Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Abnormalities in thrombotic pathways in diabetes: A tale of two platelets: 糖尿病患者血栓形成途径异常:两种血小板的故事
- First Published: 02 July 2018
What does the Acarbose Cardiovascular Evaluation (ACE) trial tell us?
阿卡波糖心血管评估(ACE)试验告诉我们什么?
- First Published: 17 May 2018
The kidney and cardiovascular outcome trials: 肾脏与心血管结局试验
- First Published: 14 October 2017
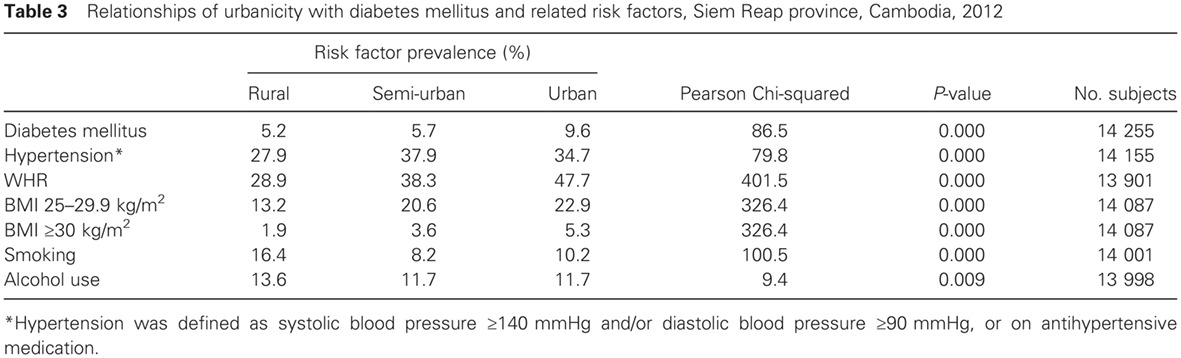
Diabetes and cardiometabolic risk factors in Cambodia: Results from two screening studies: 柬埔寨糖尿病与心血管代谢的危险因素:来自两项筛查研究的结果
- First Published: 22 May 2017
Highlights
- This paper consolidates research from two different studies in Cambodia illuminating contemporary prevalence rates of diabetes, glucose intolerance, and other non-communicable conditions associated with diabetes.
- Rates of obesity, elevated waist:hip ratio, hypertension, and diabetes were higher in urban than rural areas, with semi-urban areas experiencing intermediate rates for some factors.
- Rates of diabetes in Cambodia may be expected to rise as development continues and urban areas expand. An urgent public health response is needed to address non-communicable diseases in Cambodia.
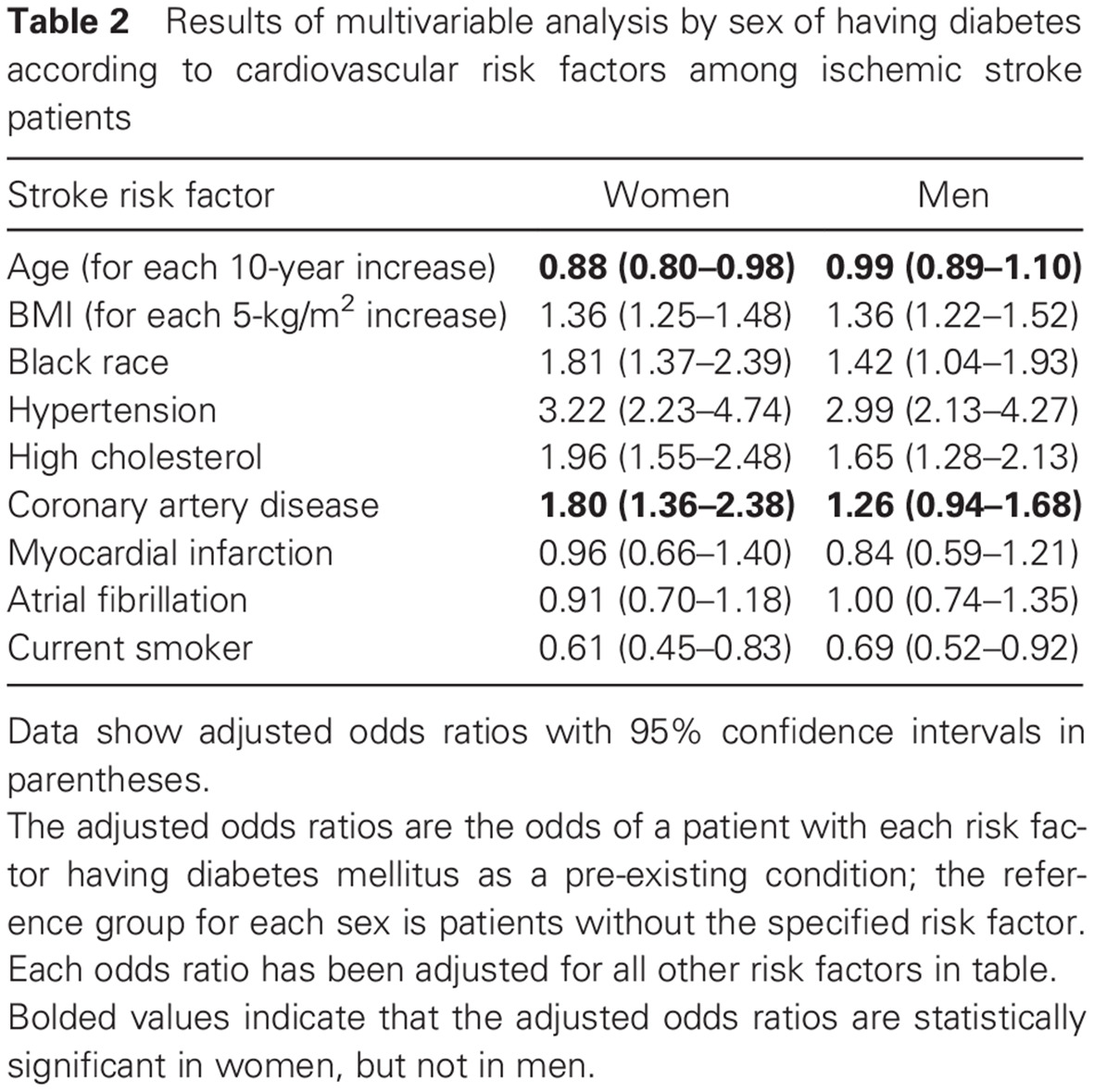
Sex differences in cardiovascular risk profiles of ischemic stroke patients with diabetes in the Greater Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky Stroke Study: 在大辛辛那提/北肯塔基脑卒中研究中合并糖尿病的缺血性脑卒中患者心血管危险因素的性别差异
- First Published: 18 May 2017
Highlights
- Among patients with incident ischemic stroke in the Greater Cincinnati Northern Kentucky Stroke Study, younger women and women with coronary artery disease (CAD) were more likely to have diabetes, whereas these associations were not significant for men.
- Our findings suggest that there is a sex-specific association between younger age and incident strokes in women with diabetes. Consequently, women with diabetes may benefit from more aggressive risk factor control.
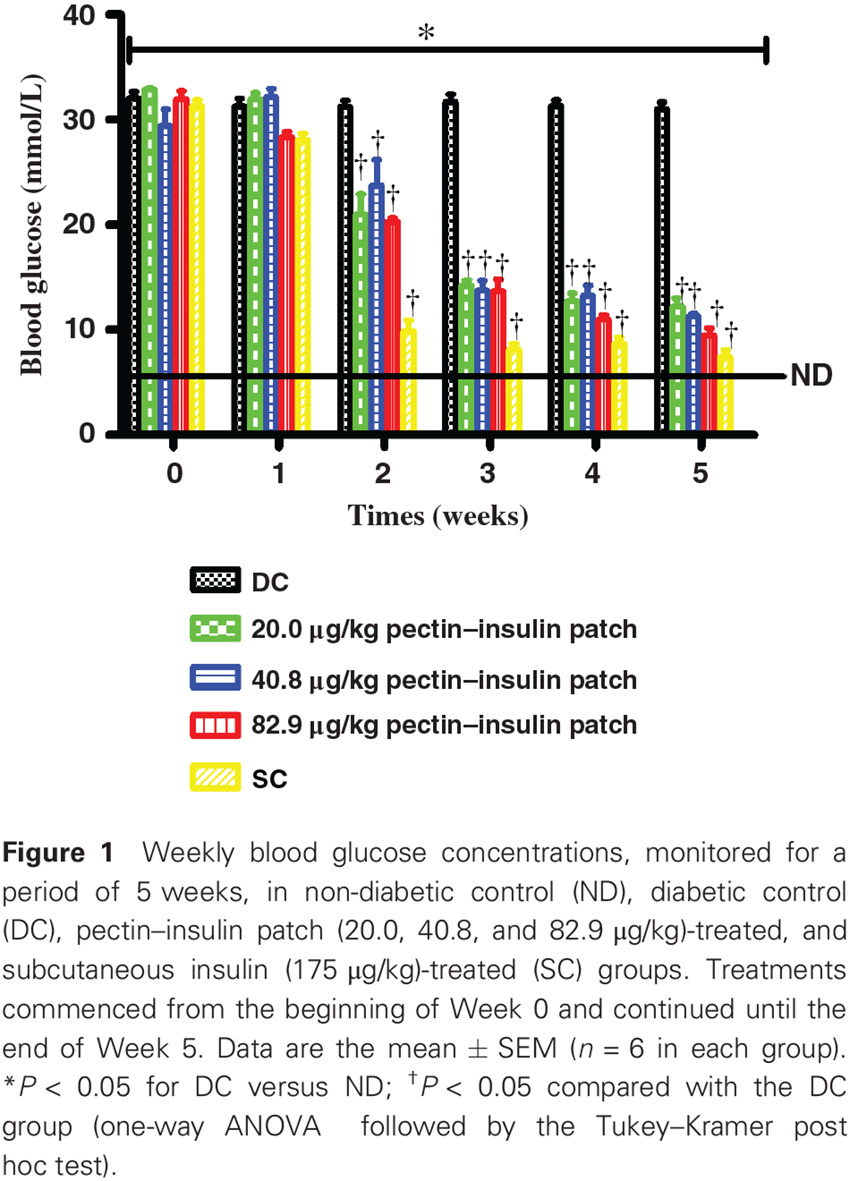
Cardioprotective effects of pectin–insulin patch in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: 果胶-胰岛素贴片对链脲霉素诱导的糖尿病大鼠心脏的保护作用
- First Published: 20 February 2017
Highlights
- Application of the transdermal pectin–insulin patch provides glycemic and hemodynamic control that attenuates the cardiac hypertrophy and cardiac inflammatory markers in diabetes.
- The observations in this study further reflect on cardiovascular hazards associated with subcutaneously administered insulin.
- Accordingly, the overall results of the study suggest that the pectin–insulin patch may be an alternative therapeutic approach in the management of diabetes.
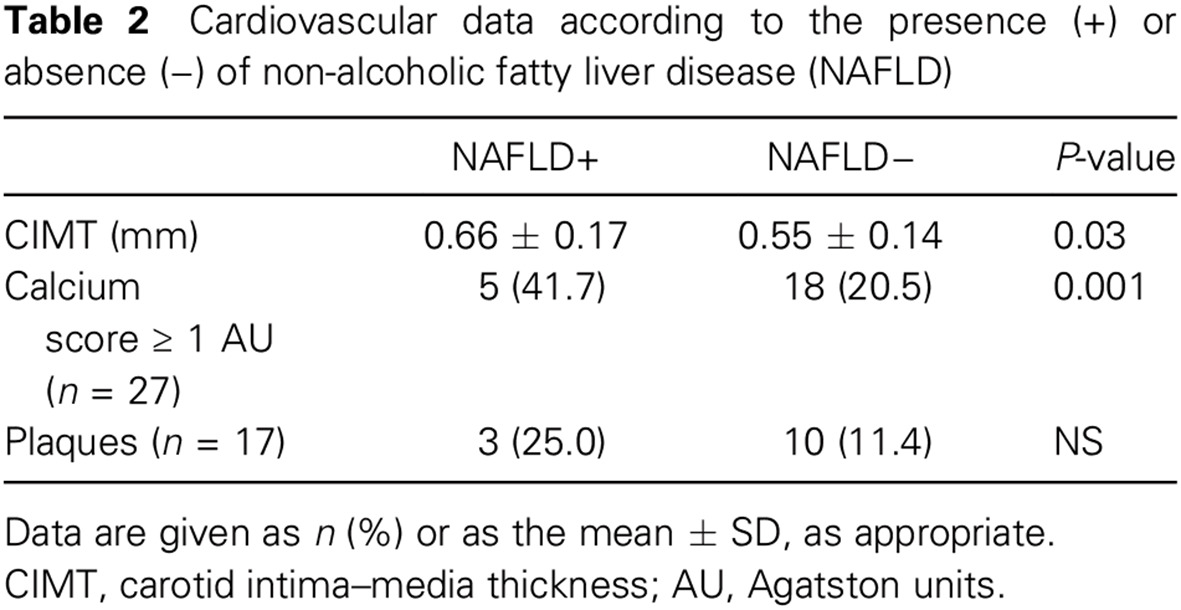
Low prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 1 diabetes is associated with decreased subclinical cardiovascular disease: 在1型糖尿病患者中非酒精性脂肪性肝病的患病率较低与亚临床心血管疾病较少相关
- First Published: 20 February 2017
Highlights
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has been associated with cardiovascular disease.
- Mediterranean type 1 diabetes (T1D) patients have a low prevalence of NAFLD, and T1D patients exhibit a low prevalence of subclinical atherosclerosis.
- The present study supports the relationship between NAFLD and subclinical cardiovascular disease even in a Mediterranean area.








