Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Combination anti-obesity medications to effectively treat bariatric surgery weight regain at an academic obesity center
- Pages: 203-209
- First Published: 24 August 2022
Association of body anthropometry and obstructive sleep apnea in children: Variations observed in Hispanic children
- Pages: 210-217
- First Published: 22 September 2022
Modification of the diabetes prevention program for the treatment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A pilot study
- Pages: 218-225
- First Published: 26 August 2022
The association between sleep duration and detailed measures of obesity: A cross sectional analysis in the ADDITION-PRO study
- Pages: 226-234
- First Published: 16 September 2022
Dietary advanced glycation products and their associations with insulin sensitivity and body weight: A 16-week randomized clinical trial
- Pages: 235-242
- First Published: 17 October 2022
Quantifying weight loss program preferences of men working in trade and labor occupations: A discrete choice experiment
- Pages: 243-252
- First Published: 24 September 2022
Interaction between increasing body mass index and spinal cord injury to the probability of developing a diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Pages: 253-260
- First Published: 03 October 2022
Impact of the built, social, and food environment on long-term weight loss within a behavioral weight loss intervention
- Pages: 261-273
- First Published: 26 October 2022
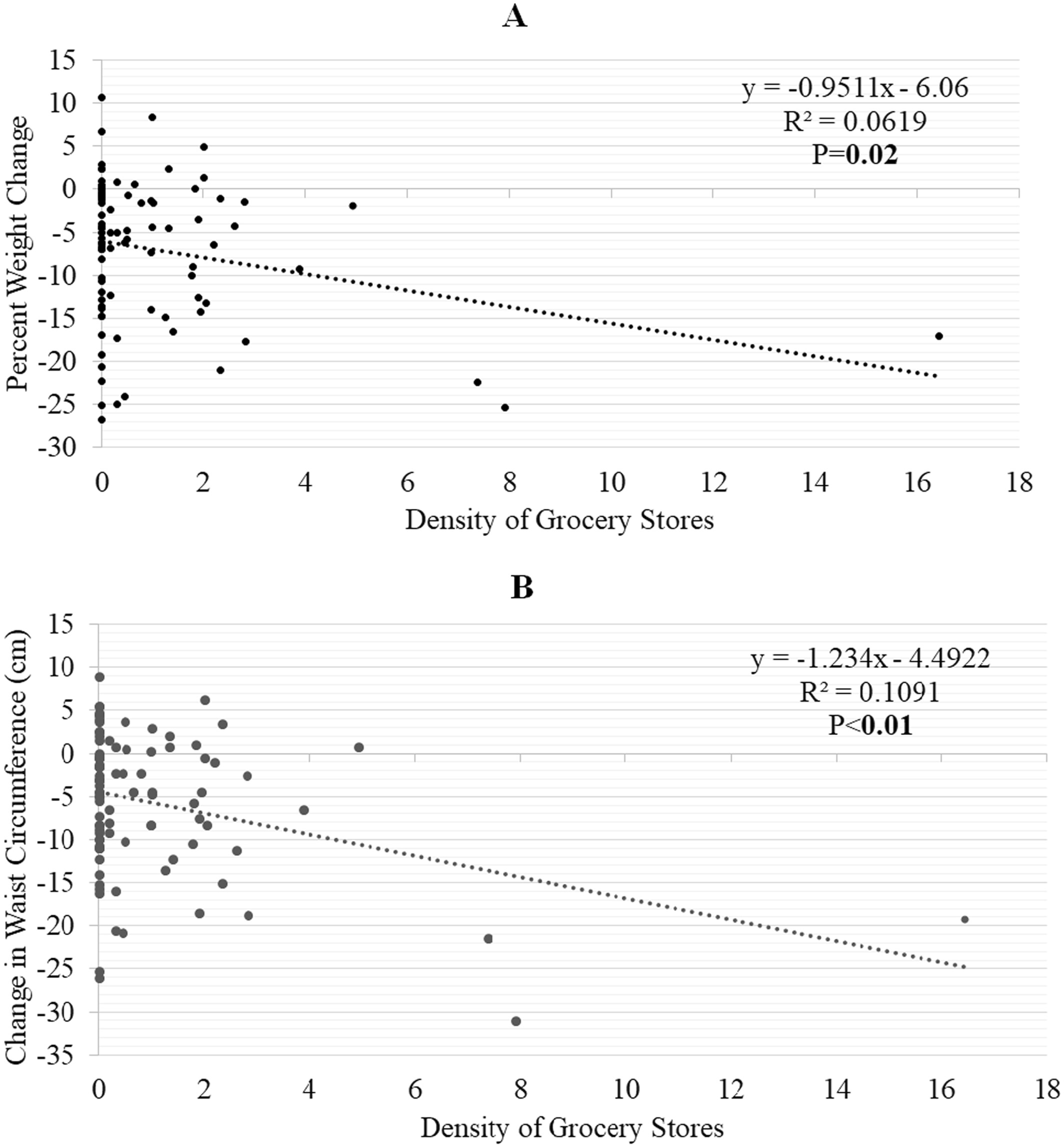
Although built, social, and community food environments can have potential direct and indirect influences on body weight (through their influence on energy intake and physical activity), these environmental factors are rarely considered as predictors of variation in weight loss. This study examined the association between built, social, and community food environments and changes in weight, moderate-to-vigorous physical activity, and dietary intake among adults who completed an 18-month behavioral weight loss intervention. Grocery store density was positively associated with weight loss at 18 months and participants living in less walkable neighborhoods had lower levels of moderate-to-vigorous physical activity at baseline but greater increases in moderate-to-vigorous physical activity at follow-up.
Physical properties of food or bile redirection do not contribute to the intestinal adaptations after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass in rats
- Pages: 274-284
- First Published: 18 October 2022
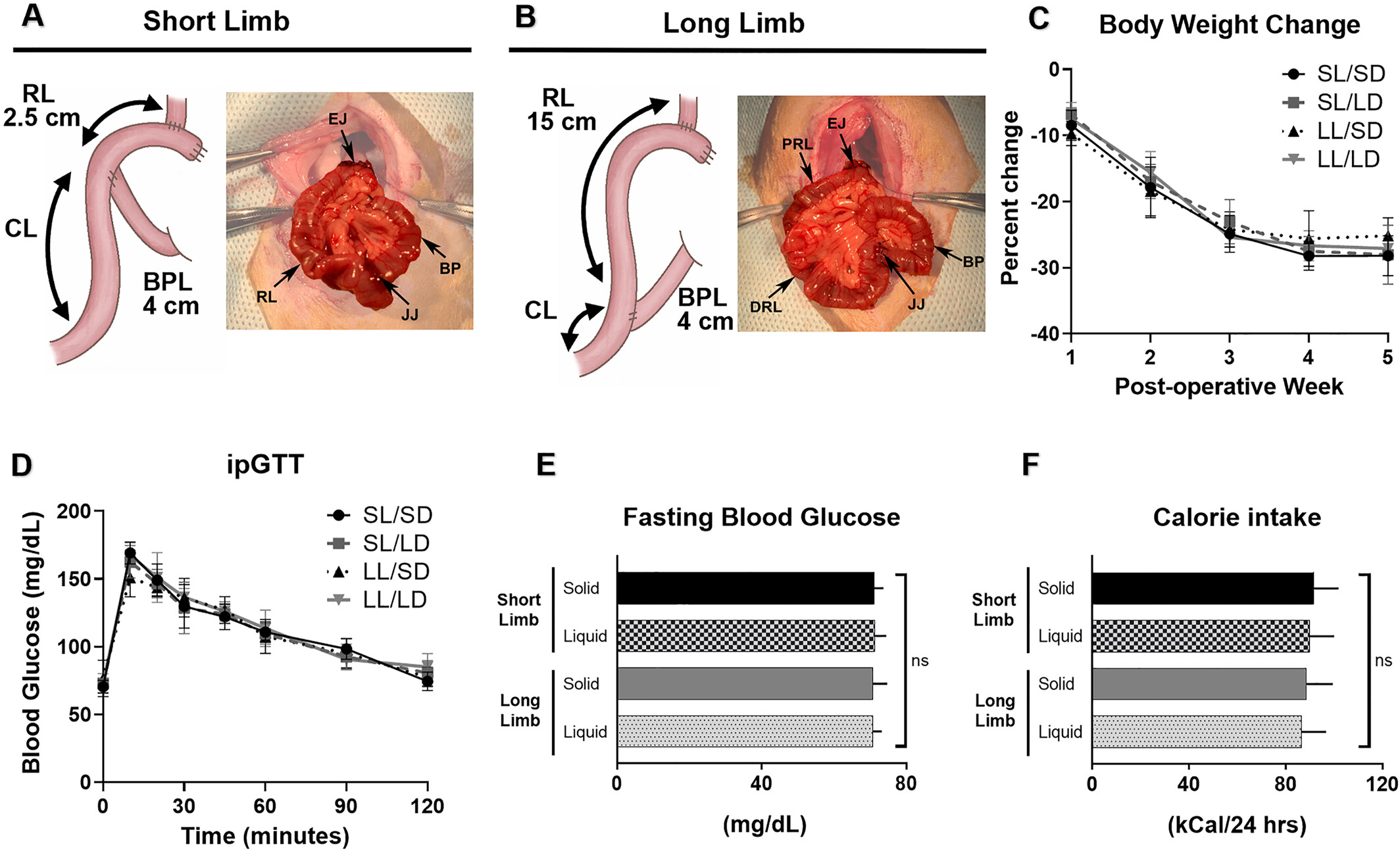
Metabolic and morphological adaptations of the intestine have been suggested to play a role in the various therapeutic benefits of Roux–en–Y Gastric Bypass (RYGB) surgery. However, the precise underlying mechanisms remain unclear. The results of our study show that RYGB surgery in rats induces weight loss and improves glucose tolerance, independent of physical properties of ingested food and biliopancreatic secretions. The regulation of intestinal glucose utilization after RYGB is not determined by food form or bile redirection. Furthermore, neither physical properties of food nor biliopancreatic secretions influence intestinal morphological adaptations in RYGB.
More than just body mass index: Using the Edmonton obesity staging system for pediatrics to define obesity severity in a multi-ethnic Australian pediatric clinical cohort
- Pages: 285-295
- First Published: 14 December 2022
The healthful plant-based diet index as a tool for obesity prevention—The healthy lifestyle community program cohort 3 study
- Pages: 296-304
- First Published: 13 December 2022

The Healthy Lifestyle Community Program (cohort 3) achieved a significant reduction in body weight (−1.8 kg) in a community-based sample of mostly clinically healthy participants. This weight loss was sustained at the end of the study (16 months). Adherence to a healthy plant-based diet correlated with improved risk markers.
Postmenopausal women's experiences of weight maintenance following a very low energy diet
- Pages: 305-319
- First Published: 21 December 2022
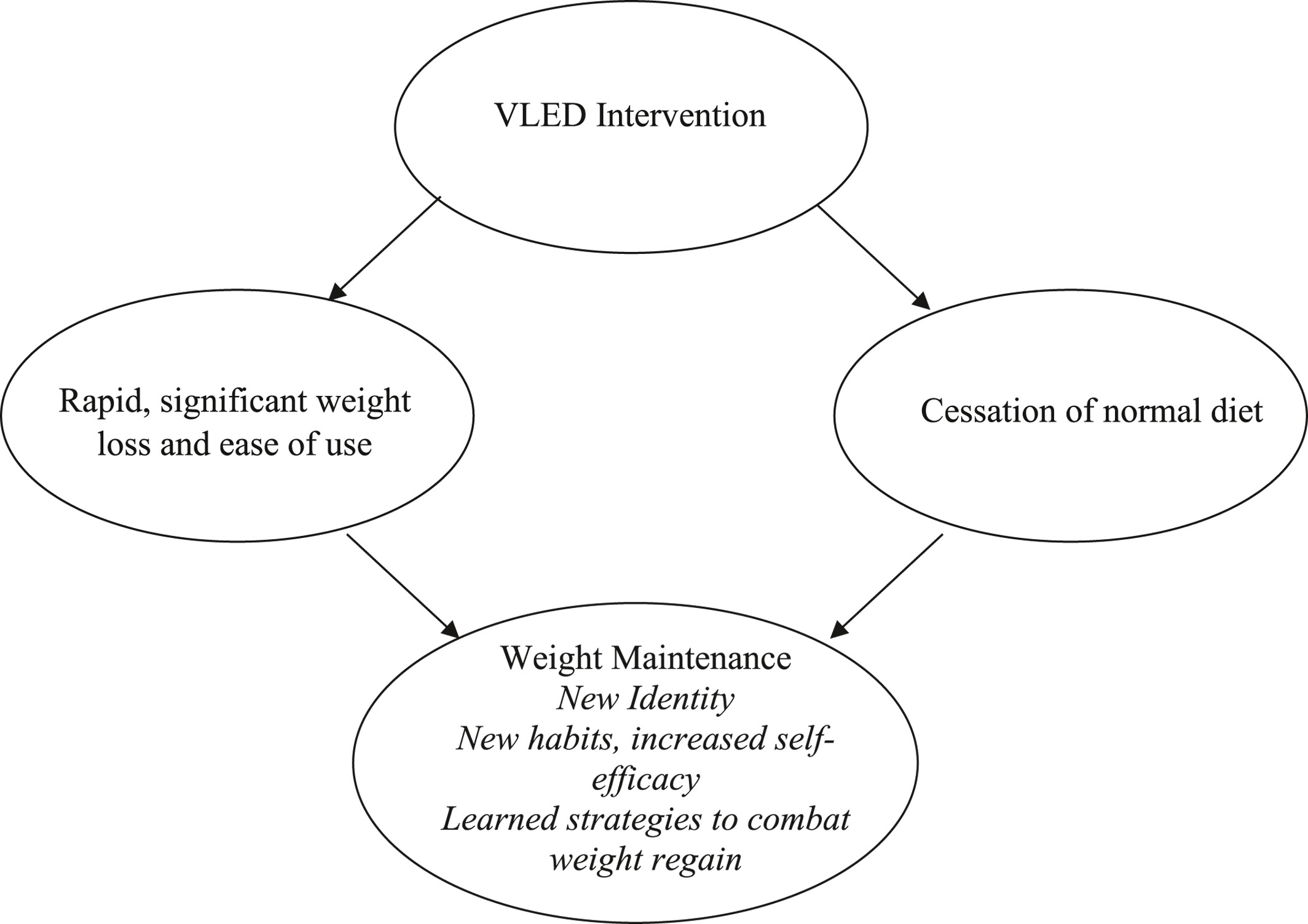
This study explored the weight maintenance behaviors and experiences of postmenopausal women who had followed a 4-month VLED for weight loss. VLEDs in the context of this study—was reported by participants to confer advantages in weight maintenance that previous weight loss attempts had not been able to do for them. Using a VLED in the context of a clinical weight loss trial conferred confidence, motivation and skills for weight maintenance among participants. These findings show that VLEDs with clinical support could be successfully leveraged to set up behaviors that will support weight maintenance in the long term.
SHORT COMMUNICATION
Mental health diagnosis attenuates weight loss among older adults in a digital diabetes prevention program
- Pages: 320-326
- First Published: 04 October 2022