Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
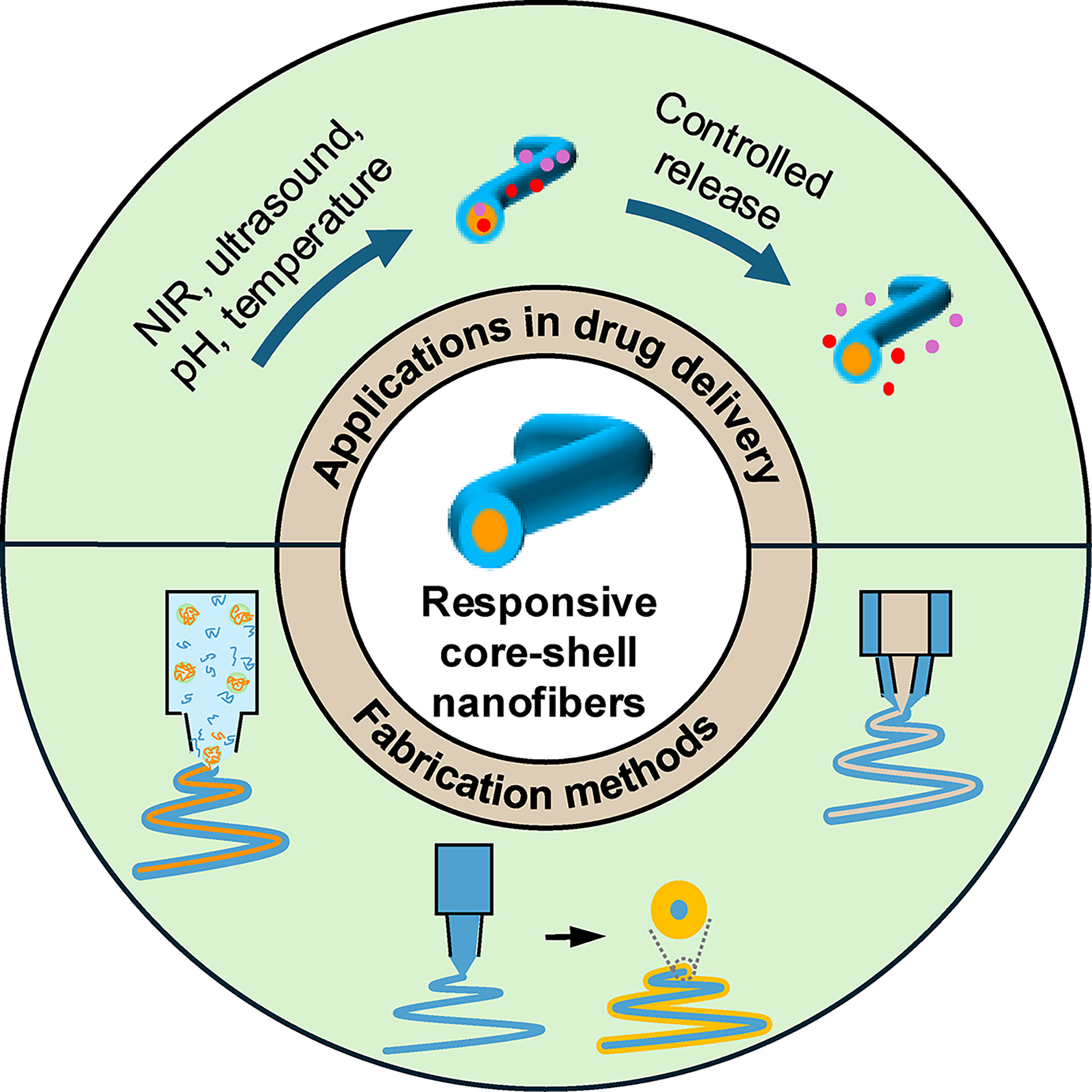
Stimuli-Responsive Core-Shell Electrospun Nanofibers for Drug Delivery: A Mini-Review
- First Published: 31 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
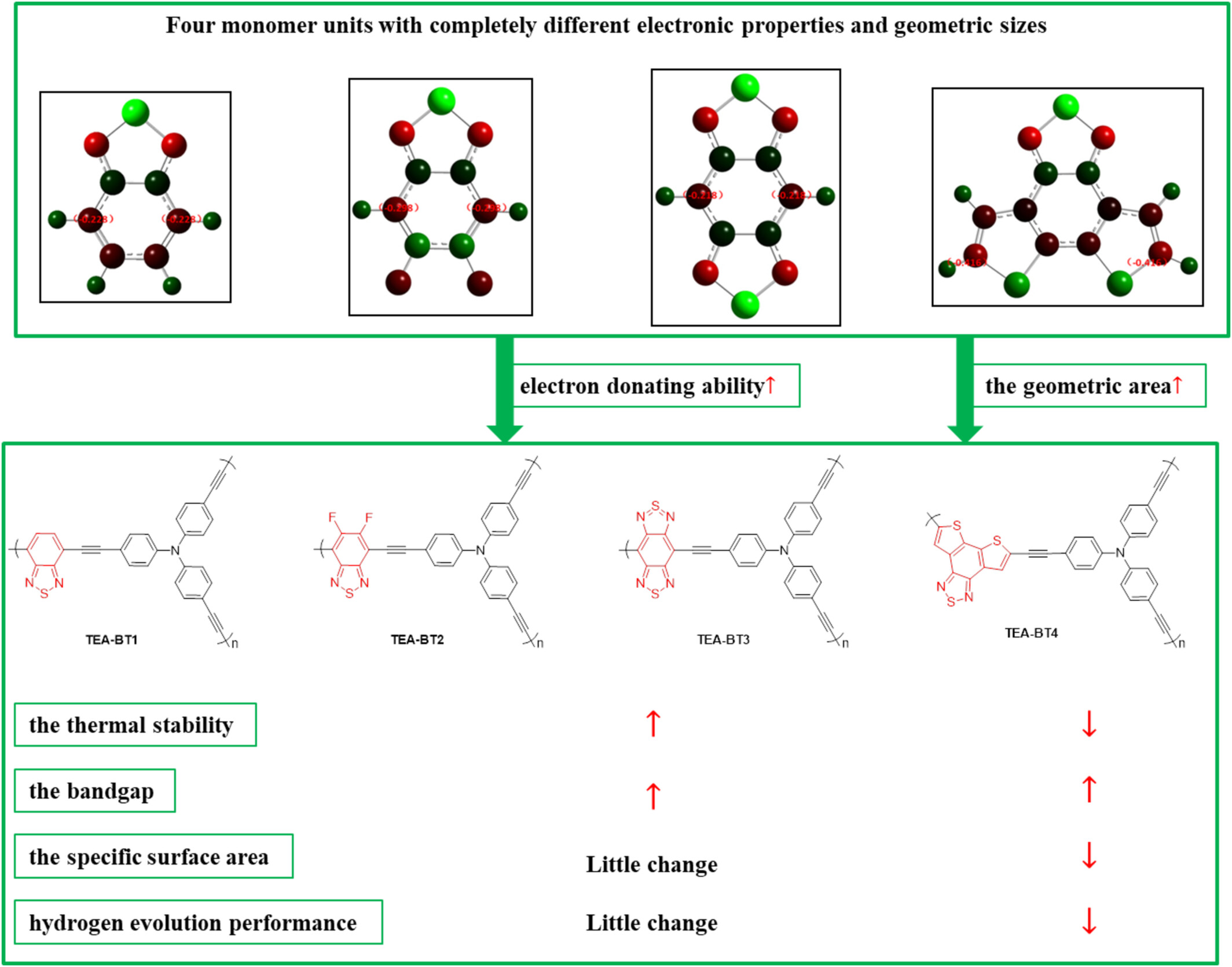
Benzothiadiazole Based Bifunctional Monomers: Design, Electronic and Geometric Effects on Their Tri(4-Ethynylphenyl)amine Based Conjugated Microporous Polymers for Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 27 January 2025
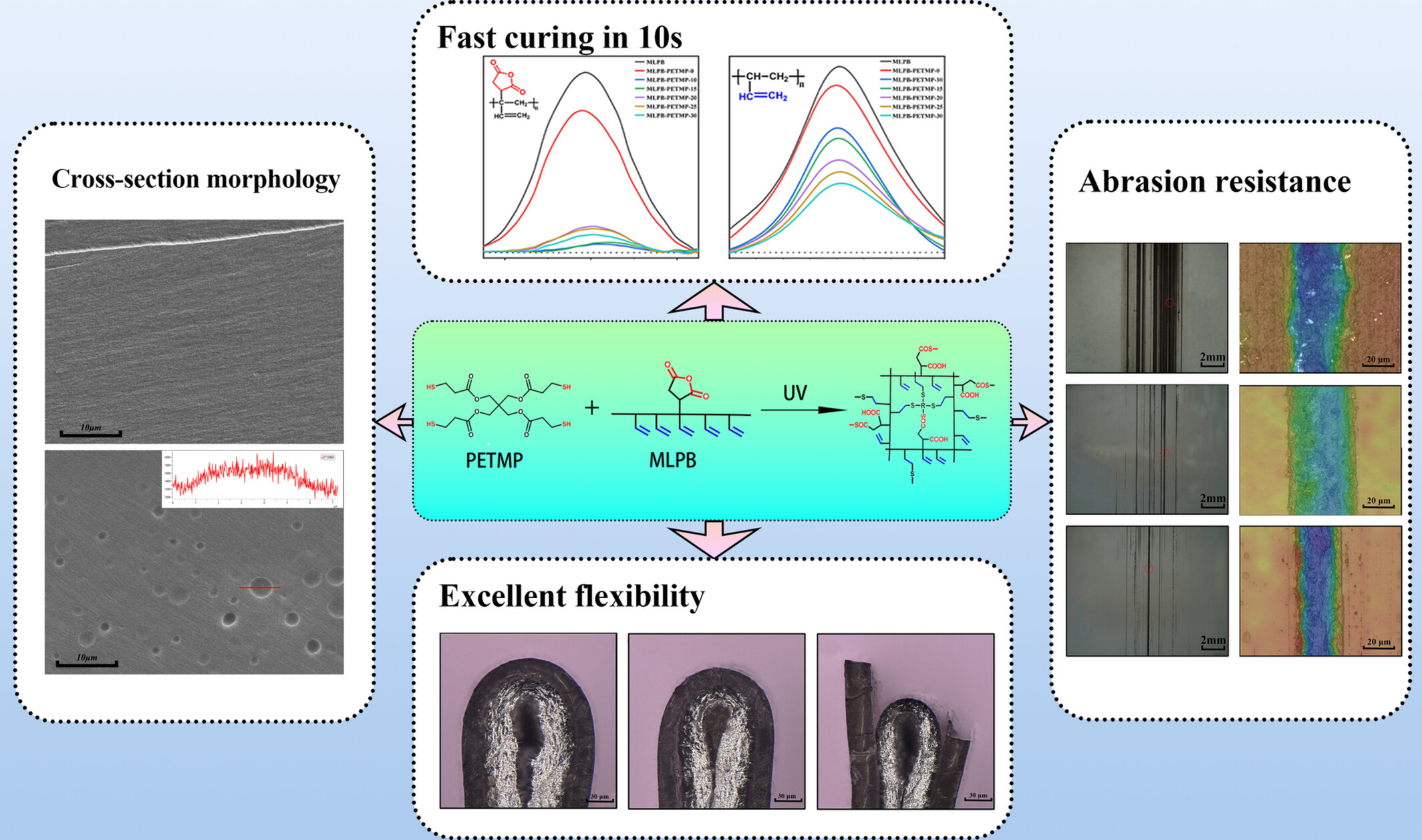
Click Preparing UV-Curable Polybutadiene Films With Good Thermal and Mechanical Performances by Using Multifunctional Mercaptan as a Cross-Linking Agent
- First Published: 26 January 2025
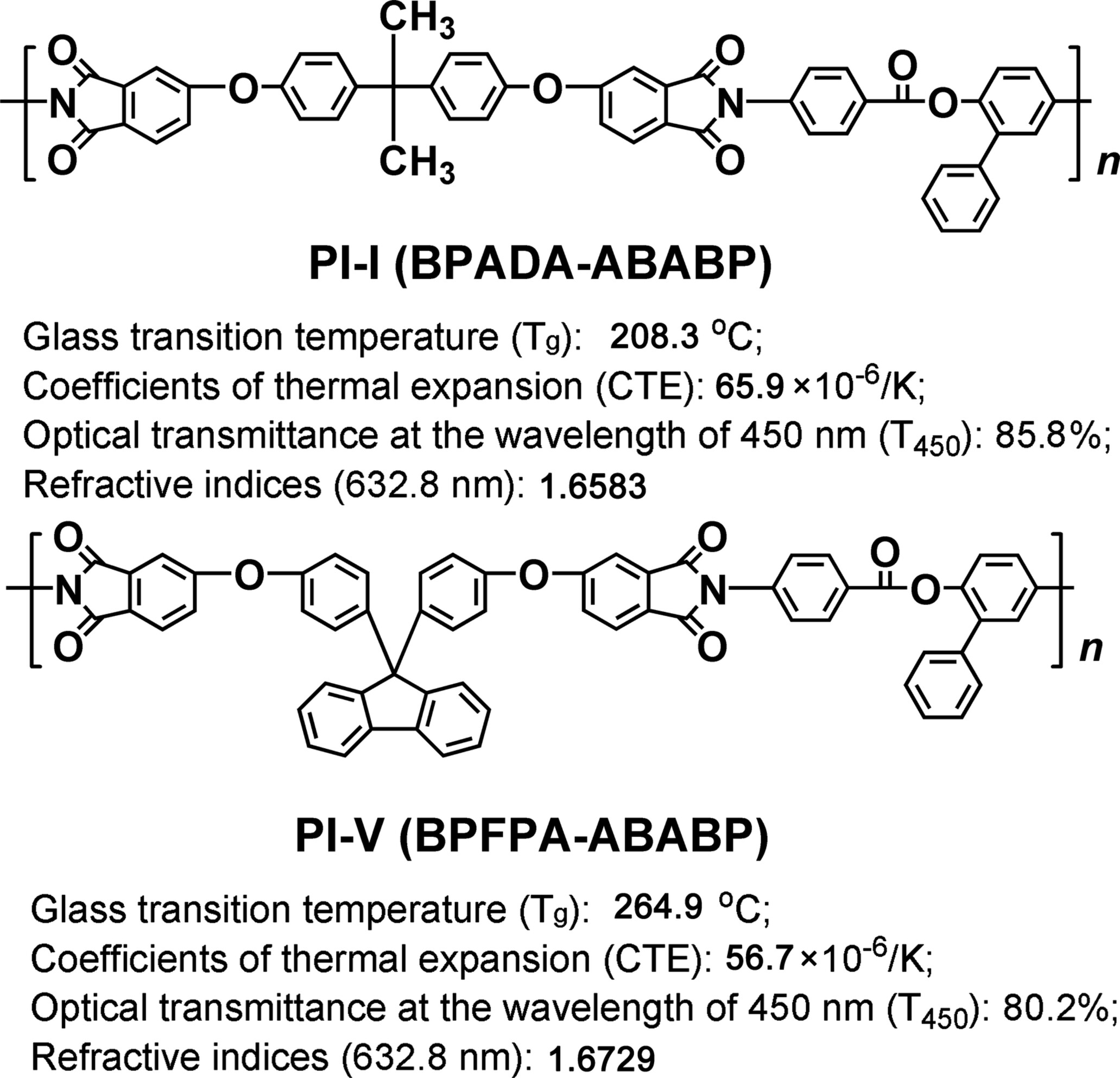
Preparation and Properties of Fluorine-Free and Organo-Soluble Polyesterimides and the Films With Good Optical Transparency and Thermal Stability
- First Published: 26 January 2025
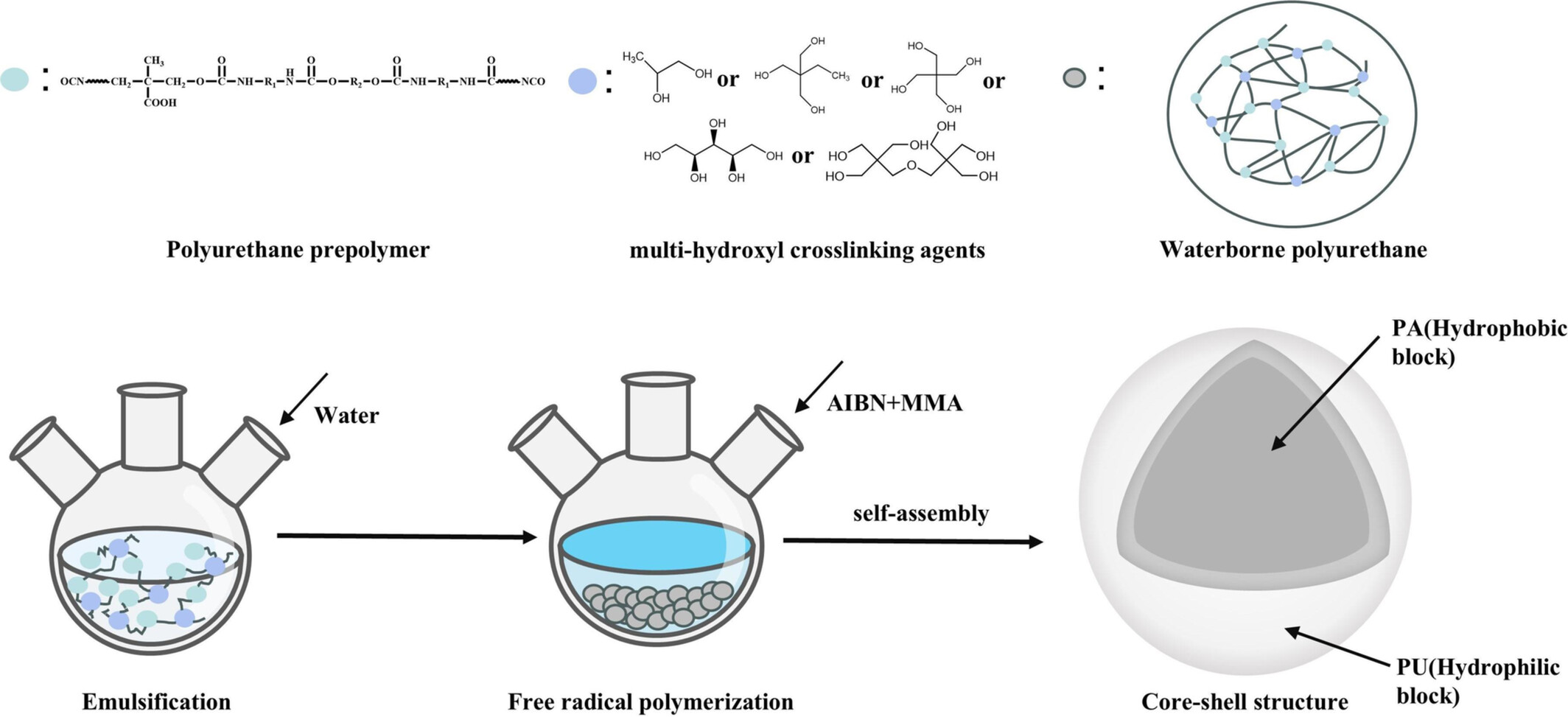
Preparation and Characterization of Waterborne Multihydroxy Crosslinked Polyurethane Hybrid Core–Shell Emulsion
- First Published: 24 January 2025
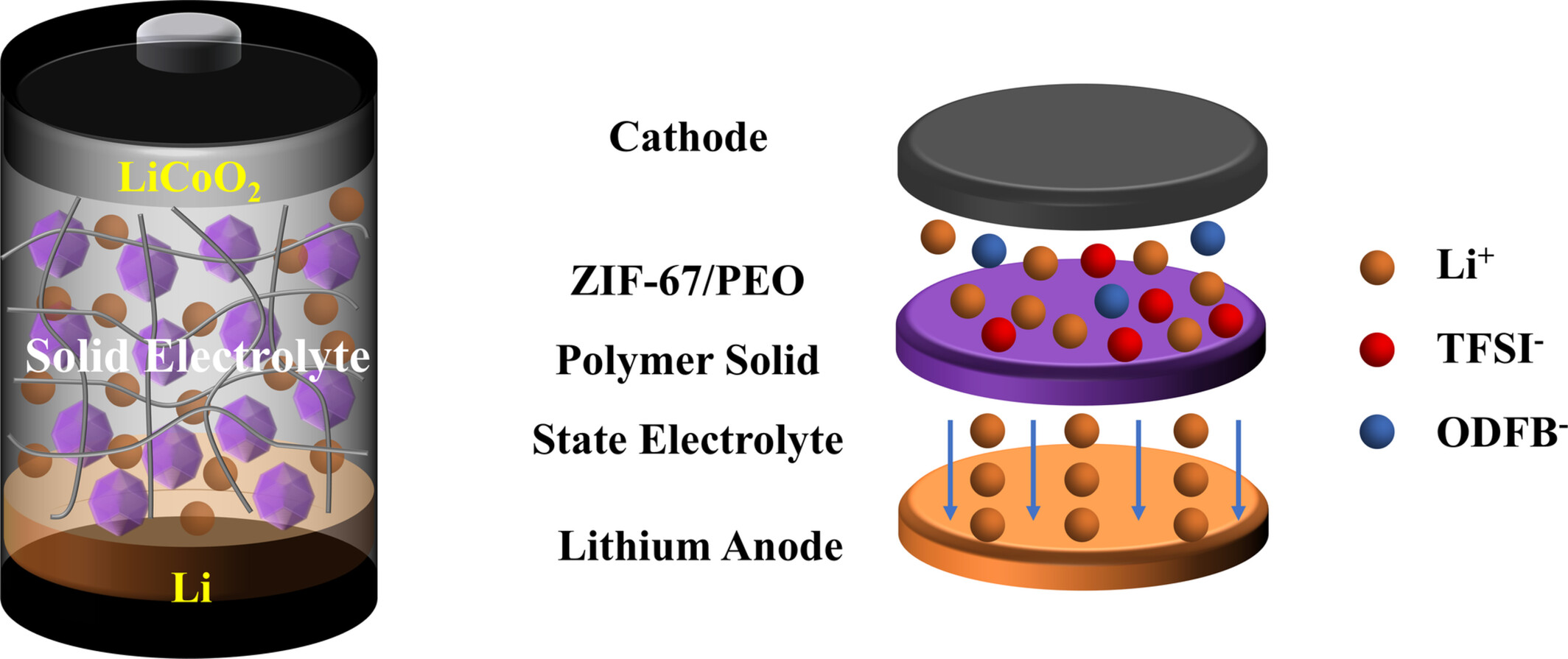
Enhancement of Solid-State Lithium-Ion Batteries Using Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 in Polyethylene Oxide-Based Composite Polymer Electrolytes for Improved Ionic Conductivity and Stability
- First Published: 27 January 2025
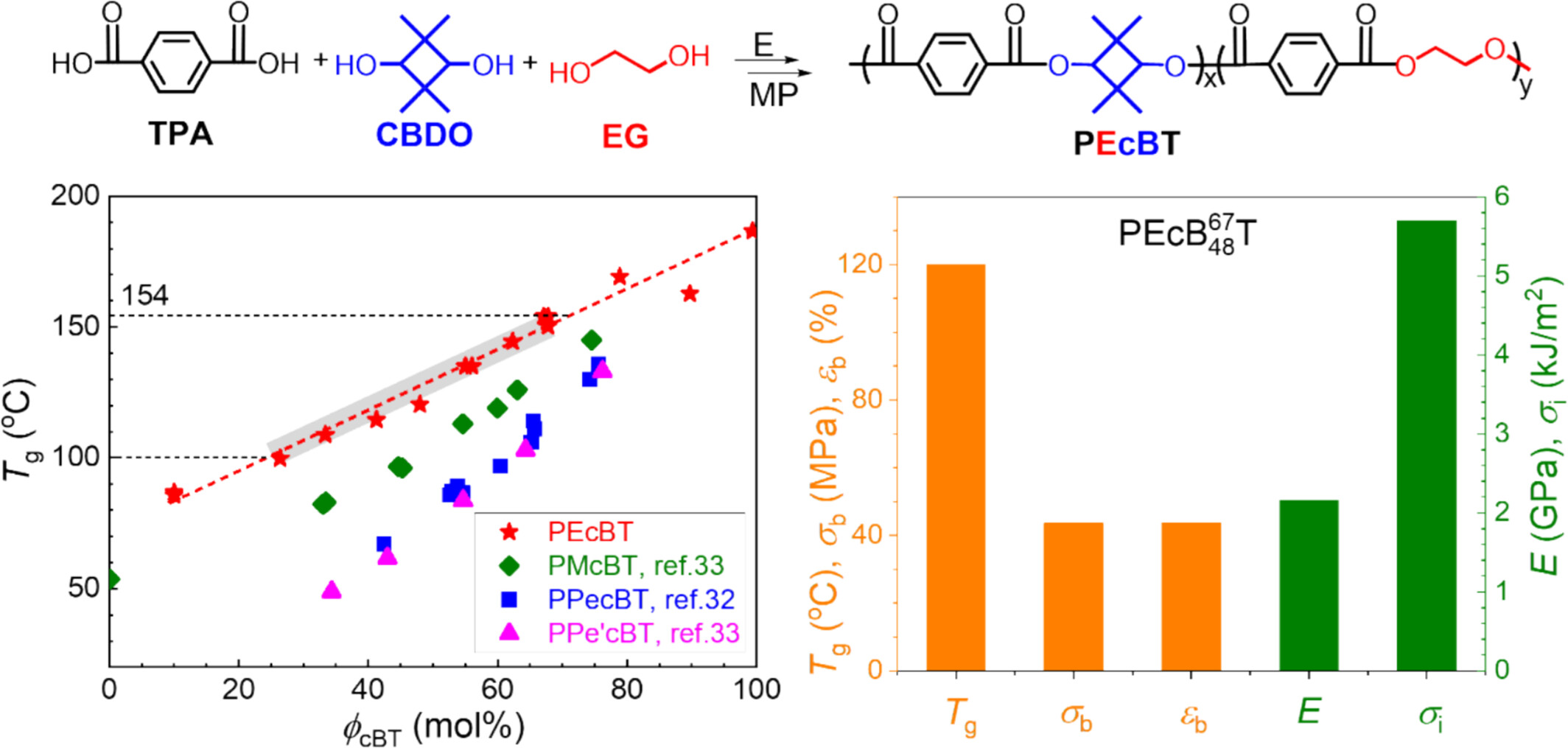
High Glass Transition PEcBT and PEPecBT Copolyesters Synthesized by Direct Esterification Route
- First Published: 26 January 2025
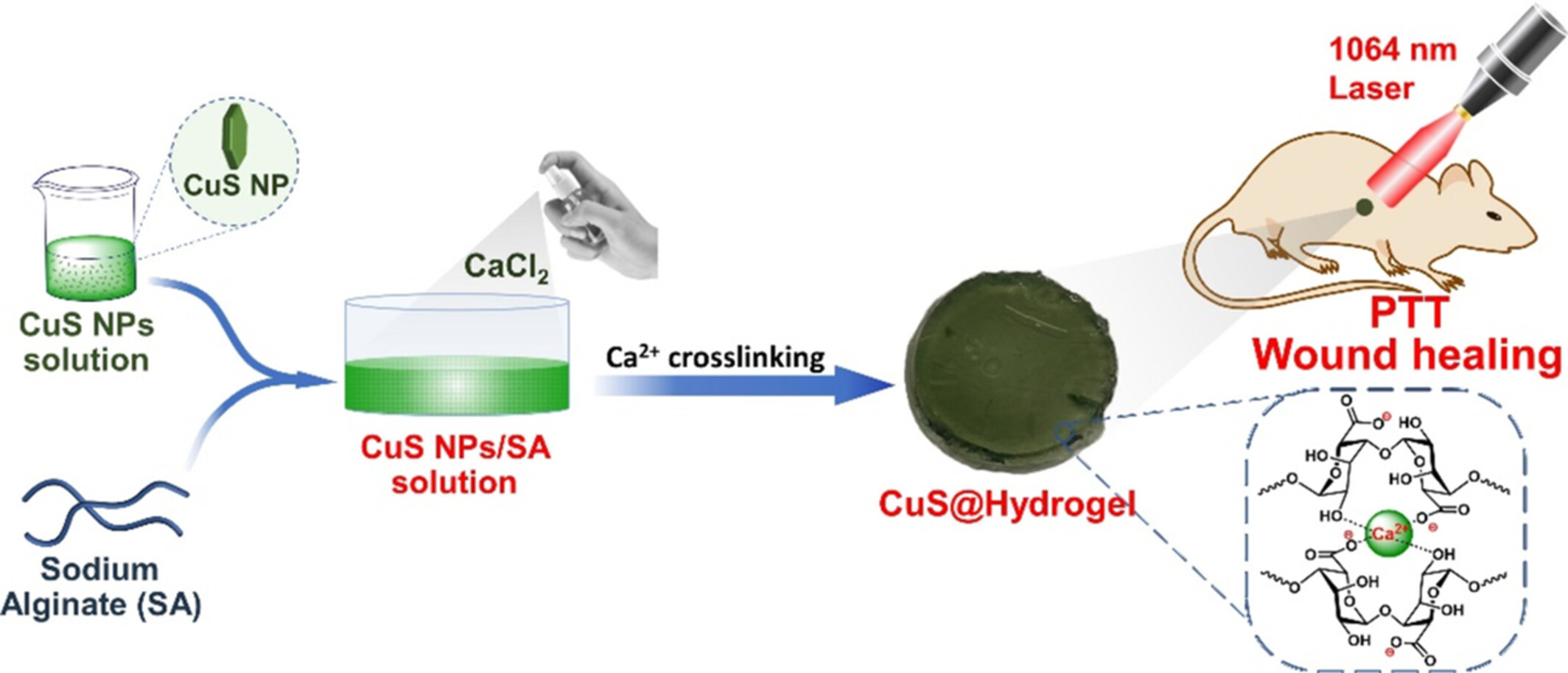
Alginate-Based Hydrogel Nanocomposites With CuS Nanoparticles Incorporation for NIR-II Photothermal Therapy of Melanoma and Wound Healing
- First Published: 22 January 2025
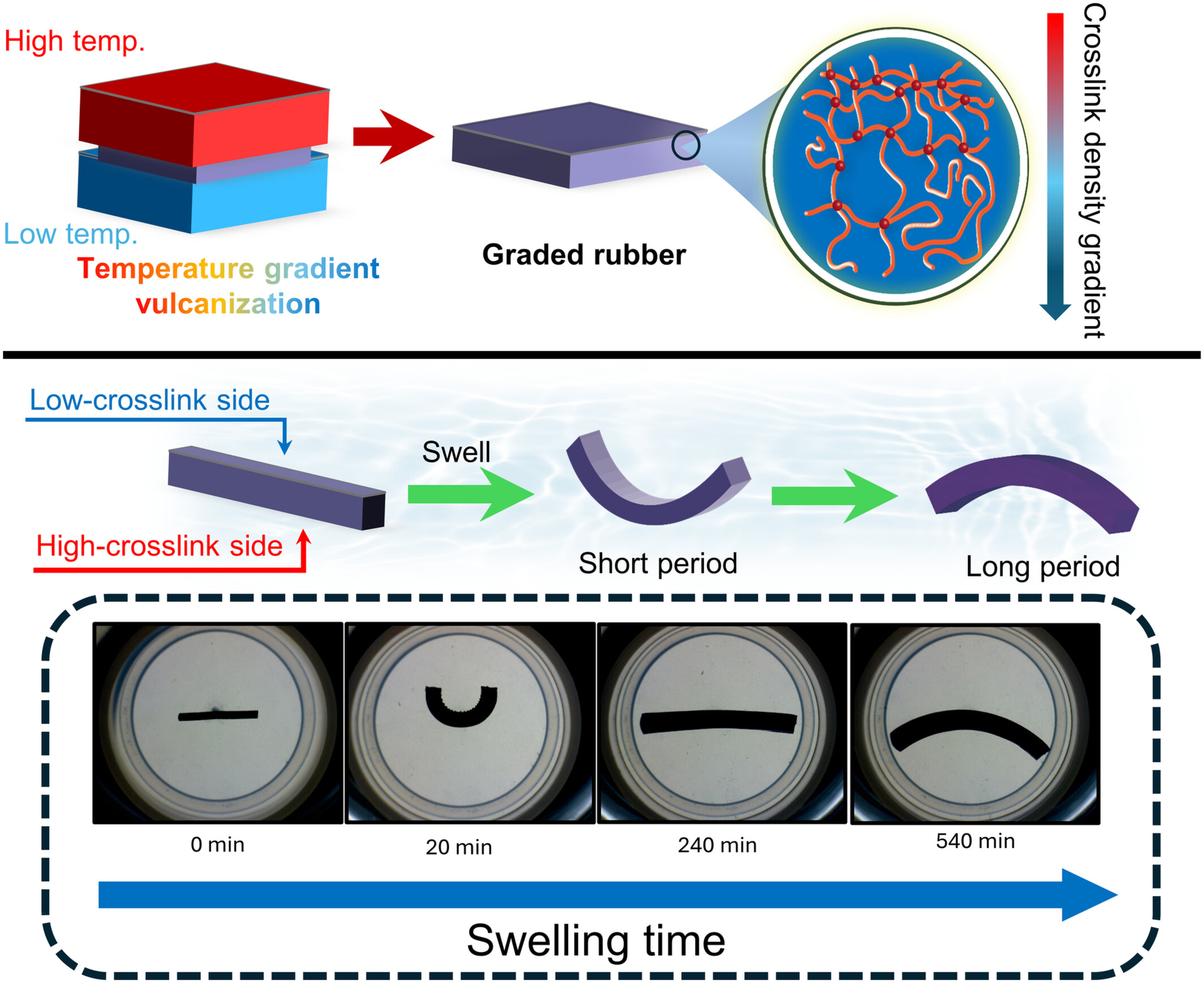
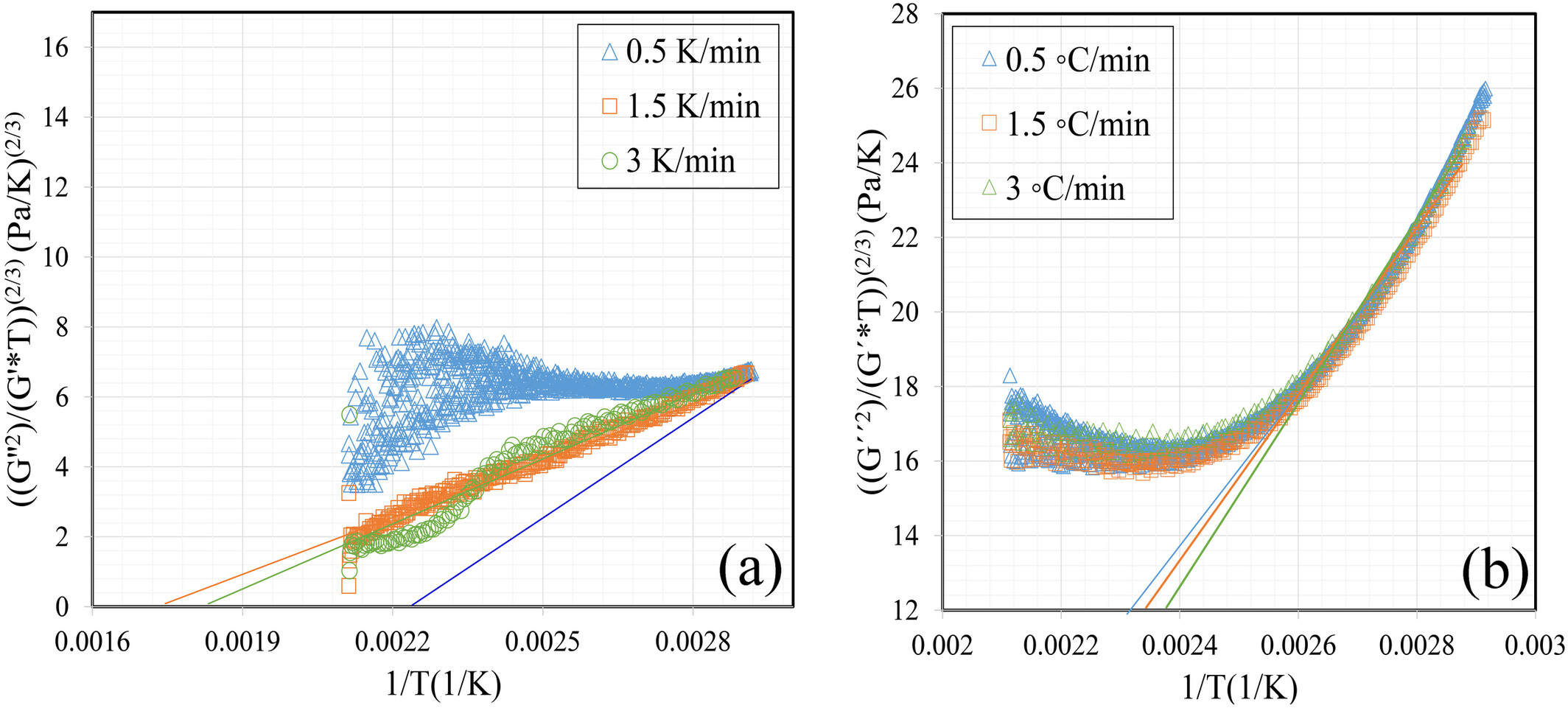
Thermo-Mechanical Degradation Kinetics of a High-Density Poly(Ethylene) Using a Closed-Cavity Rheometer
- First Published: 23 January 2025
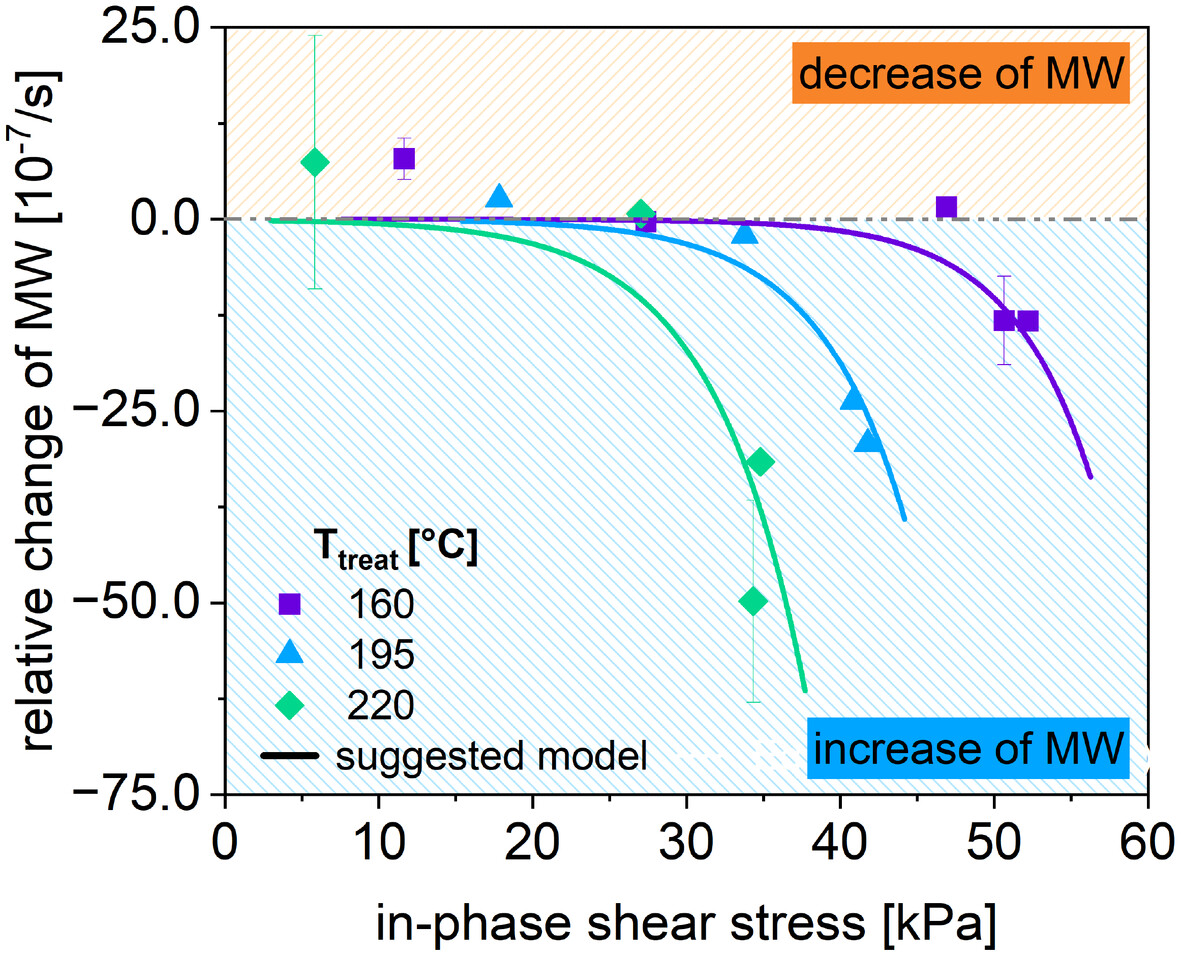
A time and material saving method to investigate multiple processing of polyolefins is developed. A commercial rheometer is used to emulate a thermo-mechanical treatment of the polymer during processing. A kinetic model is suggested to predict the change of the molecular weight as a function of time, temperature and in-phase shear stress.
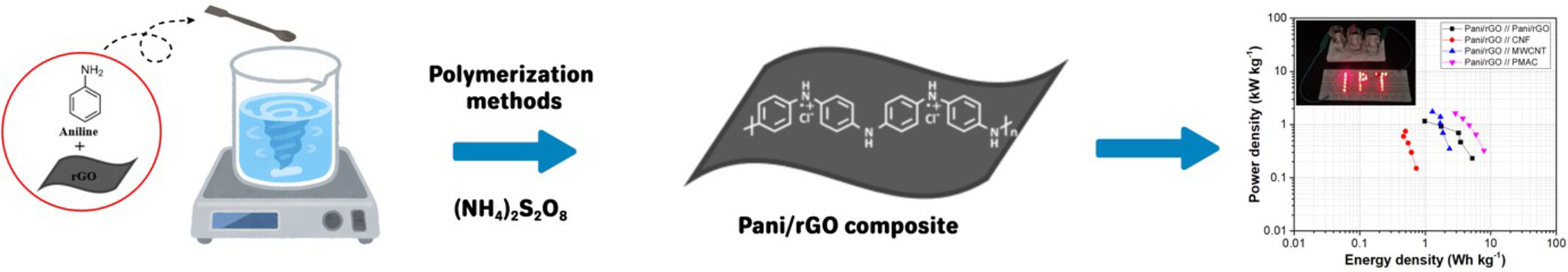
Polyaniline/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite as an Electrode for Symmetric and Asymmetric Supercapacitors
- First Published: 26 January 2025
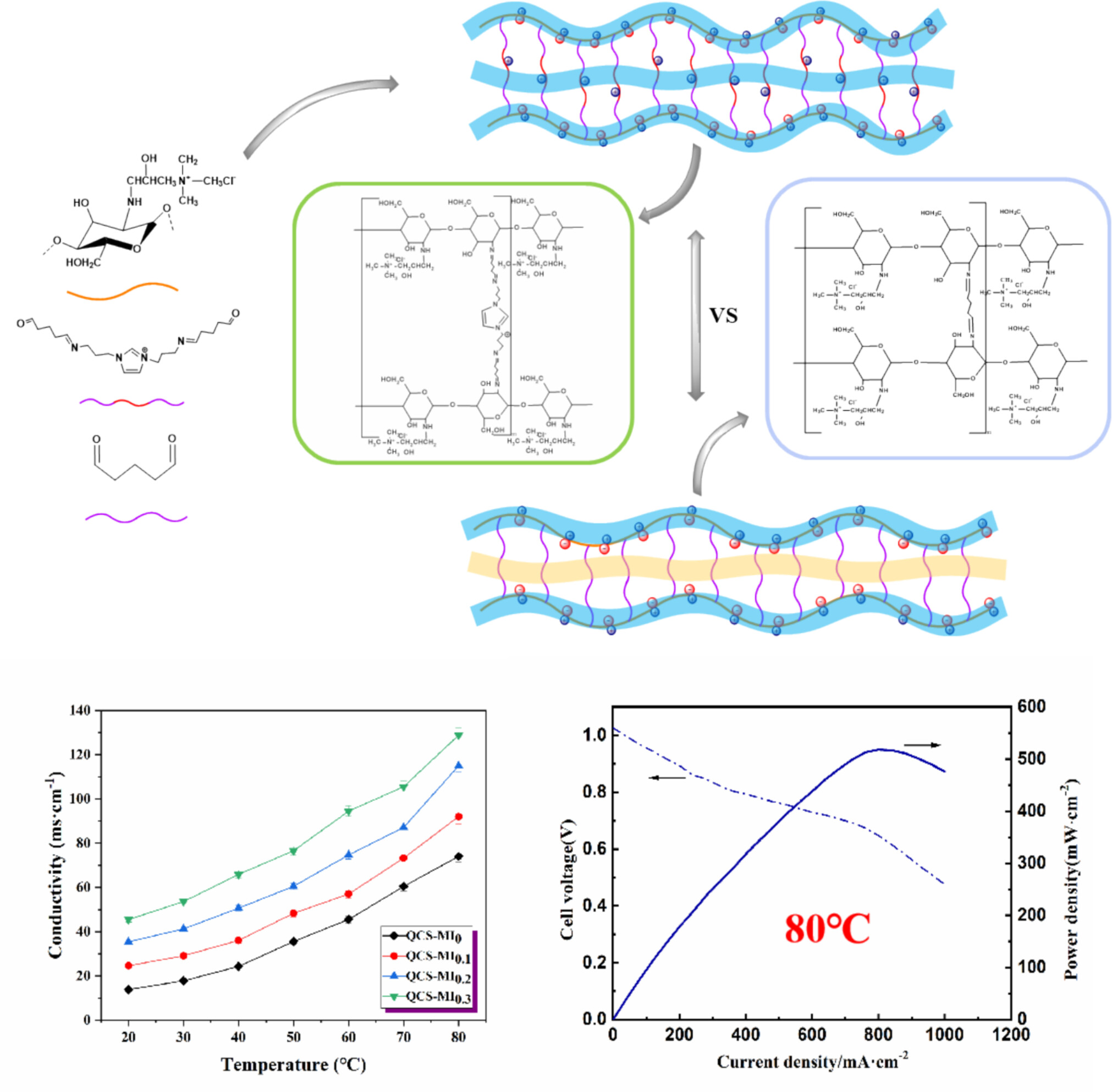
Bifunctional Imidazole Cross-Linked Anion Exchange Membrane Based on Quaternized Chitosan With High Performance
- First Published: 29 January 2025
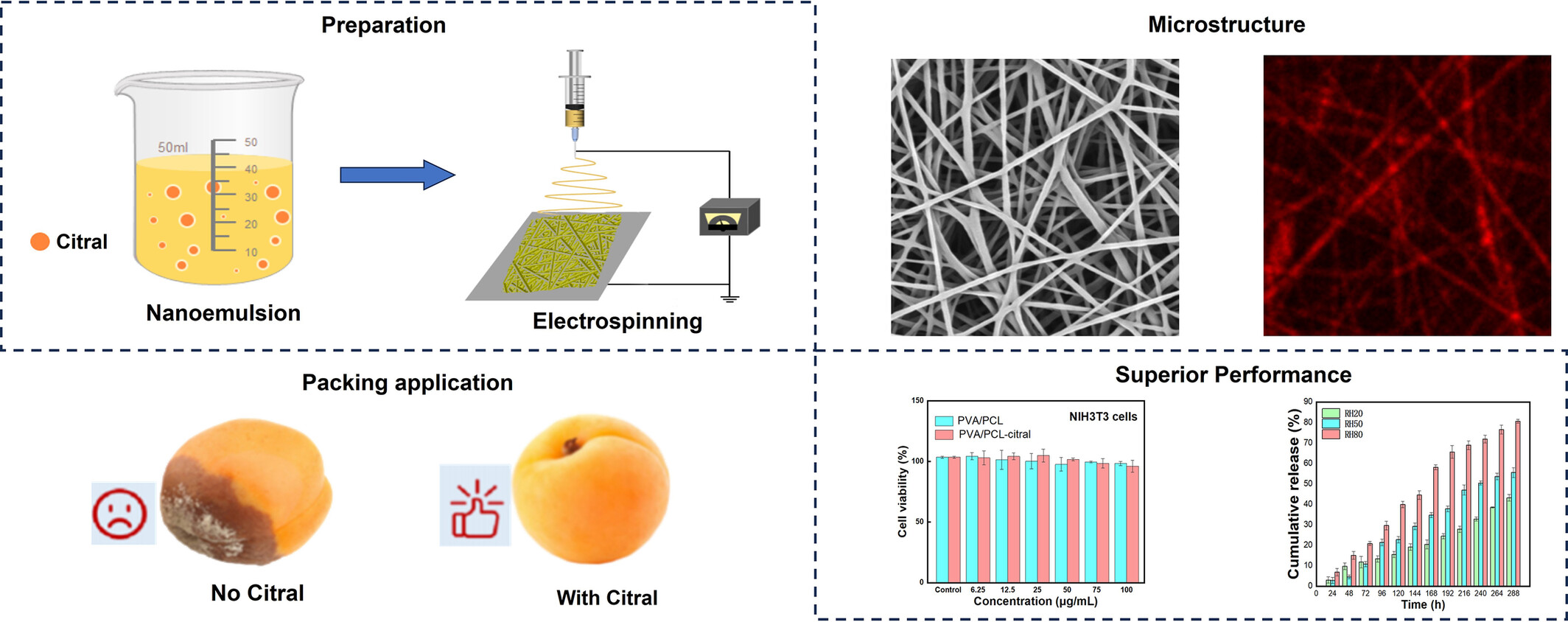
Novel Humidity-Responsive Nanofiber Film Based on Emulsion Electrospinning for Fruit Preservation
- First Published: 02 February 2025
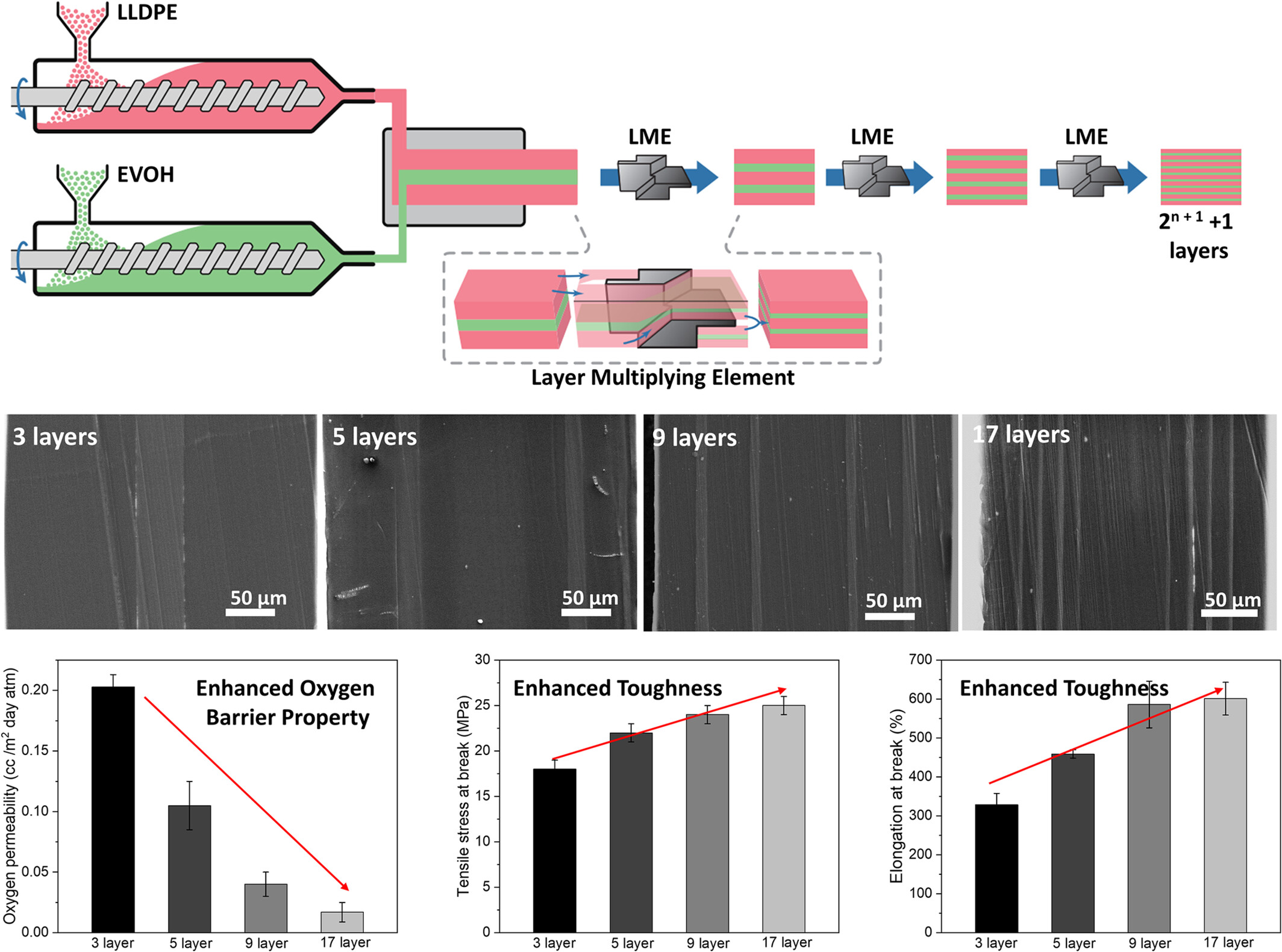
High Strength, High Barrier Polymeric Packaging Film Based on Multilayered Structure
- First Published: 02 February 2025
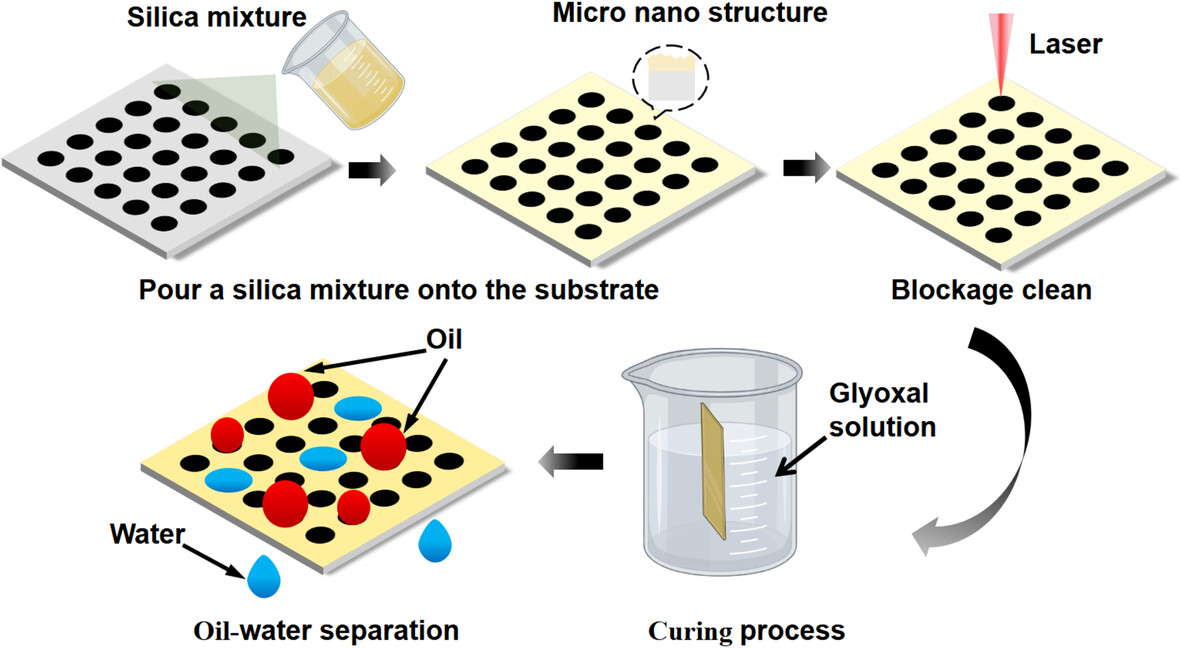
Fabrication of Polytetrafluoroethylene Composite Membrane via Laser Perforating and Nanosilica Coating for Efficient Oil–Water Separation
- First Published: 22 January 2025
Nano-Silica-Particles Filling Effect on Mechanical Properties of Silicone-Rubber Composites
- First Published: 24 January 2025
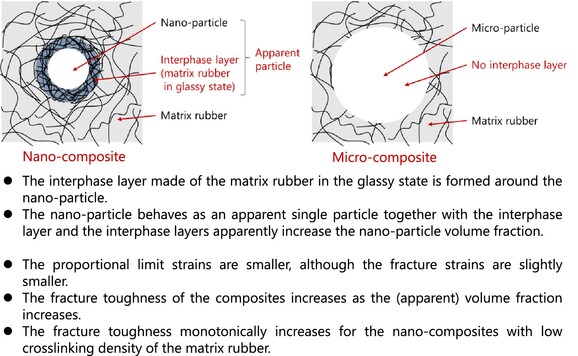
- The interphase layer made of the matrix rubber in the glassy state is formed around the nano-particle.
- The nano-particle behaves as an apparent single particle together with the interphase layer and the interphase layers apparently increase the nano-particle volume fraction.
- The proportional limit strains are smaller, although the fracture strains are slightly smaller.
- The fracture toughness of the composites increases as the (apparent) volume fraction increases.
- The fracture toughness monotonically increases for the nano-composites with low crosslinking density of the matrix rubber.
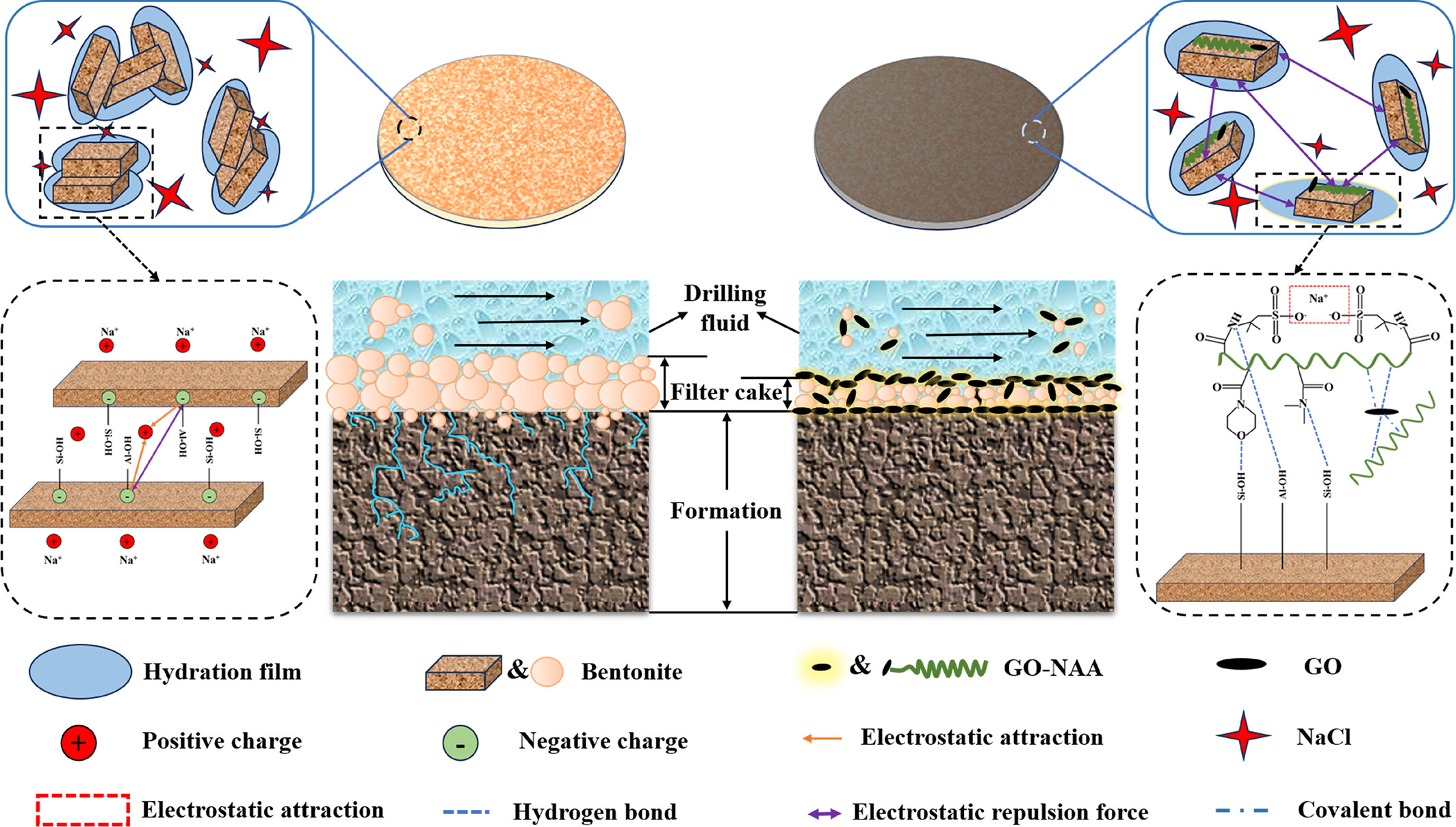
Application of Graphene Oxide/Polymer Composites as Filter Loss Reduction Agents With Water-Based Drilling Fluids
- First Published: 06 February 2025
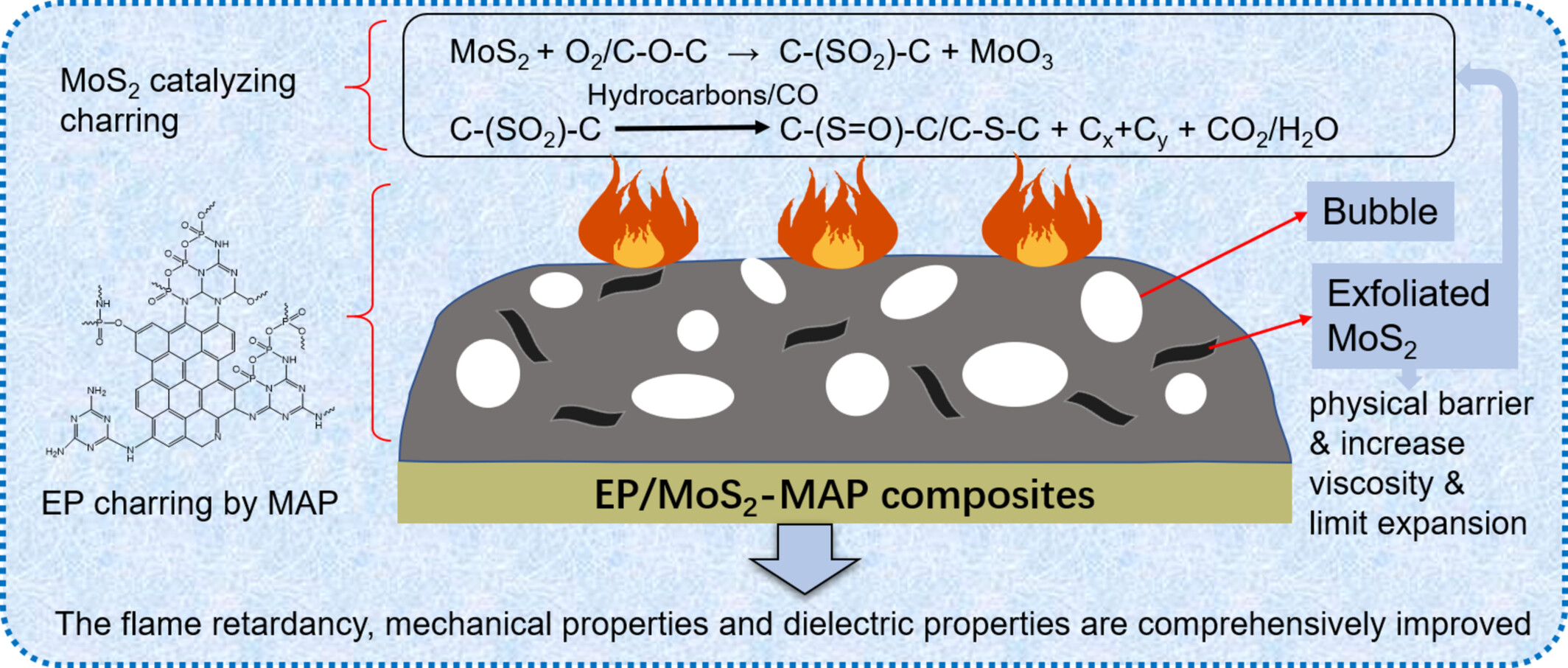
Superior Flame Retardancy, Mechanical and Dielectric Properties of Epoxy Resin Composites Based on Molybdenum Disulfide-Melamine Trimetaphosphate Crystallite Composites
- First Published: 05 February 2025
Inhibition of Wax Crystallization and Asphaltene Deposition by Star Poly(Octadecyl Acrylate-Styrene) (POA-St) for African Crude Oil
- First Published: 30 January 2025
Preparation, Characterization, and Drug Release of Electrospun Core-Shell Structured Hyaluronic Acid-Bovine Serum Albumin/Poly(ε-Caprolactone) Nanofiber Membranes
- First Published: 29 January 2025
LCST-UCST Hybrid Phase Diagram of Poly(ɛ-Caprolactone)/Poly(Styrene-co-Acrylonitrile) Blends Through Thermal and Rheological Approaches: Effects of PCL Molecular Weight and Cooling Ramp Rate
- First Published: 29 January 2025
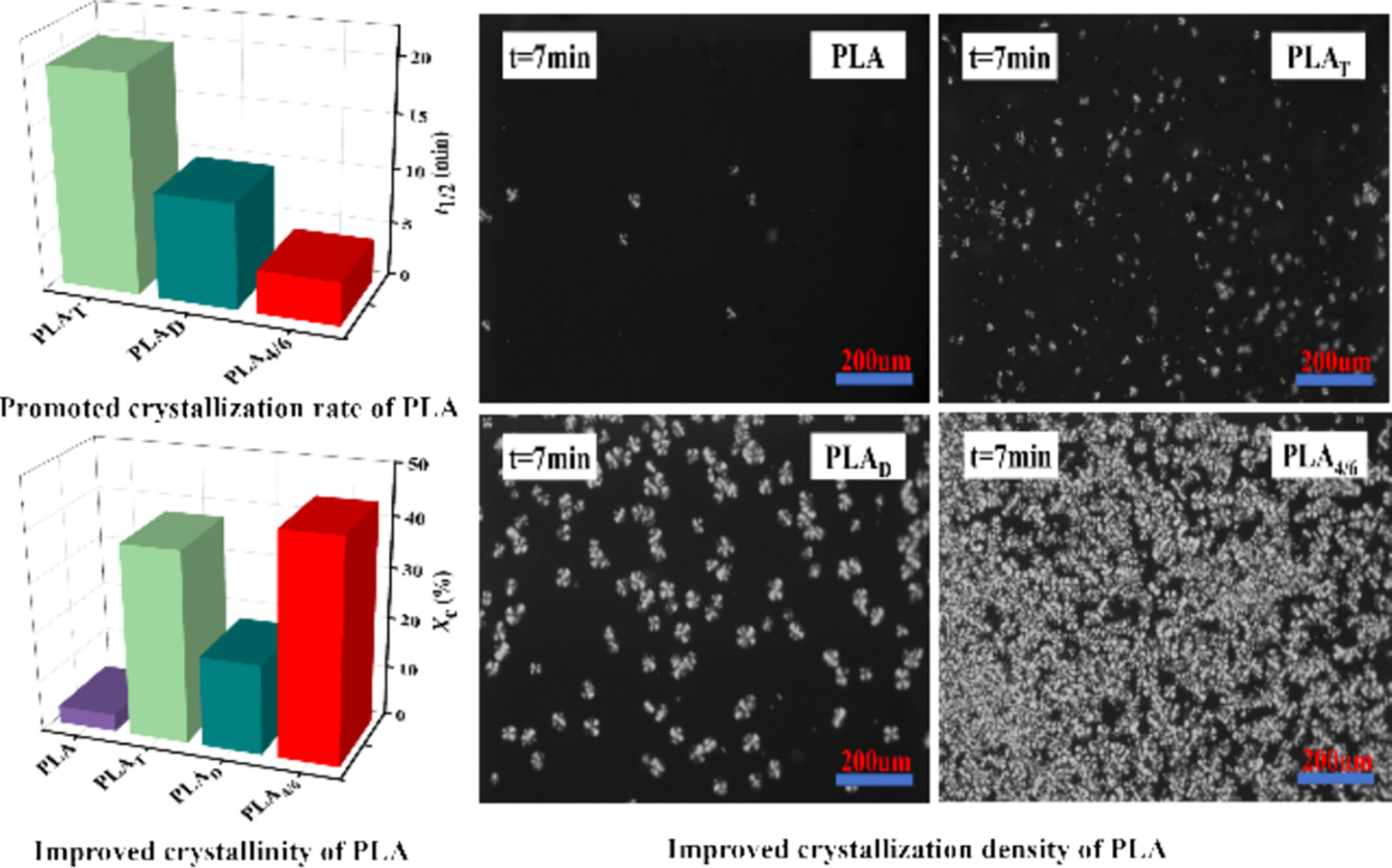
Promoting Effect of Synergetic Nucleating Agent on Crystallization Behavior of Polylactic Acid
- First Published: 29 January 2025
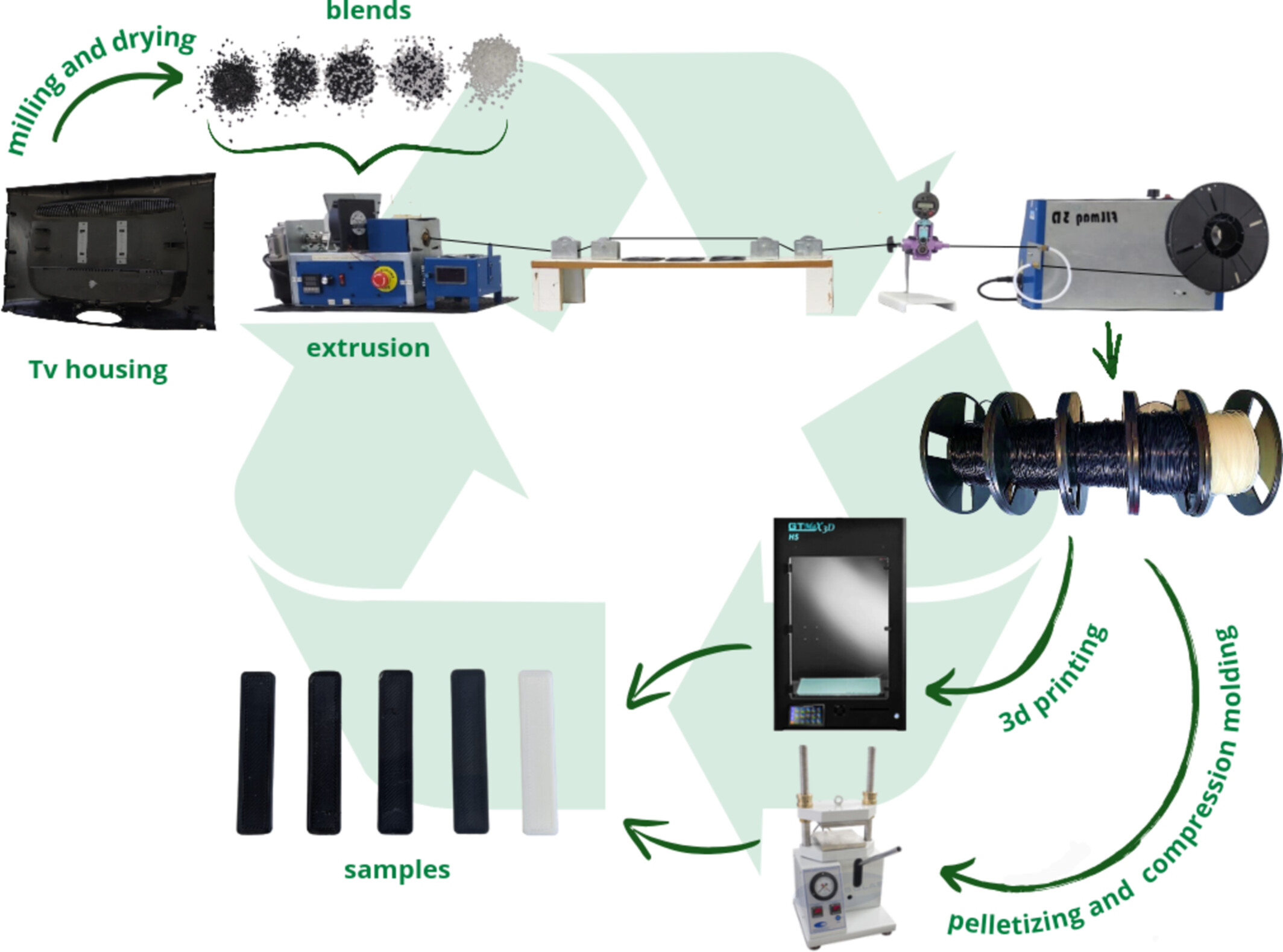
Properties of Recycled ABS and HIPS Polymers From WEEE and Their Blends With Virgin ABS Prepared by 3D Printing and Compression Molding
- First Published: 24 January 2025
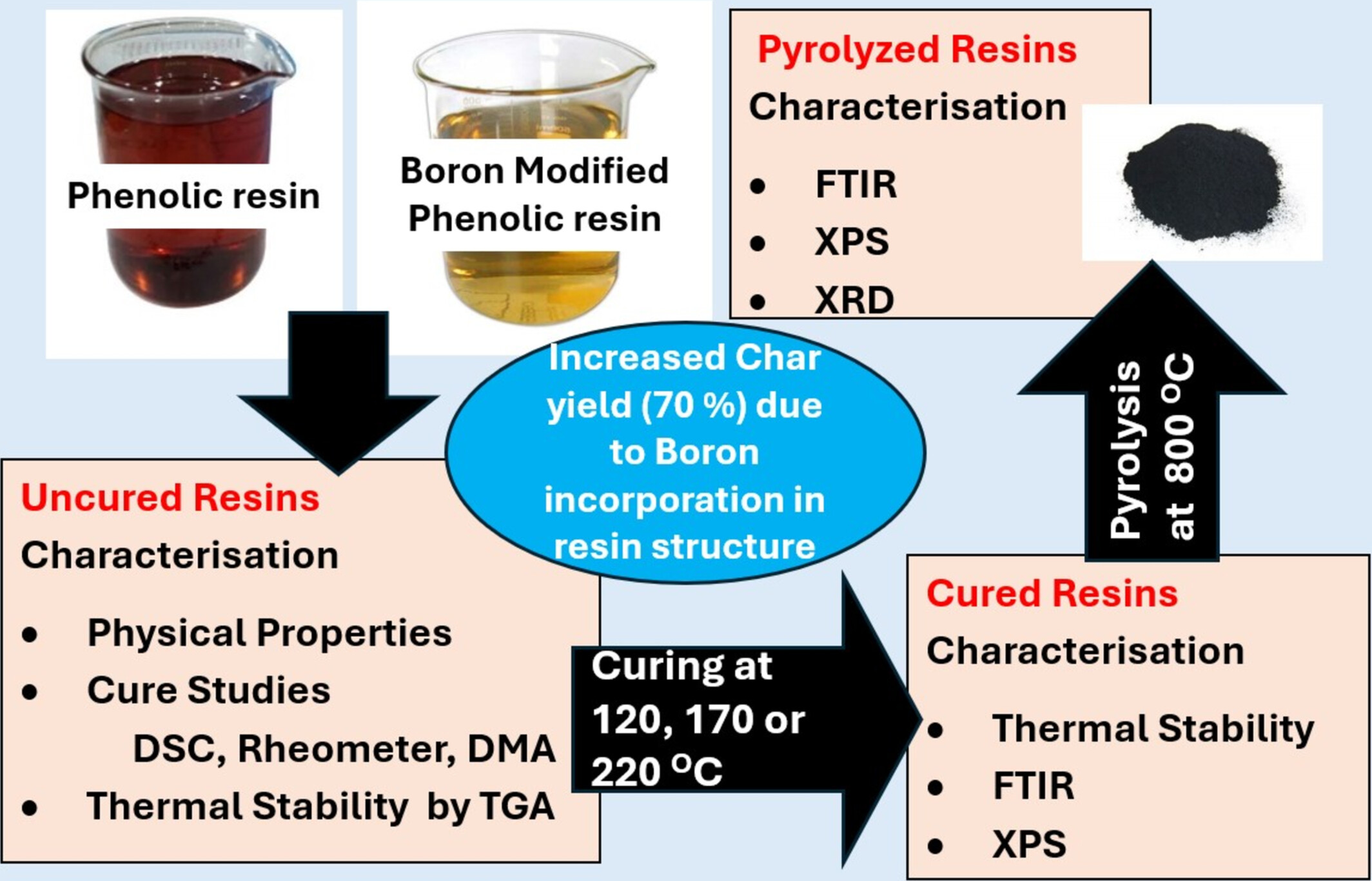
Effect of Boron Modification on Characteristics of Phenolic Resin and Its Char
- First Published: 30 January 2025
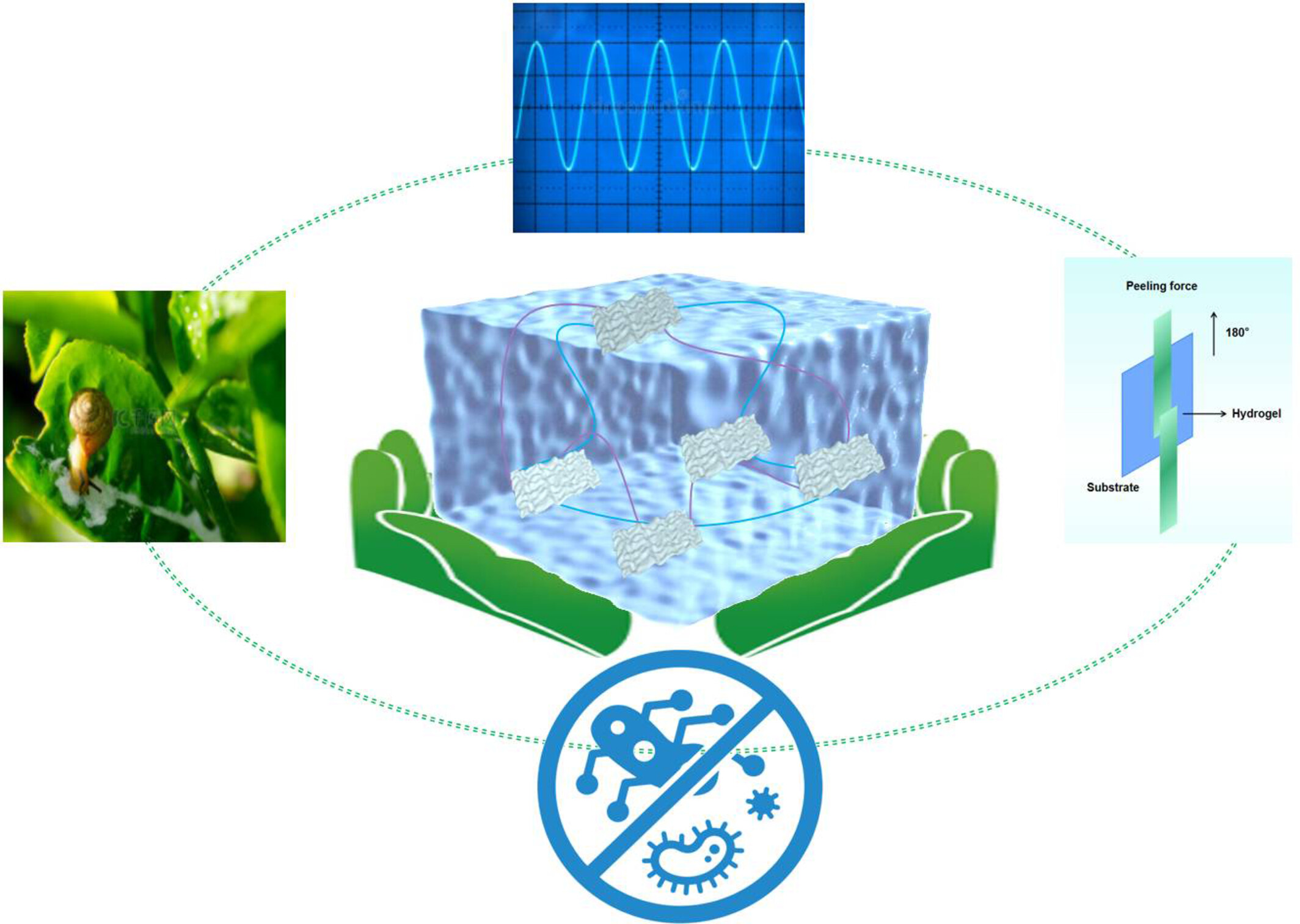
Antibacterial, Stretchable, and Self-Adhesive Laponite-TA Based Conductive Hydrogel Sensor for Human Motion Detection
- First Published: 09 February 2025
The Role of Methylene Diphenyl Diisocyanate in the Melt Blending of Poly(Butylene Adipate-co-Terephthalate) and Thermoplastic Starch
- First Published: 31 January 2025
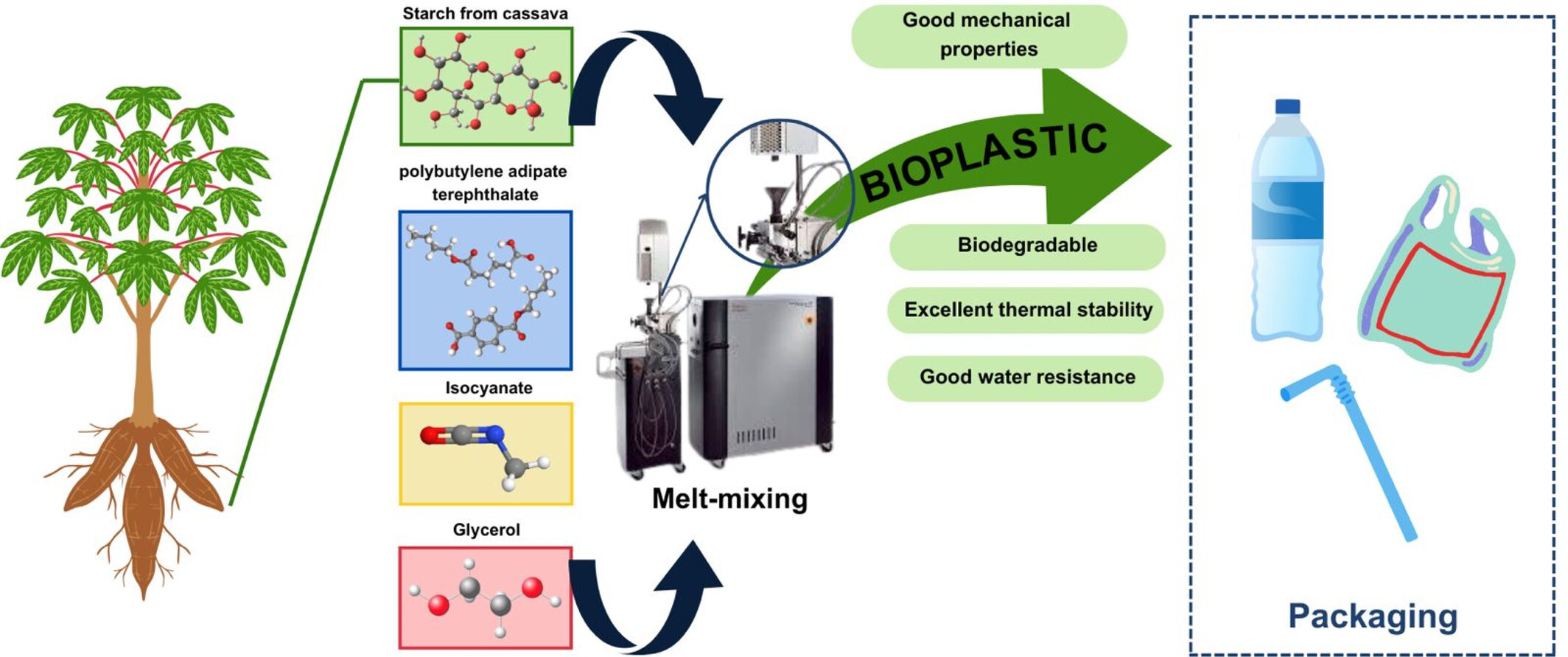
This work demonstrates that a little quantity of 4,4′-methylene diphenyl diisocyanate (MDI) can improve the interfacial adhesion between thermoplastic starch (TPS) and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate). The mechanical qualities, phase morphology, thermal behavior, crystalline structure, and water absorption have greatly increased.
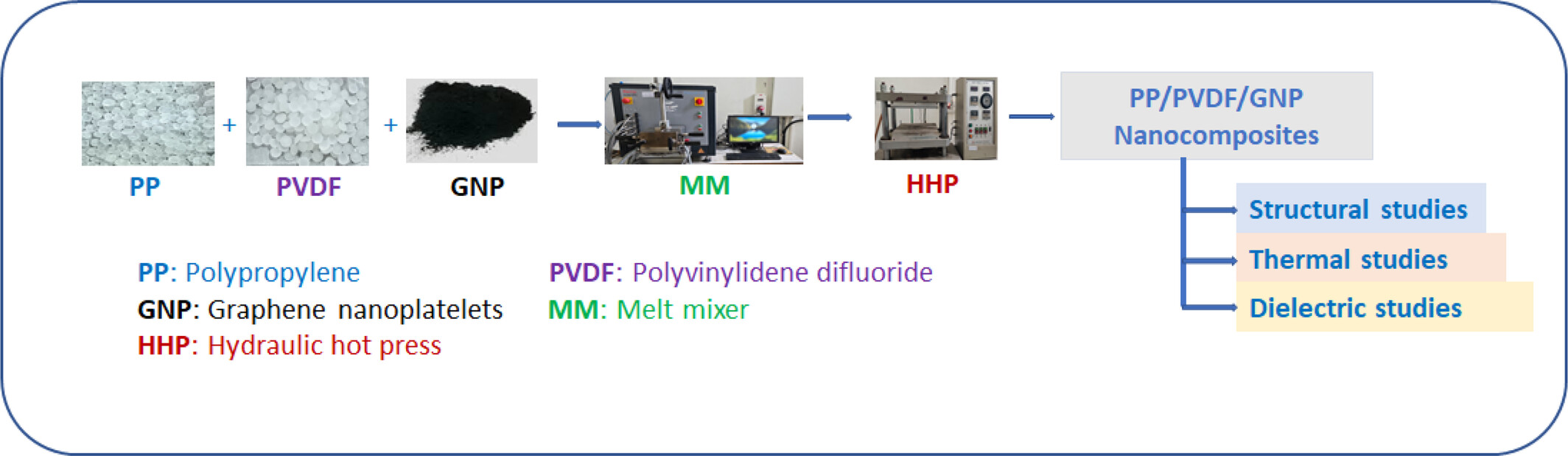
Effect of Graphene Nanoplatelets (GNP) on the Structural, Thermal, and Dielectric Properties of Polypropylene/Polyvinylidenedifluoride (PP/PVDF) Nanocomposites
- First Published: 08 February 2025
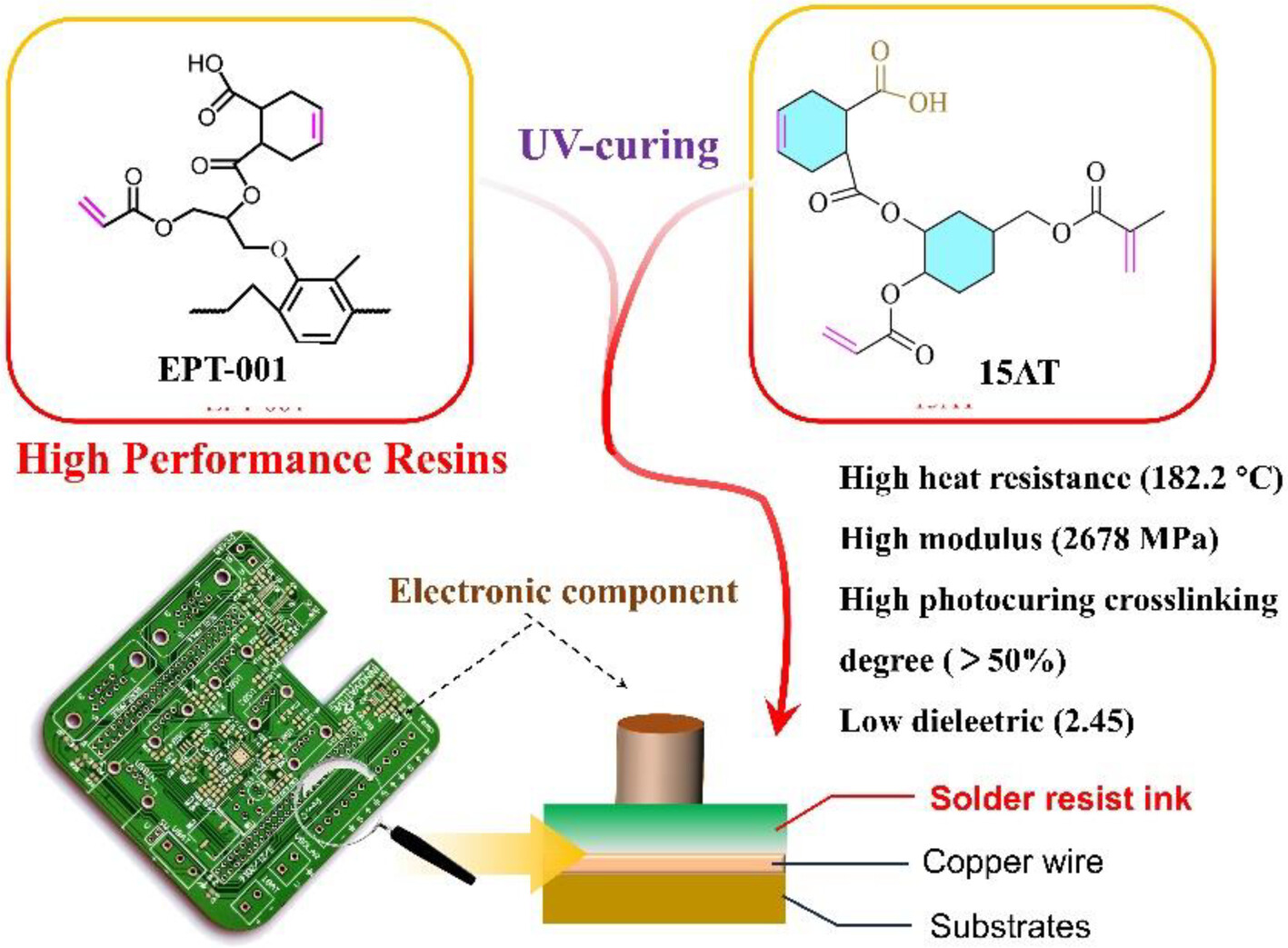
High Heat Resistance and Low Dielectric o-Cresol Formaldehyde Epoxy Resin Solder Resist Containing Photocurable Small Molecular Compound Based on 3,4-Epoxycyclohexylmethyl Methacrylate
- First Published: 03 February 2025
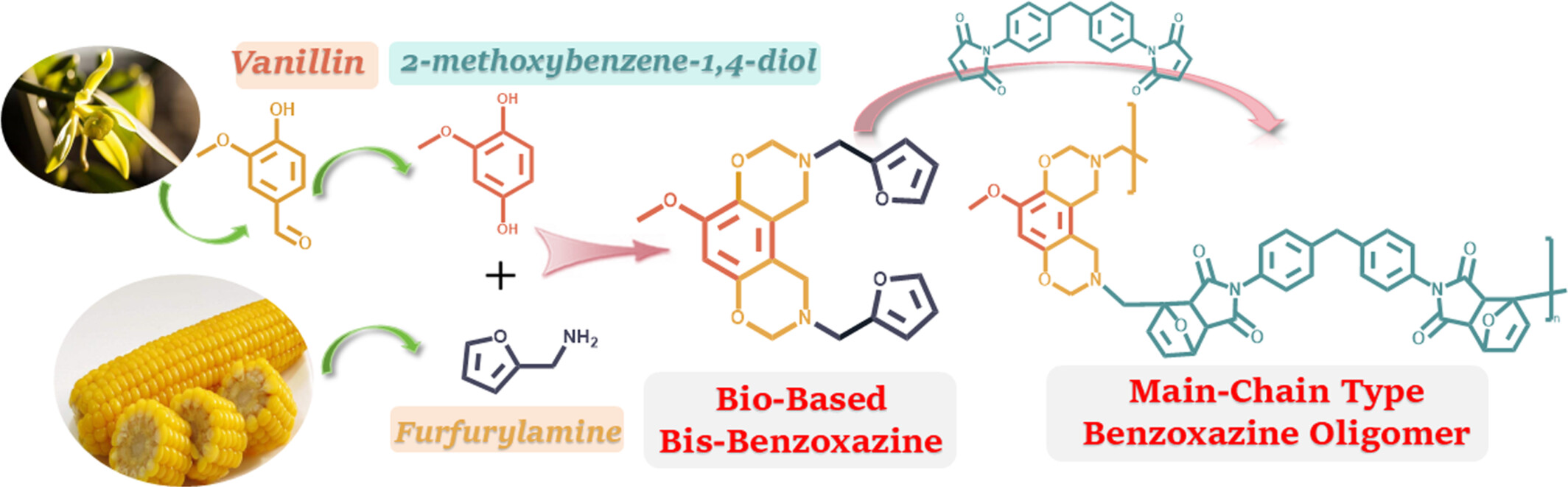
High-Performance Bio-Benzoxazine Resins Derived From Natural Renewable Vanillin: Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties of Their Thermosets
- First Published: 31 January 2025
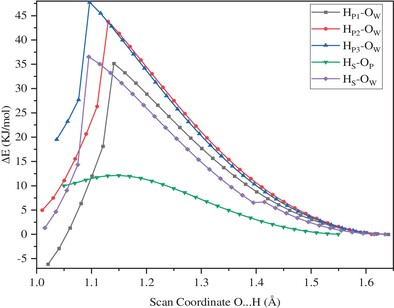
Enhancement of Phosphoric Acid-Functionalized Graphene Oxide on SPEEK Membrane Performance
- First Published: 06 February 2025
Improving i-P3HB Processing Window: Solution-Casting Blends With a-P3HB and P34HB
- First Published: 31 January 2025
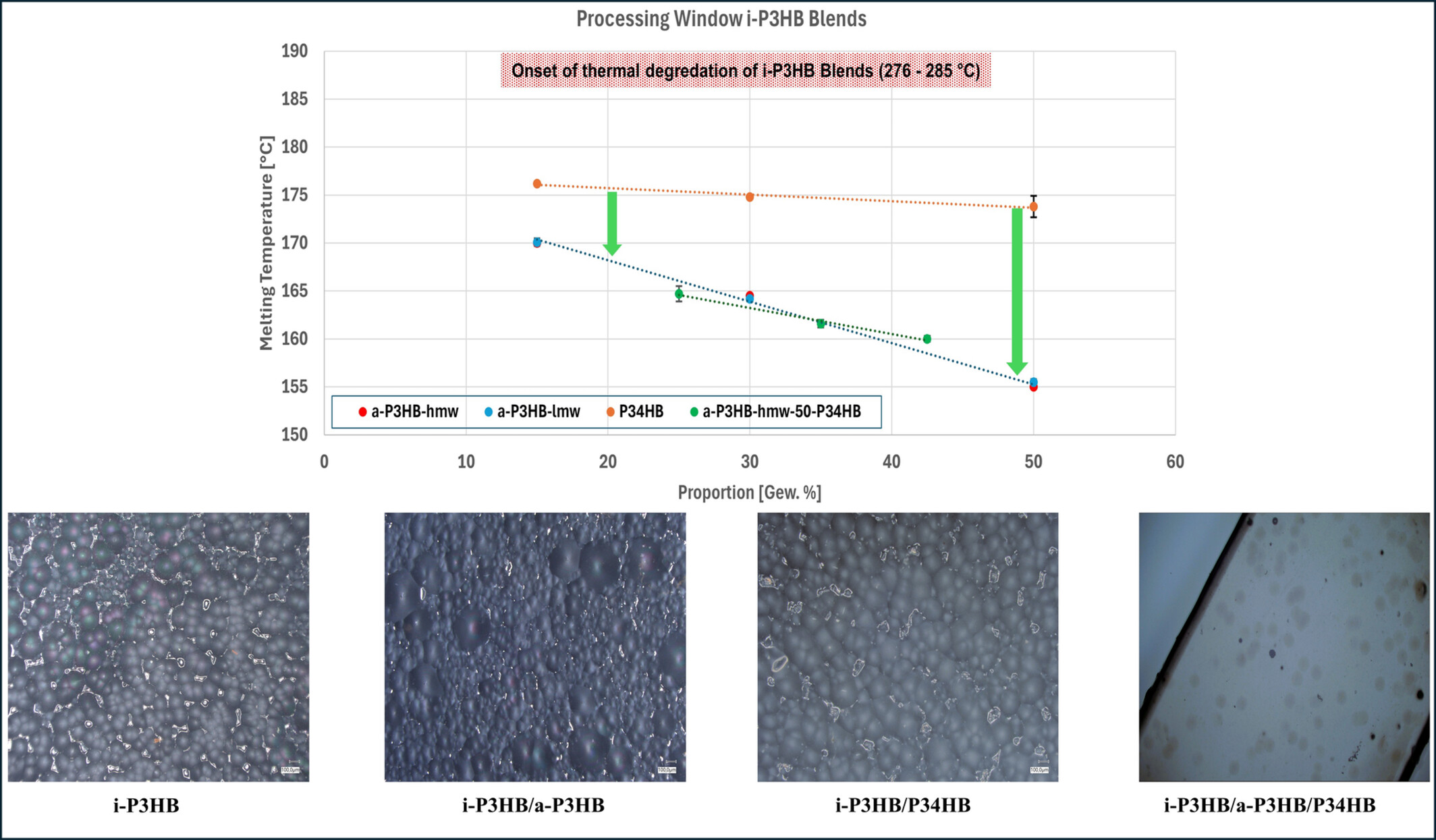
Blends of isotactic P3HB with atactic P3HB and P34HB were prepared via solution casting to address i-P3HB's limited processing window. The obtained blends exhibited reduced melting temperatures, disrupted crystallization, and improved flexibility. These improvements facilitate processing i-P3HB at lower temperatures, preventing thermal degradation and broadening its the processing window. They also expand i-P3HB's applicability in packaging, textiles, and other sectors.
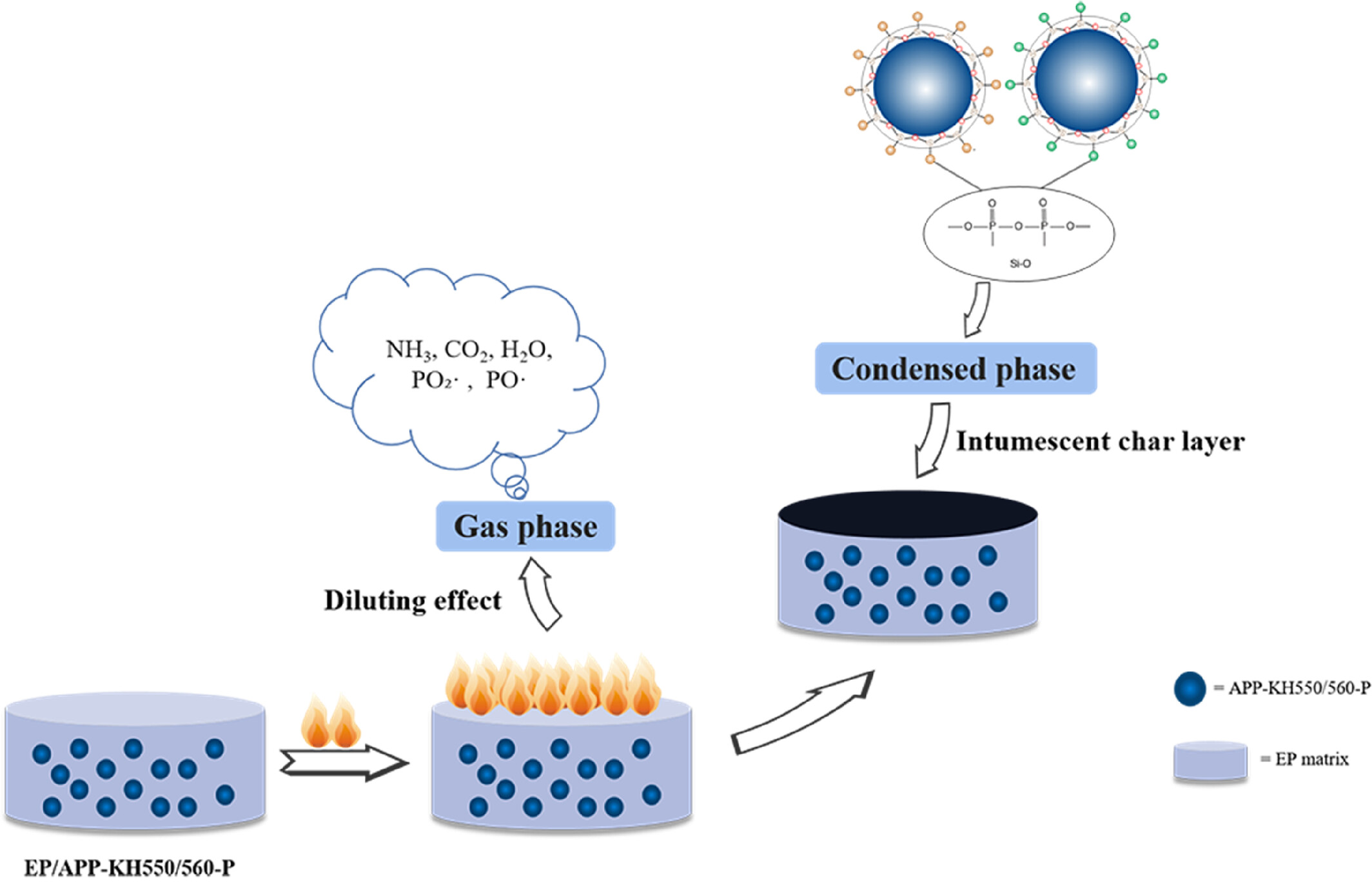
Effect of Phosphorus-Containing Silane Coupling Agents Modified Ammonium Polyphosphate on the Flame Retardancy and Mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin
- First Published: 30 January 2025
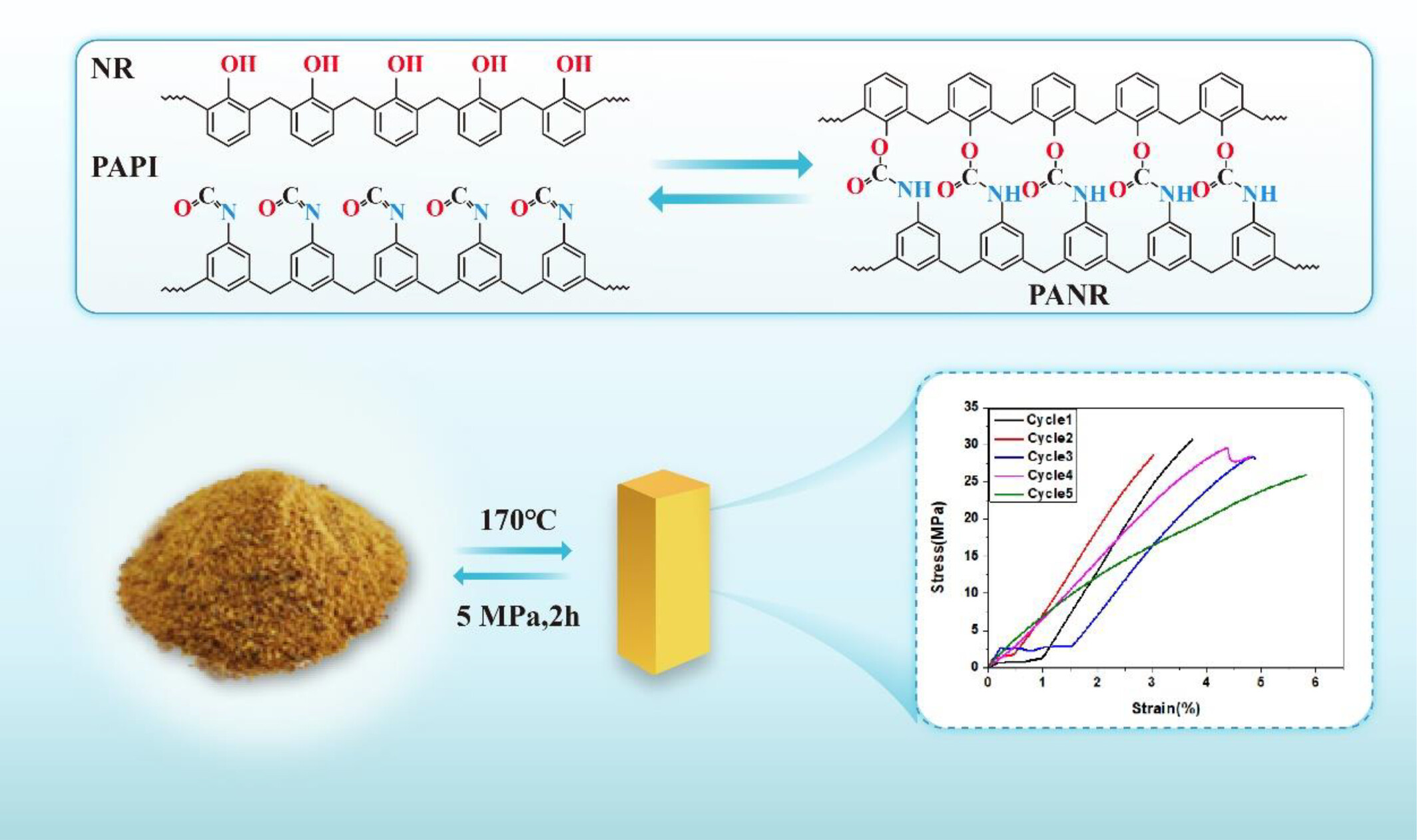
Preparation and Properties of Reprocessable Phenolic Resin Based on Modification of Long-Chain Isocyanate
- First Published: 31 January 2025