Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
2020
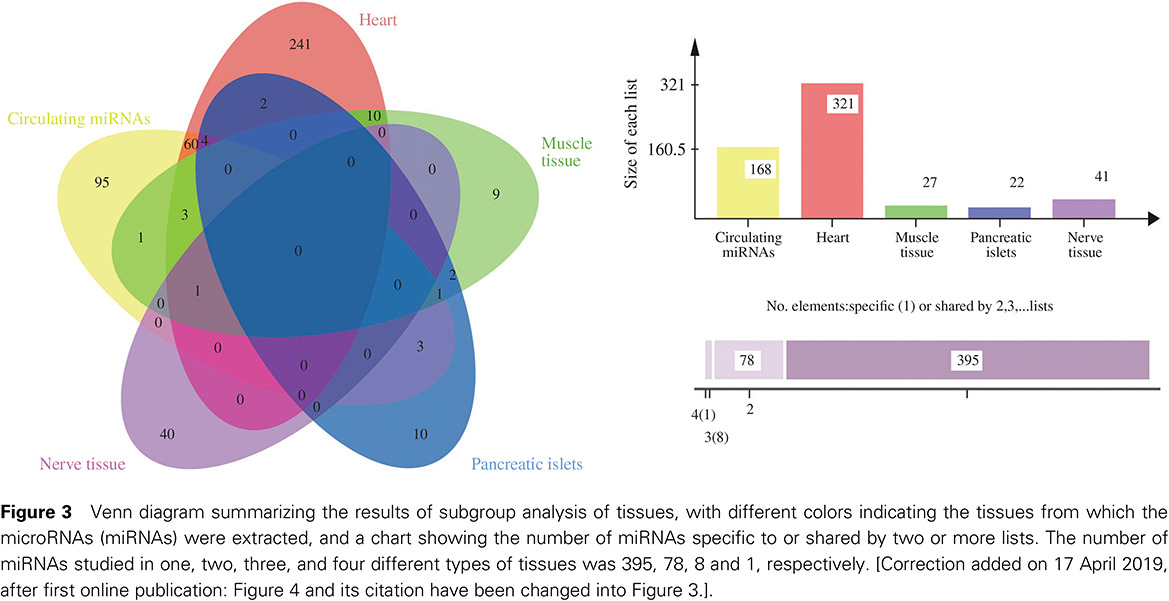
Identification of stress-related microRNA biomarkers in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
2型糖尿病的应激相关microRNA标志物:系统综述与meta分析
- First Published: 17 January 2018
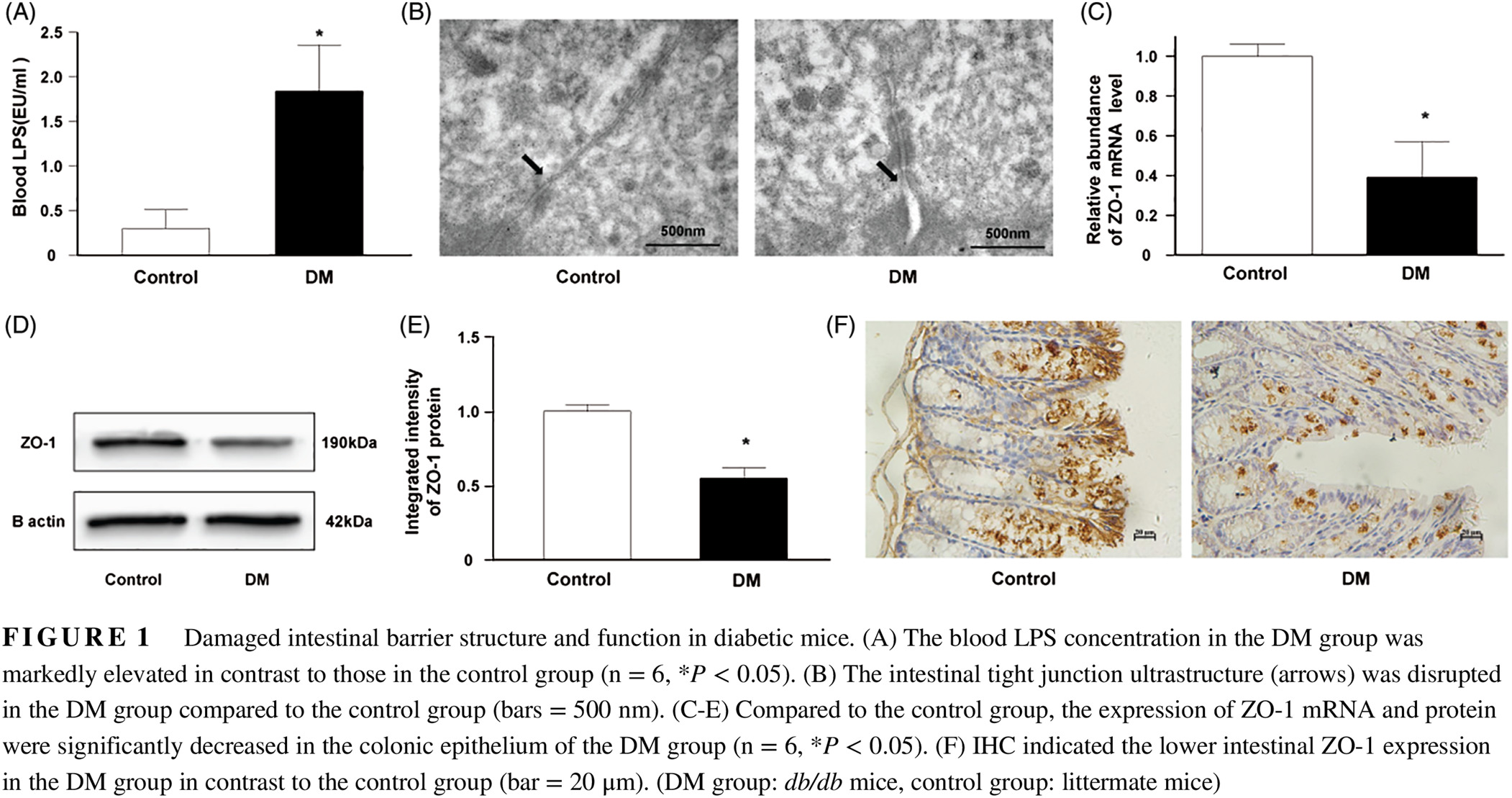
Faecalibacterium prausnitzii-derived microbial anti-inflammatory molecule regulates intestinal integrity in diabetes mellitus mice via modulating tight junction protein expression
普拉梭菌活性产物-微生物抗炎分子通过调控细胞紧密连接蛋白表达修复糖尿病小鼠肠道屏障
- First Published: 10 September 2019
Highlights
- Diabetic conditions induce compositional dysbiosis of the gut microbiota and impair gut barrier integrity.
- Diabetic conditions markedly downregulate the abundance of Faecalibacterium prausnitzii in the gut.
- Under diabetic conditions, microbial anti-inflammatory molecules from Faecalibacterium prausnitzii restore the gut barrier and ZO-1 expression possibly through the tight junction pathway.
2019
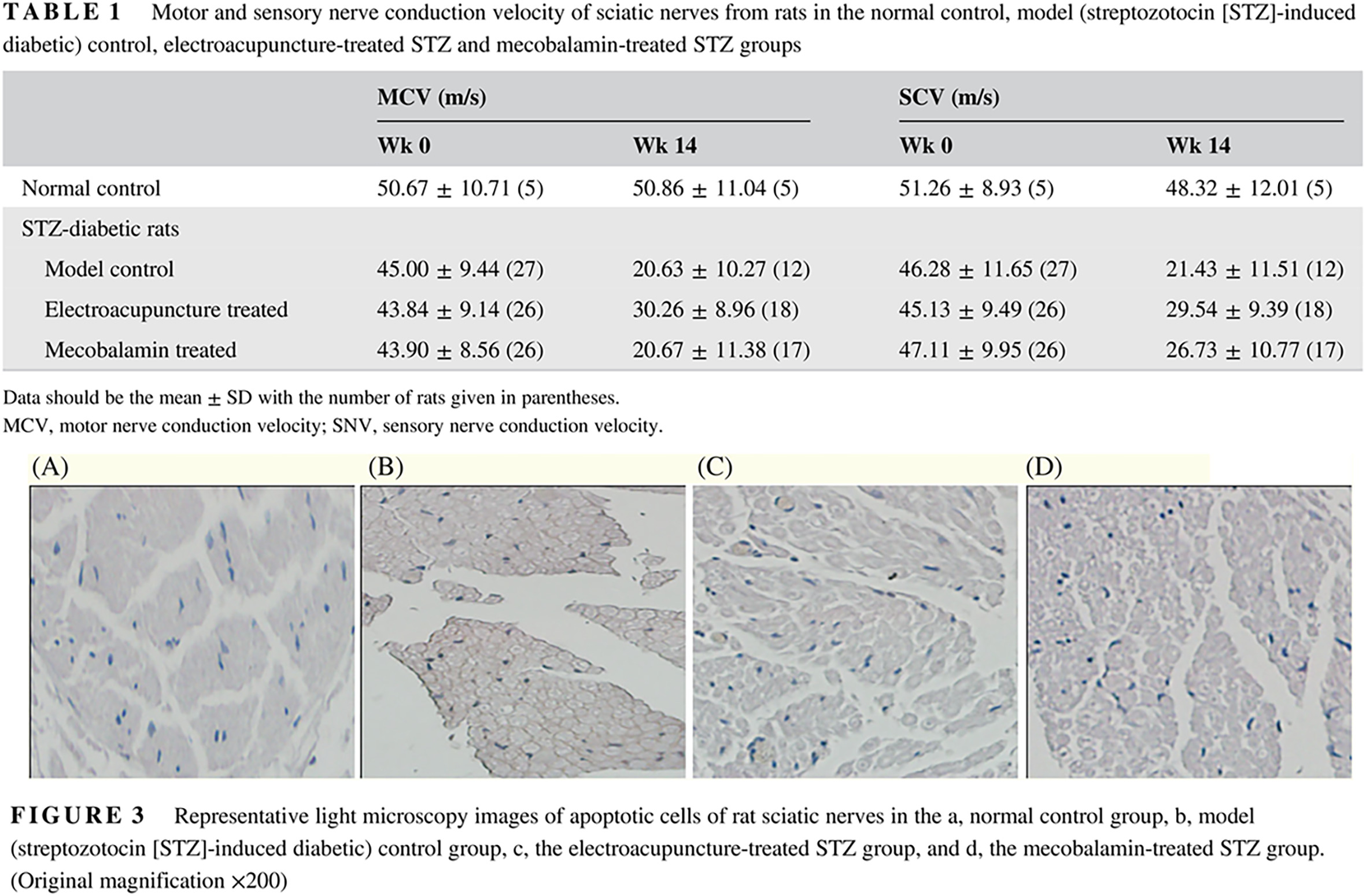
“Adjusting internal organs and dredging channel” electroacupuncture treatment prevents the development of diabetic peripheral neuropathy by downregulating glucose-related protein 78 (GRP78) and caspase-12 in streptozotocin-diabetic rats
“调脏通络”电针疗法通过下调链脲佐菌素诱导的糖尿病大鼠的GRP78和 caspase-12水平阻止糖尿病周围神经病变的发展
- First Published: 18 March 2019
Highlights
- Electroacupuncture treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) reduced cell apoptosis of sciatic nerves in diabetic rats, inhibited the occurrence of endoplasmic reticulum stress, and thus prevented sciatic nerve injuries.
- The treatment effectiveness of electroacupuncture for DPN may be mediated via downregulation of glucose-related protein 78 (GRP78) and caspase-12.
Renoprotective effects of brown adipose tissue activation in diabetic mice
棕色脂肪激活对糖尿病小鼠的肾脏保护作用
- First Published: 24 April 2019
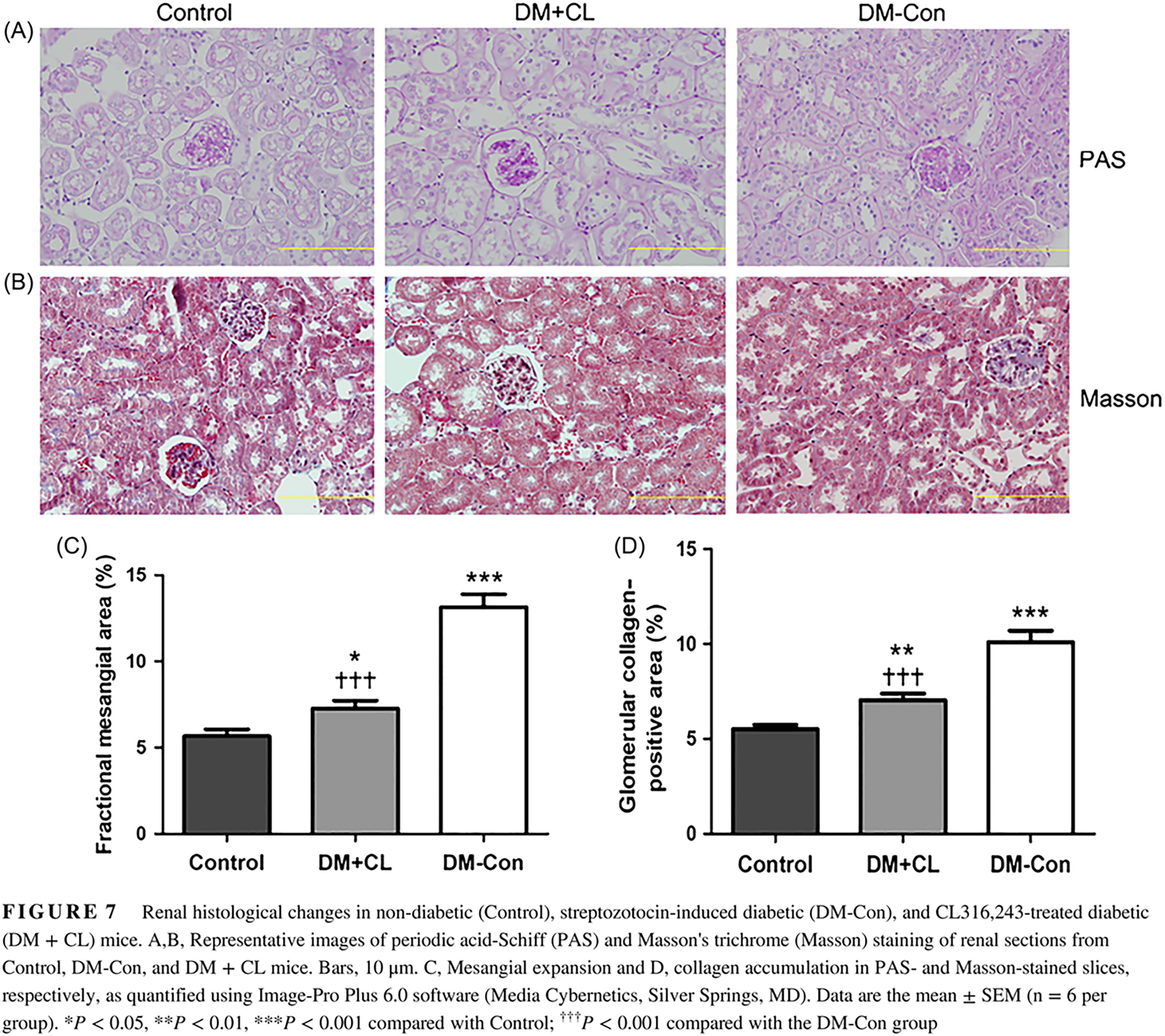
Highlights
- This study demonstrates that of brown adipose tissue (BAT) with CL316,243 attenuates the progress of diabetic kidney disease (DKD).
- Mechanistically, the activation of BAT improved concentrations of circulating adipokines and microRNAs, which further affected the diabetic kidney and reactivated the AMP-activated protein kinase/sirtuin 1/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α signaling pathway.
- The data suggest that BAT activation could be a novel therapeutic approach in the treatment of DKD.
Roux-en-Y gastric bypass decreases endotoxemia and inflammatory stress in association with improvements in gut permeability in obese diabetic rats
RYGB手术减少内毒素血症和炎症应激反应同时改善肥胖糖尿病大鼠肠道通透性
- First Published: 03 February 2019
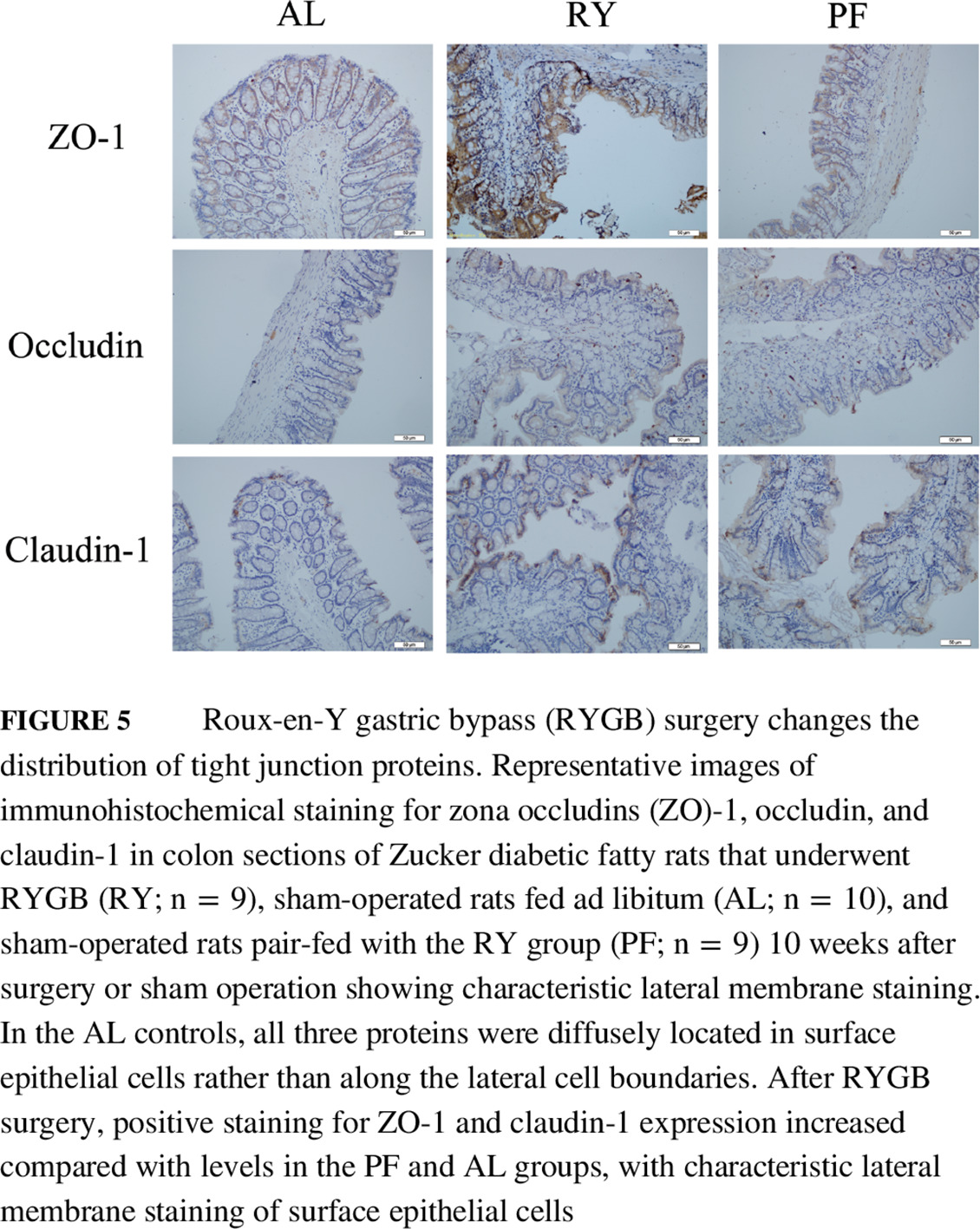
Highlights
- Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB) surgery improved glucose metabolism and the extent of inflammation and endotoxemia in Zucker diabetic fatty rats.
- Reductions in inflammatory tone and metabolic endotoxemia may be mediated by improved tight junction integrity and intestinal barrier strength induced by RYGB procedures.
Inhibition of high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) attenuates podocyte apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition by regulating autophagy flux
抑制HMGB1可以通过调节自噬流来减轻足细胞凋亡与上皮间充质转化
- First Published: 12 March 2019
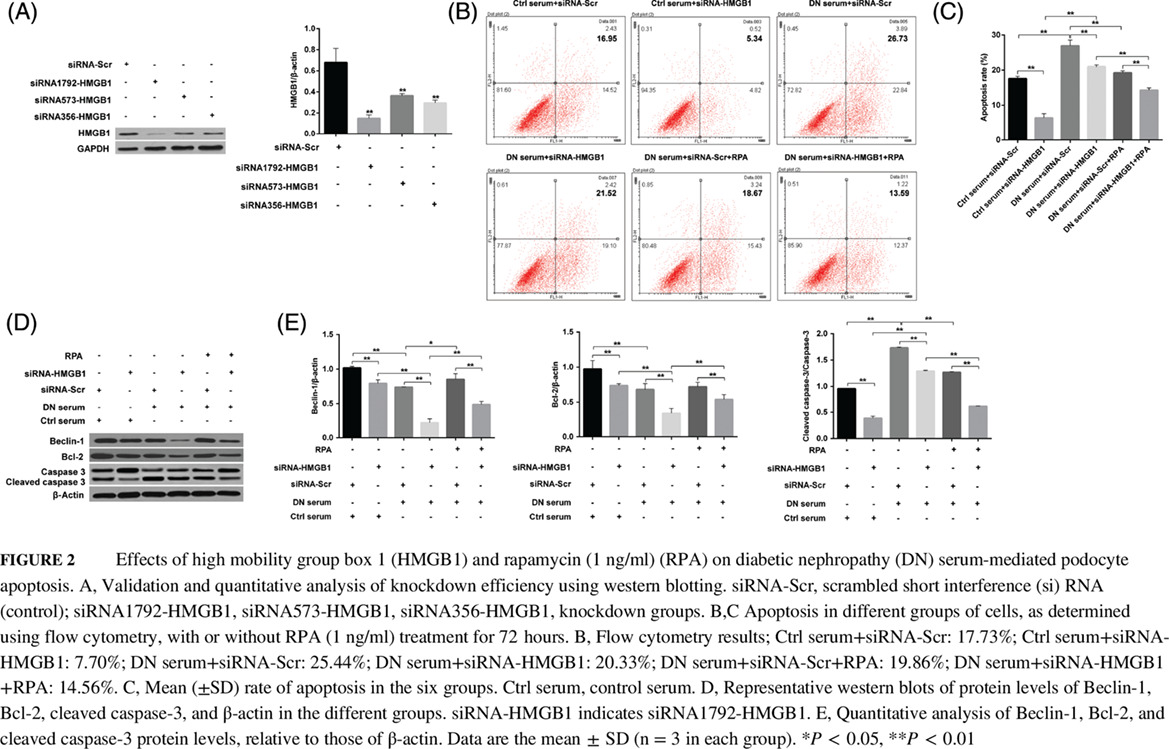
Highlights
- High mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) is overexpressed in the blood of patients with diabetic nephropathy (DN) and DN serum-treated MPC5 cells.
- The combination of HMGB1 removal and addition of rapamycin inhibited DN serum-induced cell apoptosis and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by regulating autophagy.
- The combination of HMGB1 short interference RNA and the autophagy activator rapamycin protected podocytes against apoptosis by inhibiting AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling, and blunted EMT progression by downregulating the transforming growth factor-β/smad signaling pathway.
Effect of liraglutide on the Janus kinase/signal transducer and transcription activator (JAK/STAT) pathway in diabetic kidney disease in db/db mice and in cultured endothelial cells
在合并糖尿病肾病的db/db小鼠以及培养的内皮细胞中,利拉鲁肽对Janus激酶/信号转导与转录激活因子(JAK/STAT)通路的影响
- First Published: 21 December 2018
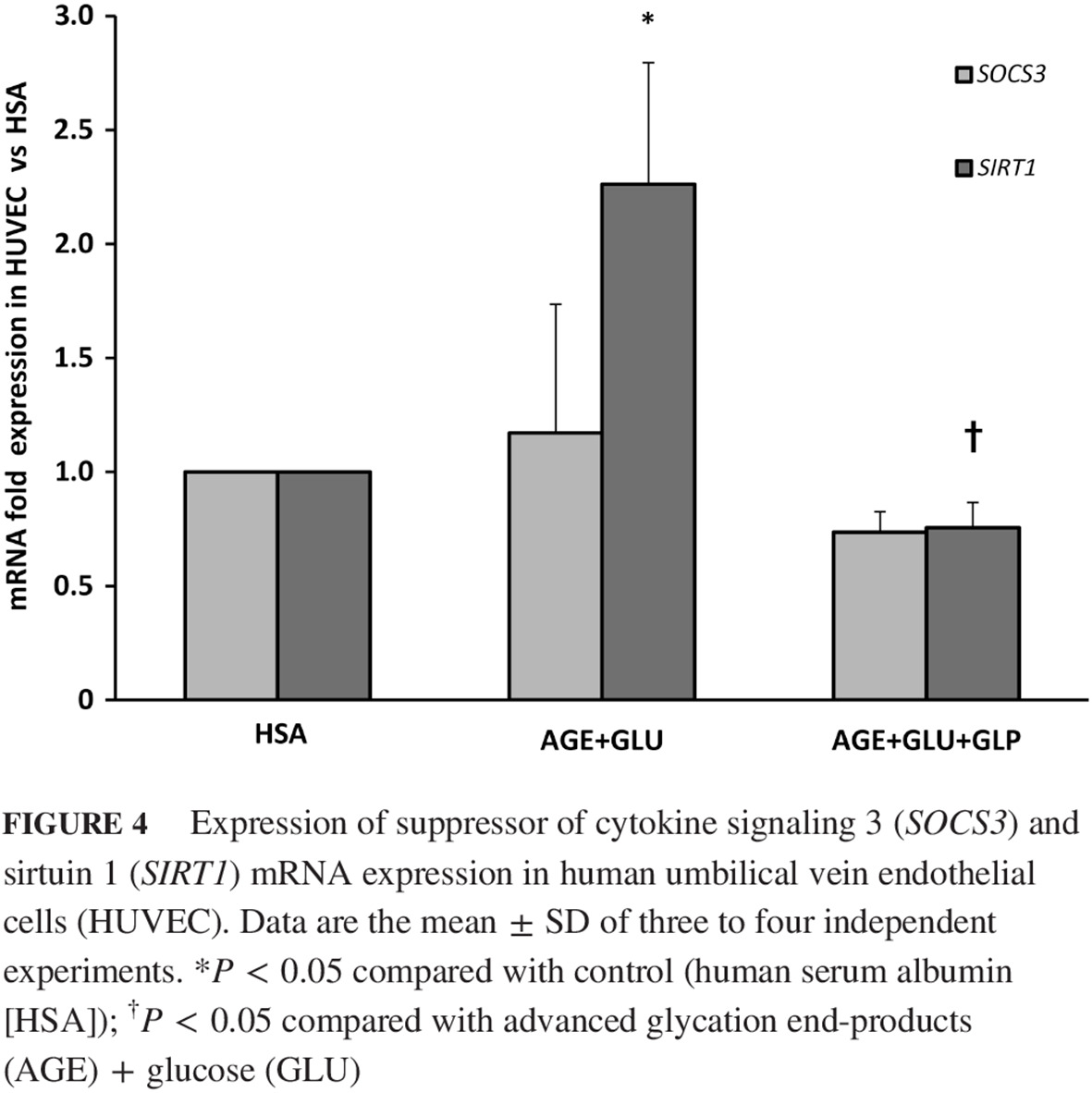
Highlights
- Diabetic conditions elevated expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT) 3 and Janus tyrosine kinase (JAK) 2.
- Diabetic conditions elevated expression of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 and sirtuin 1 (SIRT1).
- The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analog, liraglutide, is an inhibited STAT3/JAK2 expression, possibly through SIRT1 signaling.
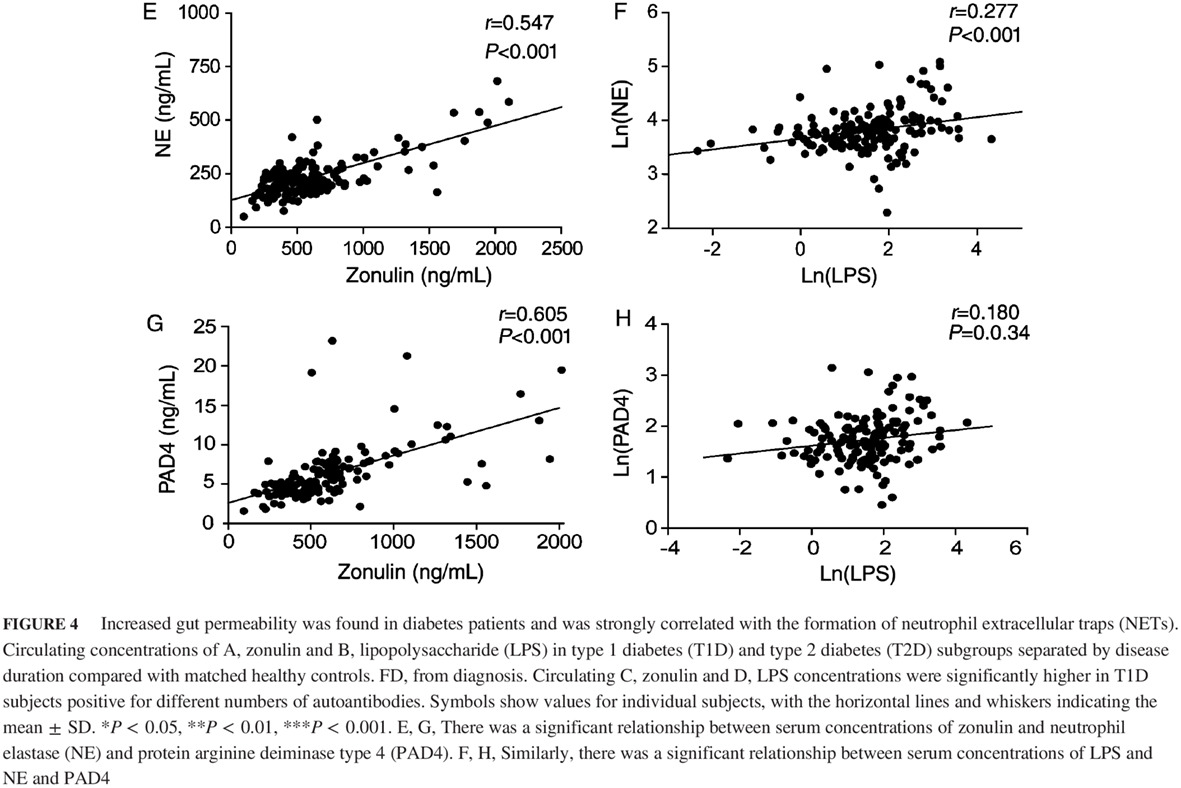
Increased formation of neutrophil extracellular traps is associated with gut leakage in patients with type 1 but not type 2 diabetes
中性粒细胞胞外诱捕网在1型而非2型糖尿病患者体内形成增多,并与其肠道渗漏密切相关
- First Published: 28 December 2018
Combined effect of GABA and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist on cytokine-induced apoptosis in pancreatic β-cell line and isolated human islets
在胰腺β细胞系与离体人类胰岛中联合使用GABA与胰高血糖素样肽-1受体激动剂对细胞因子诱导凋亡的影响
- First Published: 05 December 2018
Highlights
- GABA and a glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist additively suppressed cytokine-induced apoptosis in human islets.
- The combination of GABA and GLP-1 coactively reversed cytokine-induced suppression of insulin secretion partly by regulating sirtuin-1 (SIRT1) expression.
Peripheral pain is enhanced by insulin-like growth factor 1 and its receptors in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes mellitus
在2型糖尿病小鼠模型中胰岛素样生长因子1及其受体可增强周围疼痛
- First Published: 13 August 2018
Highlights
- Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF1) has a hyperalgesic effect in diabetic mice, which is related to the IGF1 receptor/c-raf/extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathway.
- We further explored the possible signaling pathways of pain in this study.
Effects of combined treatment with blood flow restriction and low-intensity electrical stimulation on diabetes mellitus-associated muscle atrophy in rats
限制血流与低强度电刺激联合治疗对大鼠糖尿病相关肌肉萎缩的影响
- First Published: 18 September 2018
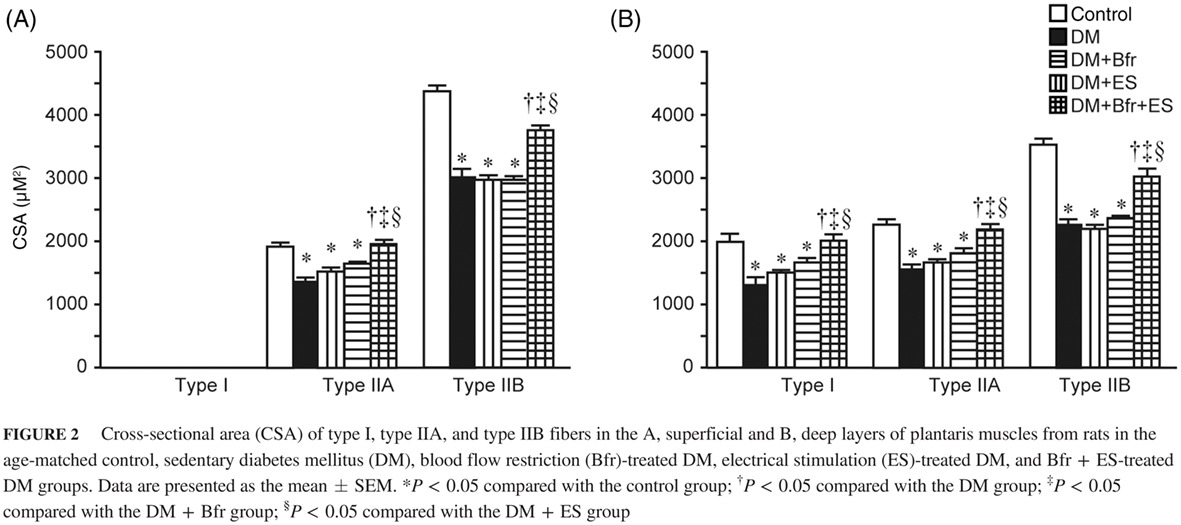
Highlights
- Combined treatment of blood flow restriction and low-intensity electrical stimulation (ES) can rescue diabetes mellitus-associated downregulation of protein synthesis and decreased translational activity and capacity.
- The study findings suggest that combined treatment with blood flow restriction and low-intensity ES has the potential to become an effective therapeutic intervention to prevent diabetes-associated muscle atrophy.
N-Acetylcysteine alleviates gut dysbiosis and glucose metabolic disorder in high-fat diet-fed mice: N-乙酰半胱氨酸改善高脂饮食小鼠的肠道菌群失衡和糖代谢紊乱
- First Published: 30 May 2018
Highlights
- N-Acetylcysteine (NAC) treatment improved gut dysbiosis and glucose metabolic disorder in high-fat diet-fed mice.
- In mice with metabolic syndrome, NAC boosted the growth of Akkermansia, Bifidobacterium, Allobaculum, and Lactobacillus.
- The changes in gut microbiota abundance after NAC treatment were associated with altered metabolic biomarkers.
2018
Low molecular-weight fucoidan protects against hindlimb ischemic injury in type 2 diabetic mice through enhancing endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation: 低分子量褐藻多糖硫酸酯通过促进内皮型一氧化氮合成酶磷酸化减轻2型糖尿病小鼠下肢缺血性损伤
- First Published: 06 April 2018
Highlights
- Diabetes often causes peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which is the main cause of foot gangrene and amputation.
- Angiogenesis in ischemic tissue is an ideal therapeutic approach to treat PAD.
- Low molecular weight fucoidan significantly promotes angiogenesis by enhancing endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation and vascular endothelial growth factor expression in ischemic muscles of db/db mice and protects against pathological injury.
Differential mRNA expression of neuroinflammatory modulators in the spinal cord and thalamus of type 2 diabetic monkeys: 在2型糖尿病猴的脊髓与丘脑中神经炎症调节因子mRNA表达的差异性
- First Published: 11 May 2018
Highlights
- Whether neuroinflammatory modulators, such as cytokines, toll-like receptors (TLR), growth factors, and cannabinoid receptors, change differentially in type 2 diabetic primates is unknown.
- We found that mRNA expression of inflammatory cytokines (interleukin-1β and tumor necrosis factor-α), TLR1, and TLR2 were upregulated in the spinal cord of diabetic monkeys, and positively correlated with plasma glucose levels.
- This study indicates that several ligands and receptors involved in neuroinflammation are simultaneously dysregulated in diabetic primates.
Mild hyperbaric oxygen inhibits the growth-related decline in skeletal muscle oxidative capacity and prevents hyperglycemia in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus: 在2型糖尿病大鼠中使用轻度高压氧可以抑制生长相关的骨骼肌氧化能力下降以及预防高血糖
- First Published: 06 April 2018
Highlights
- Exposure to mild hyperbaric oxygen inhibited the growth-related decline in skeletal muscle oxidative capacity and type shift of muscle fibers from high-oxidative to low-oxidative and prevented hyperglycemia in animals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- These results indicate that mild hyperbaric oxygen may be a useful therapy for T2DM.
Heparan sulfate inhibits inflammation and improves wound healing by downregulating the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome in diabetic rats: 硫酸乙酰肝素在糖尿病大鼠中通过下调NLRP3炎症小体抑制炎症反应并促进伤口愈合
- First Published: 24 November 2017
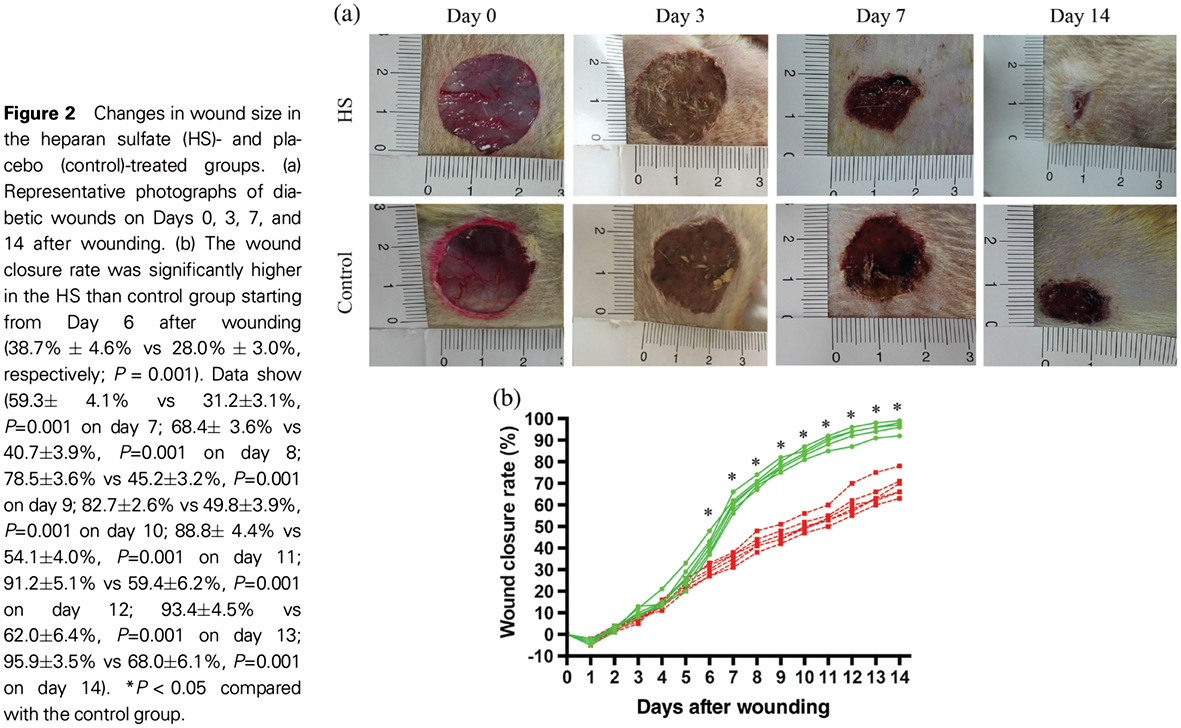
Highlights
- Heparan sulfate significantly alleviates the inflammatory reaction and reduces cleaved interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-18, and tumor necrosis factor-α production.
- Suppression of the inflammatory reaction may be mediated via downregulation of the NLR family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and upregulation of proteinase inhibitor 9 and caspase-12.
Plasma lipids affect dabigatran etexilate anticoagulation in rats with unbalanced diabetes mellitus: 在失衡的糖尿病大鼠中血脂可以影响达比加群酯的抗凝作用
- First Published: 03 July 2017
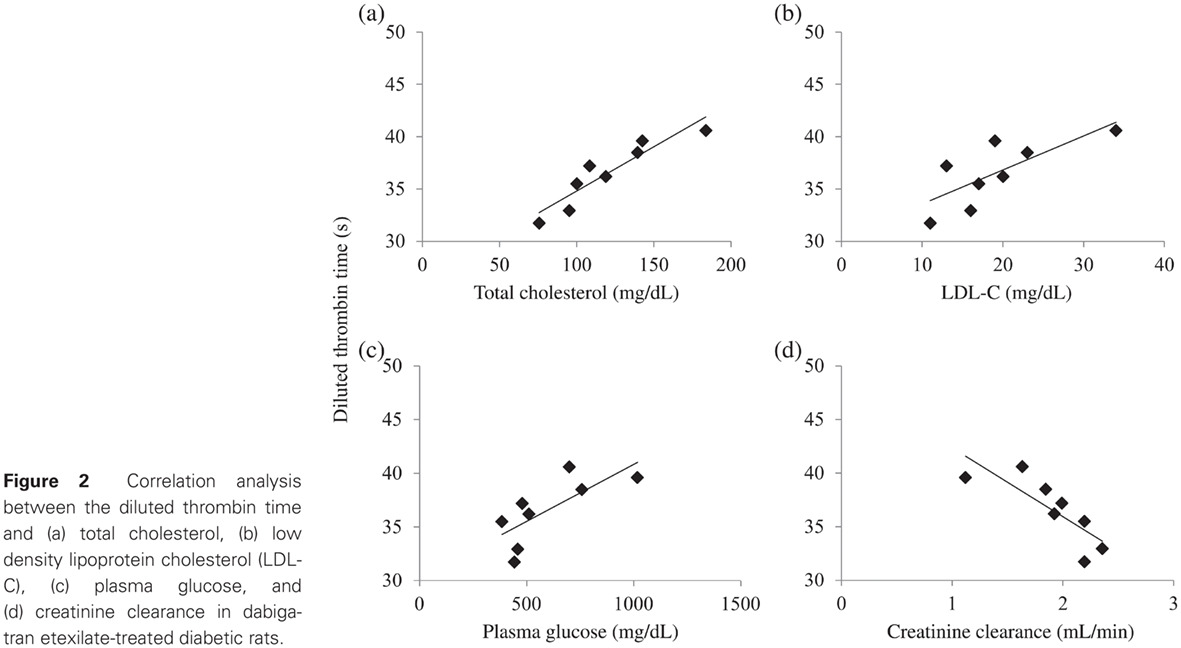
Highlights
- Diabetic rats exhibit significantly more intense dabigatran-induced anticoagulation that does not seem to be solely related to altered kidney function.
- Plasma cholesterol significantly affects dabigatran-induced anticoagulation in this setting.
- These findings could explain the similar benefits of dabigatran in reducing ischemic stroke compared with warfarin in patients with and without diabetes mellitus, despite the significantly higher intrinsic thrombotic risk in the former, as well as the lack of benefit of reducing major bleeding in diabetic patients.
Ganglioside GM3 content in skeletal muscles is increased in type 2 but decreased in type 1 diabetes rat models: Implications of glycosphingolipid metabolism in pathophysiology of diabetes: 骨骼肌中神经节苷脂GM3的含量在2型糖尿病大鼠模型中增加但在1型糖尿病大鼠模型中减少:鞘糖脂代谢在糖尿病病理生理学中的作用
- First Published: 22 May 2017
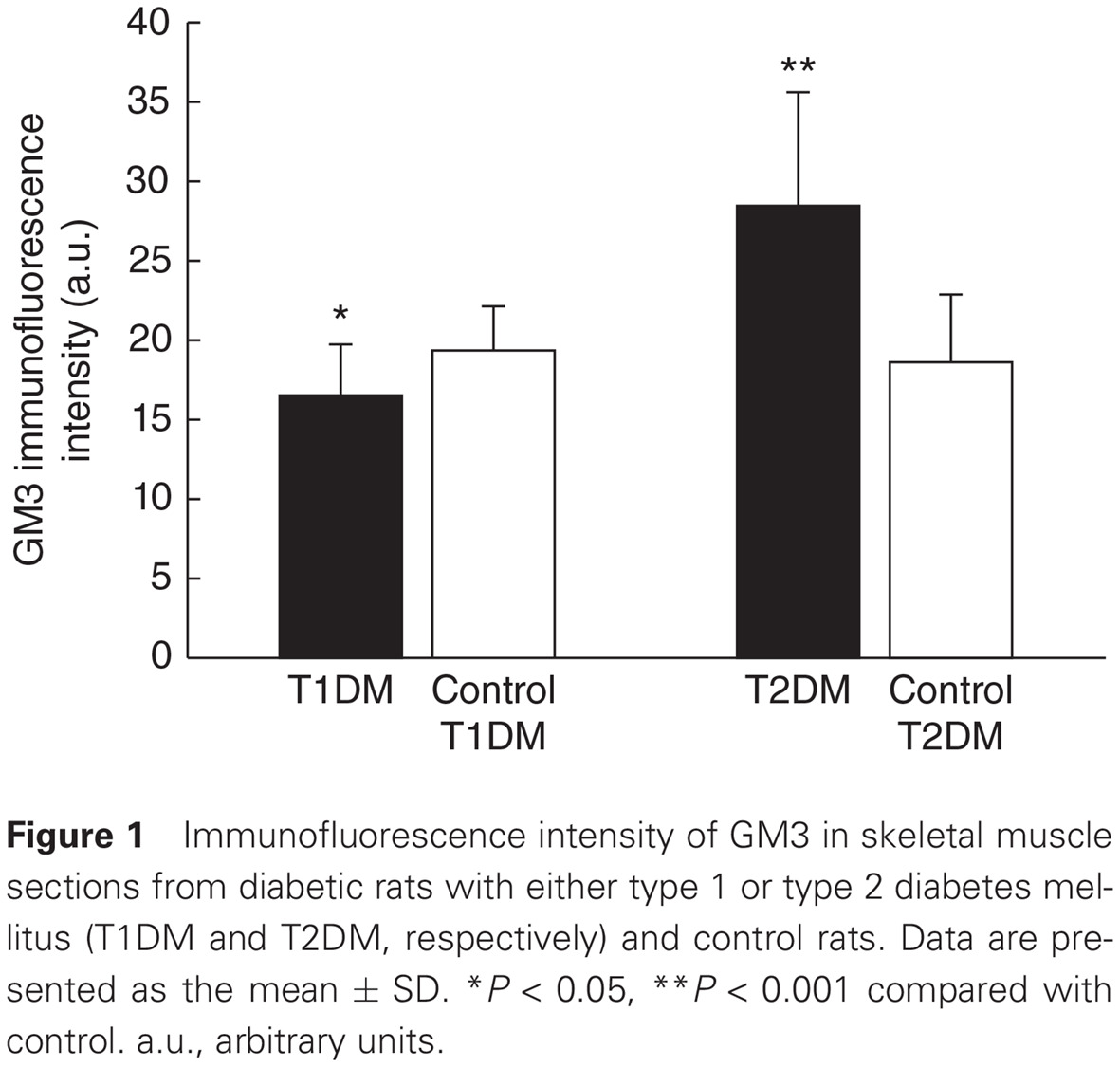
Highlights
- Skeletal muscles play an important role in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake, whereas gangliosides, such as GM3, attenuate insulin receptor signaling, thus contributing to the development of insulin resistance.
- Ganglioside GM3 muscle content was significantly higher in rats with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and significantly lower in rats with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) compared with control groups.
- Expression of GM3 precursors was significantly higher in T2DM rats, whereas ceramide expression was significantly lower in T1DM rats compared with controls.
Effects of different aerobic exercise frequencies on streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetic rats: Continuous versus short bouts and weekend warrior exercises: 不同有氧运动频率对链脲霉素-烟酰胺诱导的2型糖尿病大鼠的影响:持续运动与短时间运动以及周末运动的对照研究
- First Published: 20 April 2017
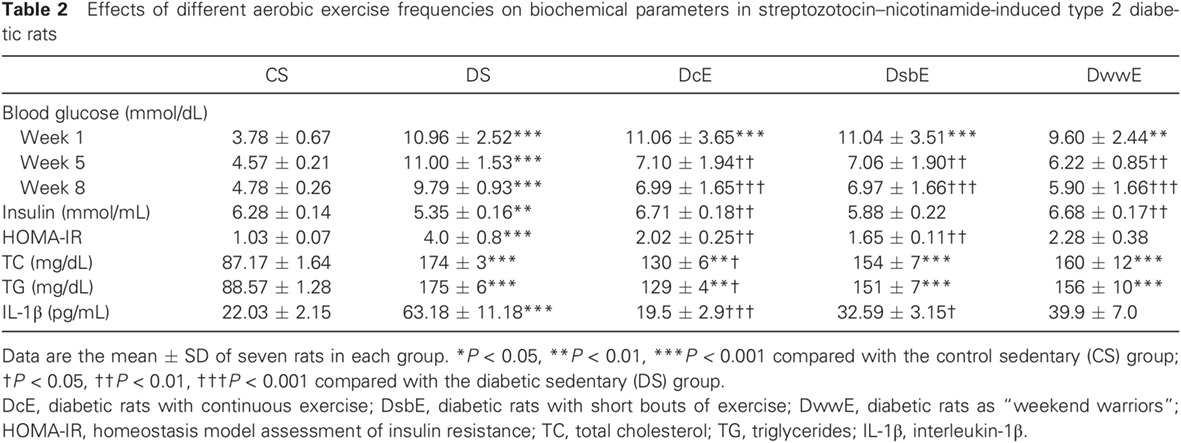
Highlights
- The findings of the present study suggest that different aerobic exercise frequencies improve diabetes markers and skeletal muscle damage in streptozotocin–nicotinamide-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus rats.
- The outcomes of different exercise modalities did not differ significantly from each other, provided that the total duration of the exercise remained constant.
Salivary gland hypofunction in KK-Ay type 2 diabetic mice: KK-Ay 2型糖尿病小鼠唾液腺功能减退
- First Published: 16 March 2017
- Saliva secretion from type 2 diabetic (T2D) mice decreased at the glandular level.
- Membrane proteins critical for fluid secretion are preserved in T2D mice.
- Decreased calcium signaling is the key for diabetes-induced hypofunction of salivary glands.




 This collection focuses on the recent progress in Basic Science of Diabetes.
This collection focuses on the recent progress in Basic Science of Diabetes.