Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Highlights from the Editors 2020
A study on the correlation between remnant cholesterol and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio in Chinese community adults: A report from the REACTION study
中国社区成年人群残余胆固醇与尿白蛋白肌酐比值的相关性研究:一份来自REACTION研究的报告
- First Published: 05 June 2020
Highlights
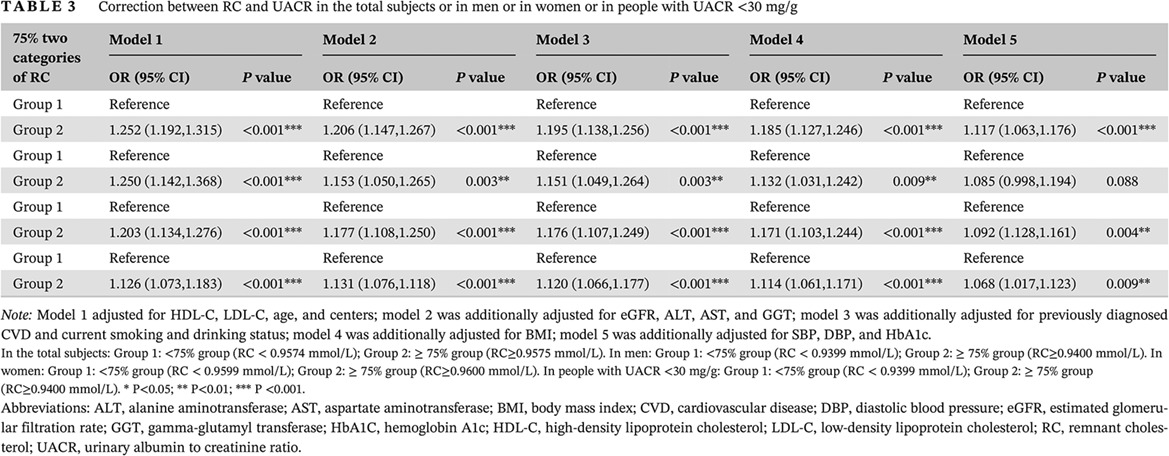
- This is the first multicenter, large-sample and cross-sectional study of the relationship between RC and urinary albumin to creatinine ratio (UACR) in the Chinese community adults.
- RC is highly correlated with UACR, and at high RC level, the patients with critical values of blood pressure, BMI, and blood glucose has a more significant correlation between RC and UACR.
Economic benefit of prescribing an adjusted renal dose of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors in type 2 diabetes patients with chronic kidney disease
调整二肽基肽酶IV抑制剂的剂量在2型糖尿病合并慢性肾病患者中的经济效益
- First Published: 20 May 2020
Highlights
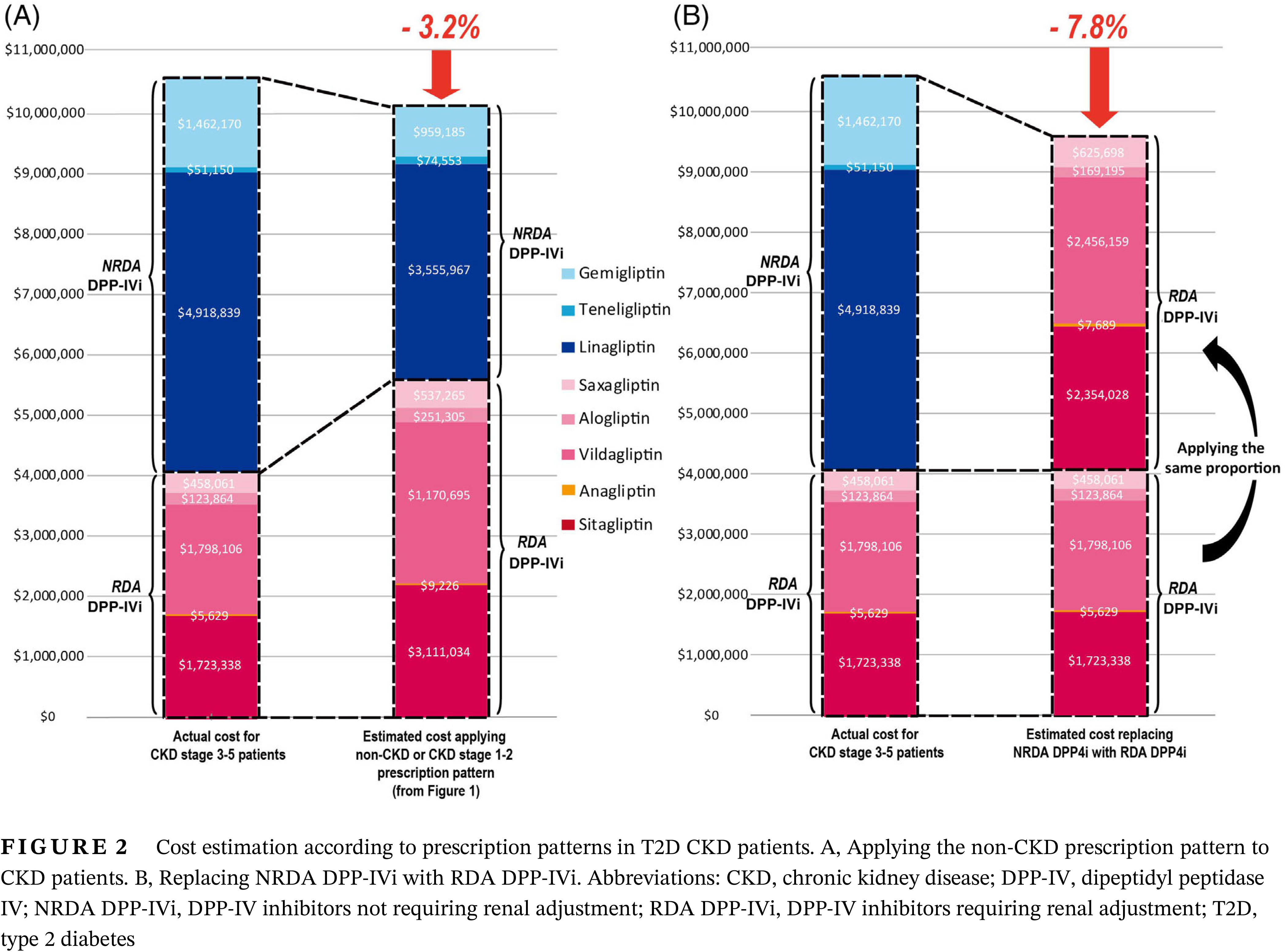
- Based on nationwide insurance data in Korea, the use of dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitors (DPP-IVi) not requiring renal dose adjustment (NRDA DPP-IVi) is widespread in the type 2 diabetes chronic kidney disease (T2D CKD) population.
- Instead of prescribing NRDA DPP-IVi, the use of DPP-IVi requiring renal dose adjustment with appropriate renal dose adjustments in T2D CKD patients can achieve a considerable annual cost saving of up to 7.8%.
GLP-1 and insulin regulation of skeletal and cardiac muscle microvascular perfusion in type 2 diabetes
GLP-1和胰岛素对2型糖尿病骨骼肌和心肌微血管灌注的调节作用
- First Published: 09 April 2020
Highlights
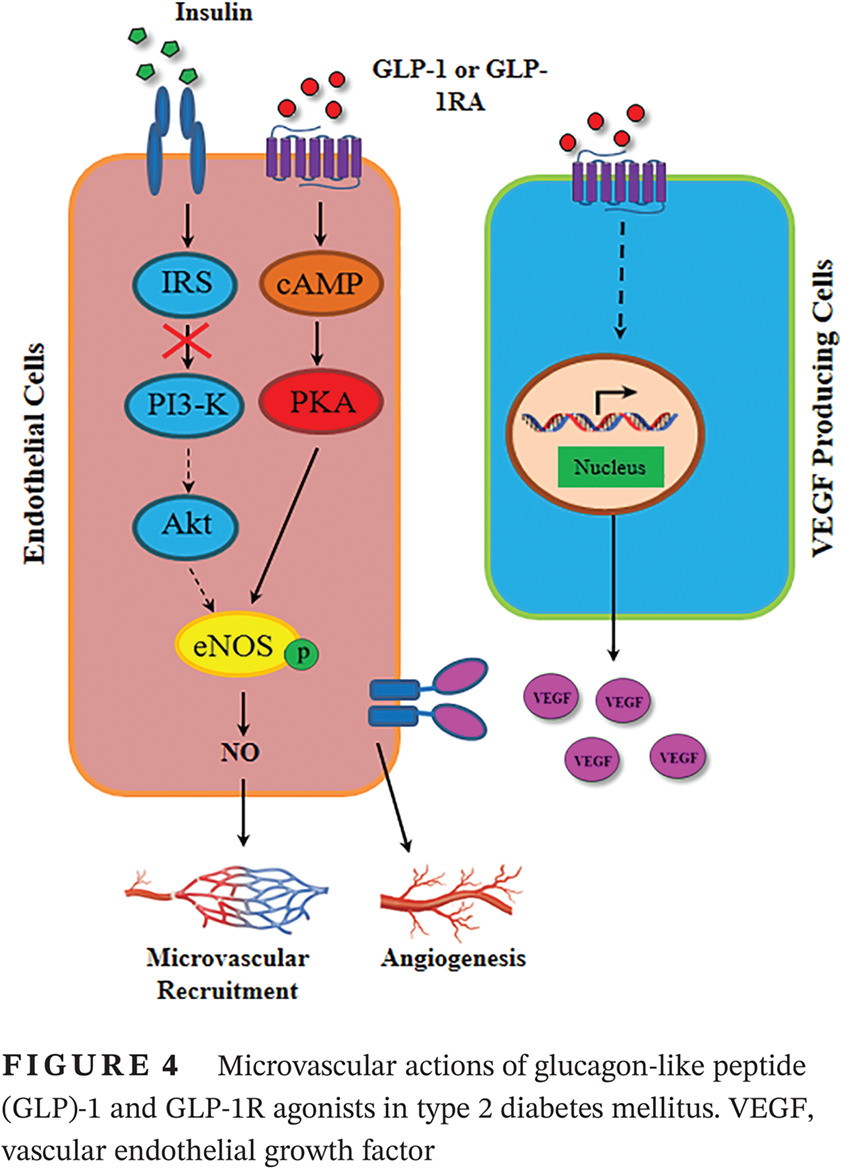
- Skeletal and cardiac muscle microvasculature critically regulates tissue perfusion and the delivery of nutrients, oxygen, and hormones and thus the health and function of skeletal and cardiac muscle. Both insulin and GLP-1 increase skeletal and cardiac muscle microvascular perfusion but insulin's action is blunted whereas GLP-1's effect is preserved in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. This may contribute to the salutary cardiovascular protective effects of the GLP-1 receptor agonists seen in multiple clinical trials.
Sonographic and other nonglycemic factors can predict large-for-gestational-age infants in diet-managed gestational diabetes mellitus: A retrospective cohort study
超声和其他非血糖因素可以预测饮食管理中的妊娠糖尿病孕妇中的大于胎龄儿:一项回顾性队列研究
- First Published: 06 April 2020
Highlights
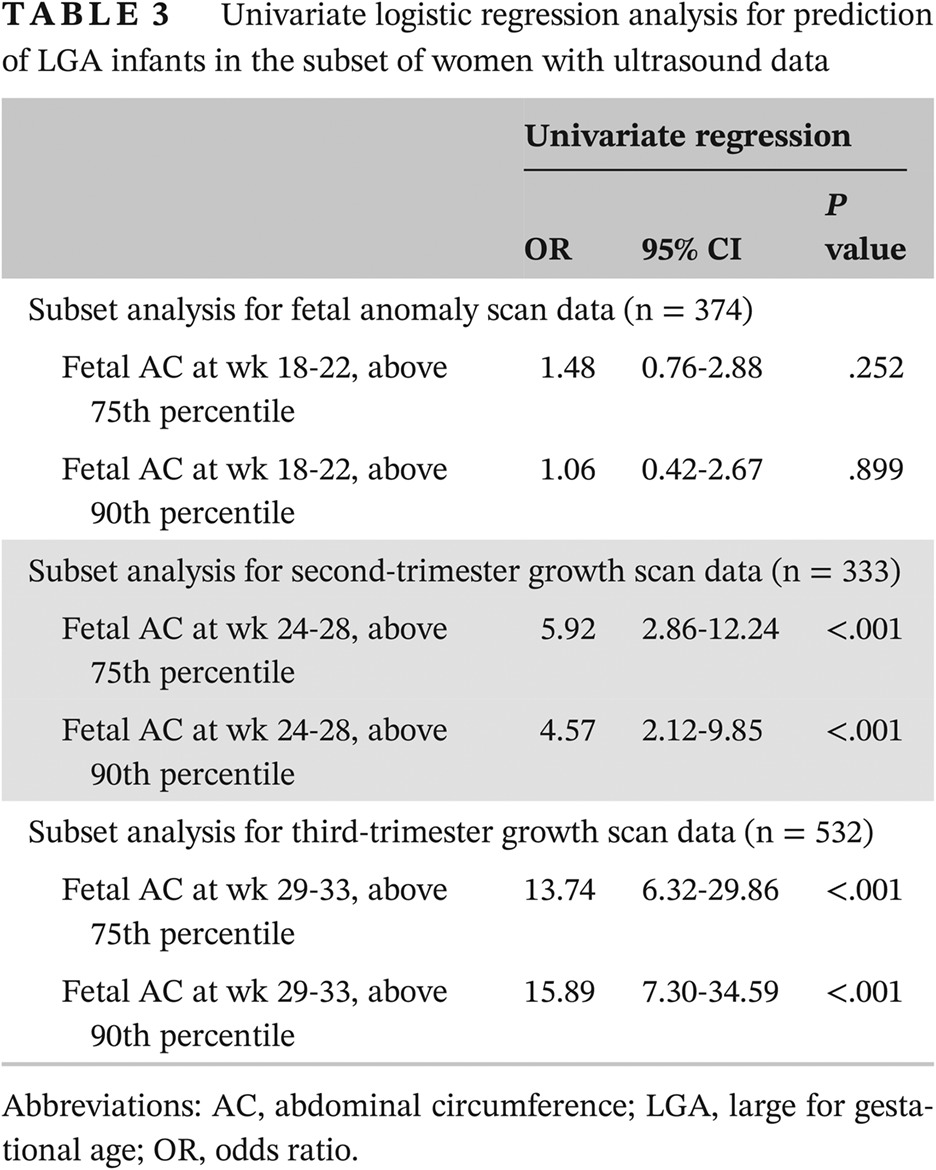
- In diet-managed gestational diabetes mellitus pregnancies, the novel large-for-gestational-age (LGA) risk factor of fetal abdominal circumference determined at 24- to 28-week fetal ultrasound can identify women at risk as well as the known risk factors of maternal parity, prepregnancy body mass index, and gestational age.
- Smoking reduces LGA risk but has other harms.
- Early identification of risk factors for LGA allows early intervention to mitigate LGA risk, such as restriction of excessive further maternal gestational weight gain and other therapies, which may include insulin, though unproven.
Follicle-stimulating hormone and estradiol are associated with bone mineral density and risk of fractures in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus
卵泡刺激素和雌二醇与男性2型糖尿病患者的骨密度和骨折风险相关
- First Published: 28 November 2019
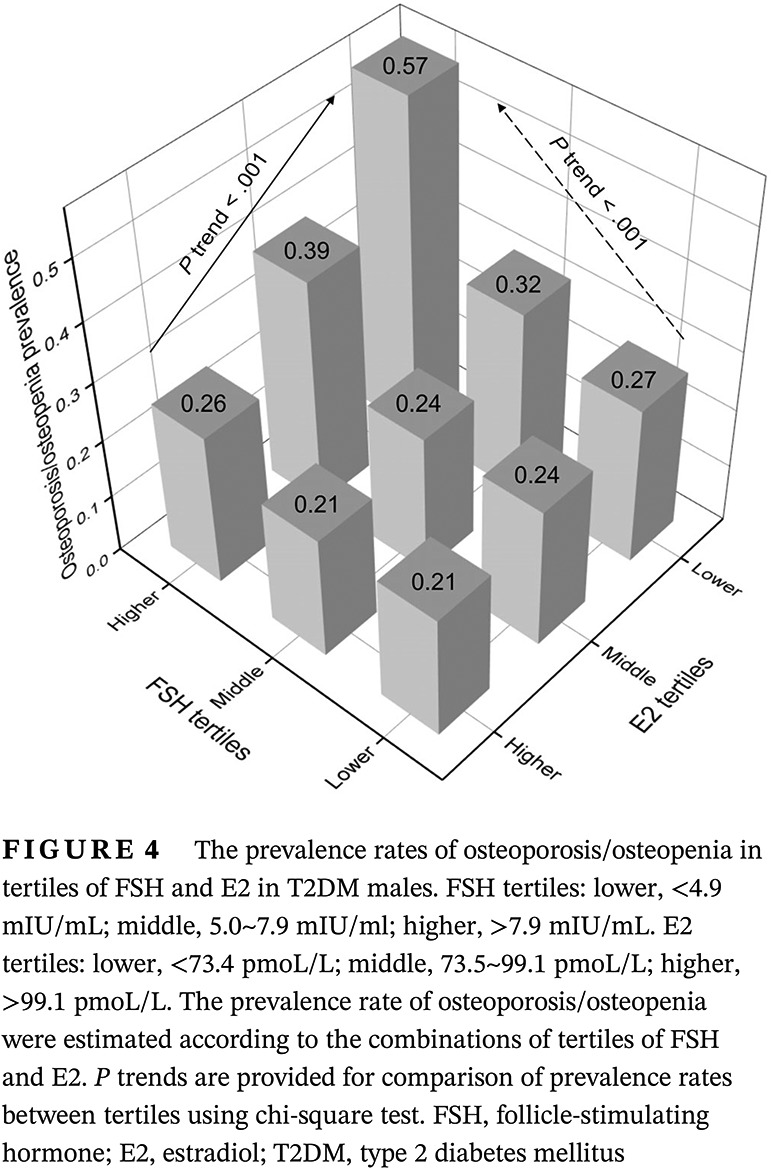
Highlights
- Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and estradiol (E2) were significantly associated with bone mineral density in male with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- FSH was strongly associated with fracture risk measured by the modified Fracture Risk Algorithm (FRAX) tool in males with T2DM.
- T2DM males with both higher FSH and lower E2 had the highest risk of incident osteoporosis/osteopenia.
The association of husbands’ smoking with wives' dysglycemia status: A cross-sectional study among over 10 million Chinese women aged 20-49
丈夫吸烟与妻子血糖异常状态的关联:一项基于1000万名20-49岁中国妇女的横断面研究
- First Published: 20 November 2019
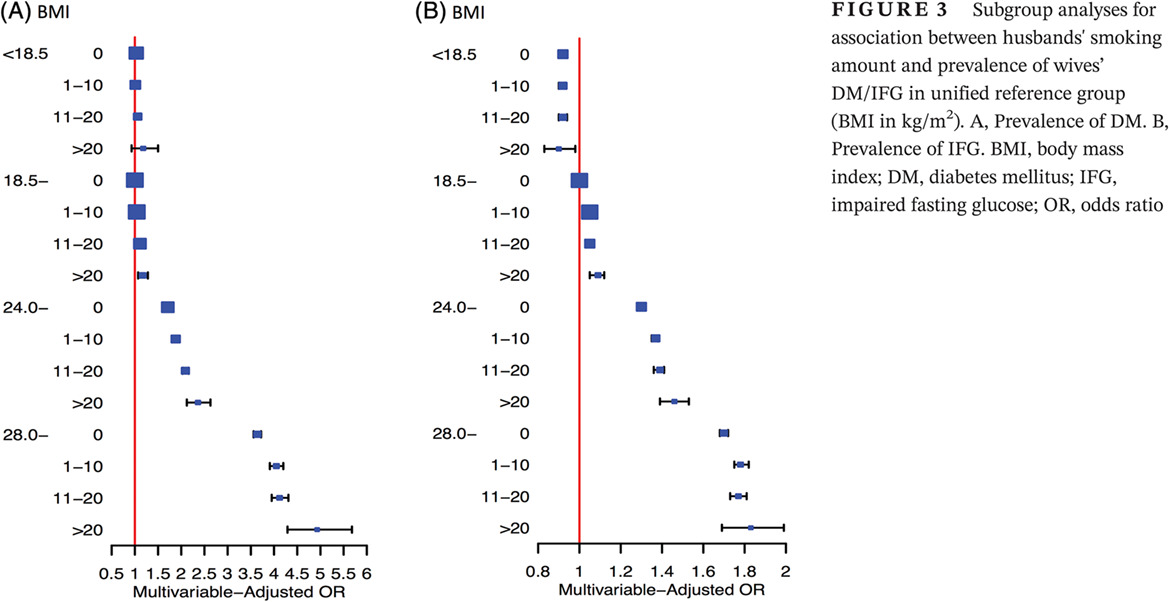
Highlights
- Women whose husbands are smokers are at an increased risk of having impaired fasting glucose or diabetes, and this association exists in both a categorical and dose-response manner.
- We found an interaction effect of body mass index and husbands’ smoking on the risk of dysglycemia in their wives.
- Husbands' smoking cessation or reduced amount of smoking is beneficial for prevention of dysglycemia in their wives.
- Practical family-oriented approaches for smoking cessation and smoking restriction are warranted.
Emerging trends and the clinical impact of food insecurity in patients with diabetes
食品安全问题对糖尿病患者的新趋势和临床影响
- First Published: 09 October 2019
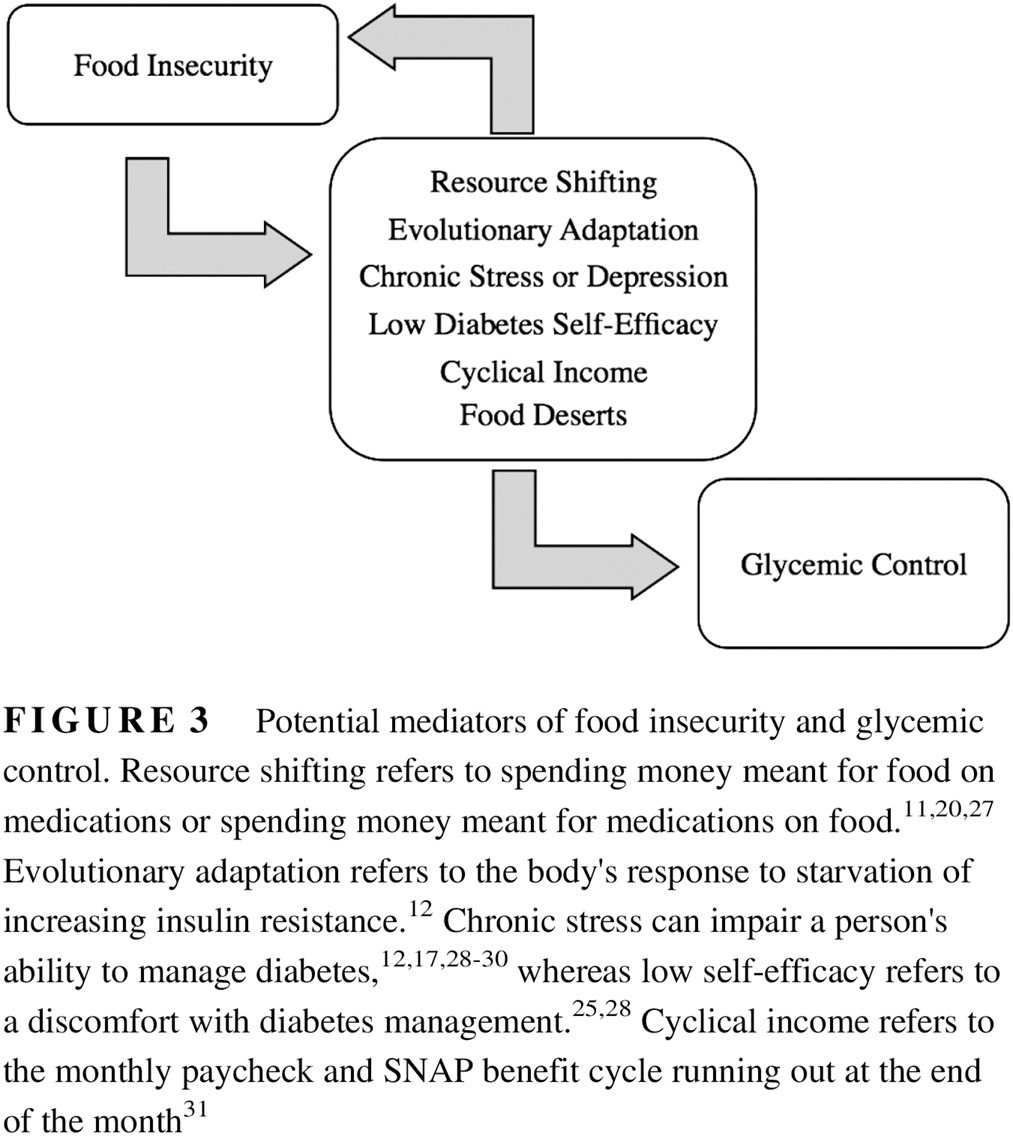
Highlights
- Food insecurity is a major public health problem that highlights social disparities and negatively affects those with chronic diseases, including diabetes.
- Interventions targeting food insecurity in those with diabetes have shown little improvement in glycemic control despite improving food security status.
- This suggests a complex relationship between glycemic control and food insecurity that is likely mediated by many diverse socioeconomic factors.
Therapeutic approaches for latent autoimmune diabetes in adults: One size does not fit all
成人隐匿性自身免疫性糖尿病的治疗方法:不能千篇一律
- First Published: 26 August 2019
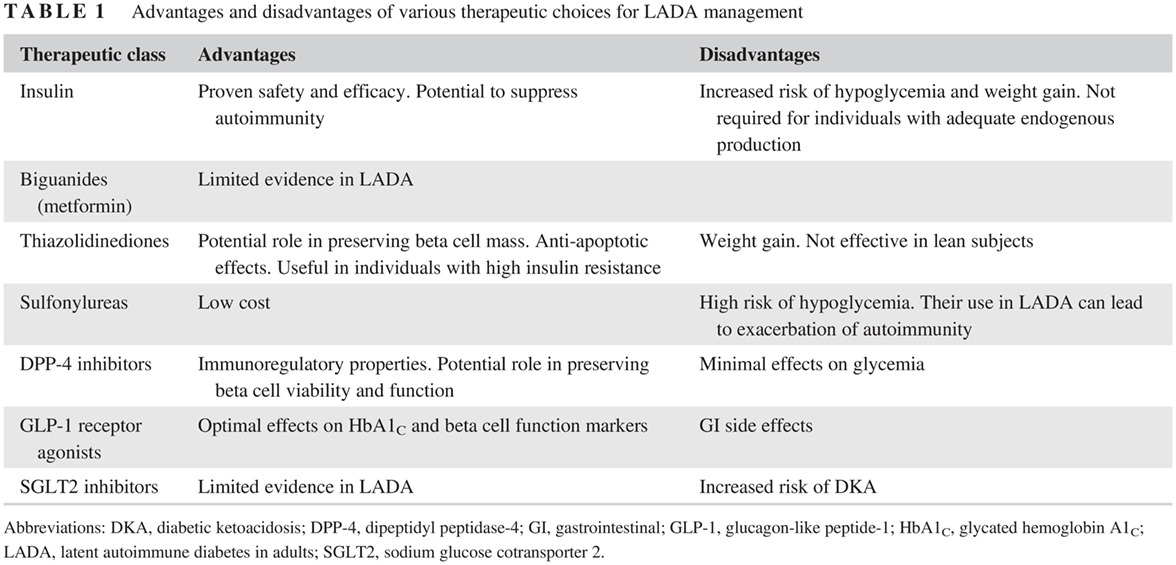
Highlights
- Latent autoimmune diabetes in adults (LADA) presents with remarkable pathophysiological and phenotypic heterogeneity.
- There is a need for further understanding the complex underlying mechanisms of the disorder.
- Apart from insulin, agents used in type 2 diabetes (T2D) management might have a role in assisting glycemic control and preserving beta cell function in people with LADA.
Dietary preferences and diabetic risk in China: A large-scale nationwide Internet data-based study
中国的饮食偏好和糖尿病风险研究:一项基于大规模互联网数据的全国性研究
- First Published: 09 July 2019
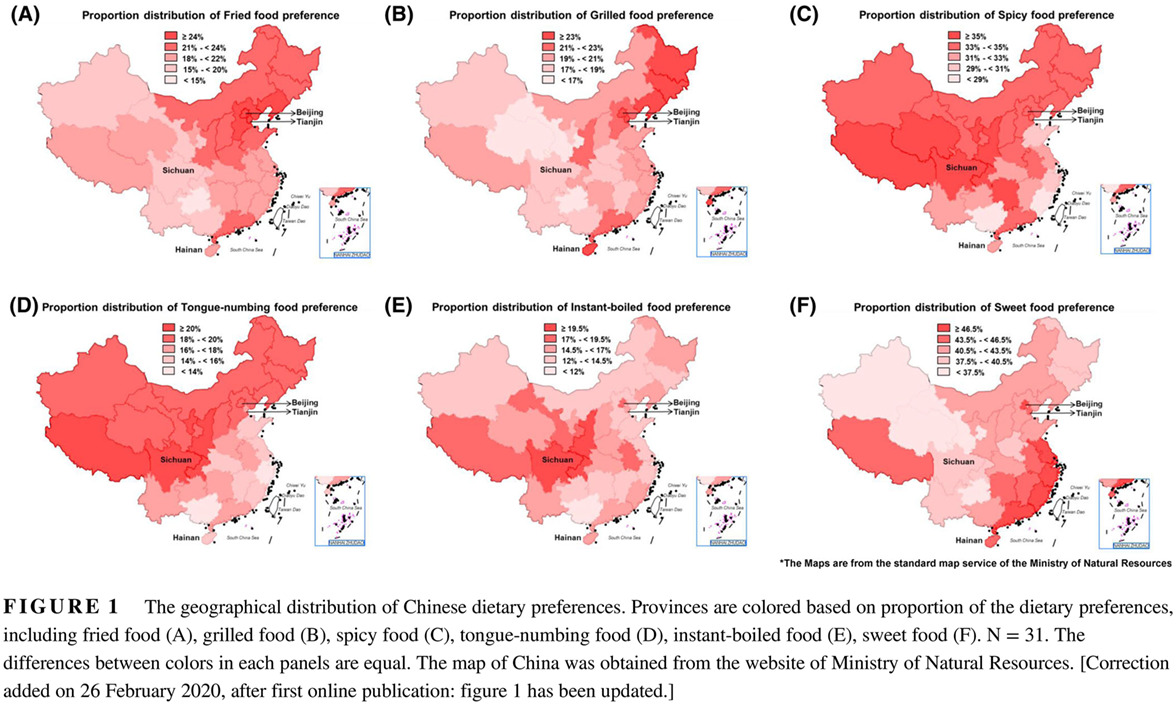
Highlights
- Chinese dietary preferences had different geographical distribution, which is related to the local climate and consumption level based on large-scale Internet passively collected data. Fried food, grilled food, and sweet food preferences were positively related to diabetes risk whereas spicy food preference was negatively correlated with diabetes risk. Dietary preferences based on passively collected Internet data could be used to predict regional prevalence of diabetes, hypertension, and BMI and showed good value for public health monitoring.
Association between birth weight and diabetes: Role of body mass index and lifestyle in later life
中国中老年人群出生体重与糖尿病风险的相关性研究:探讨成年后体重指数与生活方式的作用
- First Published: 06 June 2019
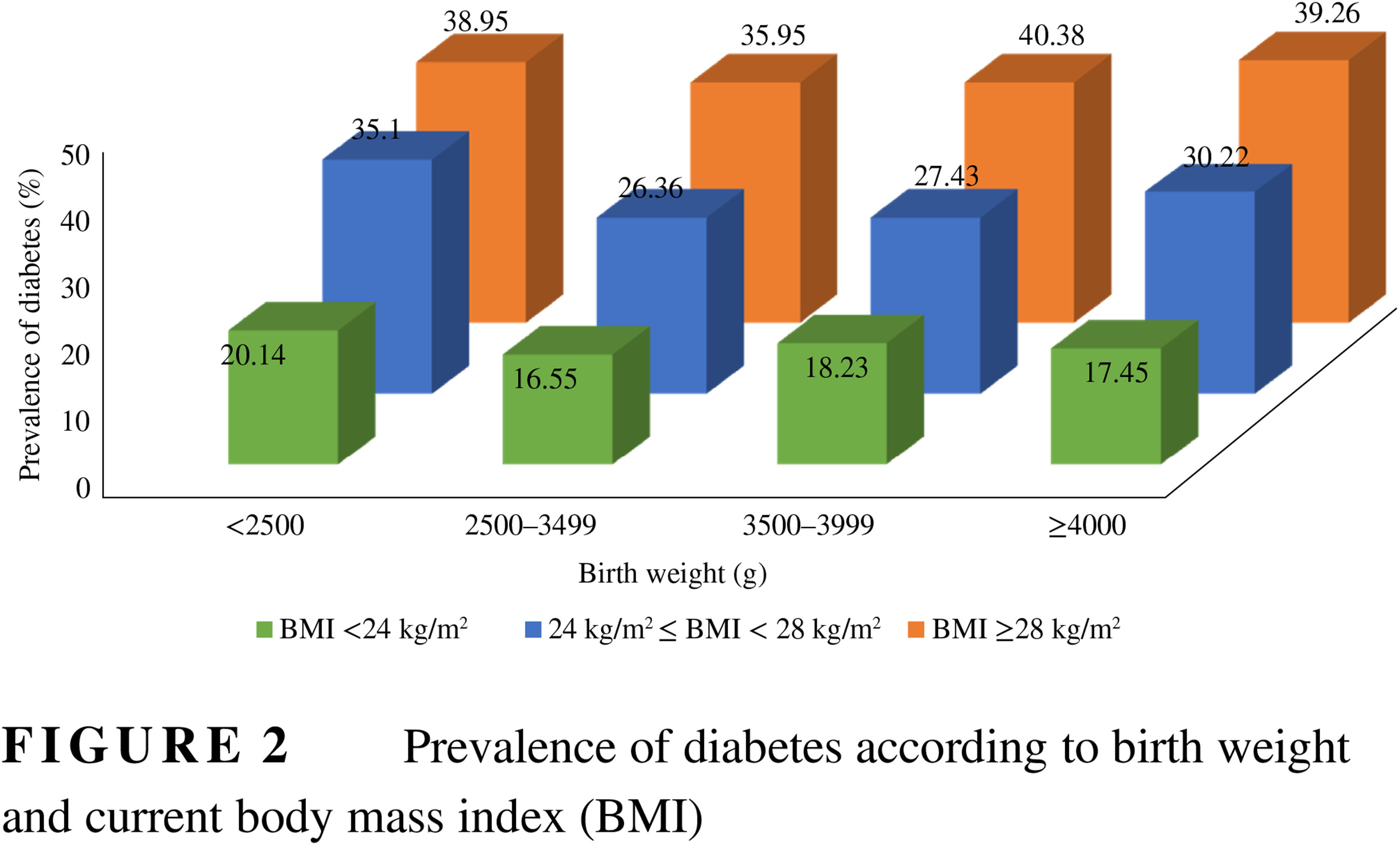
Highlights
- Some studies have indicated that low birth weight is significantly associated with diabetes, but the association is contentious, and the effects of body mass index (BMI) and lifestyle in later life on the association are unclear.
- This study provides new evidence for a U-shaped association between birth weight and the risk of diabetes.
- Normal BMI or a healthy lifestyle may mitigate the negative effects of low birth weight in the development of diabetes.









