Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Alteration in AMPA receptor subunit expression and receptor binding among patients with addictive disorders: A systematic review of human postmortem studies
- Pages: 148-155
- First Published: 09 May 2019
Postmortem studies on AMPA receptors in patients with addiction show that the hippocampus and amygdala may be pertinent to addictive disorders through their functions on learning and memory, whereas findings in other regions were inconsistent across the studies. Human postmortem studies are prone to degenerative changes after death, which emphasizes the need to investigate AMPA receptors in the living human brains.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Antidepressant amitriptyline-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation is mediated by Src family tyrosine kinase, which leads to glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA expression in rat astroglial cells
- Pages: 156-163
- First Published: 25 April 2019
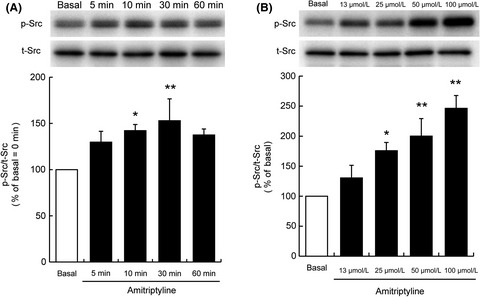
Treatment of rat C6 astroglial cells (C6 cells) with amitriptyline increased Src family tyrosine kinase phosphorylation in a time- and concentration-dependent manner. The current findings suggest that the pharmacological effect of antidepressant such as amitriptyline is mediated through an intracellular signaling pathway via the LPAR1/Gαi/o/Src family tyrosine kinase, which leads to MMP-9 activation and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor production.
Development of the School Teachers Job Stressor Scale (STJSS)
- Pages: 164-172
- First Published: 27 June 2019
Blonanserin versus haloperidol in Japanese patients with schizophrenia: A phase 3, 8-week, double-blind, multicenter, randomized controlled study
- Pages: 173-182
- First Published: 30 April 2019
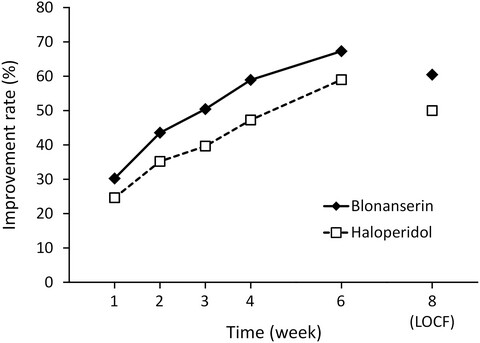
Blonanserin is as effective as haloperidol for the treatment of schizophrenia. Blonanserin is more effective for negative symptoms with a lower risk of extrapyramidal symptoms compared with haloperidol. Blonanserin is considered an appropriate antipsychotic drug to combine with cognitive remediation therapy.
Characteristics of facial muscle activity during voluntary facial expressions: Imaging analysis of facial expressions based on myogenic potential data
- Pages: 183-193
- First Published: 28 May 2019
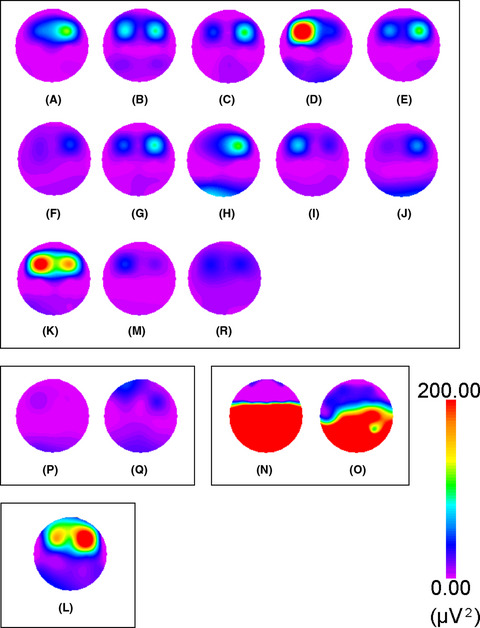
With facial myogenic potential topography, facial expressions can be evaluated objectively without being influenced by face shape or countenance. Cluster analysis of the expression of disgust showed four homogeneous subgroups. Color changes in topograms showed subtle changes in expressions that could not be supplemented with statistical processing alone, and these were useful in identifying individuality.
Moral competence and conduct disorder among Filipino children in conflict with the law
- Pages: 194-202
- First Published: 16 July 2019
This paper examines the relationship between moral competence and conduct disorder among Filipino children in conflict with the law. Aside from the association found between low moral competence and conduct disorder, other associations uncovered in this study include the relationship between conduct disorder and the presence of substance use as a dual diagnosis and history of child abuse. As of the time of publication, this is the first paper of its kind to have been conducted in the Philippines.
Effectiveness of high-frequency left prefrontal repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation in patients with treatment-resistant depression: A randomized clinical trial of 37.5-minute vs 18.75-minute protocol
- Pages: 203-208
- First Published: 25 June 2019
Regulatory system of mGluR group II in the nucleus accumbens for methamphetamine-induced dopamine increase by the medial prefrontal cortex
- Pages: 209-216
- First Published: 08 July 2019
Possible association between photic sneeze syndrome and migraine and psychological distress
- Pages: 217-222
- First Published: 09 July 2019
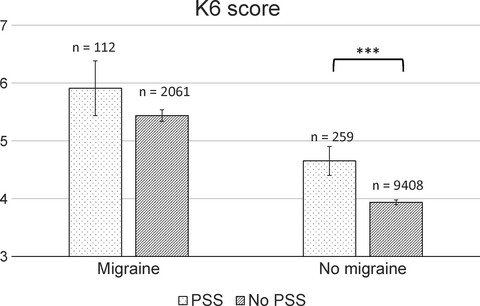
Our data obtained through a self-report questionnaire administered to 11,840 participants showed that individuals with photic sneeze syndrome were more likely to suffer from migraine and psychological distress than those without photic sneeze syndrome. Photic sneeze syndrome may be a potential target for the research of migraine and stress-related disorders.
Comprehensive behavioral analysis of heterozygous Syngap1 knockout mice
- Pages: 223-237
- First Published: 19 July 2019
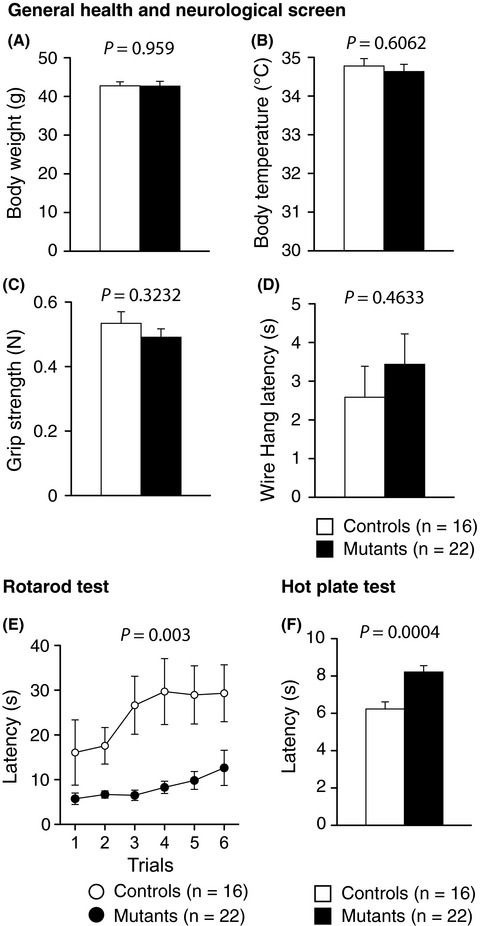
In Syngap1−/+ mice, a well-known model of SYNGAP-related ID, we could reproduce most of the previously reported cognitive and emotional deficits. The decreased sensitivity to painful stimuli and impaired motor function that we found in Syngap1−/+ mice are consistent with the common characteristics of patients with SYNGAP-related ID. We further confirmed that the Syngap1 heterozygote mouse recapitulates the symptoms of ID and ASD patients.
CASE REPORT
Concurrent, successful management of bipolar I disorder with comorbid alcohol dependence via aripiprazole long-acting injection: A case report
- Pages: 238-240
- First Published: 20 July 2019
MICRO REPORTS
Efficacy and safety of lithium and lamotrigine for the maintenance treatment of clinically stable patients with bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis of double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials with an enrichment design
- Pages: 241-246
- First Published: 26 April 2019
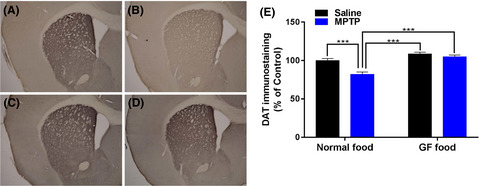
Dietary intake of glucoraphanin prevents the reduction of dopamine transporter in the mouse striatum after repeated administration of MPTP
- Pages: 247-251
- First Published: 27 May 2019
Suvorexant for insomnia in patients with psychiatric disorder: A 1-week, open-label study
- Pages: 252-255
- First Published: 08 July 2019
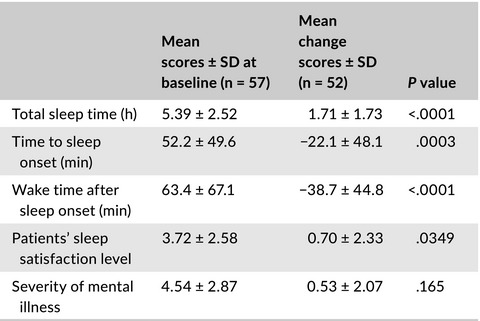
This is one-week, prospective, single-arm, clinical trial of fixed dose of suvorexant for insomnia included 57 patients with psychiatric disorders. Compared with the baseline scores, taking suvorexant was associated with significant improvements in total sleep time, time to sleep onset, wake time after sleep onset, and the patients' sleep satisfaction level at week 1.
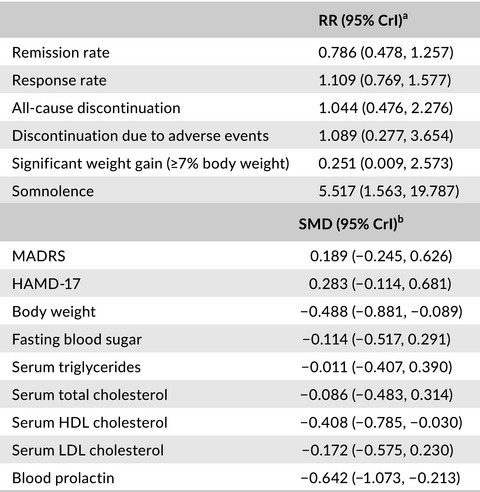
Quetiapine extended-release vs olanzapine for Japanese patients with bipolar depression: A Bayesian analysis
- Pages: 256-259
- First Published: 08 July 2019