Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 140, Issue 3
- First Published: 08 December 2022

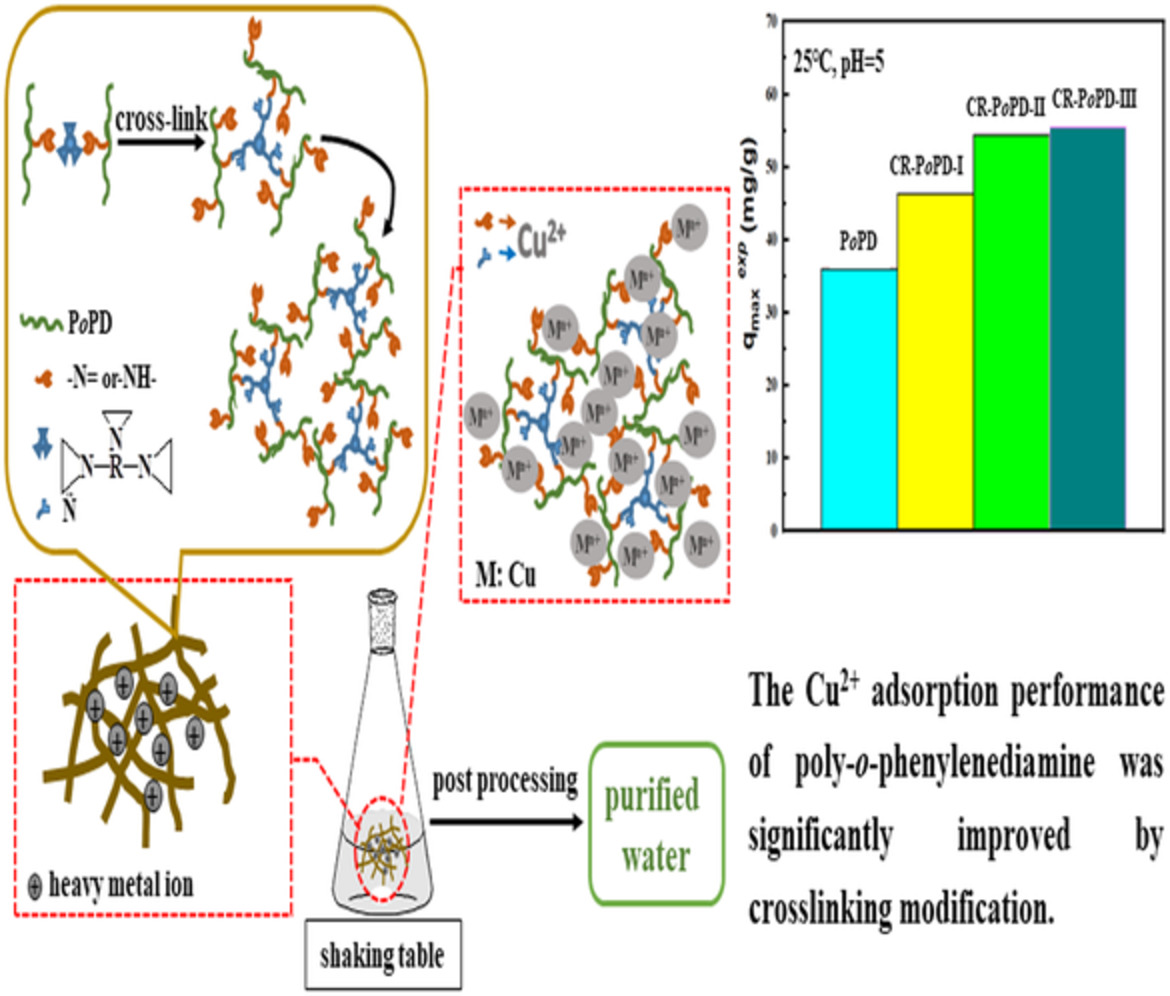
The cover picture created by Xixizhiyan Cultural Media Co. (www.xixizhiyan.com) and provided by Arzugul Muslim describes the removal of Cu2+ in aqueous solution by cross-linked poly(o-phenylenediamine). Water pollutants, including heavy metal ions, are seriously endangering human health. Conductive polymer-based adsorption materials that can be used to remove heavy metal ions have the disadvantage of poor Cu2+ removal. Cross-linking modification provides a potential solution to overcome this defect. DOI: 10.1002/app.53176
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Significantly improving the Cu2+ removal performance of conducting polymer-based adsorbent from aqueous solution through cross-linking modification
- First Published: 05 October 2022
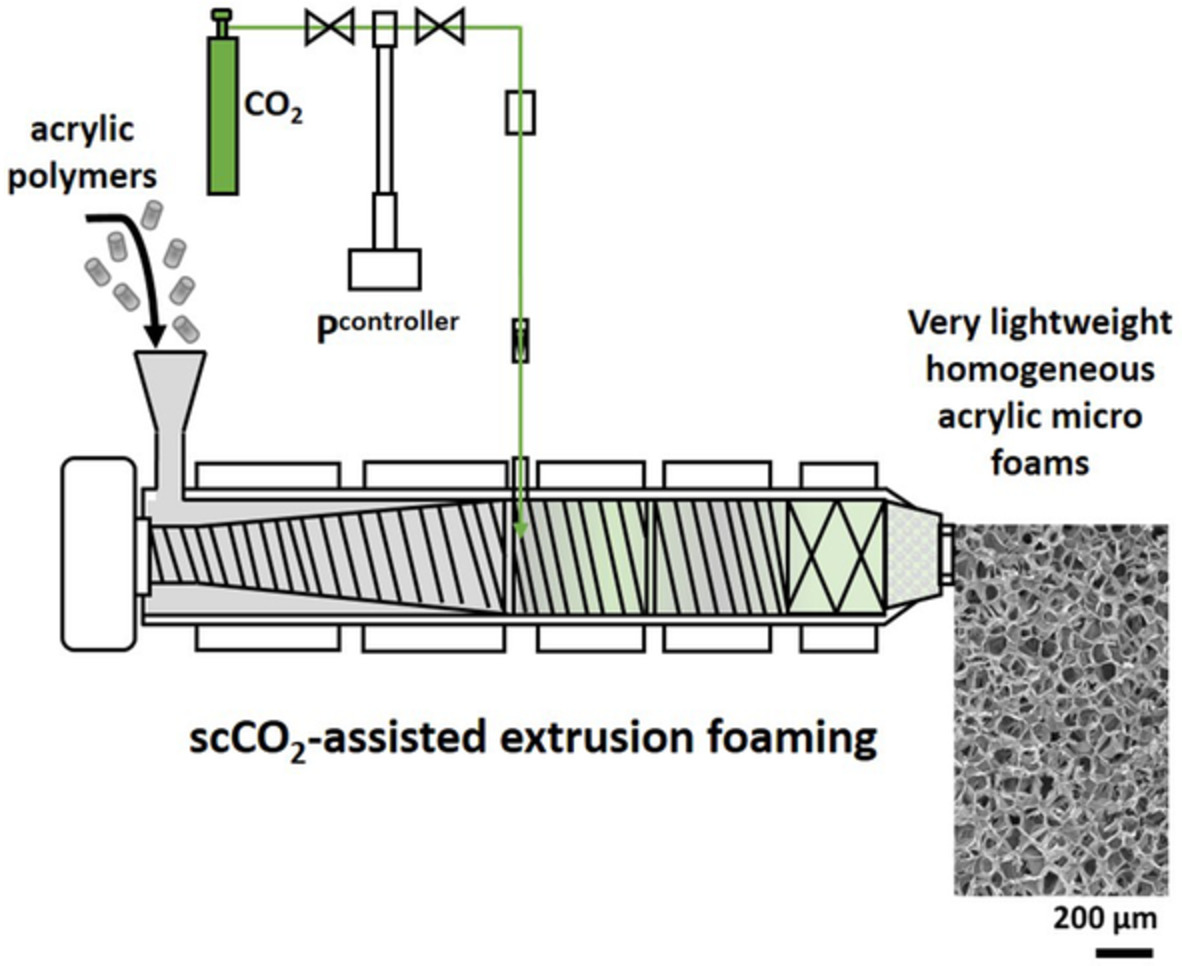
Supercritical CO2-assisted extrusion foaming: A suitable process to produce very lightweight acrylic polymer micro foams
- First Published: 15 November 2022
Synthesis and characterization of tetrafluorophenyl phosphonic acid functionalized polyacrylates as potential proton conducting materials in fuel cells
- First Published: 05 November 2022
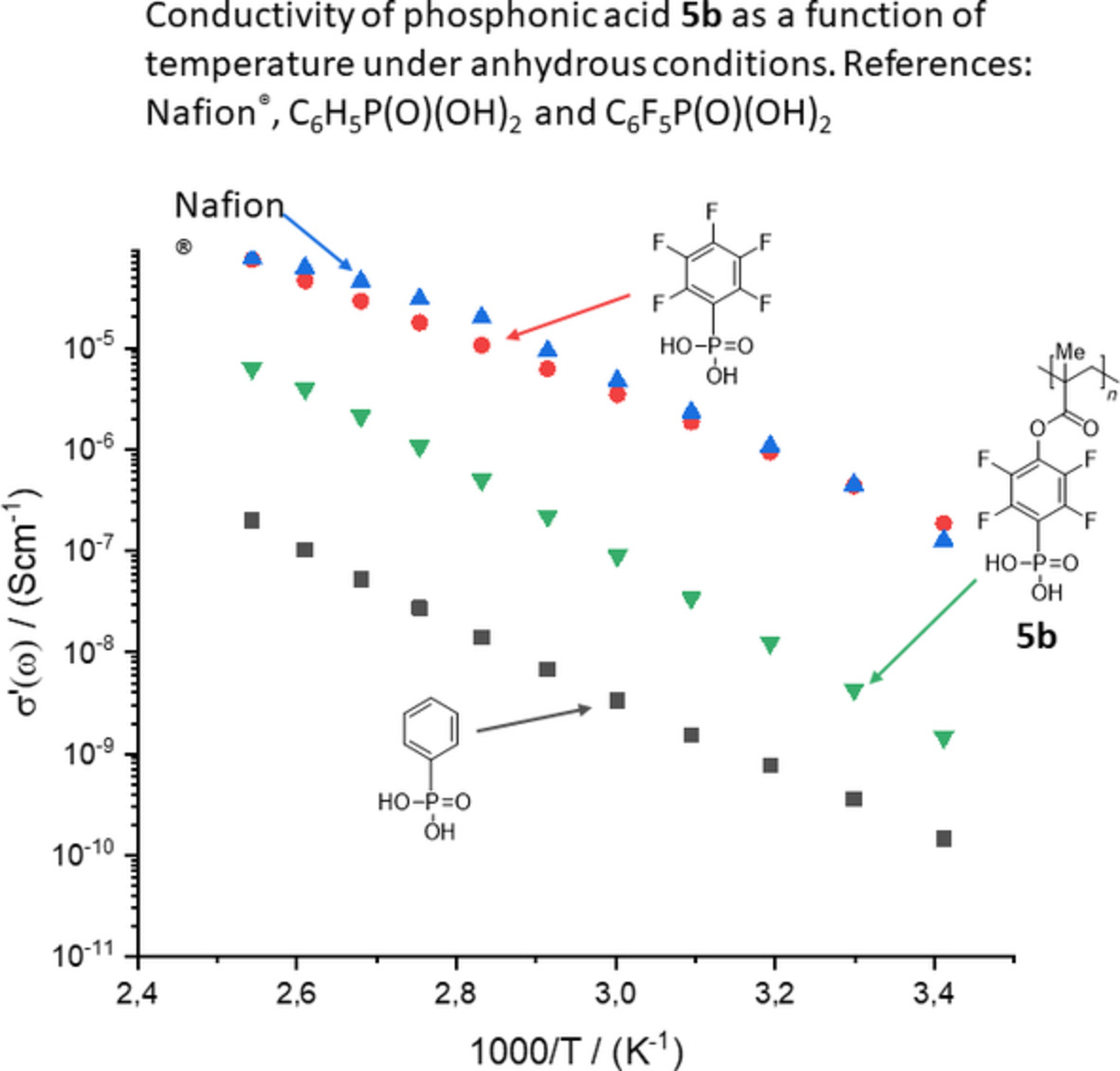
Fluorinated phosphonic acids are high-performance materials for proton conduction applications. The bonding of phosphonic acids to a polymer backbone for application as electrolytes in polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells is of broad interest. Here, we present acrylate-based tetrafluorophenylene phosphonic acid polymers with high proton conductivity under anhydrous conditions and elevated temperatures.
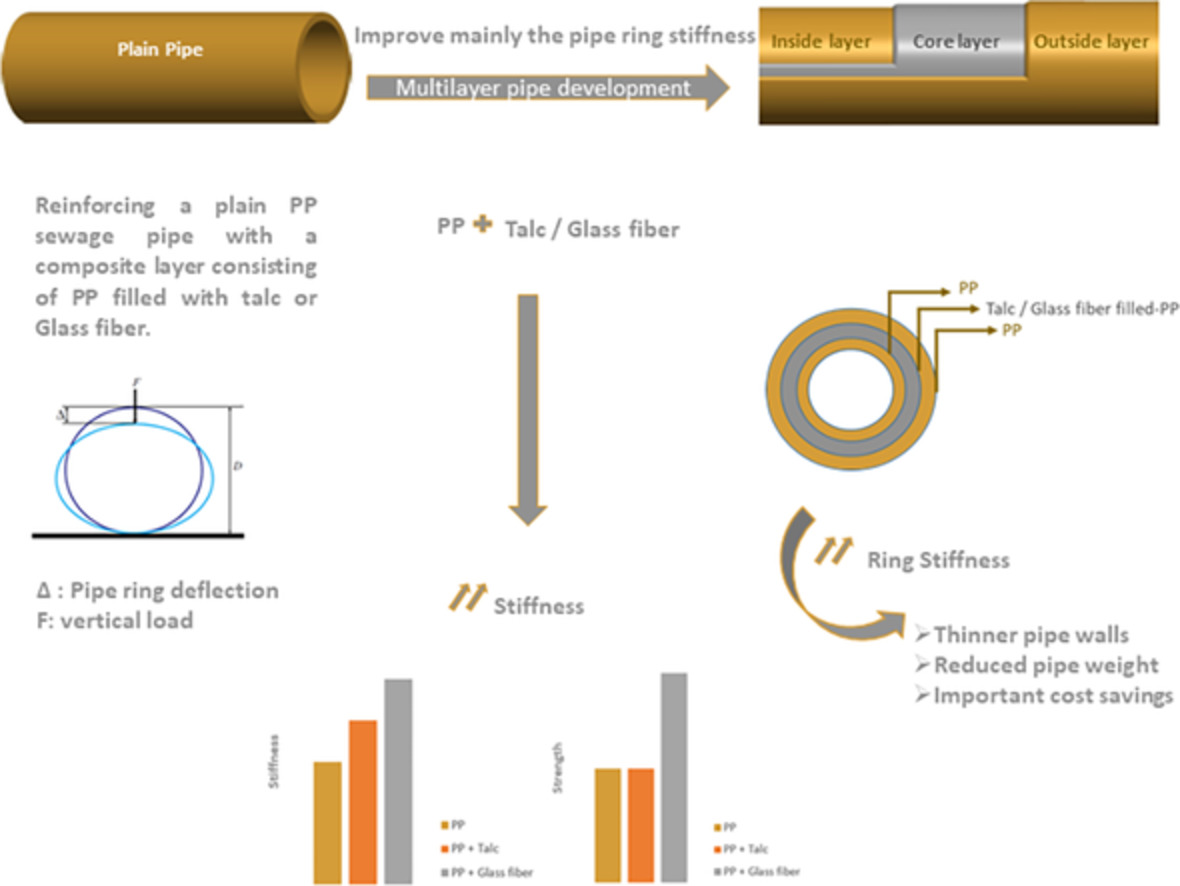
Enhancement of mechanical properties of high modulus polypropylene grade for multilayer sewage pipes applications
- First Published: 05 November 2022
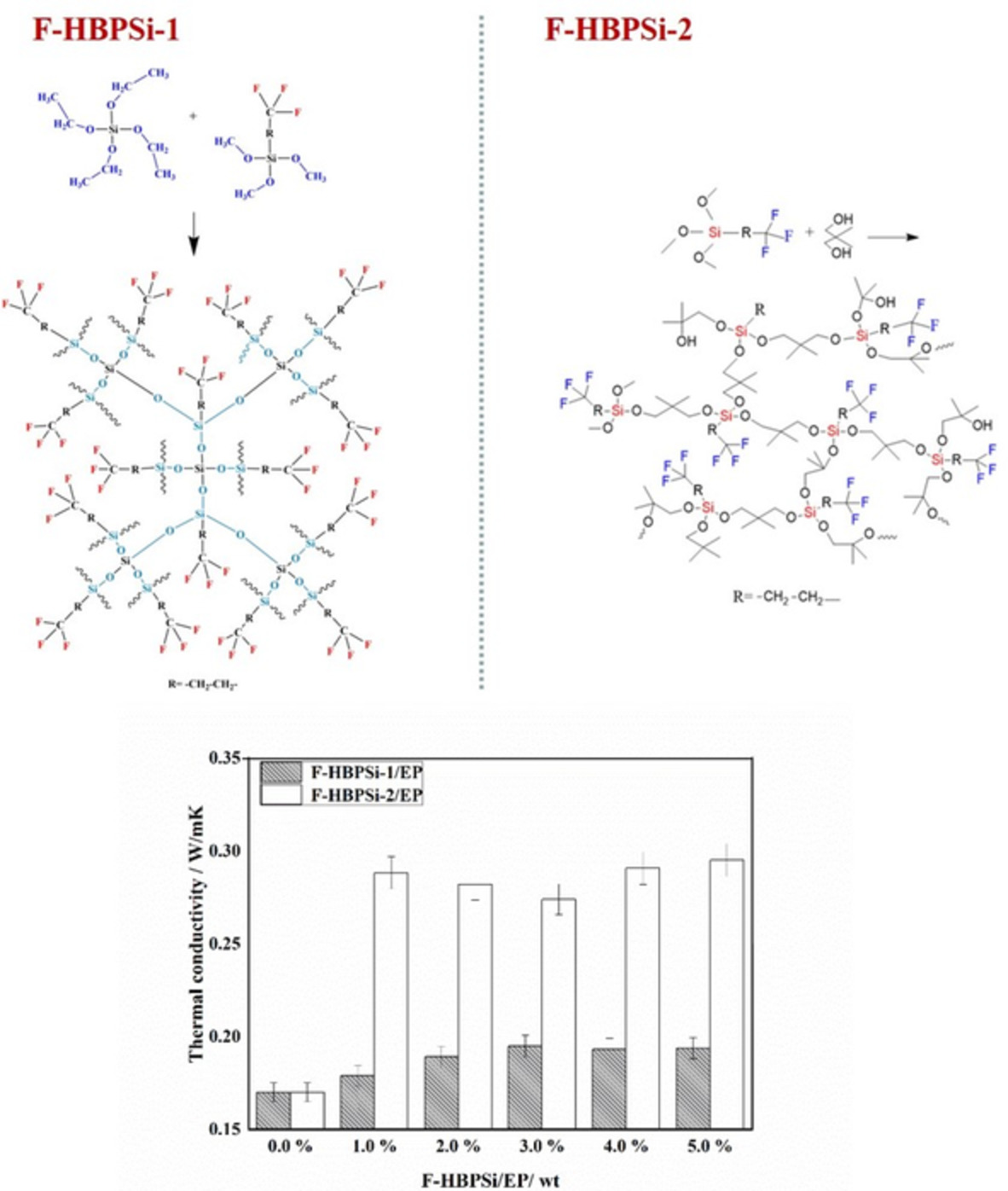
Synthesis of fluorine contained hyperbranched polysiloxane and their effect on the thermal conductivity of epoxy resins
- First Published: 05 November 2022
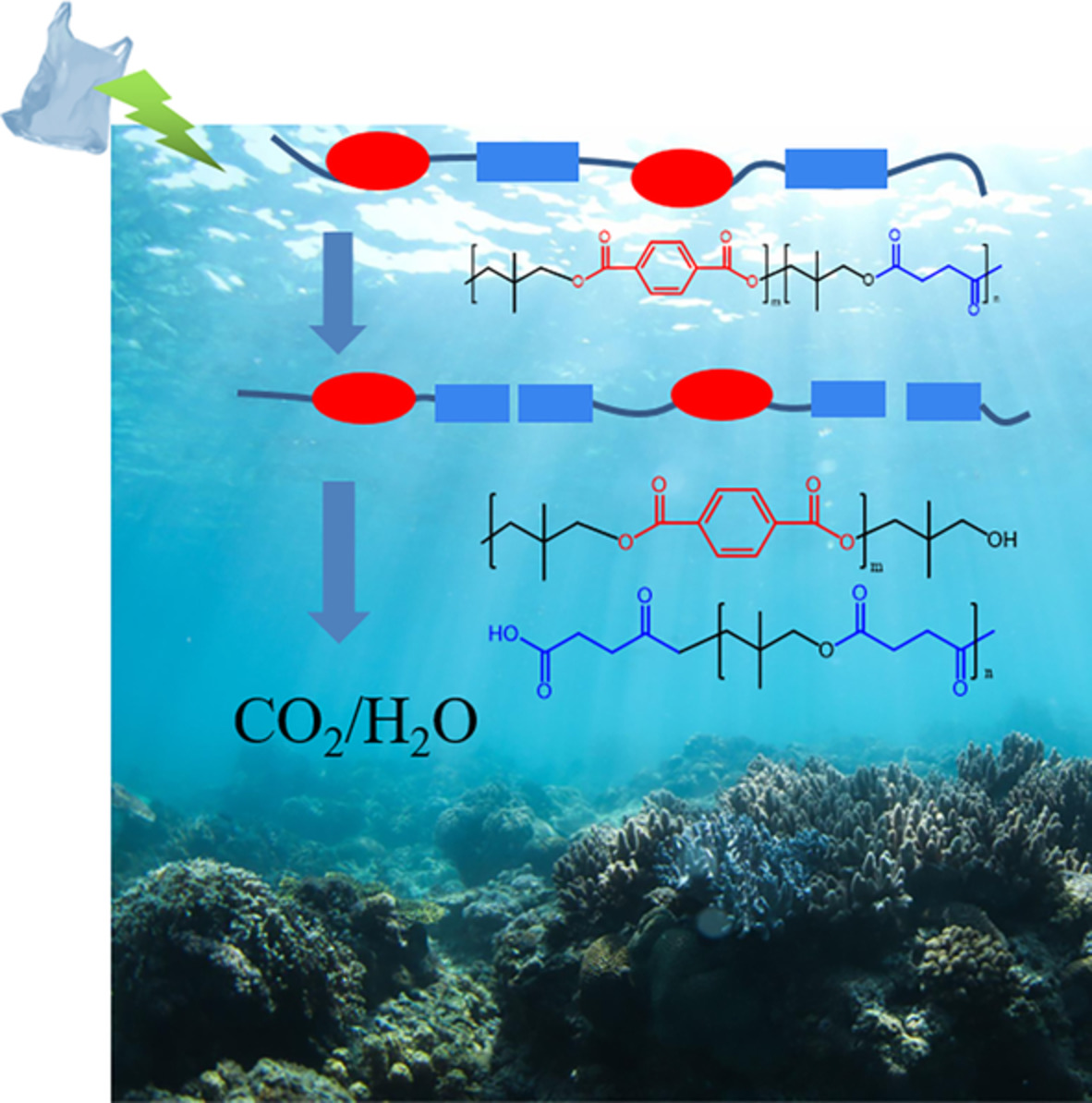
High performance and water-degradable poly(neopentyl terephthalate-co-neopentyl succinate) copolymers: Synthesis, properties, and hydrolysis in different aquatic bodies
- First Published: 05 November 2022
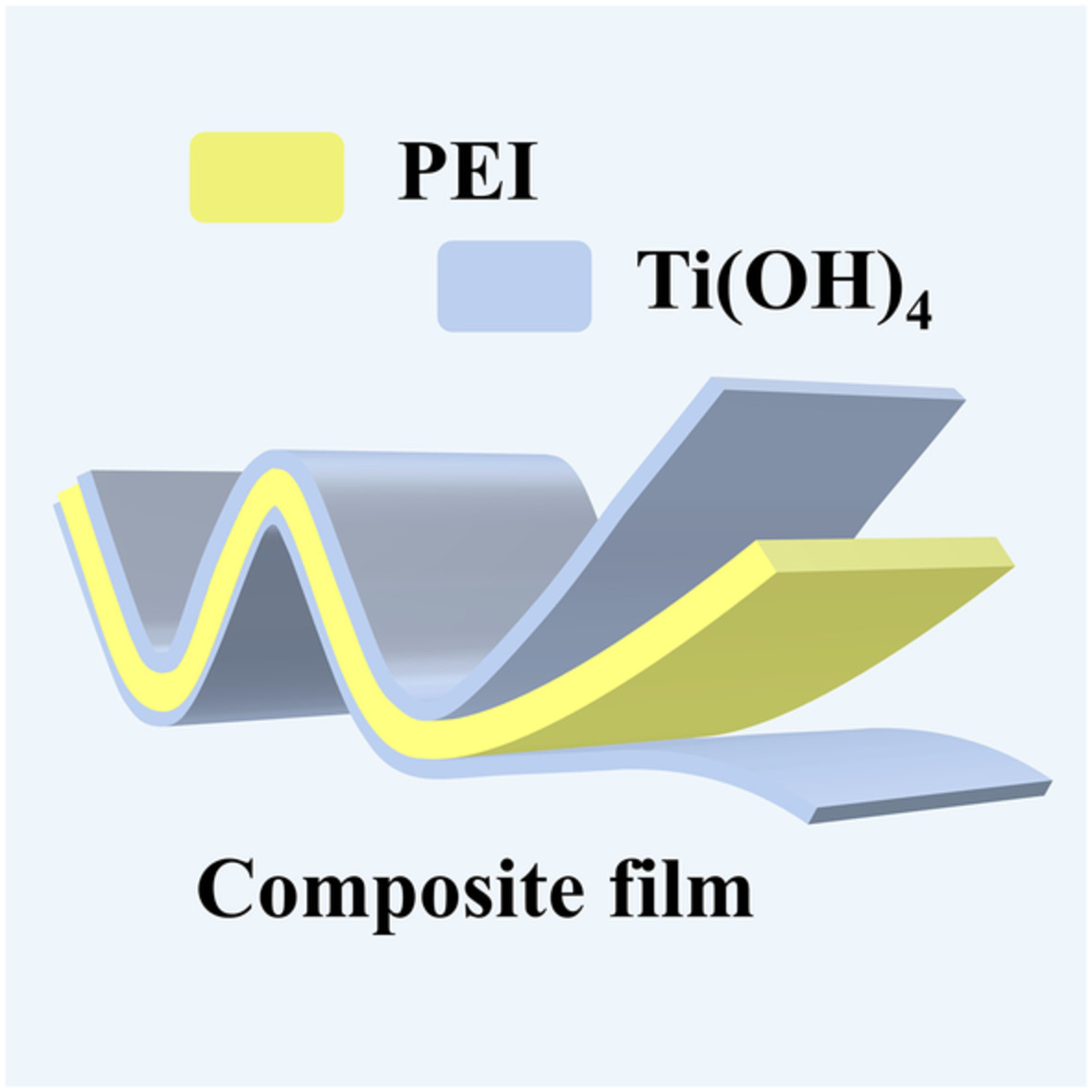
Optimization of high temperature energy storage properties of PEI-based composite dielectric based on rapid in-situ growth of inorganic functional layer
- First Published: 11 November 2022
DMTMM-mediated grafting reaction of glucuronic acid on chitosan
- First Published: 09 November 2022
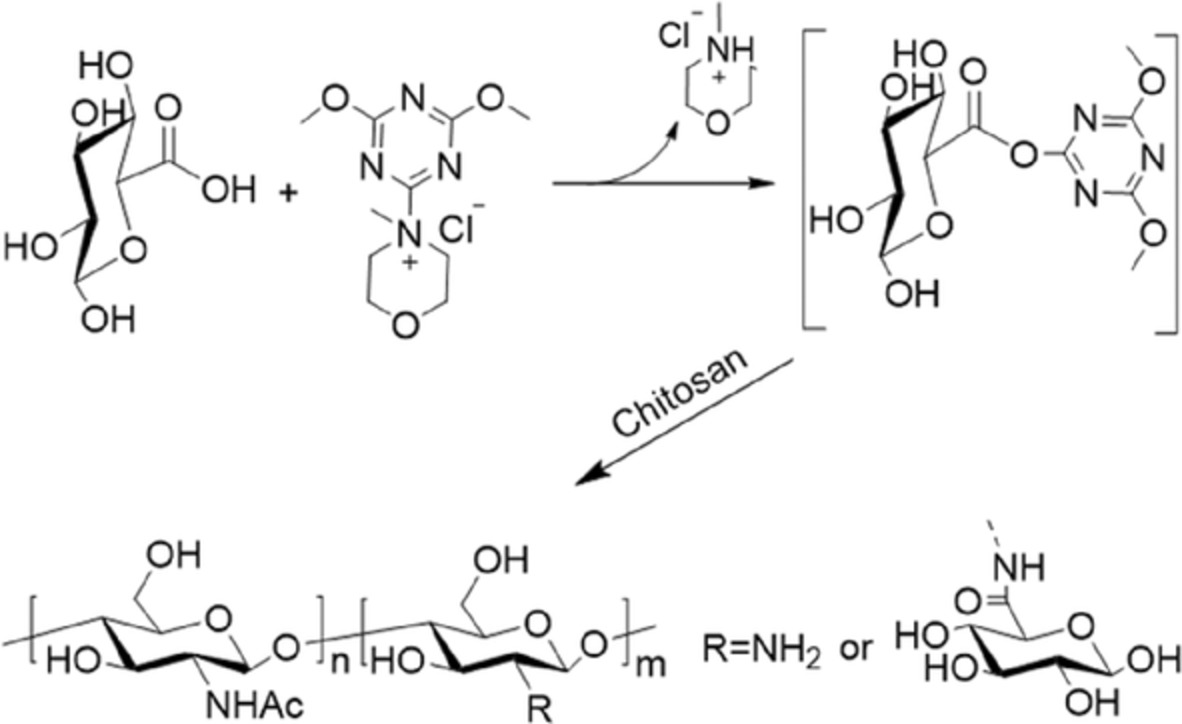
The 4-(4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazin-2-yl)-4-methylmorpholinium chloride (DMTMM) was employed to conduct the grafting of glucuronic acid (GA) on chitosan (CS) in an aqueous medium to generate a GA-CS derivative. A mechanism of condensation was described, and the structure of GA-CS was characterized. Finally, the grafting efficiency and reaction kinetics of the amidation of CS were investigated.
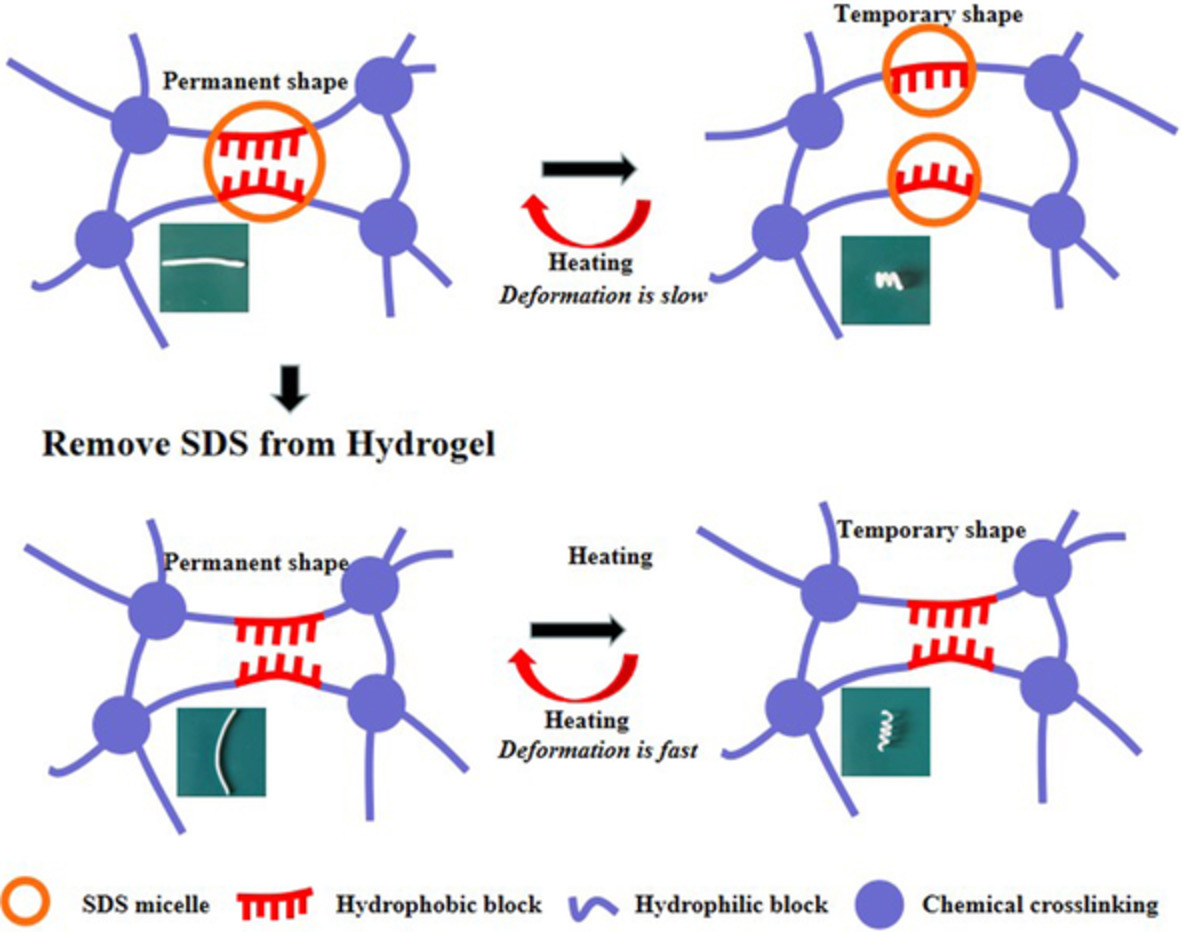
Effect of sodium dodecyl sulfate on shape-memory properties of side-chain crystalline hydrogel via micellar copolymerization
- First Published: 04 November 2022
Imine-linked covalent organic frameworks coordinated with nickel for ethylene oligomerization
- First Published: 08 November 2022
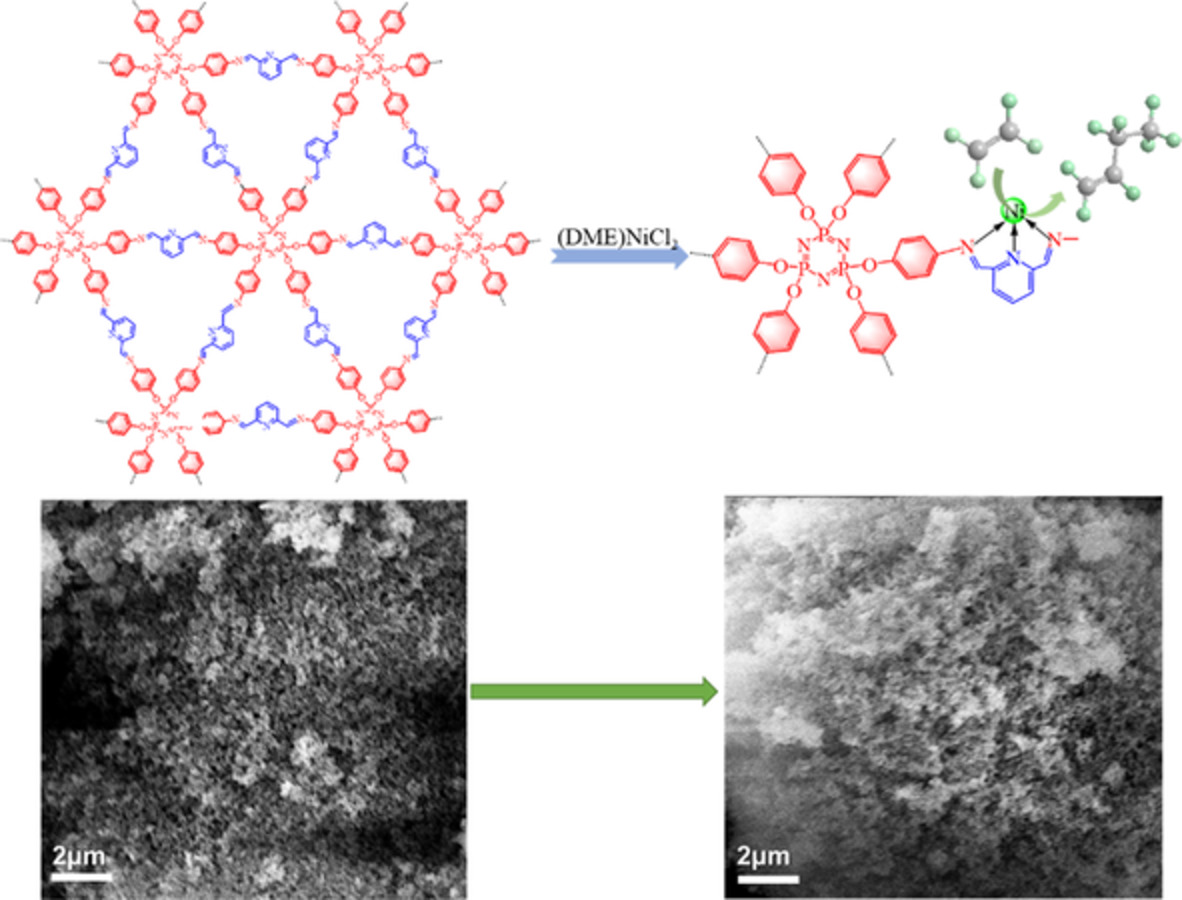
An imine-linked covalent organic frameworks (COFs) material (COF-PD) with abundant nitrogen atoms and large surface area was synthesized to provide coordination active site and facilitate the incorporation of COFs with nickel ions to form nickel-coordinated COF-PD complex (COF-PD-Ni). The large surface area of COF-PD-Ni was far lower than that of COF-PD before loading nickel because of pore blockage caused by the coordination of Ni2+. COF-PD-Ni displayed excellent catalytic activity with a strong preference for the 1-butene in ethylene oligomerization, which attributed to the faster rate of chain transferring process than the chain propagation because of the confinement effect aroused by pore features of covalent organic frameworks.
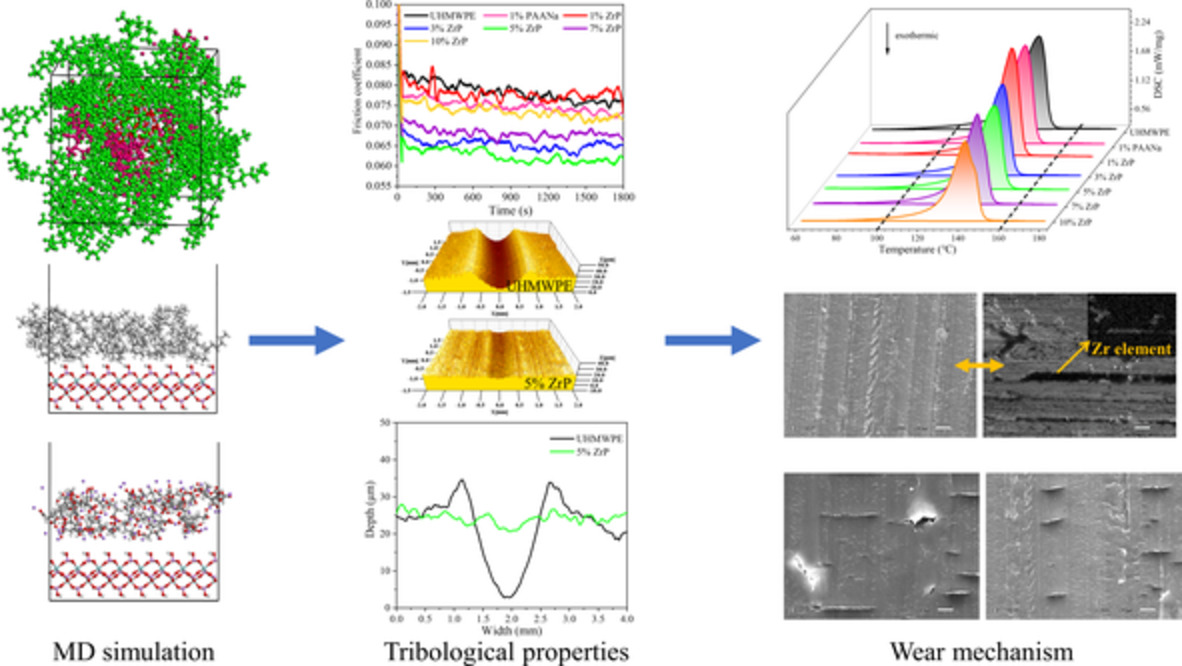
Molecular dynamics simulation of α-ZrP/UHMWPE blend composites containing compatibilizer and its tribological behavior under seawater lubrication
- First Published: 02 November 2022
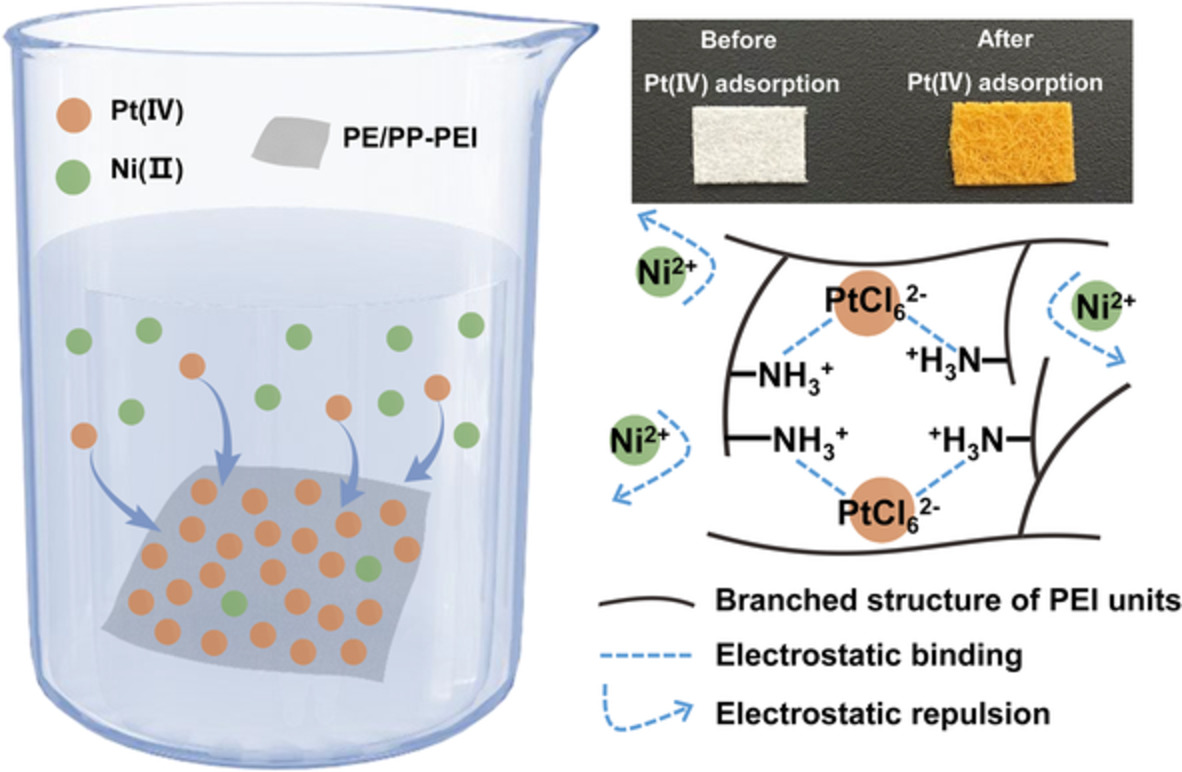
Highly selective adsorption of Pt(IV) from spent catalyst by polyethyleneimine functionalized polyethylene/polypropylene non-woven fabric
- First Published: 07 November 2022
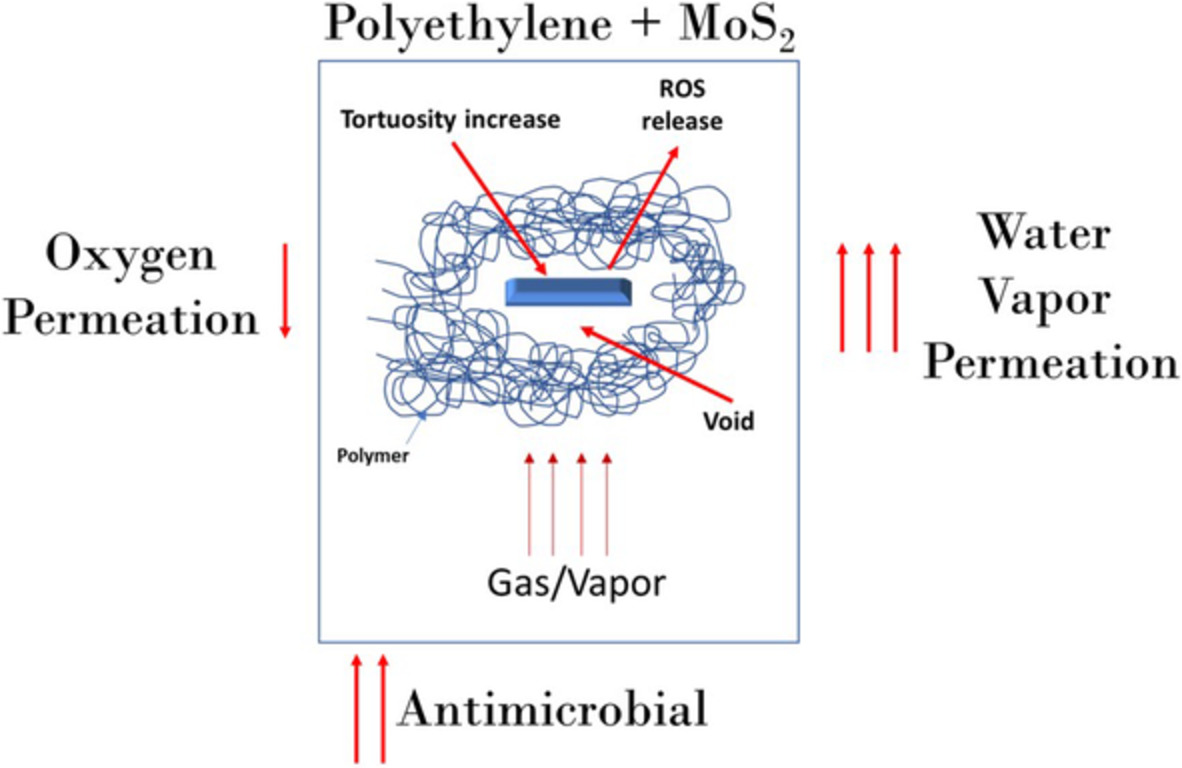
Polyethylene with MoS2 nanoparticles toward antibacterial active packaging
- First Published: 05 November 2022
Effect of natural biomass fillers on the stability, degradability, and elasticity of crop straws liquefied polyols-based polyurethane foams
- First Published: 03 November 2022
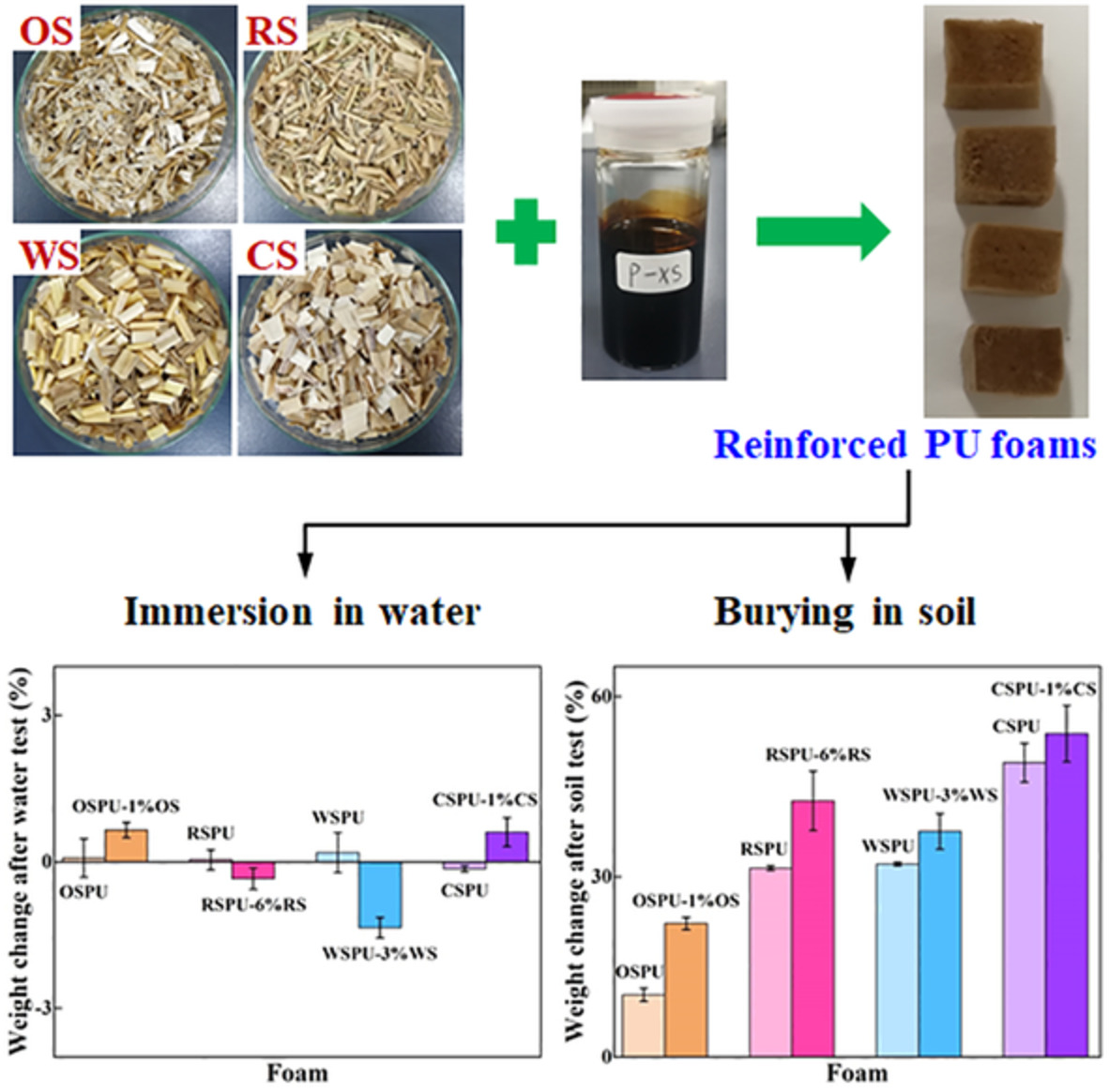
Oilseed rape straw (OS), rice straw (RS), wheat straw (WS), and corn stover (CS) particles were used to reinforce four sets of bio-polyols based polyurethane (PU) foams. The XS (OS, RS, WS, CS) reinforced foams displayed excellent stability in water, degradability in soil, thermal stability, and elastic ability, showing special applying potential in fields of degradable plastic, insulation, and elastomer.
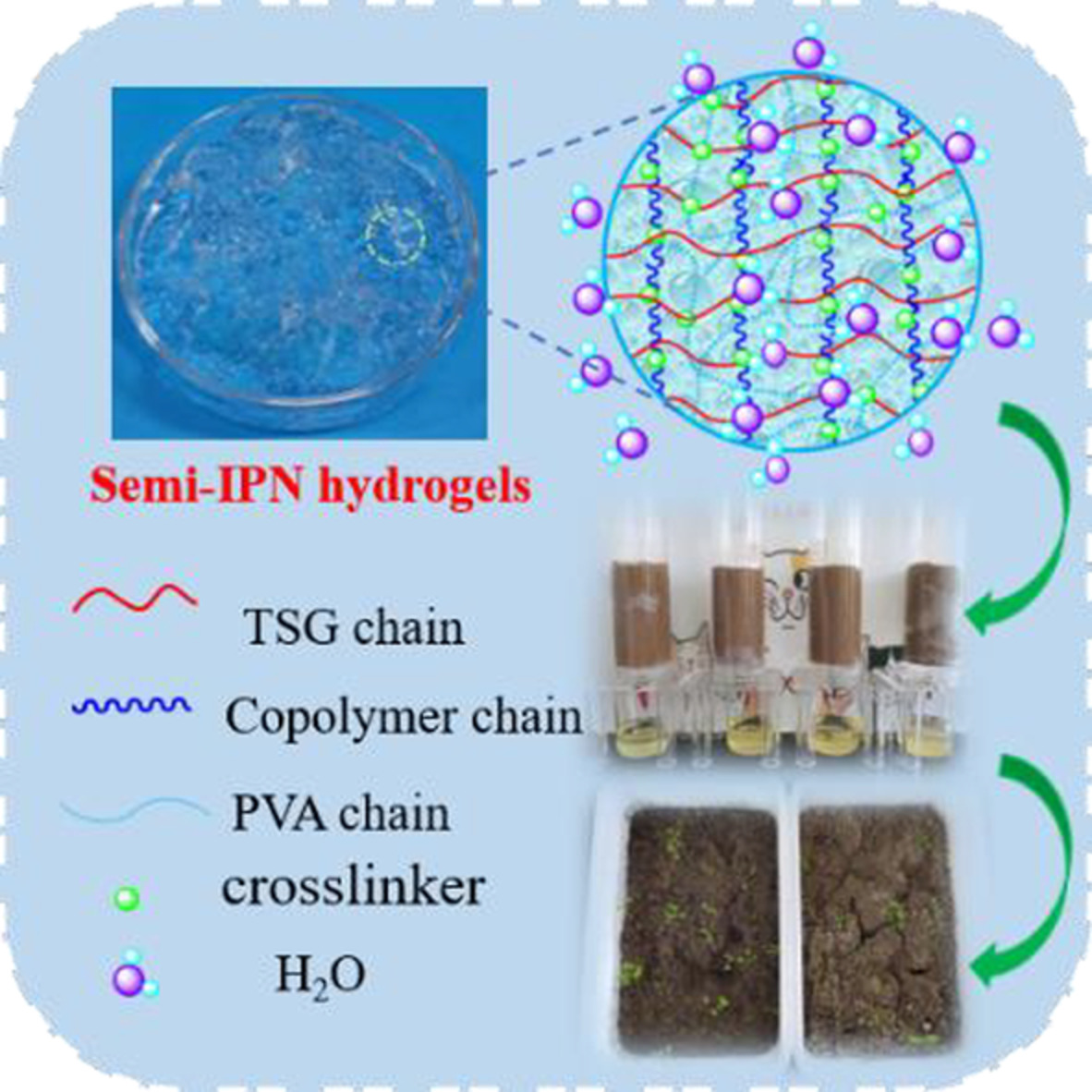
Synthesis of tamarind seed gum-based semi-IPN hydrogels with integration of fertilizer retention and anti-evaporation
- First Published: 03 November 2022
Effect of hyperbranched poly(trimellitic glyceride)/oxidized starch composite sizing agent on the adhesion of polyester yarns
- First Published: 03 November 2022
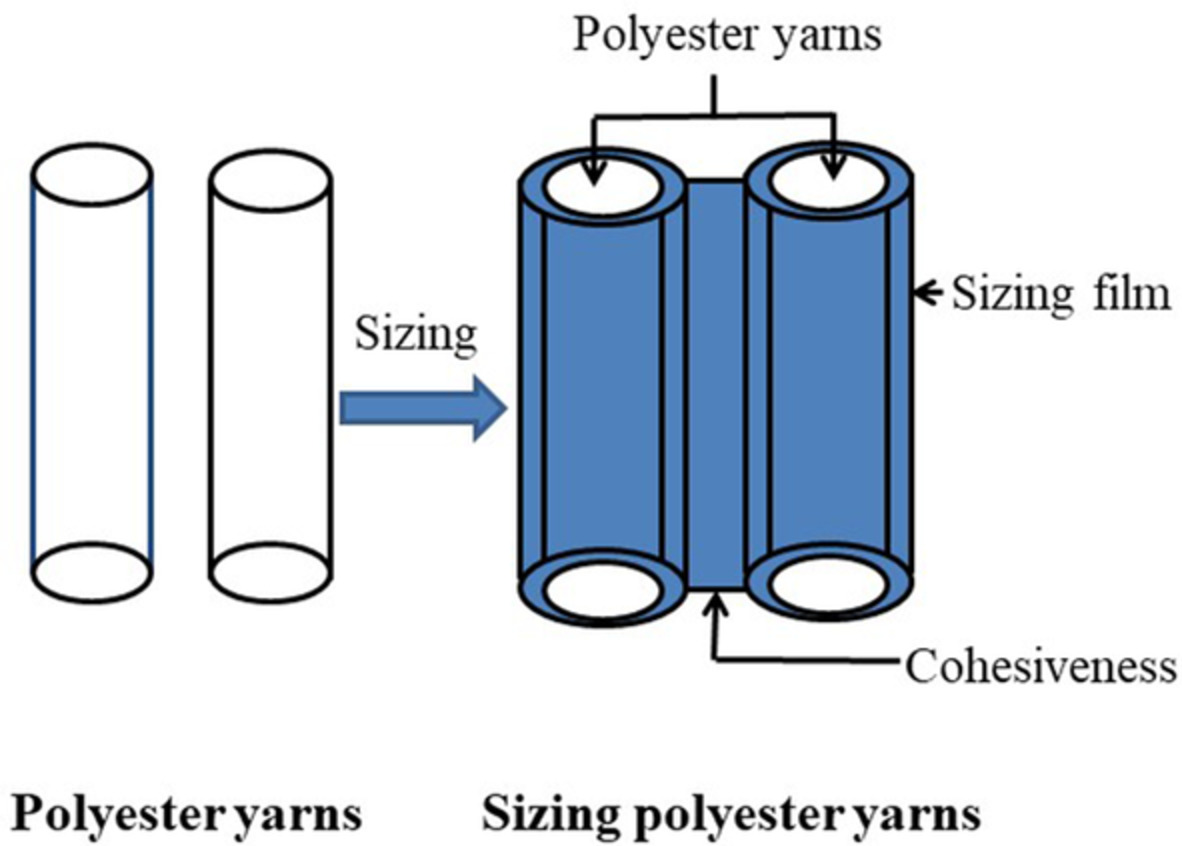
The synthesized hyperbranched poly(trimellitic glyceride) (PTG) improved the affinity of oxidized starch (OS) and PET yarns verified by mechanical properties, FT-IR, XPS, and SEM. Besides, PTG decreased apparent viscosity but increased viscosity stability of OS paste. The bigger the PTG molecular, the better.
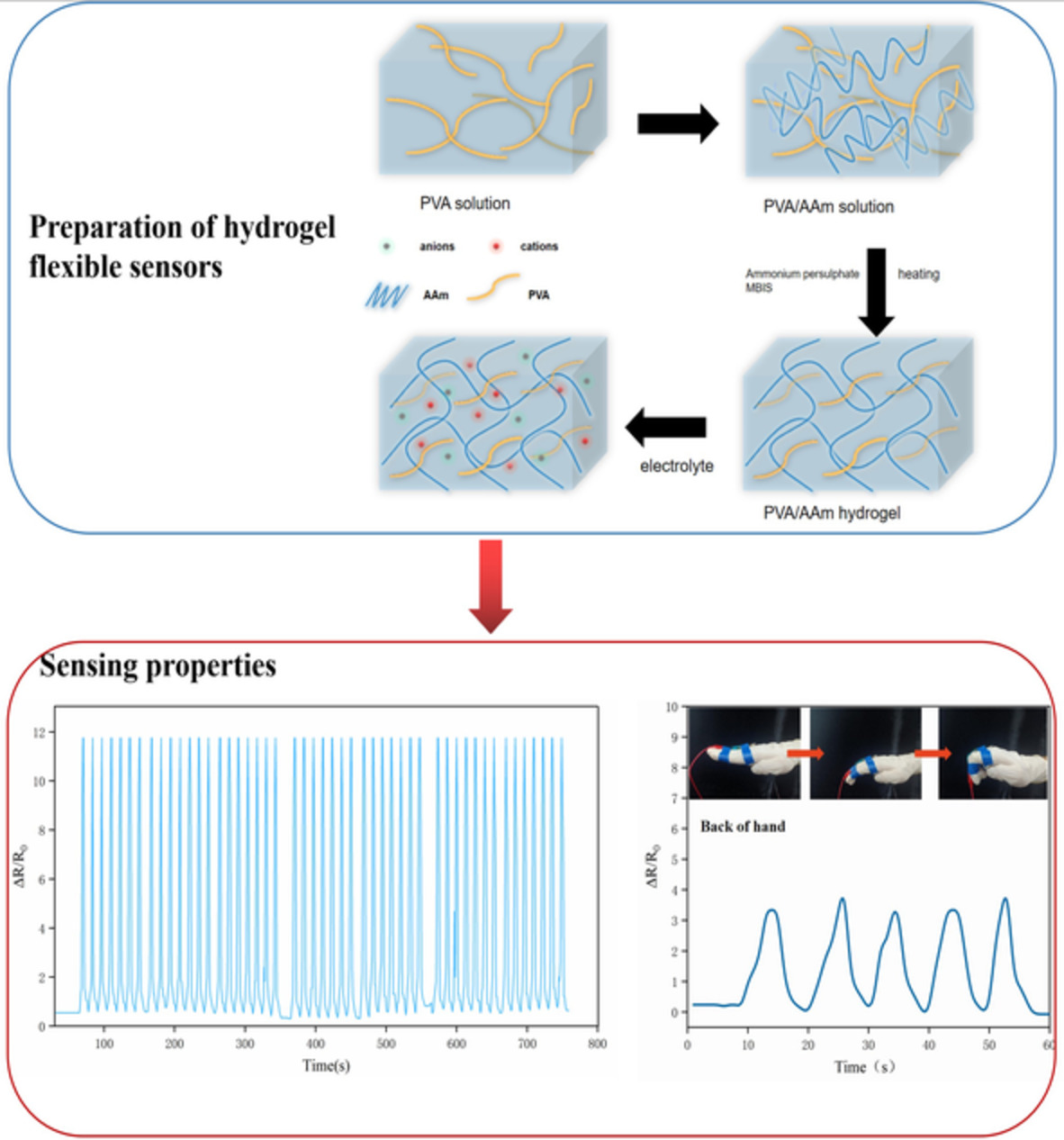
Conductive double-network hydrogel for a highly conductive anti-fatigue flexible sensor
- First Published: 10 November 2022
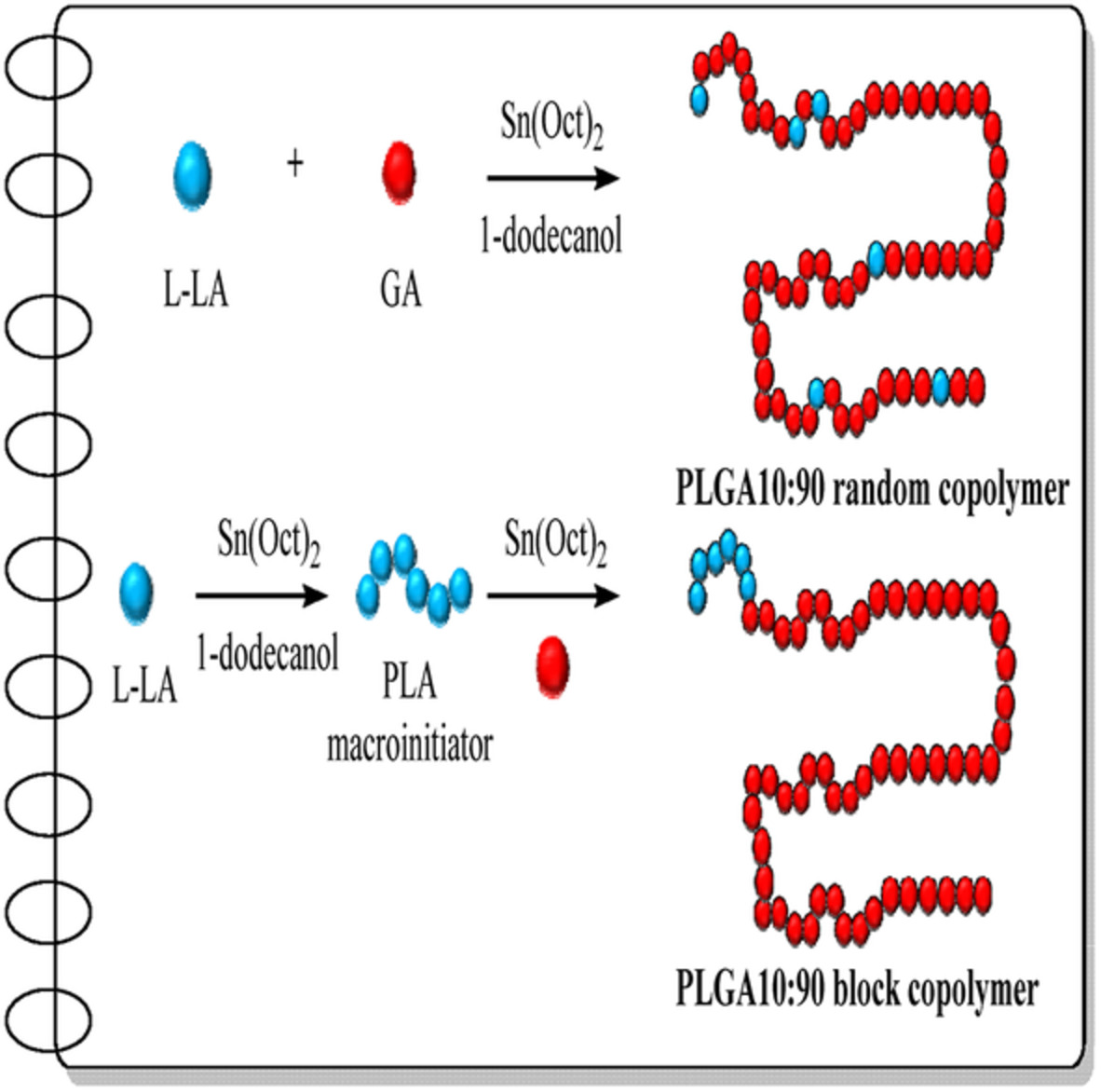
Synthesis of poly(lactide-co-glycolide) containing high glycolide contents by ring-opening polymerization as well as their structural characterizations, thermal properties, morphologies, and hydrophilicity
- First Published: 04 November 2022
Preparation and derivation mechanism of methyl methacrylate/nitrile butadiene rubber/graphene oxide composites by ball-milling
- First Published: 05 November 2022
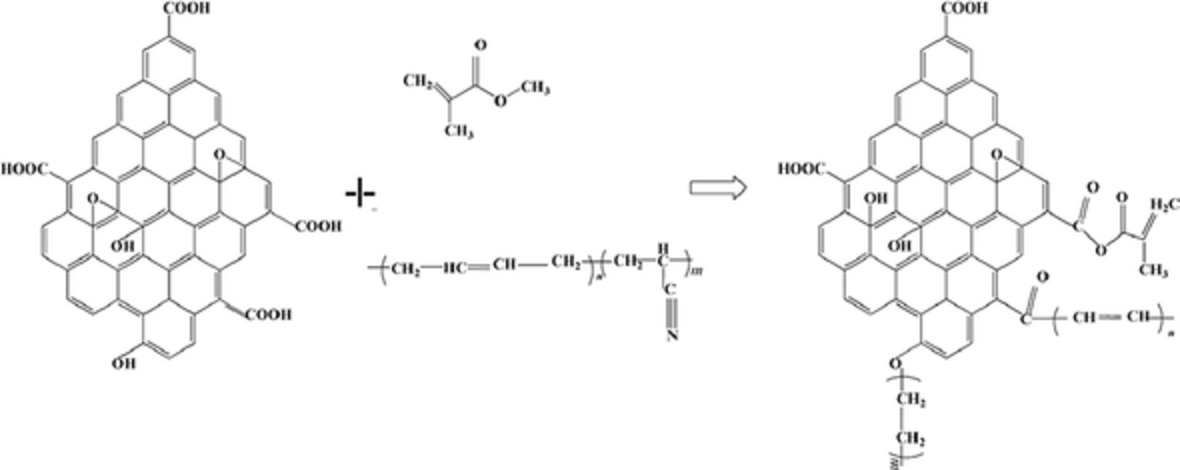
MMA/NBR/GO composite materials were prepared by ball-milling based on the mechano-chemical principle. The effects of some key process parameters, such as graphene oxide (GO) content, ball-to-powder ratio (BPR), and ball-milling time on textures and structures of MMA/NBR/GO composite materials were studied, and the derivation mechanism was examined. The results indicated composite materials with excellent dispersion stability at GO content of 0.3%, BPR of 3.87, and ball-milling time of 5 h. Under these conditions. The derivation mechanism of MMA/NBR/GO composites is the carboxyl group of GO and hydroxyl group on the benzene ring broke, and GO was then grafted onto NBR and MMA to realize stable dispersion of GO in organic media. For instance, the grafting on NBR occurred at levels of CN and CH2, meaning the presence of CC bond of >CHCN group in NBR and breakage of CC bond in CH2CH2 group. The grafting on MMA took place at CH3, meaning breakage of CO bond in CH3O group of MMA. The structural diagram of the product is provided in Figure 1.
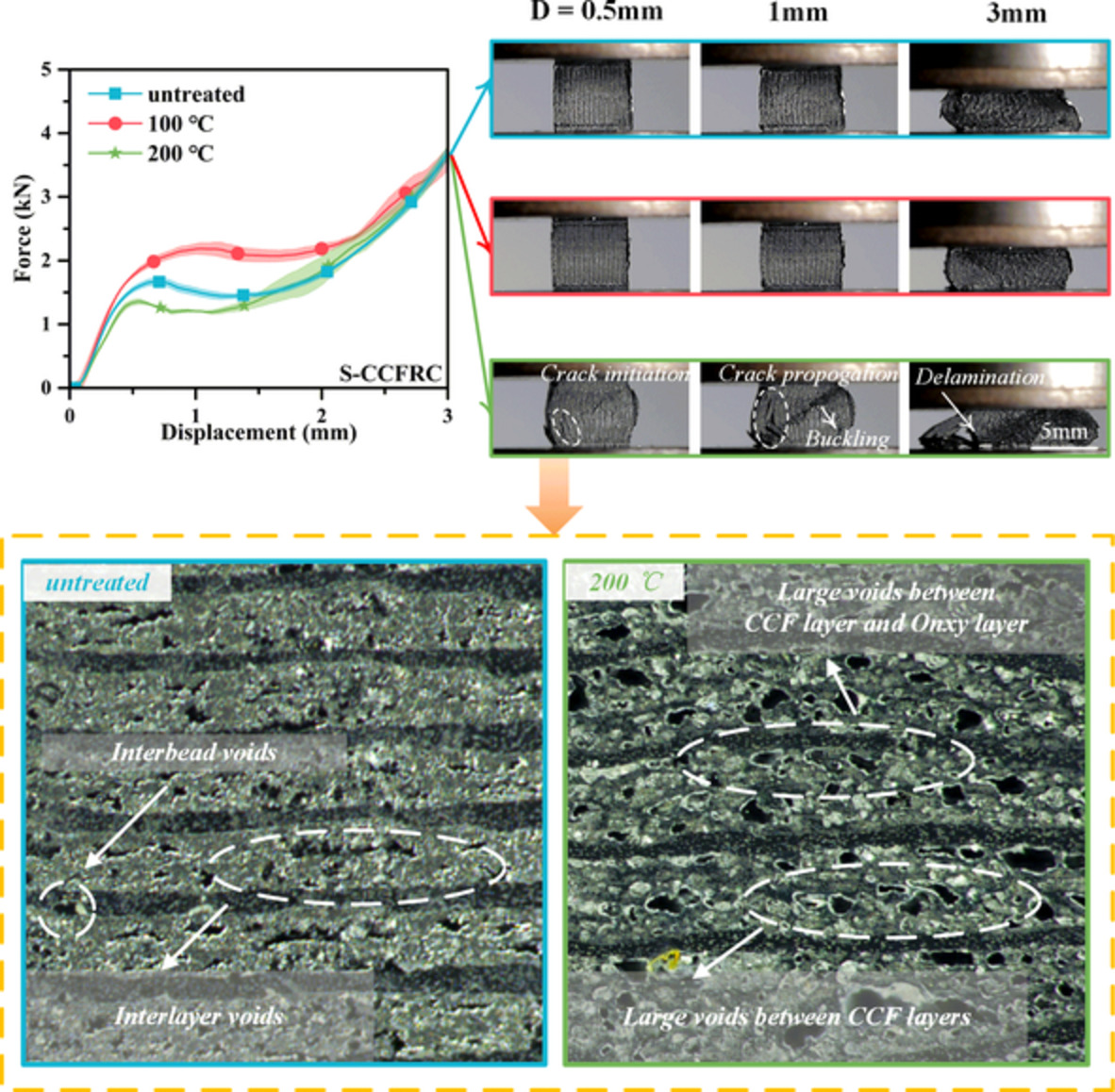
Effect of heat-treatment on compressive response of 3D printed continuous carbon fiber reinforced composites under different loading directions
- First Published: 03 November 2022
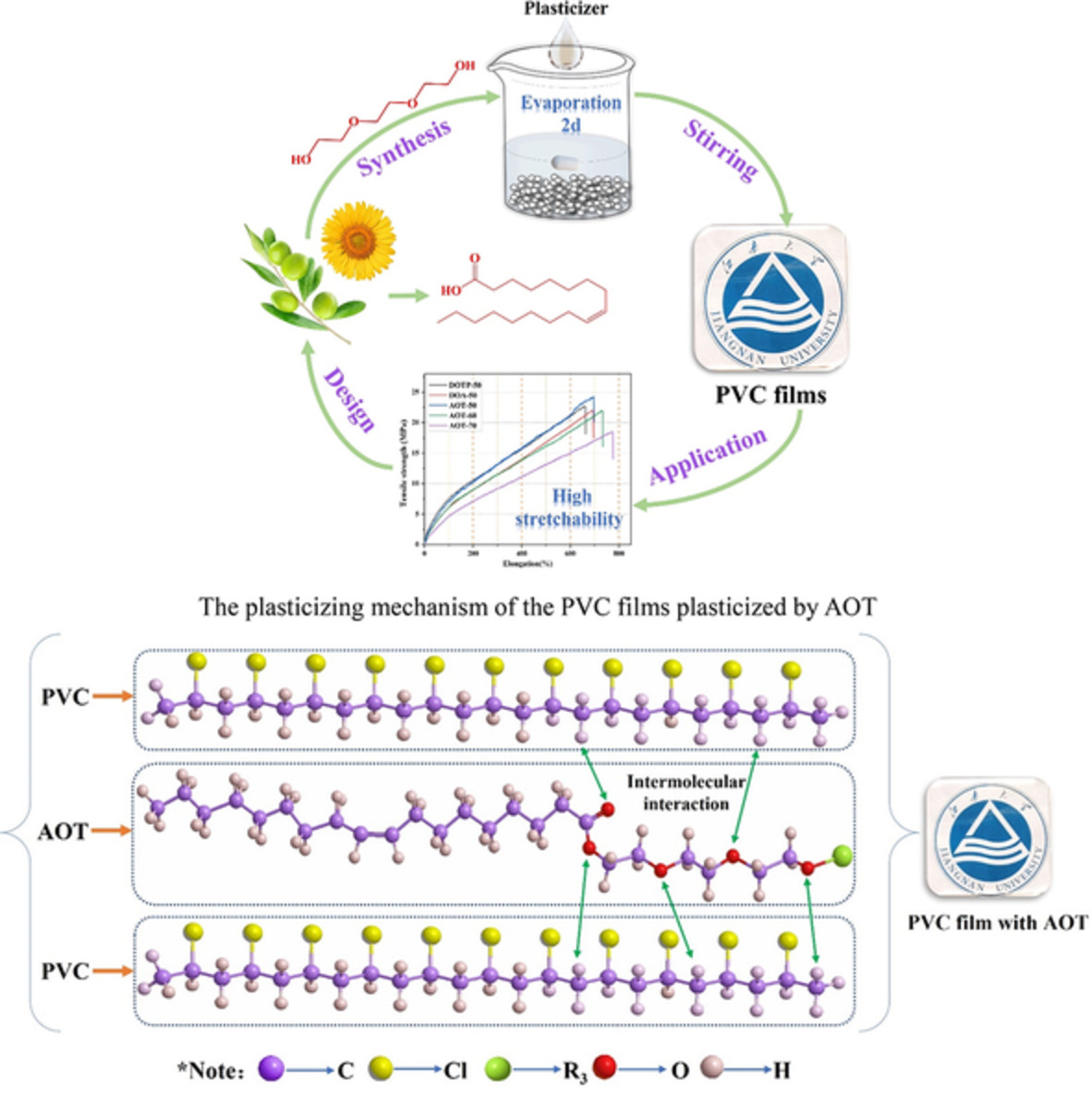
Synthesis and evaluation of epoxidized vegetable oleic acid as a novel environmental benign plasticizer for polyvinyl chloride
- First Published: 08 November 2022
Ovalbumin has unusually good wood adhesive strength and water resistance
- First Published: 02 November 2022
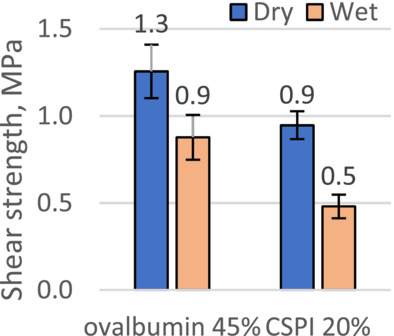
Ovalbumin dissolved in water has a surprising low viscosity at a high concentration and is a high wet strength wood adhesive, because it is high in protein. The wet strength was determined with ovalbumin-bonded plywood using a standard test and compared to soy protein which can have high wet strength if it is modified.
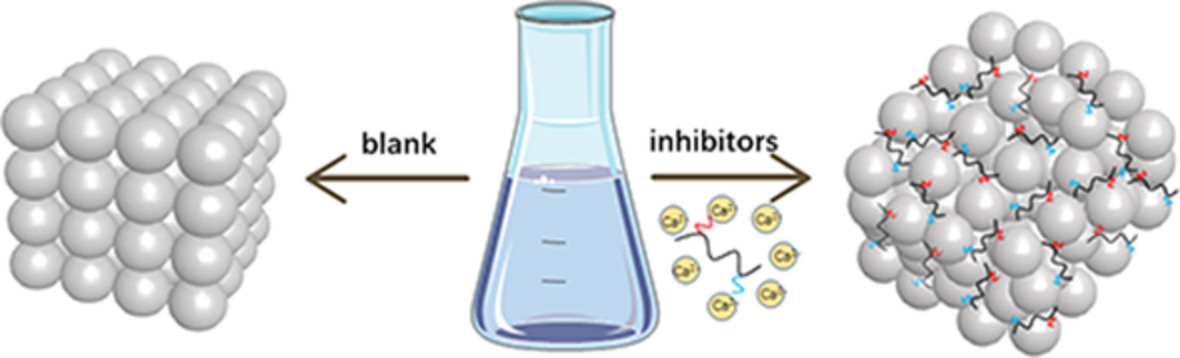
Synthesis and performance evaluation of carboxyl-rich low phosphorus copolymer scale inhibitor
- First Published: 05 November 2022
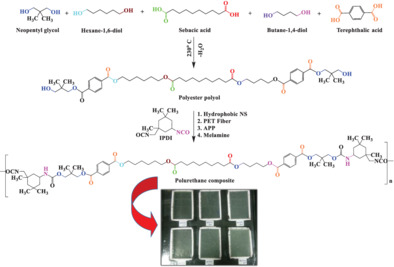
Effect of polyethylene terephthalate fiber reinforced with non-hydrophilic nano-silica on the mechanical, thermic, and chemical shielding characteristics of saturated polyurethane composite
- First Published: 09 November 2022
Variation in adhesion properties and film morphologies of waterborne pressure-sensitive adhesives containing an acid-rich diblock copolymer additive
- First Published: 09 November 2022
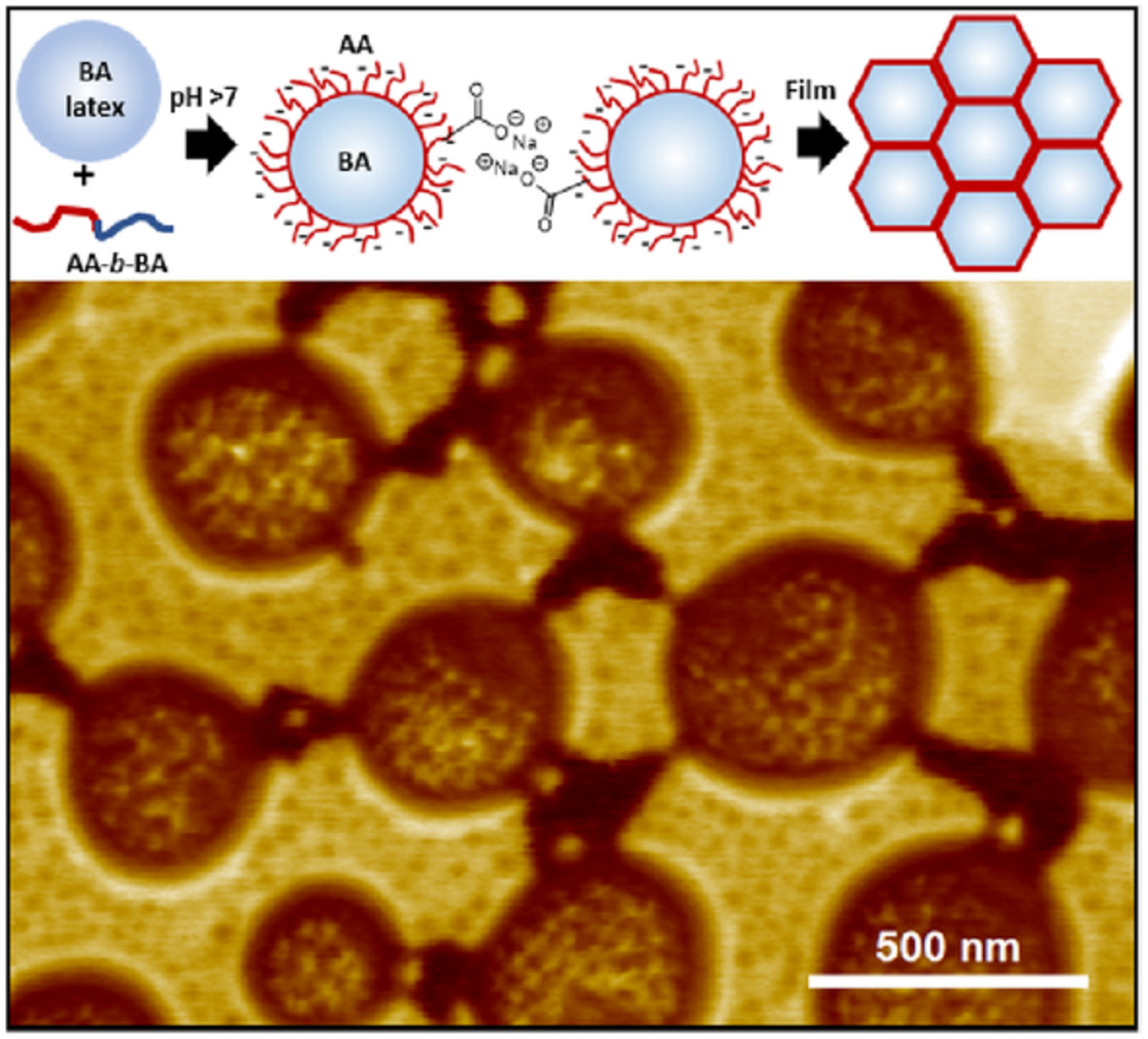
Pressure-sensitive adhesive (PSA) films containing percolated structures can exhibit increased elastic modulus and extensibility. A percolated film morphology is observed from the addition of 5 wt% of poly(acrylic acid)-block-(n-butyl acrylate) to poly(butyl acrylate)-based waterborne acrylic emulsion PSAs. Diverse morphologies are achieved under industrially relevant film preparation conditions and in some cases result in PSAs with simultaneously improved adhesion and cohesion.
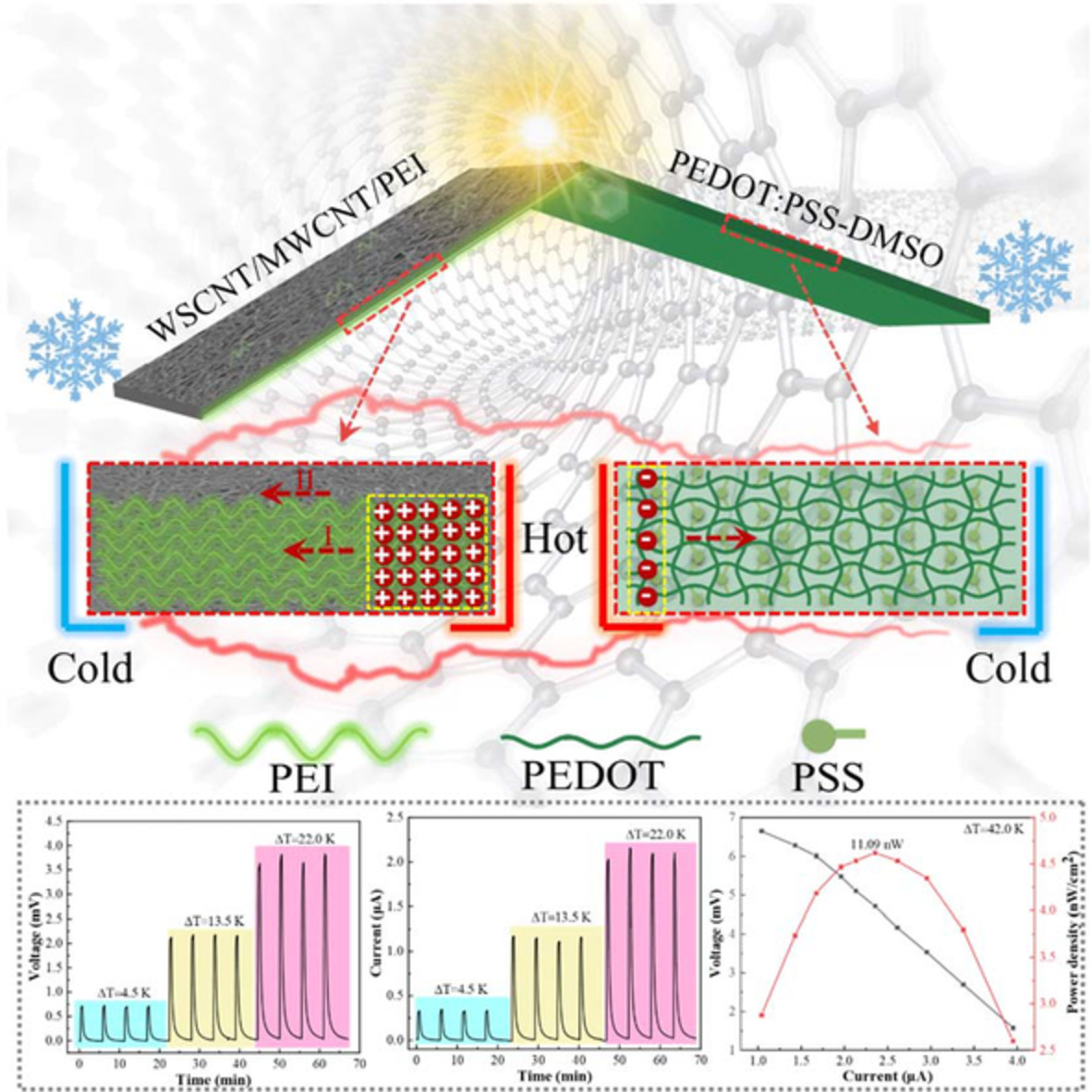
Energy harvesting and temperature sensing thermoelectric devices based on the carbon template method
- First Published: 03 November 2022
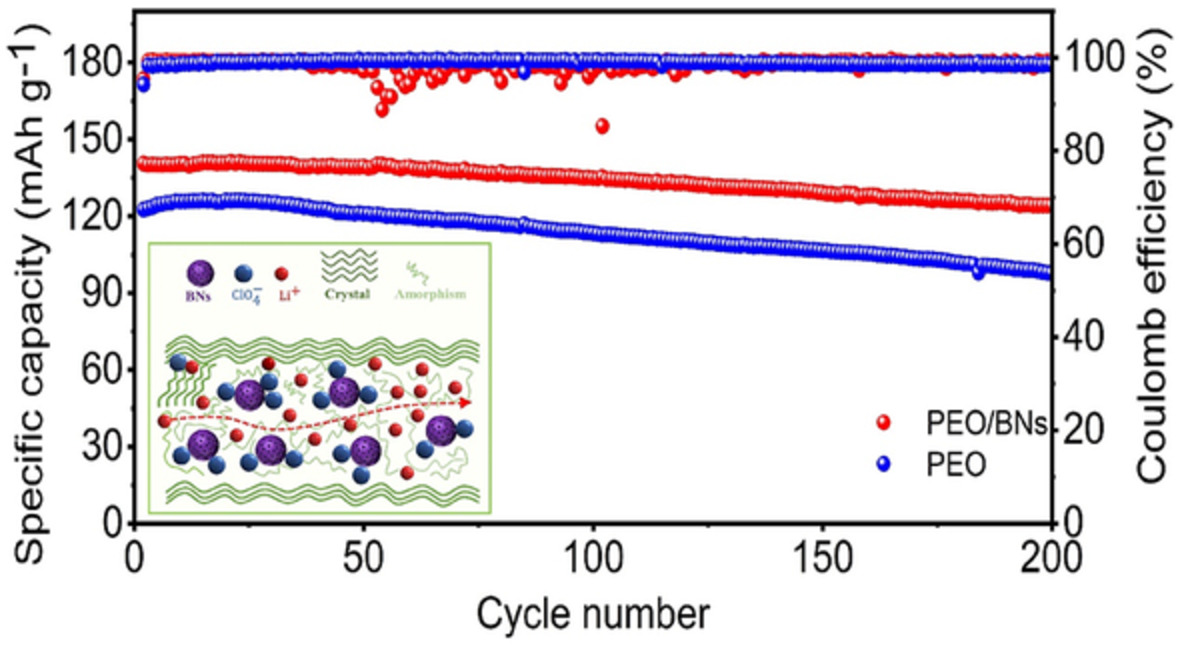
Nanocomposite polymer electrolytes for solid-state lithium-ion batteries with enhanced electrochemical properties
- First Published: 03 November 2022
Preparation and evaluation of acryloyl morpholine modified emulsion fracturing fluid thickener with high temperature resistance and salt resistance
- First Published: 17 November 2022
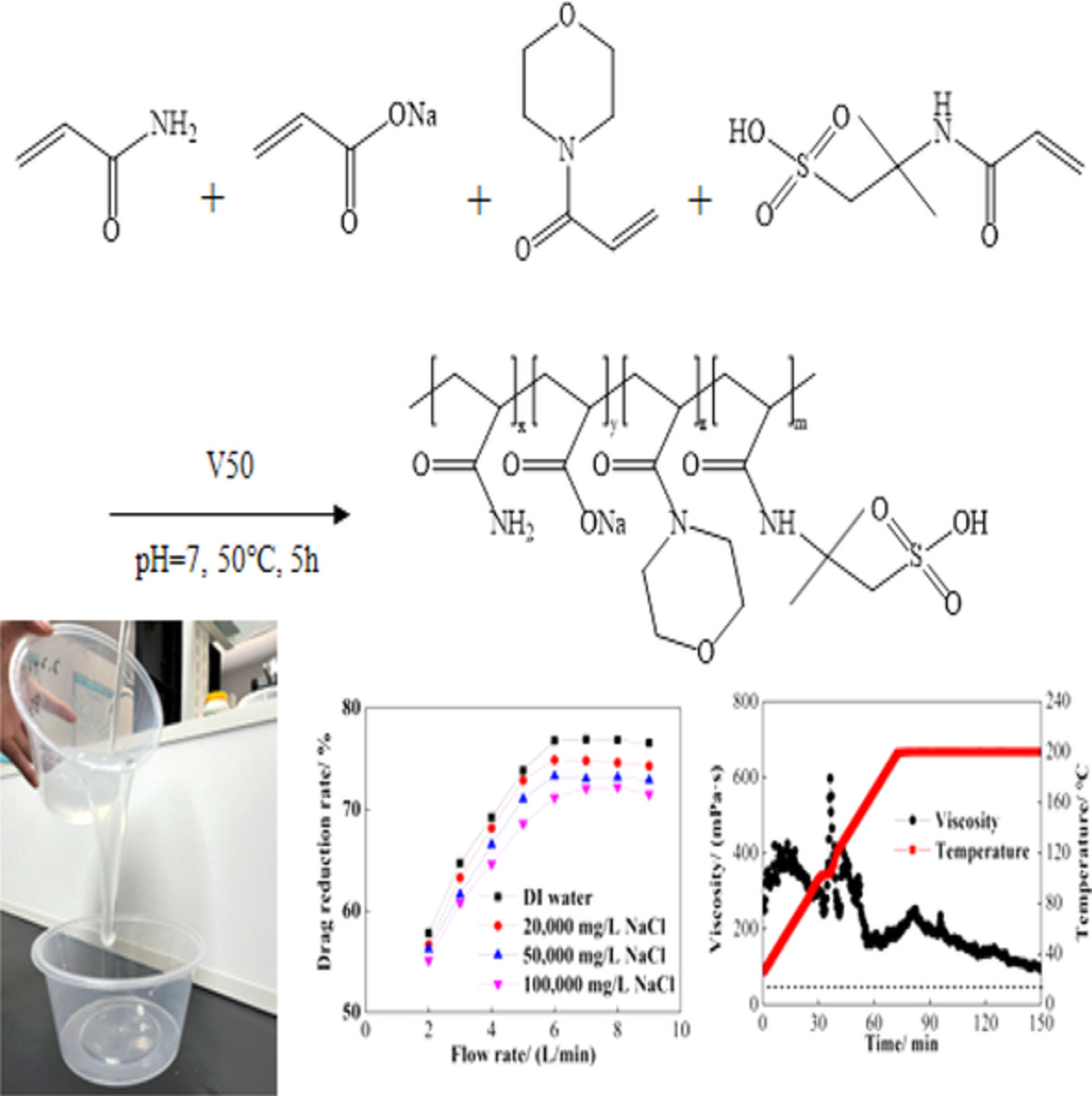
A new type of emulsion polymer thickener ASC with high temperature resistance, salt resistance, quick dissolution and high drag reduction at the same time was prepared, 2-acrylamide-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid and acryloyl morpholine were introduced to improve the temperature resistance and salt resistance of ASC. The thickener ASC could be used as a multi-functional fracturing fluid, it played a slick water role in drag reduction effect at low polymer concentration (0.08–0.12 wt%), and it played a high viscosity fracturing fluid role in sand carrying effect at high polymer concentration (2.0 wt%) used together with organic zirconium crosslinker for ultra-high temperature reservoirs even at 200°C and salinity of 100,000 mg/L, which could meet the application requirements under ultra-high temperature reservoirs.
Studies on the reactivity of epoxy/polyol/isocyanate blend resins and the properties of epoxy/polyurethane composites
- First Published: 09 November 2022
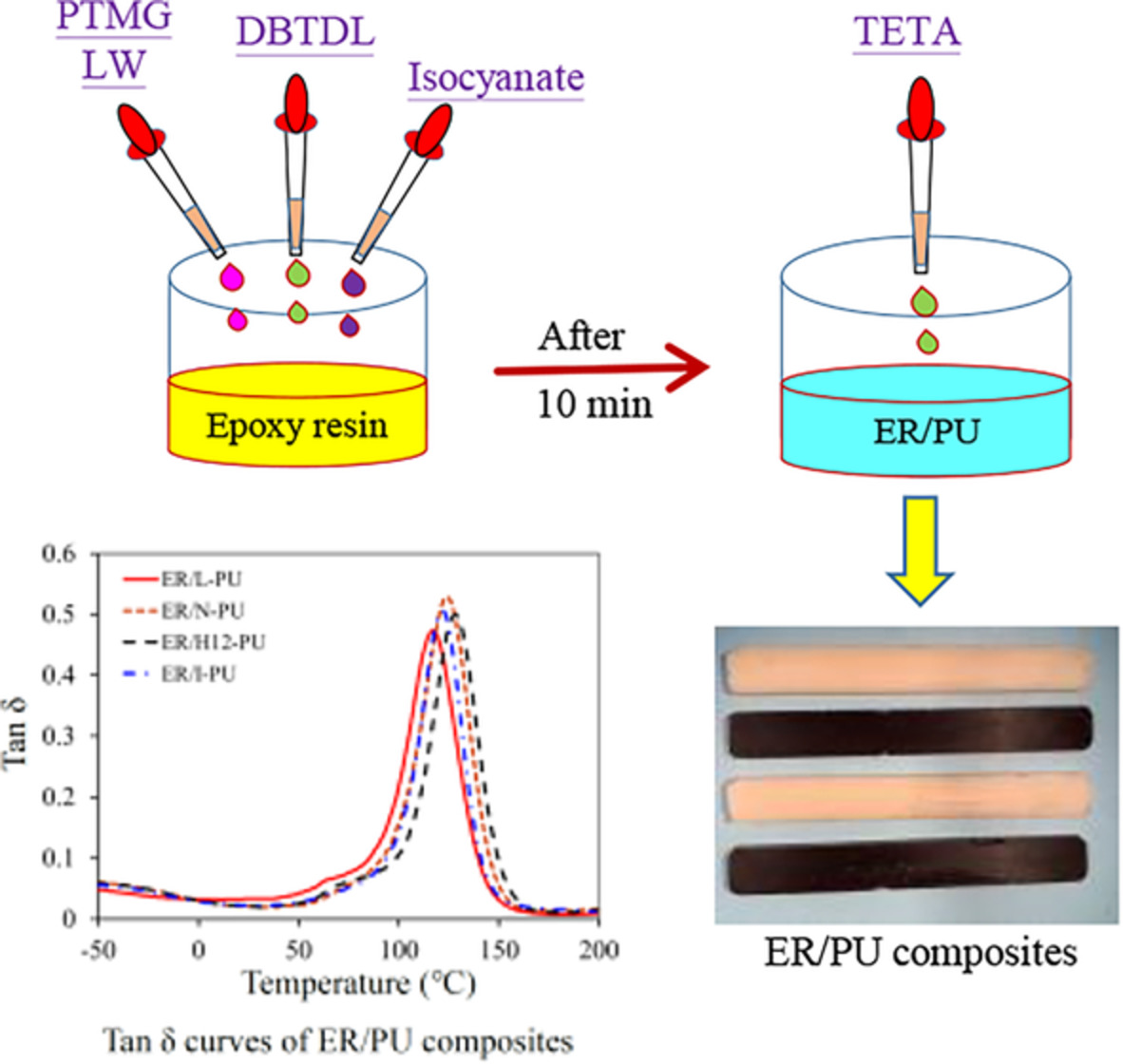
Different polyols (PTMG and LW) and isocyanate (IPDI, H12-MDI, Desmodur N, and Desmodur L) are added directly to epoxy resin, the reactivity of epoxy/polyol/isocyanate blended resins and the properties of ER/PU composites are investigated. The results show that the ER resin and the PU not only form a physical interpenetrating structure, but also undergo a copolymerization crosslinking reaction.
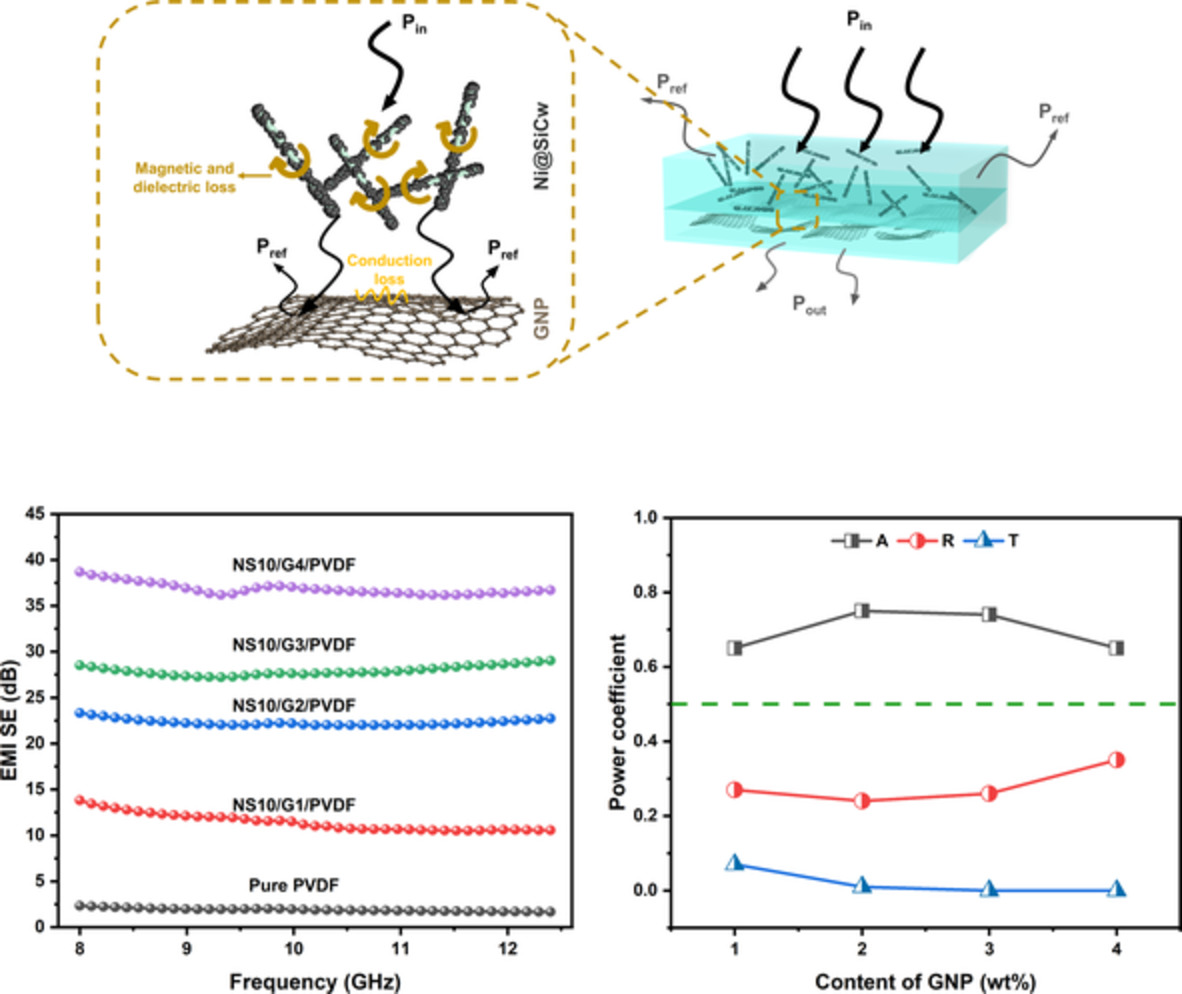
Asymmetrically structured polyvinylidene fluoride composite for directional high absorbed electromagnetic interference shielding
- First Published: 15 November 2022
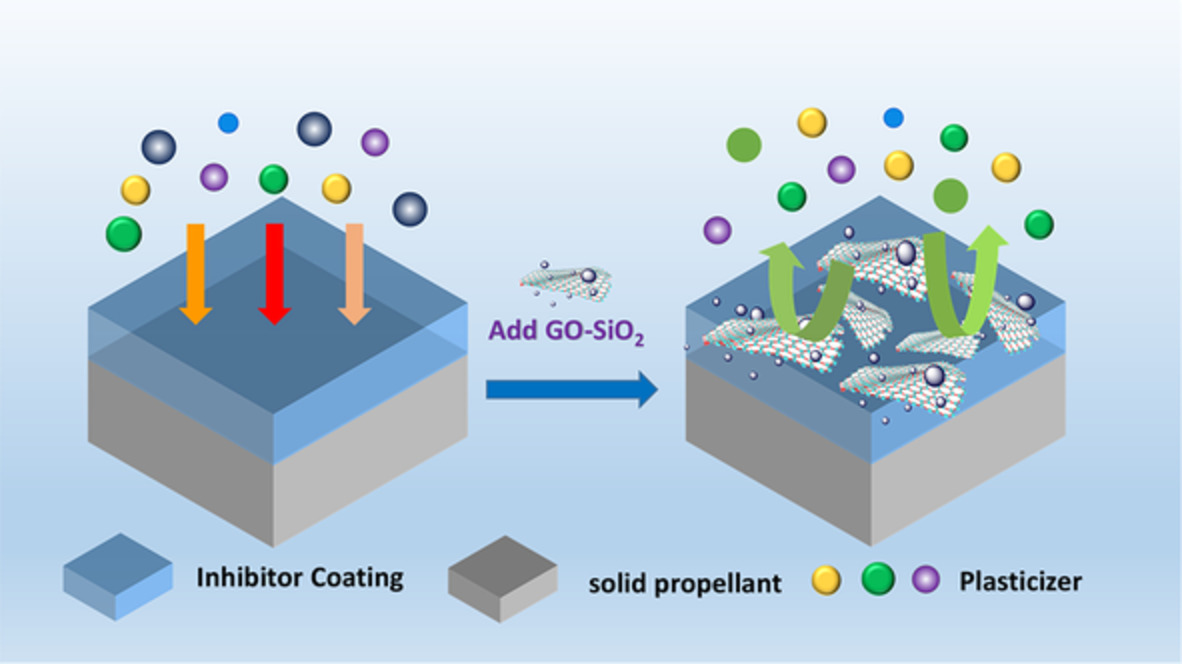
Preparation and anti-migration performance of ethylene propylene diene terpolymer composites modified with GO-SiO2 hybrid nanomaterials
- First Published: 03 November 2022
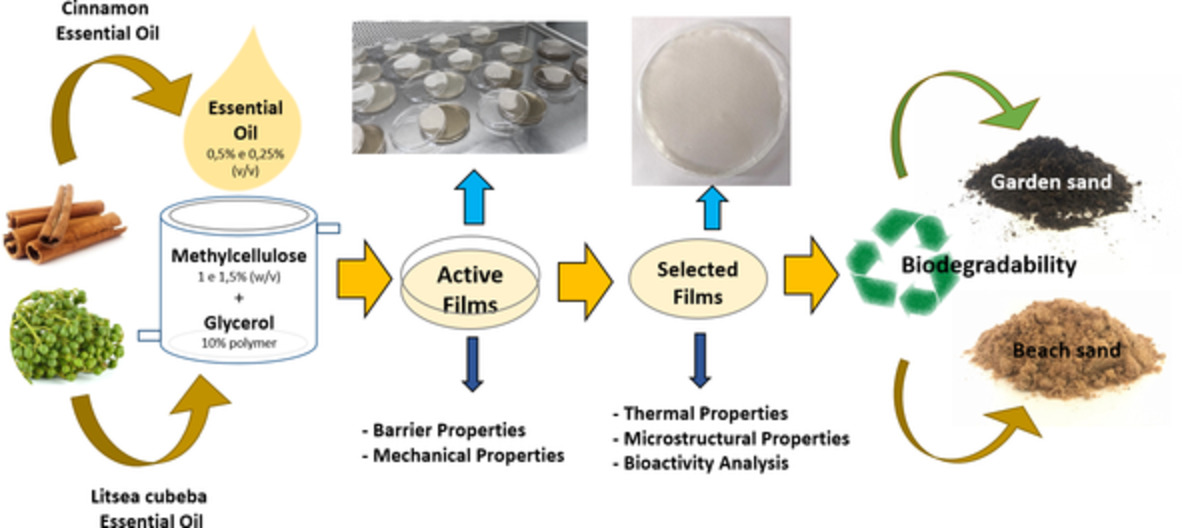
The influence of cinnamon and litsea cubeba essential oils on methylcellulose films
- First Published: 15 November 2022
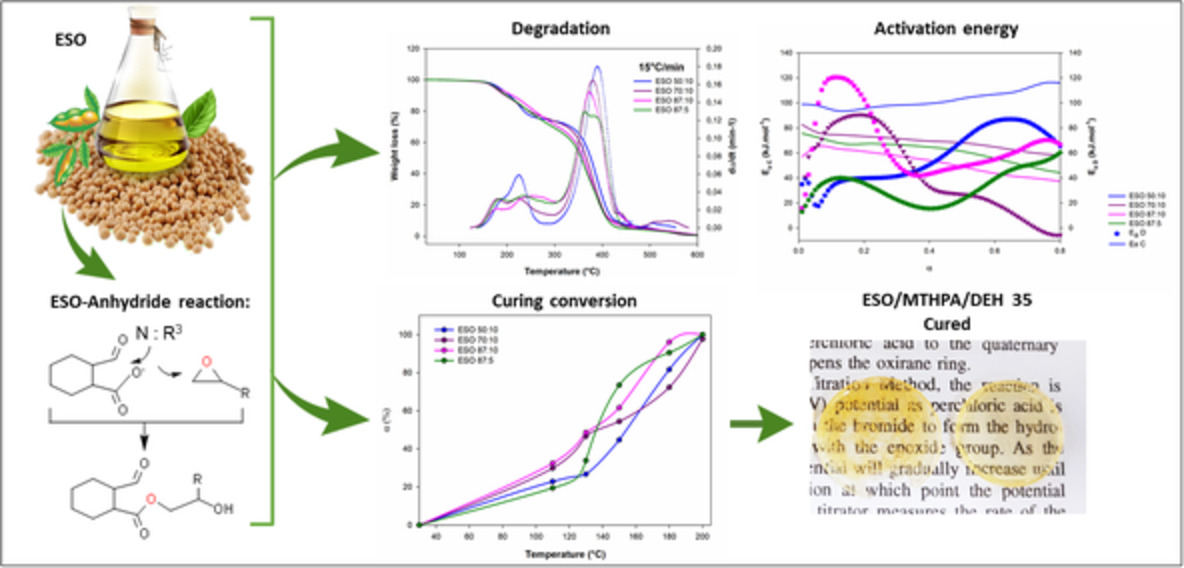
Effect of hardener and catalyst contents on curing and degradation of epoxidized soybean oil
- First Published: 08 November 2022
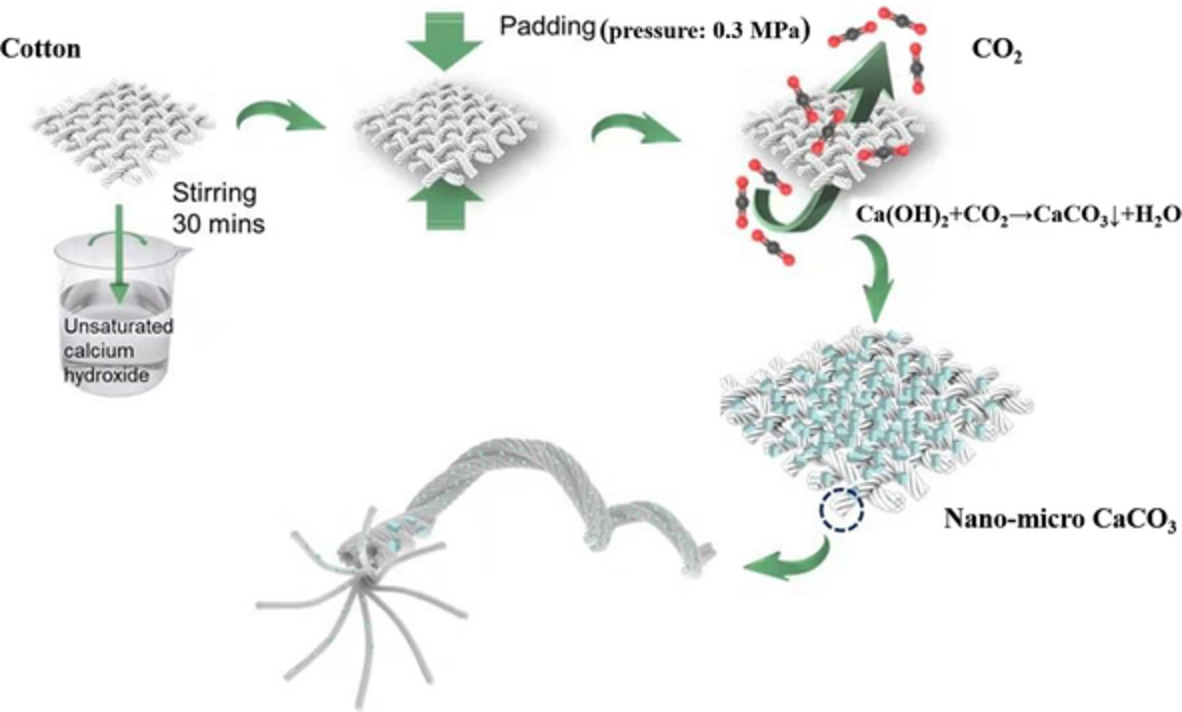
Effect of in situ deposition of calcium carbonate in cotton fiber on its mechanical properties
- First Published: 01 November 2022
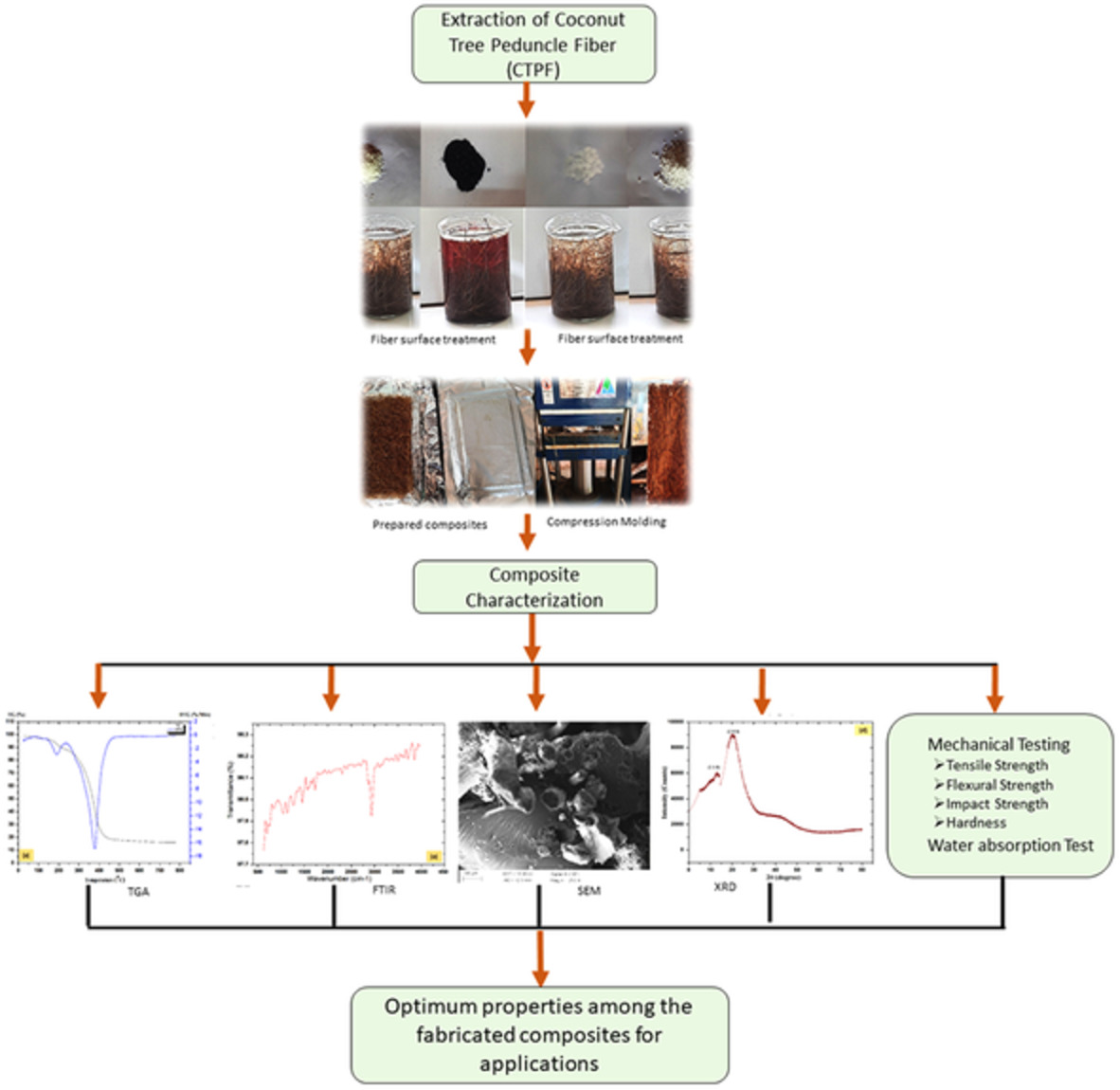
Influence of surface treatment on properties of Cocos nucifera L. Var typica fiber reinforced polymer composites
- First Published: 09 November 2022