Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
The screening and prediction of functional/bioactive compounds in foods: Editorial; how to efficiently discover functional/bioactive compounds in foods?
- First Published: 15 November 2022
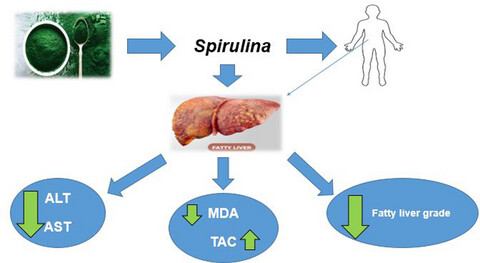
EXPRESSION OF CONCERN: The effect of Spirulina sauce, as a functional food, on cardiometabolic risk factors, oxidative stress biomarkers, glycemic profile, and liver enzymes in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patients: A randomized double-blinded clinical trial
- First Published: 11 June 2021
Metabolomics study of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels on the abnormal uterine bleeding rats by ultra-performance liquid chromatography–quadrupole–time-of-flight mass spectrometry analysis
- First Published: 13 October 2021
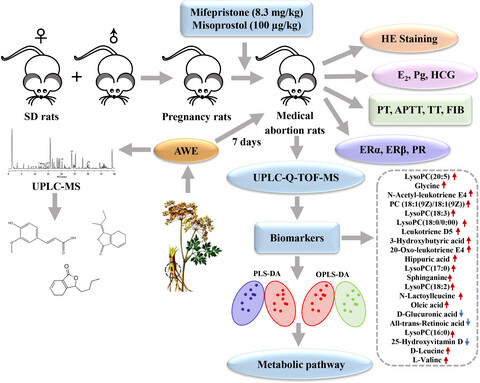
Angelica water extract could reduce alleviate pathological injury and regulate the coagulation function to promote recovery of the endometrium. Angelica water extract could increase the levels of E2, Pg, and HCG and the expression of ERα, Erβ, and PR. Angelica water extract could regulate the metabolic pathways which include the glycerophospholipid metabolism, sphingolipid metabolism, glycine, serine and threonine metabolism, and retinol metabolism.
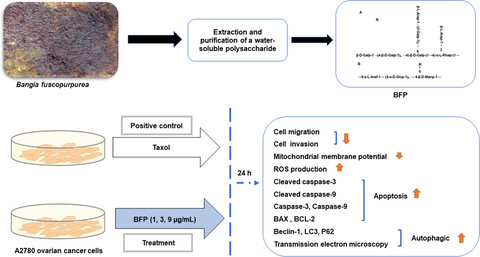
Polysaccharides isolated from Bangia fuscopurpurea induce apoptosis and autophagy in human ovarian cancer A2780 cells
- First Published: 10 October 2021
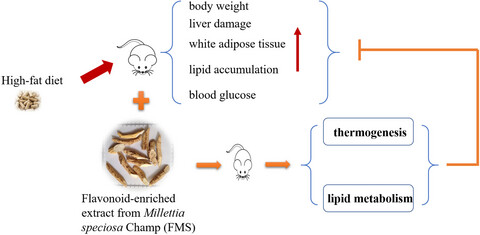
Flavonoid-enriched extract from Millettia speciosa Champ prevents obesity by regulating thermogenesis and lipid metabolism in high-fat diet–induced obese C57BL/6 mice
- First Published: 27 November 2021
Comprehensive lipidomic analysis of the lipids extracted from freshwater fish bones and crustacean shells
- First Published: 14 January 2022
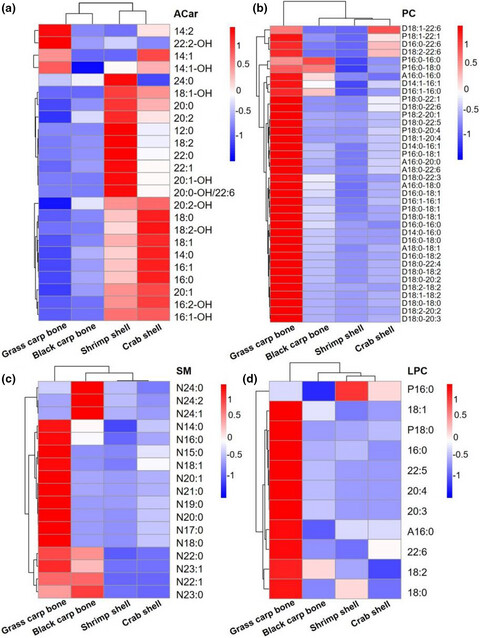
The fatty acid composition and lipid molecular species from fish bones and crustacean shells were investigated. The lipids extracted from shrimp and crab shells contained a considerable amount of eicosapentanoic acids and docosahexanoic acids. The total content of PC in shrimp shells was as high as 6.145 mmol/g.
Influenza virus entry and replication inhibited by 8-prenylnaringenin from Citrullus lanatus var. citroides (wild watermelon)
- First Published: 23 January 2022

The antiviral activities of 8-prenylnaringenin, which is the ingredient in wild watermelon, were observed against H1N1 and H3N2 influenza subtypes and influenza B viruses, excluding oseltamivir-resistant H1N1 viruses. Since oseltamivir-resistant strains were not inhibited by 8-prenylnaringenin, 8-prenylnaringenin may interact directly with viral neuraminidase.
Zebrafish obesogenic test identifies anti-adipogenic fraction in Moringa oreifera leaf extracts
- First Published: 11 February 2022

We performed zebrafish obesogenic test to identify anti-adipogenic fraction in Moringa oleifera leaf. Phenotype-driven zebrafish screening can be a reasonable strategy for identifying bioactive components in natural products. Using zebrafish obesogenic test, we identified that the dichloromethane extract of Moringa oleifera leaf and its subfraction (Fr. 2) reduced VAT accumulation in young zebrafish. In the zebrafish VAT, expression of early adipogenesis markers, cebpb and cebpd, was significantly (p < .05) decreased by Fr. 2, as was the expression of the late differentiation marker cebpa. We also confirmed that the subfractions of Fr. 2 also suppressed adipogenesis in ZOT and mouse 3T3-L1 preadipocytes.
The significance and potential of functional food ingredients for control appetite and food intake
- First Published: 18 February 2022
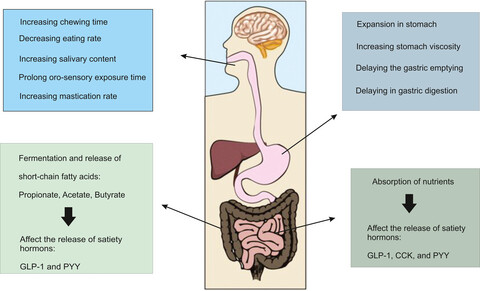
Functional foods can be one of the most influential factors in reducing appetite as long as effective ingredients, such as fiber and protein, are used to design these products. Also, functional foods should be designed to reduce appetite at different levels of oral processing, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine by various mechanisms. Therefore, the satiety power of functional food depends on the type of ingredients and their amount. Because each compound has a different mechanism of action, it is recommended to use different compounds to influence satiety in functional foods.
Evaluation of Nano-curcumin effects against Tartrazine-induced abnormalities in liver and kidney histology and other biochemical parameters
- First Published: 21 March 2022
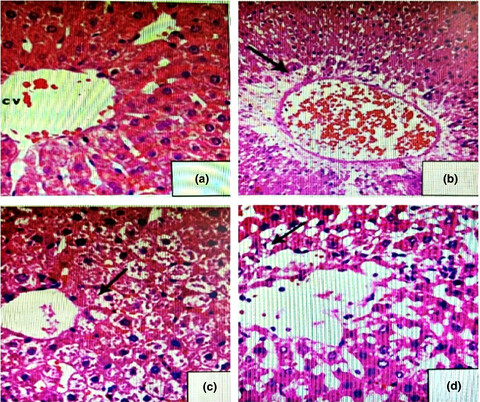
Albino male rats were investigated to evaluate the impact of Nano-curcumin (Nano-CUR) administration against Tartrazine (TZ)-induced variations in kidney and liver histology and their related functions. The results support the protective and therapeutic effects of Nano-CUR on the histology of the liver and kidneys and their related functions. Also, Nano-CUR corrects the imbalance in serum glucose (sGlu), alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), protein Kinase-C (PKC), and lipid profiles in TZ-ingested rats compared to control.
Yogurt fortification by microencapsulation of beetroot extract (Beta vulgaris L.) using maltodextrin, gum arabic, and whey protein isolate
- First Published: 11 May 2022

Beetroot extract (BE) was encapsulated using maltodextrin (MD), gum arabic (GA), and whey protein isolate (WPI) by implementing a spray-drying method. The highest total phenolic content (TPC) was obtained at 15% MD, 7.5% GA, and 10% WPI. The same results were achieved for antioxidant activity. Increasing the MD and GA contents resulted in a reduction of moisture adsorption of microencapsulated BE powder.
Comparison of the effect of saffron, crocin, and safranal on serum levels of oxidants and antioxidants in diabetic rats: A systematic review and meta-analysis of animal studies
- First Published: 13 March 2023
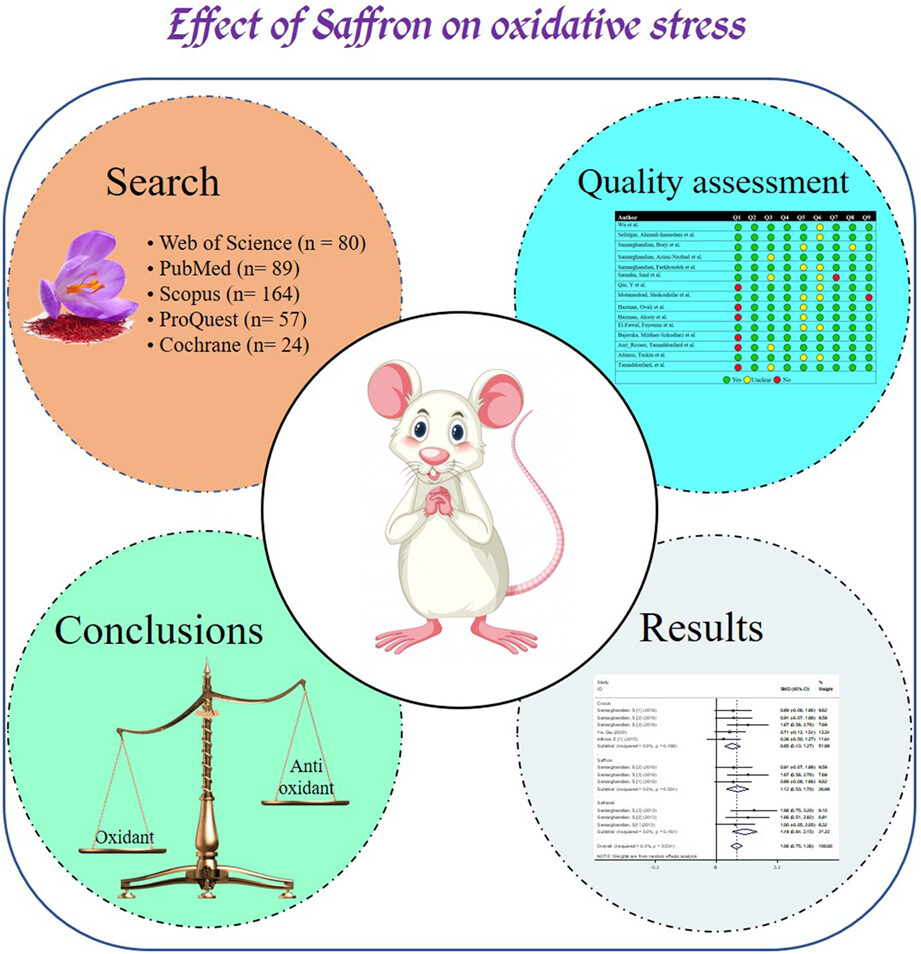
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic review and meta-analysis that has comprehensively investigated the effect of saffron and its active compounds on oxidative stress markers (oxidants and antioxidants). In this meta-analysis, 15 studies were reviewed. The results of our study showed that saffron and its active compounds (crocin and safranal) with high effectiveness led to a reduction in oxidative stress caused by long-term hyperglycemia. In addition, we showed that safranal is more effective than saffron and crocin.
LC/MS analysis of mushrooms provided new insights into dietary management of diabetes mellitus in rats
- First Published: 27 January 2023
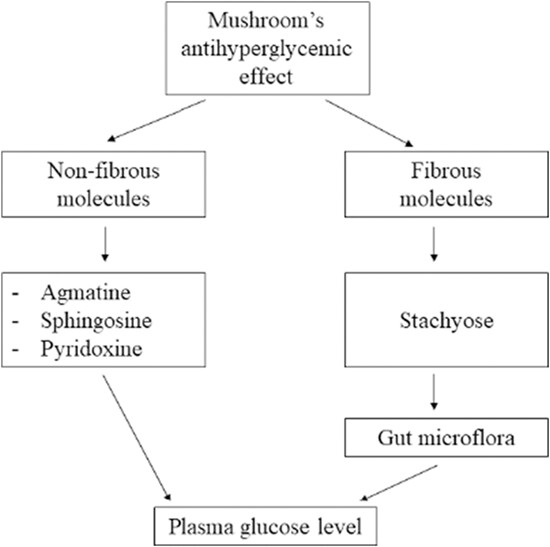
The effect of mushroom's bioactive compounds on plasma glucose level. Agmatine increases insulin secretion and glucose uptake in muscle. Sphingosine activates omega-3 fatty acid receptor (GPR120) mediating potent insulin-sensitizing effects. Pyridoxine decreases insulin resistance. Stachyose regulates the intestinal microflora balance.
Miao sour soup influences serum lipid via regulation of high-fat diet-induced intestinal flora in obese rats
- First Published: 07 December 2022
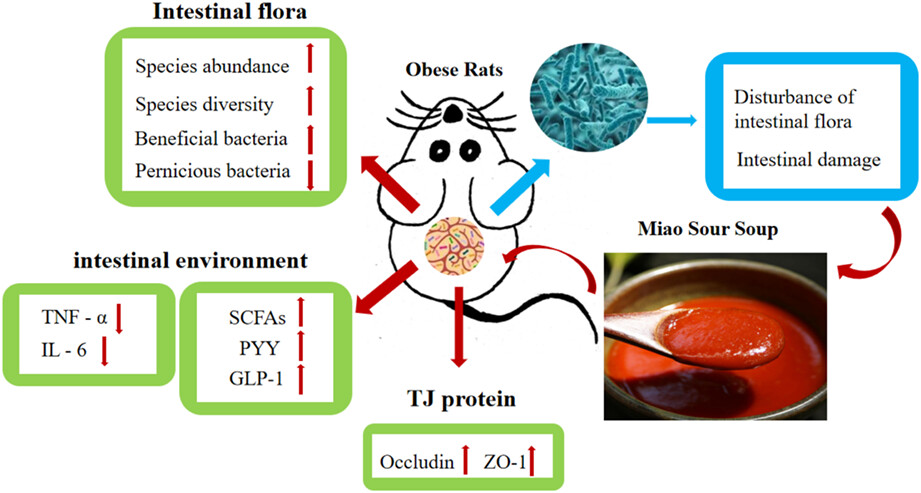
Obesity is a health condition of increasing importance. Obesity has been associated with an imbalance in the intestinal flora. Miao sour soup (SS) contains abundant short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which can be used as energy substrates to selectively stimulate the growth and reproduction of intestinal flora. This study aims to determine whether SS intervention could restore the imbalanced intestinal flora of rats with high-fat diet-induced obesity. We found improvements in the abundance and diversity of the intestinal flora, and a significant reduction in weight and serum lipid levels following intervention with SS. We believe that our study makes a significant contribution to the literature because our findings demonstrate the therapeutic potential of dietary intake of SS in achieving weight loss and reducing serum lipid levels, thus ameliorating the effects of obesity induced by high-fat diet.
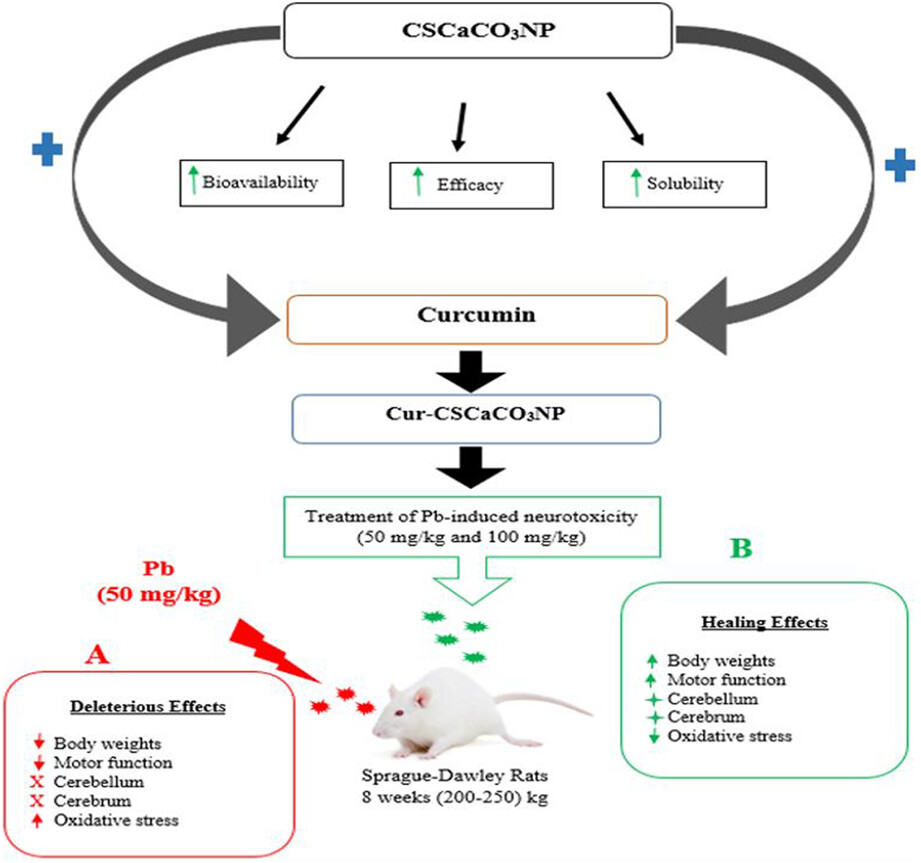
Curcumin-loaded cockle shell-derived calcium carbonate nanoparticles ameliorates lead-induced neurotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress
- First Published: 30 October 2022
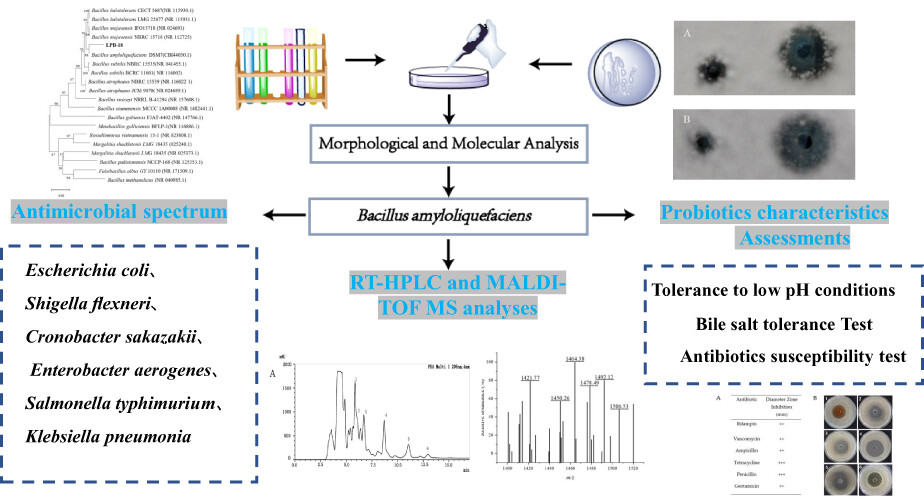
Isolation of a potential probiotic strain Bacillus amyloliquefaciens LPB-18 and identification of antimicrobial compounds responsible for inhibition of food-borne pathogens
- First Published: 12 December 2022
Prediction of winter wheat leaf chlorophyll content based on VIS/NIR spectroscopy using ANN and PLSR
- First Published: 06 October 2022
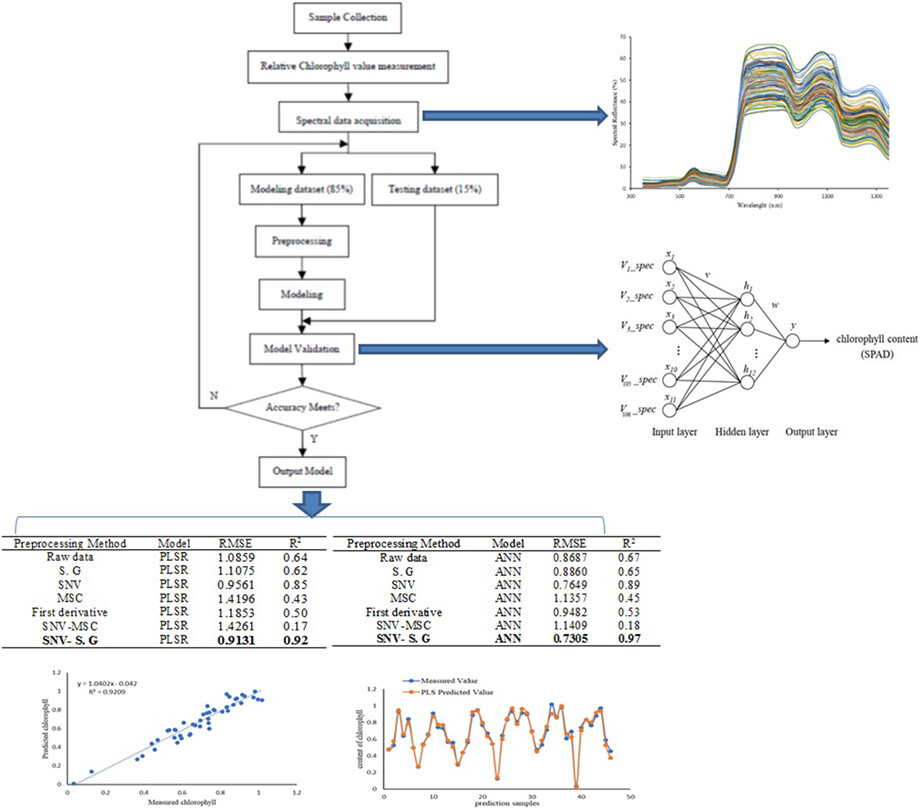
In this research, the amount of winter wheat leaf chlorophyll was nonlinearly predicted by visible–near-infrared spectroscopy by methods of artificial neural networks (ANN) along with partial least squares regression (PLSR). The consequences of estimation of LCC for ANN model (𝑅2 = .97) were better than the PLSR model (𝑅2 = .92).
Neuroprotective effects of a novel peptide from Lignosus rhinocerotis against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells by inhibiting NF-κB activation
- First Published: 12 September 2022
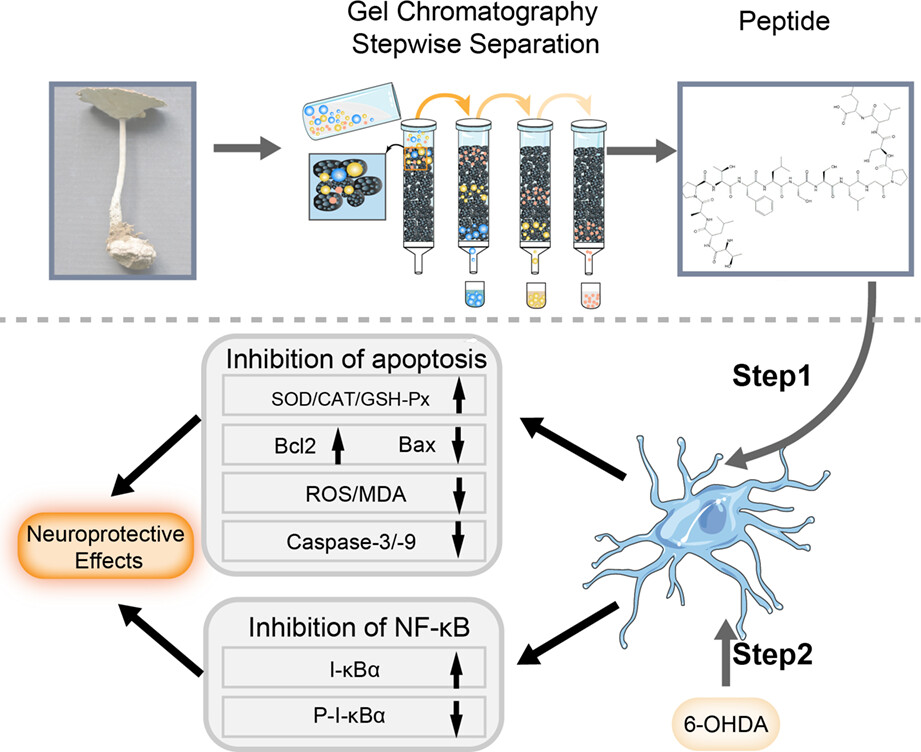
In this study, a novel peptide (LRP) was extracted from the fruiting bodies of L. rhinocerotis using gel filtration chromatography. We determined the amino acid sequence of LRP, which was conducive to its artificial synthesis. Moreover, with NF-κB as the target, the neuroprotective function of LRP was explored. LRP may have the potential to act as a neuroprotective agent.
Panax ginseng abuse exhibits a pro-inflammatory effect by activating the NF-κB pathway
- First Published: 03 September 2022
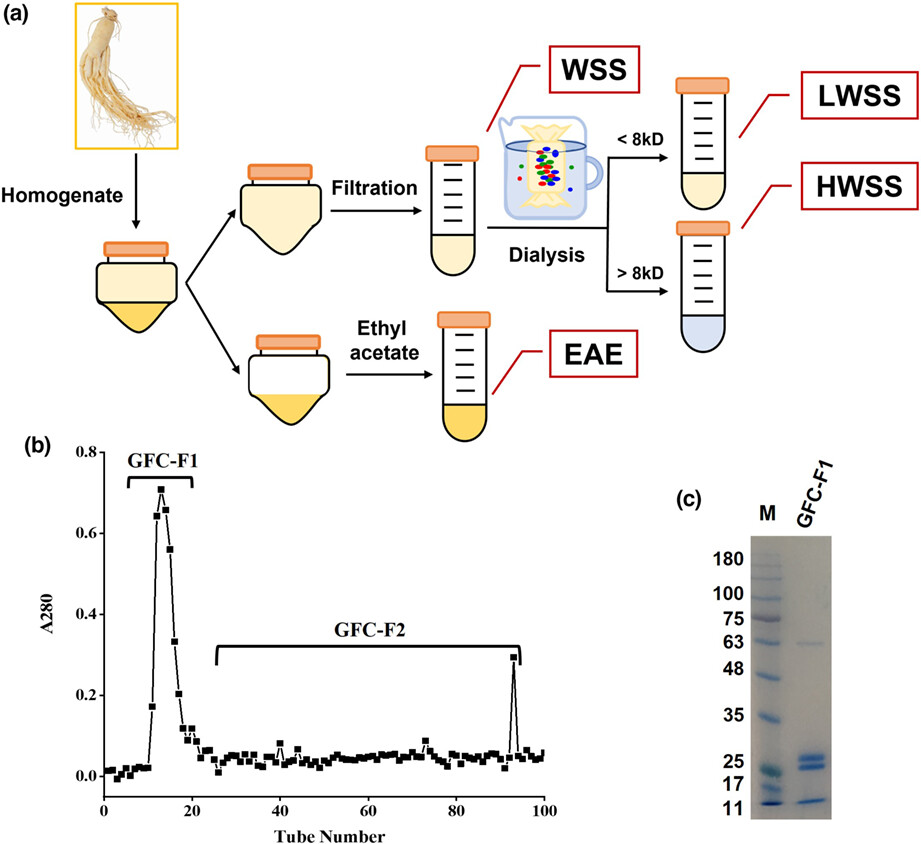
Excessive consumption of panax ginseng may cause over-activation of the immune system forming "ginseng abuse syndrome". The present results suggested that GFC-F1 purified from ginseng is the crucial component that caused "ginseng abuse syndrome". Moreover, GFC-F1 activates the NF-κB pathway to trigger the immune system leading to inflammatory responses through inducing the phosphorylation of p65 and IκBα.
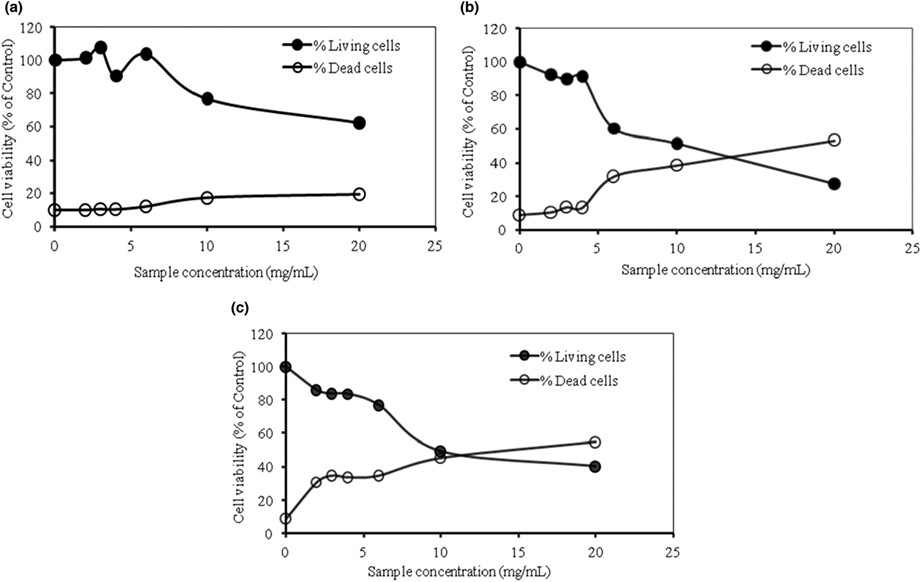
Effects of Allium roseum L. extracts on the proliferation and the differentiation of the acute myeloid leukemia cell line U937
- First Published: 27 July 2022