Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 139, Issue 30
- First Published: 01 July 2022
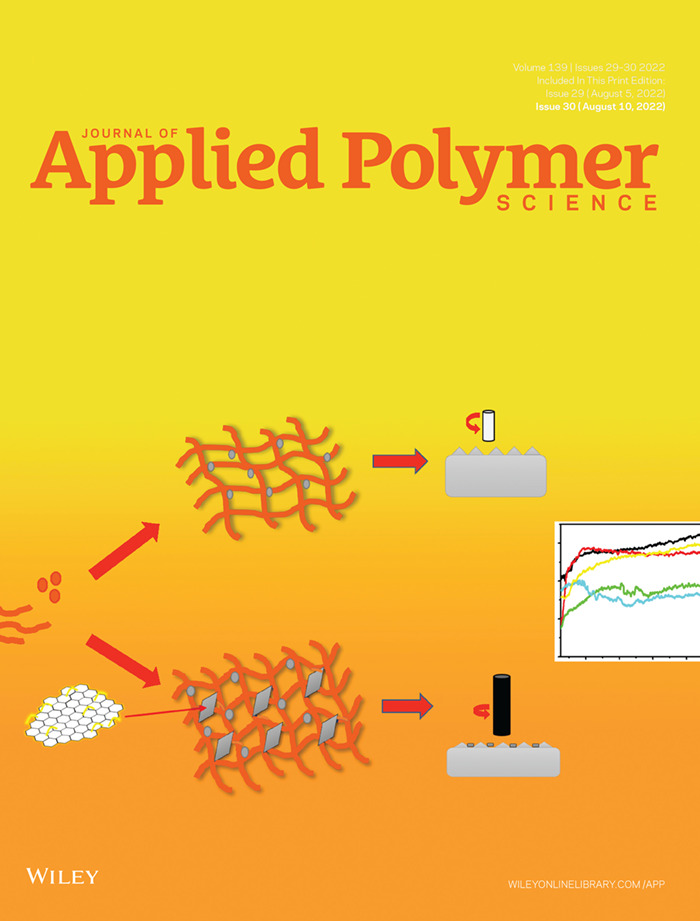
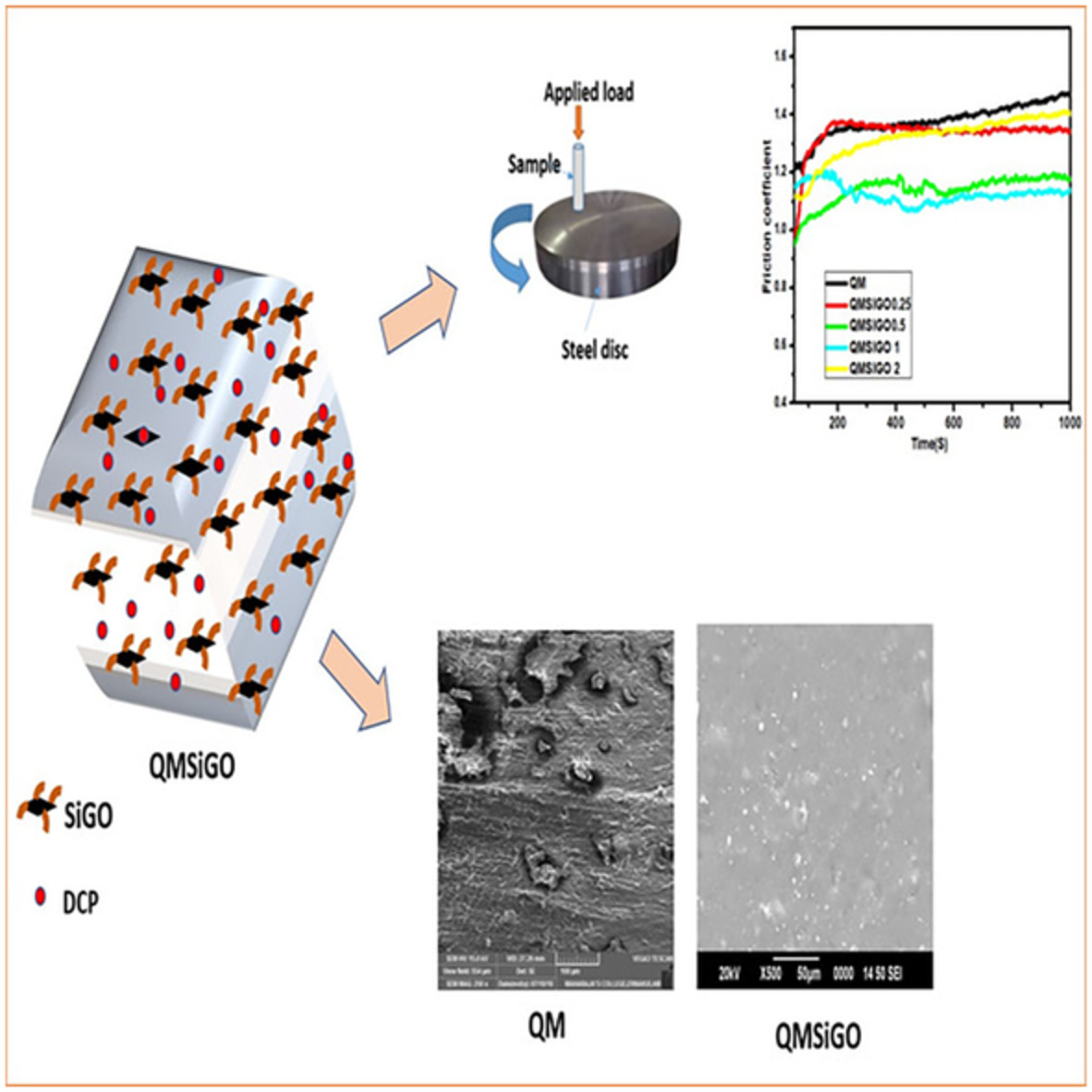
This cover image designed by Sarath P.S. in consultation with Dr. Soney C. George features a Silicone rubber (QM) loaded with silane modified graphene oxide (SiGO) that exhibits superior mechanical, thermal, and tribological capabilities. The lubricating effect of graphene oxide played a major role in improving the tribological features of QMSiGO composites. The friction coefficient is dramatically reduced when SiGO is added, largely due to the creation of a lubricant film that smooths the material surfaces and reduces frictional heat, lowering the COF and specific wear rate. DOI: 10.1002/app.52299
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
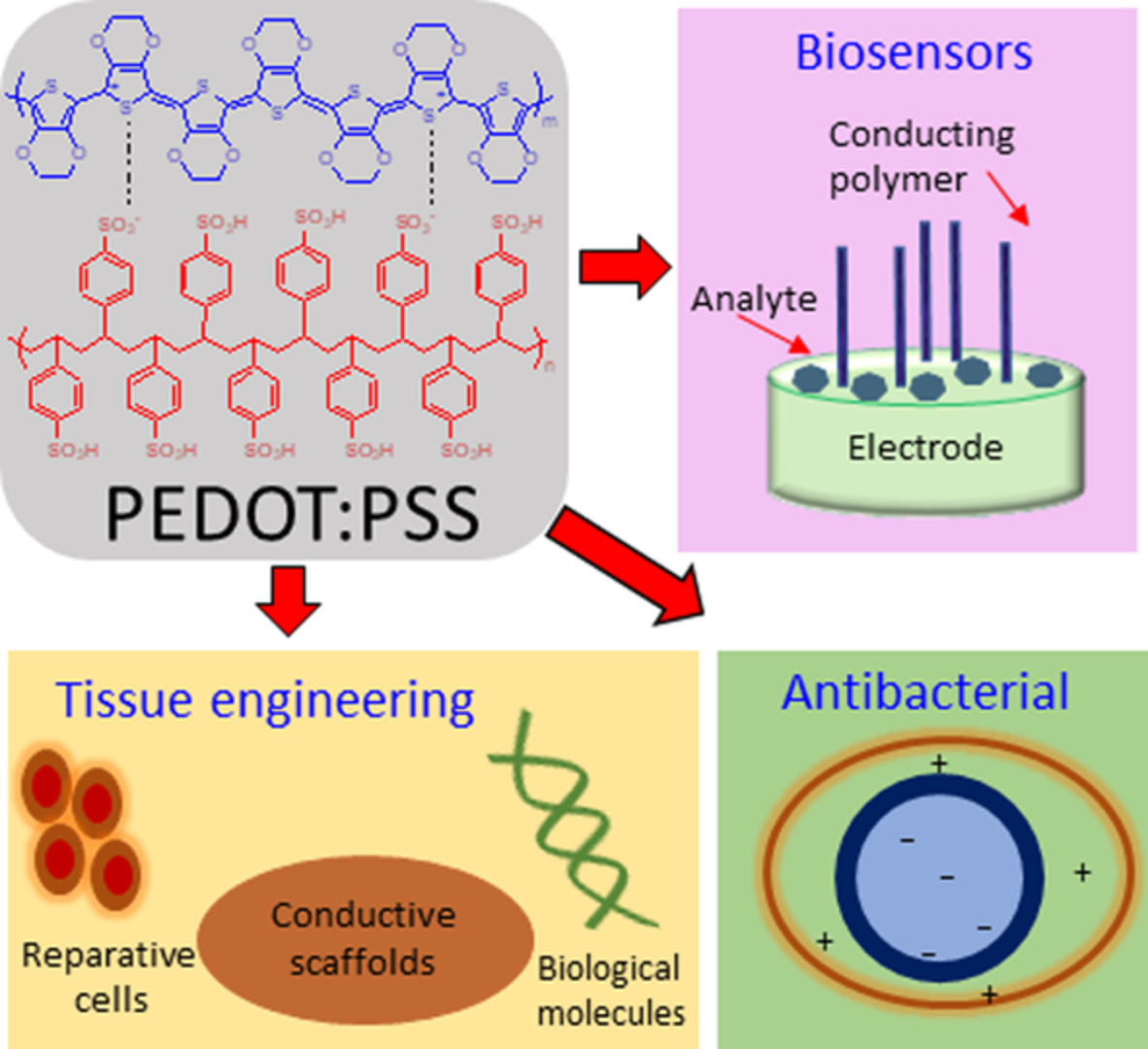
Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene):Poly(styrene sulfonate) in antibacterial, tissue engineering and biosensors applications: Progress, challenges and perspectives
- First Published: 26 May 2022
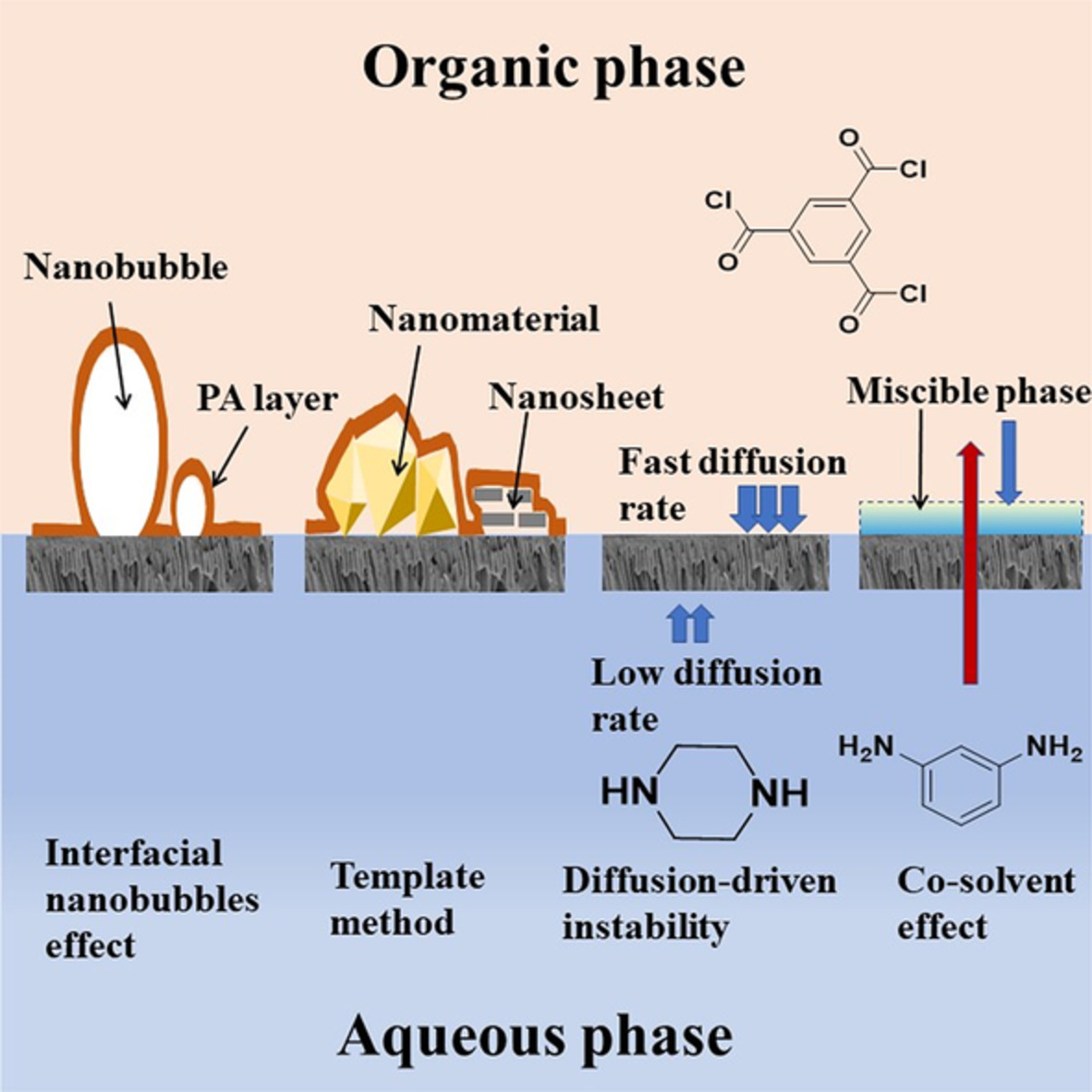
Constructing highly rough skin layer of thin film (nano)composite polyamide membranes to enhance separation performance: A review
- First Published: 09 June 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Fabrication, characterization and properties of silane functionalized graphene oxide/silicone rubber nanocomposites
- First Published: 03 March 2022
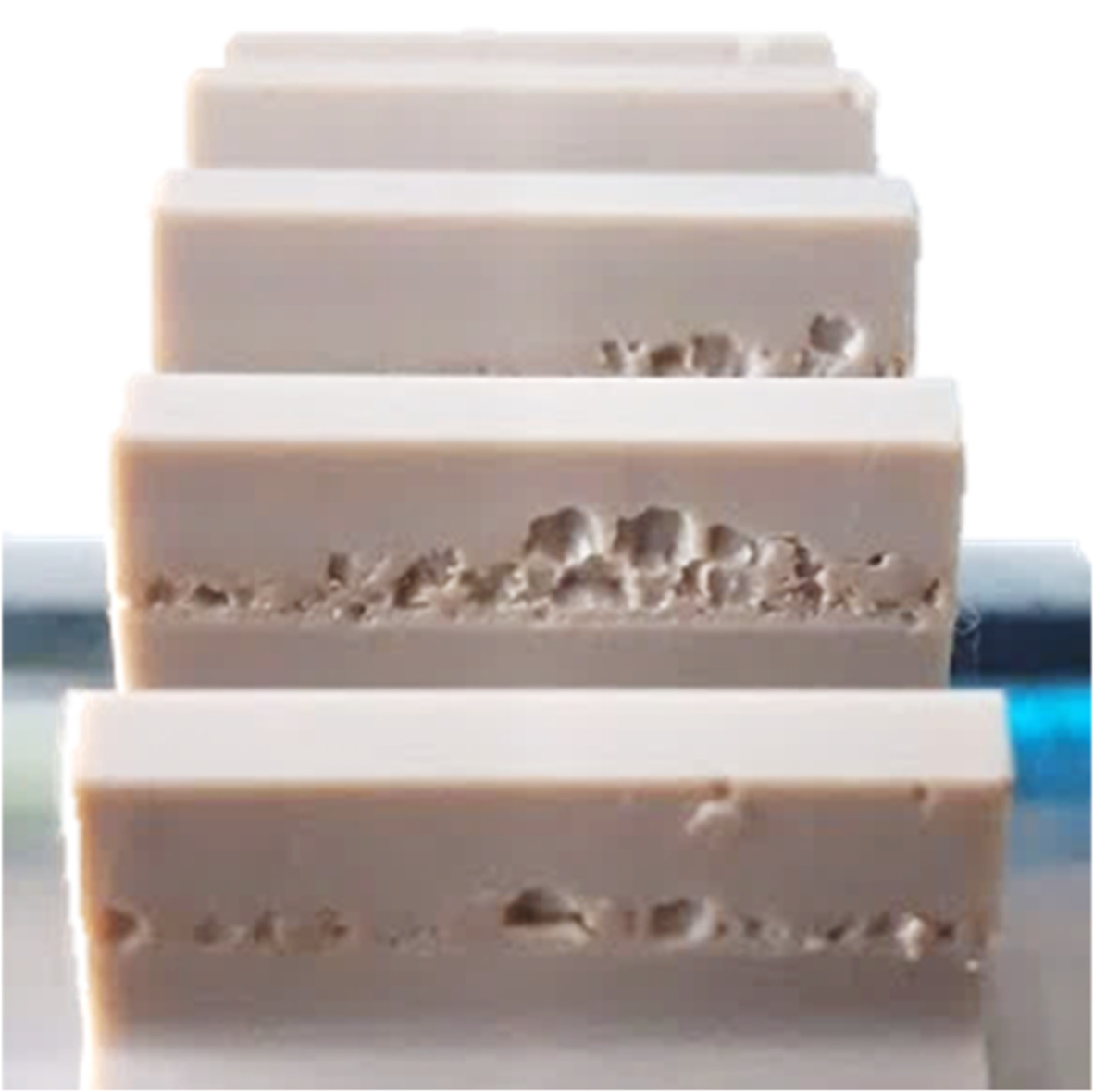
Facile construction of cationic lignin modified bentonite–alginate nanocomposite gel for sustained release of alachlor
- First Published: 20 May 2022

The cationic lignin was prepared by the etherification reaction of lignin and used to modify bentonite by ion exchange. After modified with cationic lignin, the hydrophobicity and the adsorption capacity of bentonite for alachlor had been remarkably enhanced. Meanwhile, the electrostatic attraction between cationic lignin and alginate made bentonite better dispersed in alginate gel and significantly reduced the permeability of alginate gel. Finally, the modified bentonite-alginate nanocomposite gel obtained better sustained release property.
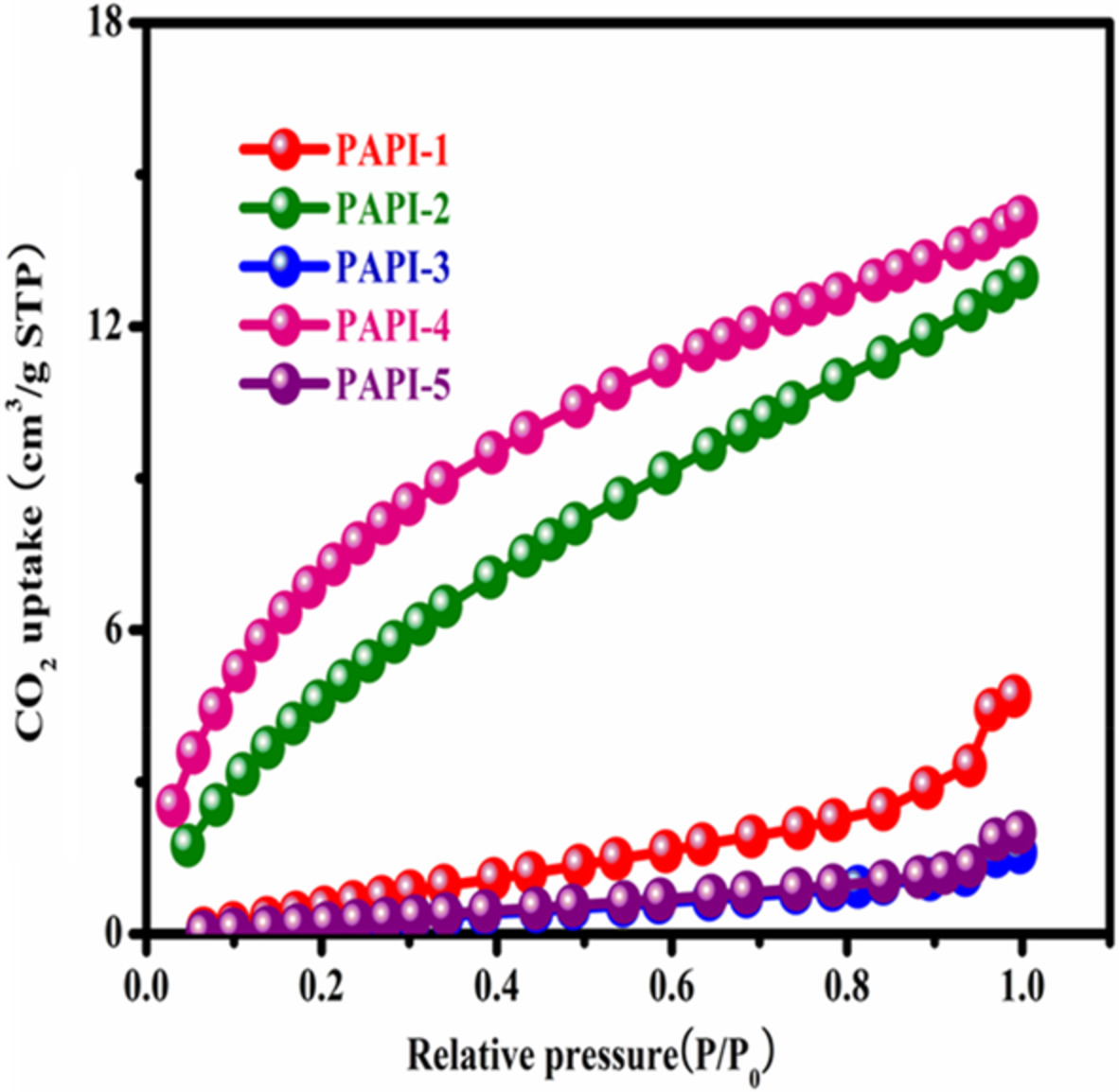
Preparation and performance for CO2 adsorption of large-scale microporous fiber membrane based on electrostatic spinning technology
- First Published: 21 May 2022
Incorporation of CO2-polyols into ester-based waterborne polyurethane: An effective strategy to improve overall performance
- First Published: 25 May 2022
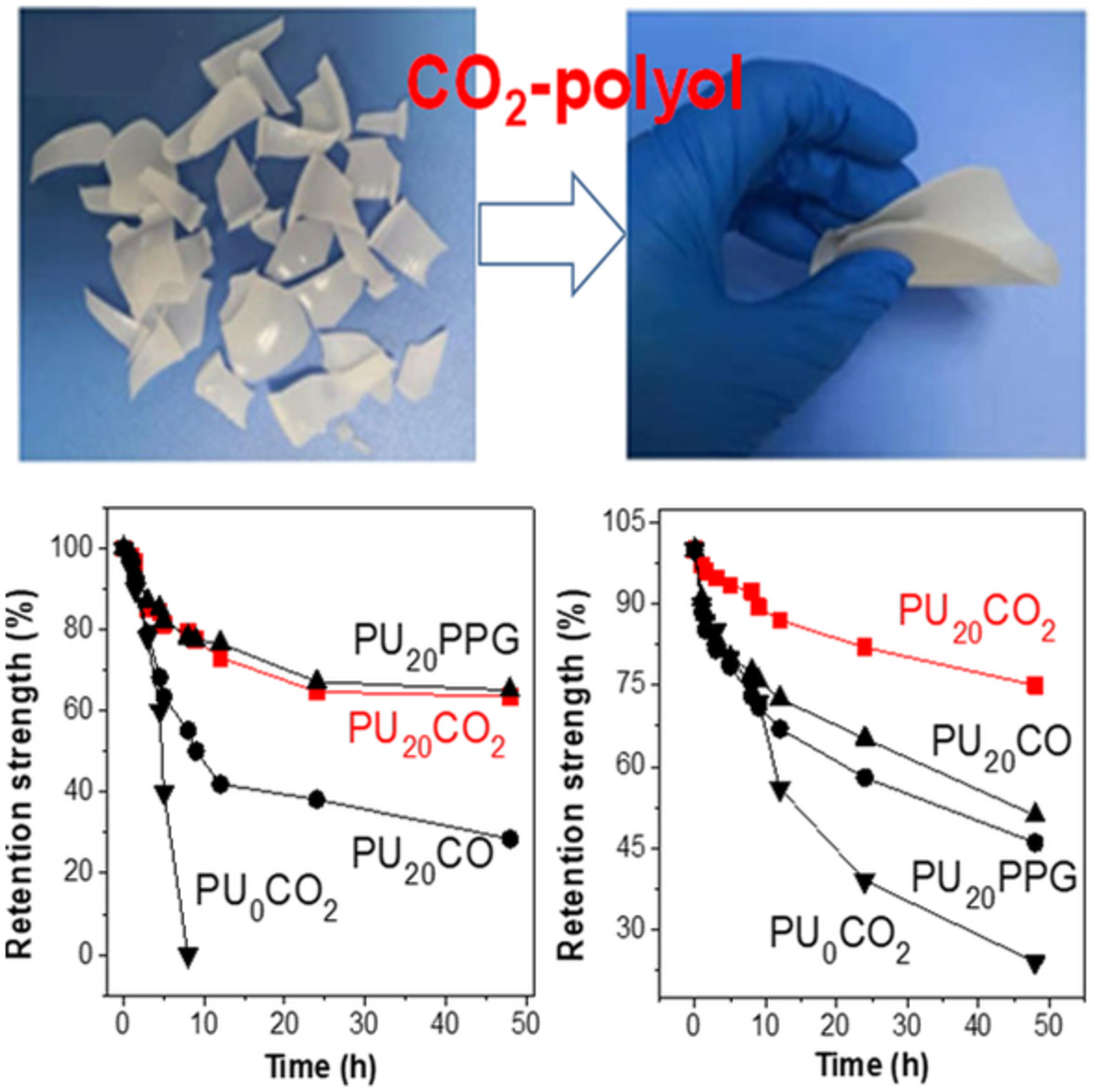
Amorphous structural CO2-polyol was used to modify oligoesterol-based water-borne polyurethanes (WPUs, PU0CO2), resulting in improved low temperature film forming, and comprehensive hydrolysis/oxidation resistance properties. Excellent intact films can be easily formed even at 3 ºC by adding CO2-polyol into the oligoesterol-based WPUs. Moreover, WPUs modified by CO2-polyol show superior hydrolysis/oxidation resistance properties than that of control samples based on castor oil or poly(propylene oxide) glycol. Notably, the all-around aging resistance of oligoester-based WPUs intensified with an increase of CO2-polyol content. This work indicates that the CO2-polyol may be a promising modified material to improve comprehensive aging resistance and low temperature film forming for oligoester-based WPUs.
Damage mechanisms and tooth flank load capacity of oil-lubricated peek gears
- First Published: 20 May 2022
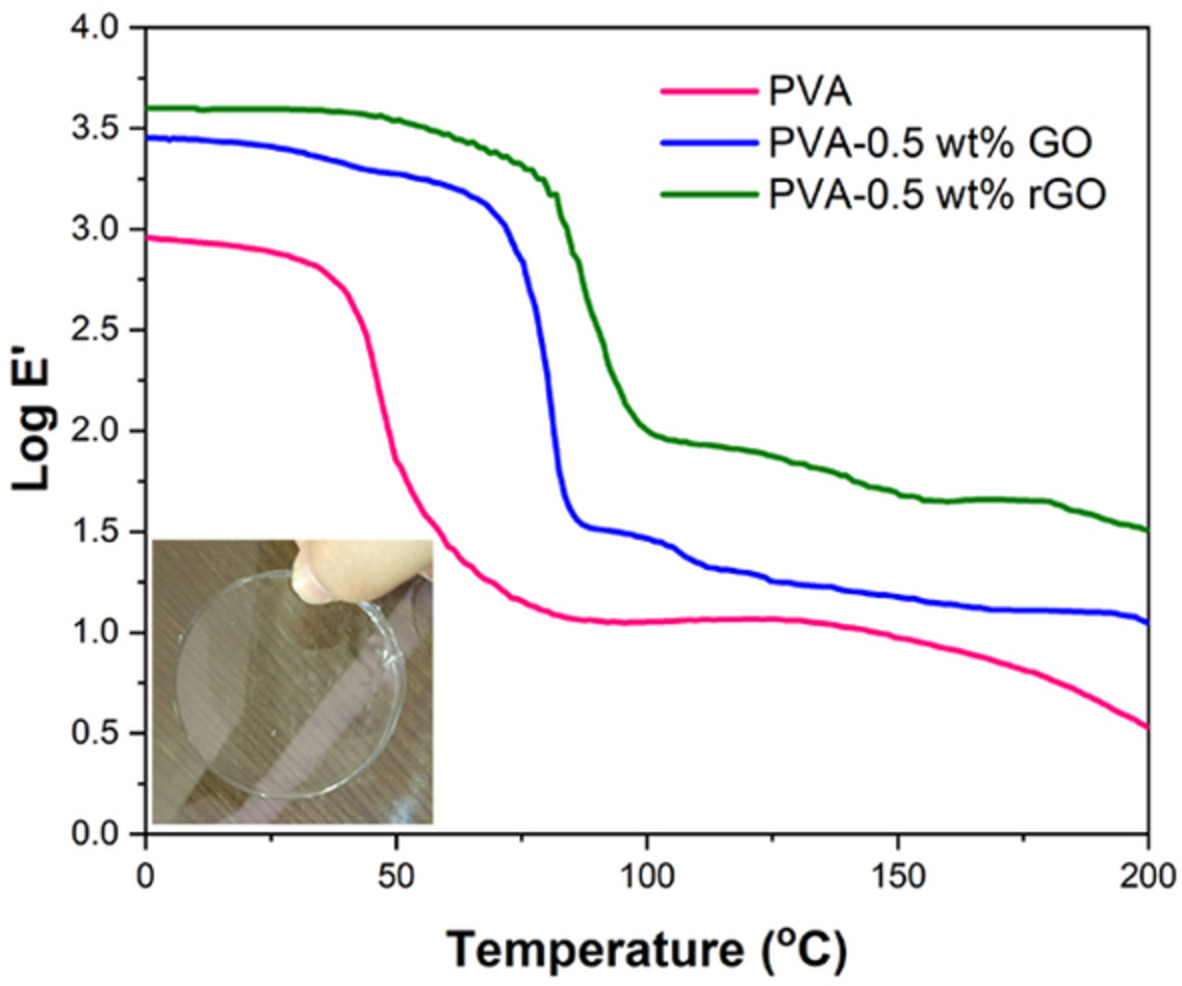
The effect of graphene-based nanofillers on the structure, thermal, and mechanical properties of poly(vinyl alcohol)
- First Published: 20 May 2022
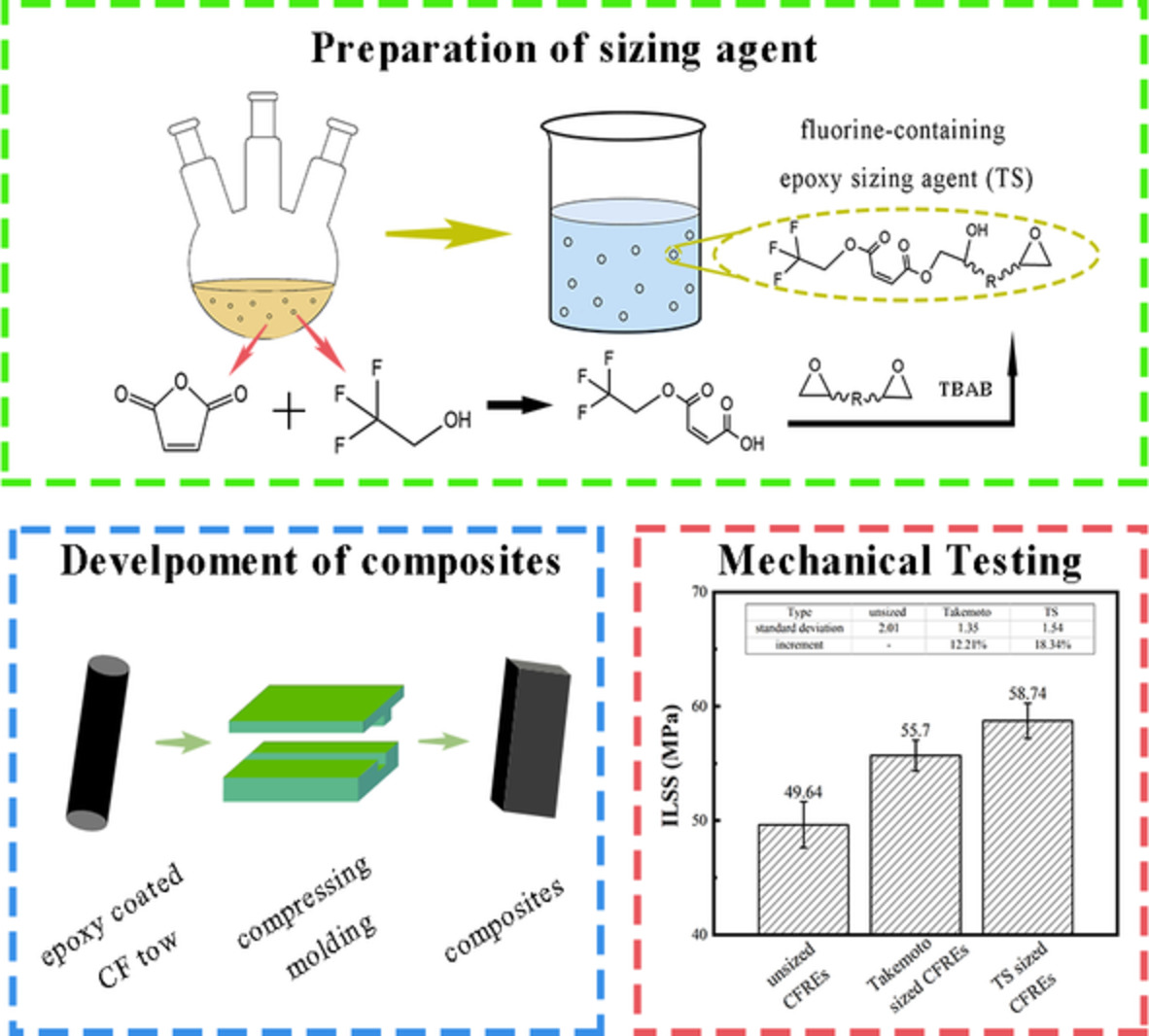
Interlaminar improvement of carbon fiber/epoxy composites via fluorine-containing high-epoxy-value sizing agent
- First Published: 06 June 2022
Mechanical and thermal properties of polydimethylsiloxane/magnetite nanocomposites for cancer treatment by localized hyperthermia and photothermal ablation
- First Published: 26 May 2022
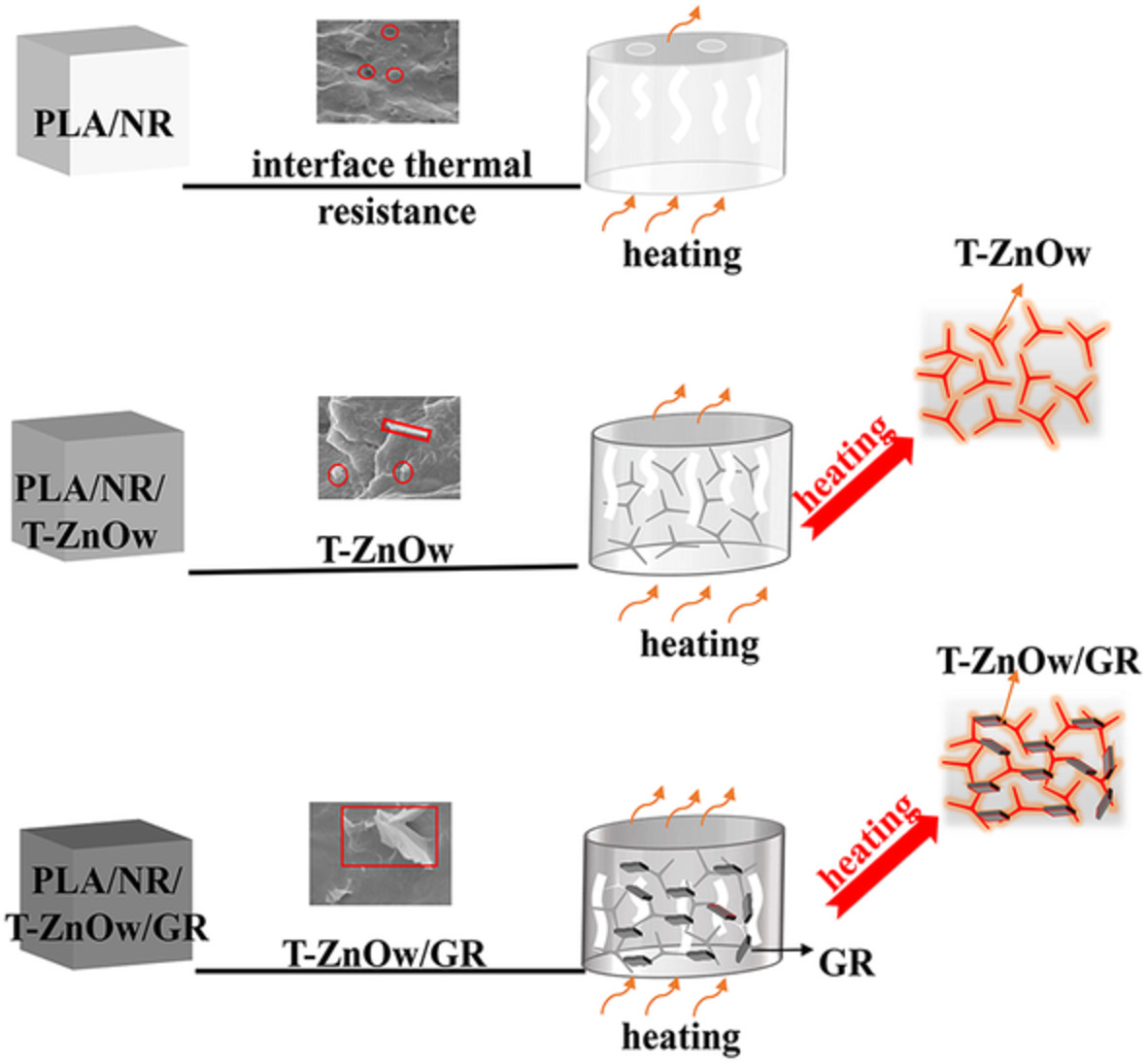
Shape memory, thermal conductivity, and mechanical property of polylactic acid and natural rubber composites reinforced by an inorganic thermal conductive network
- First Published: 25 May 2022
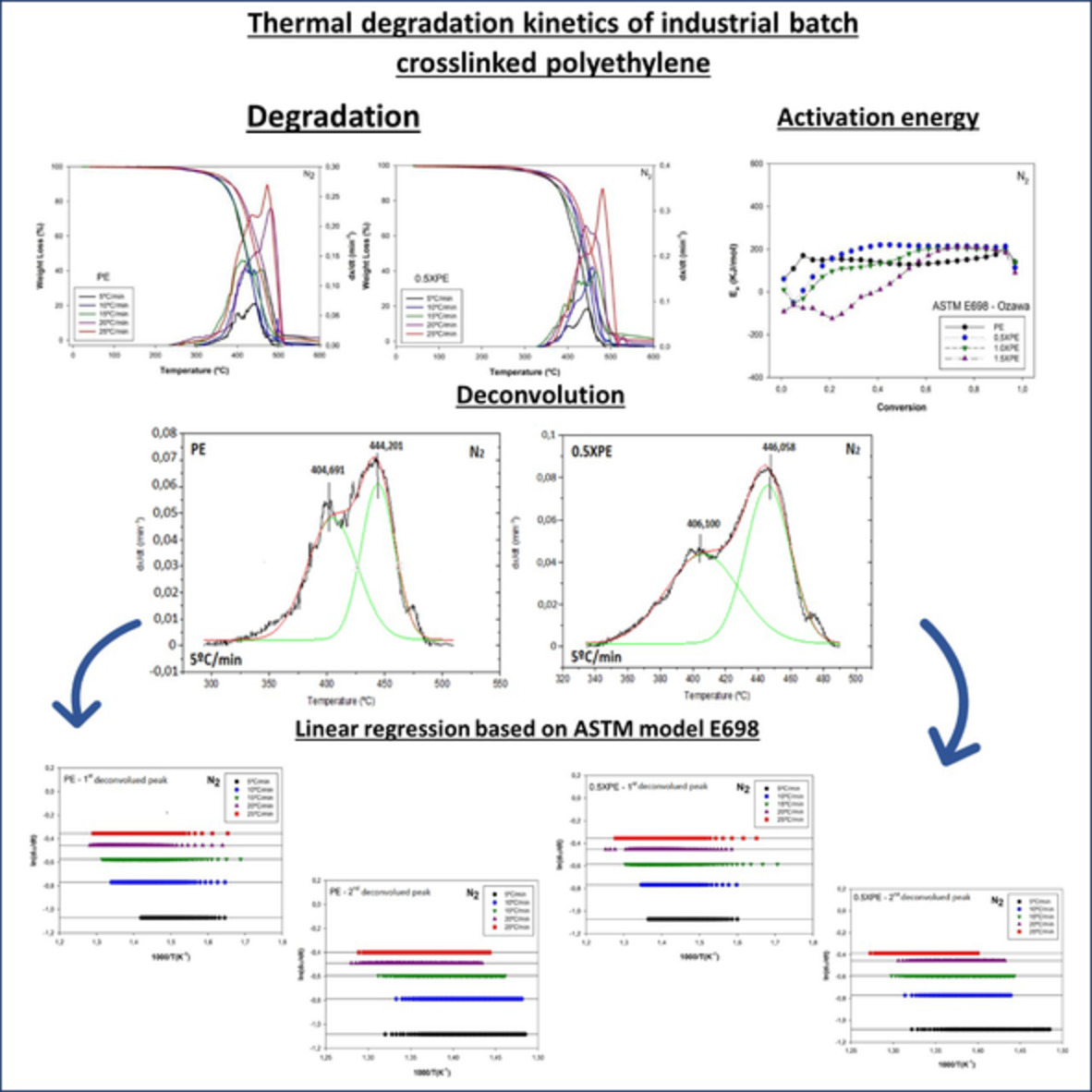
Thermal degradation kinetics of industrial batch crosslinked polyethylene
- First Published: 24 May 2022
Effect of graphitic additives on the rheology of cellulose solutions for the preparation of templated carbon fiber precursors
- First Published: 25 May 2022
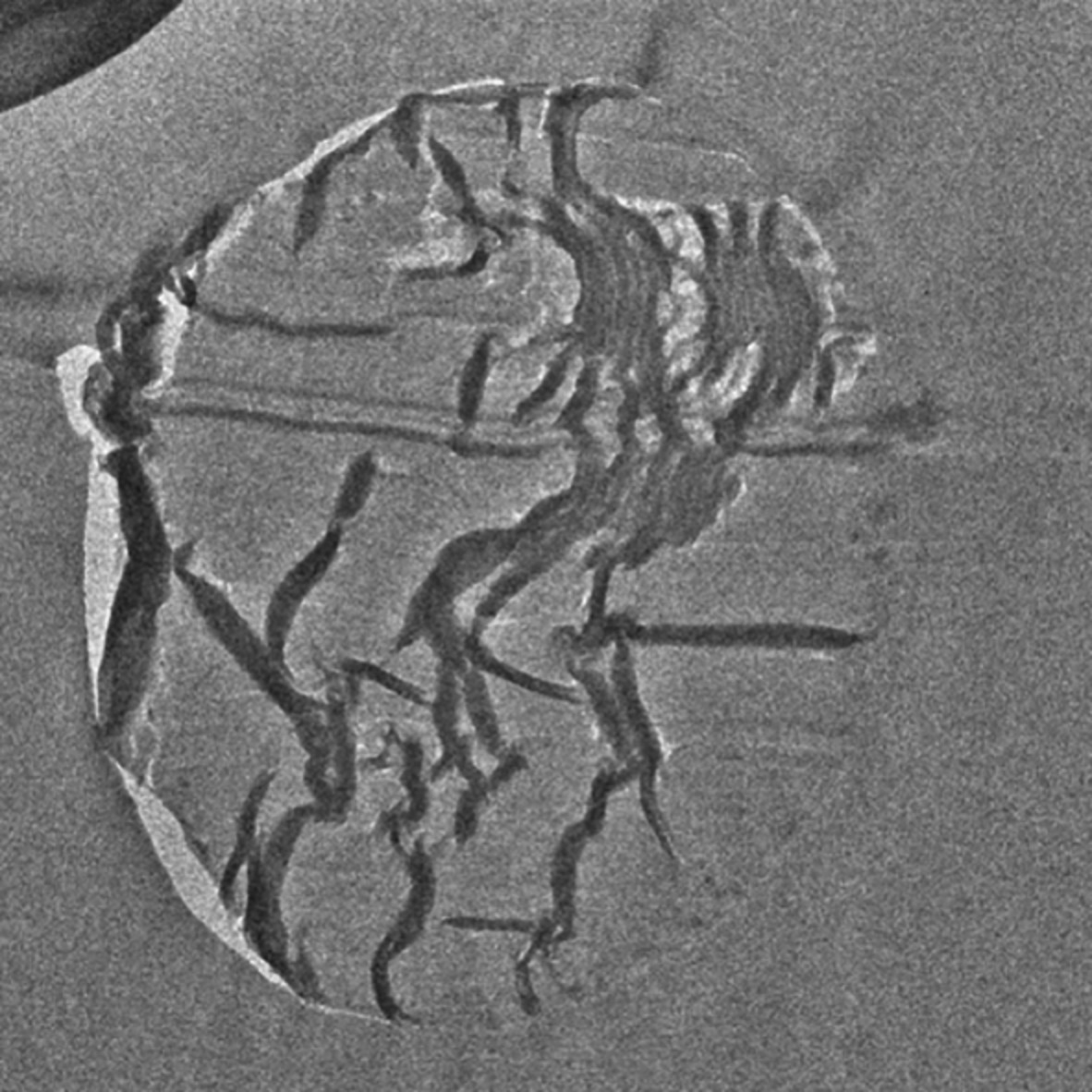
This study demonstrates the preparation of hybrid fibers out of cellulose and carbon nanomaterials in ionic liquid, including analysis of their rheological properties, which strongly influence their spinning process. Carbon nanotubes are shown to only subtly thicken the dispersion, while graphene oxide can interact more strongly with cellulose and produce a more rigid network.
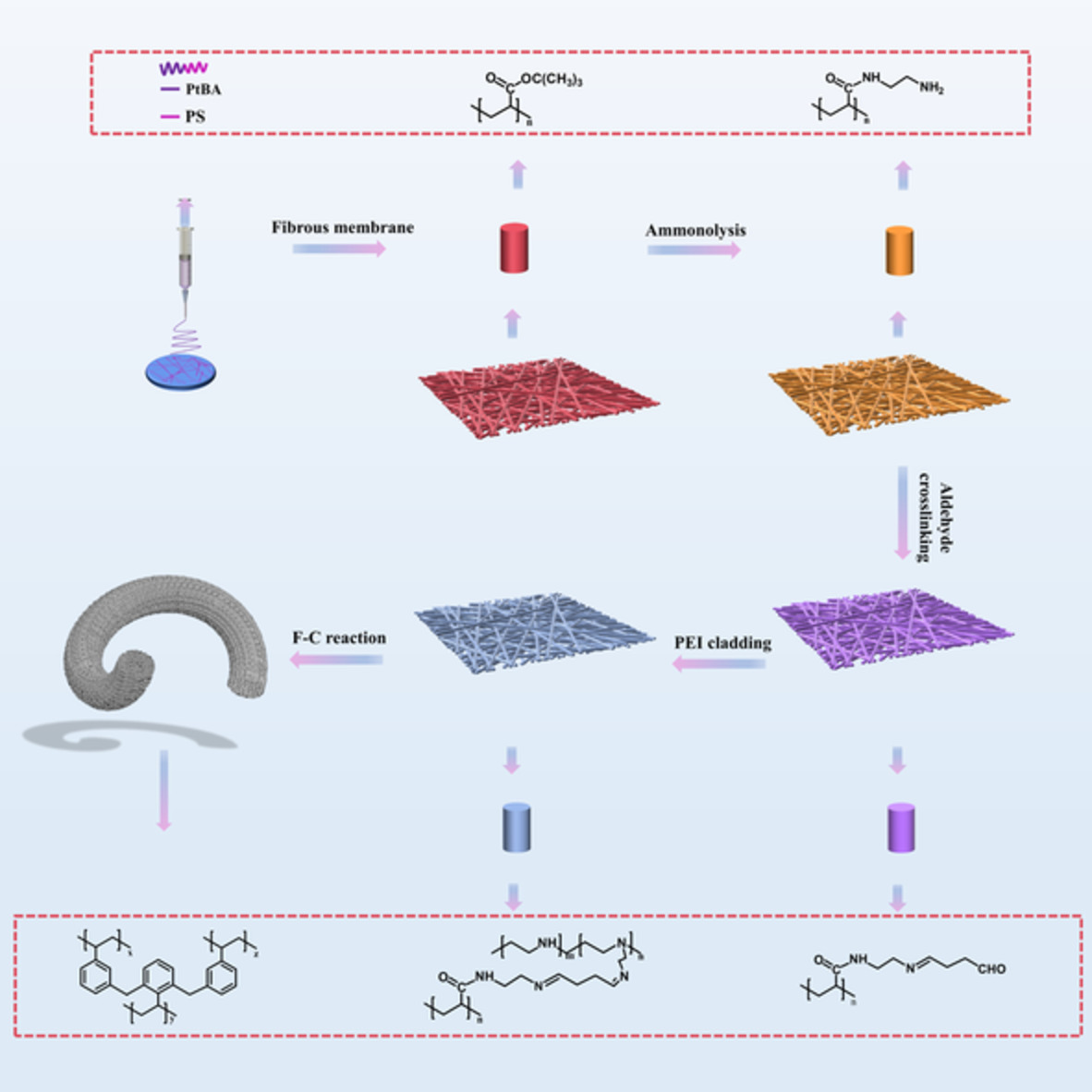
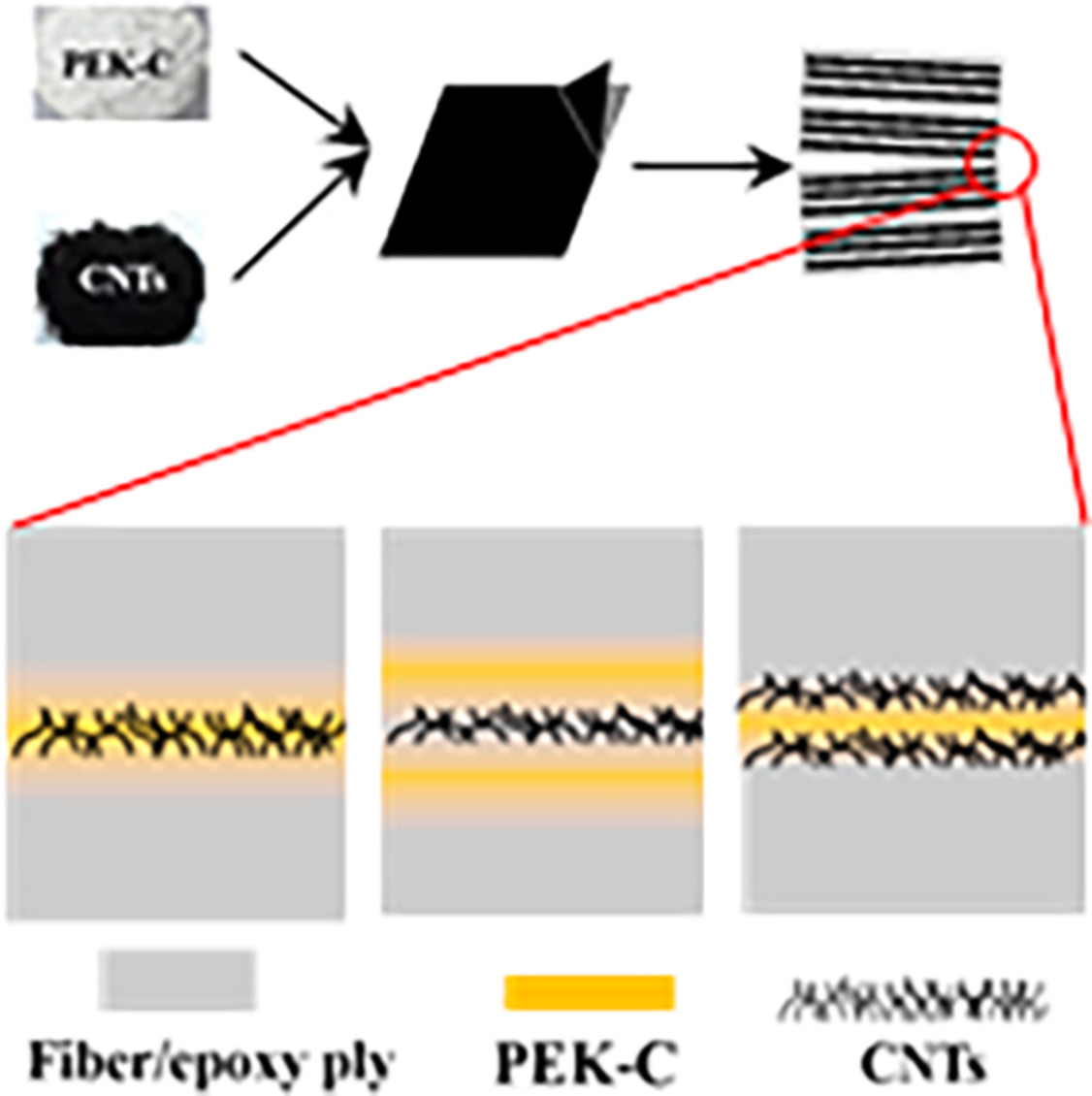
Influence of carbon nanotubes/polyetherketone-cardo interlayer structure on mode II interlaminar fracture toughness of the interleaved carbon fiber reinforced epoxy composites
- First Published: 04 June 2022
Synthesis and characterization of polyimidazolium species on silica nanoparticles: Study on cytotoxicity and removal of nitrate from water
- First Published: 28 May 2022
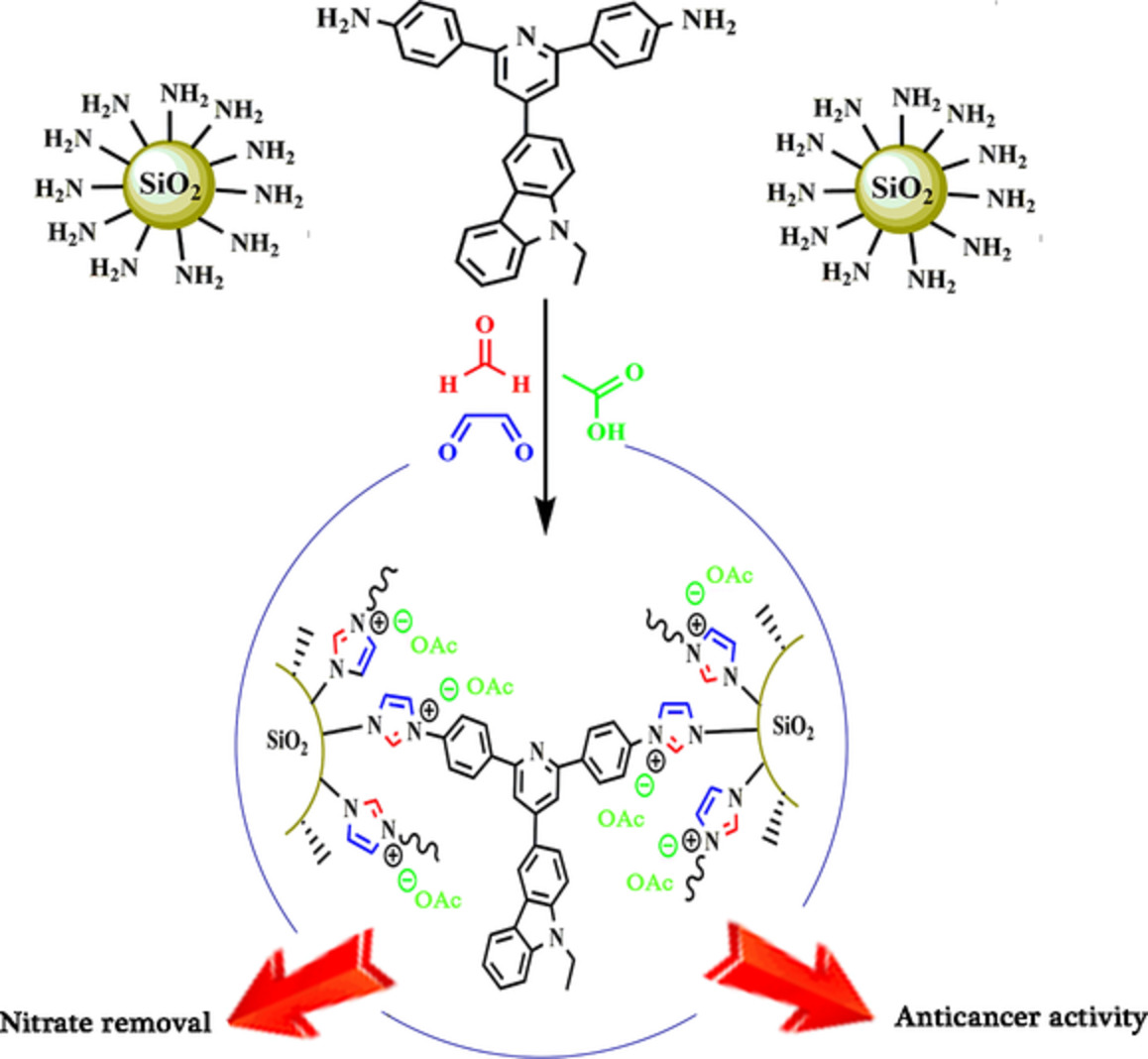
Novel thermostable polyimidazolium nanocomposite was prepared based on modified nano silica particles with terminated amine groups and used to removal of nitrate ions from water with high removal efficiency (90.56%), maximum adsorption capacity (Qmax = 37.73 mg g−1) and strong cytotoxic agent against HL60 cells.
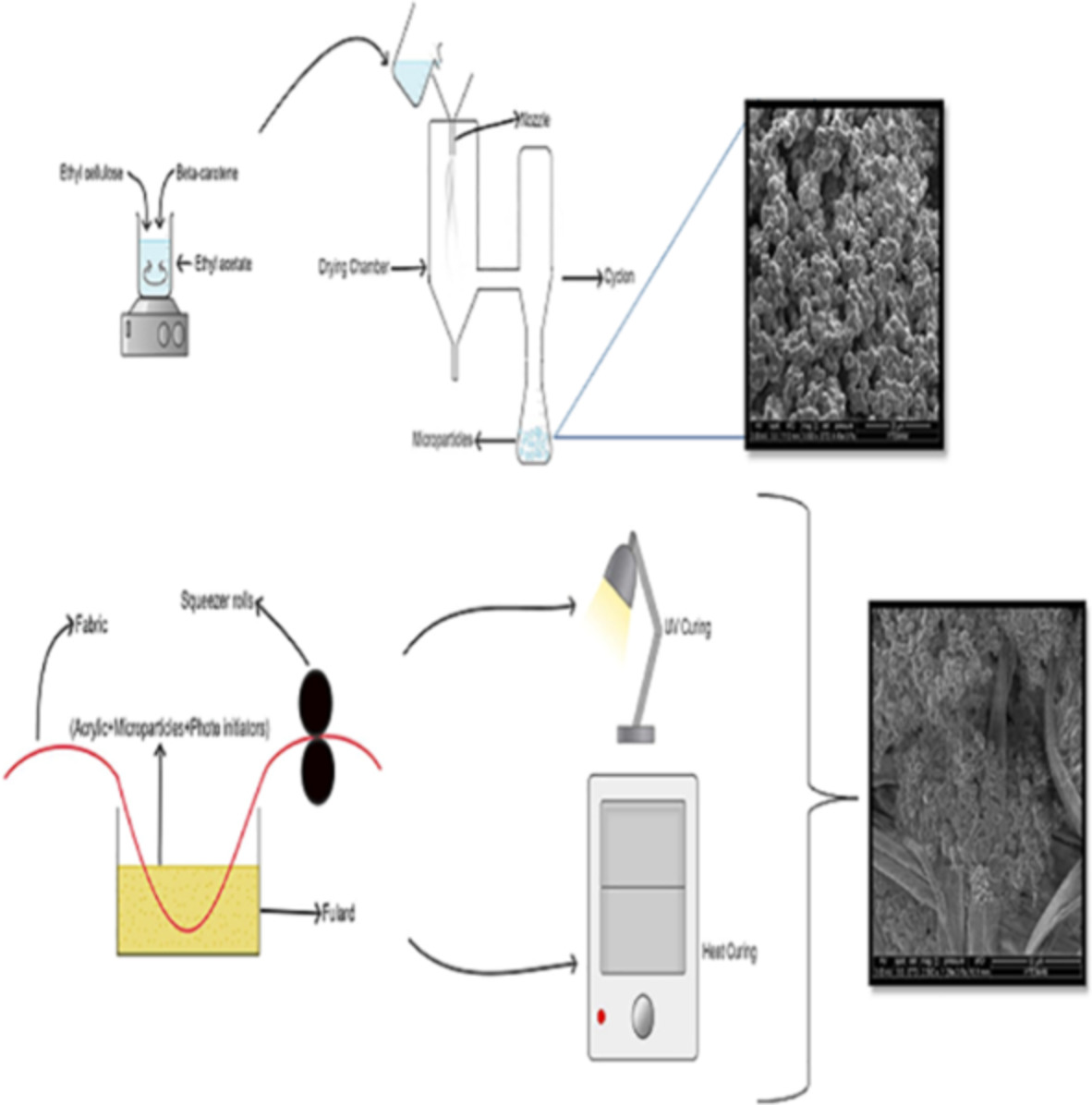
UV curing: An alternative method for fixation of β-carotene containing microparticles substances onto cotton fabrics by acrylic binder
- First Published: 04 June 2022
Effects of ammonium persulfate on coconut wood (Cocos nucifera L.) cellulose, hemicellulose, and lignin polymers: Improved sound absorption capacity
- First Published: 27 May 2022
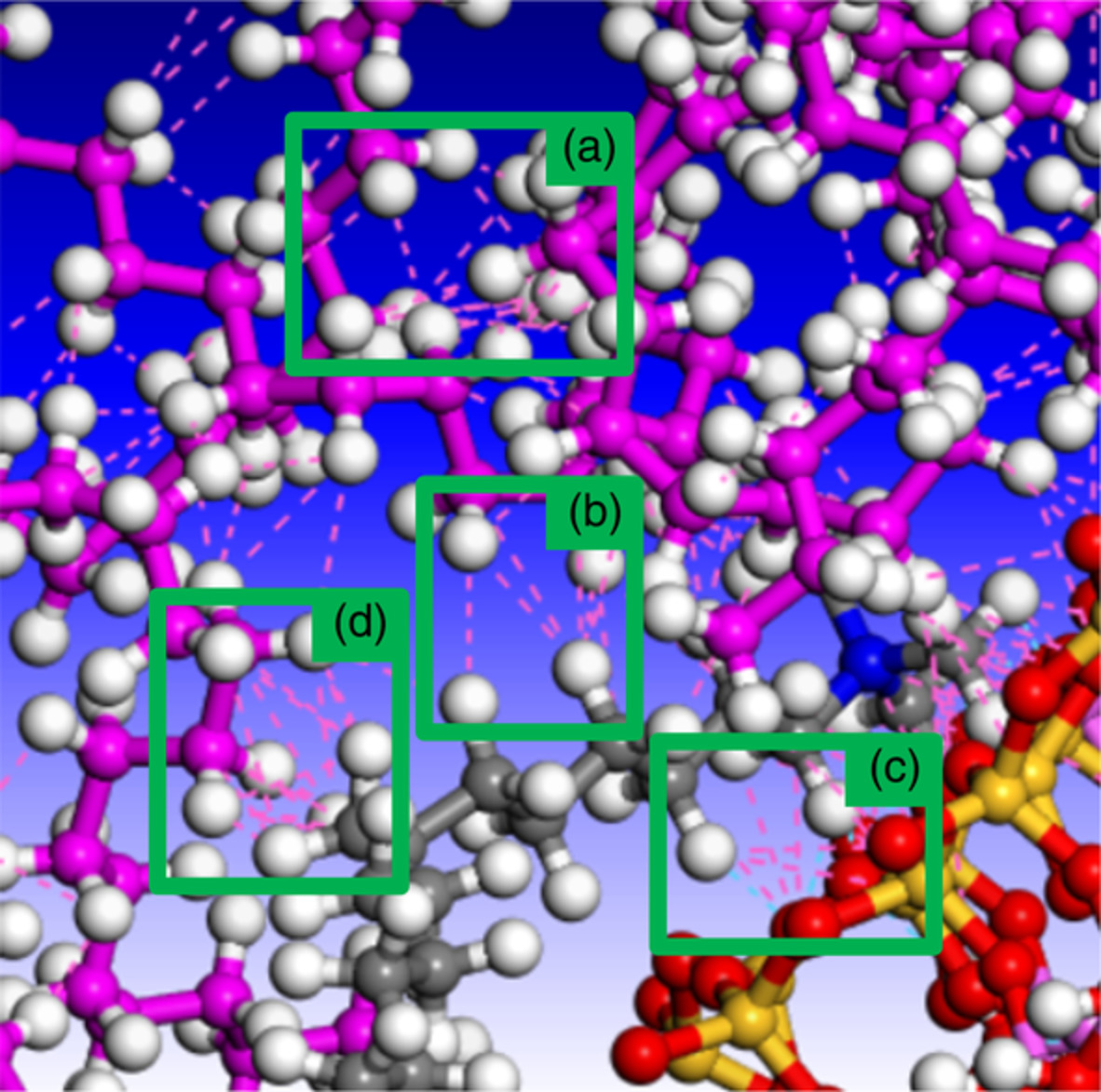
Internal topology and water transport in tetrafunctional epoxy resins
- First Published: 30 May 2022
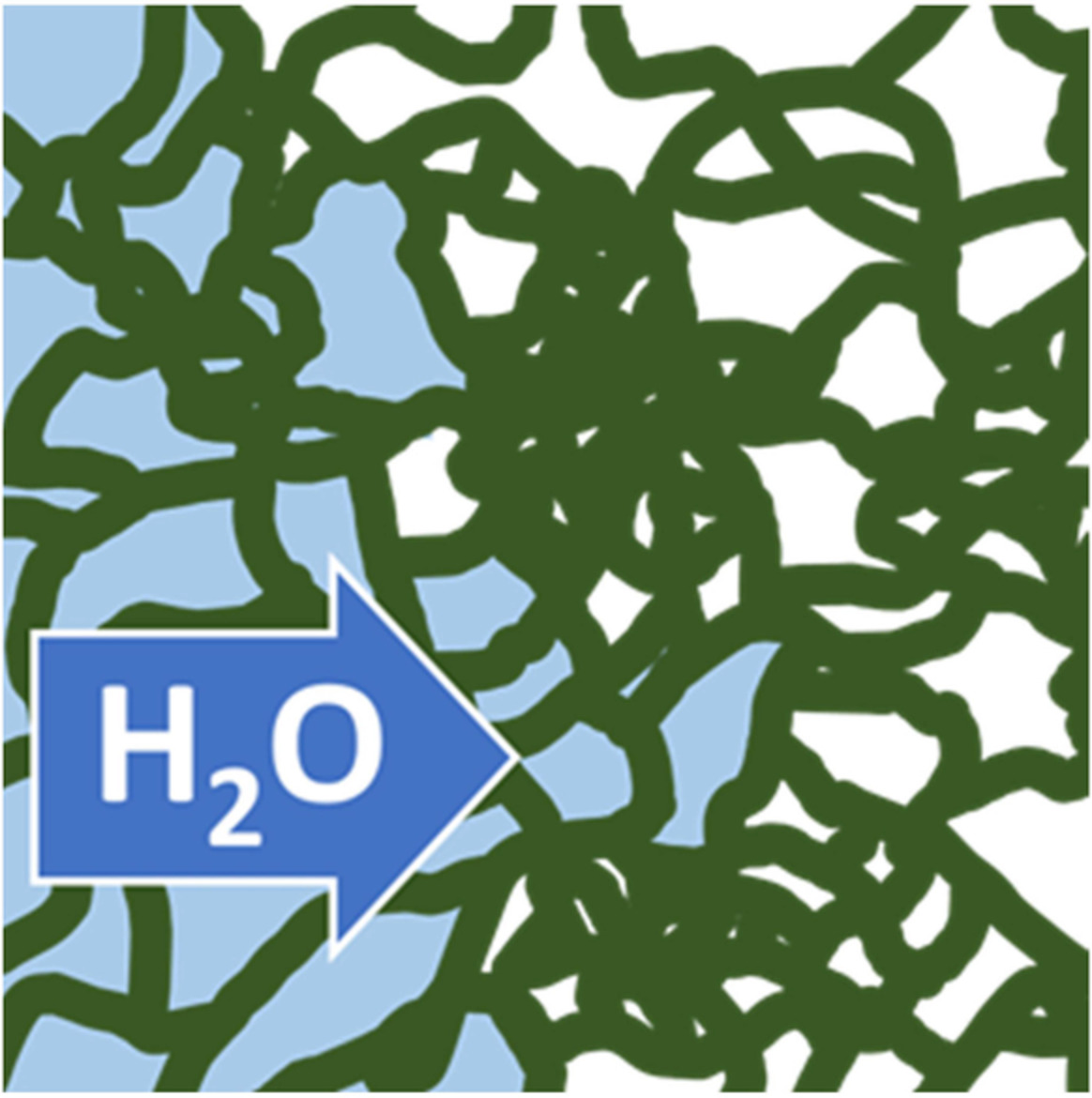
The internal topology of an epoxy-phenolic resin is controlled using only the cure schedule, and its effect on moisture uptake is investigated using dynamic vapor sorption. Absorption isotherms shows that the presence of heterogeneously cross-linked nanostructures has no effect on the overall extent, or kinetics, of water sorption. In contrast, minimal surface oxidation results in significantly increased moisture content.
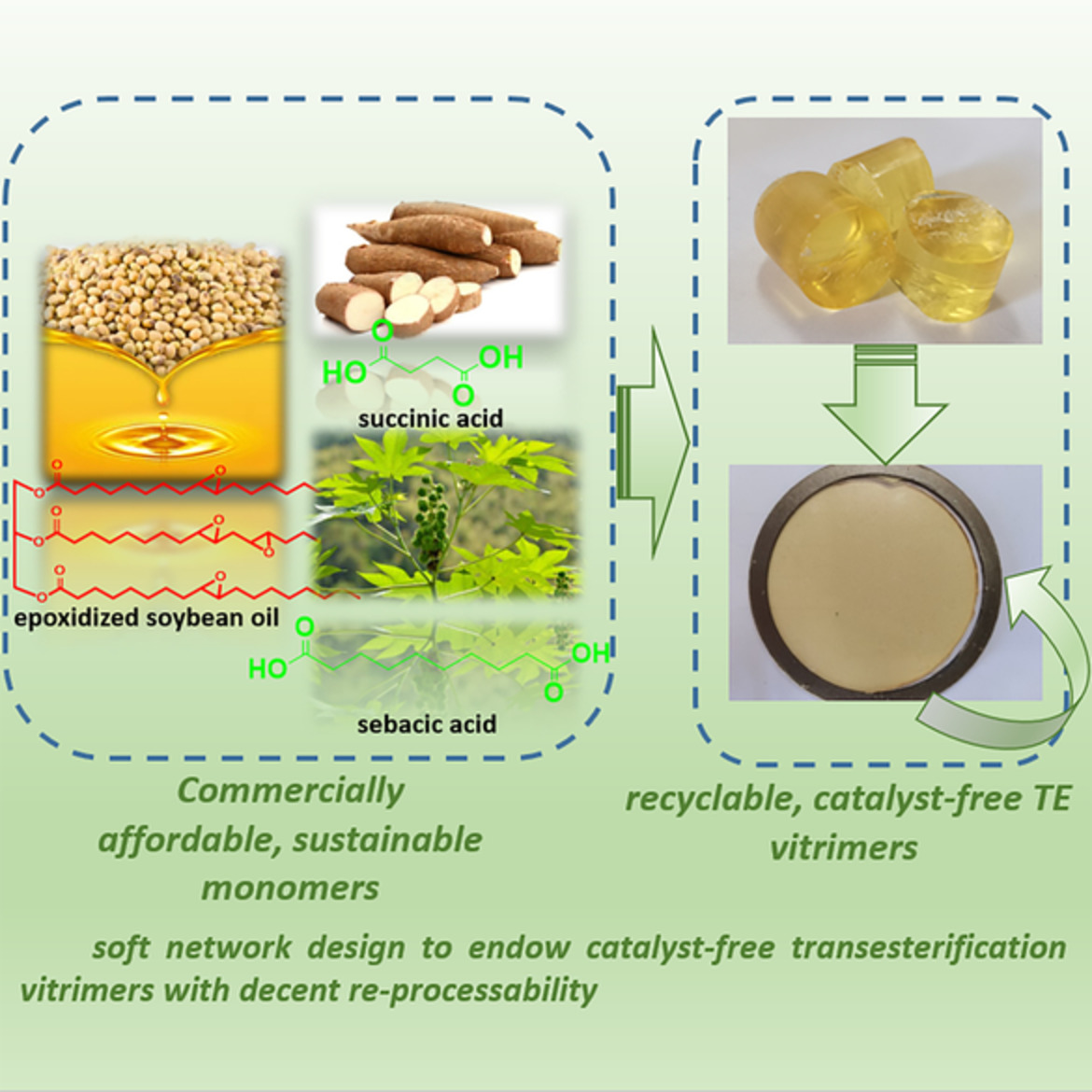
Soft, fully bio-based poly-hydroxyl thermosets based on catalyst-free transesterification with decent re-processability
- First Published: 02 June 2022
Surface engineering of Si wafers with tunable surface morphology and stiffness via visible light induced thiol-ene click polymerization with 4-(N,N-diphenylamino)benzaldehyde as an organocatalyst
- First Published: 30 May 2022
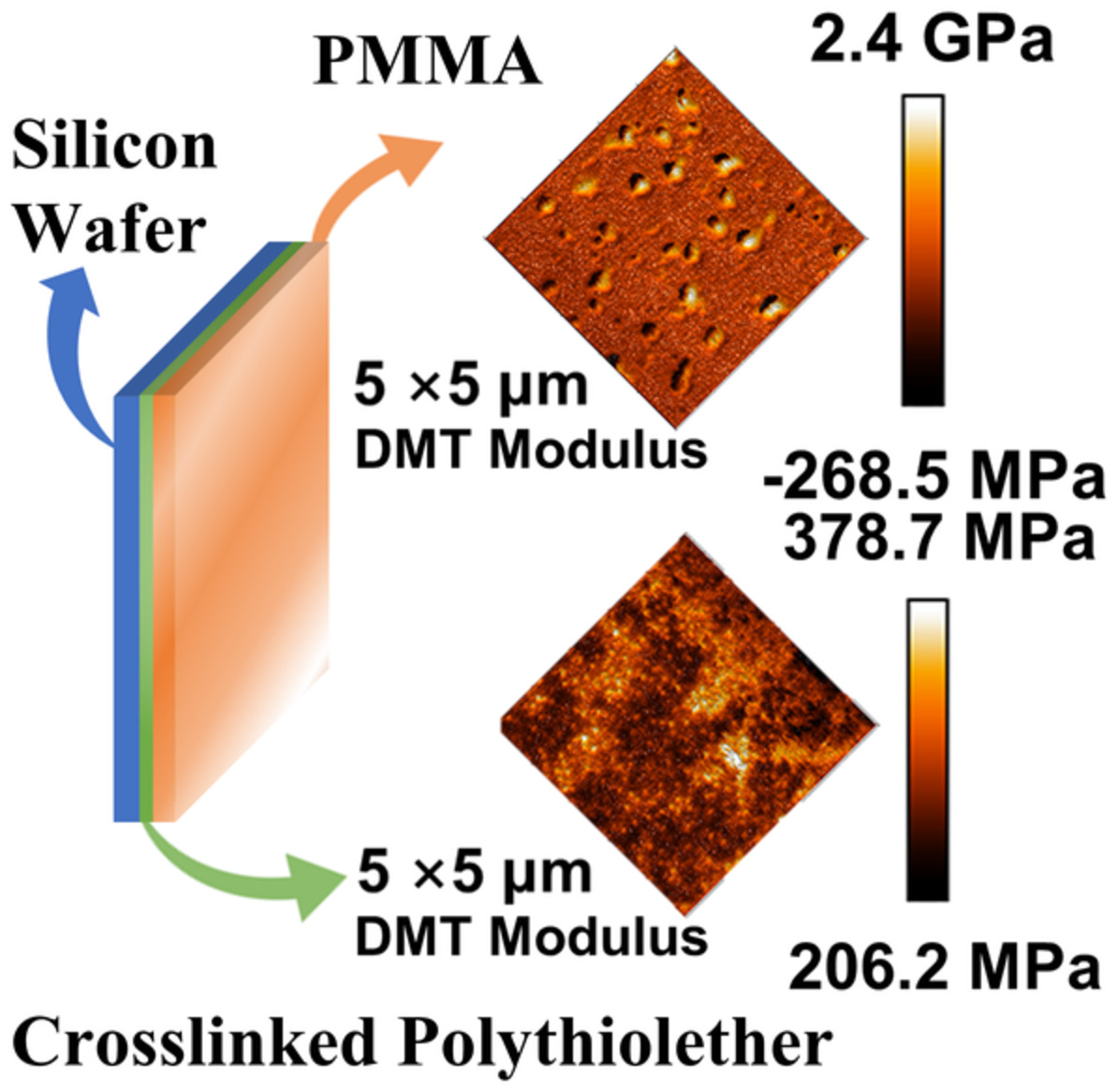
Two grafted polymer layers with tunable thickness and Young's modulus are deposited on silicon wafer by a photoactivated polymerization with 4-(N,N-diphenyl-amino)benzaldehyde as organocatalyst. The middle damping layer is soft crosslinked polythioether with trimethylolpropane tris(2-mercaptoacetate) and pentaerythritol triallyl ether as monomer and top protecting layer is stiff poly(methyl methacrylate).
Effects of microstructure on the breakdown characteristics of polyethylene–montmorillonite nanocomposites
- First Published: 07 June 2022
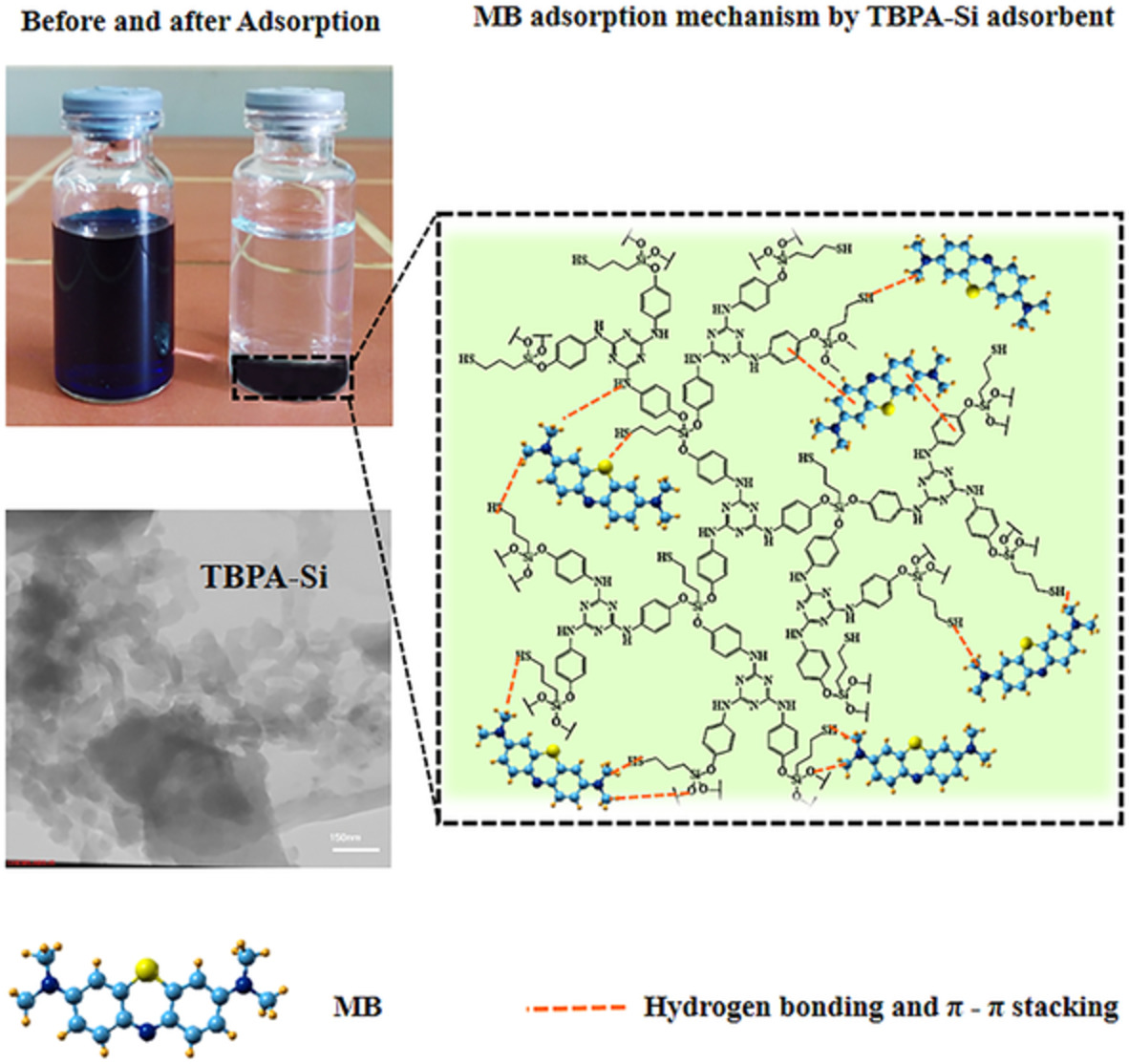
Comparative study on the adsorption characteristics of a triazine-Si hybrid polymer adsorbent and the natural adsorbents for removal of methylene blue from industrial wastewaters
- First Published: 25 May 2022
Structured pattern hollow fiber membrane designed via reverse thermally induced phase separation method for ultrafiltration applications
- First Published: 25 May 2022
Low cross-linked polyimide aerogel with imidazole for CO2 adsorption
- First Published: 25 May 2022
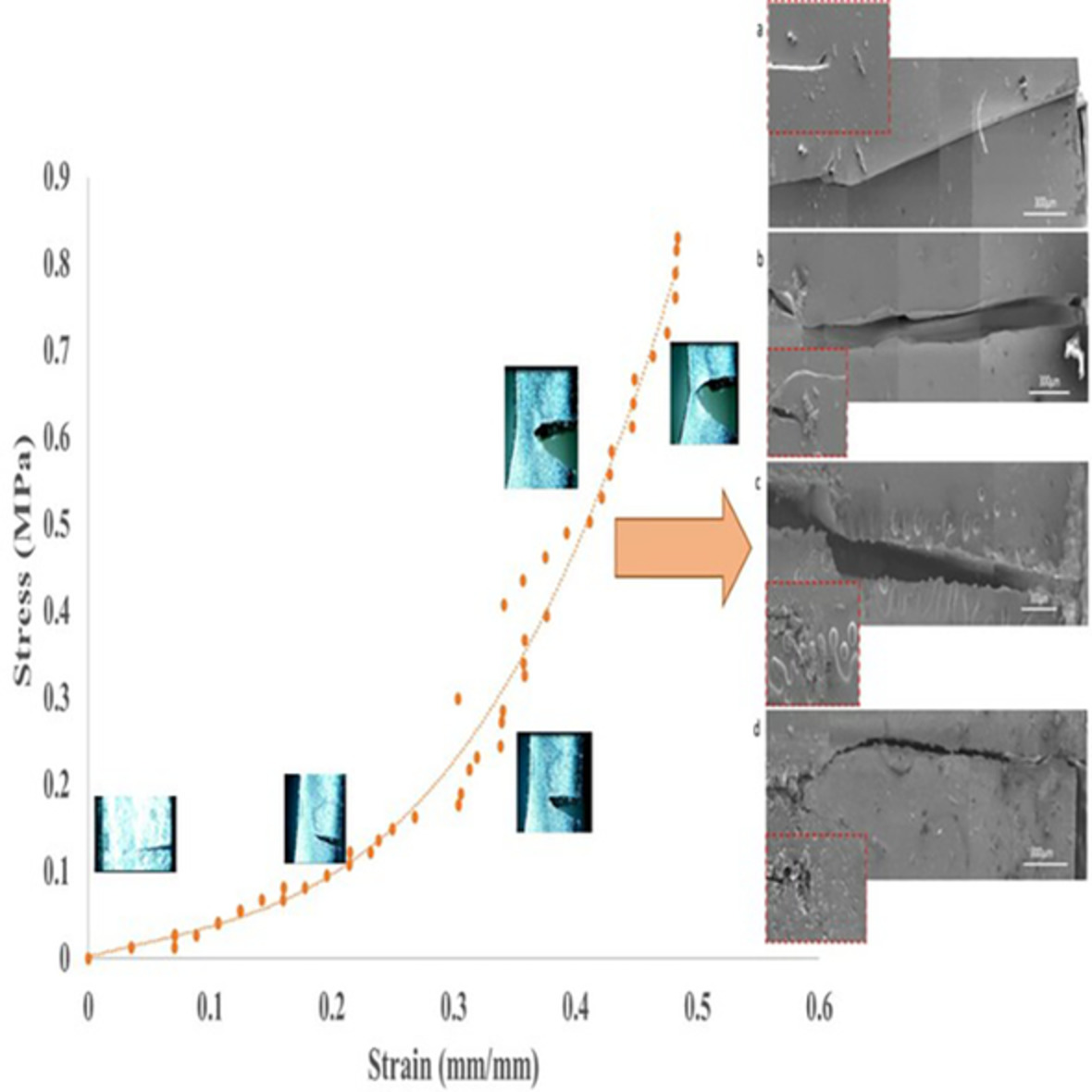
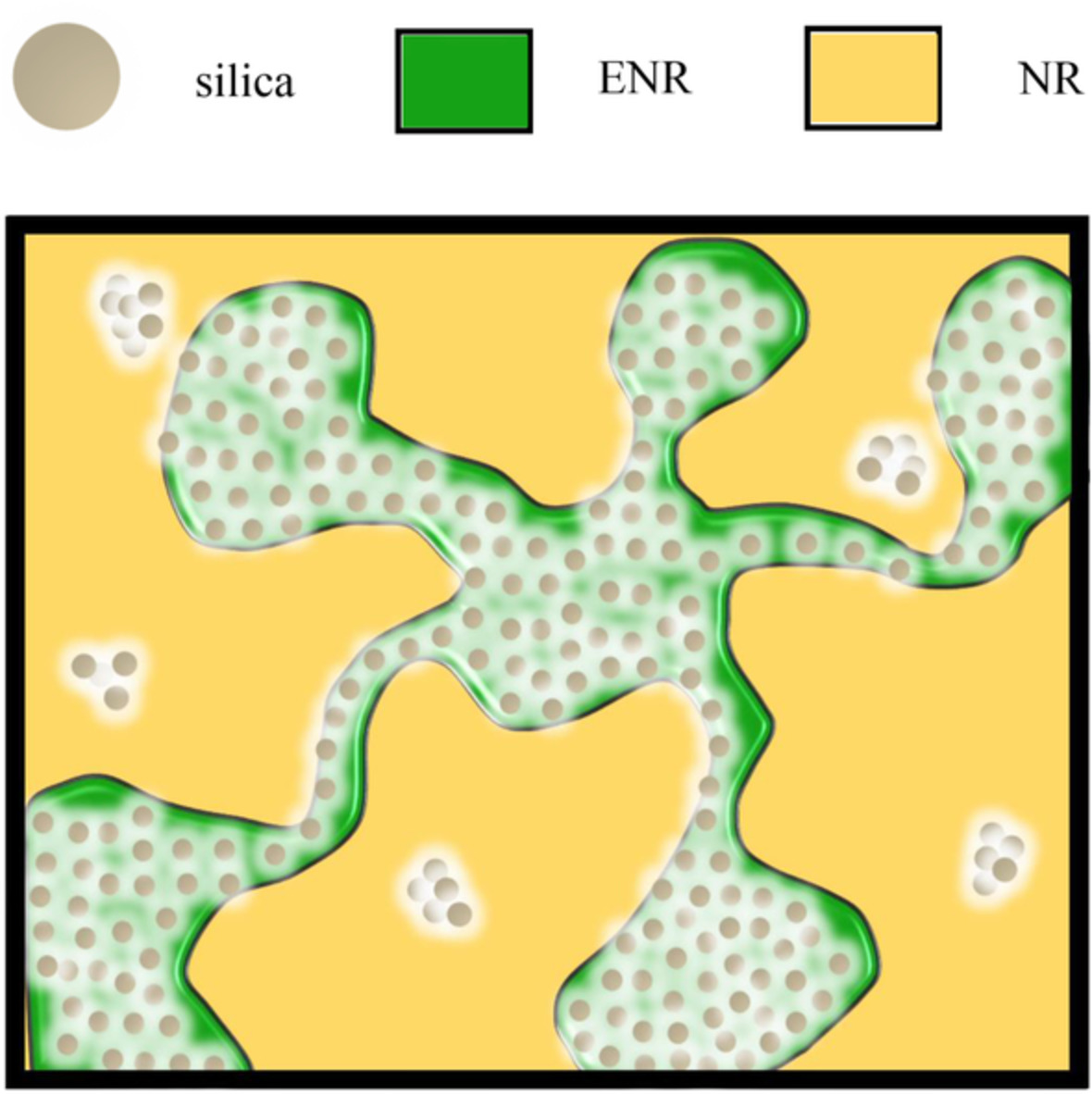
Performance enhancement of bio-based rubber composites using epoxidized natural rubber for silica without carbon emissions and volatile organic compounds
- First Published: 30 May 2022
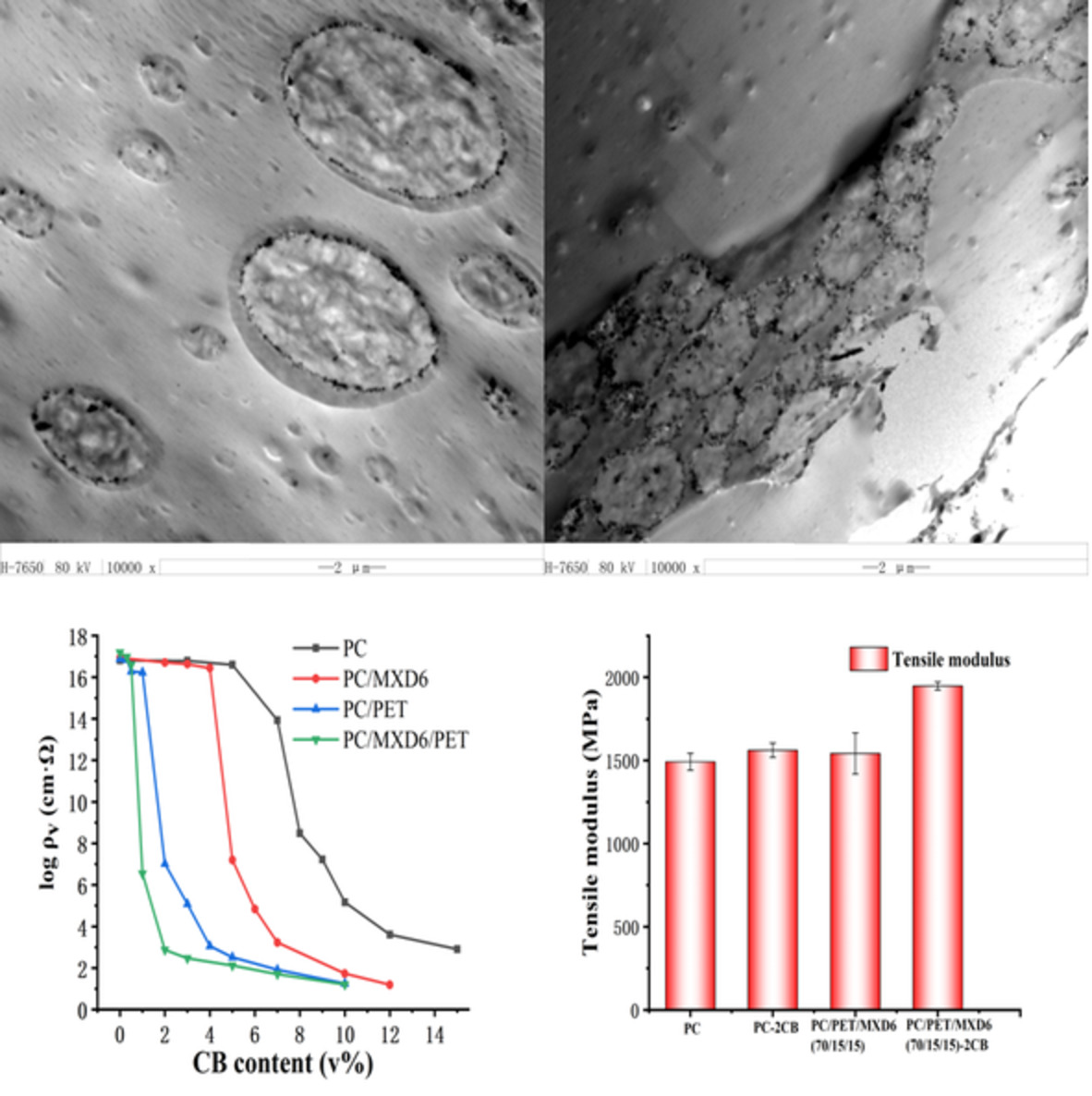
Conductive polycarbonate composites prepared by a ternary polymer blend approach involving sea-island-type interfacial carbon black networks
- First Published: 26 May 2022
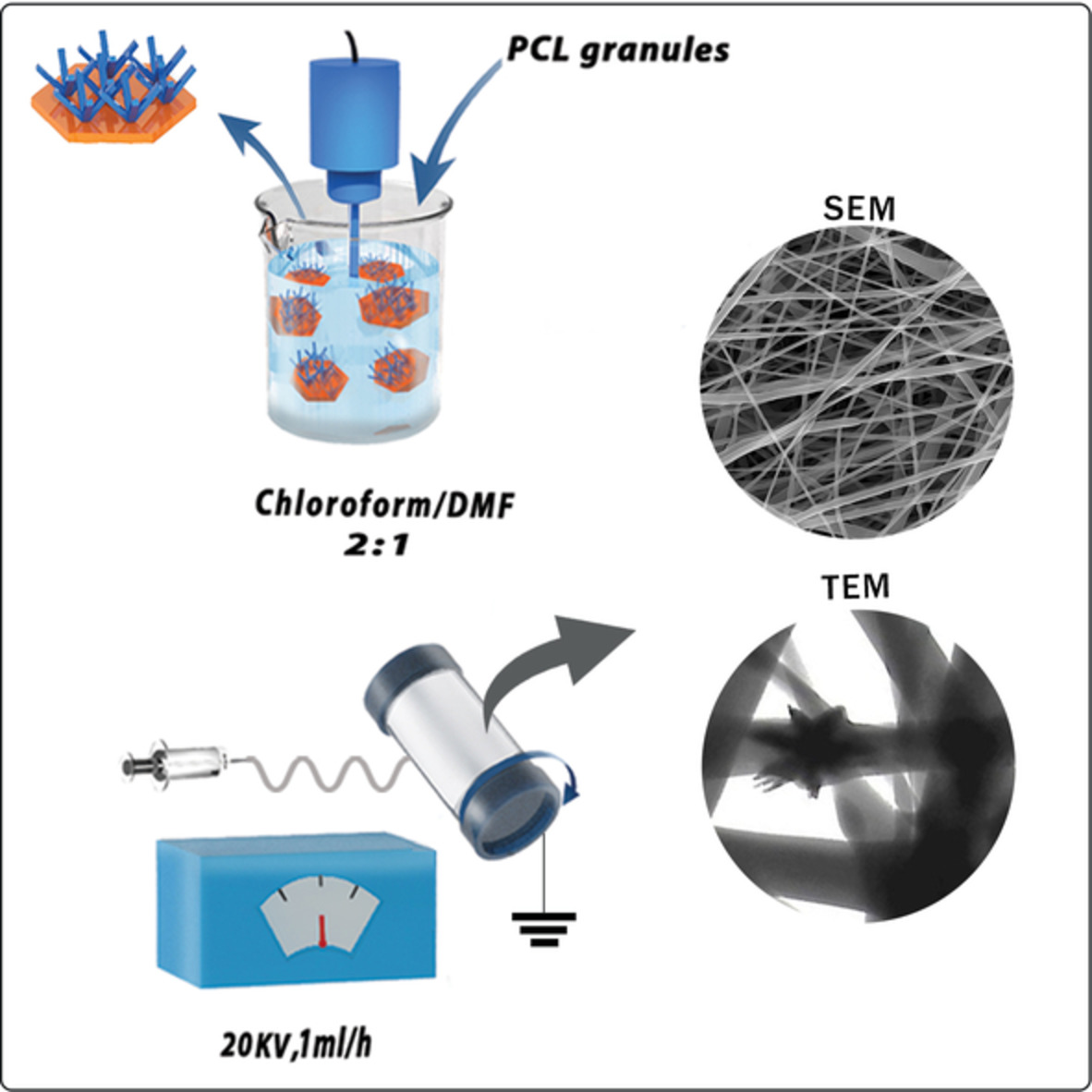
Enhancing mechanical and antibacterial properties of polycaprolactone nanocomposite nanofibers using decorated clay with ZnO nanorods
- First Published: 02 June 2022
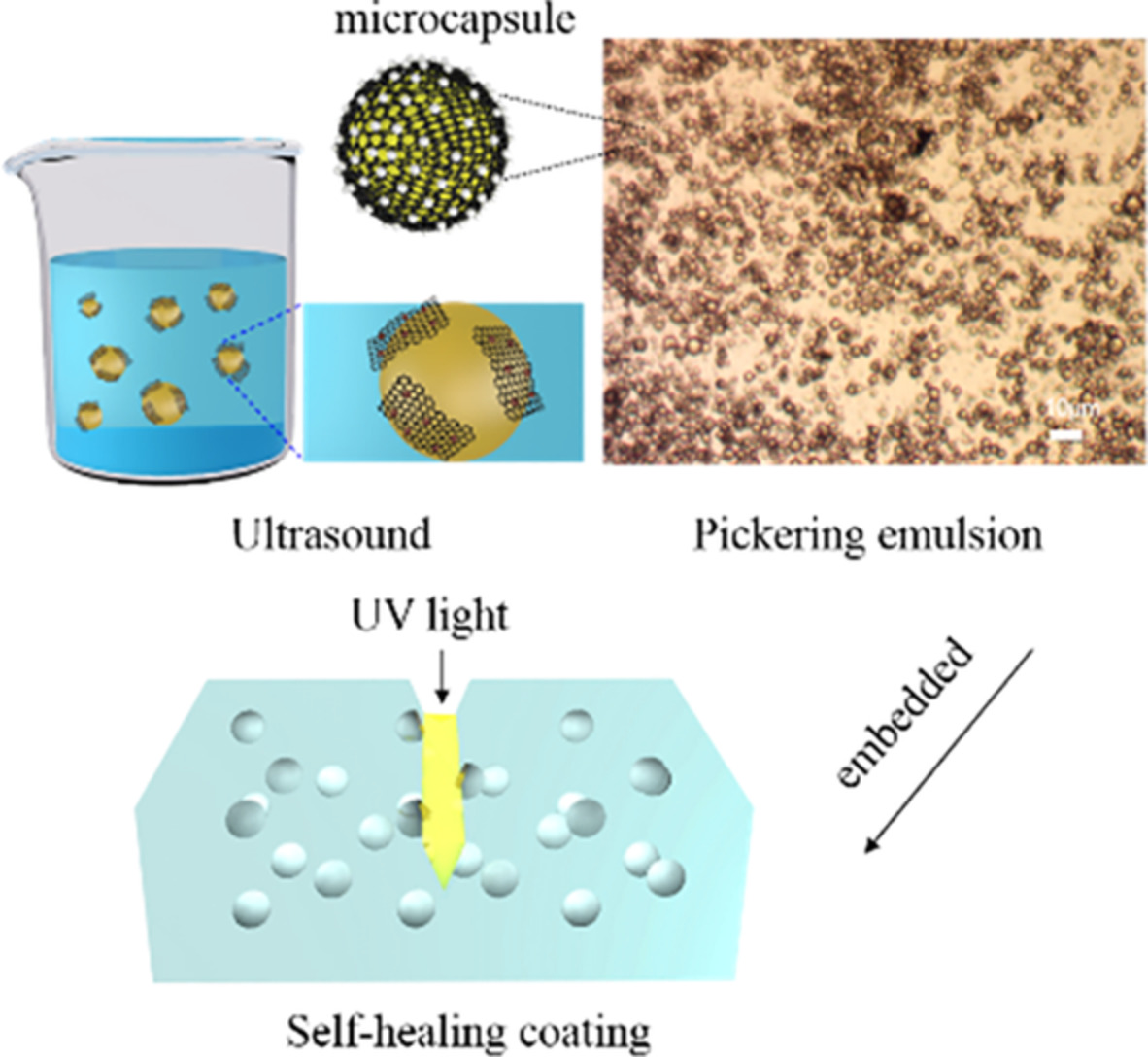
Self-assembled graphene oxide microcapsules in Pickering emulsions for photo-responsive self-healing epoxy coatings
- First Published: 03 June 2022
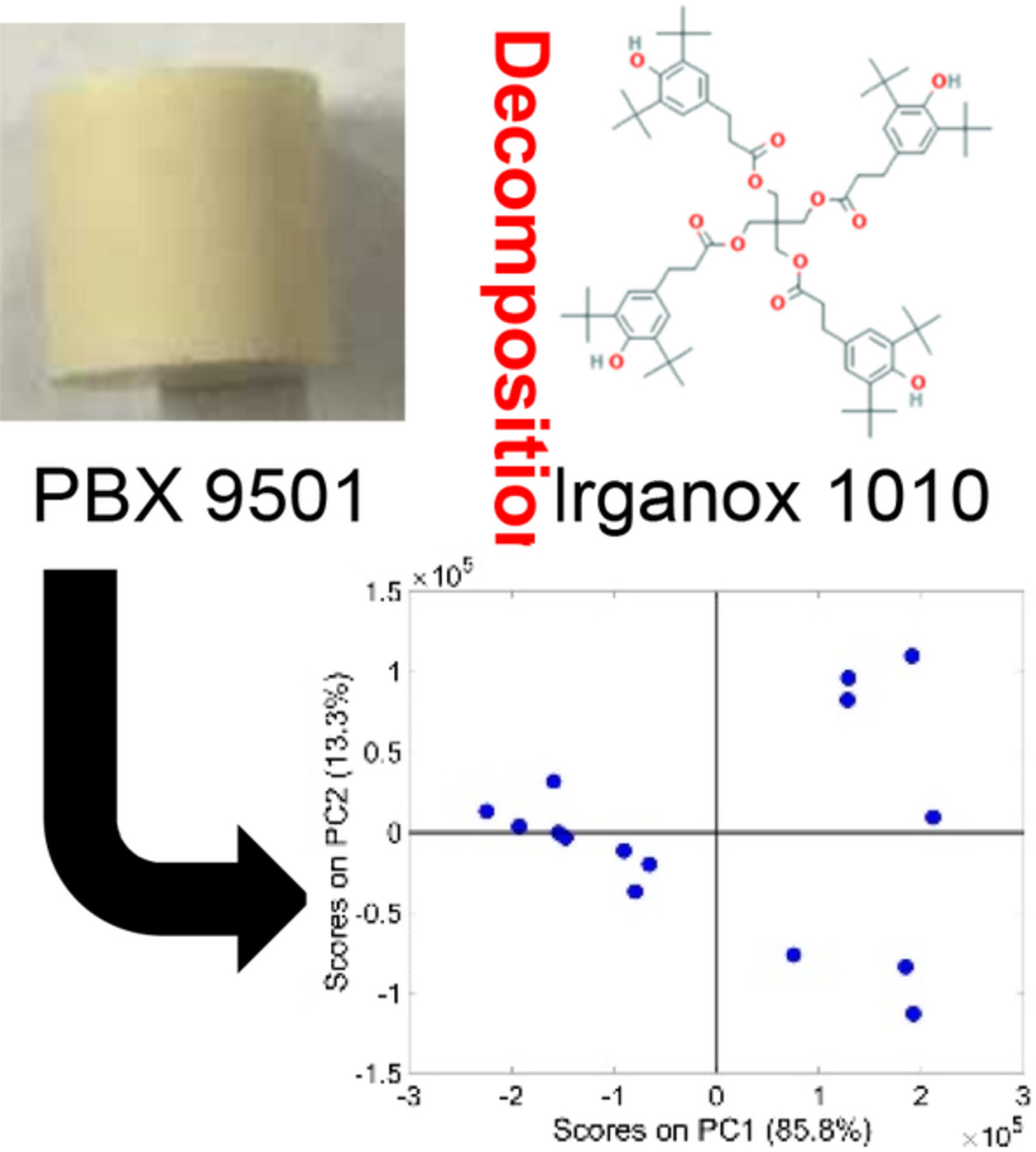
Decomposition of Irganox 1010 in plastic bonded explosives
- First Published: 06 June 2022
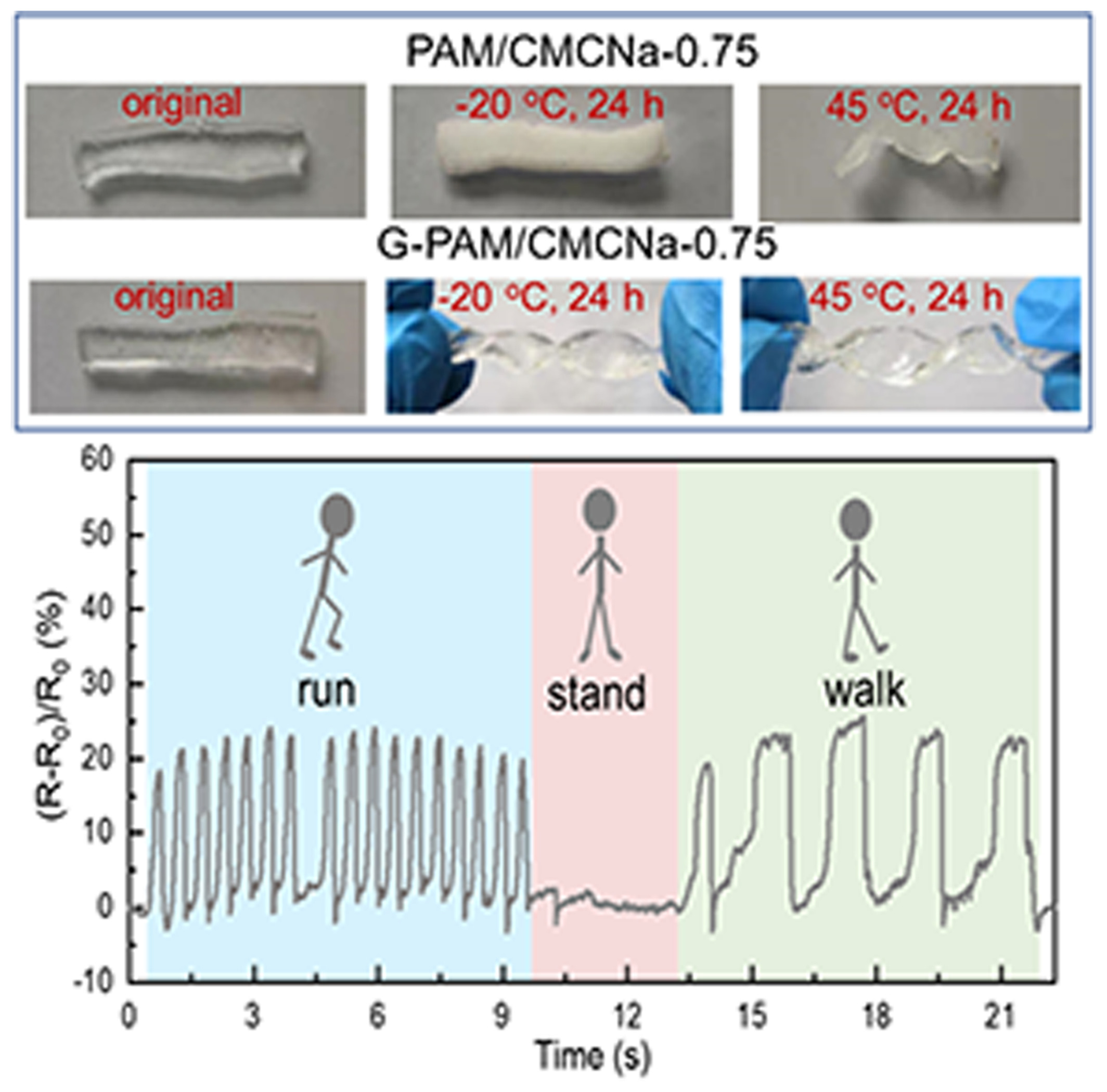
Outstanding temperature-tolerant conductive polyacrylamide/sodium carboxymethylcellulose hydrogel with ultra-stretchability and good strain sensing performance
- First Published: 02 June 2022
Effect of CaSt2/ESO thermal stabilizers on the preparation, thermal stability, and thermal stability mechanism of self-made vinylidene chloride-methyl acrylate copolymer resin film
- First Published: 07 June 2022
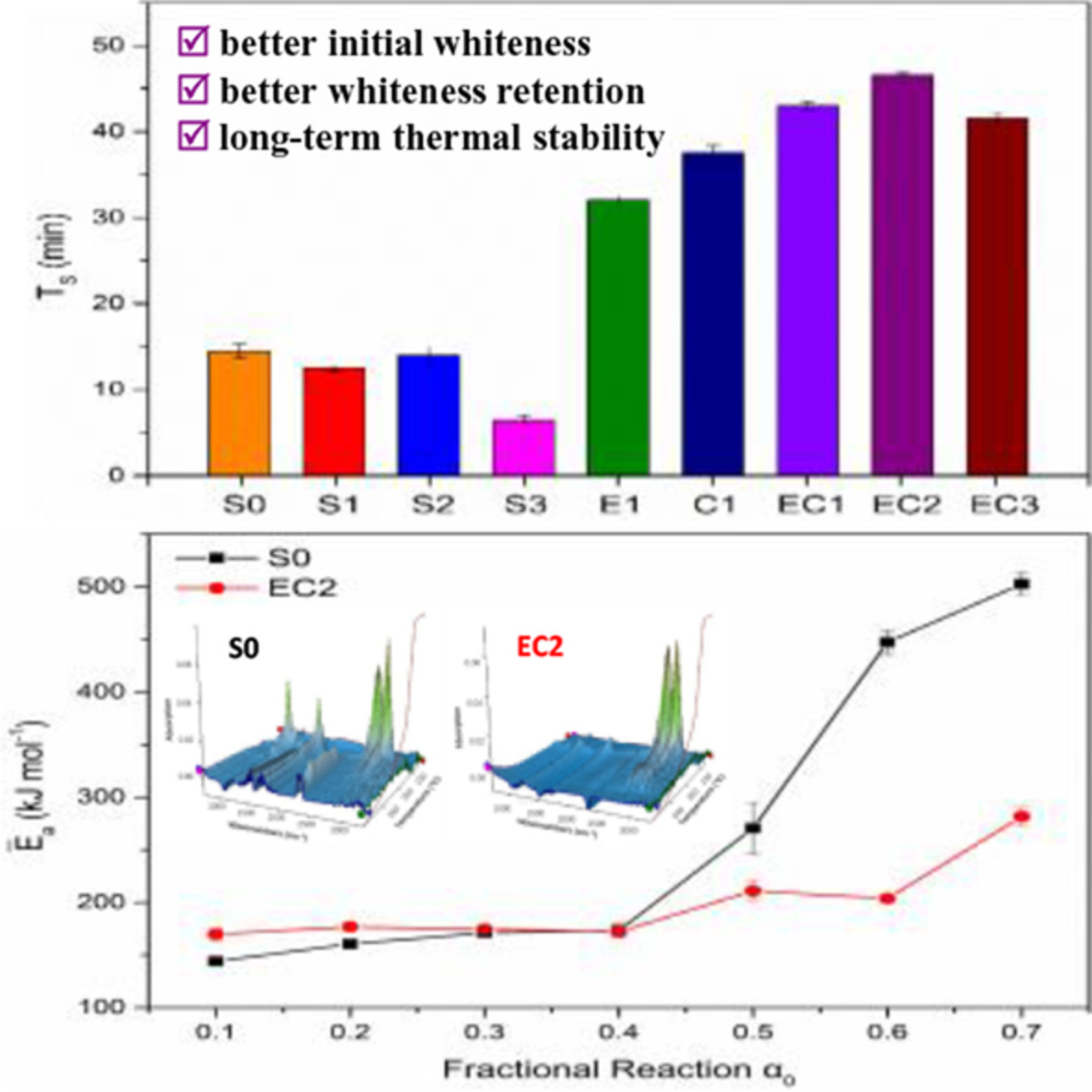
CaSt2/ESO were incorporated into the self-made PVDC-MA film with excellent initial whiteness, whiteness retention to enhance thermal stability. Generalized master plot methods showed that after adding CaSt2/ESO, the kinetic model followed by PVDC-MA transformed from three-dimensional diffusion to two-dimensional diffusion model in the initial thermal degradation stage.
Zwitterion grafted forward osmosis membranes with superwetting property via atom transfer radical polymerization
- First Published: 02 June 2022
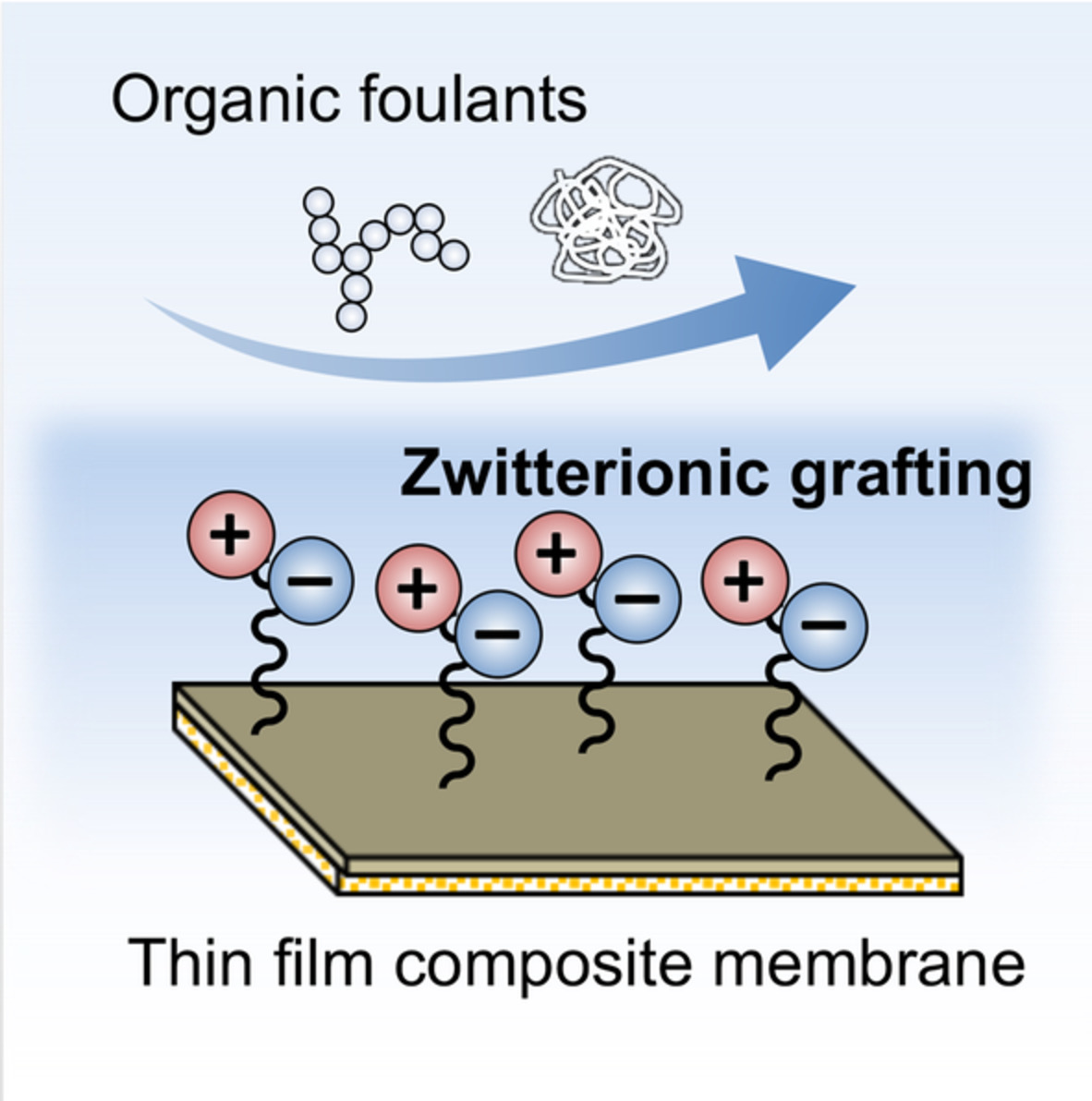
Zwitterionic poly(2-methacryloyloxyethyl phosphorylcholine) was successfully grafted onto traditional polyamide membrane via atom transfer radical polymerization for antifouling forward osmosis process. The grafted membrane retained the salt rejection performance of the pristine membrane and showed much improved antifouling properties when treating organic foulants-contained feed solutions.
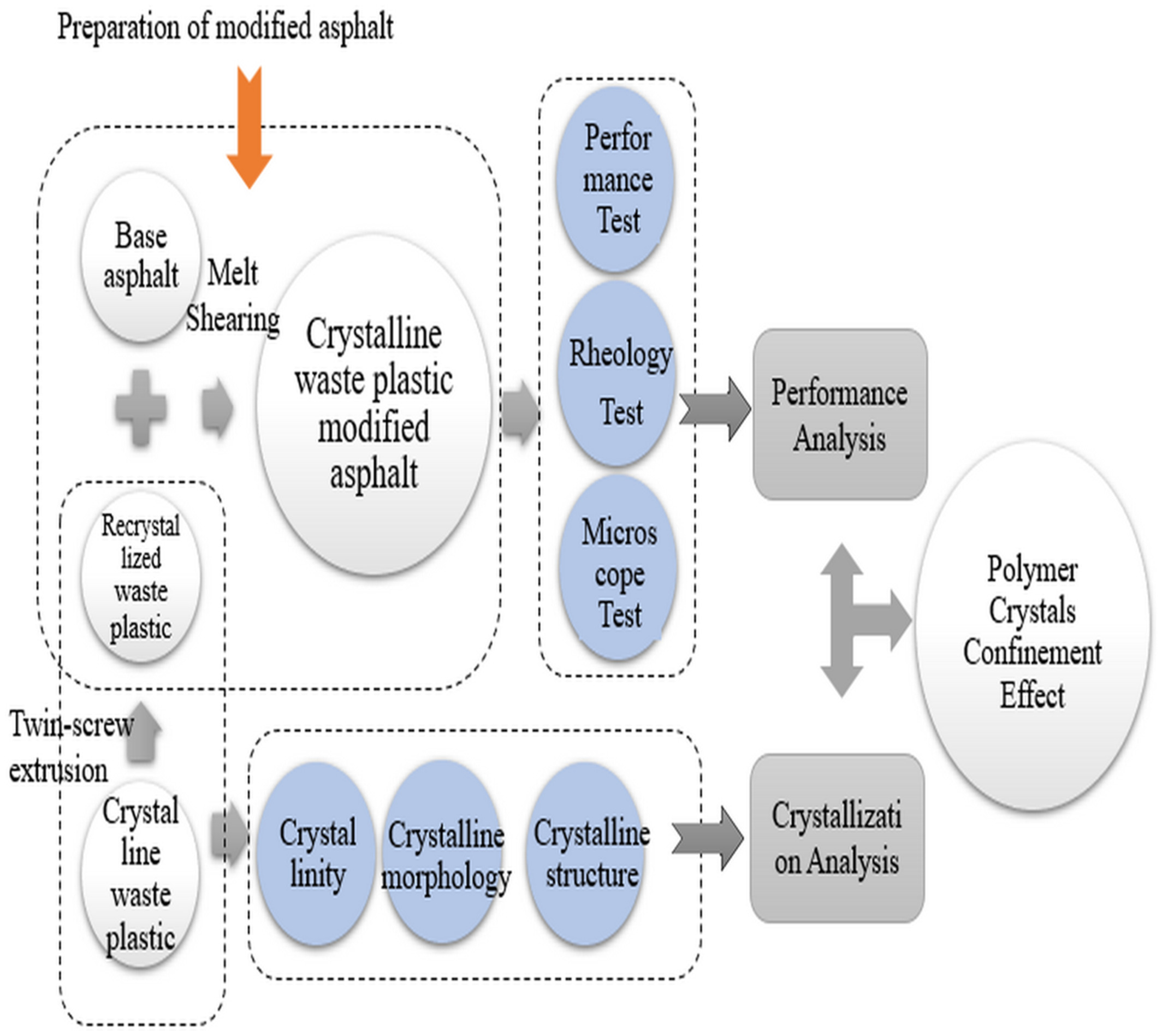
Reutilization of crystalline waste plastics for modified asphalt using twin-screw extrusion: Polyethylene and polypropylene as typical subjects
- First Published: 03 June 2022
Effects of different polyolefin copolymers on properties of melt mixed polypropylene blends
- First Published: 02 June 2022
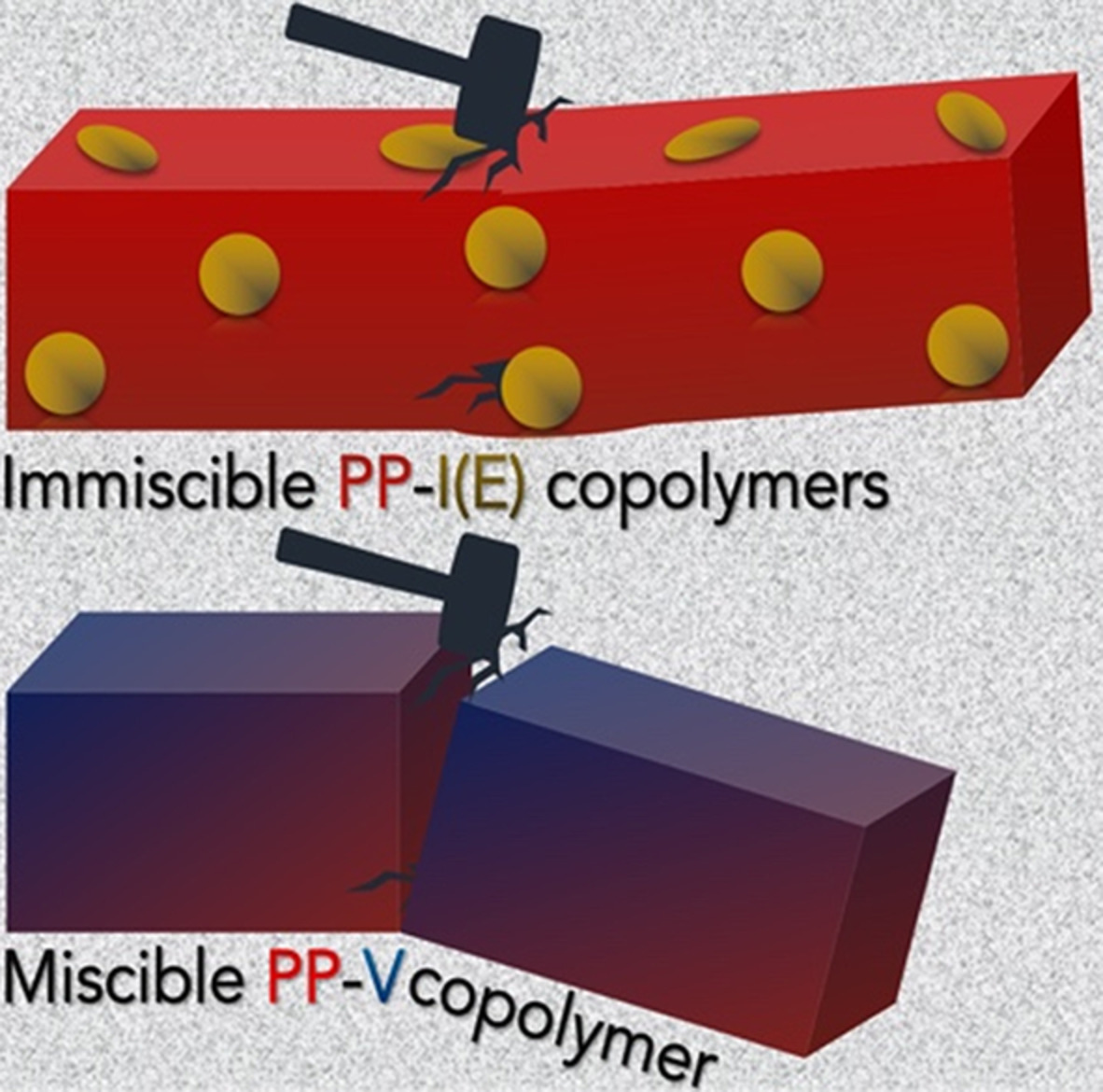
The immiscible copolymers that is, ethylene-octene random block (Engage, E) and ethylene-octene multi-block (Infuse, I) enhanced the impact strength for polypropylene significantly while the miscible one that is, ethylene-propylene copolymer (Versify, V) delivered insignificant effects. Immiscible copolymer particles act as reinforcing factor to resist and dissipate the impact load over the matrix, and thereby, improve the impact strength for the resultant blends.
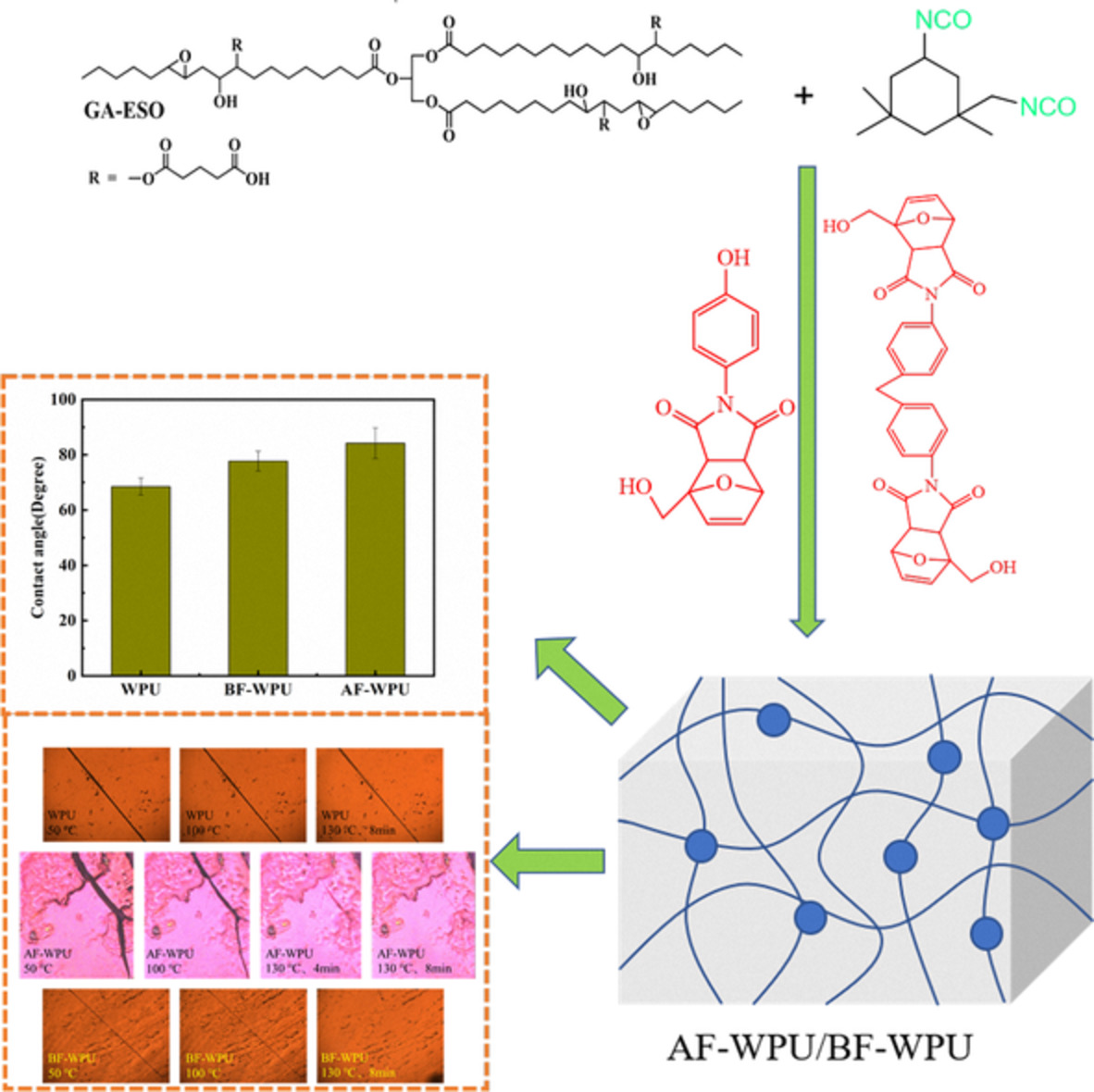
Synthesis of self-healing soybean oil-based waterborne polyurethane based on Diels–Alder reaction
- First Published: 02 June 2022
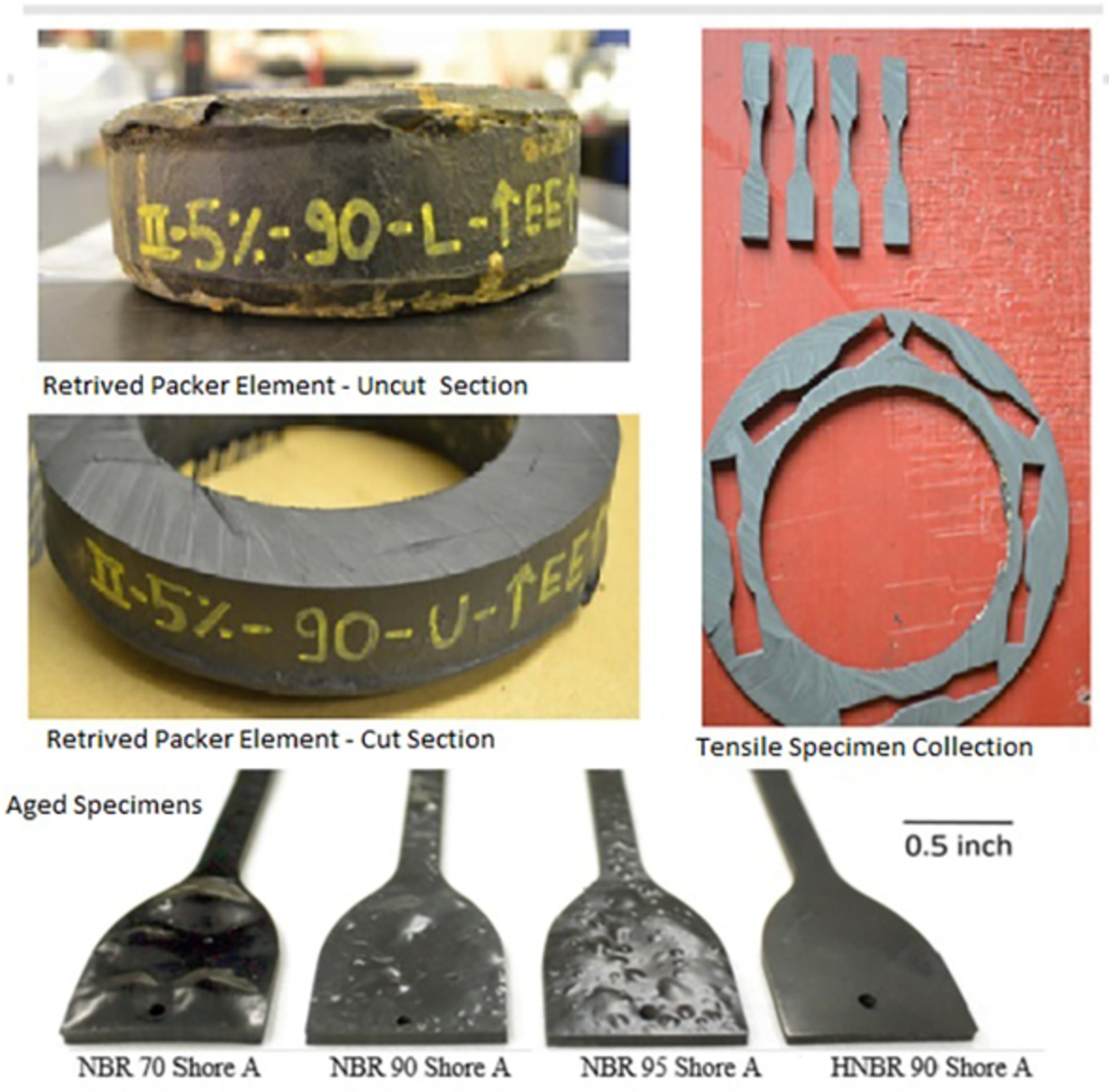
Study of hydrogen sulfide effect on acrylonitrile butadiene rubber/hydrogenated acrylonitrile butadiene rubber for sealing application in oil and gas industry
- First Published: 09 June 2022
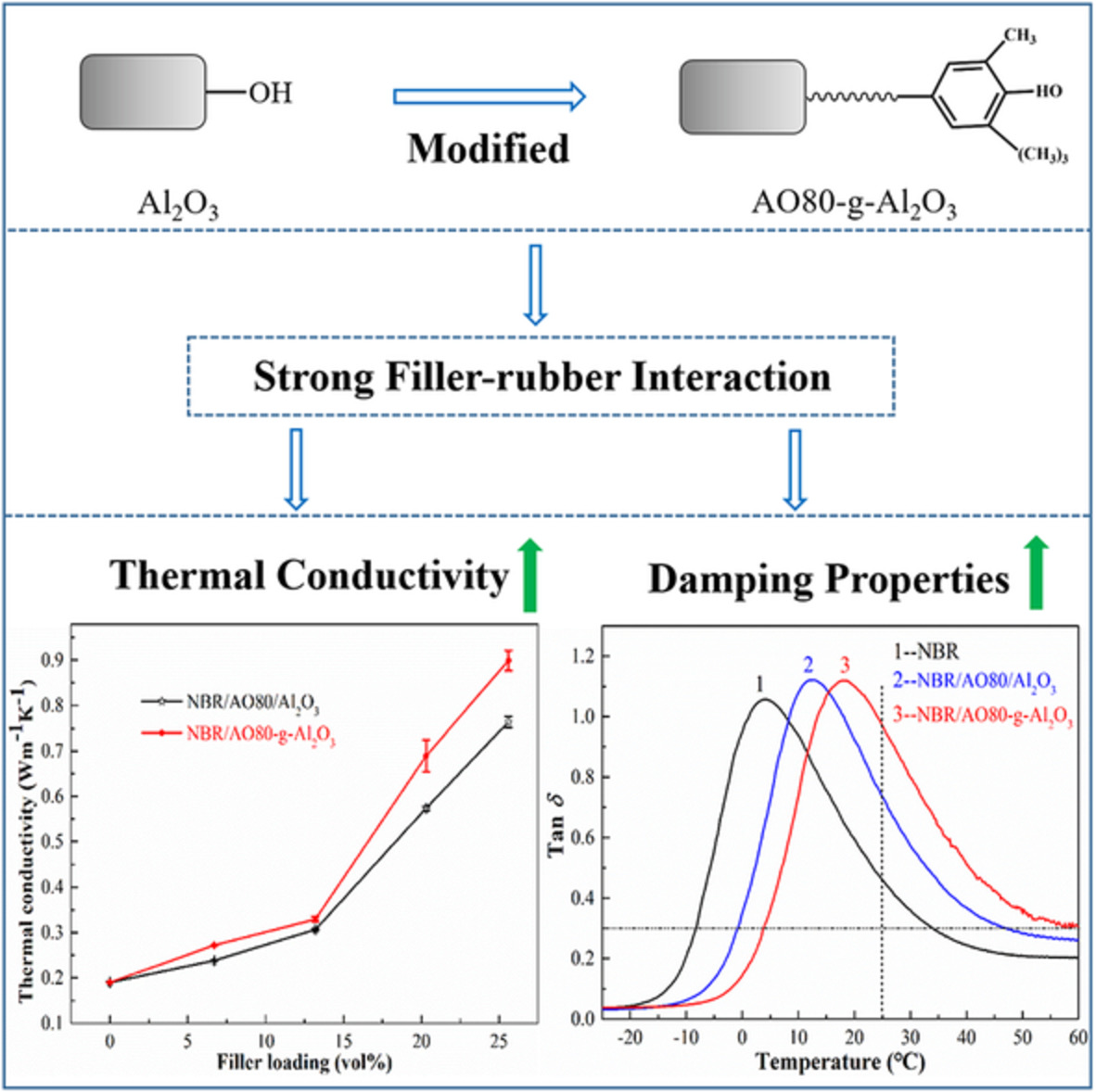
Enhancements in damping properties and thermal conductivity of acrylonitrile-butadiene rubber by using hindered phenol modified alumina
- First Published: 30 May 2022
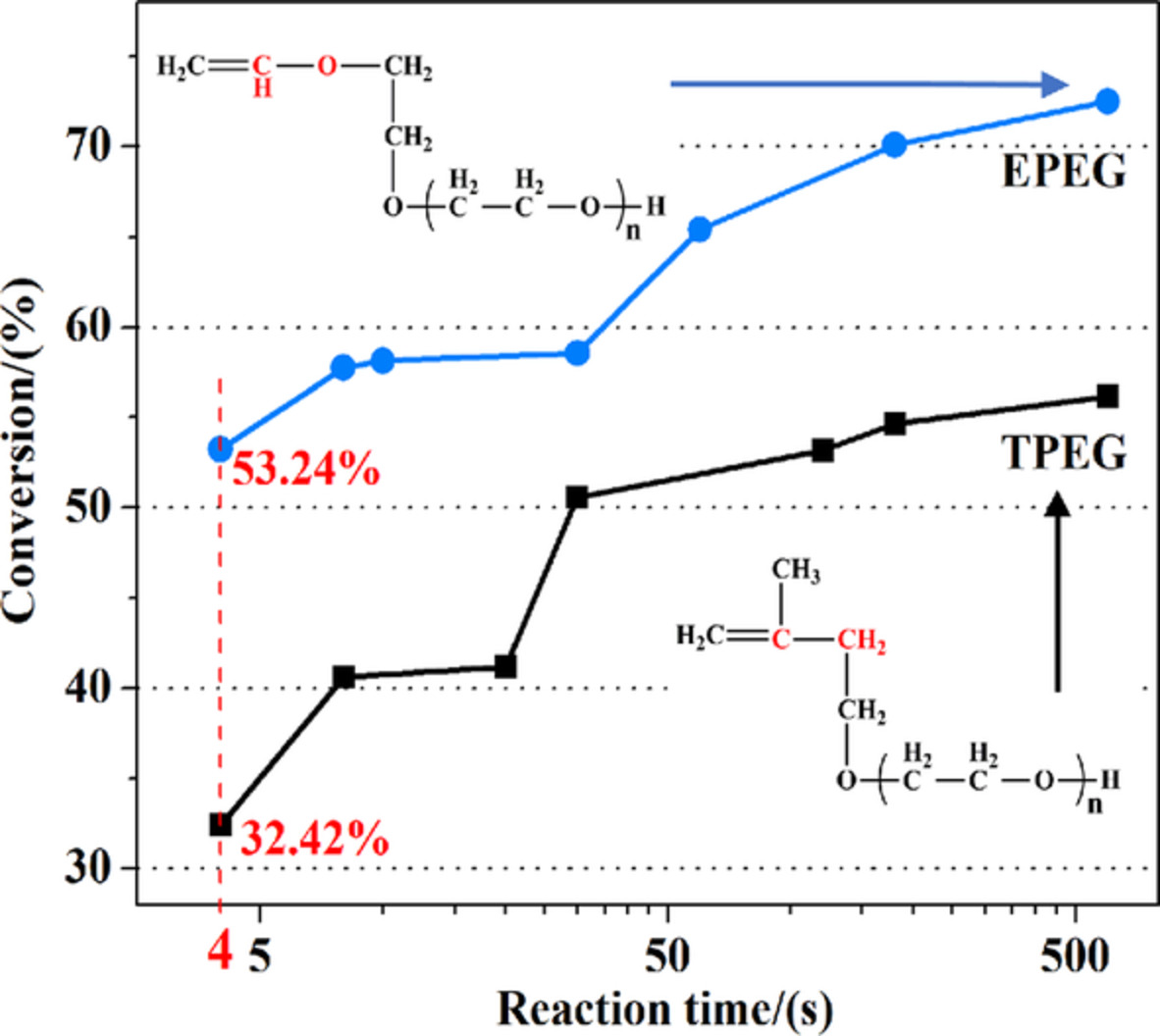
Study on the polymerization process and monomer reactivity of EPEG-type polycarboxylate superplasticizer
- First Published: 01 June 2022