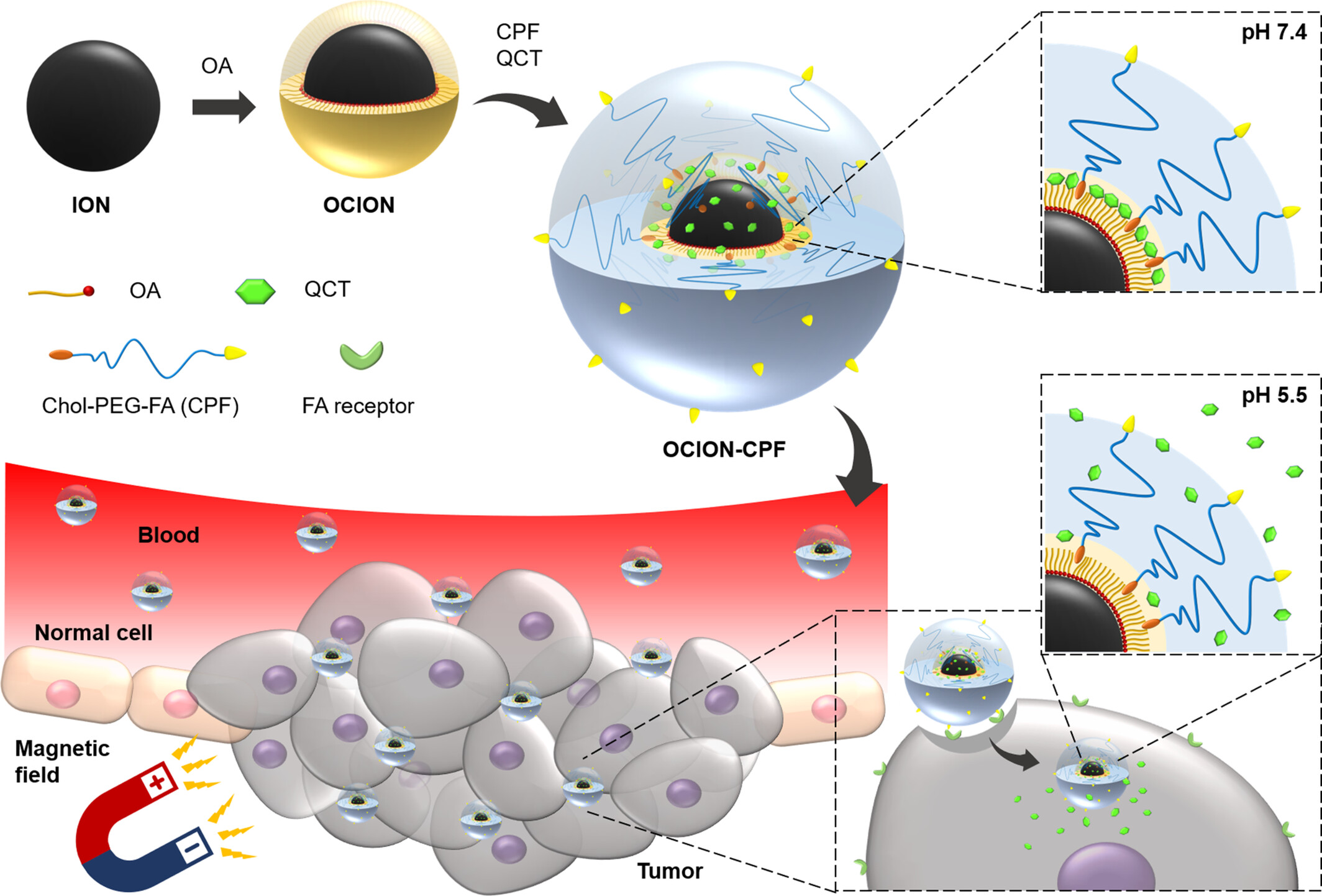
The Integration of Cholesterol-Polyethylene Glycol-Folic Acid Conjugate and Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for A Multi Targeted and Stimuli Responsive Drug Delivery System of Quercetin
- First Published: 13 March 2025
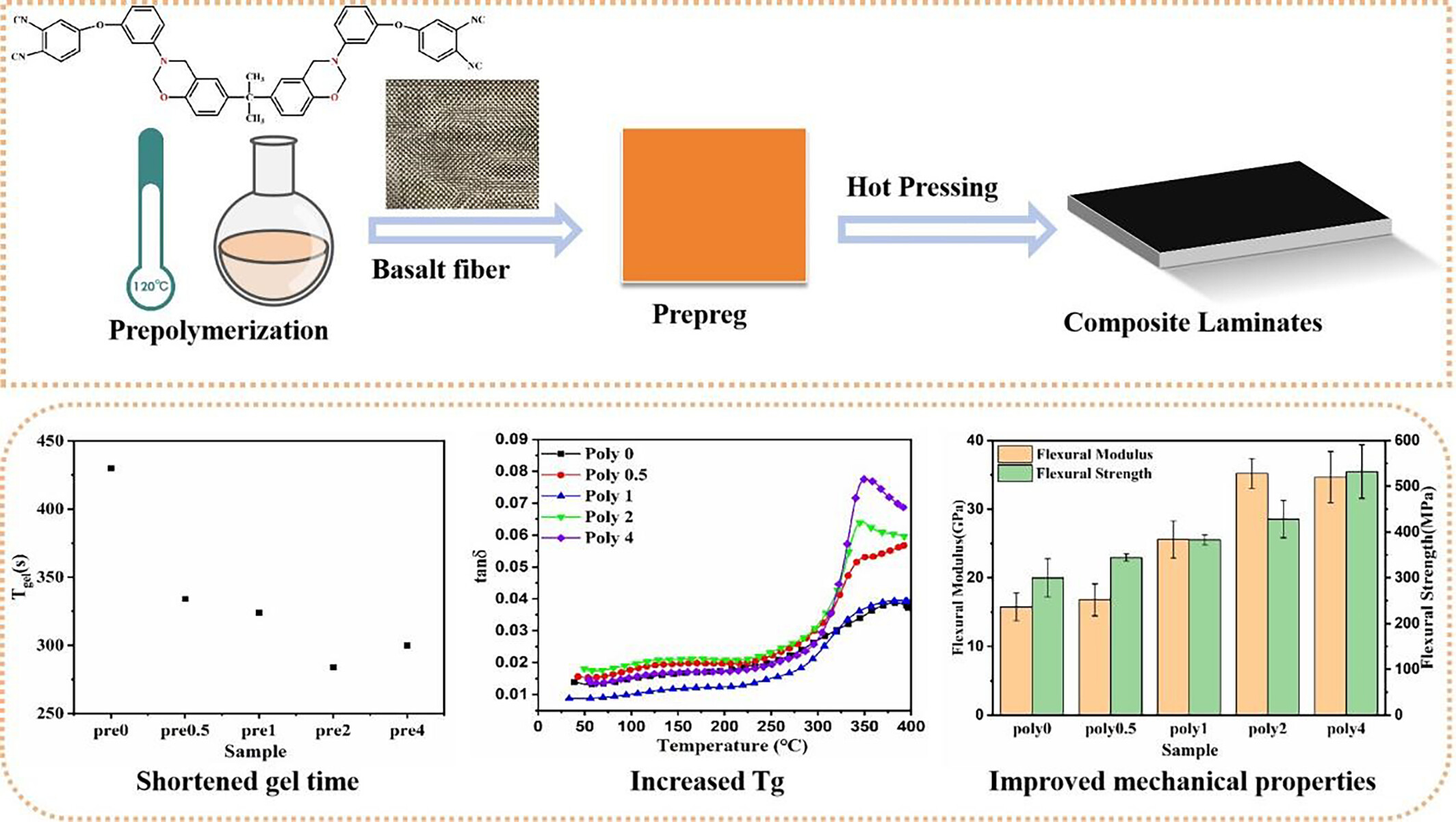
Probing the Effect of Prepolymerization on the Structure and Properties of Phthalonitrile Resin/Basalt Fiber Composites
- First Published: 06 March 2025
Preparation and Performance of High Bio-Based and Abrasion-Resistant Tread Rubber Based on Itaconate Rubber
- First Published: 09 March 2025
Designing and Development of Innovative N95 Respirator Using Nanofibres Produced by Air-Assisted Electrospinning
- First Published: 18 March 2025
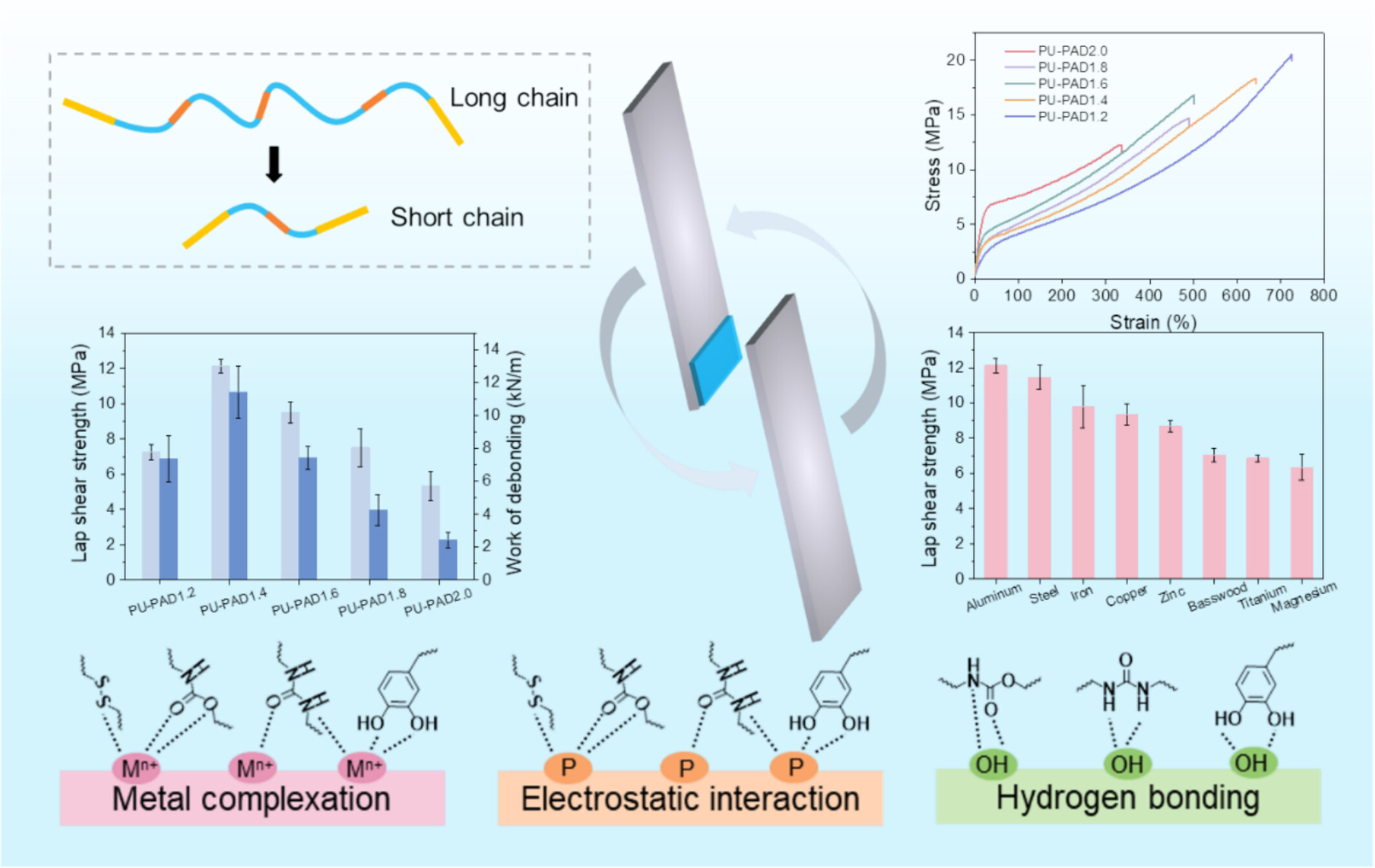
Synergistic Optimization of Cohesive Energy and Adhesive Force by Regulating End-Capping Catechol and Chain Extender 4-Aminophenyl Disulfide Toward Enhancing Bonding Strength of Hot-Melt Polyurethane
- First Published: 18 March 2025
4-Perchloratobutyl Acrylate, a New Monomer for Self-Crosslinking Thermosetting Acrylic Resins
- First Published: 10 March 2025
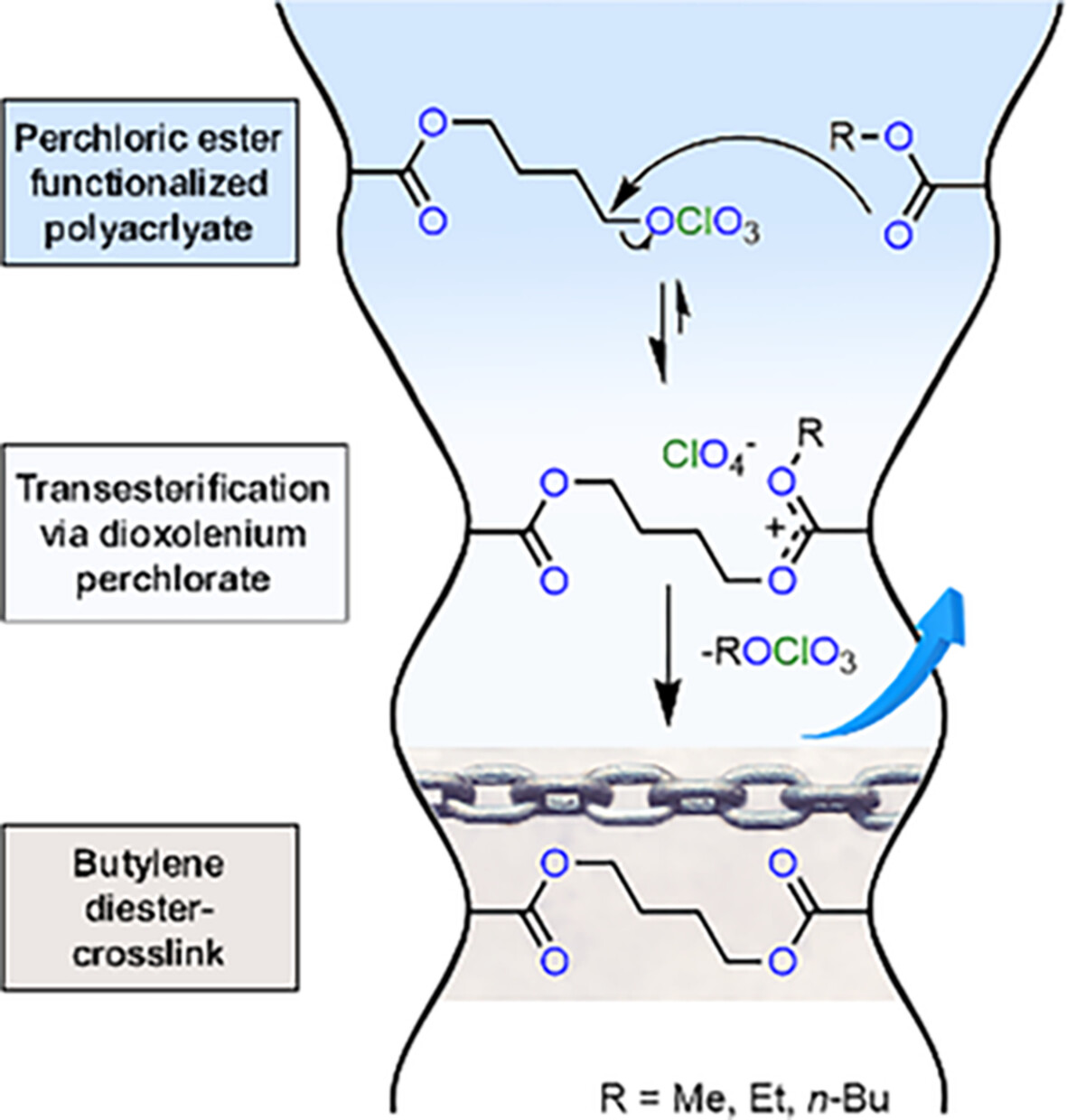
4-Perchlorato-butyl acrylate (pCBA) is synthesized and copolymerized with short-chain alkyl acrylates (Me, Et, nBu) to form a 1 K polyacrylate binder. Thermal curing at 105°C–135°C gives a thermoset by transesterification of perchlorate and alkyl ester, resulting in a butylene crosslink connecting two acrylic esters and volatile alkyl perchlorates that evaporate from the resin.
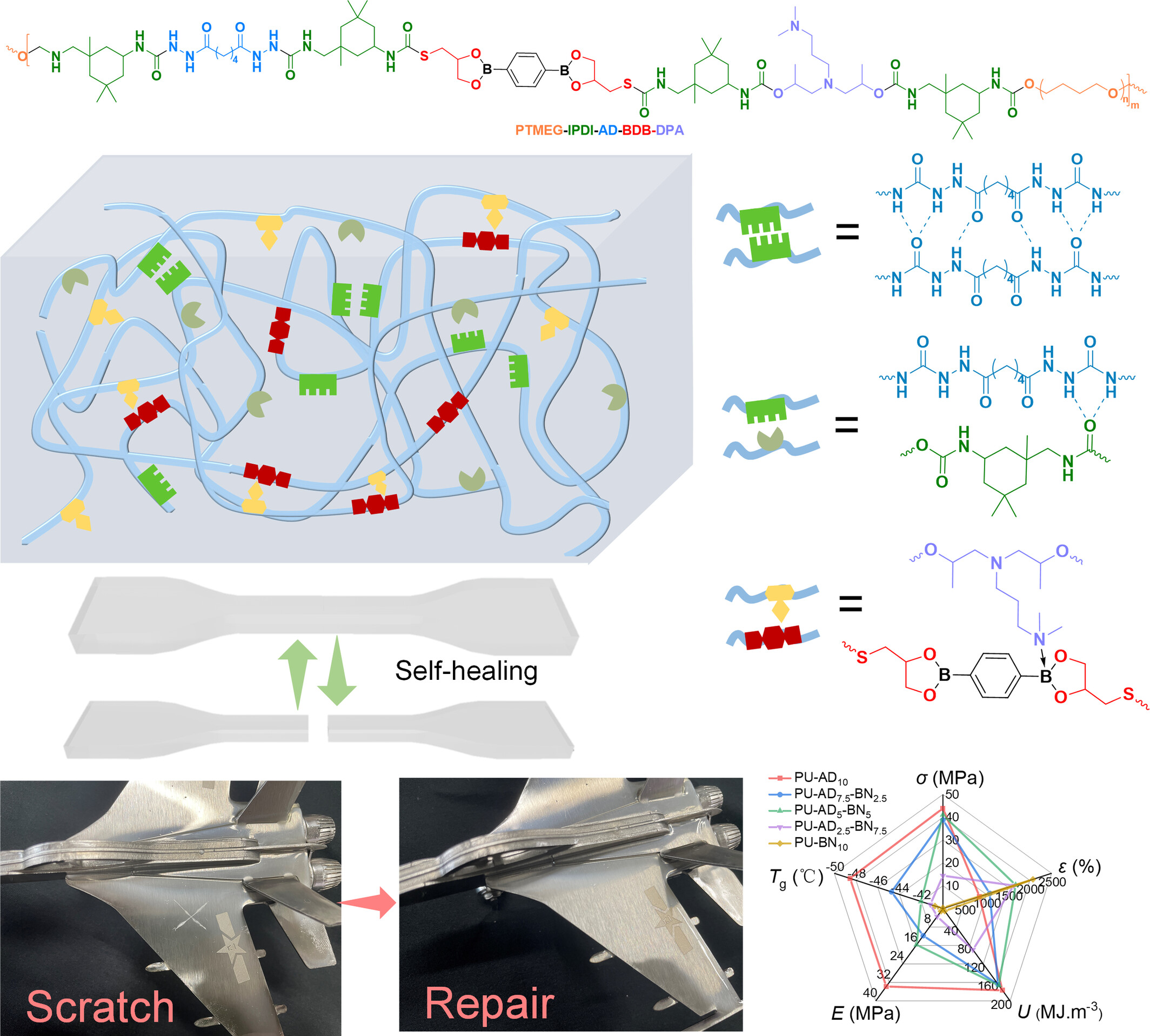
Enhanced Multifunction in Polyurethane Elastomers via Regulation of Triple-Crosslinked Network With Dynamic Covalent and Noncovalent Bonds
- First Published: 12 March 2025
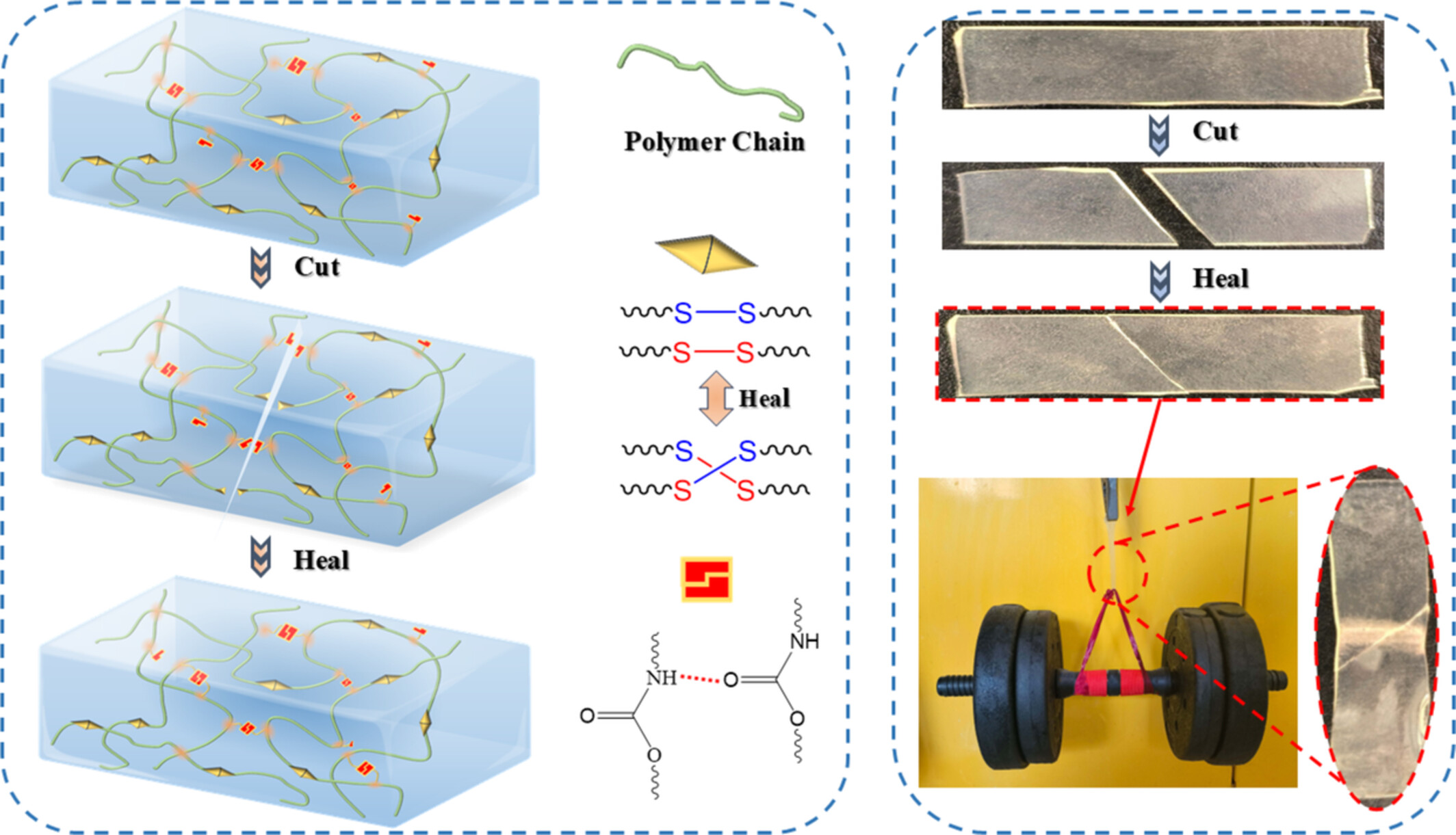
Self-Healing and Recyclable Waterborne Polyurethane With Ultra-High Toughness Based on Dynamic Covalent and Hydrogen Bonds
- First Published: 13 March 2025
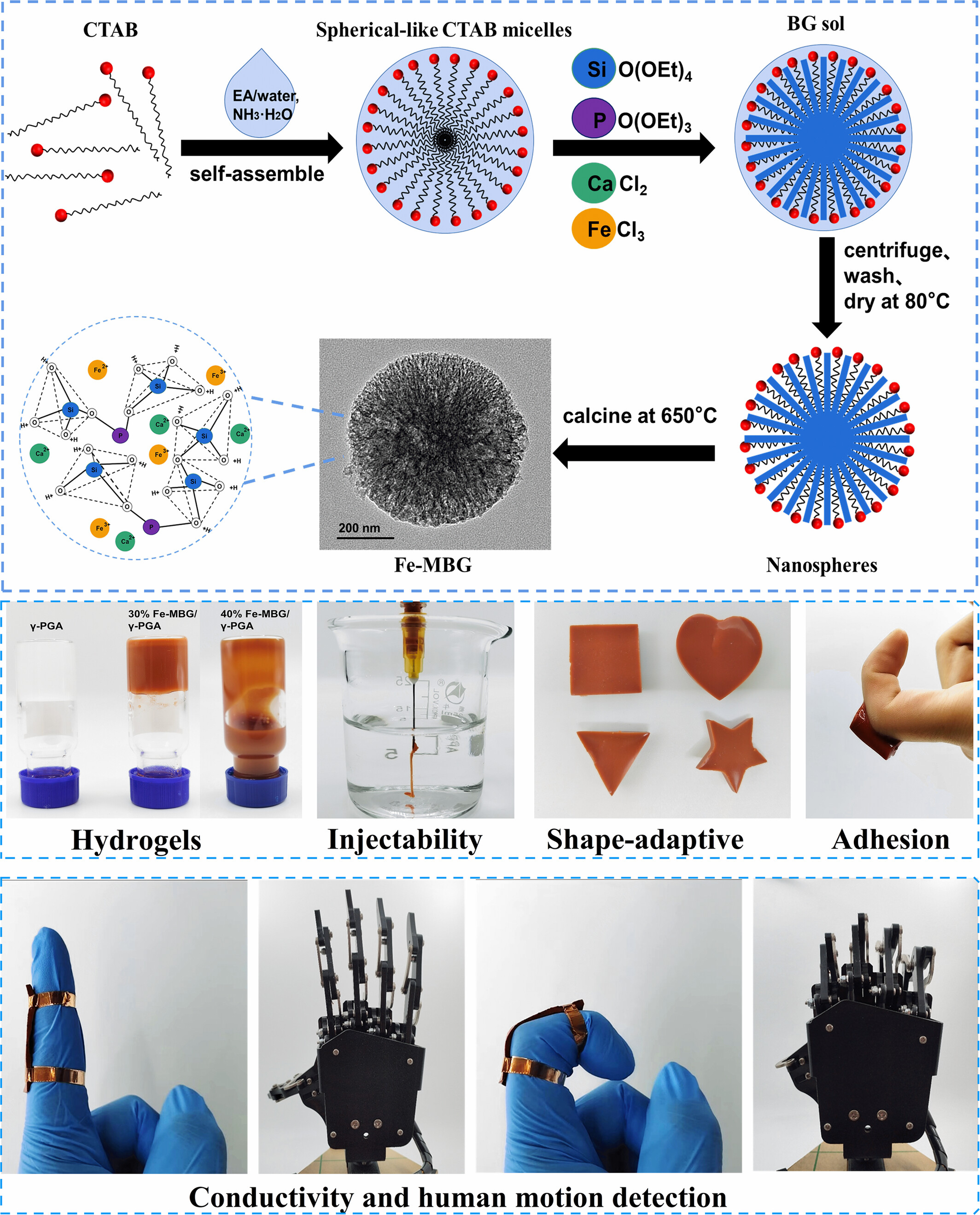
Adhesive, Injectable, and Conductive Poly (γ-Glutamic Acid) Hydrogels Reinforced by Iron-Doped Mesoporous Bioglass Nanospheres for Bone Tissue Engineering
- First Published: 13 March 2025
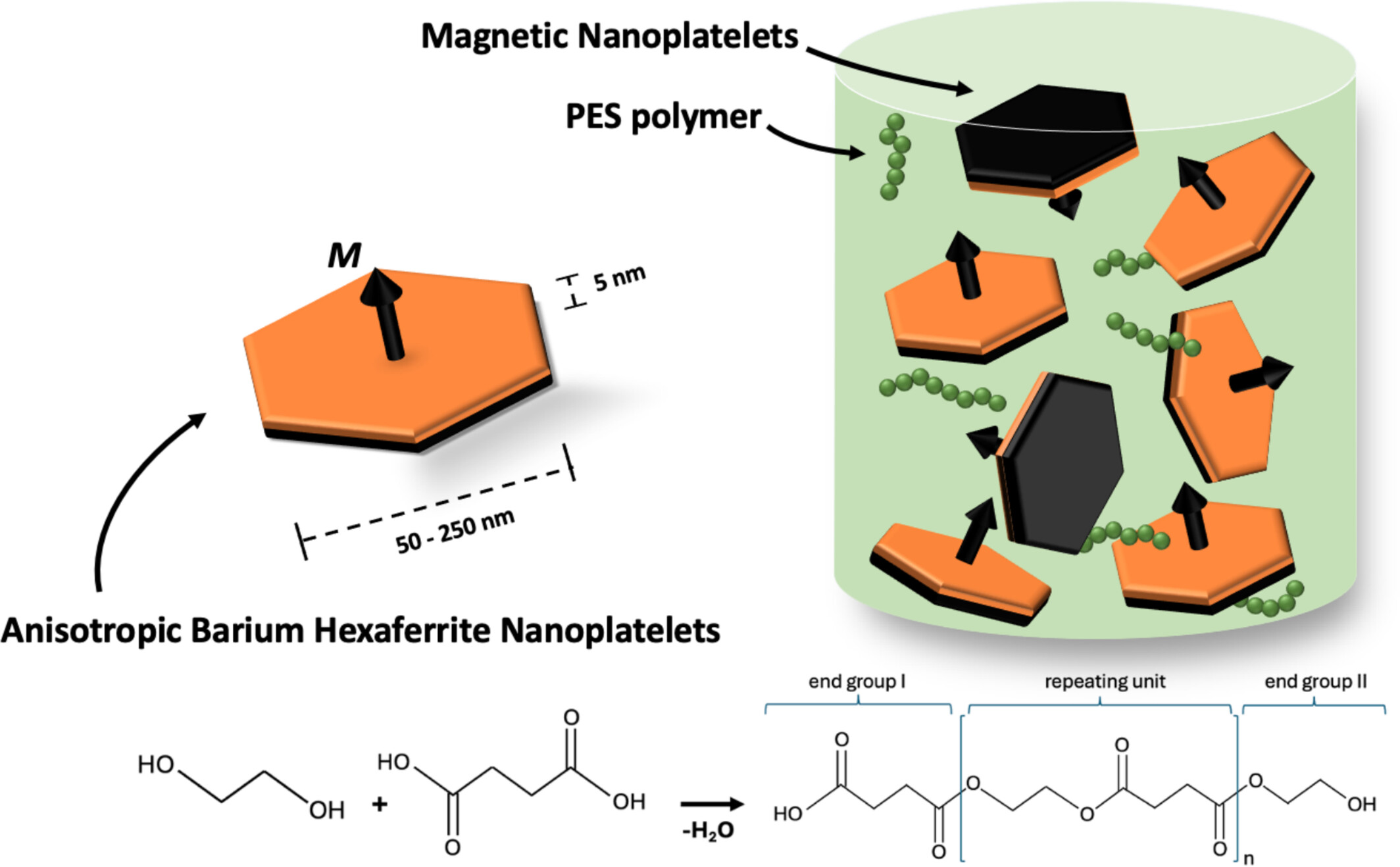
In Situ Polymerization of Barium Hexaferrite Ferrofluids for Poly(Ethylene) Succinate Magnetic Nanoparticle Composites
- First Published: 12 March 2025
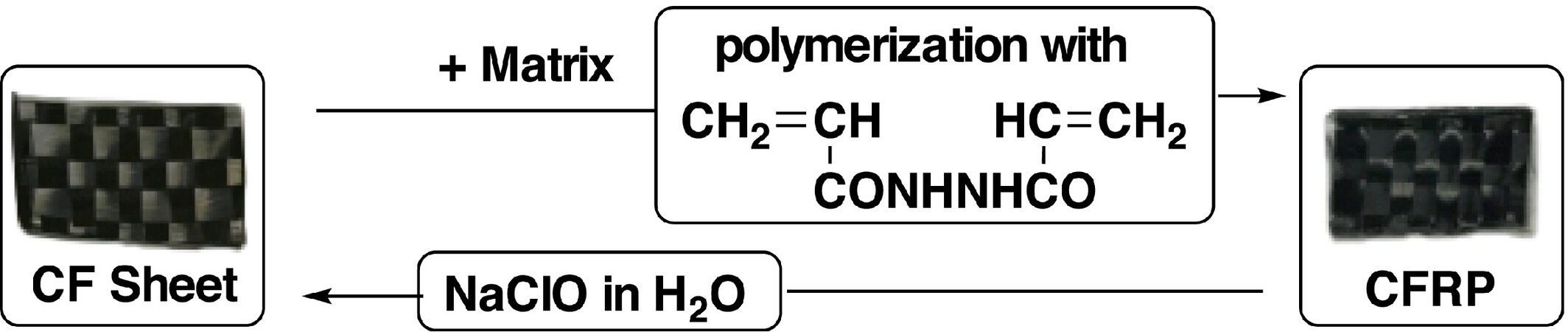
Preparation of Carbon Fiber–Reinforced Polymer Using Oxidatively Degradable Matrix Polymer: Recovery and Reuse of Carbon Fiber Sheet
- First Published: 13 March 2025
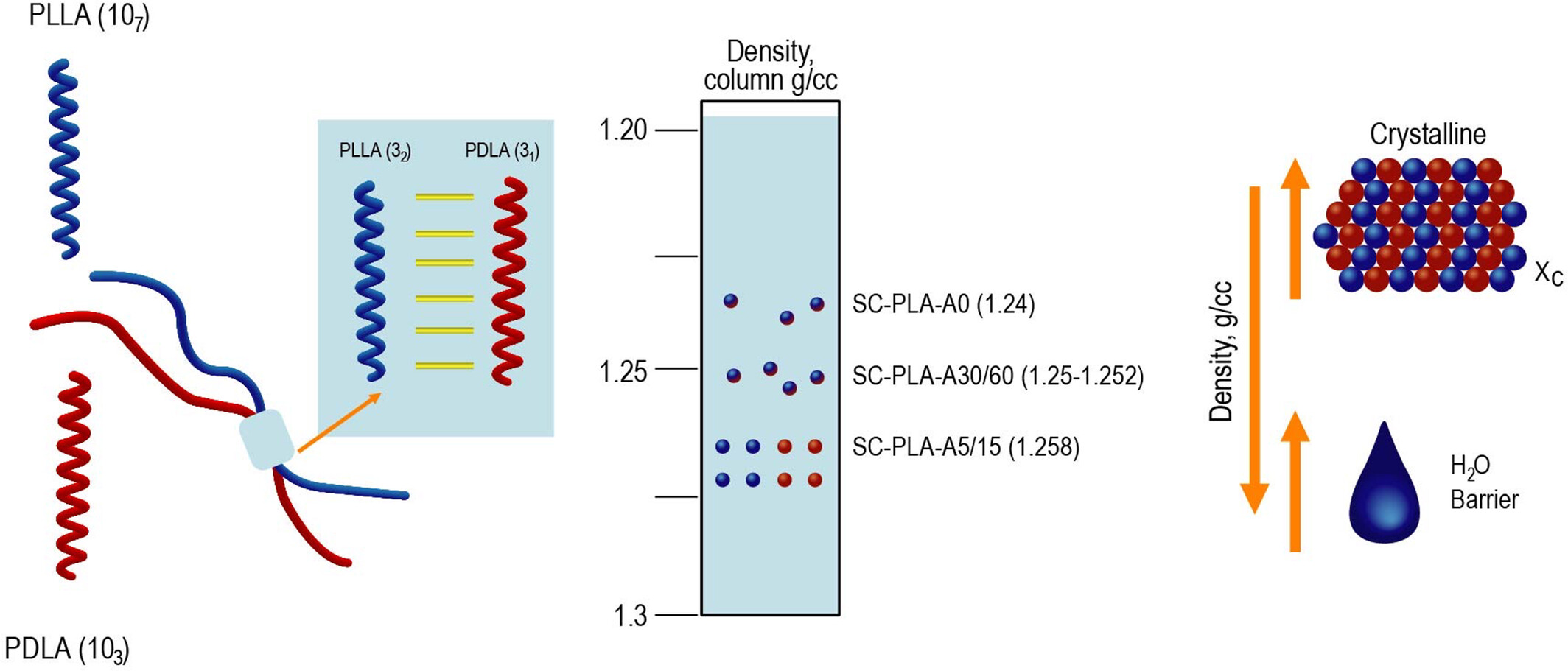
Density and Crystallinity Correlations: Enhancing Moisture Barrier Properties in Poly(l-Lactic Acid), Poly(d-Lactic Acid), and Stereocomplex-Poly(l,d-Lactic Acid) Films
- First Published: 13 March 2025
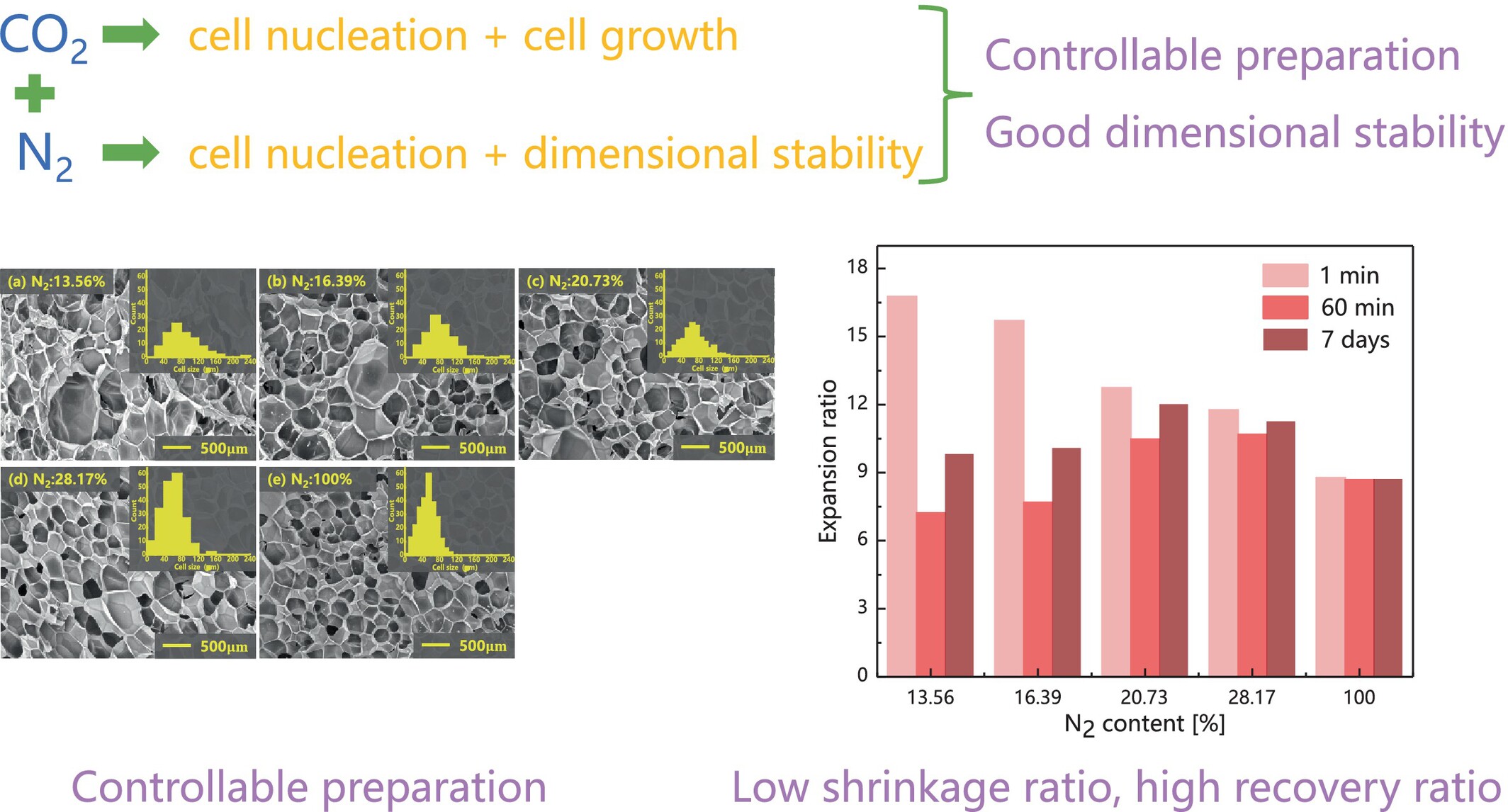
Low-Shrinkage Thermoplastic Polyamide Elastomer Foam Prepared by Microcellular Foaming With CO2 and N2 Co-Blowing Agent
- First Published: 21 March 2025
The Effect of Foaming Agents on the Structure and Properties of Epoxy Resin
- First Published: 18 March 2025
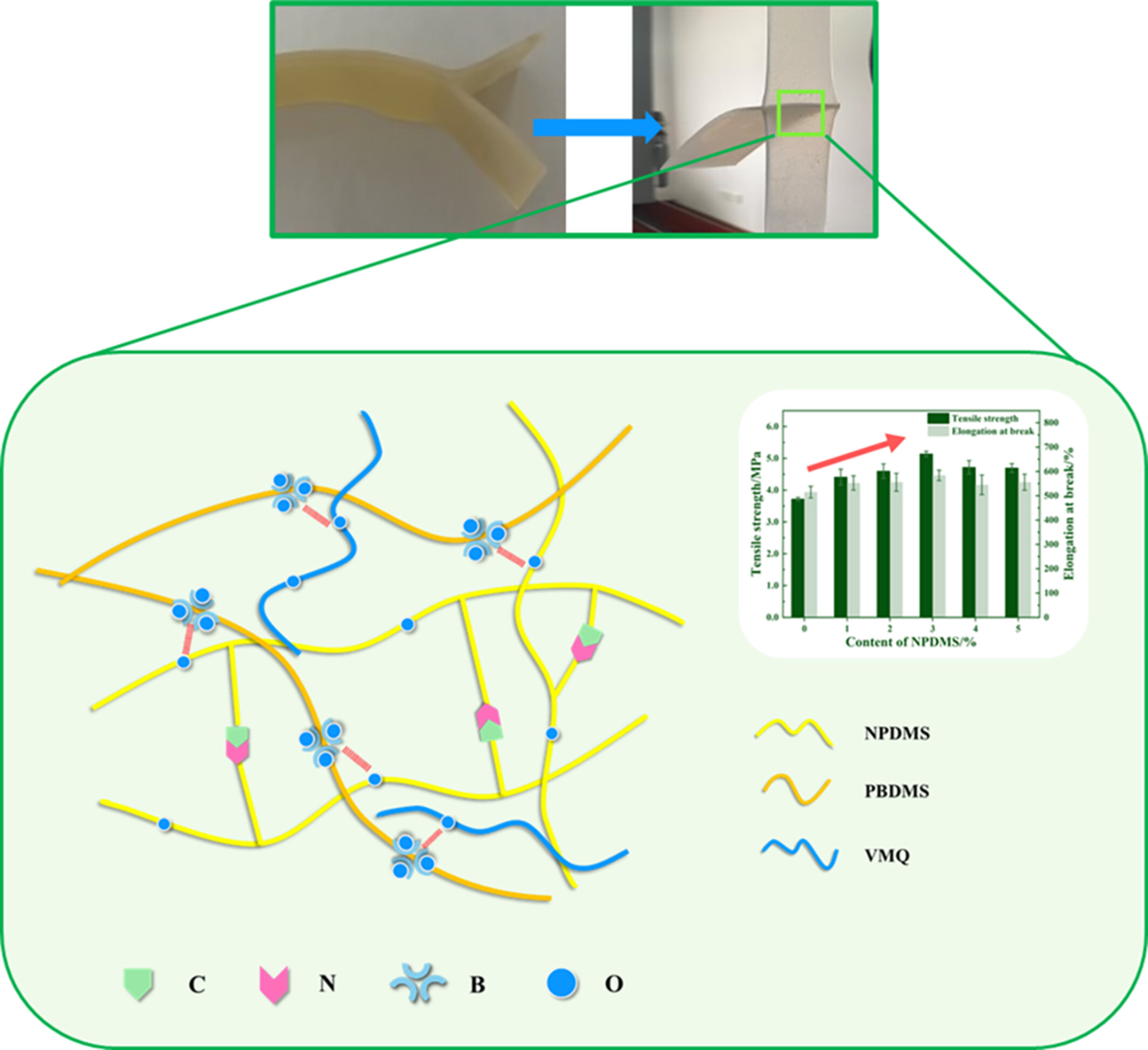
Performance Improvement of Silicone Rubber Self-Adhesive Tape With Dual-Network Structure of Reversible Covalent Bond
- First Published: 18 March 2025
Enhance the Durable Antistatic Properties of Aqueous Dispersion XNBR Films of Light Color With Grafting Hydrophilic Sodium Polyacrylate
- First Published: 24 March 2025
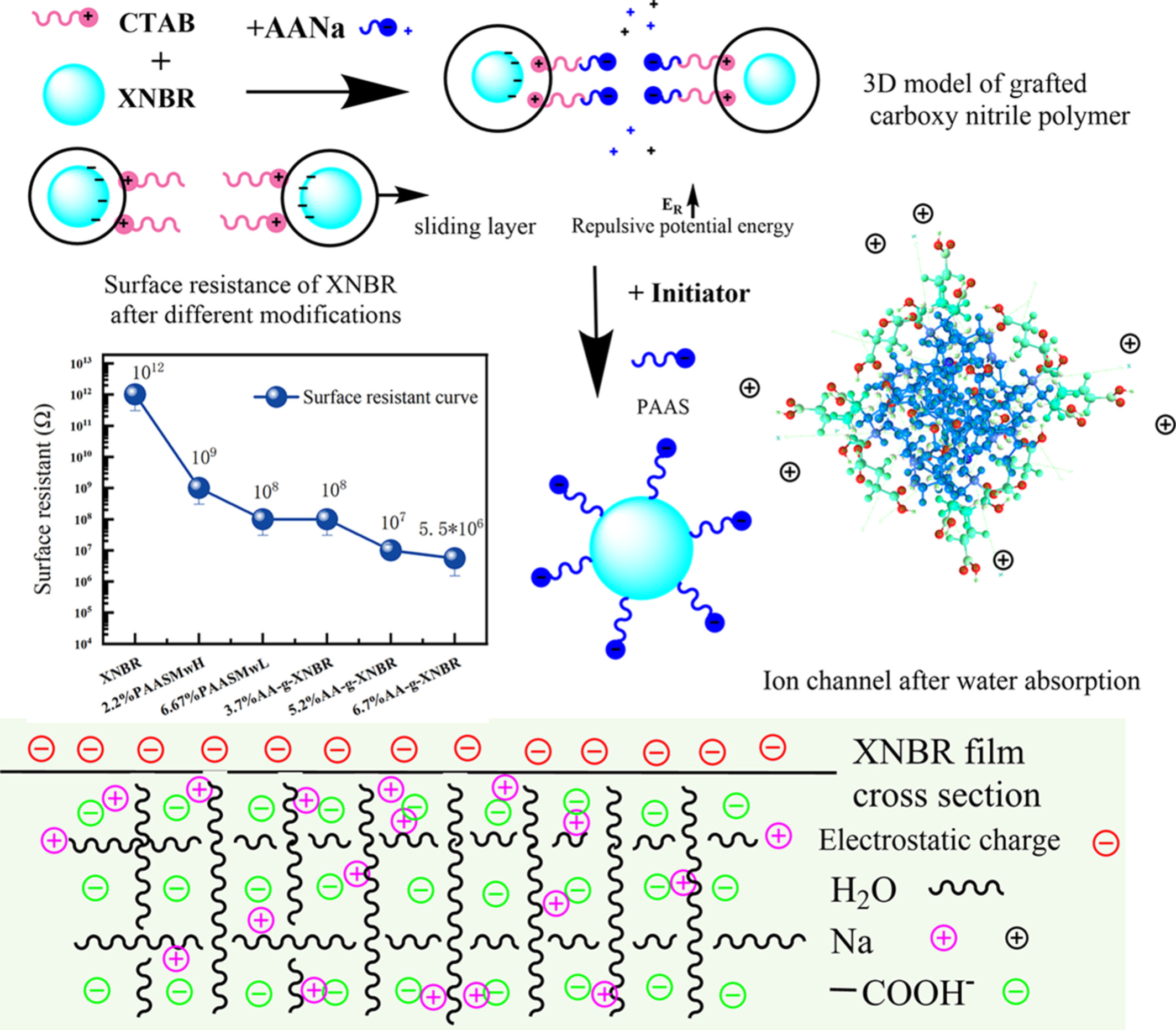
As a stabilizer, 0.00078 mol/L CTAB can stabilize XNBR latex with sodium acrylate. At the concentration of AANa in XNBR of 5.2 wt%, the surface resistance decreases to 107 Ω at 50% humidity. The surface resistance is 107–108 Ω after 10 washes. The tensile strength and elongation at break are 4.19 MPa and 482.95%, respectively.
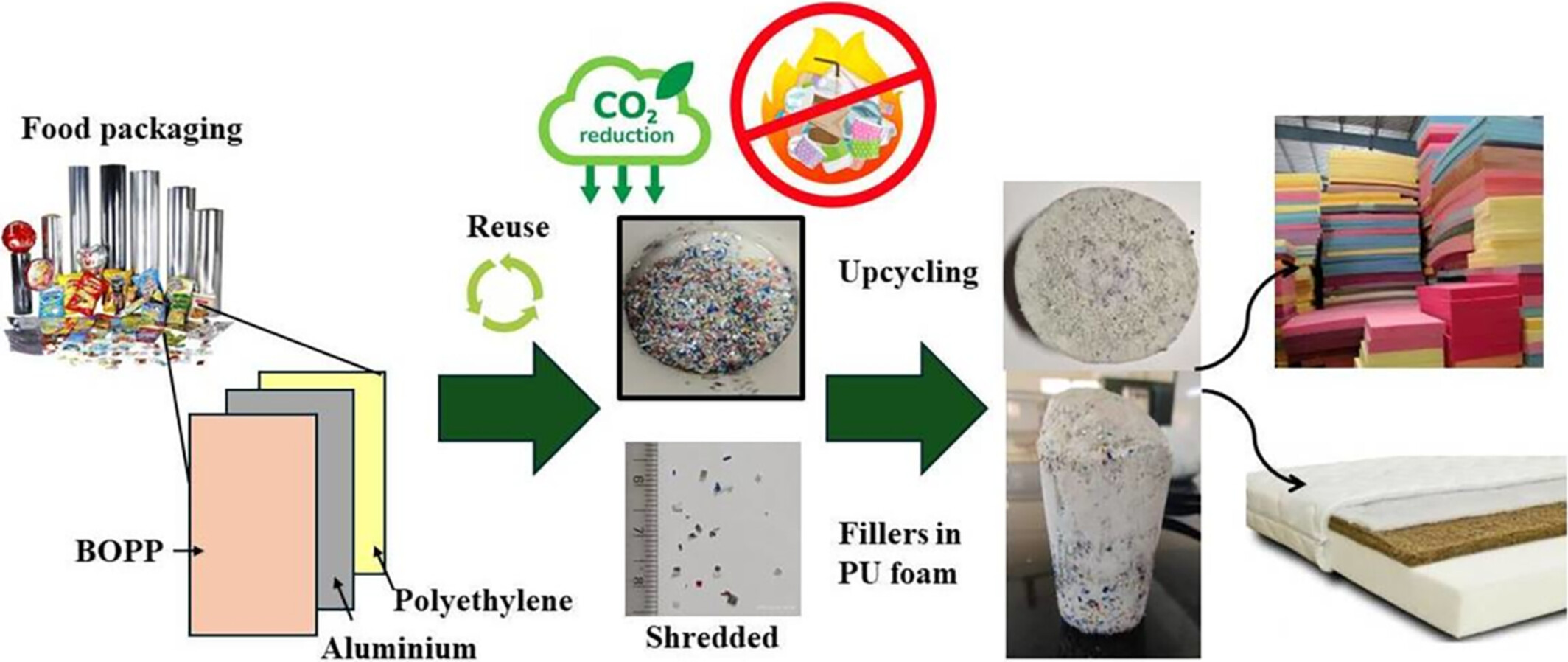
Recycling Waste Metallized Biaxially Oriented Plastic Films as Filler in Polyurethane Foams: Properties and Environmental Impact
- First Published: 10 March 2025
Kinetic Analysis of PVC Composites Modified With Different Types of Layered Double Hydroxides
- First Published: 17 March 2025
Efficient Removal of Methylene Blue by Sodium Alginate-Carboxymethyl Cellulose-Kaolin Composite Microbeads
- First Published: 13 March 2025
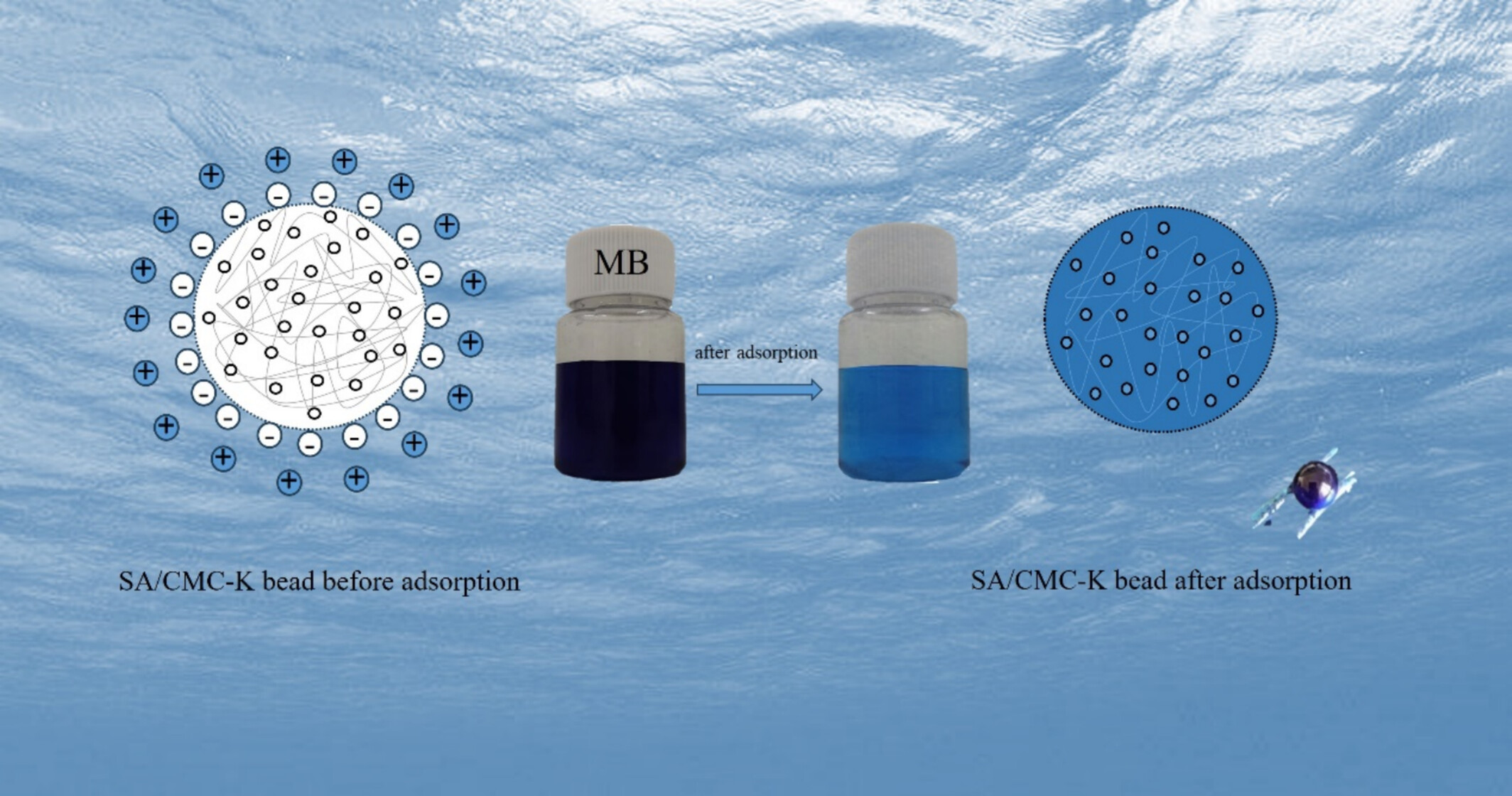
A novel biosorbent for the removal of the toxic dye methylene blue from wastewater. Prepared by a simple and mild physical gelation process. Remained stable and efficient after cycles, exhibited excellent adsorption capacity. Excellent adsorption capacity and reusable, as sustainable dye removal adsorbents.
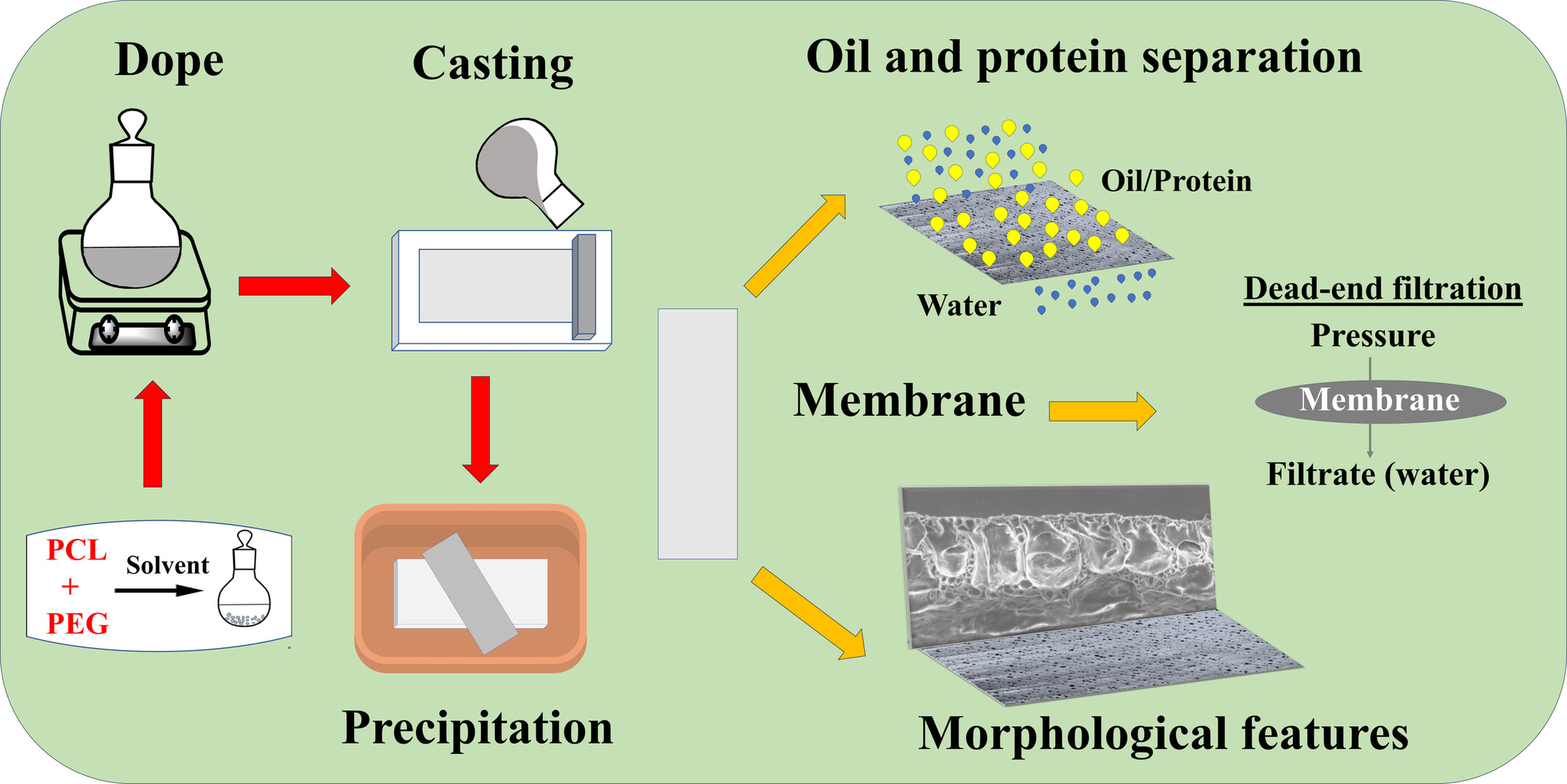
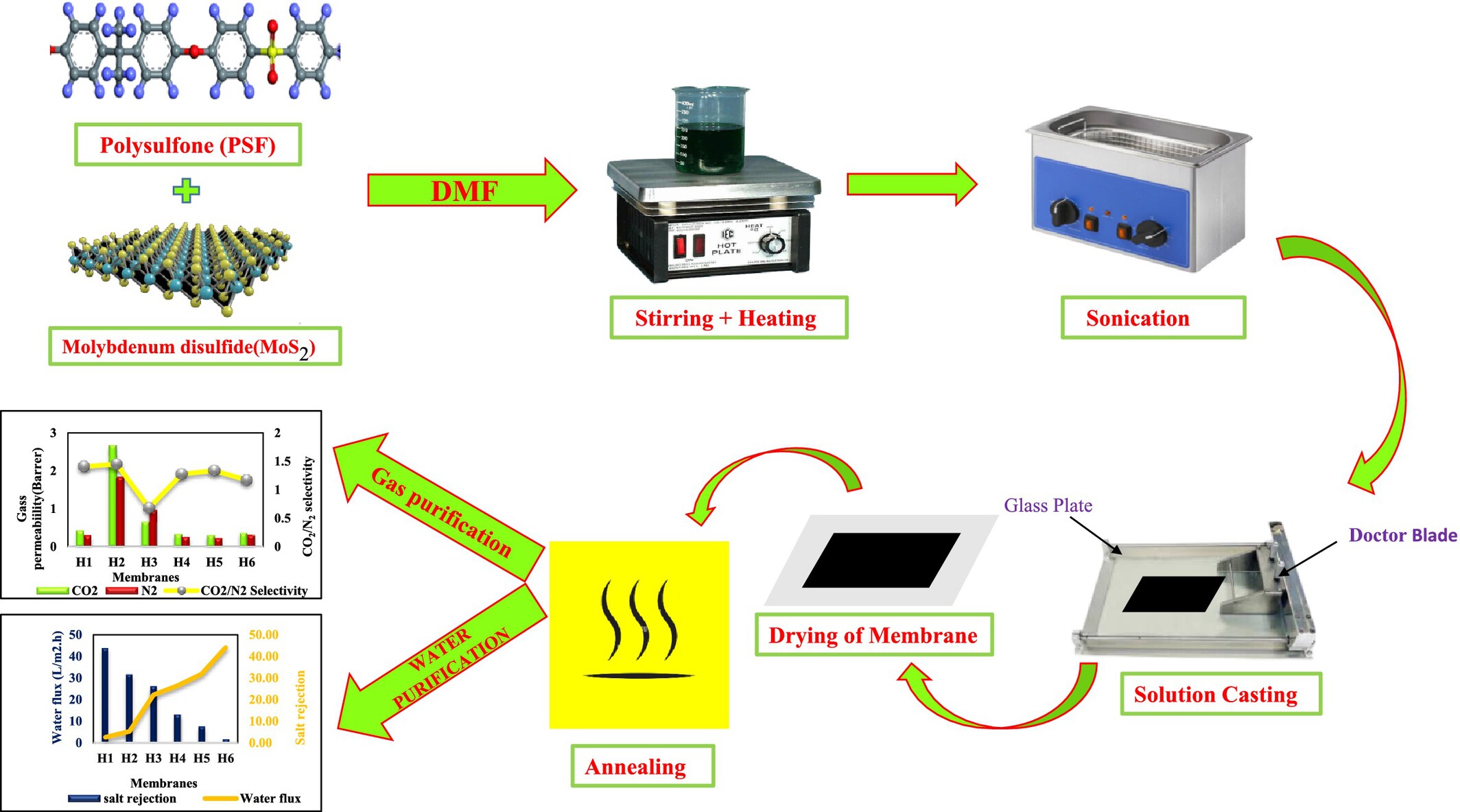
Effect of Additive Molecular Weight and Dope Composition on the Morphology and Performance of Poly(ε-Caprolactone)/Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Asymmetric Membranes
- First Published: 17 March 2025
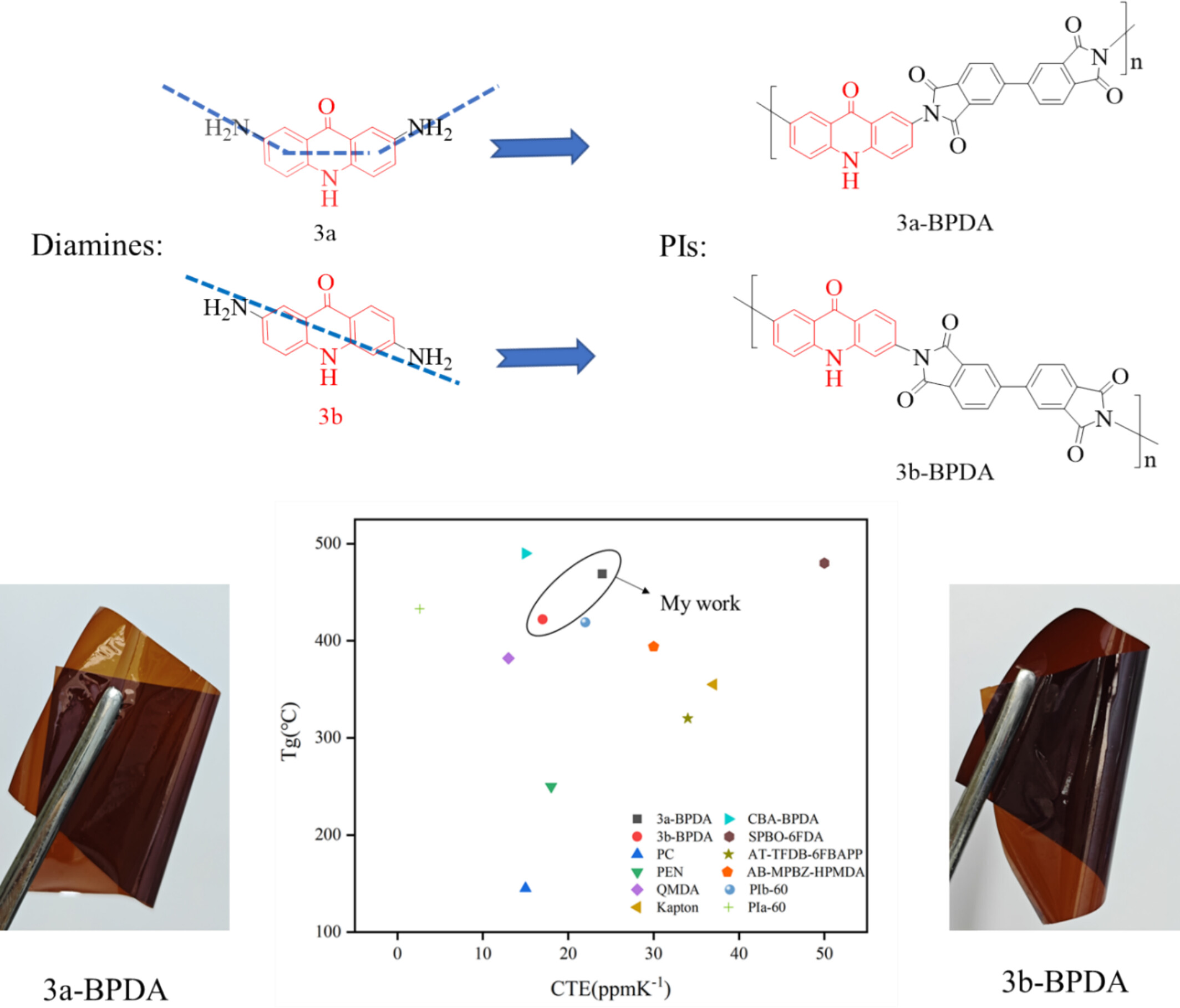
Synthesis of High Tg and Low CTE Polyimides From Acridinone Diamines With Various Linearity
- First Published: 13 March 2025
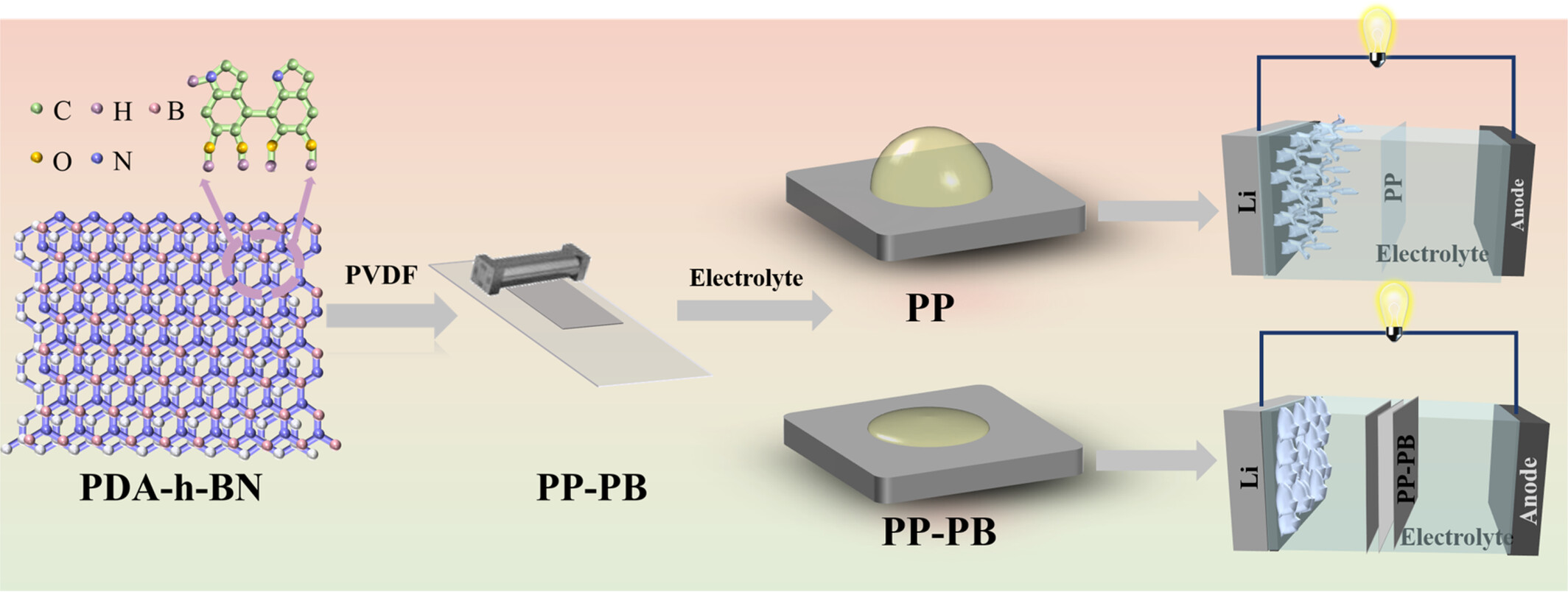
Polydopamine Doped Hexagonal Boron Nitride Coating Separator With Excellent Heat Resistance and Wettability for High-Performance Lithium Metal Batteries
- First Published: 20 March 2025
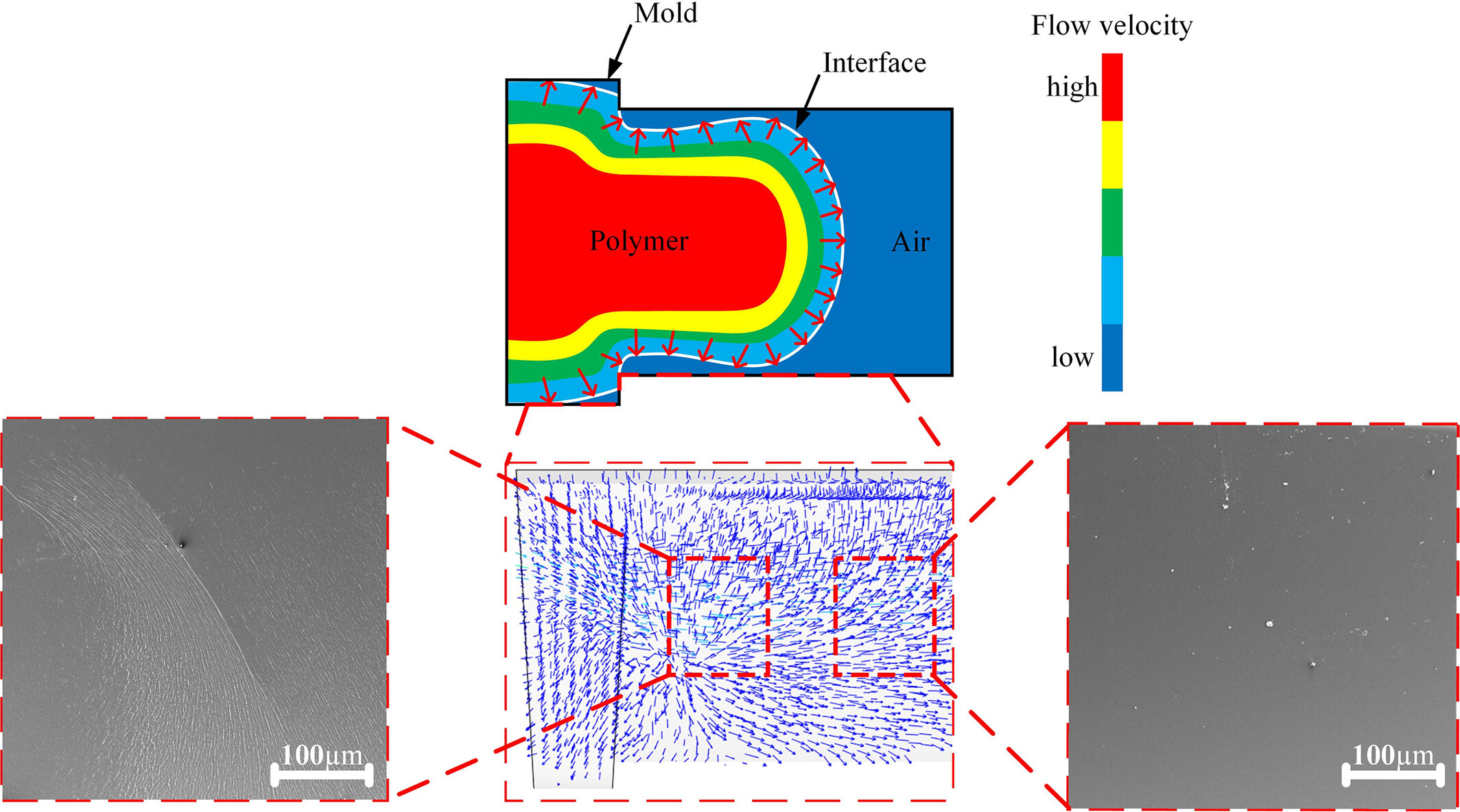
Simulation and Experimental Study of the Flow Mechanism of Injection-Molded Materials for Optical Non-Spherical Cylindrical Lens
- First Published: 19 March 2025
Modulating Membrane Performance by Optimizing Coagulation Temperature and Dipping Time
- First Published: 18 March 2025
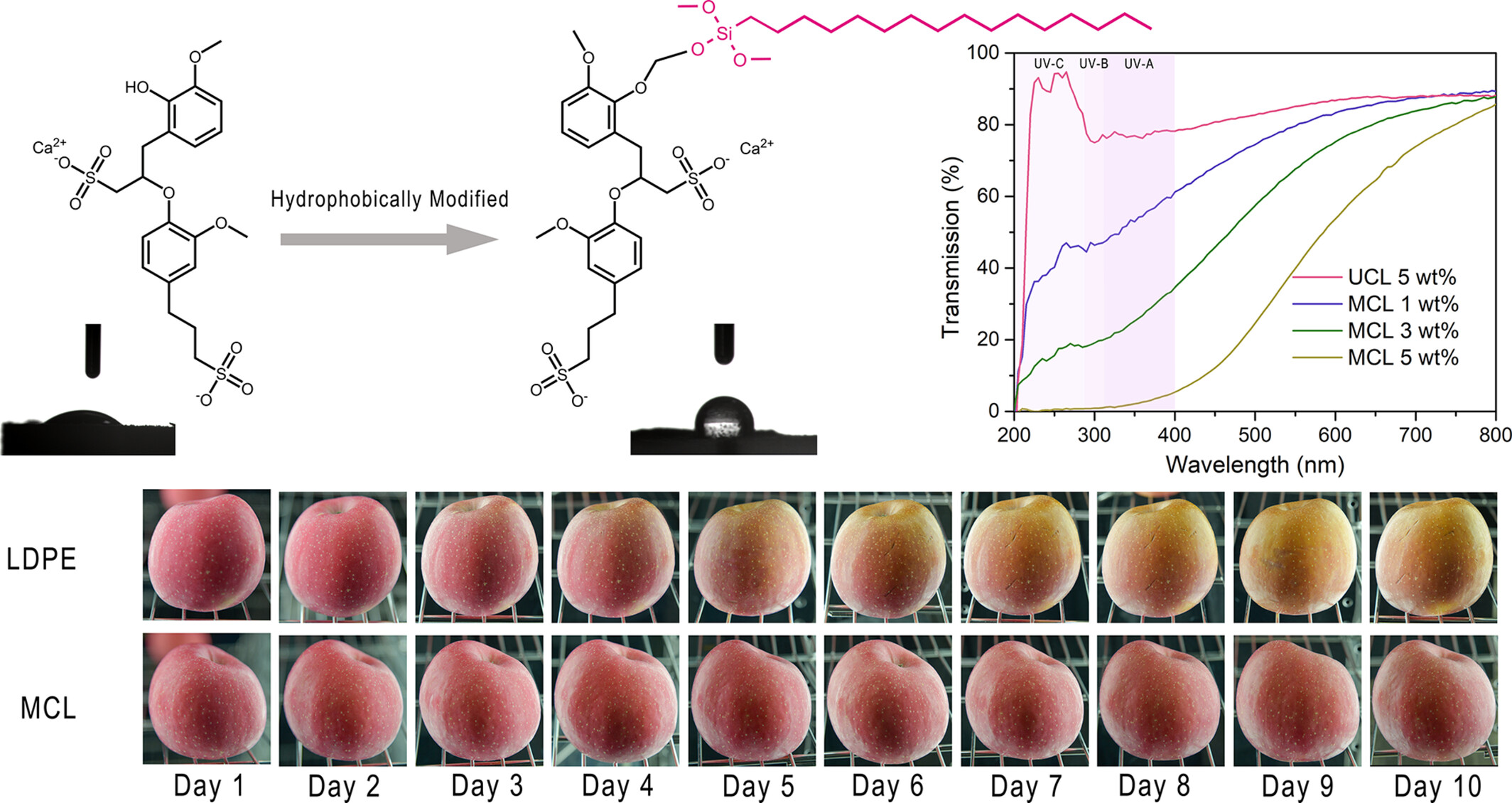
Polyethylene/Hydrophobic Calcium Lignosulfonate Composite Film for Anti-Photooxidation of Fuji Apples
- First Published: 20 March 2025
Lavender Essential Oil-Loaded Composite Fiber Membrane Prepared by Coaxial Electrospinning for High-Performance, Antibacterial, and Lasting-Fragrance Air Filtration
- First Published: 26 March 2025
A Novel Poly(Diol Citrate) Containing N-Hydroxysuccinimide Ester: Synthesis and Its Enabled Hydrogel Adhesive
- First Published: 18 March 2025
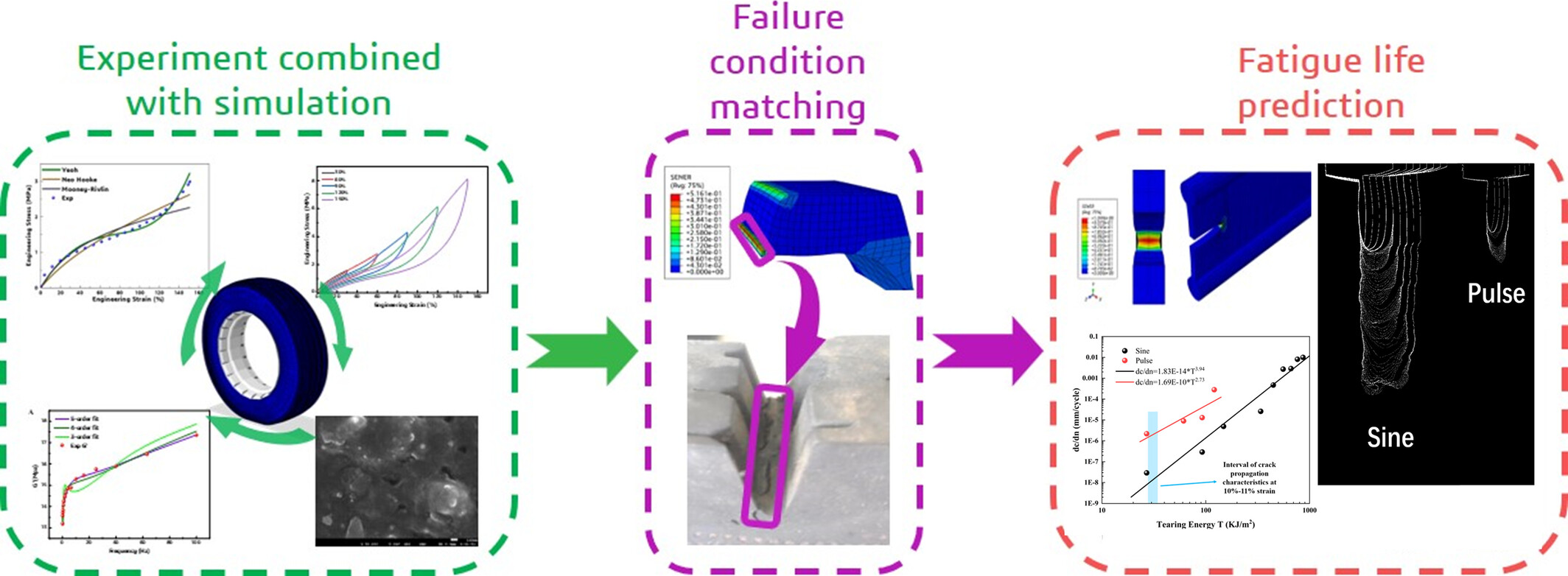
Fatigue Life Prediction of a Groove Bottom of Green All Steel Radial Rubber Tires
- First Published: 21 March 2025
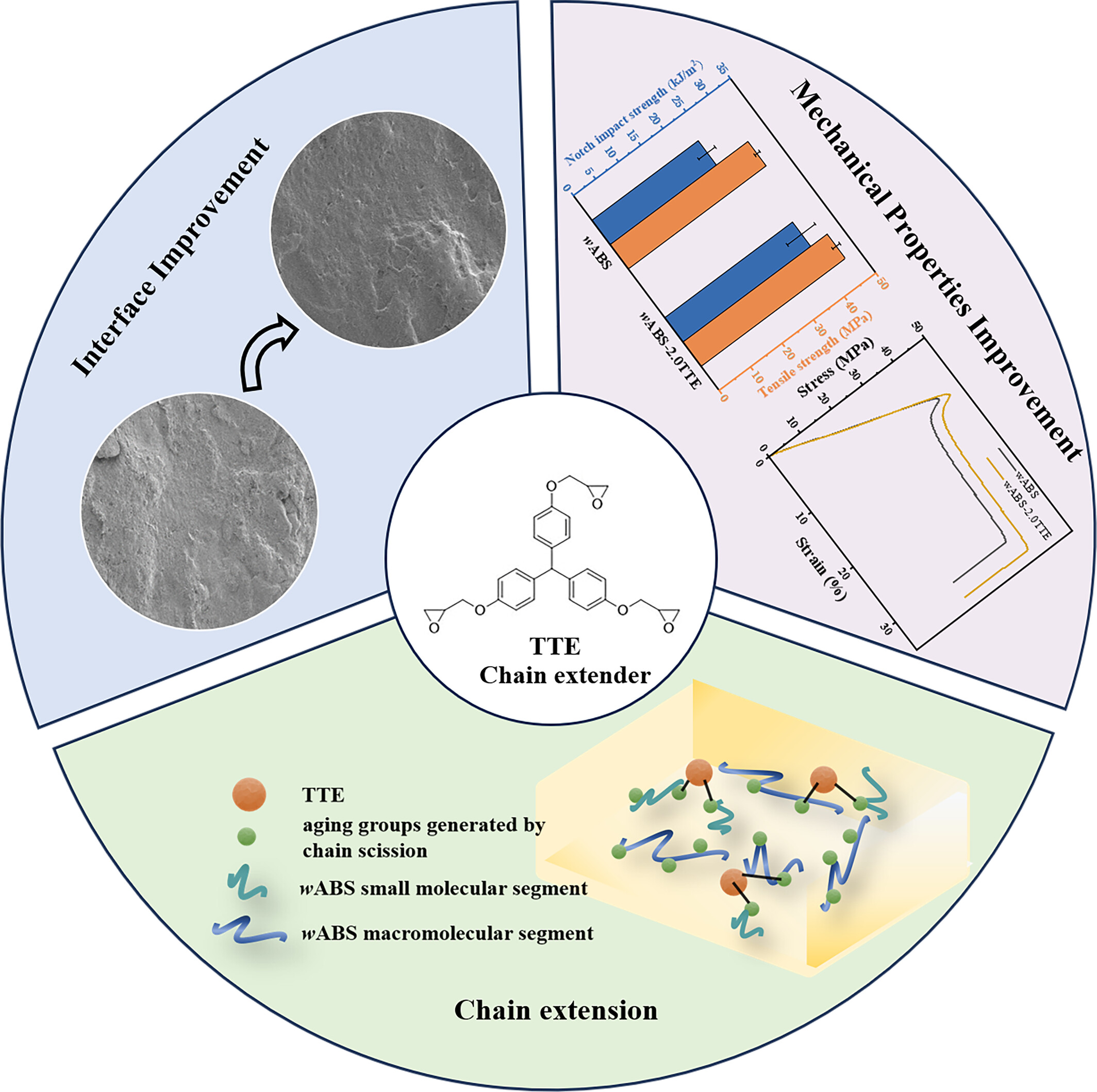
Toughening and Chain-Extending Effect of Tris(4-Hydroxyphenyl)methane Triglycidyl Ether for Waste Acrylonitrile-Butadiene-Styrene
- First Published: 23 March 2025
High-Flux Thin Film Composite Membranes Prepared by Interfacial Polymerization With Pyridine or Pyrimidine Structured Diamines as Aqueous Phase Monomers for Efficient Organic Solvent Nanofiltration
- First Published: 18 March 2025
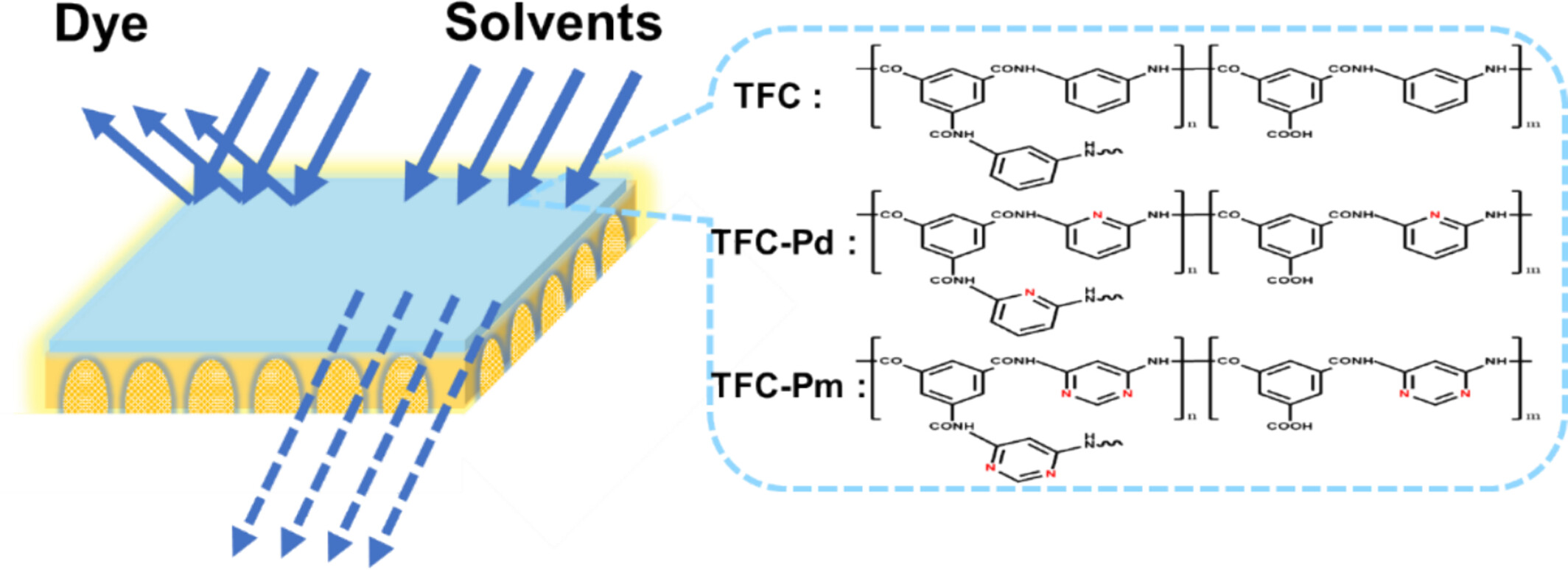
High-flux thin film composite organic solvent nanofiltration membranes were prepared by interfacial polymerization with pyridine or pyrimidine structured diamine monomers instead of traditional MPD monomers. The results showed that the TFC-Pd and TFC-Pm membranes have higher permeability than conventional TFC membranes, and their EB rejection was more than 90%. Moreover, they also have good organic solvent resistance and long-term stability.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Colorimetric Dye-Loaded, Adhesive, and Stretchable Hydrogel Sensor: A Sensitive and Visible H2S Gas Sensing Platform”
- First Published: 12 April 2025