Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
Carbazole-based dual-functional chemosensor: Colorimetric sensor for Co2+ and fluorescent sensor for Cu2+ and its application
- First Published: 30 November 2021
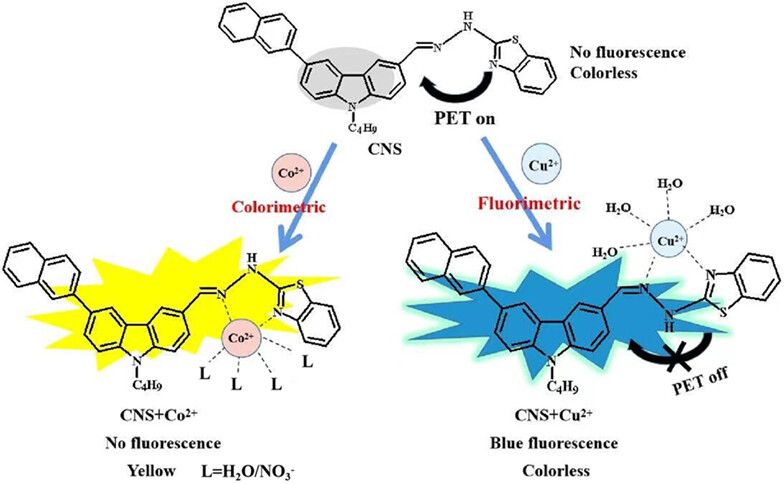
A new carbazole-based fluorescent chemosensor (CNS) was synthesized for the detection of Co2+ and Cu2+ in different solvent systems.
CNS can selectively detect Cu2+ and recognize Co2+ in a naked eye by UV-vis and fluorescence spectroscopy.
CNS has been successfully applied to fluorescence imaging of Cu2+ in HeLa cells and detection of Cu2+ in real water samples.
Selective fluorescent detection of Zn2+ by a rhodanine-based chemosensor
- First Published: 19 April 2022
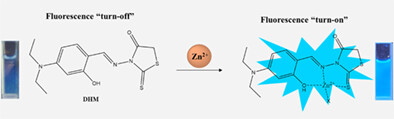
A rhodanine-based fluorescent chemosensor DHM was synthesized for detecting Zn2+. DHM showed unique fluorescence change on detecting Zn2+ with a low detection limit (1.33 μM). DHM could analyze Zn2+ in a real environment and be recyclable with EDTA. DHM-doped test kit was used for recognizing Zn2+. Binding feature of DHM to Zn2+ was illustrated by ESI-mass, NMR titration, and calculations.
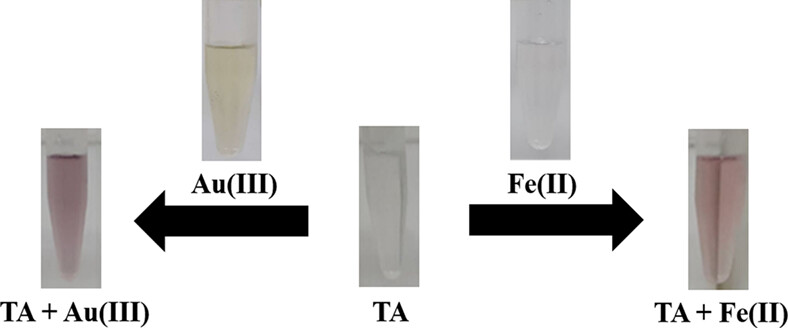
Tannic acid as a chemosensor for colorimetric detection of Fe(II) and Au(III) ions in environmental water samples
- First Published: 14 February 2022
A molecular biomimetic sensor of tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine-based iron(III) complex for acrylamide detection: Electrochemical study and DFT calculations
- First Published: 28 September 2021
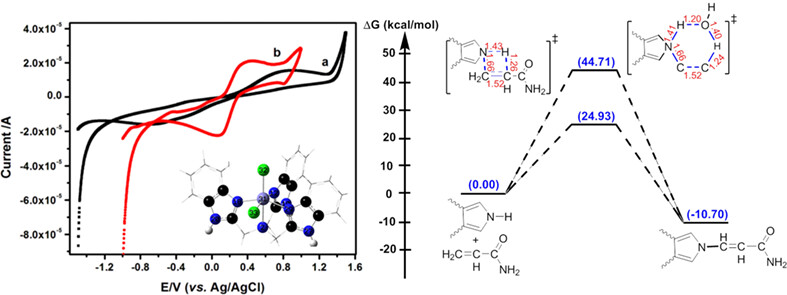
A new biomimetic sensor (BS) has been prepared by modifying the carbon paste electrode (CPE) based on [Fe(NTB)Cl2]Cl (FeC) {NTB = tris(2-benzimidazolylmethyl)amine} for the electrochemical detection of acrylamide (AA). the constructed BS was successfully applied for the evaluation of AA in various potato chips and the results were comparable to those obtained from other electrochemical methods.
Electrochemical evaluation of magnetic reduced graphene oxide nanosheet-modified glassy carbon electrode on dopamine electrochemical sensor for Parkinson's diagnostic application
- First Published: 26 July 2023
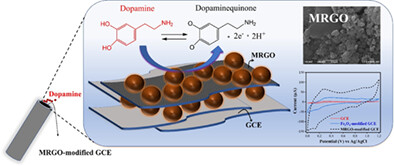
Magnetic reduced graphene oxide (MRGO) consists of graphene layer tethered with the spherical Fe3O4. The oxygen-based functional groups on the surface of MRGO could act as chemically active sites for the attachment of dopamine. The MRGO nanosheet has been proven to be an effective glassy carbon electrode modifier with a remarkable electroactive surface area of approximately 0.0104 cm2, demonstrating stable and sensitive electrochemical performance toward dopamine.
Two silver(I) complexes: Synthesis, structures, and electrochemical H2O2 sensing
- First Published: 16 February 2022
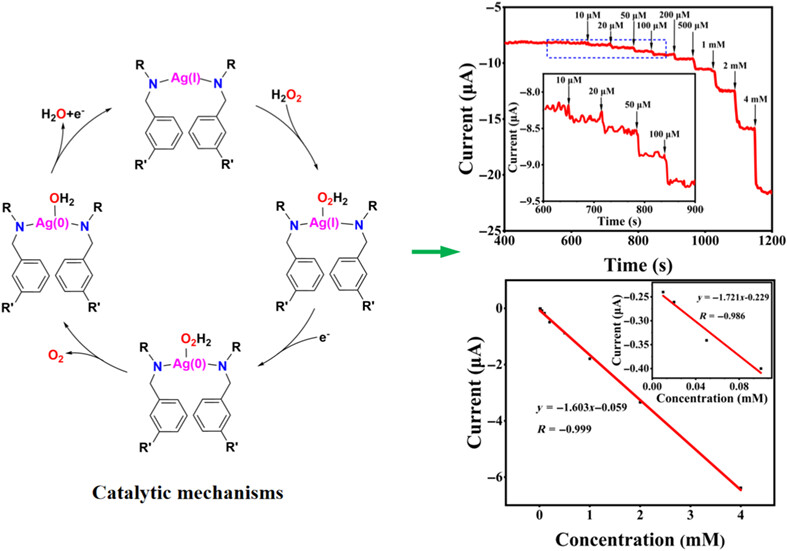
Two new Ag(I) complexes were synthesized and characterized. Their Ag(I) centers displayed different coordination geometric structures: two-coordinated linear in 1, whereas four-coordinated distorted tetrahedron in 2. The electrochemical sensing performance of Ag(I) complexe-modified carbon paste electrode (CPE-1 and CPE-2) toward H2O2 was evaluated by chronoamperometry in 0.2 M phosphate buffer saline (pH = 6) at −0.2 V. The CPE-1 was found to have a wide linear response from 1.0 × 10−5 to 4.0 × 10−3 M, lower detection limit of 1.73 μM, excellent anti-interference ability, and stability. The CPE-2 does not have recognition properties for H2O2, which may be due to the large steric hindrance around Ag(I) centers that is not easy to combine with hydrogen peroxide to form a catalytic transition state. The results reveal that the Ag(I) complexes may be used as effective components of electrode materials.
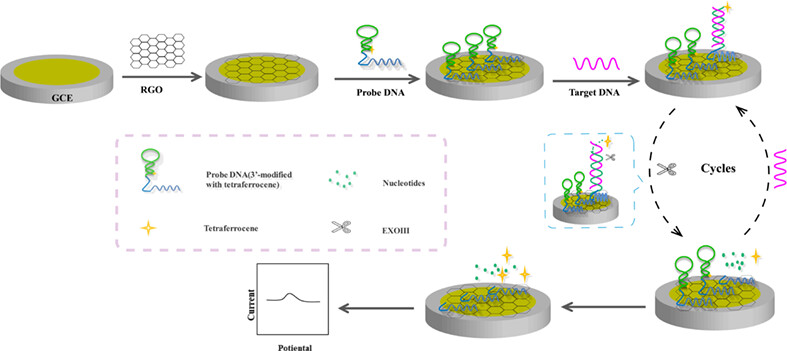
A sensitive electrochemical DNA sensor based on reduced graphene oxide modified electrode
- First Published: 30 May 2022
Highly sensitive carbon paste electrode modified with a synthesized ferrocenyl Schiff base for trace determination of Ce(III) in real samples
- First Published: 04 December 2021
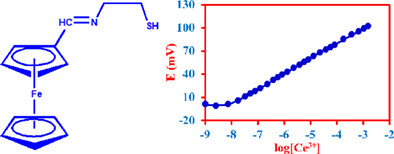
A recently new synthesized Schiff base was used as a modifier in carbon paste matrix to develop a potentiometric cation sensor. The constructed modified carbon paste sensor represents a Nernstian slope of 19.4 mV/decade to cerium(III) from 7.5×10-9 to 1.5×10-3 M and a low detection limit of 5.4 × 10-9 M. The sensor was carried out as an indicator electrode in potentiometric titration and determination of cerium(III) ion in mineral and spring water samples.
Reduced graphene oxide/titanium carbide MXene nanocomposite-modified electrode for electrochemical hemoglobin biosensor
- First Published: 09 November 2021
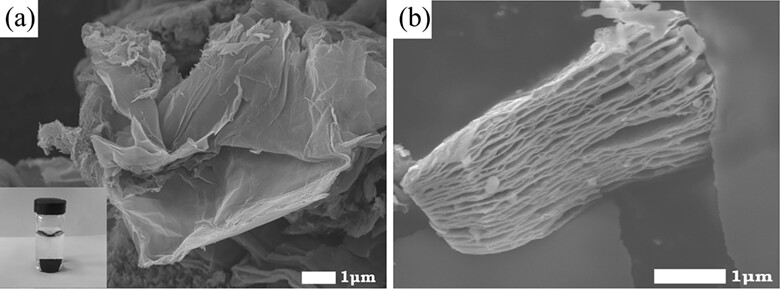
Reduced graphene oxide and titanium carbide nanocomposite was prepared by the self-assembly method and used for electrode modification. Then, an electrochemical hemoglobin biosensor was prepared on the nanocomposite-modified electrode, and used for the determination of trichloroacetic acid and hydrogen peroxide.
Screen-printed electrode-based homogeneous electrochemical aptasensor for mercury (II) based on reduced graphene oxide and exonuclease III-driven cyclic reaction
- First Published: 08 August 2022
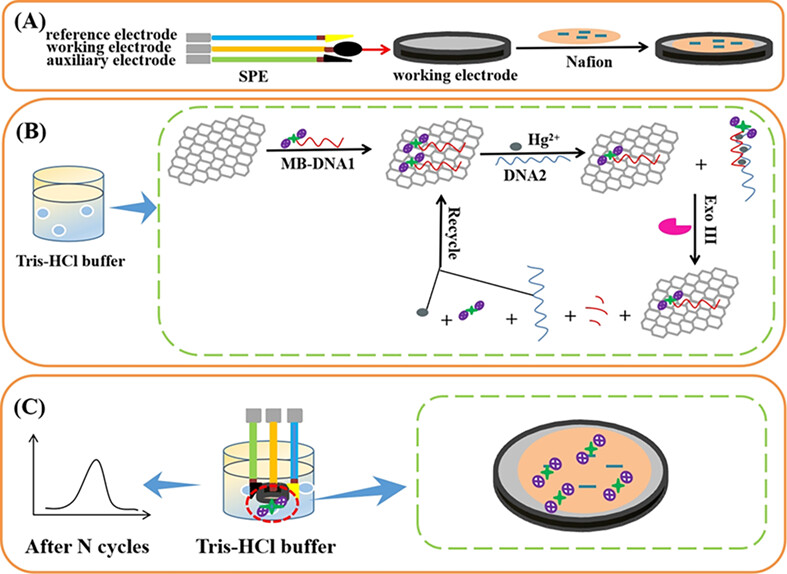
A novel disposable and portable electrochemical aptasensor based on reduced graphene oxide was constructed for the detection of mercury (II) using exonuclease III-induced cyclic reaction as a signal amplification strategy. The use of the designed DNA strand can greatly improve detection selectivity, and the employment of a homogeneous system can effectively save cost and simplify operation steps.
Comparison of a single-use pH test strip and a glass electrode for potentiometric titration
- First Published: 11 April 2023
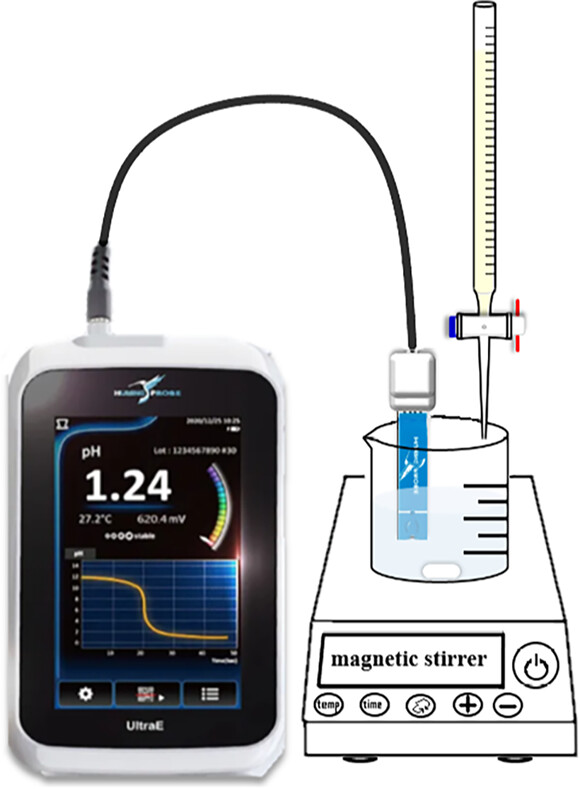
- A new commercial product which is carbon based with acetaminophen as the pH detection layer.
- It is a promising alternative device for the potentiometric titration of neutralization experiments.
- The pKa, pKb and pH values determined using the glass electrode and the strip-pH electrode systems differed by less than 5%.
Heavy metal-free electrochemical detection of pyrophosphate ions by Nafion/carbon dots decorated screen printed carbon electrodes
- First Published: 29 March 2023
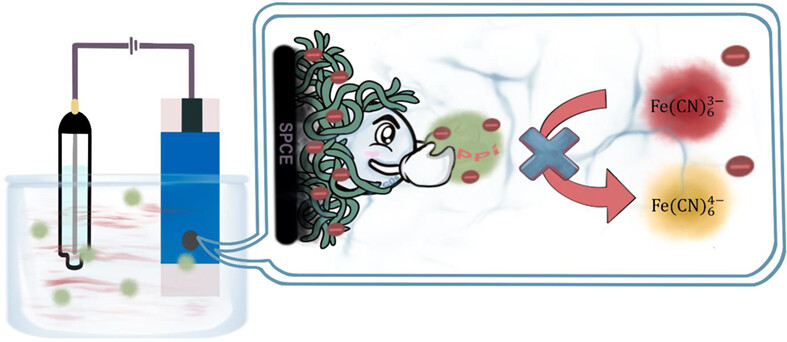
An electrochemical biosensor integrating Nafion-mixed carbon dots and screen-printed carbon electrodes for pyrophosphate ion detection is presented. A linear connection is established between the square wave voltammetry current and the pyrophosphate ion concentration between 50 and 1 μM, and the limit of detection is determined to be 1.01 μM. This assay is suitable for the usage of complicated urine matrices without the inclusion of heavy metals, making it practical for clinical monitoring.
Dual-mode color-changing pH sensor based on fluorescent MOF embedded photonic crystal hydrogel
- First Published: 06 May 2022
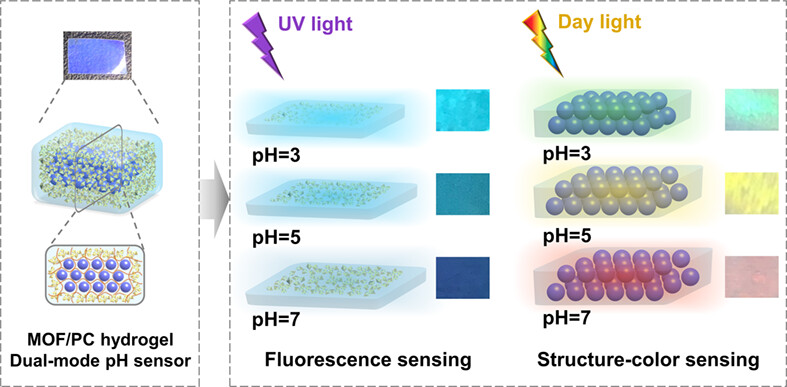
Novel dual-mode color-changing sensor (MOF/PC hydrogel) was achieved by taking advantages of the stimuli-responsive color-changing ability of photonic crystals and the sensing performance of luminescent MOF. When immersed in pH solutions, the structure color of MOF/PC hydrogel changed quickly, and its fluorescence intensity showed good linear relationship with pH, both ensuring the visual and quantitative pH sensing.
A rapid and label-free fluorescent sensor for kojic acid based on the inner filter effect
- First Published: 27 August 2022
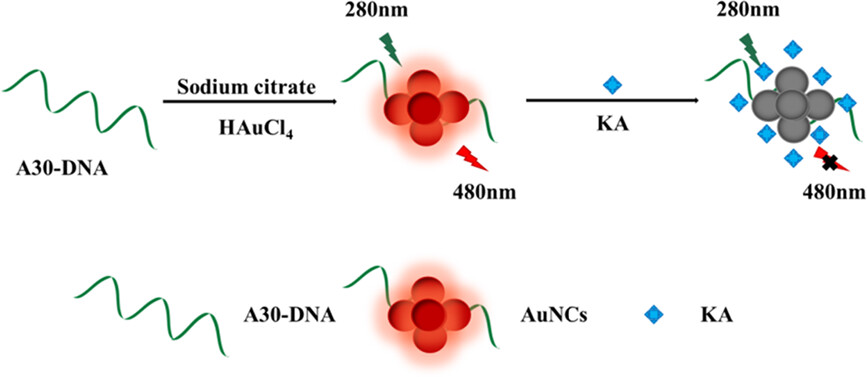
A label-free fluorescent sensor was developed for the detection of kojic acid based on the fluorescence internal filtering effect between gold nanocluster and kojic acid. In the presence of kojic acid, the fluorescence intensity decreased significantly owing to the strong absorption of kojic acid on excitation spectrum of gold nanoclusters. The whole detecting procedure could be accomplished within 5 min.
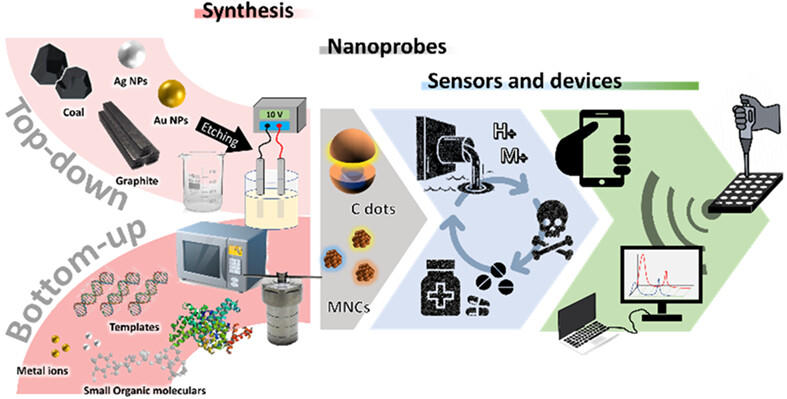
Fluorescent carbon dots and noble metal nanoclusters for sensing applications: Minireview
- First Published: 21 June 2022
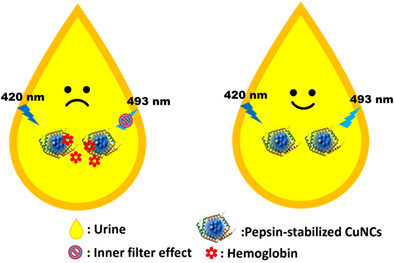
Blue-green emission of pepsin-stabilized copper nanoclusters ultrafast detection of hemoglobin in human urine
- First Published: 05 July 2022
Vancomycin functionalization of gold nanostars for sensitive detection of foodborne pathogens through surface-enhanced Raman scattering
- First Published: 09 December 2022
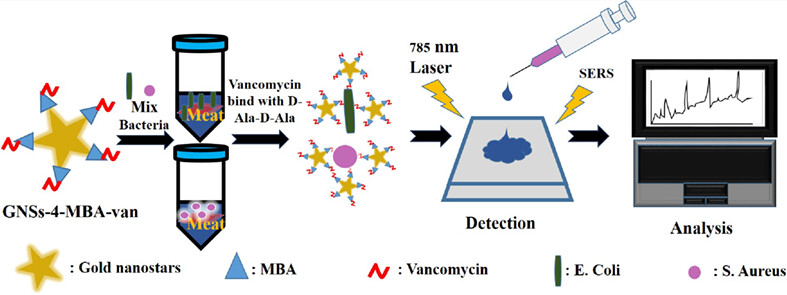
A new surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) biosensor was developed based on green synthesized Au-seed mediated gold nanostars. Subsequently, gold nanostars were modified with vancomycin as recognition phase and immobilized with 4-Mercaptobenzoic acid as Raman reporter as well as linker for vancomycin conjugation. Finally, bacteria were determined by utilizing the bacteria's high affinity with vancomycin and measuring the signal intensity elevation of SERS tags.
A simple uric acid assay by using 3-hydroxytyramine as a chromogenic colorimetric sensor in human serum samples: Density functional theory supported mechanistic approach
- First Published: 14 February 2023
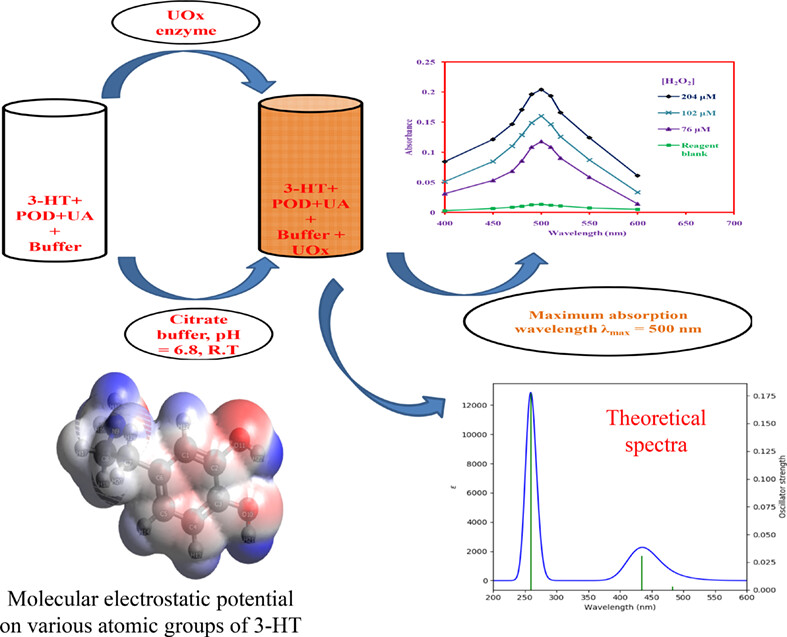
- A rapid, sensitive, convenient and accurate assay method for the determination of clinically important biomarker uric acid (UA) in human serum samples has been developed.
- The analytical sensing signal is based on the oxidative addition of 3-HT producing orange colored product.
- Density functional theory supported mechanistic approach for the colored product formation.
- The method has been validated thoroughly by various analytical steps.
Potentiometric determination of copper(II) ions based on a porphyrin derivative
- First Published: 07 June 2022
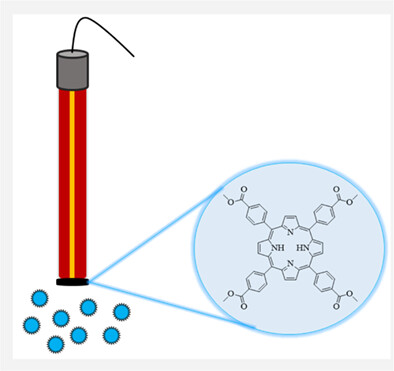
In this study, a novel potentiometric sensor was developed for the determination of Cu2+ ions. The developed sensor exhibits a linear response over a wide concentration range and has a very low detection limit. In addition, the copper(II)–selective sensor has advantages such as high selectivity, short response time, low cost, good repeatability, and stability.
Silver/graphene–polypyrrole composite for levosimendan detection
- First Published: 21 March 2023
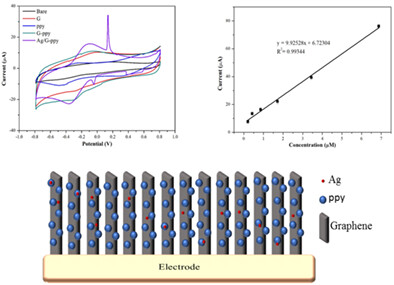
A novel silver/Graphene–polypyrrole (Ag/G–PPy)-modified electrode for levosimendan detection. The Ag/G–PPy-modified electrode showed current signals toward levosimendan concentrations ranging from 0.21 to 6.88 μM and exhibited a low detection limit of 0.12 μM. Accordingly, the proposed electrode can serve as a simple and inexpensive electrochemical sensor for levosimendan detection.