Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER
Cover: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 7/2022
- Page: 1005
- First Published: 18 July 2022
In this figure, MgFe2O4@SiO2 nanorods created at ambient conditions were characterized by UV-VISIBLE, TGA, XRD, FE-SEM, HR-TEM, and BET analysis to establish their physical nature. As revealed by VSM, these rods are magnetic. EDS confirms elemental composition. XRF affords fluorescence properties. These rods are capable of quickly degrading methyl orange. More details will be discussed by Prof. Radhakrishnan M. Tigote and his coworkers on page 1032–1041 in this issue.
CONTENTS
Contents: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 7/2022
- Pages: 1006-1011
- First Published: 18 July 2022
ISSUE INFORMATION
Issue Information: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 7/2022
- First Published: 18 July 2022
ARTICLES
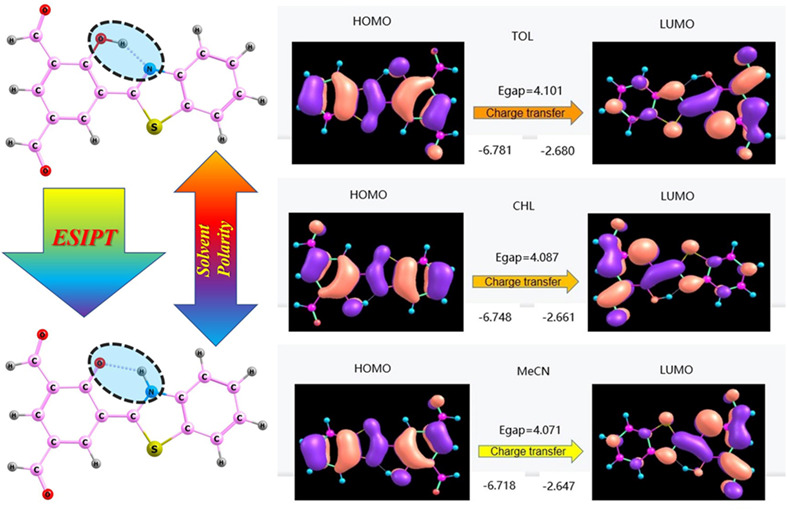
Solvent polarity-dependent ESIPT behavior for 5-(benzothiazole-2-yl)-4-hydroxyisophthalaldehyde fluorophore: A theoretical study
- Pages: 1012-1019
- First Published: 03 July 2022
Fabrication of a visible-light-driven p-type NiWO4/n-type SnO2 heterojunction with efficient photocatalytic activity for degradation of Amaranth
- Pages: 1020-1031
- First Published: 13 June 2022
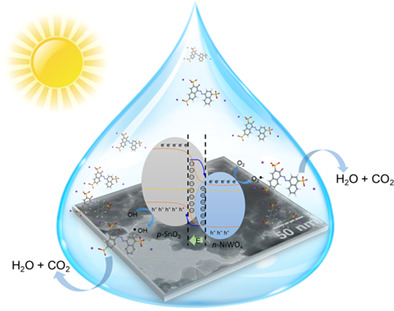
This work presents a novel p-type SnO2/n-type NiWO4 heterojunction was synthesized via simple chemical impregnation method. The obtained NiWO4/SnO2 possessed a p-n heterojunction structure at the contact interface. Visible light response range and carrier transmit status were successfully adjusted in heterojunction. The electron-hole pairs from photogenerated process accelerated to the degradation of Amaranth dye.
Structural studies of silica-supported spinel magnesium ferrite nanorods for photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange
- Pages: 1032-1041
- First Published: 22 April 2022
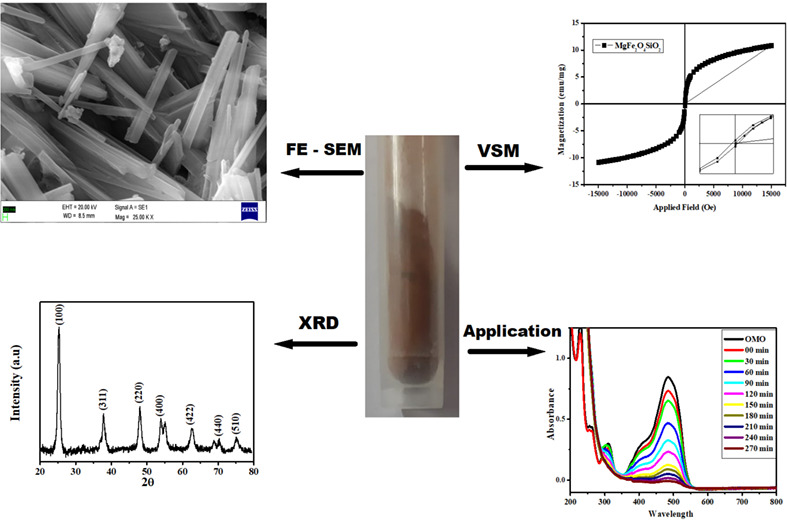
The synthesized magnetic MgFe2O4@SiO2 nanorods show an optical band gap of 3.1 eV, with λmax at 334 nm and average particle size 36 nm, with FCC crystal structure. SEM & TEM confirm the rod-like structure. EDS, XRF studies reveal the presence of Si, Mg, Fe and O. The surface area, pore volume, and pore diameter are 19.2 m2 g−1, 2.46 cm3 g−1, 5.10 nm respectively.
Formation of a p-n heterojunction photocatalyst by the interfacing of graphitic carbon nitride and delafossite CuGaO2
- Pages: 1042-1050
- First Published: 13 May 2022
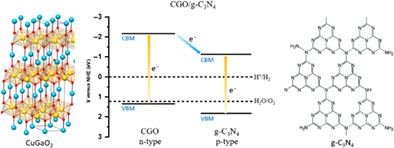
The CuGaO2/g-C3N4 composite has been found to form a p-n heterojunction capable of generating an increased photocurrent for water reduction, compared to its isolated components. Its activity lies in the enhanced photo-generated charge transfer in the photo-catalyst. Orbital hybridization possibly enable this phenomenon, as was evidence by XPS and XAS analyses.
New chitosan modified with epichlohydrin and bidentate Schiff base applied to removal of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions
- Pages: 1051-1059
- First Published: 22 June 2022
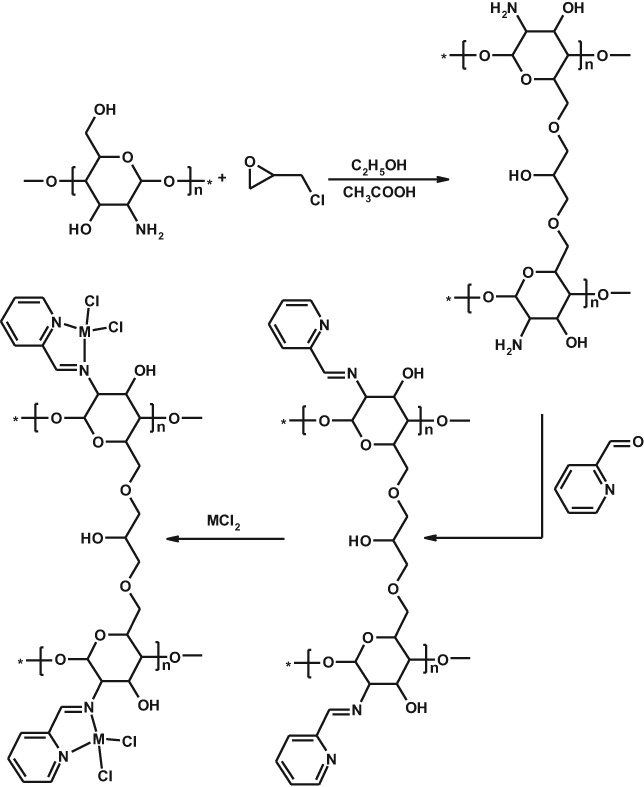
Modified chitosan with epichlohydrin and bidentate Schiff base ligand (CEP) was successfully synthesized, characterized and its removal ability of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions was studied. At optimal conditions, the maximum removal percentage of Pb2+ and Cd2+ ions was found to be 95 and 79%, respectively. The adsorption process followed the second-order kinetic model for Pb(II) and the first-order kinetic model for Cd(II). In addition, the effect of interface ions was investigated and it was found that the presence of divalent cations only affected the adsorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) using CEP. Finally, the CEP adsorbent has undergone five regeneration experiments and adsorption efficiency was reduced by about 9 and 12% for Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, respectively.
Potentiometric determination of copper(II) ions based on a porphyrin derivative
- Pages: 1060-1069
- First Published: 07 June 2022
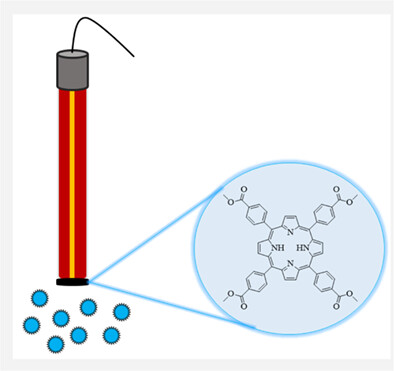
In this study, a novel potentiometric sensor was developed for the determination of Cu2+ ions. The developed sensor exhibits a linear response over a wide concentration range and has a very low detection limit. In addition, the copper(II)–selective sensor has advantages such as high selectivity, short response time, low cost, good repeatability, and stability.
Quantification of anthocyanins in blueberries (Vaccinium spp.) by modified QuEChERS and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
- Pages: 1070-1078
- First Published: 13 June 2022
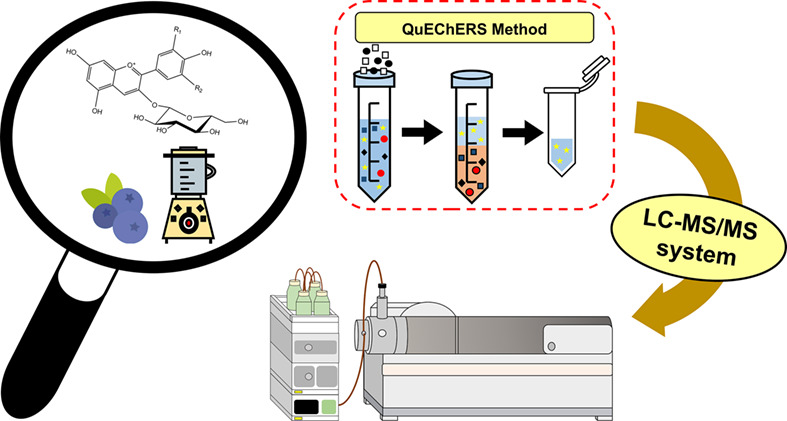
A method based on themodified quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged, and safe method (QuEChERS) wasdeveloped for the determination of 6 common types of anthocyanins inblueberries using LC-MS/MS. This proposed method provided an efficient andsensitive approach for the qualitative and quantitative determination of thecommon anthocyanins in blueberry samples.
Novel Gd2O3/SrFe12O19@Schiff base chitosan (Gd/SrFe@SBCs) nanocomposite as a novel magnetic sorbent for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution
- Pages: 1079-1087
- First Published: 11 July 2022
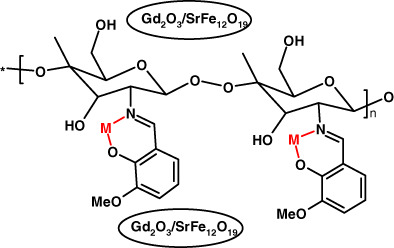
In this work, a new modified Gd2O3/SrFe12O19 nanocomposite/Schiff base chitosan was prepared, and it was characterized using FT-IR, XRD, DSC, VSM, FE-SEM, X-ray energy dispersive spectrum (EDS), and map analysis. All results confirm that the Gd2O3/SrFe12O19 nanocomposite/Schiff base chitosan was successfully prepared. EDS and map analysis predicts that all elements are well distributed to the compound. VSM shows that the title compound has high saturation magnetic of 17.35 emu/g with high coercivity of 4664 Oe. In addition, Gd2O3/SrFe12O19 nanocomposite/Schiff base chitosan was used as a new adsorbent for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution, and the results confirm that the removal efficiency of Pb(II) (98%) is higher than Cd(II) (78%) ion. At best conditions, the maximum adsorption capacity for Pb(II) is 183.75 and for Cd(II) is 146.25 mg/g. According to adsorption results, we proposed thio compound to removal of other heavy metal ions such as Hg(II), Cr(VI), and Zn(II) using the adsorption process.
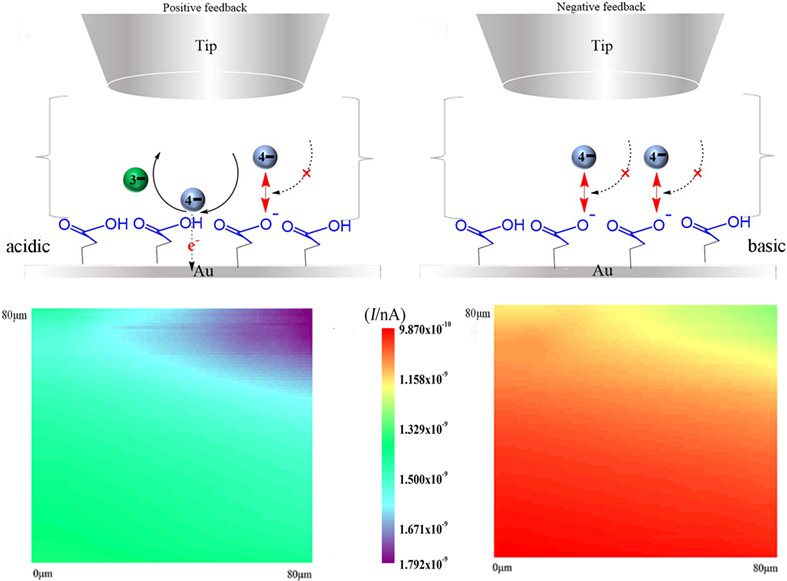
Study of the electrostatic repulsion of the carboxylic surface in the diffusion layer by scanning electrochemical microscopy
- Pages: 1088-1095
- First Published: 04 July 2022
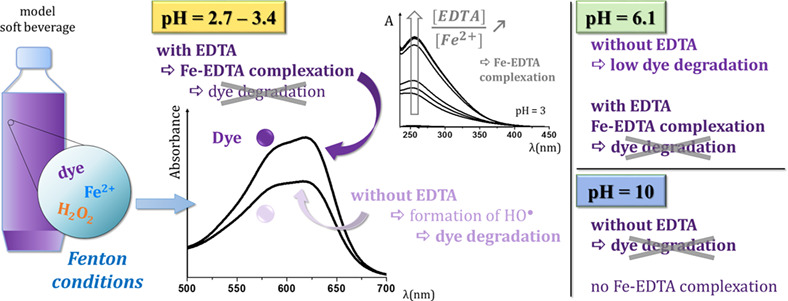
Improvement of color stability using a chelating agent in model soft beverages subjected to Fenton reaction
- Pages: 1096-1105
- First Published: 12 July 2022
Synthesis, computer-aided ADMET prediction, and molecular docking of novel 3,5,6-trichloropyridin-2-yl derivatives as potential antimicrobial agents
- Pages: 1106-1120
- First Published: 25 June 2022
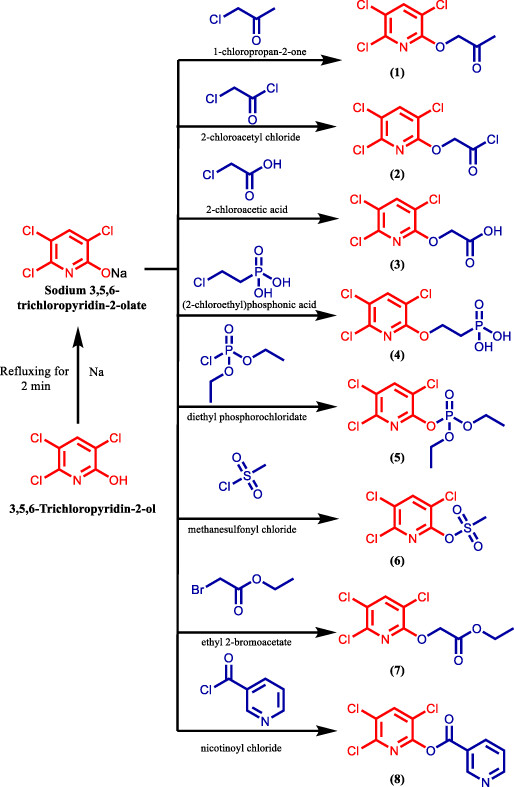
3,5,6-Trichloropyridin-2-yl based molecules derivatives were synthesized. The compounds were designed to meet the urgent need for novel antimicrobial agents. Most of compounds exhibited superior antibacterial activity compared to amoxicillin. Molecular docking and ADMET parameters of the compounds were in silico computed.
RETRACTION
PREVIEW
Preview: Journal of the Chinese Chemical Society 7/2022
- Page: 1122
- First Published: 18 July 2022