Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
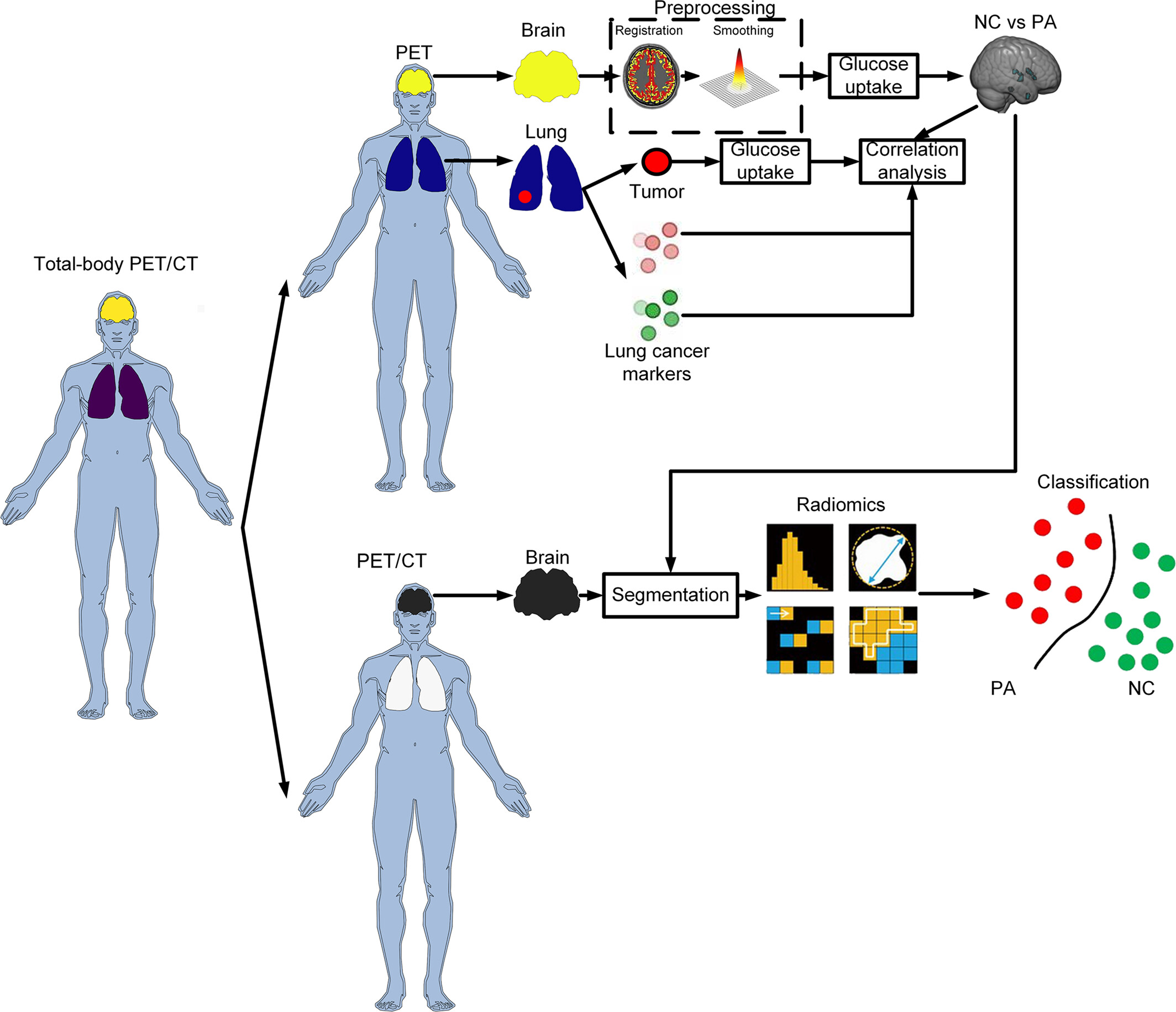
Metabolic and textural changes in the brain of non-small cell lung cancer patients: A total-body positron emission tomography/computed tomography study
- Pages: 109-119
- First Published: 06 June 2023
Fully automated radiosynthesis of [18F]mG4P027 for mGluR4 imaging
- Pages: 120-127
- First Published: 20 June 2023
Prognostic and discriminatory abilities of imaging scoring systems in predicting COVID-19 adverse outcomes
- Pages: 128-140
- First Published: 27 June 2023
Computed tomography (CT) had a higher sensitivity (80% vs. 60%) and positive likelihood ratio in predicting both mortality and or any adverse outcomes such as ICU admission, ventilatory support need, and mortality as compared to Lung Ultrasound score. Thus, CT is superior to ultrasound in ruling out severe outcomes of COVID-19. Lung ultrasound score had a slightly higher specificity compared to CT in both mortality prediction and prediction of any adverse outcome. Lung ultrasound's performance is thus better in ruling in the occurrence of the adverse outcomes. The use of LUS can be superior as regards to the prediction of adverse events and patients' stratification as it is more specific in rolling out such adverse outcomes.
REVIEW
Advanced neuroimaging in the fetal brain: An update on technical advances and clinical findings
- Pages: 141-150
- First Published: 06 June 2023
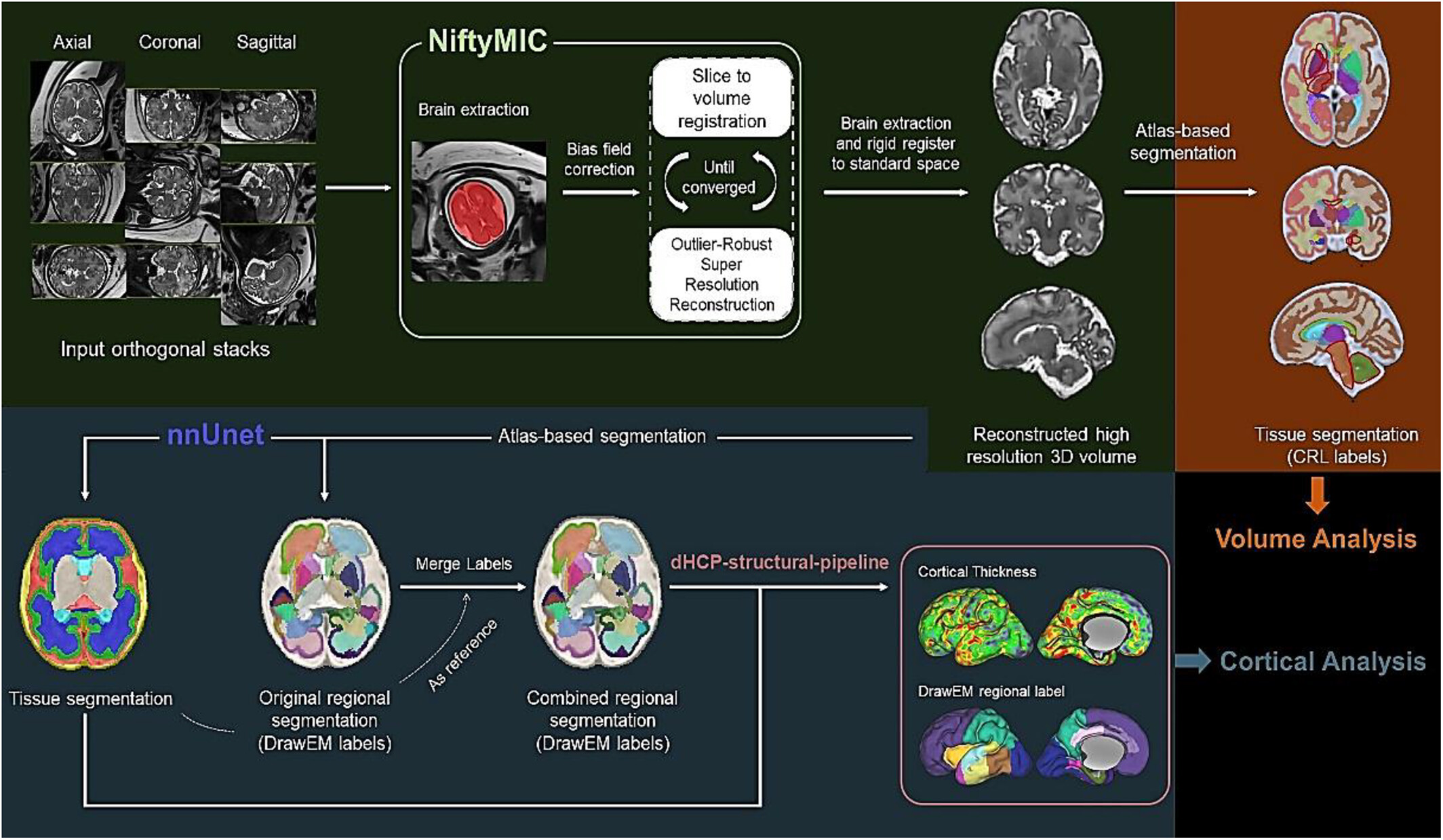
Over the past years, there have been many technical and clinical advances in fetal neuroimaging, primarily in MR, which are summarized in this review. In addition to providing highly detailed qualitative assessment of fetal brain development, advanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) methods such as three-dimensional high-resolution MRI, diffusion MRI, and functional MRI can provide quantitative morphological assessment of tissue microstructure, as well as functional activity.
Graph neural networks for image-guided disease diagnosis: A review
- Pages: 151-166
- First Published: 27 June 2023
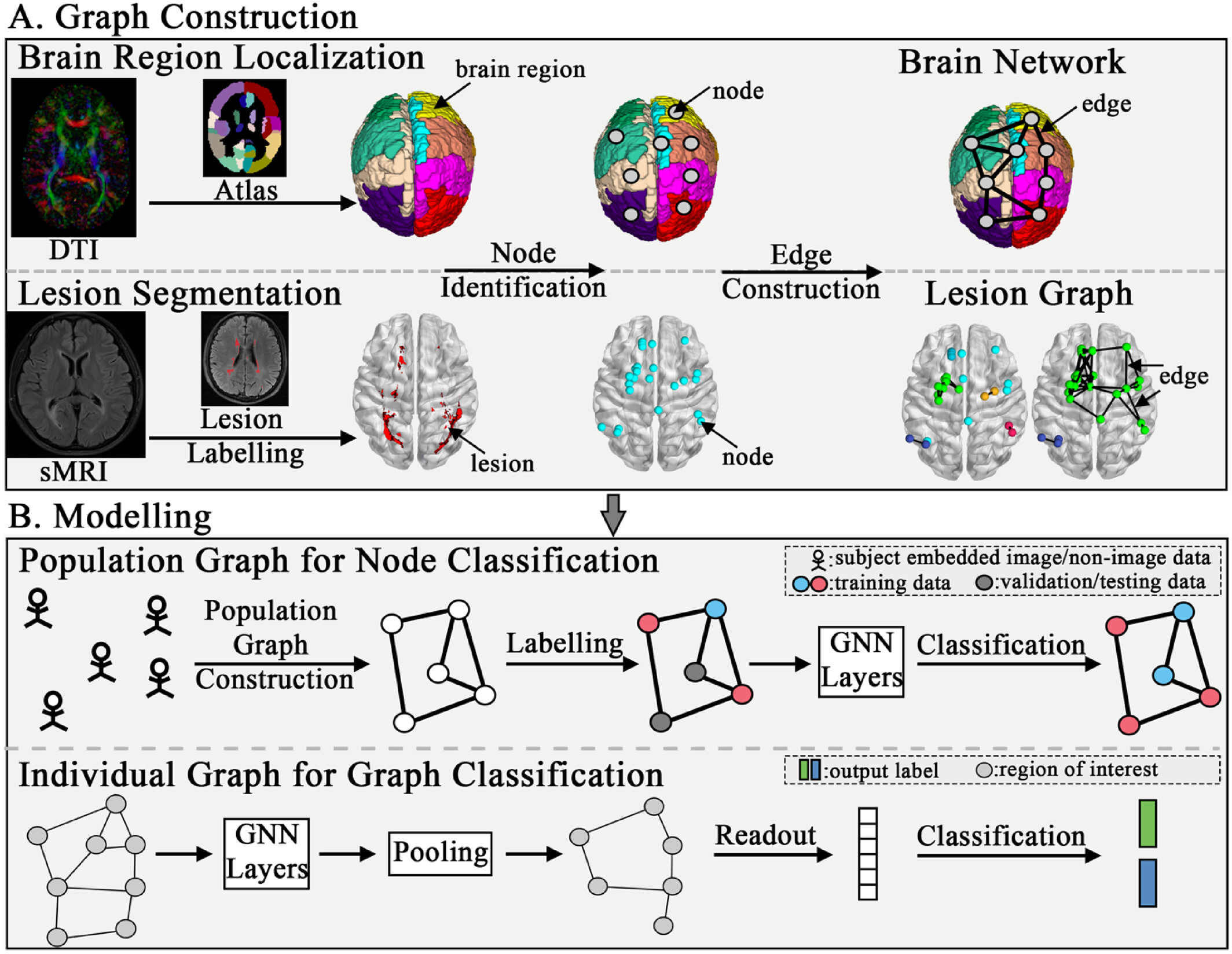
Graph Neural Network (GNN)-based algorithms have achieved promising results in the detection of various diseases, due to the ability of capturing the hidden spatial patterns in irregular structures, by aggregating the node features, edge features, and graph structure information. This paper systematically reviews common-used GNN-based algorithms for image-based disease diagnosis, including general workflow, limitations and further directions.
Radiobioinformatics: A novel bridge between basic research and clinical practice for clinical decision support in diffuse liver diseases
- Pages: 167-189
- First Published: 18 June 2023
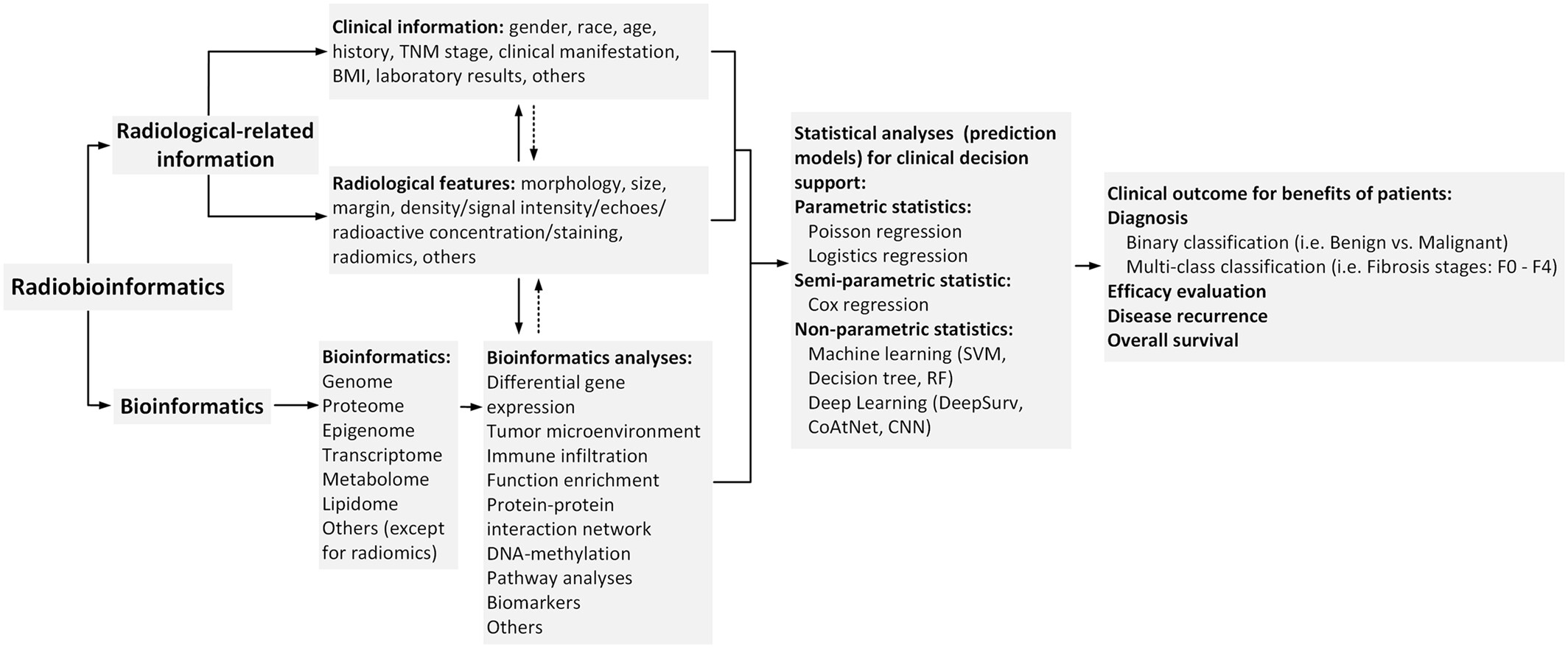
(1) The review paper discusses the importance of radiobioinformatics, a technique that combines radiological features and bioinformatics in diagnosis and prognosis of diffuse liver diseases. (2) The paper elaborates on pathological categorizations of diffuse liver disease, evaluation of multiomics approaches, and potential value of predictive models. (3) The paper also demonstrates the role of artificial intelligence in improving the accuracy of medical imaging and the use of omics technologies for noninvasive biomarker discovery.
COMMENTARY
Super-stable homogeneous embolic agents advance the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 190-194
- First Published: 15 June 2023
CASE IMAGE
Extranodal involvement of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder detected on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose-positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- Pages: 195-197
- First Published: 01 June 2023





![Fully automated radiosynthesis of [18F]mG4P027 for mGluR4 imaging](/cms/asset/449c9461-17cd-4477-ba5f-073980a0233f/ird325-toc-0001-m.jpg)






