Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Pictures
Cover Picture: An Efficient Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Evolution System using Silicon Nanomaterials with Ultra-High Aspect Ratios (Energy Technol. 11/2014)
- Page: 857
- First Published: 10 November 2014

Hydrogen from the Sun: The cover image illustrates Si nanowire arrays with ultra-high aspect ratios for the application of photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution. As described in the Full Paper by Duck Hyun Lee and colleagues at the University of Michigan and Silicium Energy on page 889, the authors have created such wafer-scale nanowire arrays using the combination of block copolymer lithography and metal-assisted etching. Thus, the fabrication of the Si nanowire cells was performed using scalable manufacturing techniques, and they exhibited high absorbance of incident light, a reduced minority carrier transport distance, and a high chemical reaction surface area. These structural advantages of the Si nanomaterials developed here enabled us to achieve remarkably high photocurrents and hydrogen evolution efficiencies.
Inside Cover: One-Dimensional, Additive-Free, Single-Crystal TiO2 Nanostructured Anodes Synthesized by a Single-Step Aerosol Process for High-Rate Lithium-Ion Batteries (Energy Technol. 11/2014)
- Page: 858
- First Published: 10 November 2014

Driving Battery Development with Nanostructures: The cover picture shows the synthesis of highly oriented, single-crystalline TiO2 nano-columns directly on the current collector by using an aerosol chemical vapor deposition (ACVD) process. As described in the Full Paper on page 906 from Pratim Biswas and colleagues at Washington University in St. Louis and Indian Insitute of Technology, Bombay, the nanostructures exhibit excellent electrochemical performance and rate capability even without the presence of any binding agents or conductive additives. This makes them extremely suitable for high-rate lithium-ion battery anodes such as in electric vehicles and hybrid electric vehicles.
Graphical Abstract
Review
Solid Mixed-Metal-Oxide Catalysts for Biodiesel Production: A Review
- Pages: 865-873
- First Published: 24 October 2014
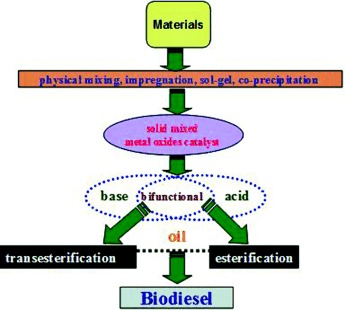
Sir Mix-a-lot: In comparison with single metal oxides, solid mixed-metal-oxide catalysts with enhanced basic and/or acid strength, specific surface areas, and stability are more promising candidates for catalyzing transesterification and esterification reactions. The state of the art of the utilization as well as the preparation of solid mixed-metal-oxide catalysts for the production of biodiesel are described in this Review.
Communication
Upgrading Carbon Dioxide/Methane Mixtures by using a Hybrid Membrane–Condensed Rotational Separation Process
- Pages: 874-876
- First Published: 11 September 2014
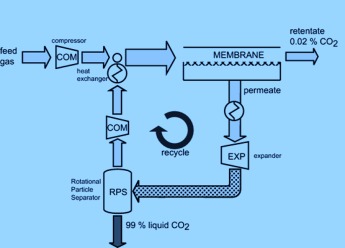
Membranes are used to upgrade heavily contaminated methane gas to pipeline specifications. In the hybrid system considered in this Communication, the methane is removed from the permeate stream by using a low-temperature distillation process with condensed rotational separation (CRS). Compared to a hybrid amine-CRS process, the energy and volume use are reduced by a factor of two.
Full Papers
Synergistic Hydrogen-Donating Ability of Petroleum Distillates and Hydrogen During Noncatalytic Thermal Processing
- Pages: 877-881
- First Published: 31 October 2014
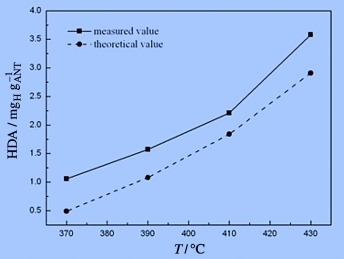
Making a donation: In this study, the probe method is applied to determine the hydrogen donating ability (HDA) of hydrogen, petroleum distillates, and the mixture of them, respectively. Through comparison and analysis of the three HDAs, the synergy during the thermal processing under hydrogen is quantified, and combined with the structure properties of the distillates, the reaction path or activation possibility of hydrogen is discussed.
Dimethyl Ether Synthesis from Syngas over the Admixed Cu/ZnO/Al2O3 Catalyst and Alkaline Earth Oxide-Modified HZSM-5 Zeolite
- Pages: 882-888
- First Published: 18 September 2014
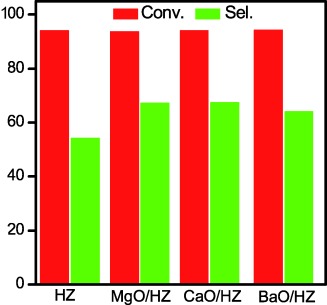
Ether ore: The modification of HZSM-5 zeolite with alkaline earth oxides especially MgO and CaO is applied to the catalytic synthesis of dimethyl ether and is shown to significantly decrease the selectivity to undesired byproducts, due to the reduced amount of strong acid sites. This greatly improves the selectivity to dimethyl ether, while scarcely affecting the conversion of CO.
An Efficient Photoelectrochemical Hydrogen Evolution System using Silicon Nanomaterials with Ultra-High Aspect Ratios
- Pages: 889-896
- First Published: 18 September 2014

The straight doping: Wafer-scale ultra-high aspect ratio Si nanomesh/nanowires (feature size≈20 nm) were fabricated and utilized to produce an efficient photoelectrochemical hydrogen evolution system. The Si nanomesh cell yielded extreme optical absorptivity, high external quantum efficiency, and high photocurrent. Detailed studies suggest that both the n+ pp+ doping and thickness of nanostructures are keys to the enhancement of the hydrogen evolution efficiency.
Graphitic Petal Micro-Supercapacitor Electrodes for Ultra-High Power Density
- Pages: 897-905
- First Published: 22 October 2014
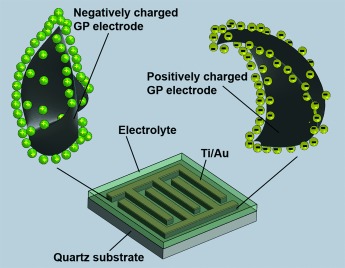
High-power micro-supercapacitors based on graphitic petal electrodes are designed and fabricated, and charge/discharge rates up to 100 000 mV s−1 (1000 times faster than conventional supercapacitors) are achieved in 1 M H2SO4 aqueous electrolyte. The resulting devices exhibit excellent energy and power densities as well as good cyclic stability.
One-Dimensional, Additive-Free, Single-Crystal TiO2 Nanostructured Anodes Synthesized by a Single-Step Aerosol Process for High-Rate Lithium-Ion Batteries
- Pages: 906-911
- First Published: 18 September 2014
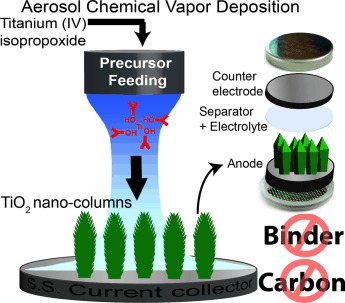
Incredible nanostructures! Perfectly oriented, single crystal TiO2 nano-columns are fabricated by a single-step process directly on the current collector using aerosol chemical vapor deposition (ACVD). The highest specific capacity ever reported for anatase TiO2 is obtained, in addition to the exceptional cycling performance and rate capability, even without the use of any conductive additives or binding agents.
Conversion of Calophyllum inophyllum Oil with a High Free Fatty Acid Content to Biodiesel using a Starch-Derived Catalyst
- Pages: 912-920
- First Published: 22 September 2014
Starch Trek: Biodiesel is produced from Calophyllum inophyllum oil using a starch-derived catalyst. The catalyst, obtained by the sulfonation of carbonized starch, is characterized by various techniques. The catalyst is capable of esterification and transesterification reactions under the conditions studied, and a very high biodiesel yield is achieved under the optimized conditions.
Diamondoid-Structured Cu–Dicarboxylate-based Metal–Organic Frameworks as High-Capacity Anodes for Lithium-Ion Storage
- Pages: 921-927
- First Published: 07 October 2014
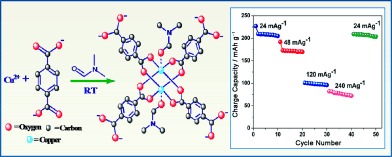
Diamondoid is an anode′s best friend: A versatile electrochemical synthetic route is proposed for the preparation of a diamondoid-structure [Cu2(C8H4O4)4]n metal–organic frameworks for Li-ion batteries. This material constitutes new class of porous crystalline materials that have the ability to reversibly store Li+ ions. Galvanostatic charge/discharge studies suggest that the terephthalate network reversibly reacts with Li with high capacity retention.
A New Concept for High-Performance Fuel Cell Design with Controlled Component Mixing using Jet Flow
- Pages: 928-933
- First Published: 10 September 2014
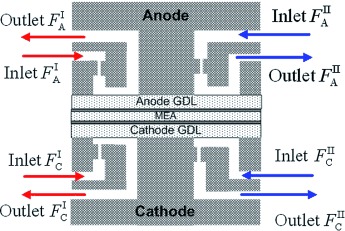
Turning on the jets: A new concept is proposed for a high-performance fuel cell design. The concept is based on the intensification of mass transfer processes due to implementing multiple contact zones with jet flow and preventing the intermixing of the reactants and products. A proof of concept is performed by comparing the new fuel cell design with conventional a PEMFC, and the new design shows significantly improved performance.
Book Review
Fuels and Fuel-Additives. By S. P. Srivastava and J. Hancsók
- Pages: 934-935
- First Published: 15 September 2014






