Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
Exploring the health benefits and functional properties of goat milk proteins
- Pages: 5641-5656
- First Published: 27 June 2023
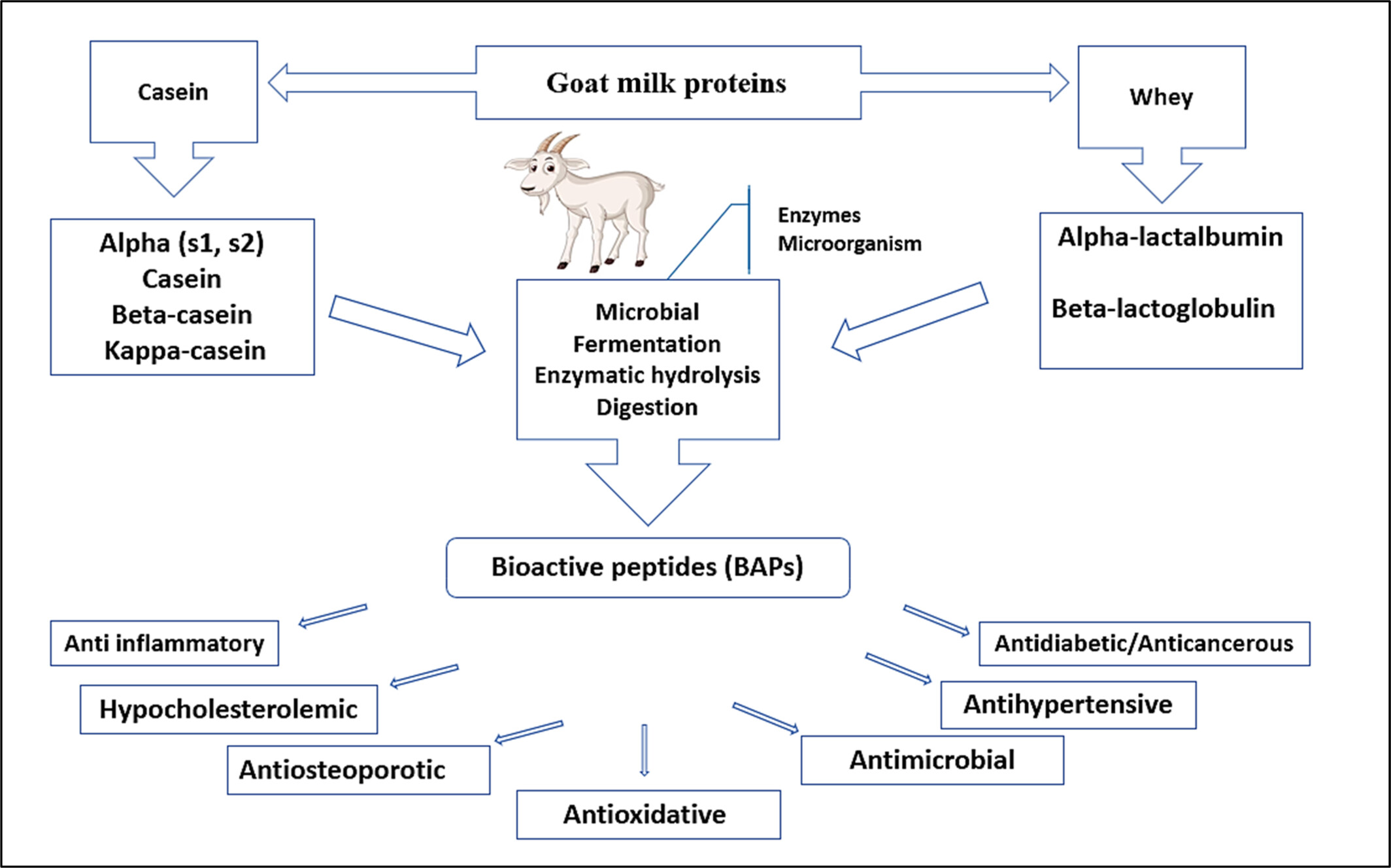
Future research on goat milk proteins will focus on their potential as a functional food ingredient, their effects on gut health and microbiota, and their therapeutic potential for various health conditions. This research may lead to the development of new functional food products that promote health and prevent disease. Additionally, it may pave the way for the use of goat milk proteins as a therapeutic agent for a range of health issues.
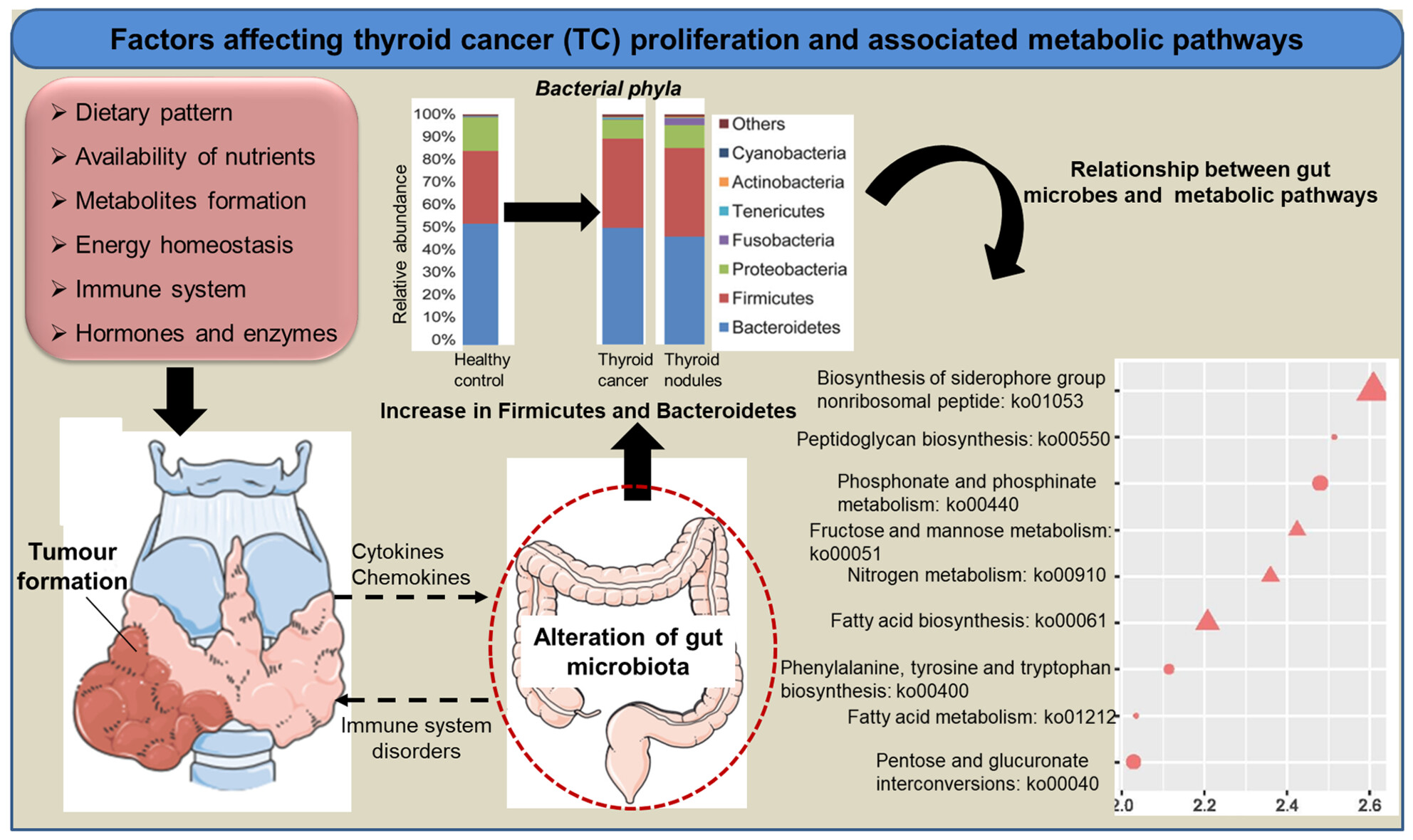
Exploring the oral-gut microbiota during thyroid cancer: Factors affecting the thyroid functions and cancer development
- Pages: 5657-5674
- First Published: 08 July 2023
Research progress on the fibrinolytic enzymes produced from traditional fermented foods
- Pages: 5675-5688
- First Published: 07 August 2023
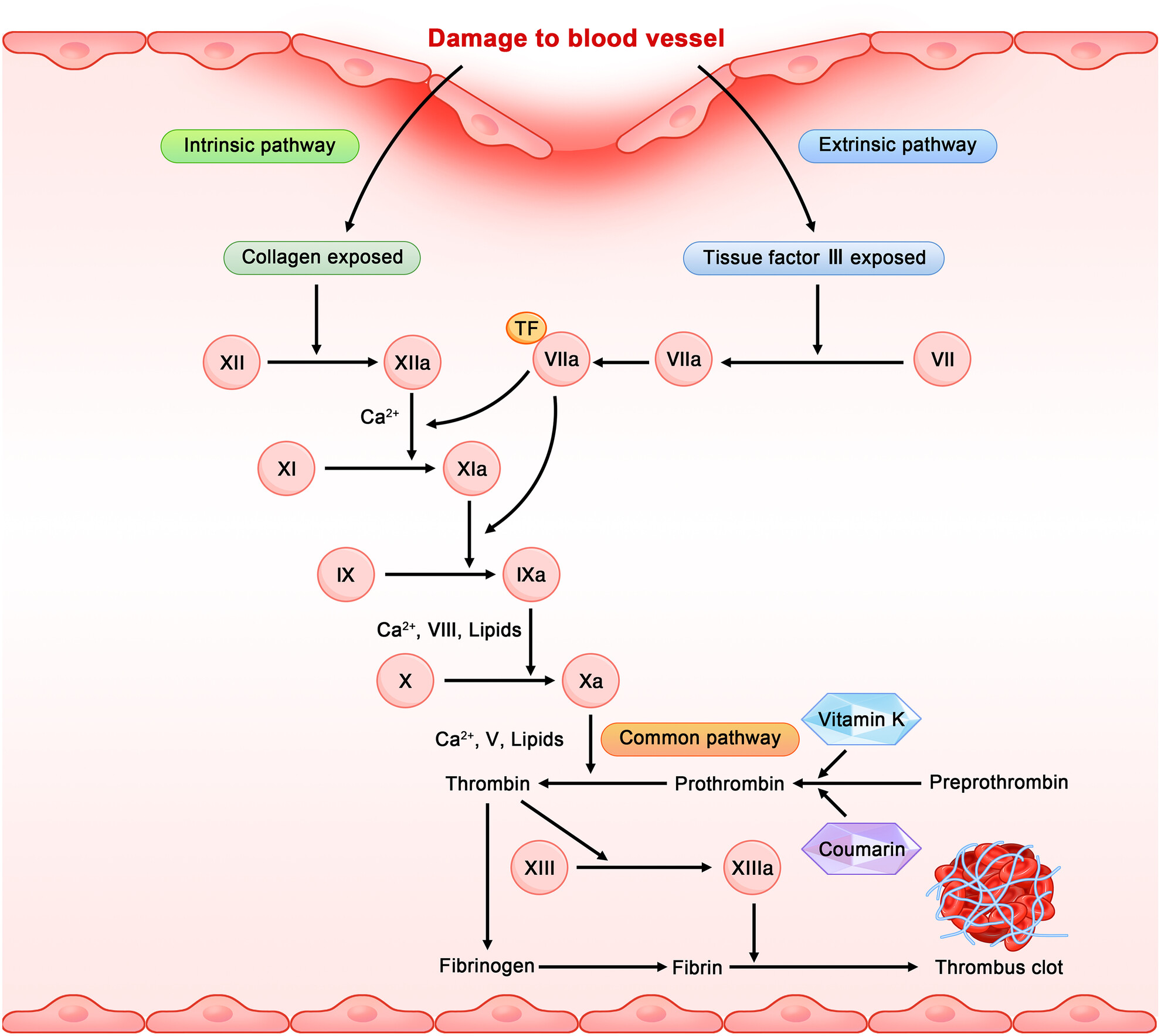
This article focuses on fibrinolytic enzymes produced by microorganisms during the fermentation of traditional fermented foods. First, we provide an overview of the sources of fibrinolytic enzymes, including strains that produce such enzymes. Then, we discuss the optimization of fermentation process, purification, and physicochemical properties of fibrinolytic enzymes separately. Finally, we summarize the thrombolytic effects of fibrinolytic enzymes in humans and mice, respectively.
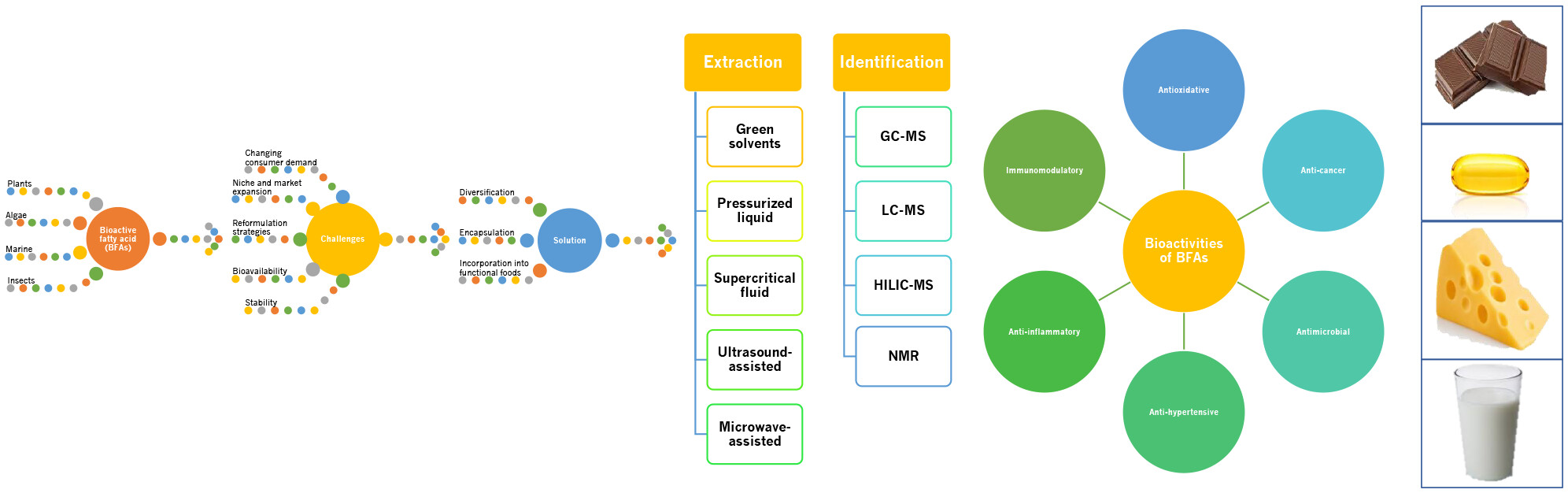
Bioactive fatty acids from non-conventional lipid sources and their potential application in functional food development
- Pages: 5689-5700
- First Published: 06 July 2023
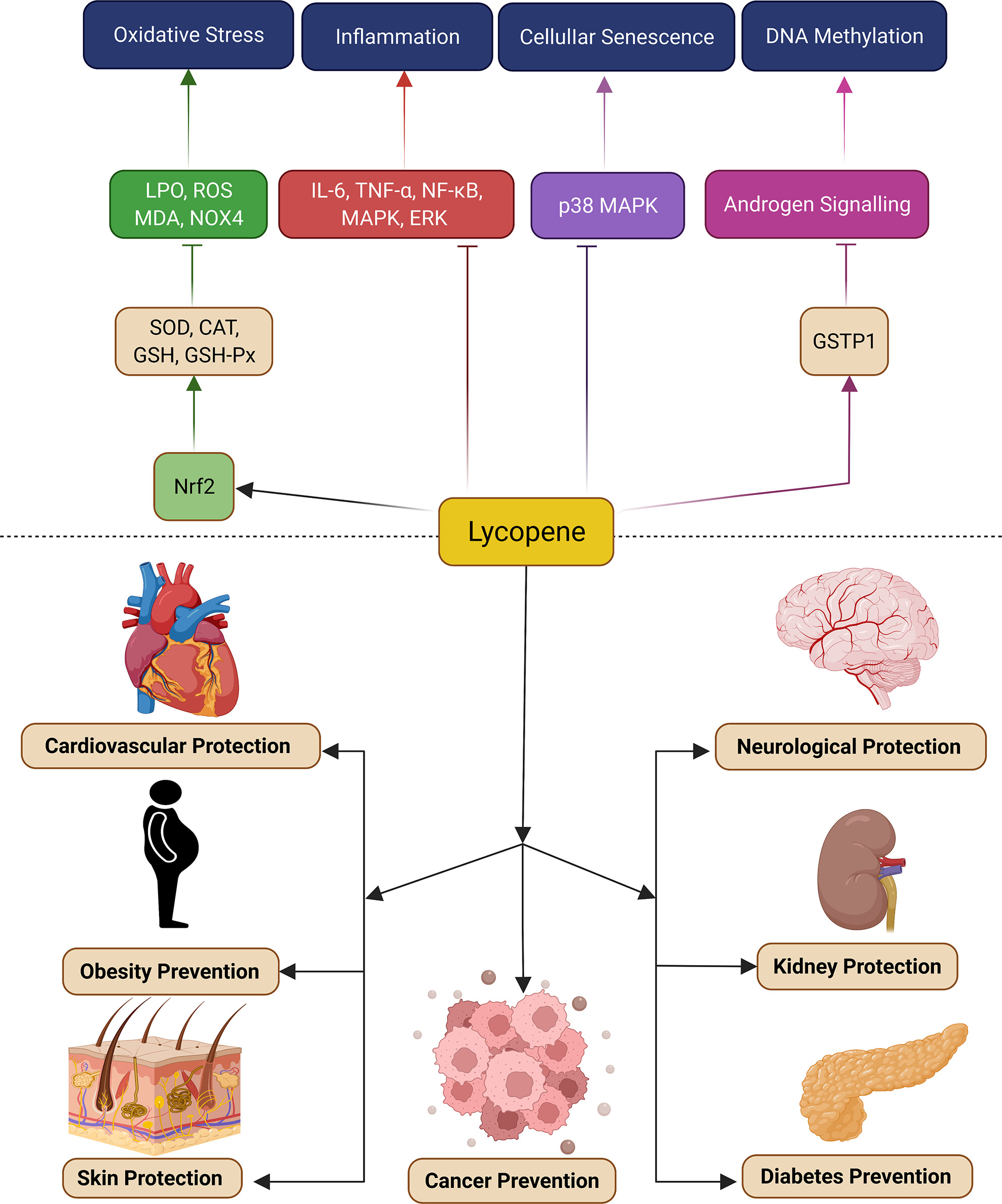
Pharmacological potentials of lycopene against aging and aging-related disorders: A review
- Pages: 5701-5735
- First Published: 27 June 2023
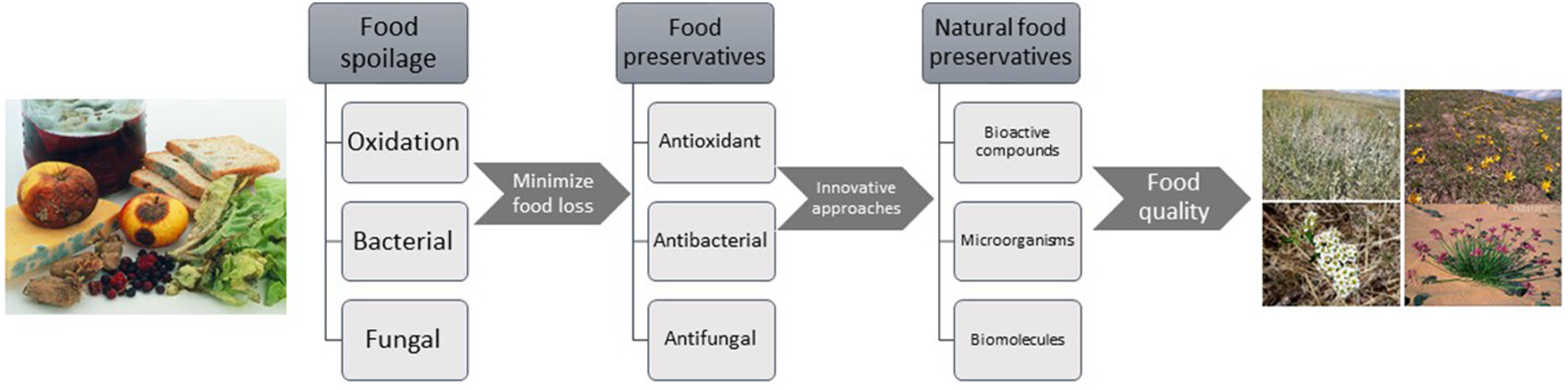
A review of the bioactive properties of Mongolian plants, with a focus on their potential as natural food preservatives
- Pages: 5736-5752
- First Published: 05 July 2023
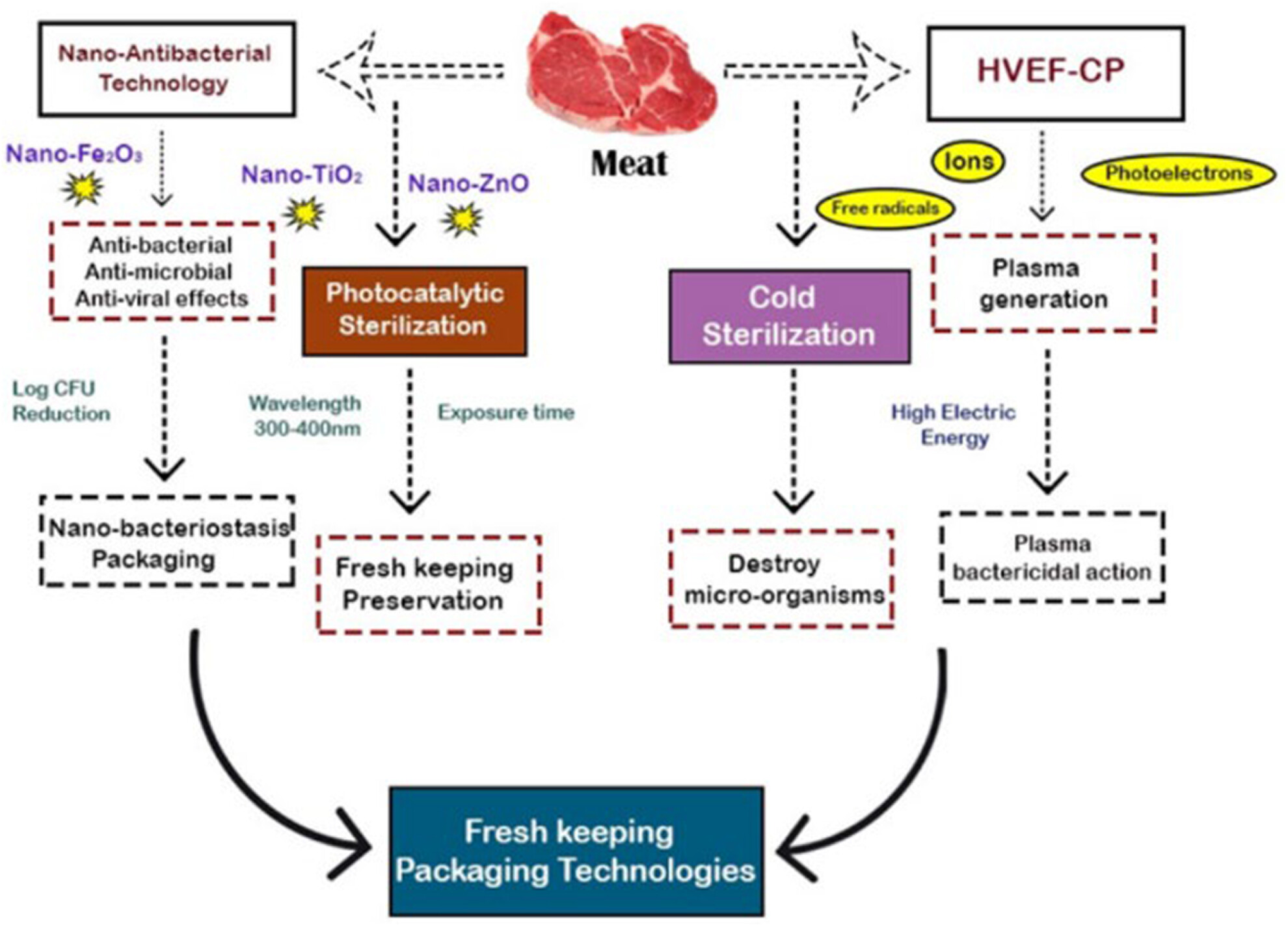
Advances in the application of functional nanomaterial and cold plasma for the fresh-keeping active packaging of meat
- Pages: 5753-5772
- First Published: 09 July 2023
A review on waste valorization, biotechnological utilization, and management of potato
- Pages: 5773-5785
- First Published: 14 July 2023
One of the most popular, cost-effective agricultural crops that are consumed globally is the potato. Due to the expanding food crisis, there is an increase in the demand for potato-based agro-food items. At the same time, it is noted that this pathway of ecological pollution from large-scale wastes is challenging to manage. Several by-products of industrial potato production, such as PPs, starch, flakes, and granules, are disposed of despite being rich sources of nutrients and bioactive ingredients.
Dietary inflammatory index and elevated serum C-reactive protein: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 5786-5798
- First Published: 06 July 2023
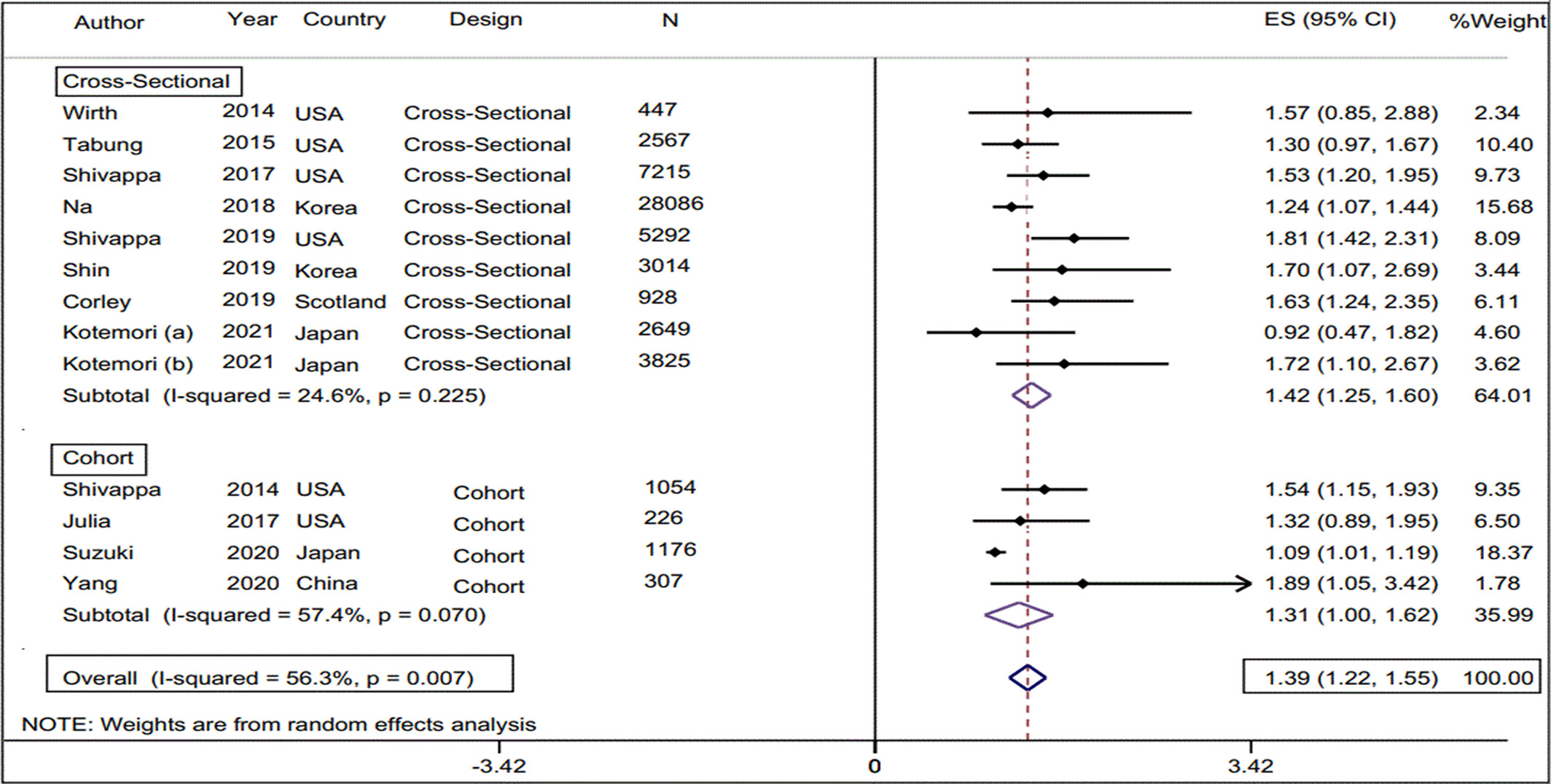
This systematic review and meta-analysis examined the relationship between the dietary Inflammatory Index (DII) and the odds of elevated CRP (E-CRP). The findings suggest that higher DII scores are associated with increased odds of E-CRP, indicating a potential link between dietary inflammation and elevated serum CRP levels. Further well-designed studies are needed to explore the intricate relationship between diet, inflammatory biomarkers, and their impact on health outcomes.
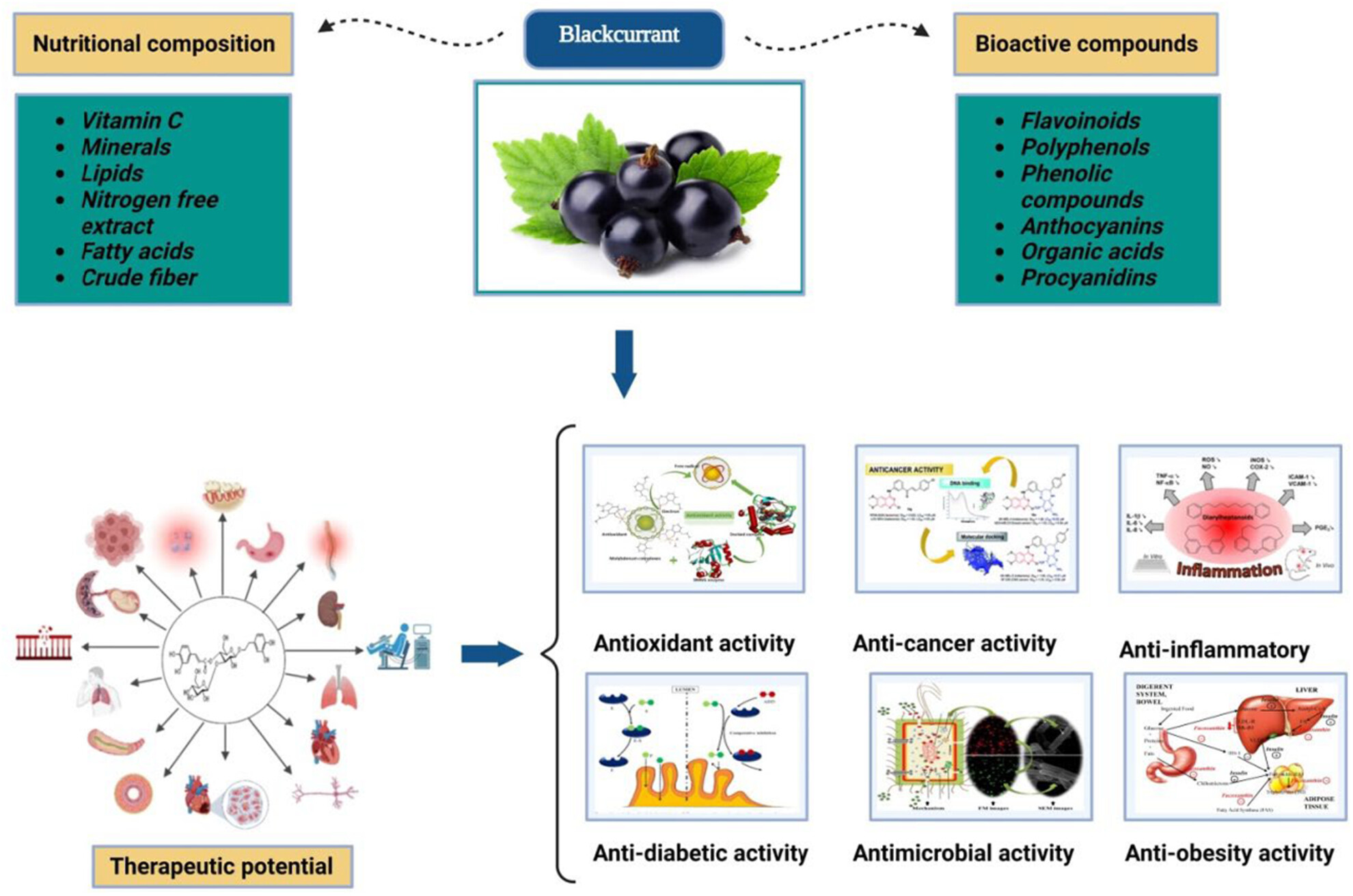
Biological activities, therapeutic potential, and pharmacological aspects of blackcurrants (Ribes nigrum L): A comprehensive review
- Pages: 5799-5817
- First Published: 15 August 2023
Tea's anti-obesity properties, cardiometabolic health-promoting potentials, bioactive compounds, and adverse effects: A review focusing on white and green teas
- Pages: 5818-5836
- First Published: 15 August 2023
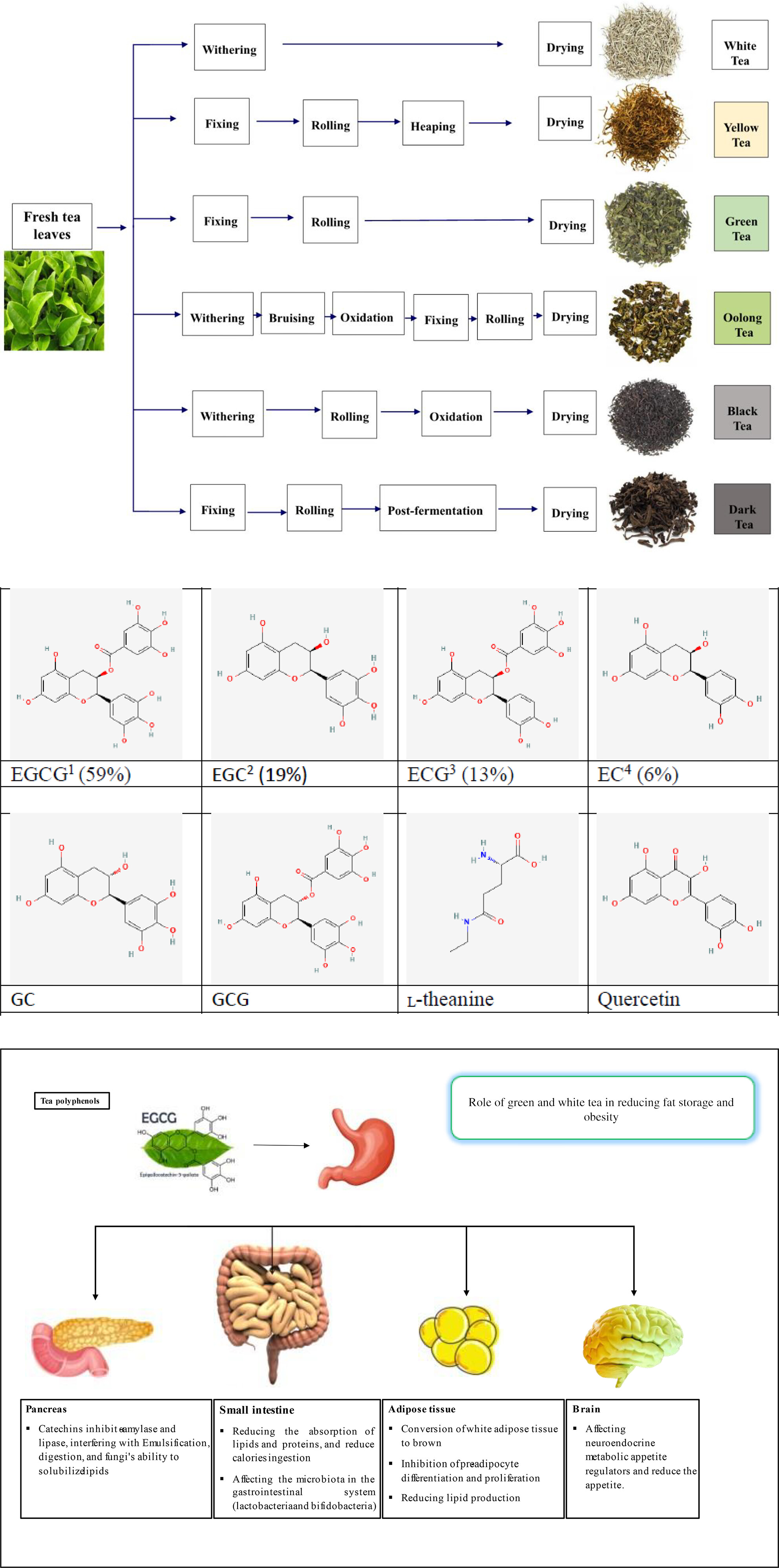
We provide an update on the health benefits of white and green teas in this review, based on recent research done to present. After a general introduction, we have focused on the tea's anti-obesity and human health-promoting potentials, adverse effects, and new approaches to the tea and its bioactive compounds. It has been found that tea's health benefits are due to its bioactive components, mainly phenolic compounds. Of these, catechins are most abundant. This beverage (or its extracts) has potential anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, which could contribute to body weight control and improvement of several chronic diseases. However, some studies have mentioned the possibility of toxic effects, so reducing tea consumption is a good idea, especially during pregnancy's last trimester. Additionally, new evidence will provide insight into the possible effects of tea on human gut microbiota and even on the viruses responsible for SARS-CoV-2. A beverage like this may favor beneficial gut microbes, which may have important implications due to the influence gut microbiota has on human health.
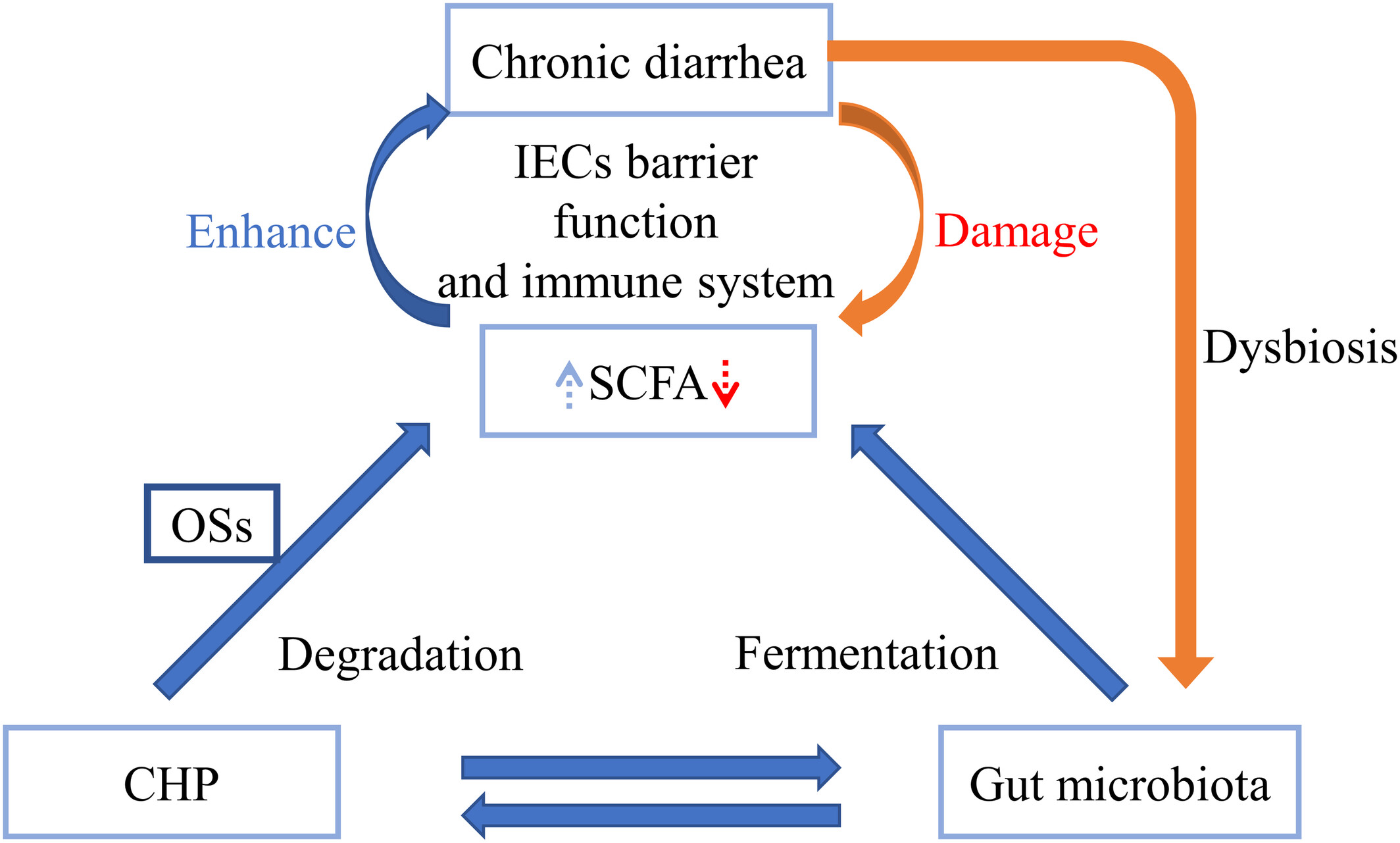
Relationship among Chinese herb polysaccharide (CHP), gut microbiota, and chronic diarrhea and impact of CHP on chronic diarrhea
- Pages: 5837-5855
- First Published: 06 August 2023
An update on the potential mechanism of gallic acid as an antibacterial and anticancer agent
- Pages: 5856-5872
- First Published: 31 August 2023
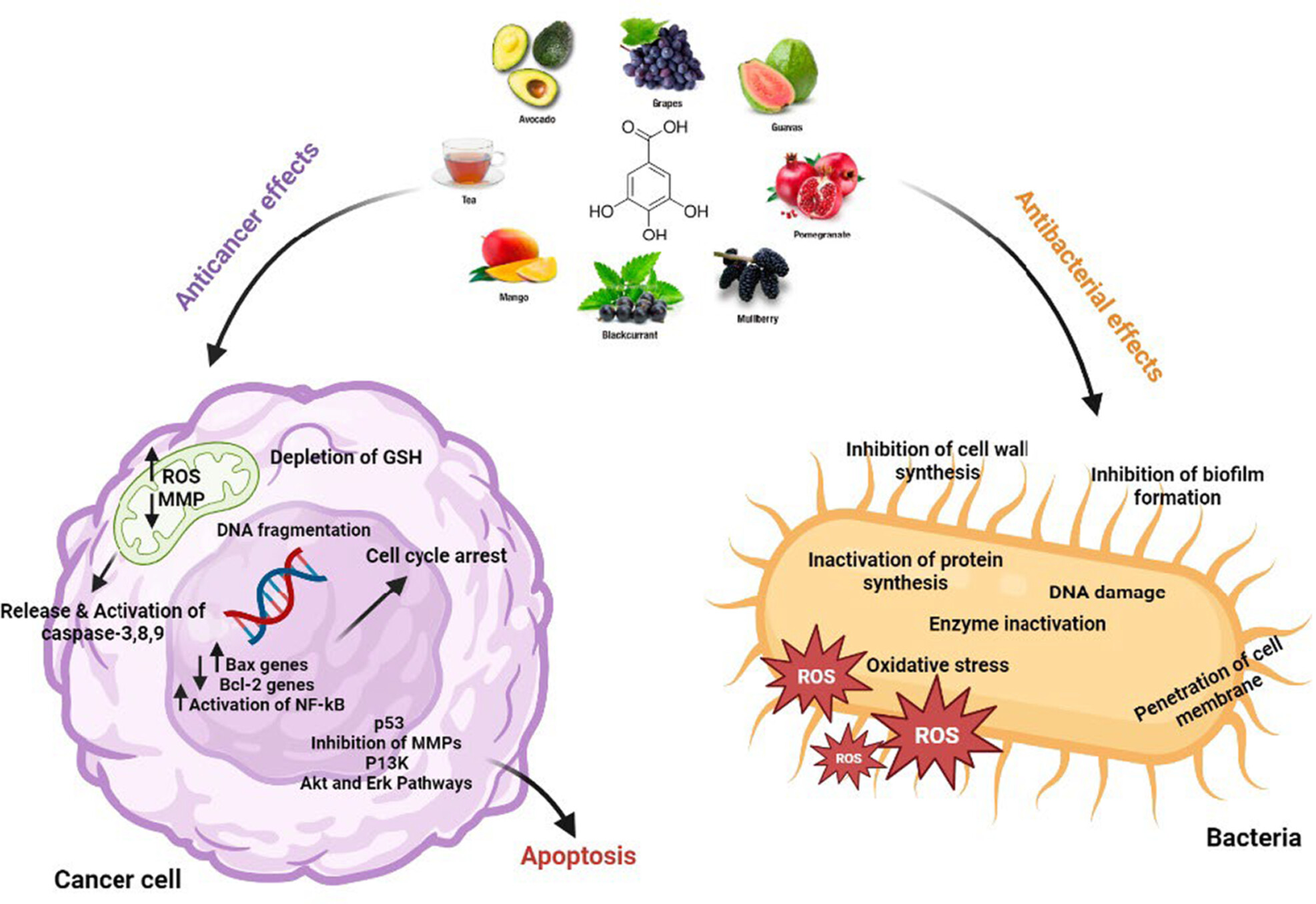
Gallic acid (GA) has been identified as one of the most important plant polyphenols that have health-promoting effects in various aspects. Various studies have shown that GA inhibits bacterial growth by altering membrane structure, and bacterial metabolism, and inhibits biofilm formation and growth. GA inhibits cancer cell growth by targeting different signaling pathways in apoptosis, increasing reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, targeting the cell cycle, and inhibiting oncogenes and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) expression.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
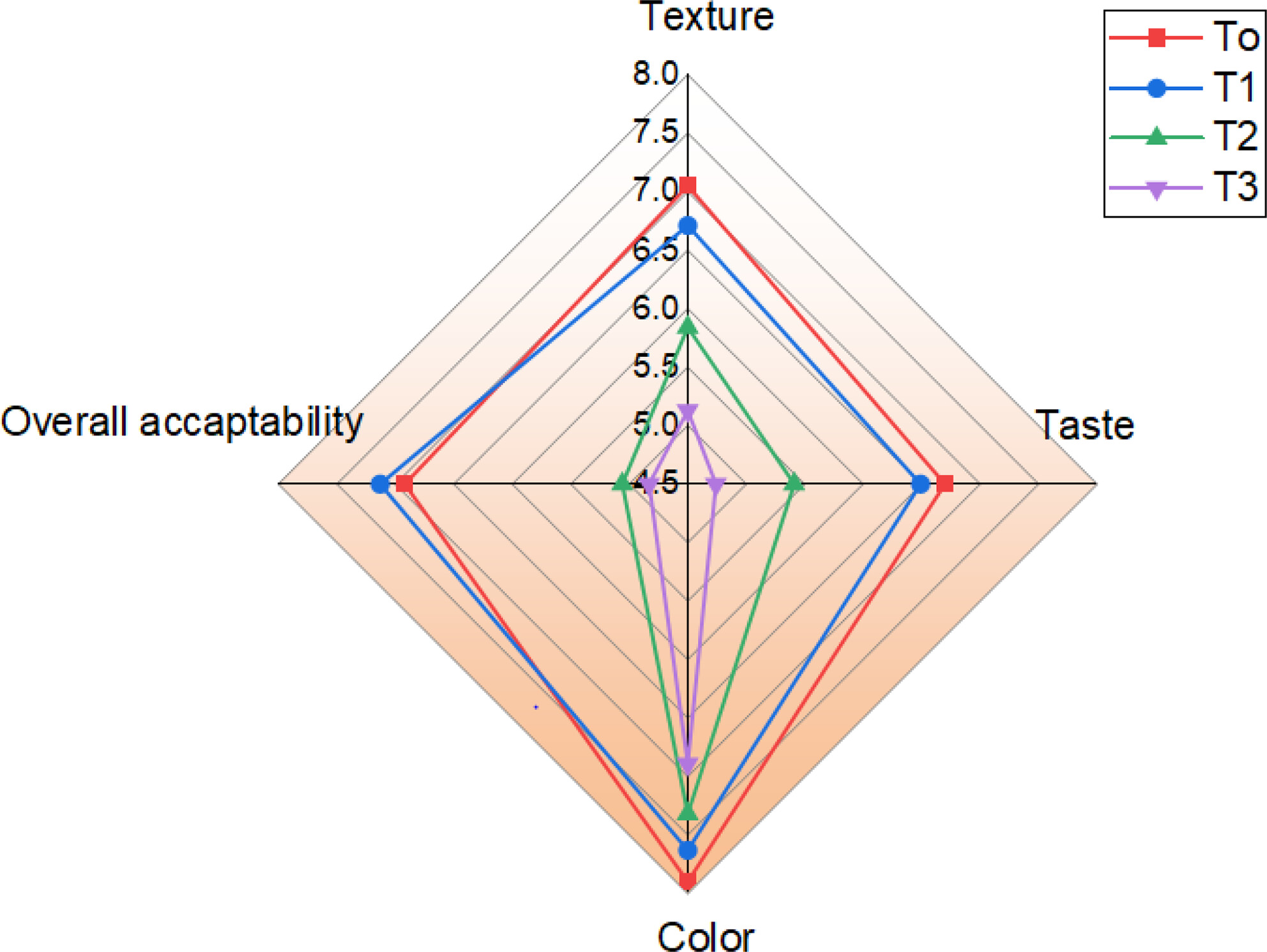
The use of hydrogel structures in production of extruded rice and investigation of its qualitative characteristics
- Pages: 5873-5881
- First Published: 07 June 2023
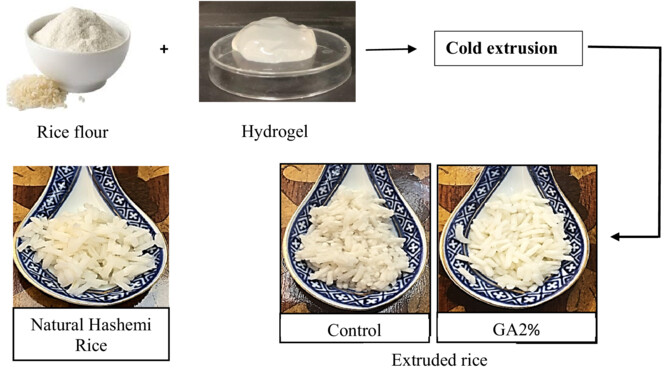
The hydrogel (GA1: gellan (0.5%)-alginate (0.5%), GA2: gellan (1%)-alginate (1%), GAX 1%: gellan (0.5%)-alginate (0.5%)-xanthan (0.1%), and GAX2%: gellan (1%)-alginate (1%)-xanthan (0.2%)) significantly increased water absorption ratio, water solubility index, water absorption index, and textural properties of extruded rice. GA2% rice sample showed similar texture characteristic, cooking feature, and color parameter to natural rice (Natural Hashemi Rice) and, ultimately, showed better organoleptic properties.
Evaluation of zinc oxide nanocomposite with Aloe vera gel for packaging of chicken fillet against Salmonella typhi and Salmonella para typhi A
- Pages: 5882-5889
- First Published: 23 June 2023
Use of mandarin and persimmon fruits in water kefir fermentation
- Pages: 5890-5897
- First Published: 11 August 2023
Do cooking and food preparation skills affect healthy eating in college students?
- Pages: 5898-5907
- First Published: 07 August 2023
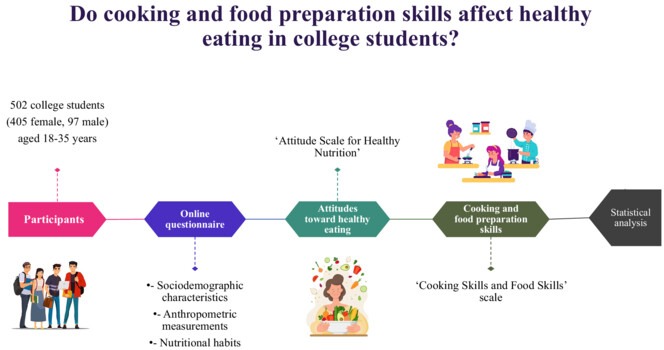
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between food and cooking skills and healthy eating attitudes in college students. A positive correlation was found between the total score and sub-factor scores of the ‘Cooking Skills and Food Skills’ scale and the total score of the ‘Attitude Scale for Healthy Nutrition’. Cooking and food skills seem to be positively associated with healthy attitudes. Considering this association, interventions to improve food and cooking skills may help promote healthy eating attitudes in students.
Potato peel waste fermentation by Rhizopus oryzae to produce lactic acid and ethanol
- Pages: 5908-5917
- First Published: 07 September 2023
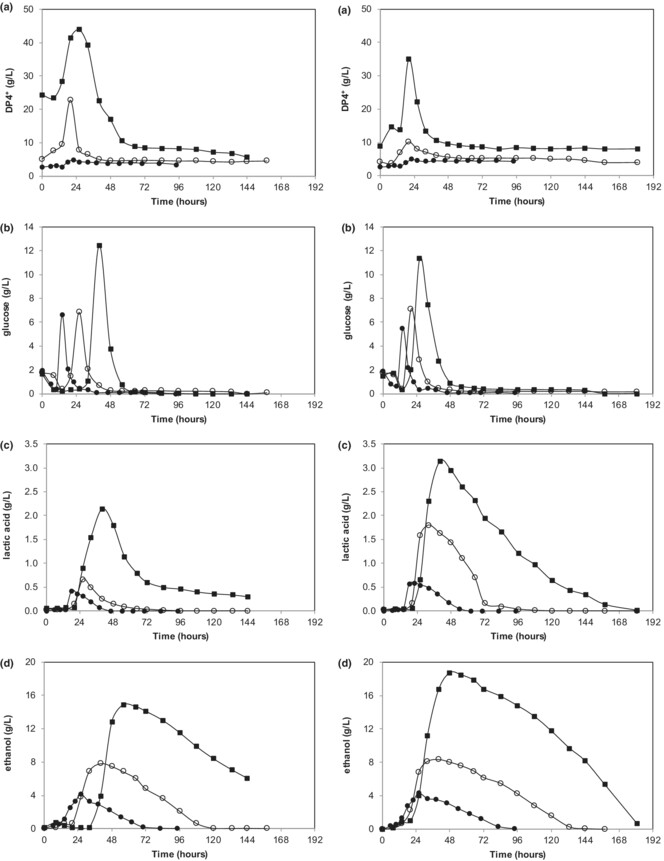
Rhizopus oryzae is able to utilize potato peel waste to produce DP4+, glucose, lactic acid, and ethanol. Potato peel waste particle size of 1–2 mm and loading rate of 8% were optimal for fermentation. PPW size of less than 0.125 mm and loading rate of more than 8% are not suitable due to high viscosity. 18.83 g/L of ethanol was produced at a rate of 9.41 g/L day with a yield of 0.235 g/gPPW. 3.14 g/L of lactic acid was produced at a rate of 1.89 g/L day with a yield of 0.039 g/gPPW.
Evaluation of the therapeutic effect of Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl seed extract on hyperthyroidism: A double-blind placebo-controlled pilot clinical trial
- Pages: 5918-5927
- First Published: 04 July 2023
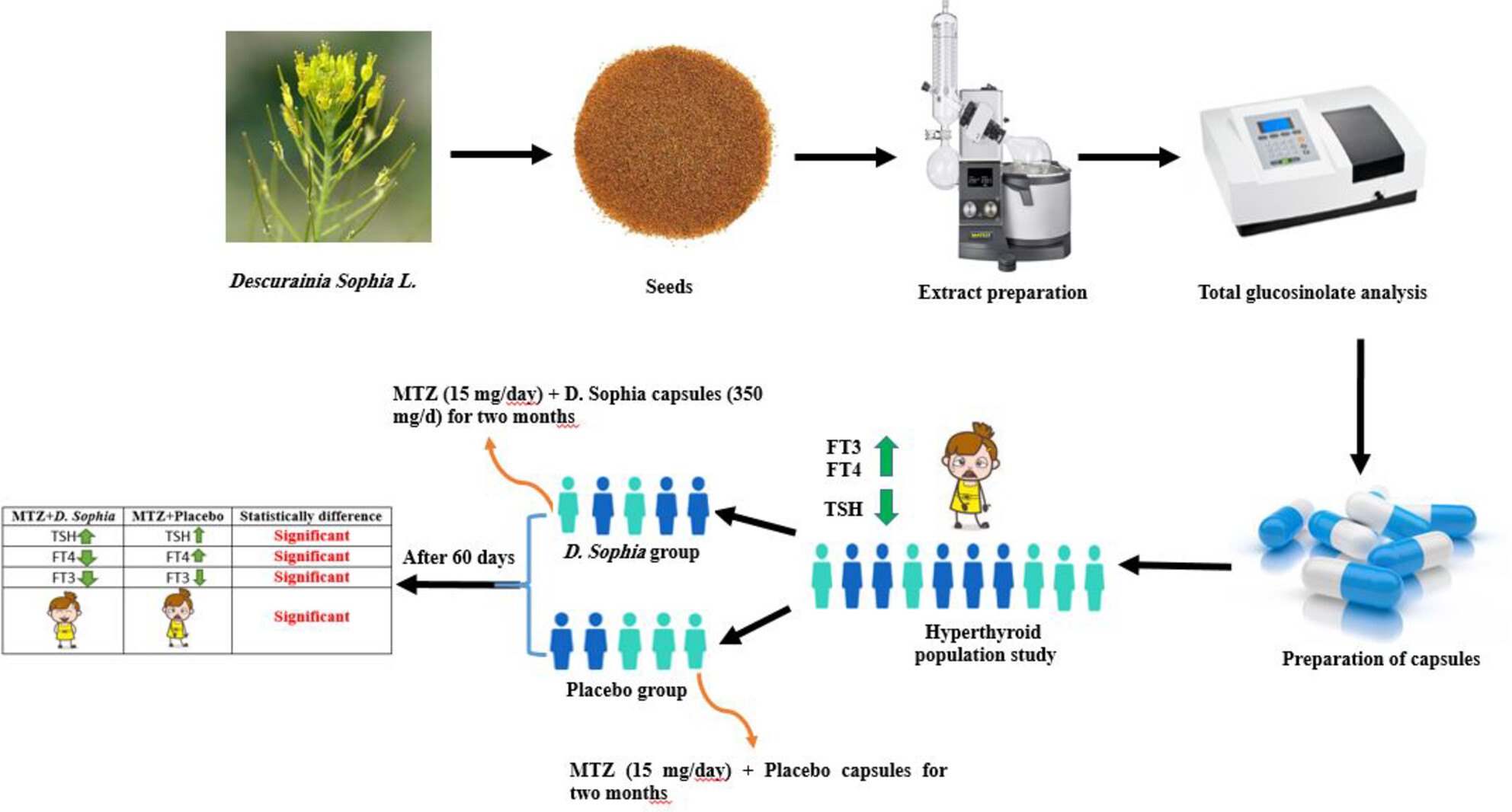
The seeds of Descurainia sophia (L.) Webb ex Prantl contain goitrogenic glucosinolates, such as gluconapin (3-butenyl glucosinolate). Because of the important role of iodine in the synthesis of thyroid hormones and the inhibitory activity of D. sophia on iodine uptake by the thyroid gland, this study aimed to determine the effects of D. sophia syrup on clinical and biochemical variables of thyrotoxicosis in hyperthyroid patients.
Genotype by yield* trait (GYT) biplot analysis: A novel approach for phenotyping sunflower single cross hybrids based on multiple traits
- Pages: 5928-5937
- First Published: 24 June 2023
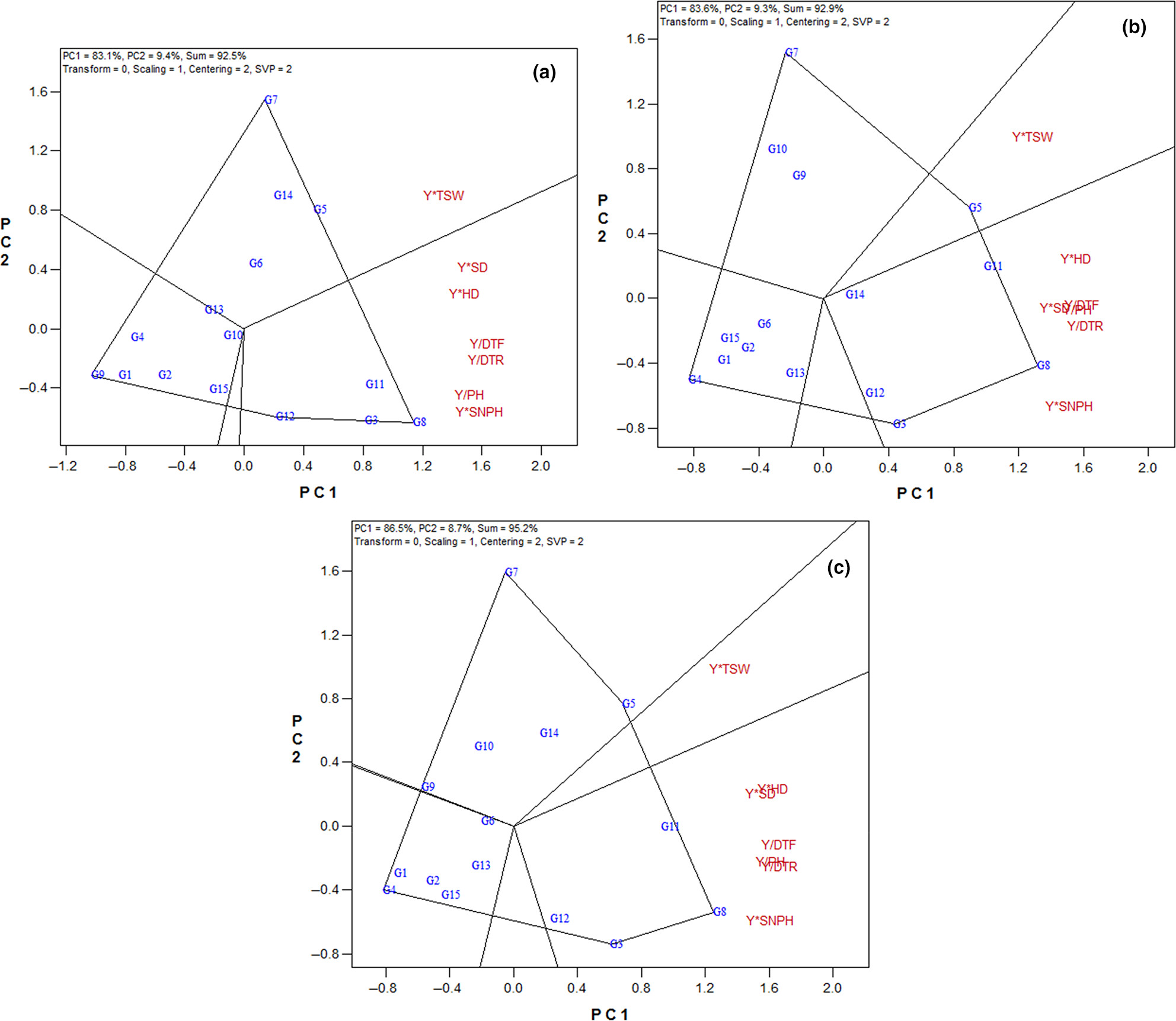
In this study, the methods of genotype × trait (GT) and genotype × yield × trait biplot (GYT) were used to identify interrelationships between different traits and to select the best sunflower hybrids based on multiple traits. Generally, the graphical method of the GYT biplot provides a practical and efficient new way to identify superior genotypes based on multiple traits in sunflower breeding programs.
Effects of resveratrol on tolerance to ischemia/reperfusion injury in aged male mice: Role of autophagy and apoptosis
- Pages: 5938-5947
- First Published: 28 June 2023
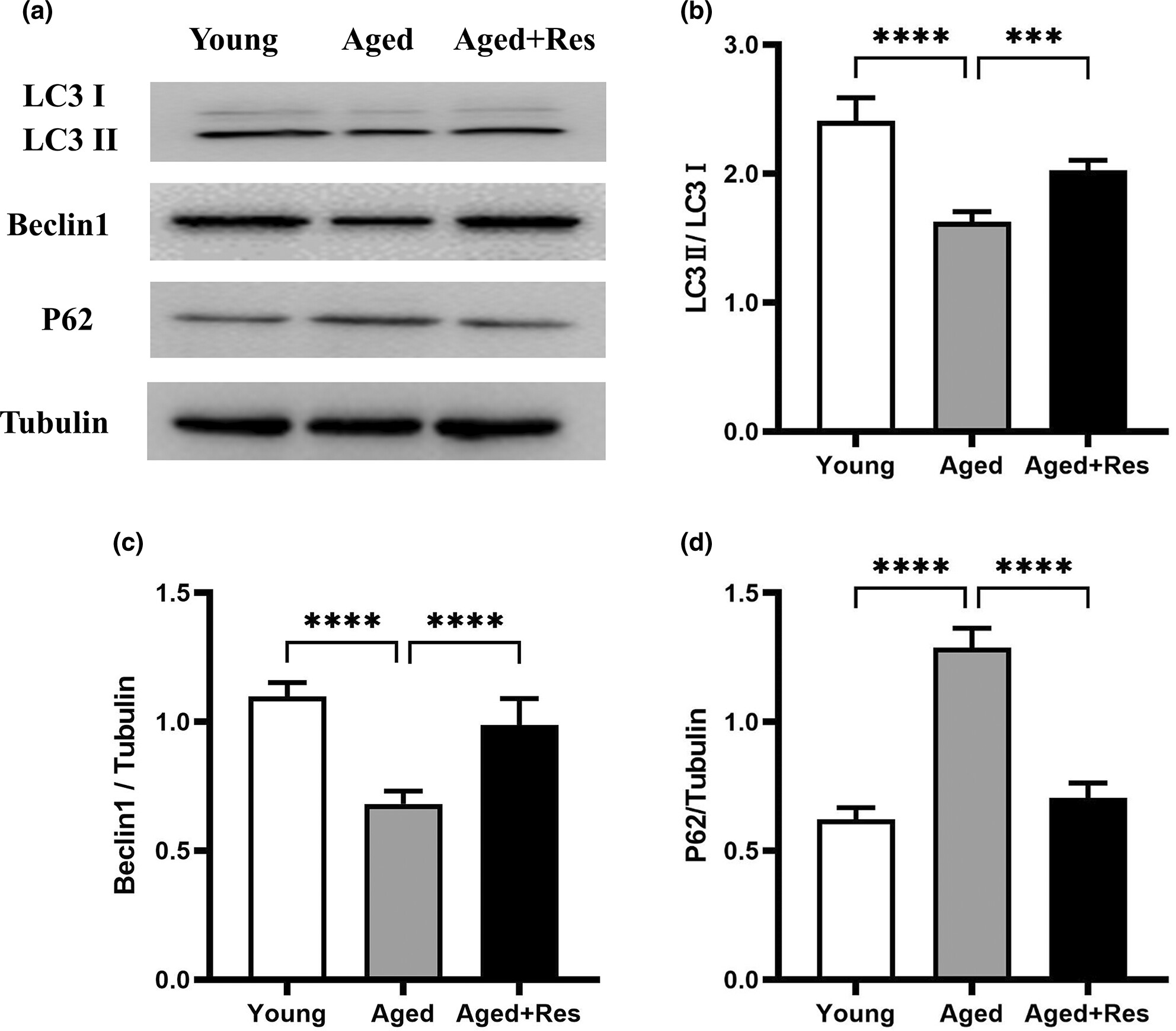
Autophagy and apoptosis play important roles in cardiac I/R injury. However, it remains largely unclear whether resveratrol can reduce the ischemic vulnerability of aged myocardium by regulating apoptosis and autophagy. The present study shows that resveratrol attenuates ischemic/reperfusion injury vulnerability of senile myocardium by inhibiting apoptosis and upregulating autophagy through SIRT1 signaling pathway.
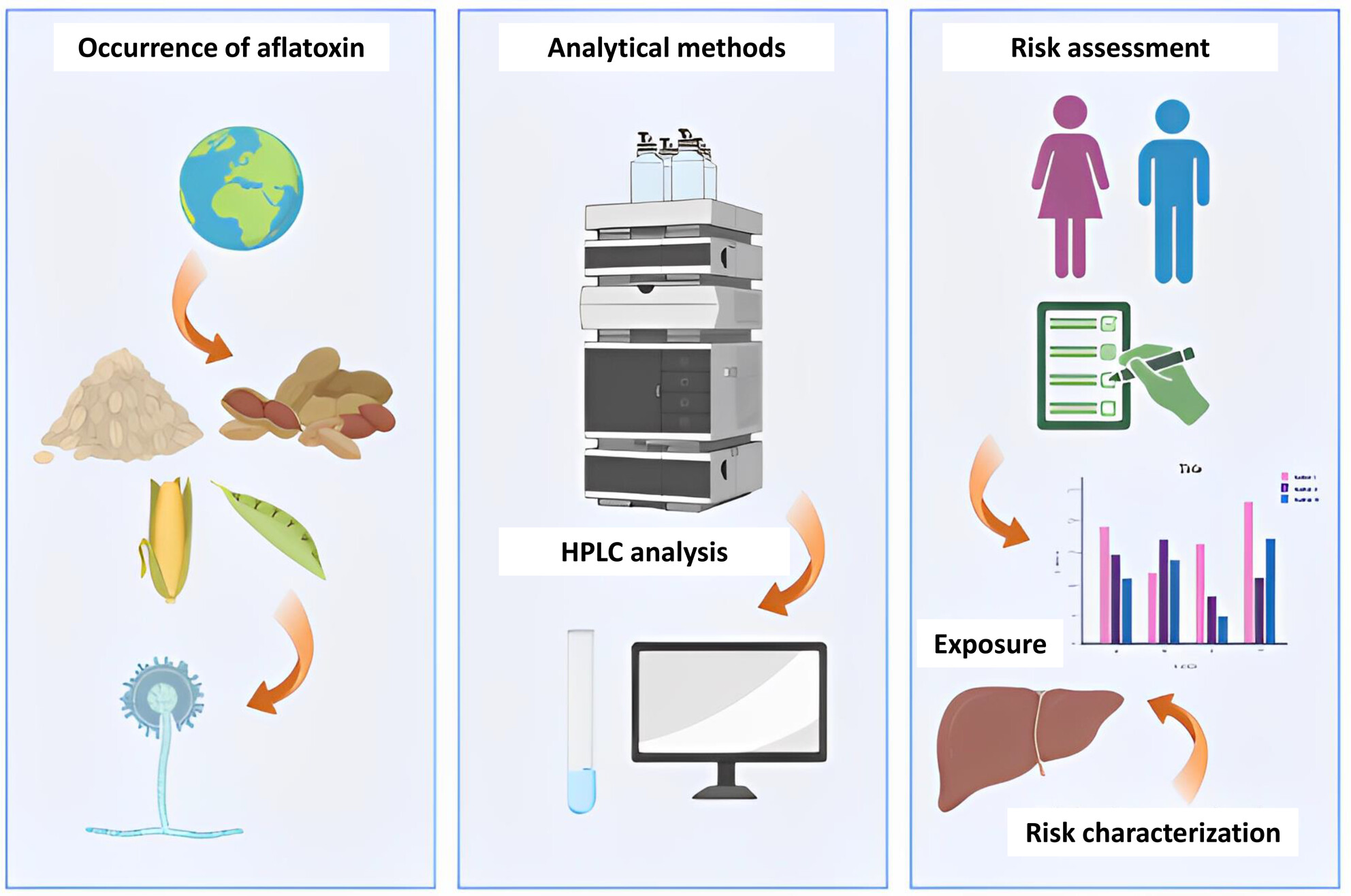
Aflatoxins in food products consumed in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia: A preliminary dietary risk assessment
- Pages: 5948-5958
- First Published: 27 June 2023
Determinants of food security status of household in west Gojjam zone, Ethiopia
- Pages: 5959-5966
- First Published: 26 June 2023
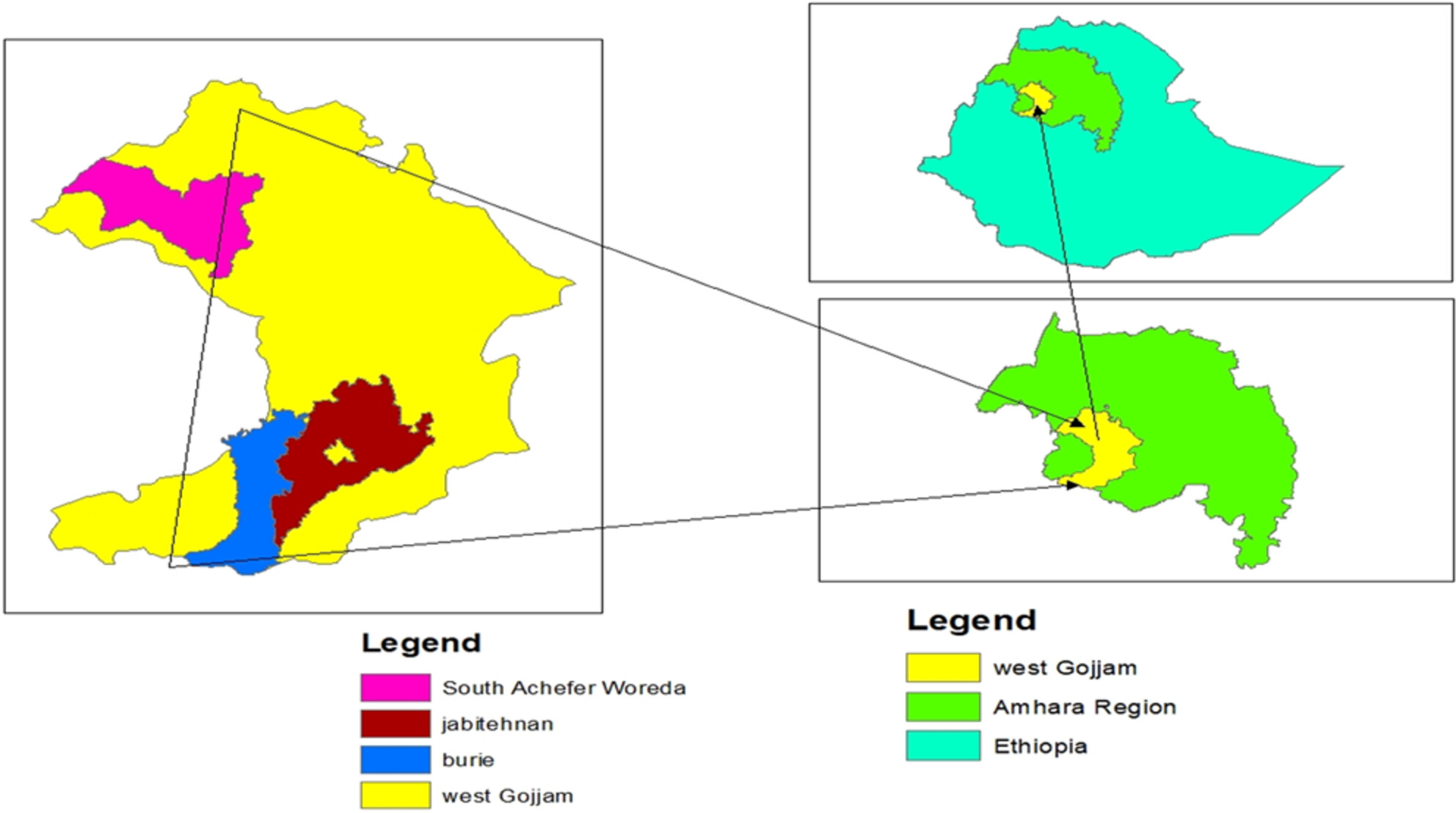
Food is important for human beings so that everyone can have enough of it. Food security is based on a variety of factors, including how well agricultural production is doing, how many people are employed in the food industry, what public policies are put in place to improve food production strategy and food security of the household. Therefore, this study focuses on identifying the determinants of food security of the household.
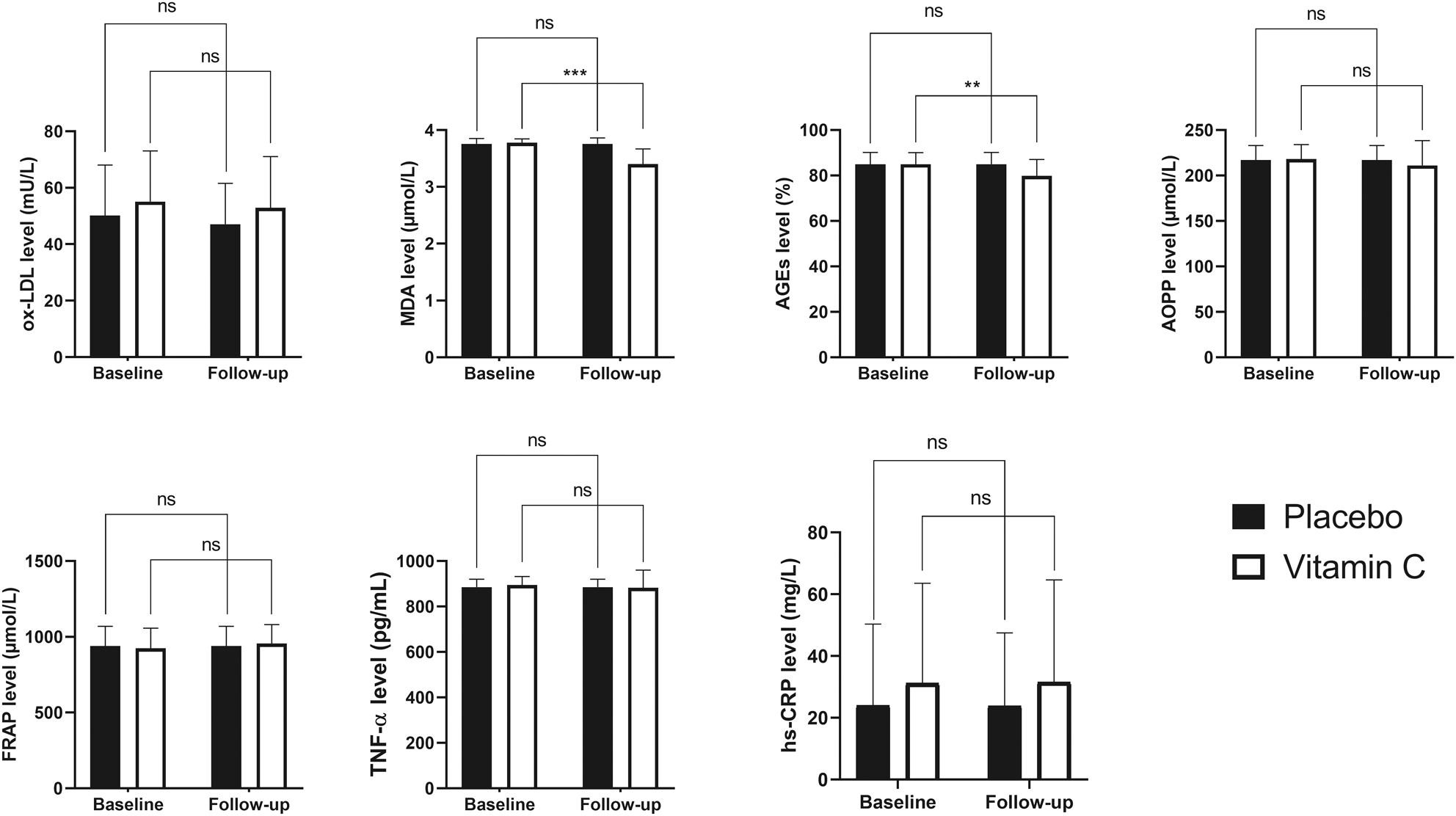
Vitamin C supplementation lowers advanced glycation end products (AGEs) and malondialdehyde (MDA) in patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial
- Pages: 5967-5977
- First Published: 30 June 2023
The internal aqueous phase gelation improves the viability of probiotic cells in a double water/oil/water emulsion system
- Pages: 5978-5988
- First Published: 02 July 2023
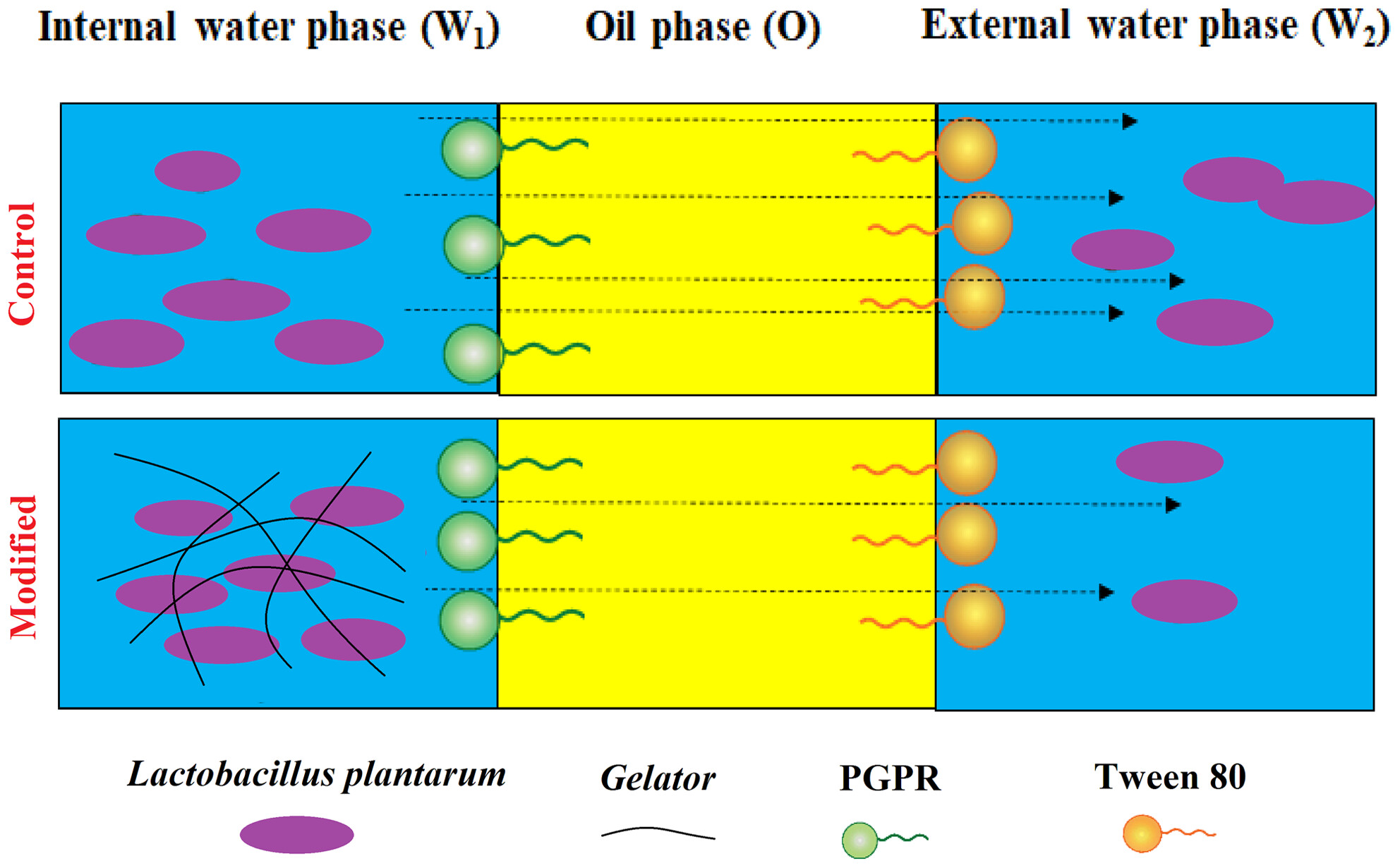
The stability of W1/O/W2 emulsion significantly increased after W1 gelation. A significant increase was observed in the encapsulation efficiency after W1 gelation. The apparent viscosity of emulsions was significantly increased after W1 gelation. W1/O/W2 emulsion containing gum tragacanth had the highest probiotics viability.
Nervonic acid reduces the cognitive and neurological disturbances induced by combined doses of D-galactose/AlCl3 in mice
- Pages: 5989-5998
- First Published: 06 July 2023
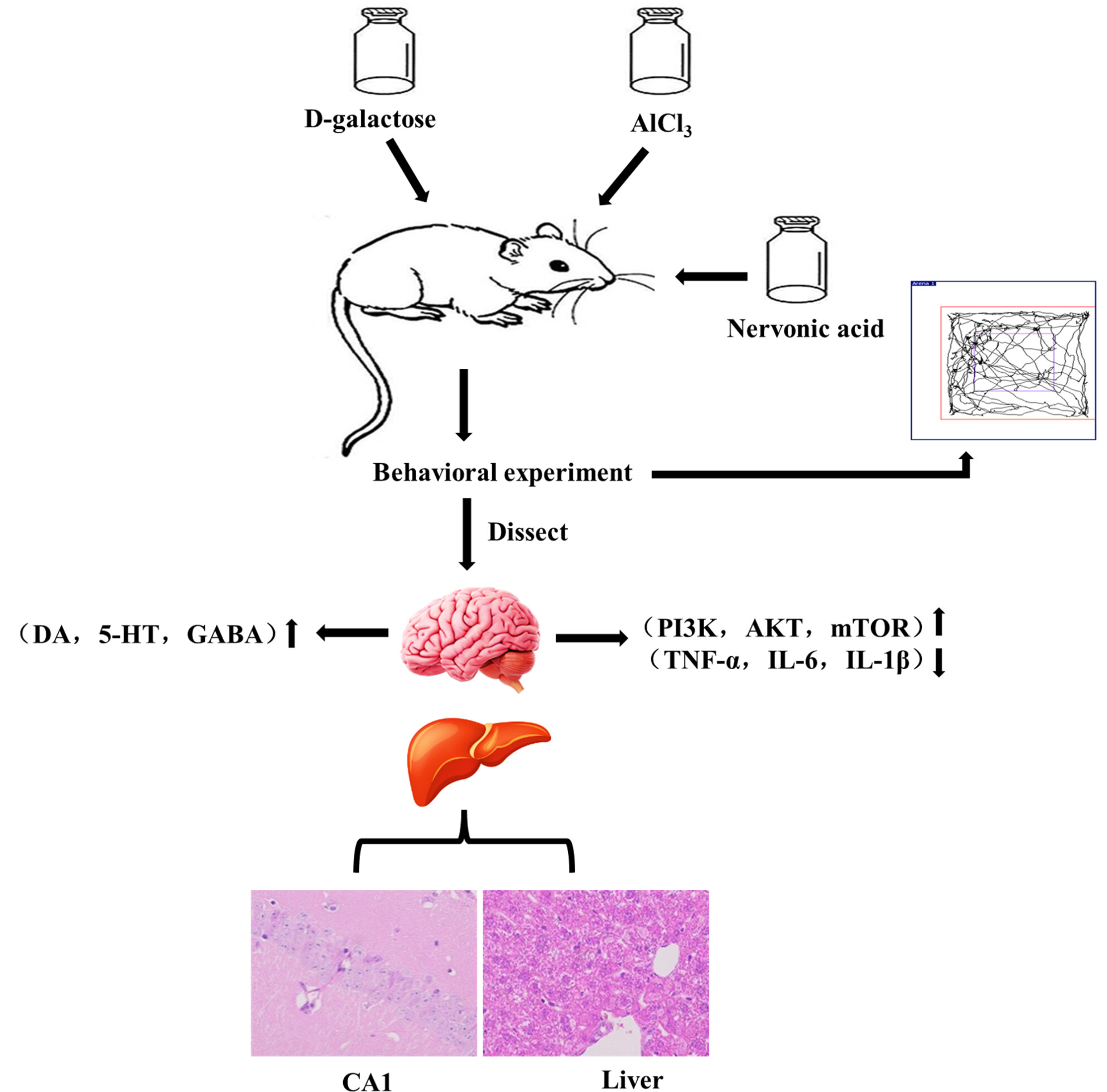
Nervonic acid (NA) is a kind of ultra-long-chain monounsaturated fatty acid which can repair nerve cell damage caused by oxidative stress. In this study, the combined dose of D-galactose/AlCl3 was used to establish a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. These results suggest that NA has the potential to be developed as antioxidant drug for the prevention and early therapy of AD.
Preclinical study of pachyman inducing ferroptosis against ovarian cancer: Biological targets and underlying mechanisms
- Pages: 5999-6009
- First Published: 29 June 2023

Our bioinformatics findings reveal the biological actions, key genes, and signaling pathways targeting ferroptosis in Pachyman treating ovarian cancer potentially. This study will better contribute to complete understanding of Pachyman-mediated network mechanisms in treating ovarian cancer. Notably, identified interactions of drug and core gene may lay a theoretical foundation for the research and development of ovarian cancer drugs targeting ferroptosis.
Infant feeding choices among Panamanian mothers: A qualitative study
- Pages: 6010-6019
- First Published: 06 July 2023
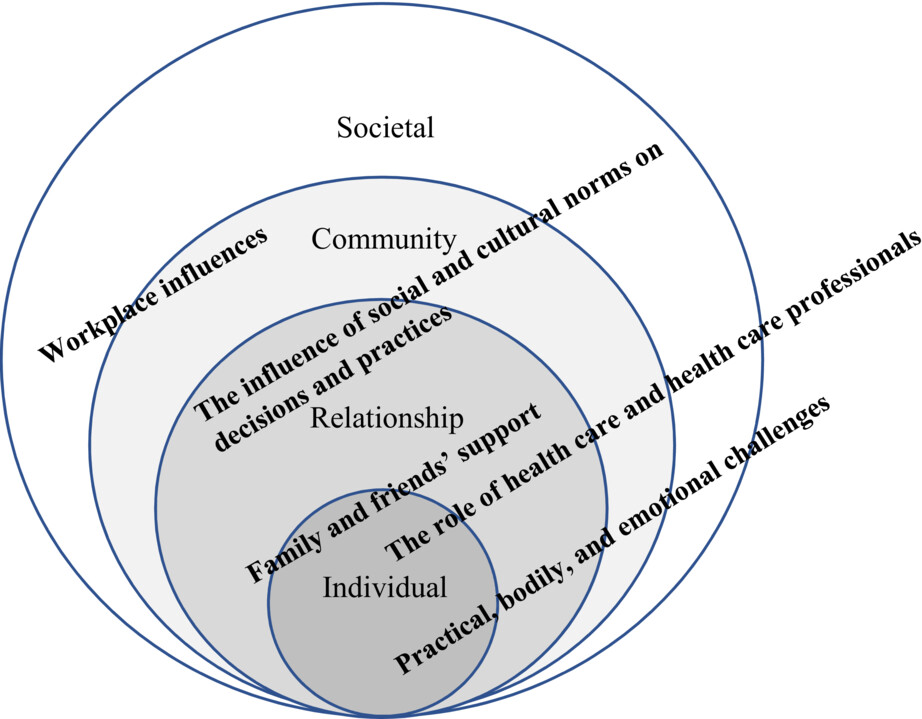
In this article we make a novel contribution to the literature, presenting (we believe for the first time) the experiences of Panamanian mothers in regard to their infant feeding decisions. This qualitative study opens a new avenue of research to develop our understanding of the factors that influence infant feeding decisions by Panamanian mothers and demonstrates the importance of understanding the complexity of the social norms surrounding infant feeding. The study concludes that current Panamanian breastfeeding policies do not address the impact of family and friends on the decisions of Panamanian mothers. Further is study is also required of the impact workplace policies, routines and support make to feeding decisions and international comparative analysis may prove a fruitful in this regard.
Compositional profiling and sensory analysis of cauliflower by-products-enriched muffins
- Pages: 6020-6031
- First Published: 20 July 2023
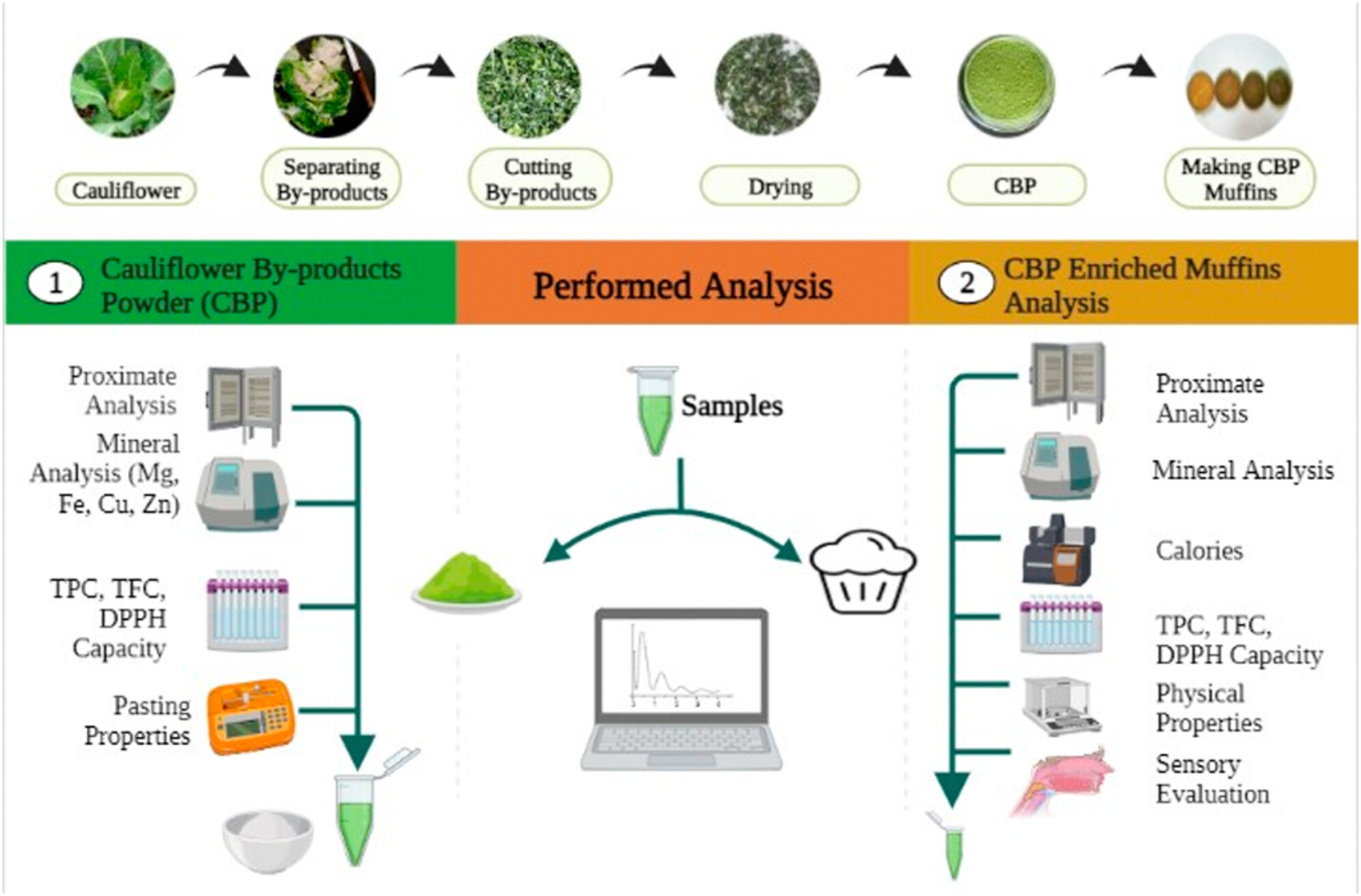
Cauliflower by-products (leaves, stems, stalks) were successfully utilized in muffins as a model system and their feasibility of incorporation was investigated. Cauliflower by-products powder (CBP) based muffin formulations were made by the progressive replacement of wheat flour (WF) that resulted supplementation of wheat muffins with 10% CBP is a beneficial approach to enrich them with nutrients and intensify their antioxidant potential.
Combined antifungal effects of the vapor phases of Zataria multiflora and Cinnamomum zeylanicum essential oils against Aspergillus flavus and Penicillium citrinum in vitro and cheese
- Pages: 6032-6040
- First Published: 28 June 2023
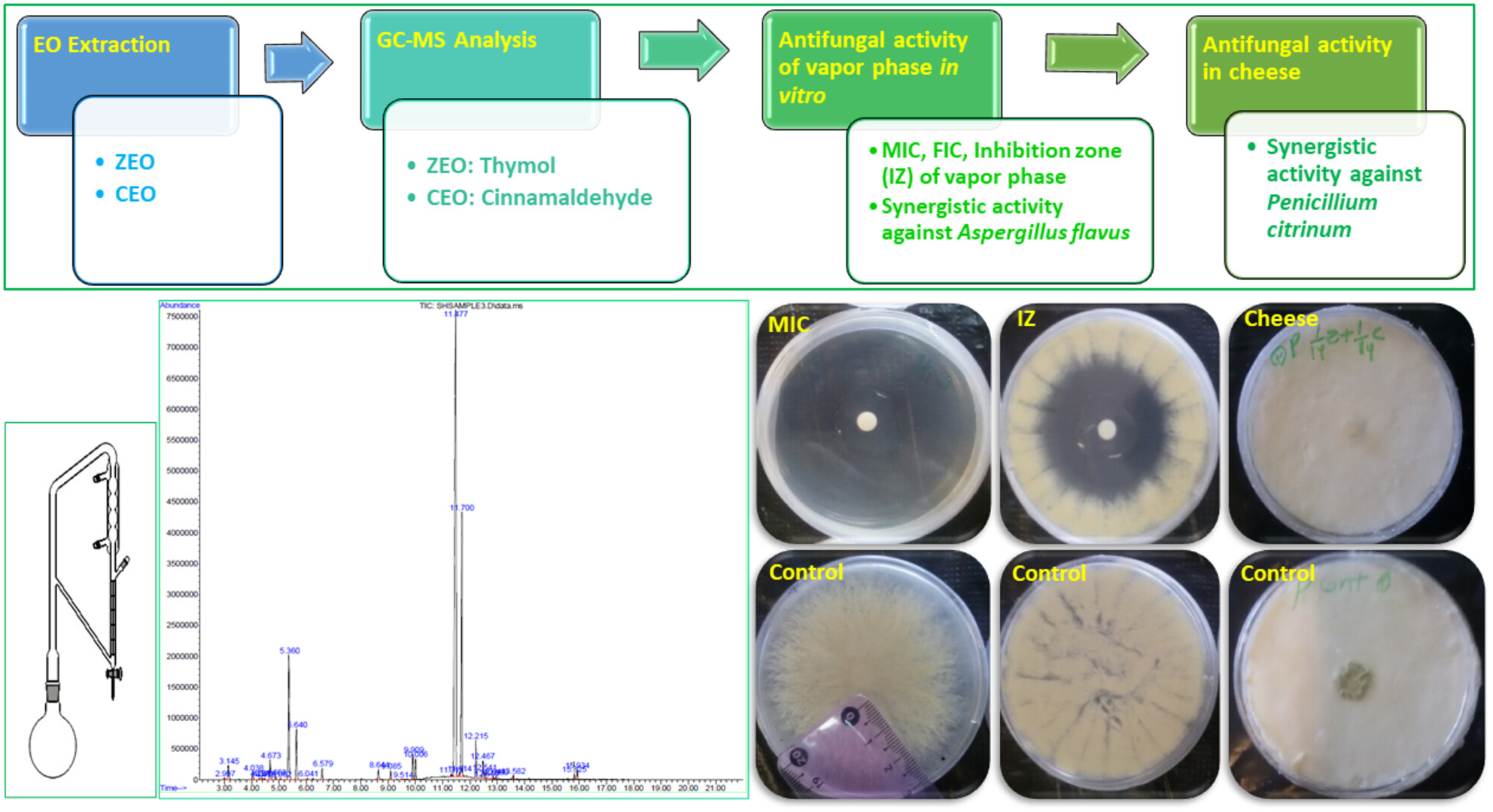
In this study, the antifungal activity of Z. multiflora (ZEO) and C. zeylanicum (CEO) essential oils vapors were examined. The vapor phases of ZEO and CEO showed significant antifungal effects. The combination of ZEO and CEO showed synergistic effect against A. flavus in vitro. The combination of ZEO and CEO could also synergistically inhibit P. citrinum in cheese.
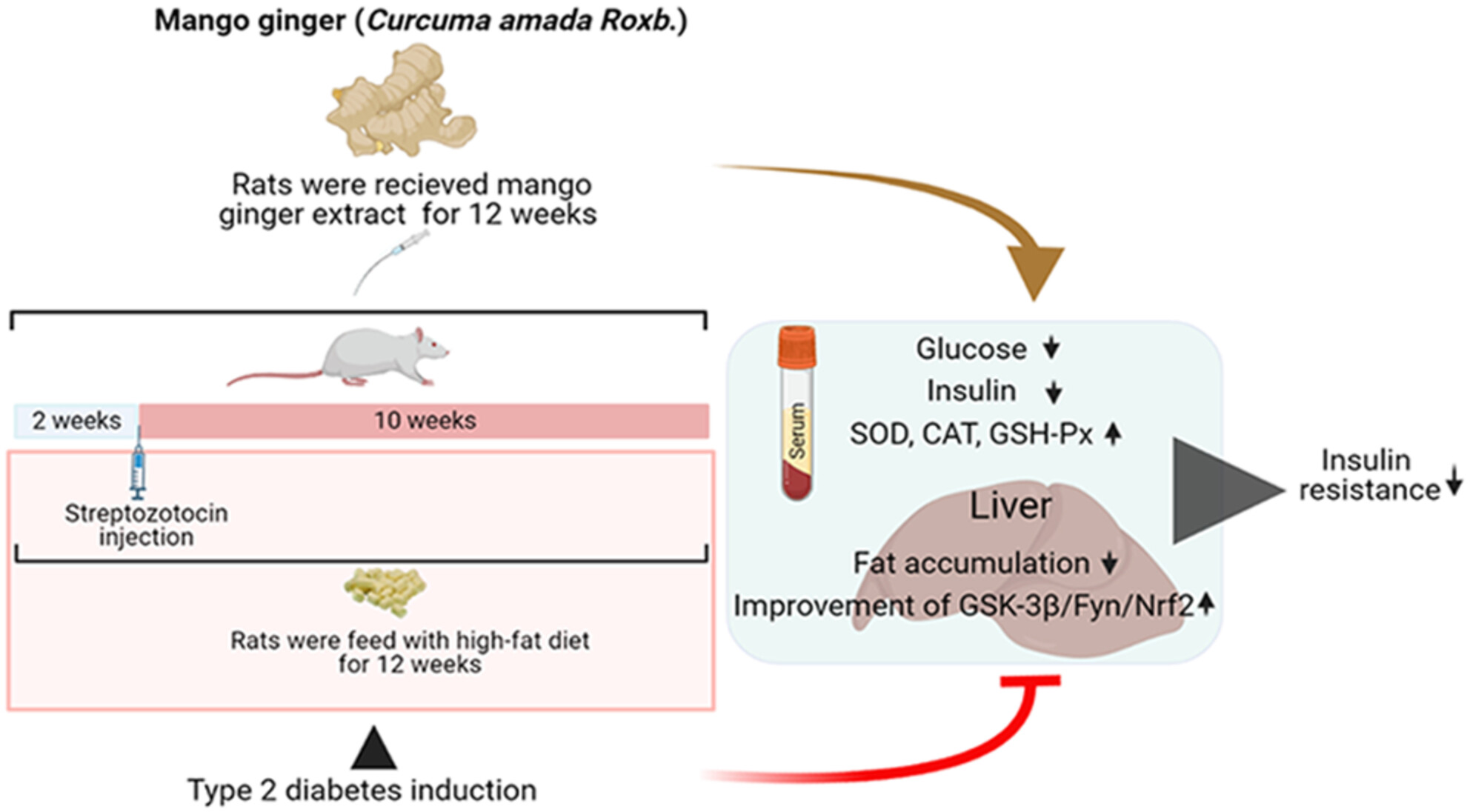
Mango ginger (Curcuma amada Roxb.) may alleviate the effect of high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced diabetes by activation of the GSK-3β/Fyn/Nrf2 pathway
- Pages: 6041-6051
- First Published: 04 July 2023
Physiochemical properties of Sarawak's adapted Liberica coffee silverskin utilizing varying solvents
- Pages: 6052-6059
- First Published: 06 July 2023
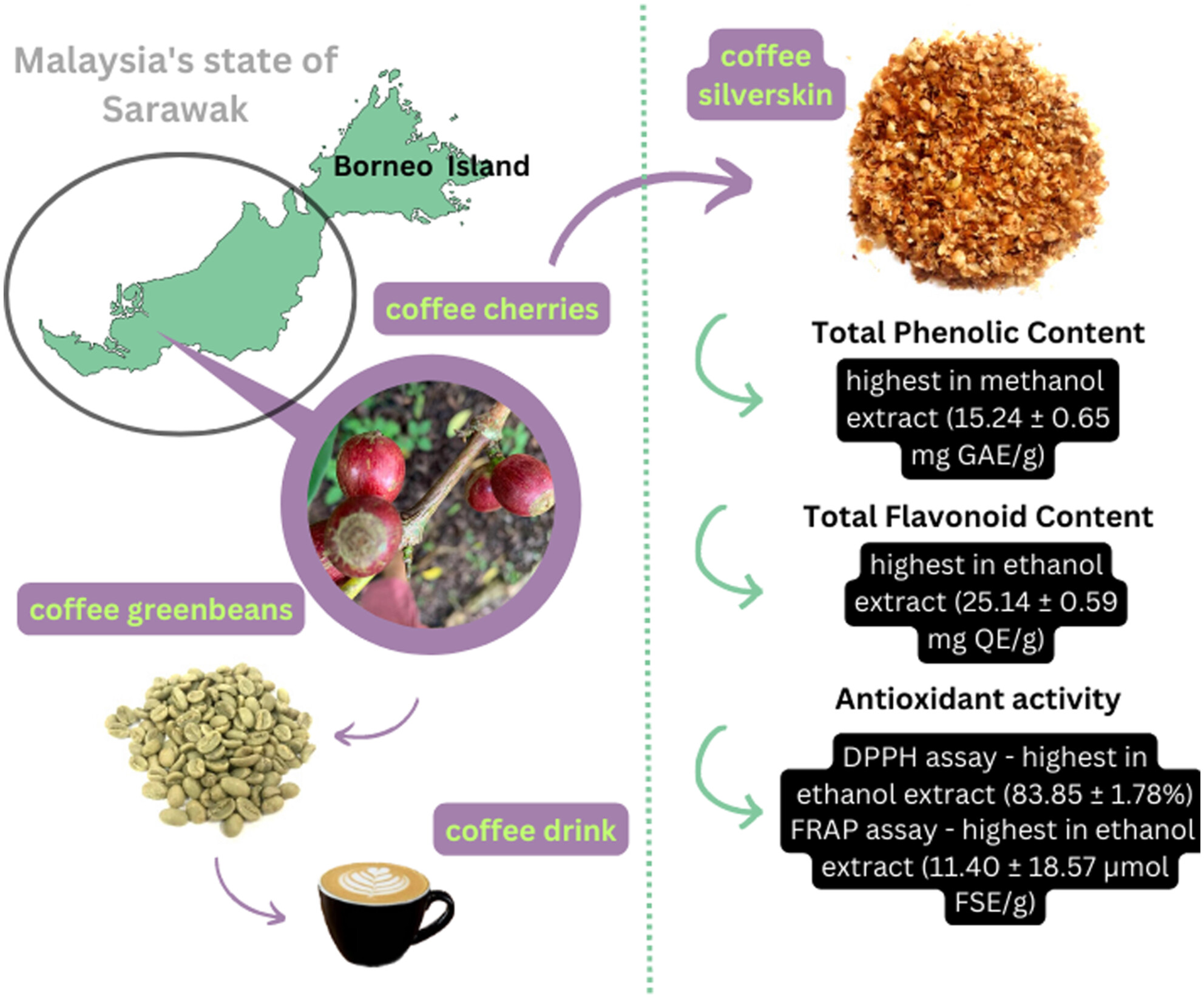
This study focused on the Liberica coffee silverskin (CS) indigenous to the land of Malaysian state of Sarawak. The CS was found to be high in phenolic content, flavonoid content, and antioxidant activity. Even with different solvents used for extraction, the Liberica CS shows promising beneficial phenolic compounds for further utilization in the coffee market.
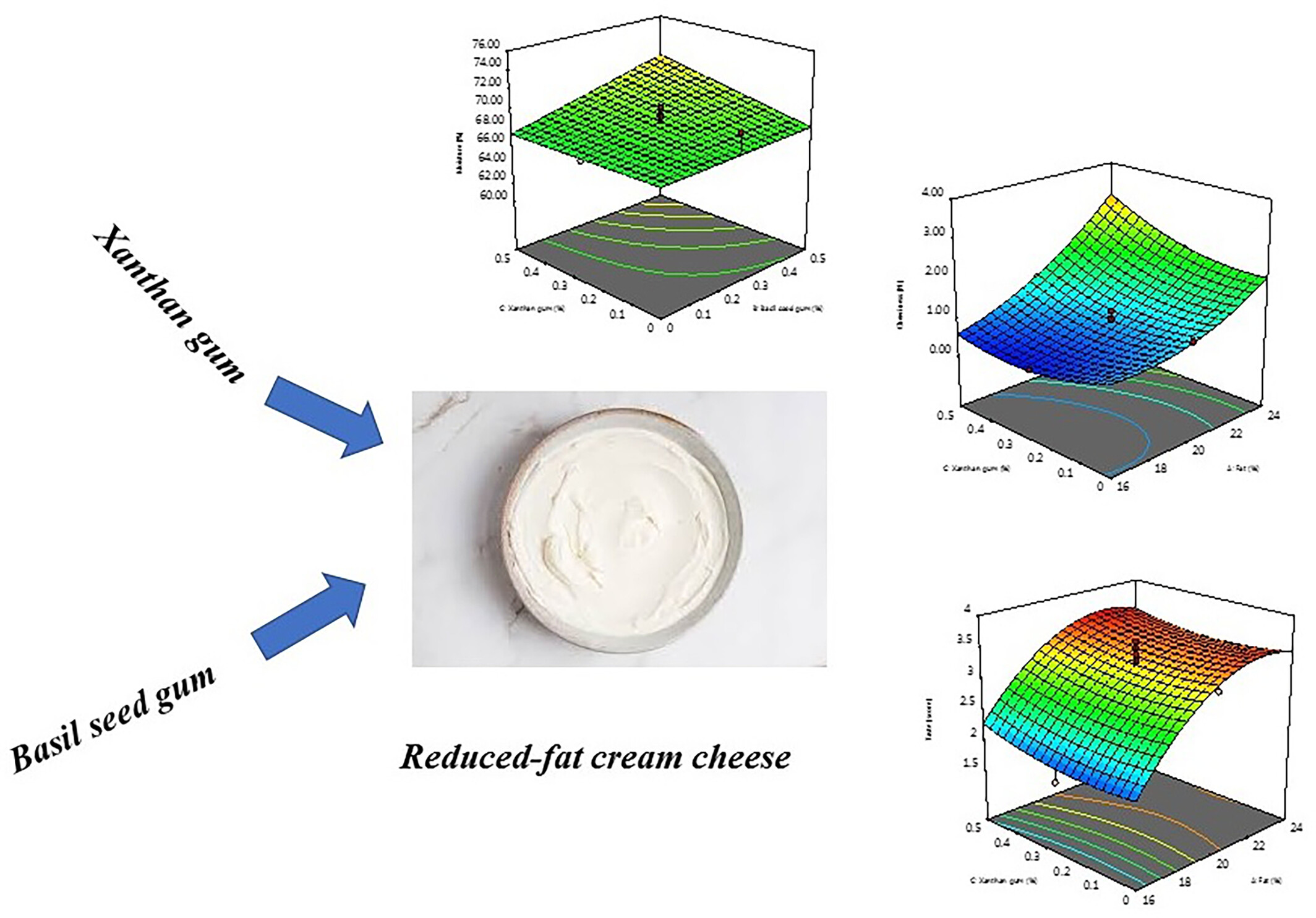
Effect of basil seed and xanthan gum on physicochemical, textural, and sensory characteristics of low-fat cream cheese
- Pages: 6060-6072
- First Published: 04 July 2023
The effects of unsaturated fatty acids on psoriasis: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
- Pages: 6073-6084
- First Published: 05 July 2023
Extraction of protein from apricot kernel oil press cake (AKOPC) through innovative techniques and the formulation of supplemented yogurt
- Pages: 6085-6095
- First Published: 21 July 2023
When supplementary skimmed milk powder (SMP) was substituted with apricot kernel protein (AKP) in the yogurt manufacturing process, the total solids, average titratable acidity, total protein, and fat contents of the yogurt were increased. In contrast, pH and syneresis values decreased as AKP increased in the resulting yogurt, whether fresh or after 7 days of cold storage. Substitution of additional SMP with AKP in yogurt production might be recommended up to 35%.
Comparison of micronutrients in adult enteral formulas widely used in clinical practice
- Pages: 6096-6105
- First Published: 05 July 2023
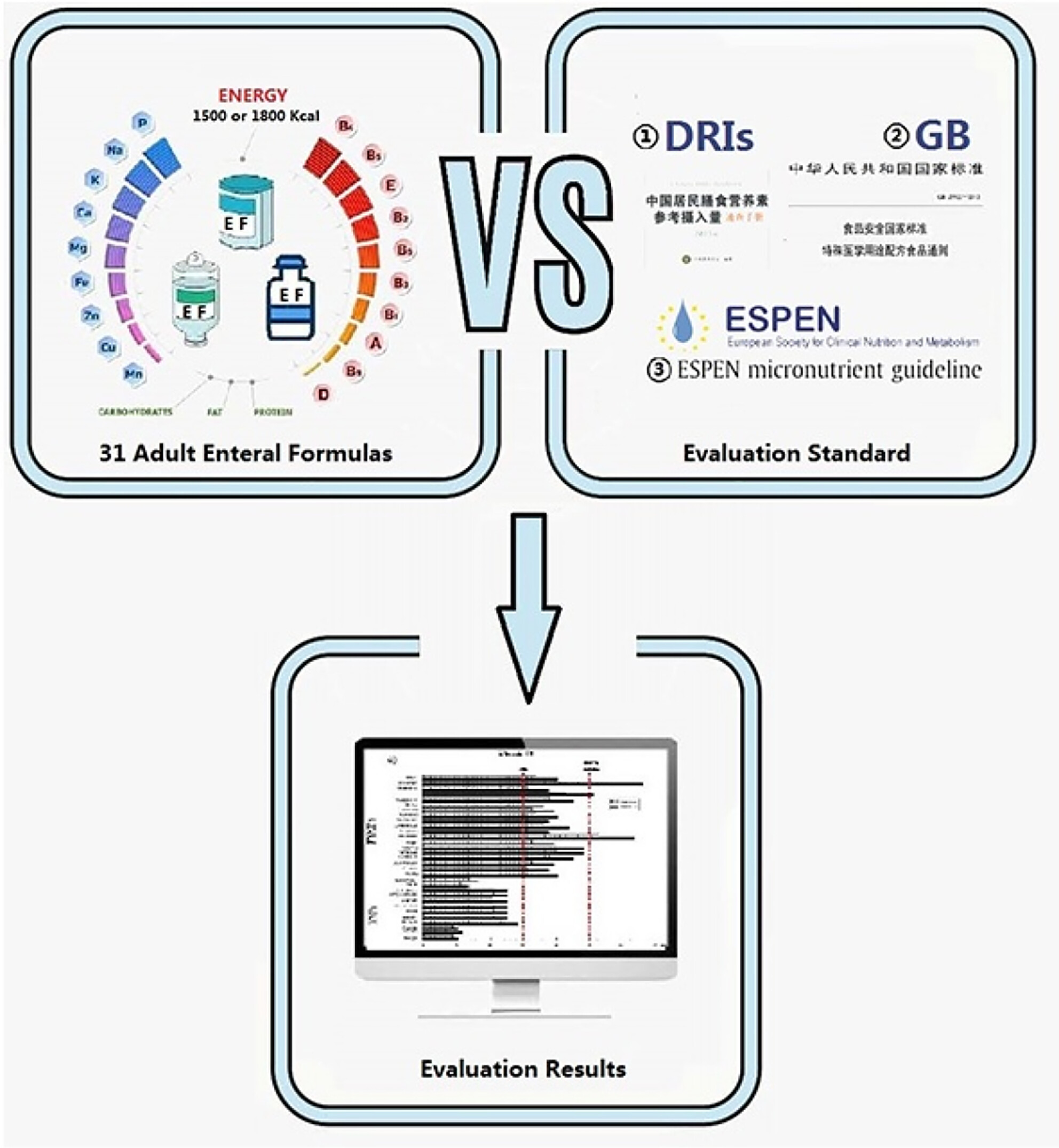
The results could provide a basis for research and to develop more suitable enteral formulas by manufacturers and help to administer more effective enteral nutrition support for patients on long-term total enteral nutrition by clinical dietitians in clinical practice, especially individualized treatment.
The effect of anthocyanin from Dioscorea alata L. after purification, identification on antioxidant capacity in mice
- Pages: 6106-6115
- First Published: 18 July 2023
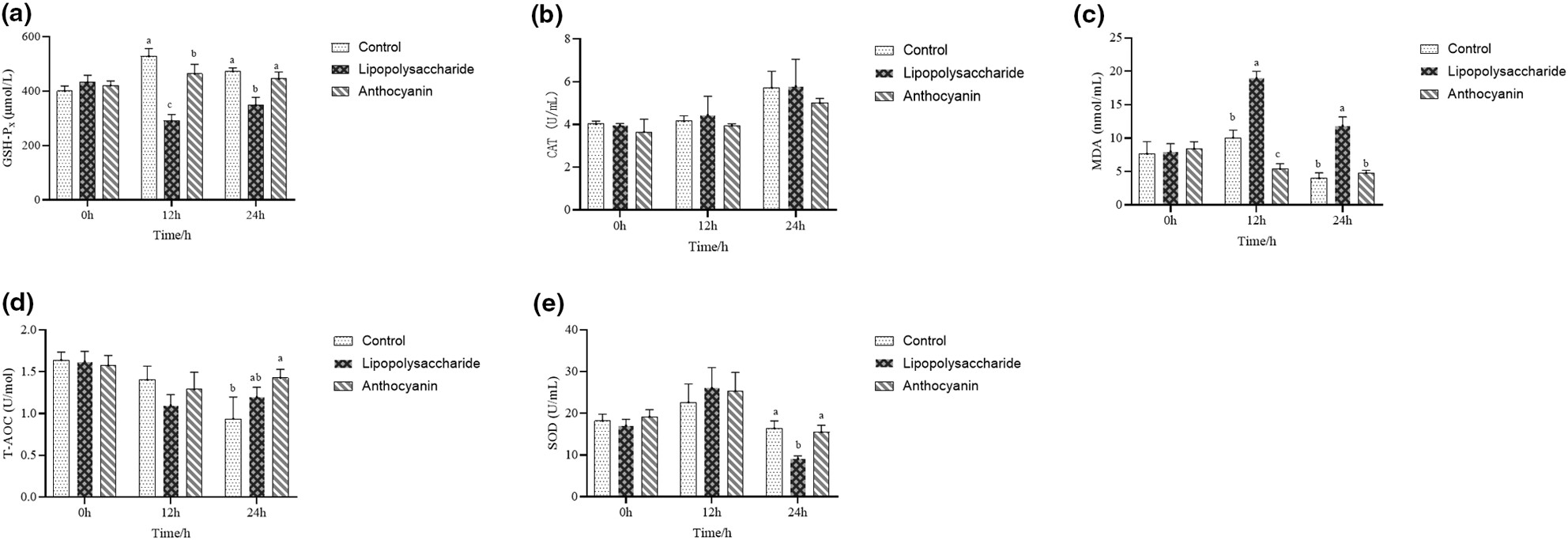
In our study, the purity of anthocyanin increased to 39.59 ± 1.56%, 60.18 ± 1.97%, and 81.08 ± 1.97% after purification via AB-8 macroporous resin, Sep-Pak C18 solid phase, and LH-20 Sephadex stepwise. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometer results indicated that paeoniflorin-3,5-O-dihexoside, petunin-3-O-feruloyl-glucoside-5-O-glucoside, cyanidin-3-O-feruloyl glucoside-5-O-glucoside, cyanidin-3-O-sophoroside, and petunin-3,5-O-dihexoside were the major compounds. The purified anthocyanin exhibited stronger antioxidant activity than the unpurified extract and ascorbic acid, whereas weaker than that of cyanidin-3-O-glucoside in general, which was assessed using DPPH, ABTS, and Fe3+ reducing capacity methods and the purified anthocyanin increased GSH-Px, total antioxidant capacity, and superoxide dismutase activities and decreased malondialdehyde concentration on serum in mice after administering lipopolysaccharide for 24 h (p < .05).
A data fusion approach for nondestructive tracking of the ripening process and quality attributes of green Hayward kiwifruit using artificial olfaction and proximal hyperspectral imaging techniques
- Pages: 6116-6132
- First Published: 06 July 2023
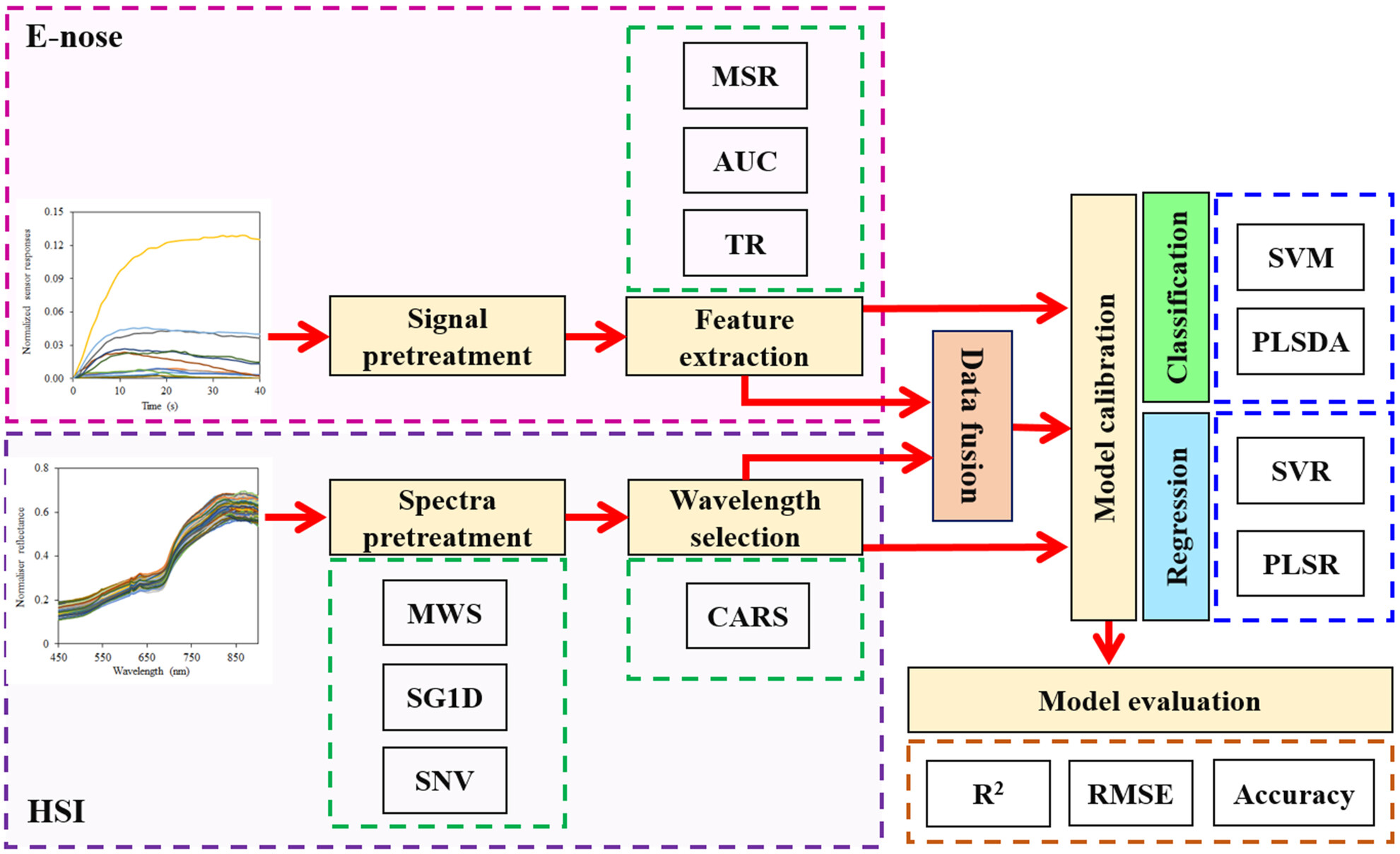
A data fusion, based on hyperspectral imaging (HSI) and electronic nose (e-nose) systems, was performed in this study to inspect the postharvest ripening process of Hayward kiwifruit. Performance evaluations proved that the fusion of olfactory and reflectance data improves the performance of machine learning algorithms. The data fusion-based SVM discriminated the kiwifruit samples based on storage time with a classification accuracy 94.44% in the test stage. The SVR model predicted the kiwifruit firmness, SSC, and TA with the R2 values of 0.962, 0.964, and 0.955, respectively. It was concluded that the hybrid of e-nose and HSI systems coupled with the SVM algorithm delivers an effective tool for accurate and nondestructive monitoring of kiwifruit quality during storage.
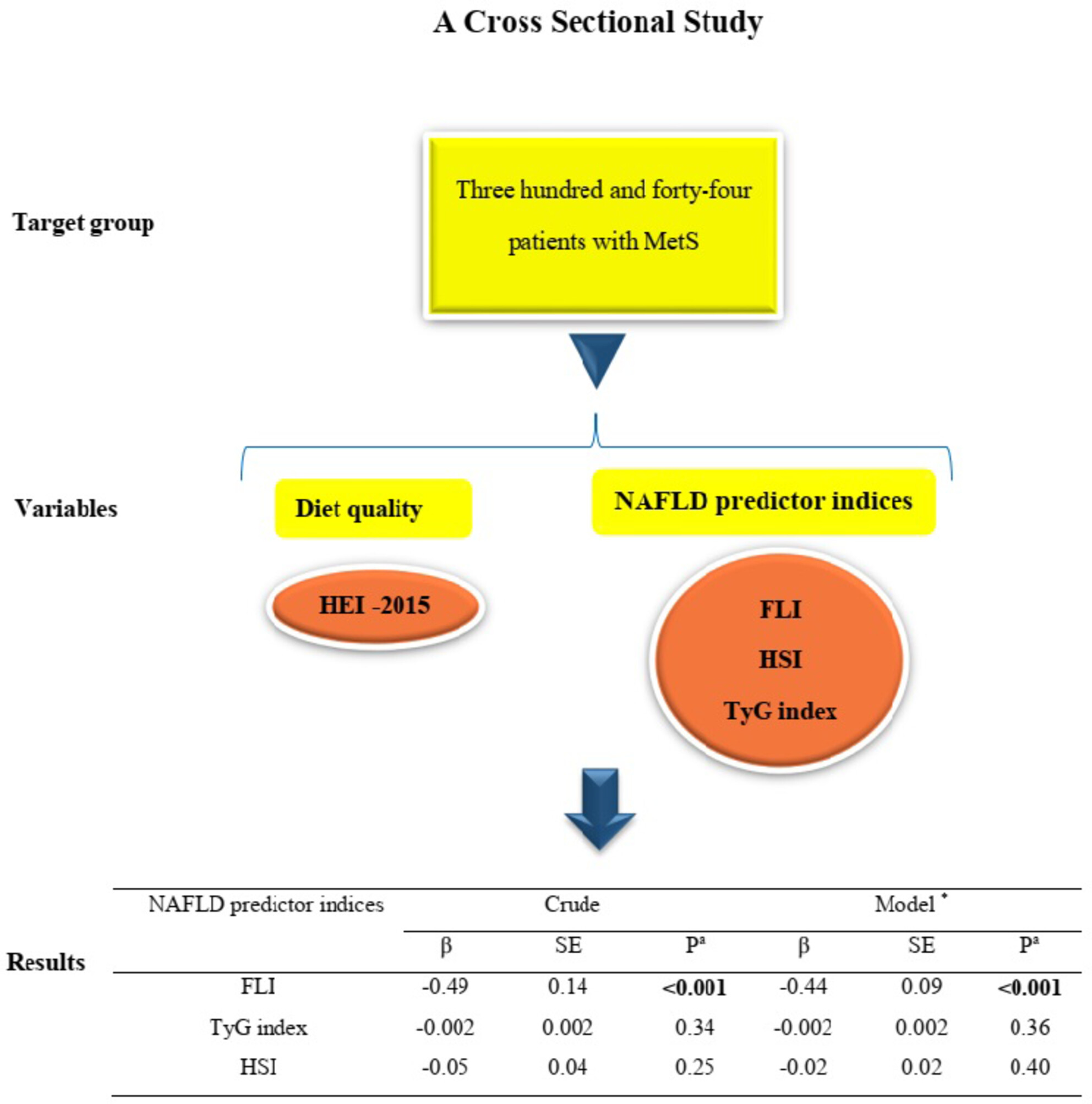
Relationship between diet quality and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease predictor indices in Iranian patients with metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study
- Pages: 6133-6139
- First Published: 04 July 2023
Escherichia coli O157:H7 beef carcass contamination and its antibiotic resistance in Awi Zone, Northwest Ethiopia
- Pages: 6140-6150
- First Published: 05 July 2023
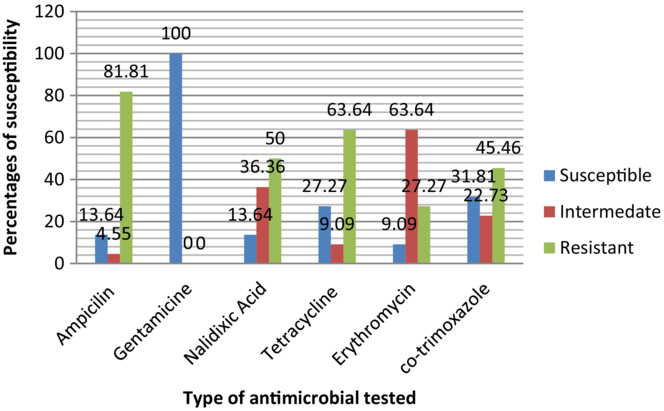
Escherichia coli O157:H7 was carcass contaminant at selected abattoirs and butcher shops in Awi Zone. Escherichia coli O157:H7 showed different susceptibility and resistance patterns toward antimicrobial disks. Butcher shops are the major risk factor for E. coli O157:H7 occurrence in beef. Contamination of carcasses during transport due to open and uncleaned vehicle transportation from the abattoir to retail shops and unhygienic handling and storage of carcasses at butcher shops are the major sources of contamination.
The suppression of the differentiation of adipocytes with Mallotus furetianus is regulated through the posttranslational modifications of C/EBPβ
- Pages: 6151-6163
- First Published: 05 July 2023
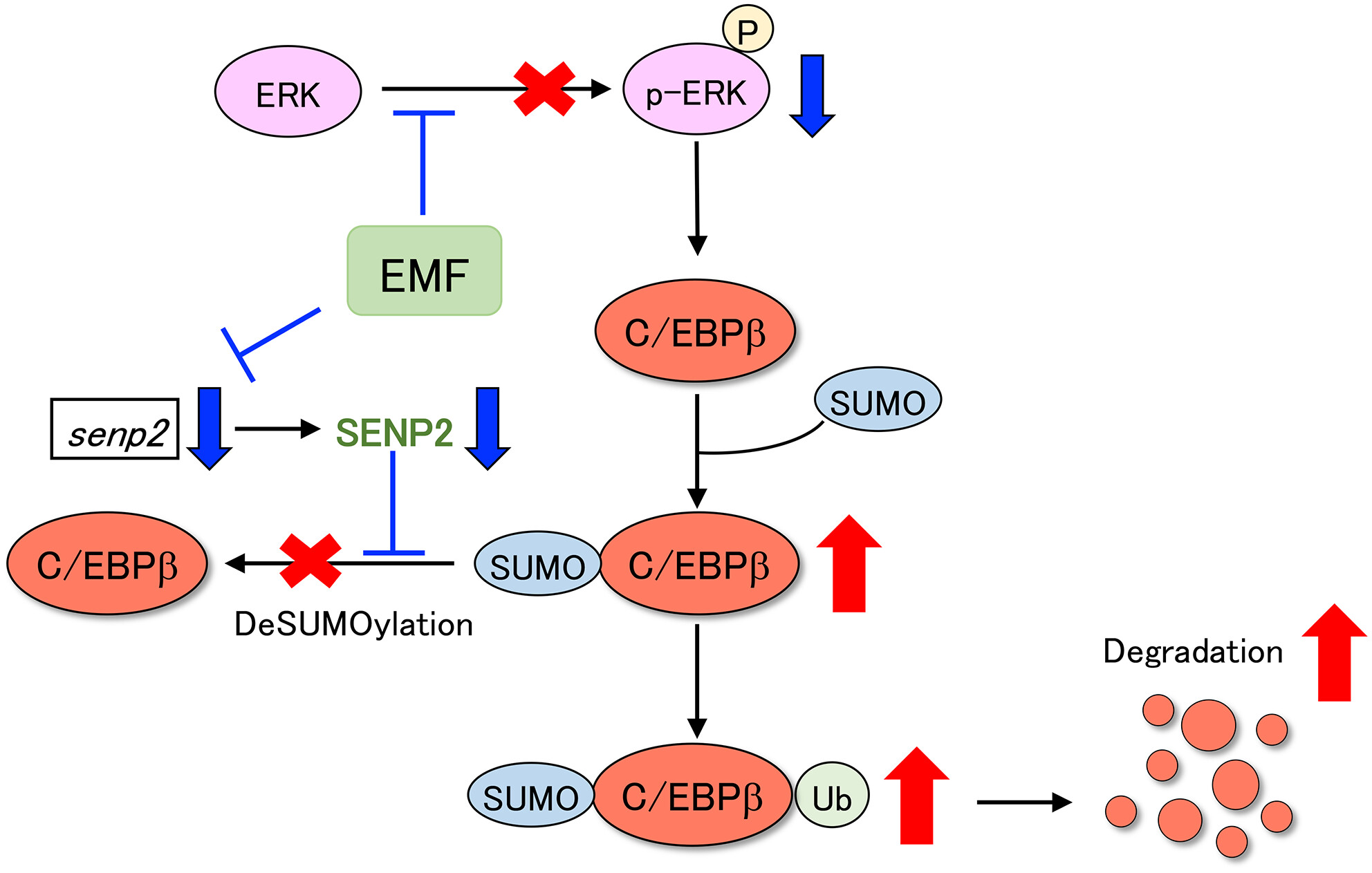
The treatment of Mallotus furetianus extract (MFE) significantly suppressed the increase in body weight and adipose tissue weight in obesity model mice. The treatment of MFE suppressed the expression of transcription factors that involves at the early stage of differentiation of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. The expression of C/EBPβ, one of the transcription factors, was decreased at the level of posttranslational modification by MFE, followed by the suppressions of PPARγ and C/EBPα transcriptionally.
Coagulation temperature and smoking time determine product quality and shelf life of the acid-heat coagulated Circassian cheese
- Pages: 6164-6177
- First Published: 06 July 2023

Process parameters of acid-heat coagulated cheeses were investigated. In this context, the effects of coagulation temperature, smoking time, seasonal changes, and storage time were evaluated in terms of textural, microstructural, and ripening properties of cheese. This article will contribute to the industry in determining the process parameters of acid-heat coagulated cheeses and will provide solutions to fill the gap in the literature.
CO2-mediated bloater defect can be induced by the uncontrolled growth of Enterobacteriaceae in cucumber fermentation
- Pages: 6178-6187
- First Published: 19 July 2023
Effect of preserved eggs on the health of SD rats, and anti-tumor action of HT-29 cells
- Pages: 6188-6198
- First Published: 26 July 2023
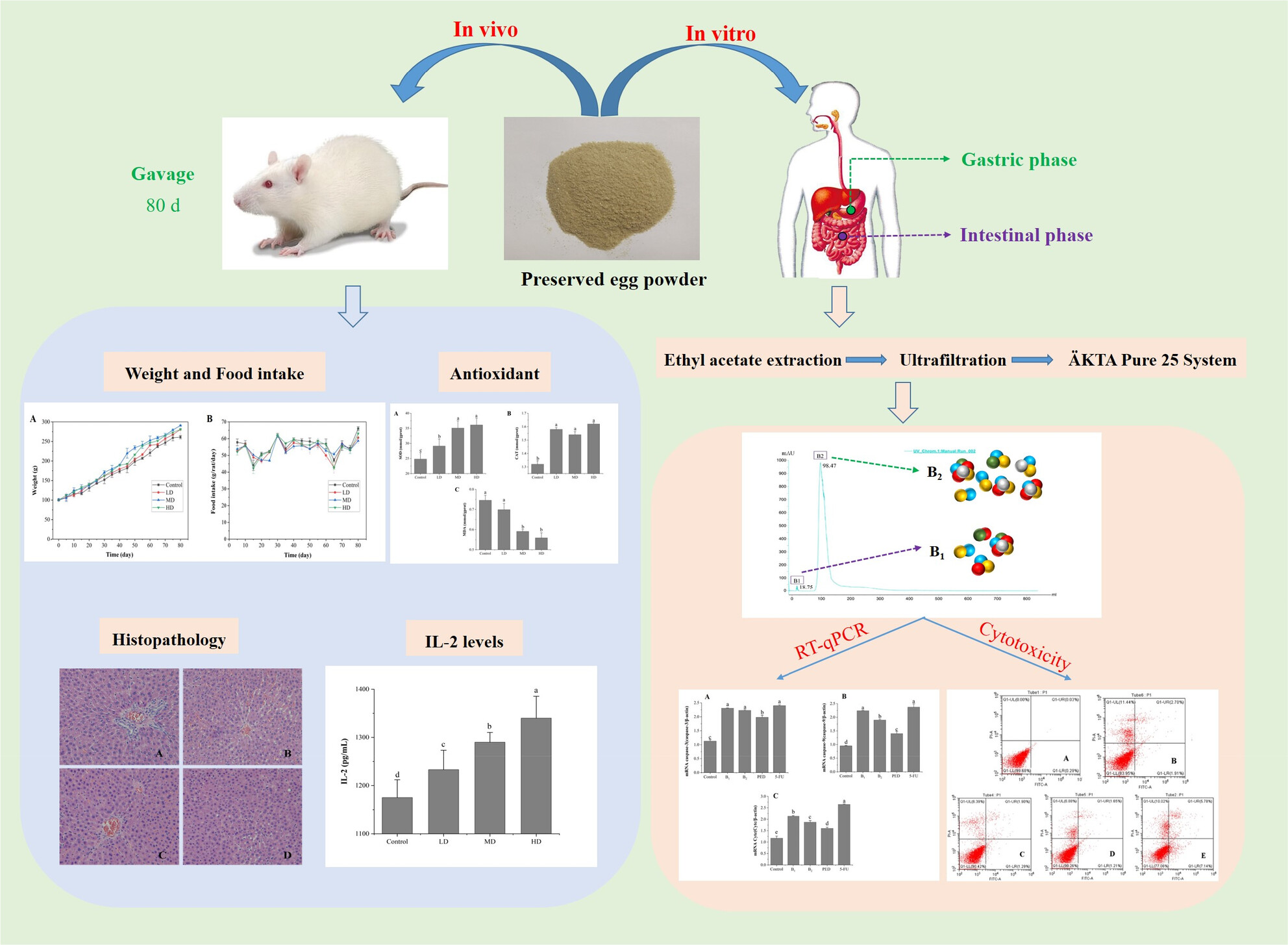
Our study demonstrated that preserved eggs did not affect normal physiological functions in rats, whose dietary behavior, body pH, and organ indices remained normal. It also had significant antioxidant effects. Two water-soluble fractions, B1 and B2, with MW ≥10 kDa, were screened from preserved eggs. Their anti-tumor mechanism was to induce apoptosis in HT-29 cells by up-regulating the expression of pro-apoptotic factors CytC, caspase-3 and caspase-9 mRNA.
3′sialyllactose and 6′sialyllactose enhance performance in endurance-type exercise through metabolic adaptation
- Pages: 6199-6212
- First Published: 18 July 2023
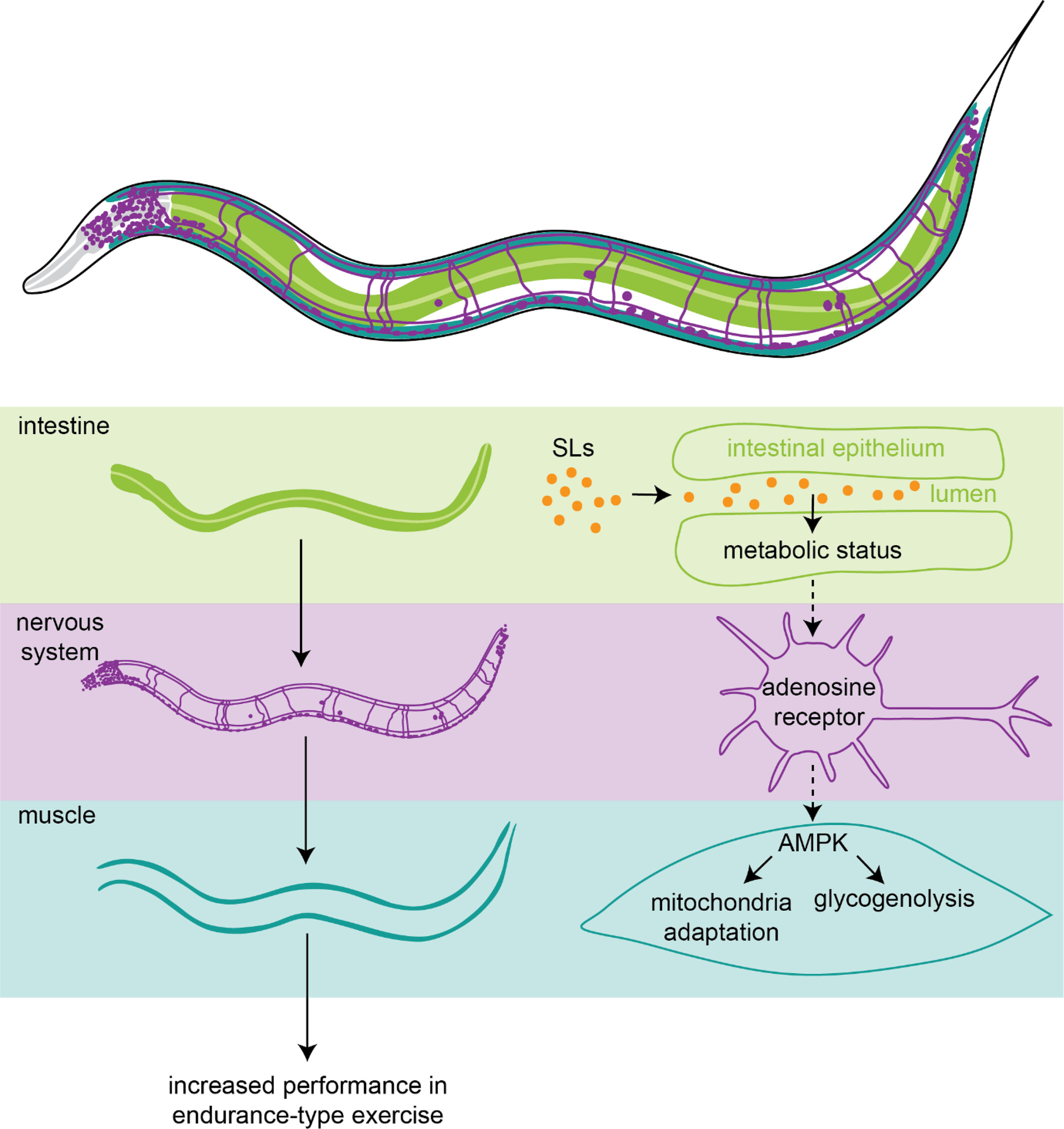
3′sialyllactose (3′SL) and 6′sialyllactose (6′SL) decrease exhaustion after endurance exercise in nematodes; 3′SL and 6′SL cause changes in metabolism during exercise, with a switch from beta oxidation to glycogenolysis; The increase in endurance performance requires AMPK and adenosine receptor signaling; Sialyllactoses likely signal from the intestine to the nervous system toward muscle cells, where metabolic adaptation increases exercise performance.
Effectiveness of Lactiplantibacillus plantarum in enhancing the folate content of injera made with different cereals
- Pages: 6213-6222
- First Published: 19 July 2023
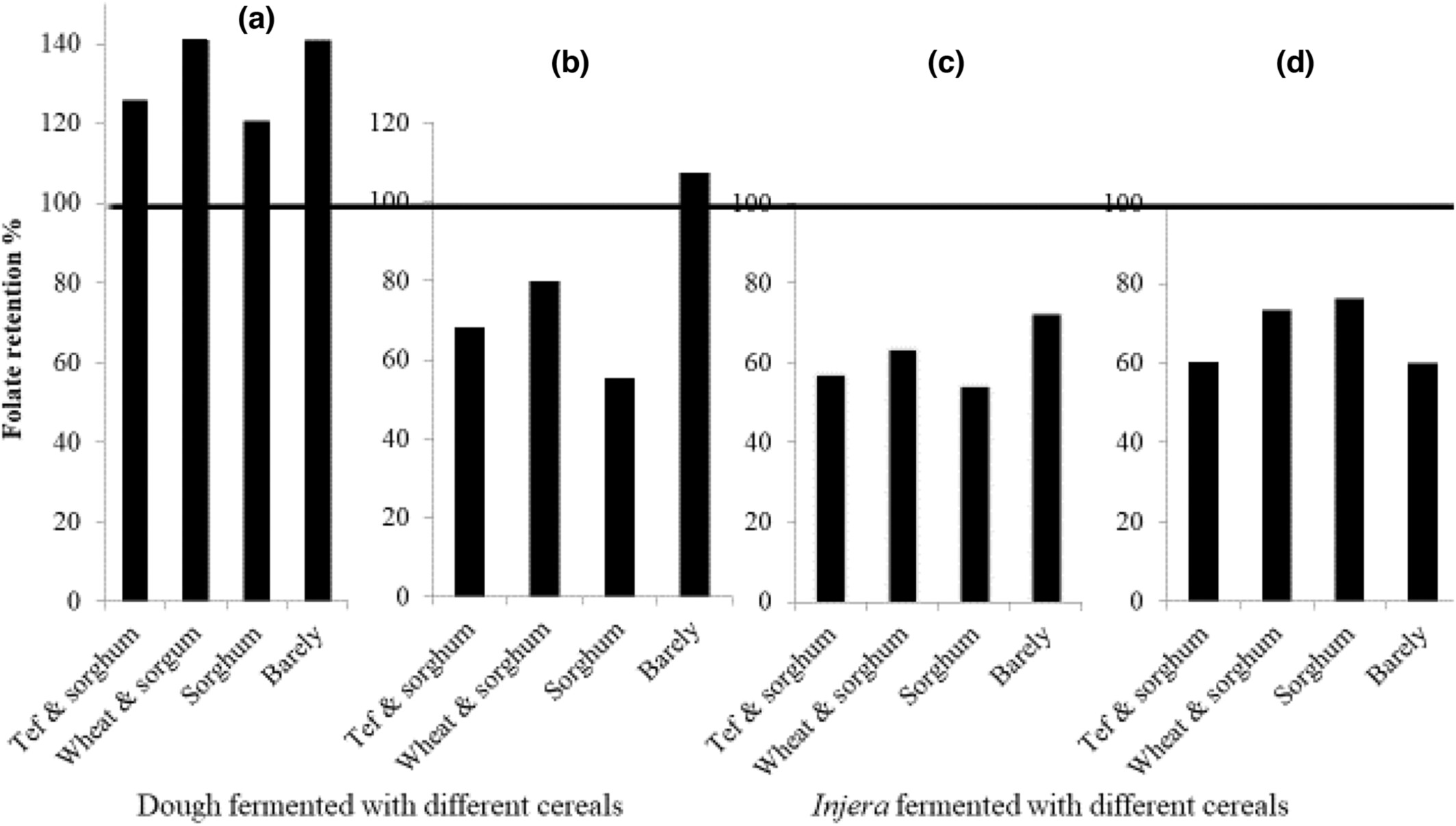
- Lactiplantibacillus plantarum strain can be used as a potential folate source not only for injera made with tef but also for any injera that could be made with other cereals.
- Consumption of any injeras fermented with L. plantarum contributed much more to folate RNI of children and women of reproductive ages than consumption of injera fermented with ersho.
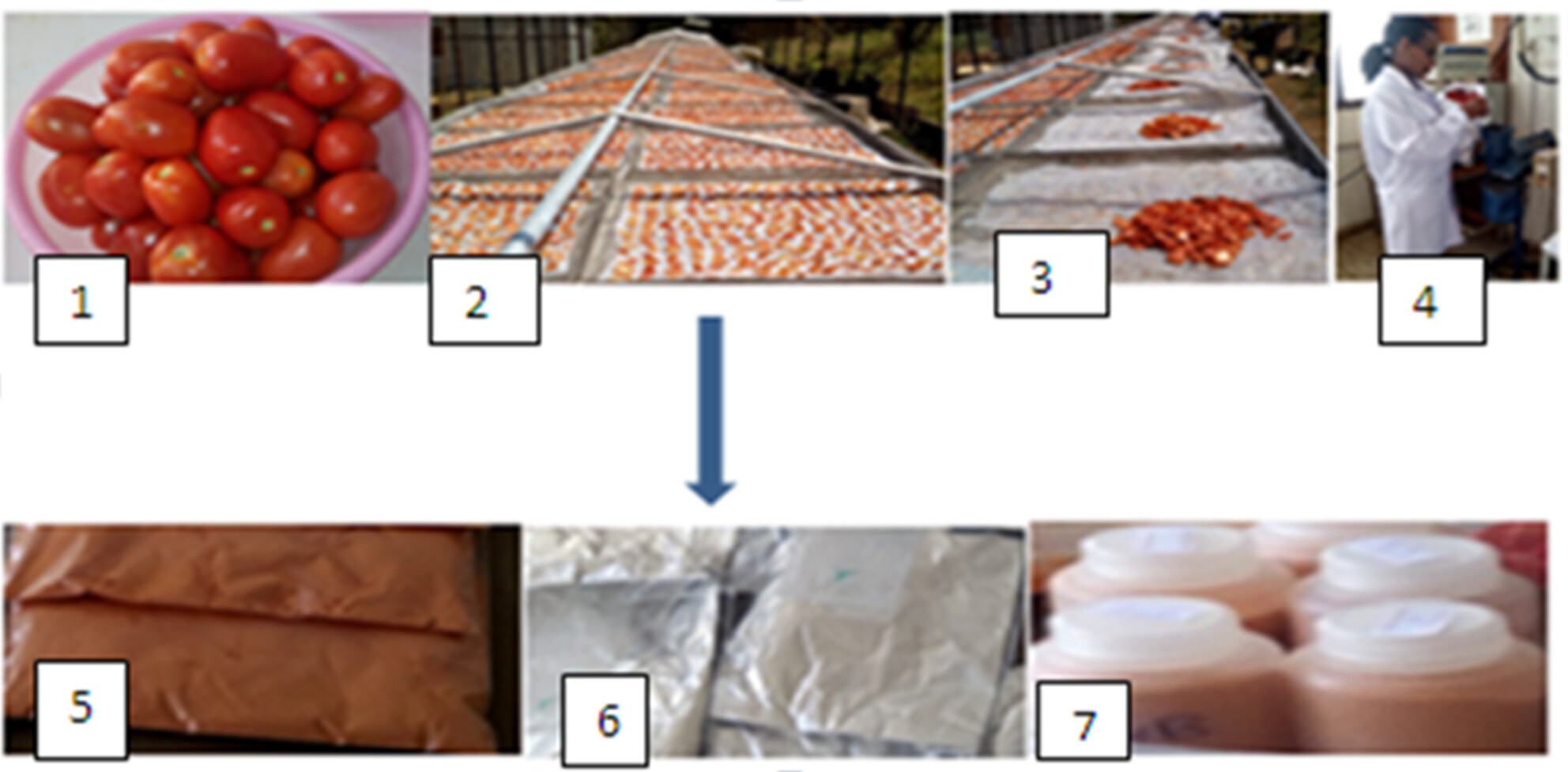
Effect of packaging materials on lycopene vitamin C and water activity of dried tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) powder during storage
- Pages: 6223-6230
- First Published: 11 July 2023
Physicochemical, sensory, and antioxidant characteristics of stirred-type yogurt enriched with Lentinula edodes stipe powder
- Pages: 6231-6240
- First Published: 19 July 2023
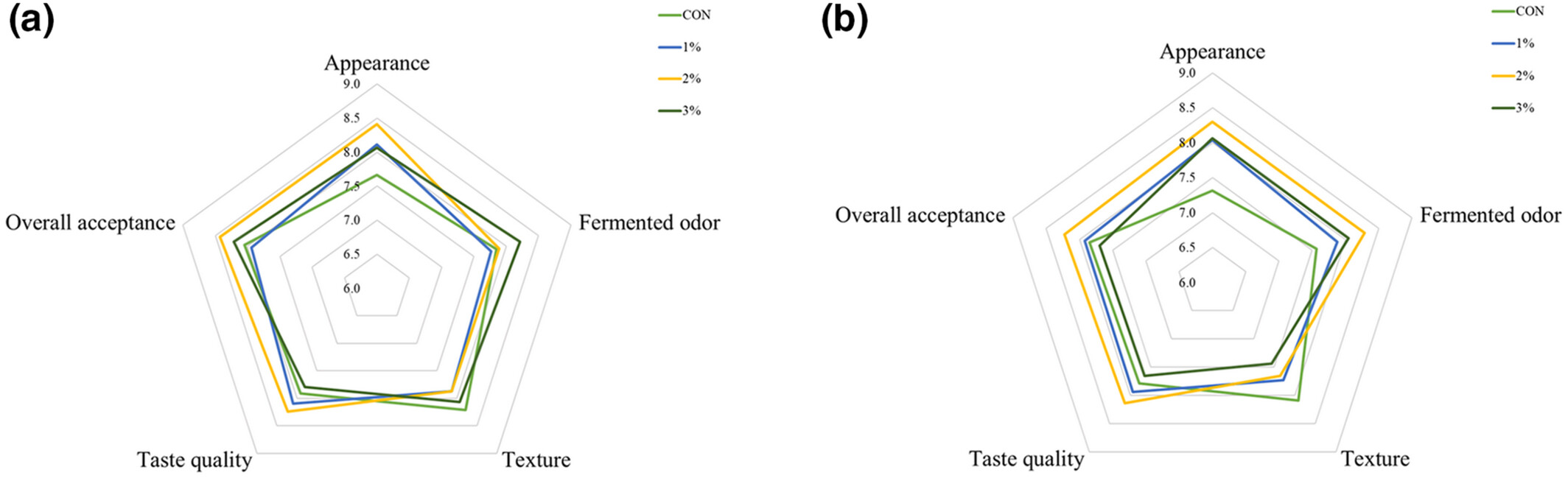
According to the methodical examination of the physicochemical, sensory, and antioxidant properties of flavored yogurts which fortified with different amounts of Lentinula edodes stipe (LES), we found that the LES was beneficial to improve some physicochemical (pH, viable lactic acid bacteria density, and syneresis) and sensory properties (fermented odor and taste quality), and the antioxidant activity (ABTS and DPPH radical scavenging activity) of the plain yogurt, which has the potential to be used in functional yogurt. The results above were also helpful for the rational utilization of LES toward value-added products.
Contribution to the improvement of the nutritional and functional properties of bread by incorporating cinnamon powder (Cinnamomum verum)
- Pages: 6241-6248
- First Published: 13 July 2023
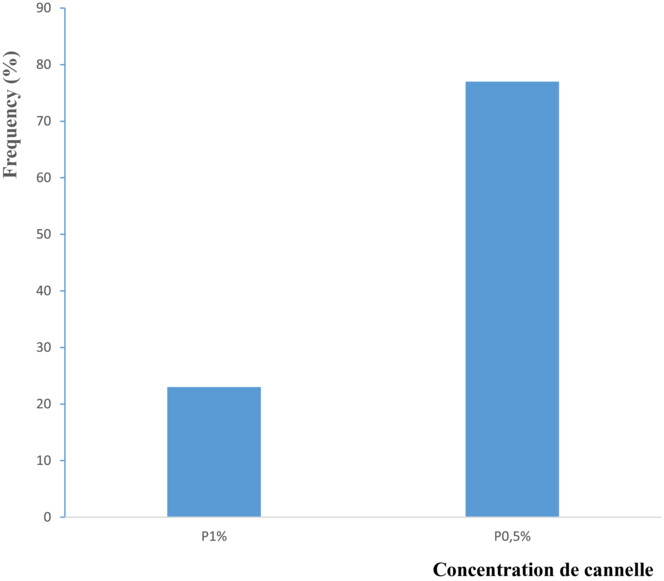
This study has demonstrated the influence of the incorporation of 0.5% and 1% of cinnamon powder in bread. From the organoleptic point of view, the bread with 0.5% cinnamon was more appreciated by the panelists than the bread with 1% cinnamon. Cinnamon has, therefore, a good nutritional potential to be used in the food industry and to develop new products.
Building deep learning and traditional chemometric models based on Fourier transform mid-infrared spectroscopy: Identification of wild and cultivated Gastrodia elata
- Pages: 6249-6259
- First Published: 11 July 2023
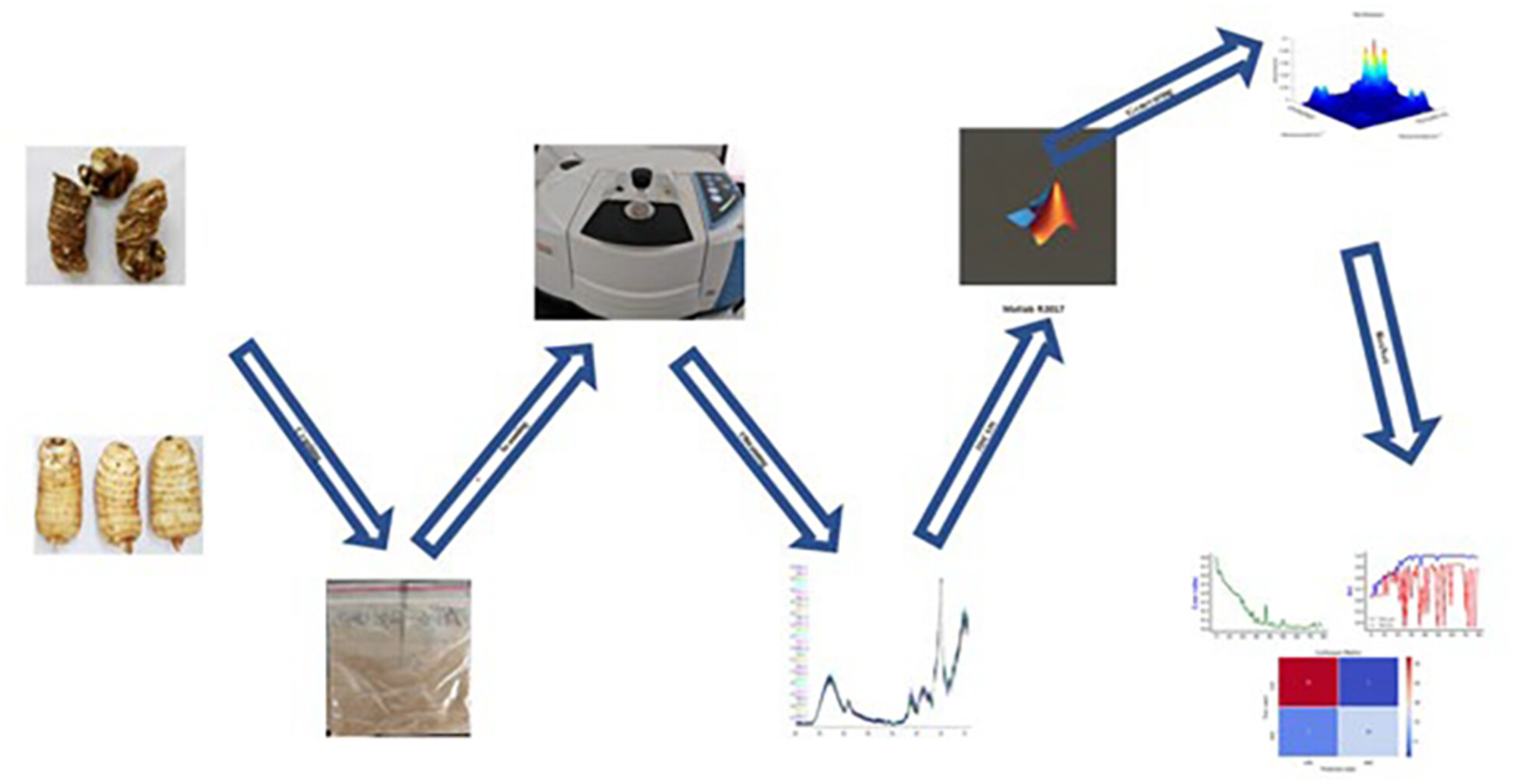
To identify wild and cultivated Gastrodia elata quickly and accurately, this study is the first to apply three-dimensional correlation spectroscopy (3DCOS) images combined with deep learning models to the identification of G. elata. The results concluded that the deep learning model is more effective than the traditional chemometric model and has greater potential for application in the identification of wild and cultivated G. elata.
Improving the textural and microstructural quality of cow meat by black chokeberry, grape, and hawthorn vinegar-based marination
- Pages: 6260-6270
- First Published: 17 July 2023
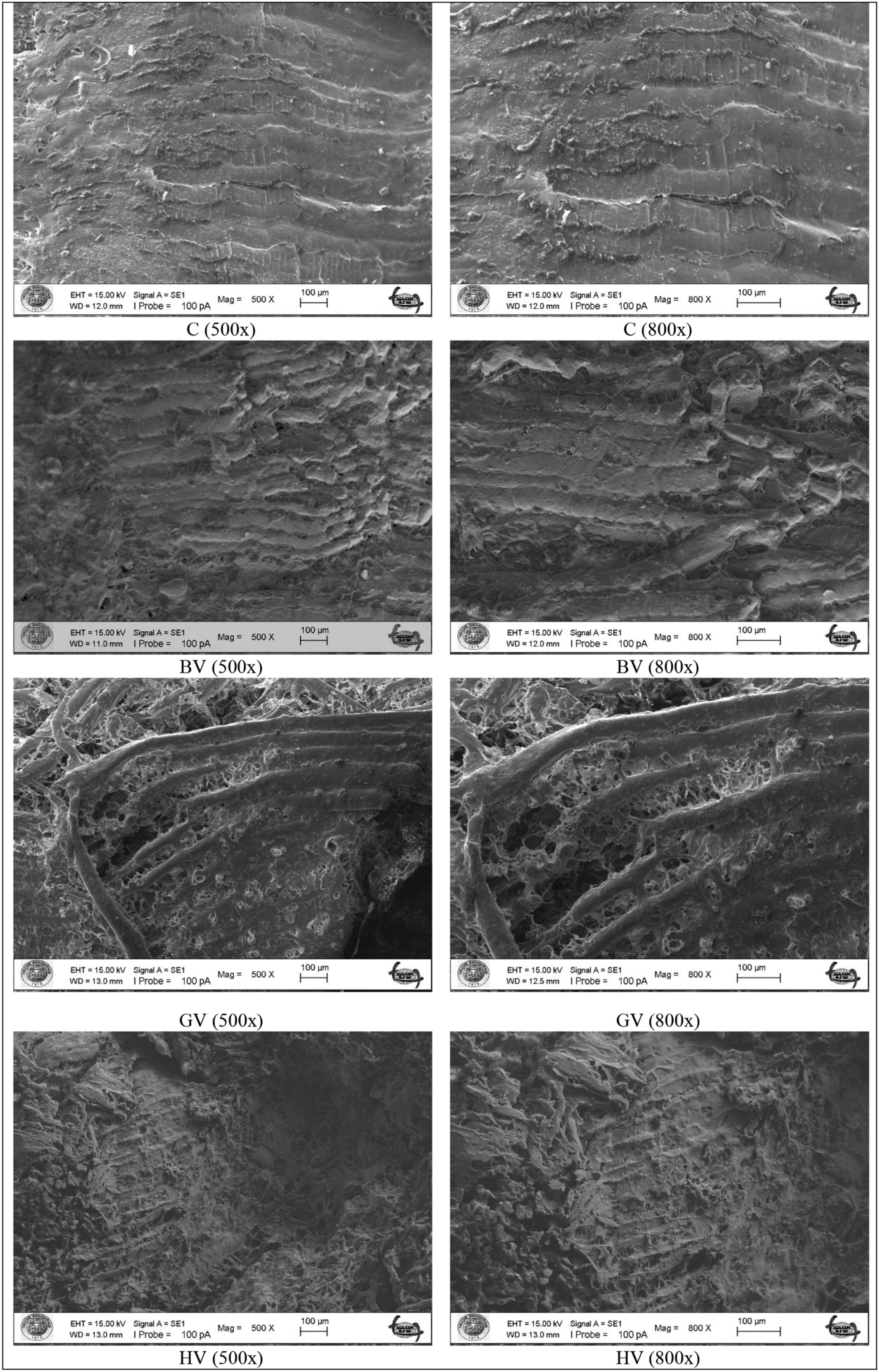
In this study, the effects of black chokeberry, grape, and hawthorn vinegars on the textural and technological properties of old cow meat were investigated. The results suggest that grape vinegar-based marinade may be a promising natural tenderizer to improve textural characteristics of tough meats.
Dioscoreae Rhizoma starch improves chronic diarrhea by regulating the gut microbiotas and fecal metabolome in rats
- Pages: 6271-6287
- First Published: 10 August 2023
Yam starch alleviated the symptoms of chronic diarrhea in rats, and its effect is better than that of the water extract and crude polysaccharides of yam; it improved intestinal injury of rats with chronic diarrhea; it increased the abundance and diversity of intestinal microbiotas in rats with chronic diarrhea and regulated the abnormal intestinal microbiotas; and it displayed a beneficial role by regulating phenylalanine, tyrosine, and tryptophan biosynthesis; tyrosine metabolism; vitamin B6 metabolism; and purine metabolism.
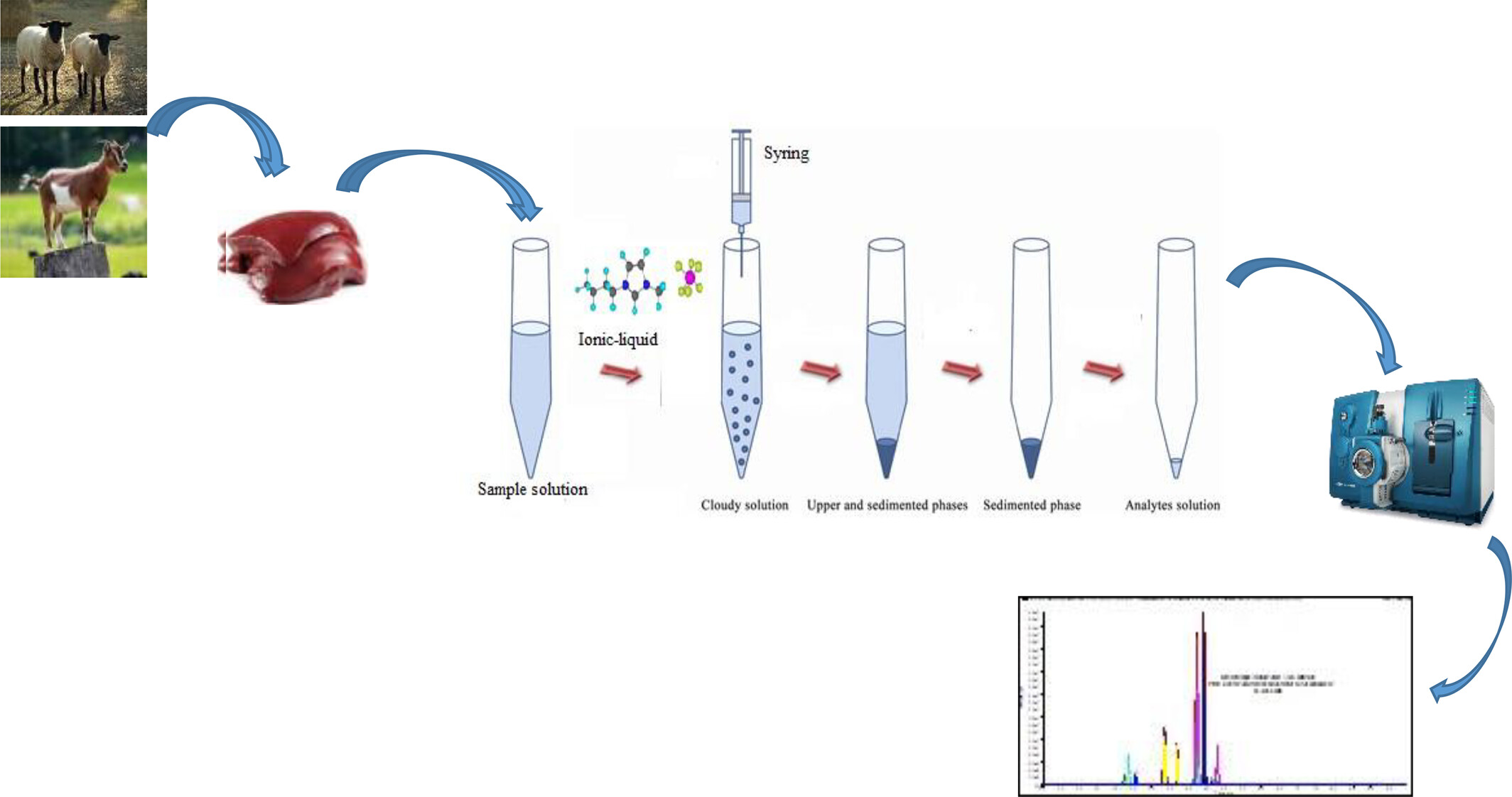
Ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of anthelmintic drug residues in small-stock meat followed by LC-ESI-MS/MS detection
- Pages: 6288-6302
- First Published: 22 July 2023
Investigation of the antimicrobial, antioxidant, hemolytic, and thrombolytic activities of Camellia sinensis, Thymus vulgaris, and Zanthoxylum armatum ethanolic and methanolic extracts
- Pages: 6303-6311
- First Published: 24 July 2023
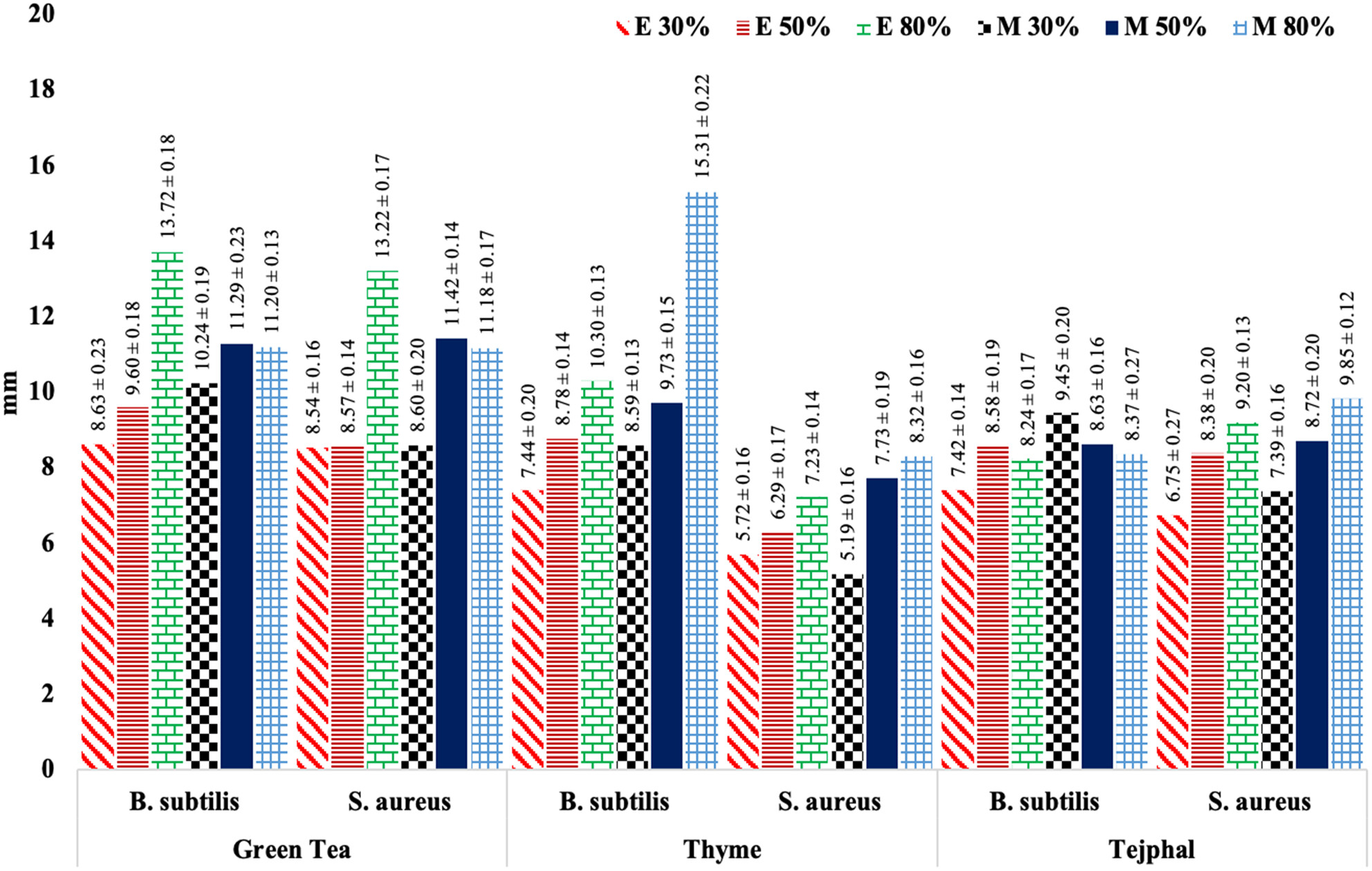
The antibacterial, antifungal, biofilm inhibition, antioxidant, hemolytic and thrombolytic activities of Camellia sinensis, Thymus vulgaris and Zanthoxylum armatum ethanol and methanol extracts at different concentrations were determined. This study has highlighted the significant antimicrobial, antioxidant, hemolytic and thrombolytic activities of Camellia sinensis, Thymus vulgaris and Zanthoxylum armatum extracts that could be beneficial to treat various diseases (cancer, diabetes and respiratory diseases) and may be utilized as functional ingredient in preparation of functional foods and drinks.
Pharmacological effect of Argyrolobium roseum (Camb.) Jaub & Spach extracts against lead-induced toxicity in rats
- Pages: 6312-6323
- First Published: 24 July 2023
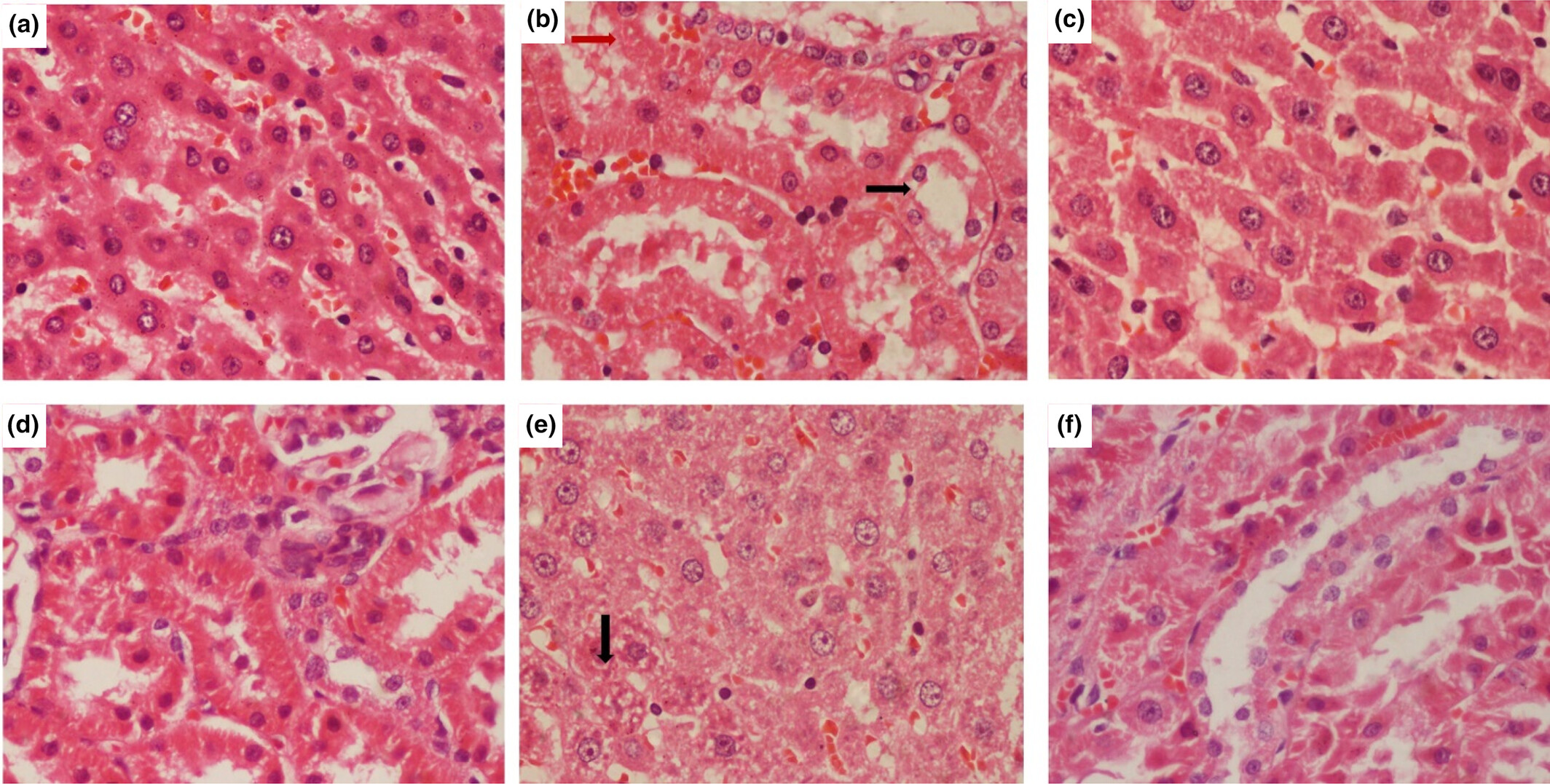
The current study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic effect of aqueous and ethanolic extracts of Argyrolobium roseum (Camb.) Jaub & Spach against Pb-induced toxicity in rats. The findings of this study show that Pb inductions damage the kidney and liver tissues, and caused severe oxidative damage and functional disturbance due to accumulation in these organs of rats.
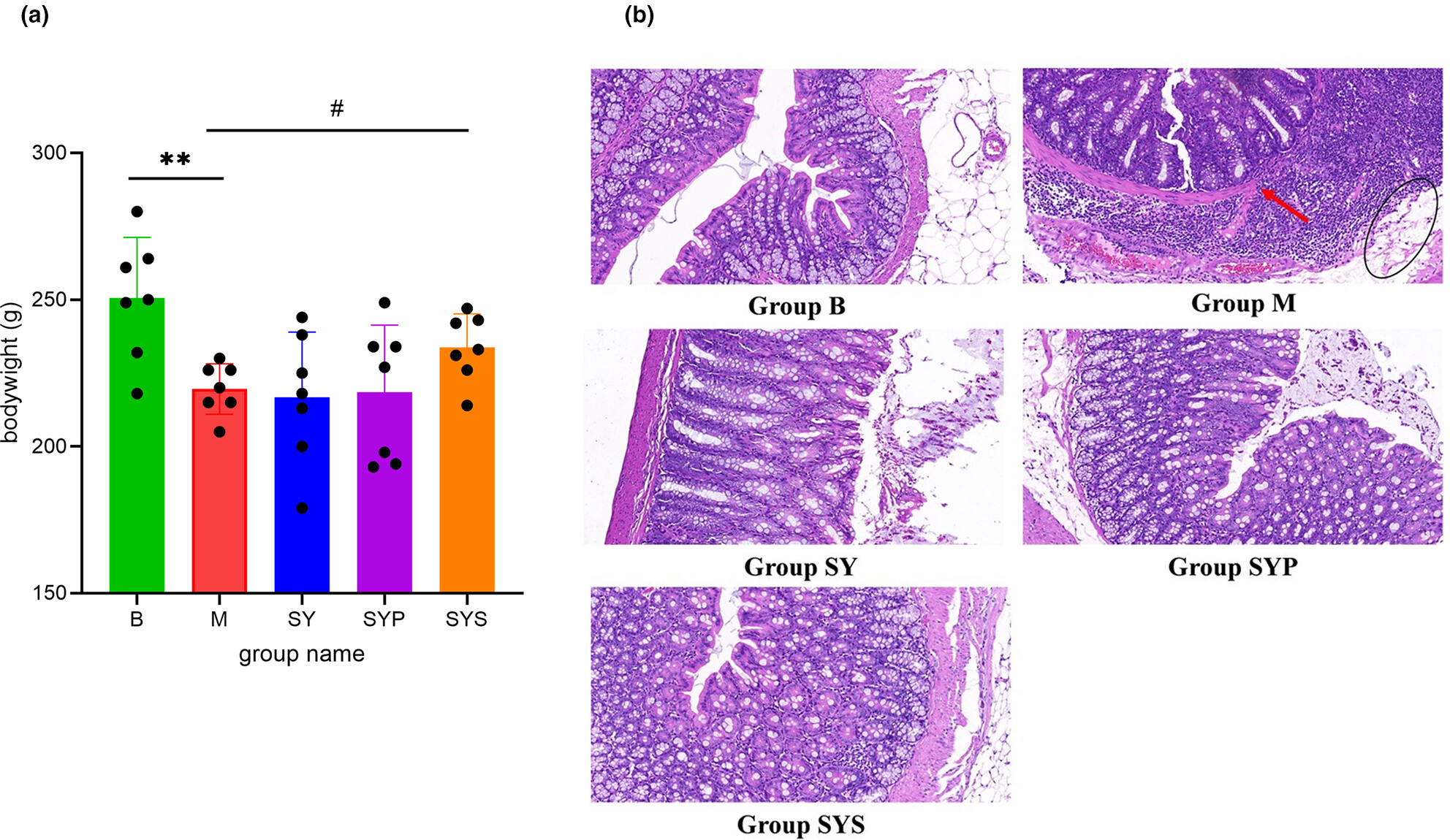
Effects of isoflavone and probiotic intake on calcium transport and bone metabolism biomarkers in female rats
- Pages: 6324-6335
- First Published: 23 July 2023
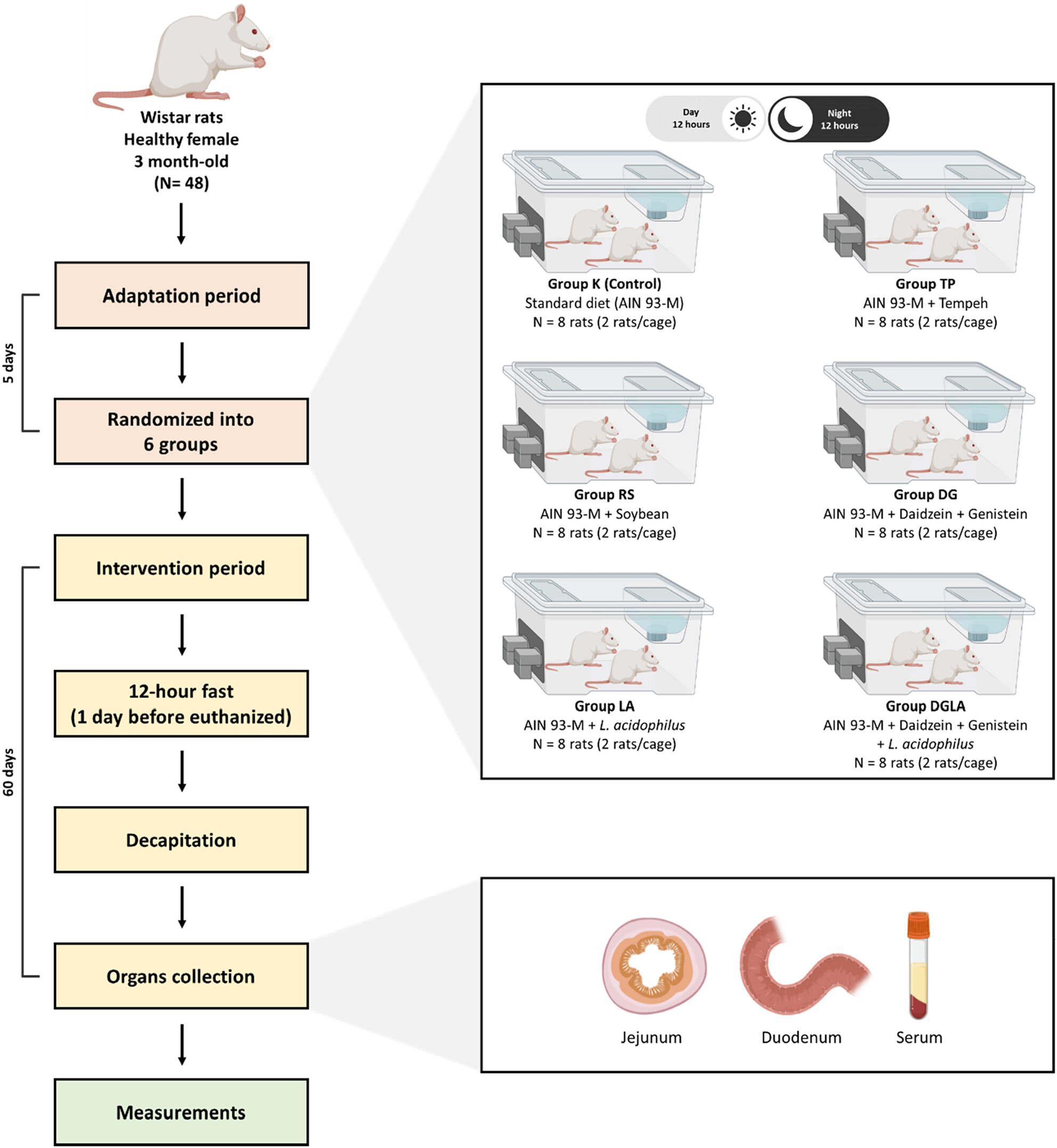
This study investigated the effects of isoflavones and probiotics on calcium transport and bone metabolism in female rats. The results showed that daidzein and genistein improved calcium transport in the duodenum and reduced pyridinoline serum concentrations, while tempeh and soybean diets reduced calcium transport in the jejunum. However, no synergistic effect of the combination of daidzein, genistein, and L. acidophilus on calcium transport and bone metabolism was observed.
Lipidomic analyses of five Carya illinoinensis cultivars
- Pages: 6336-6348
- First Published: 31 July 2023
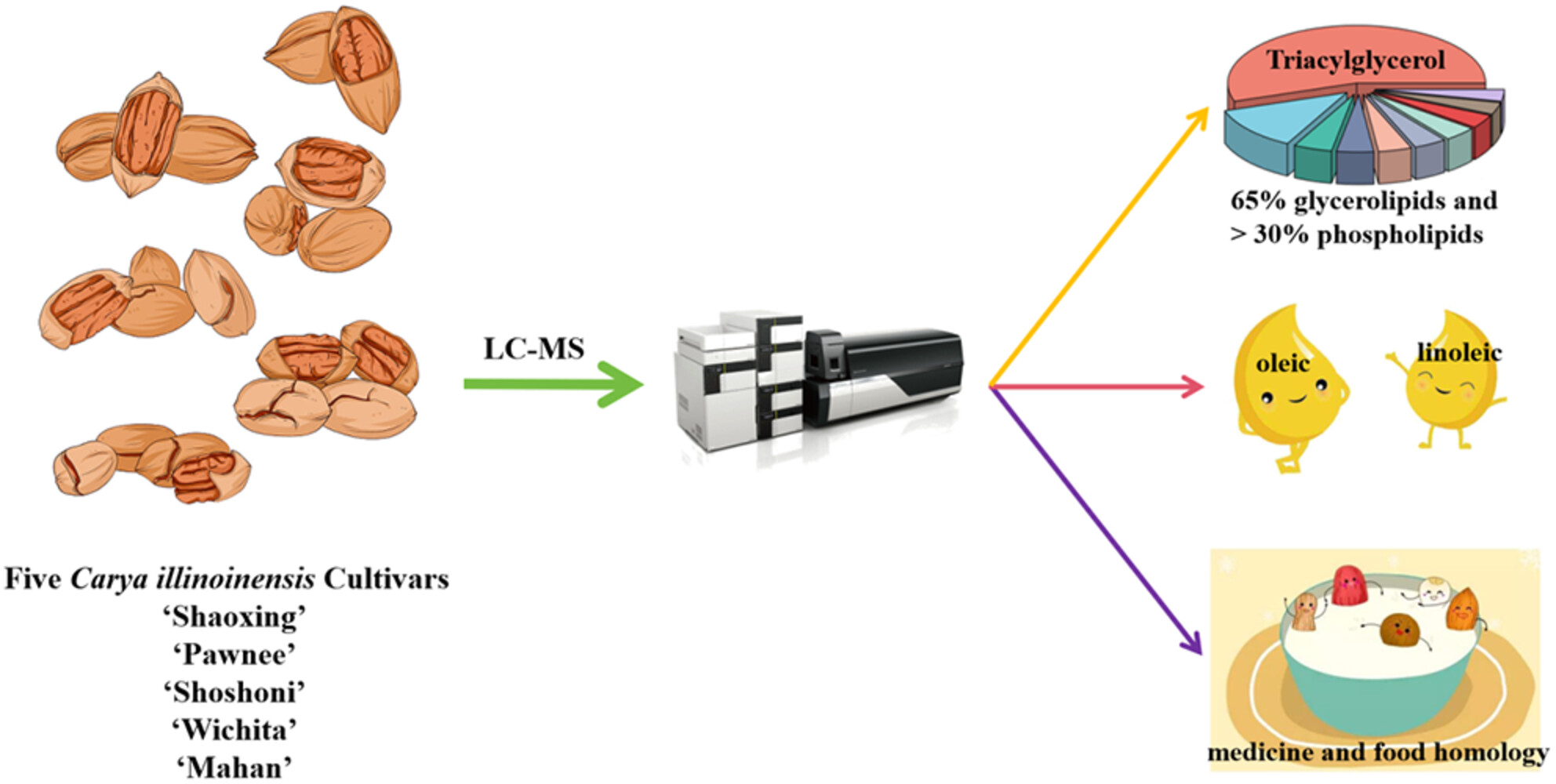
Carya illinoinensis (Wangenh.) K. Koch, nuts are a renowned health food. However, there are many cultivars of this nut tree, and their mature kernel lipid composition has not been thoroughly studied. Therefore, we used liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS) to analyze the lipid composition of mature nuts of five C. illinoinensis cultivars. In the mature kernels of all cultivars, there were 58 lipid types which were mainly composed of glycerolipids (c. 65%) and phospholipids (>30%). TG accounted for the largest proportion of mature nuts of all cultivars, exceeding 50%; and DG, Cer, PC, and PE were also relatively high. Additionally, nuts contain fatty acids, mainly oleic, linoleic, and linolenic acids. Our research provides a new perspective for the processing and utilization of plant and edible oils, and for the use of C. illinoinensis kernels in the development of medicine and food science.
Association between empirical dietary inflammatory index, odds, and severity of anxiety disorders: A case–control study
- Pages: 6349-6359
- First Published: 27 July 2023
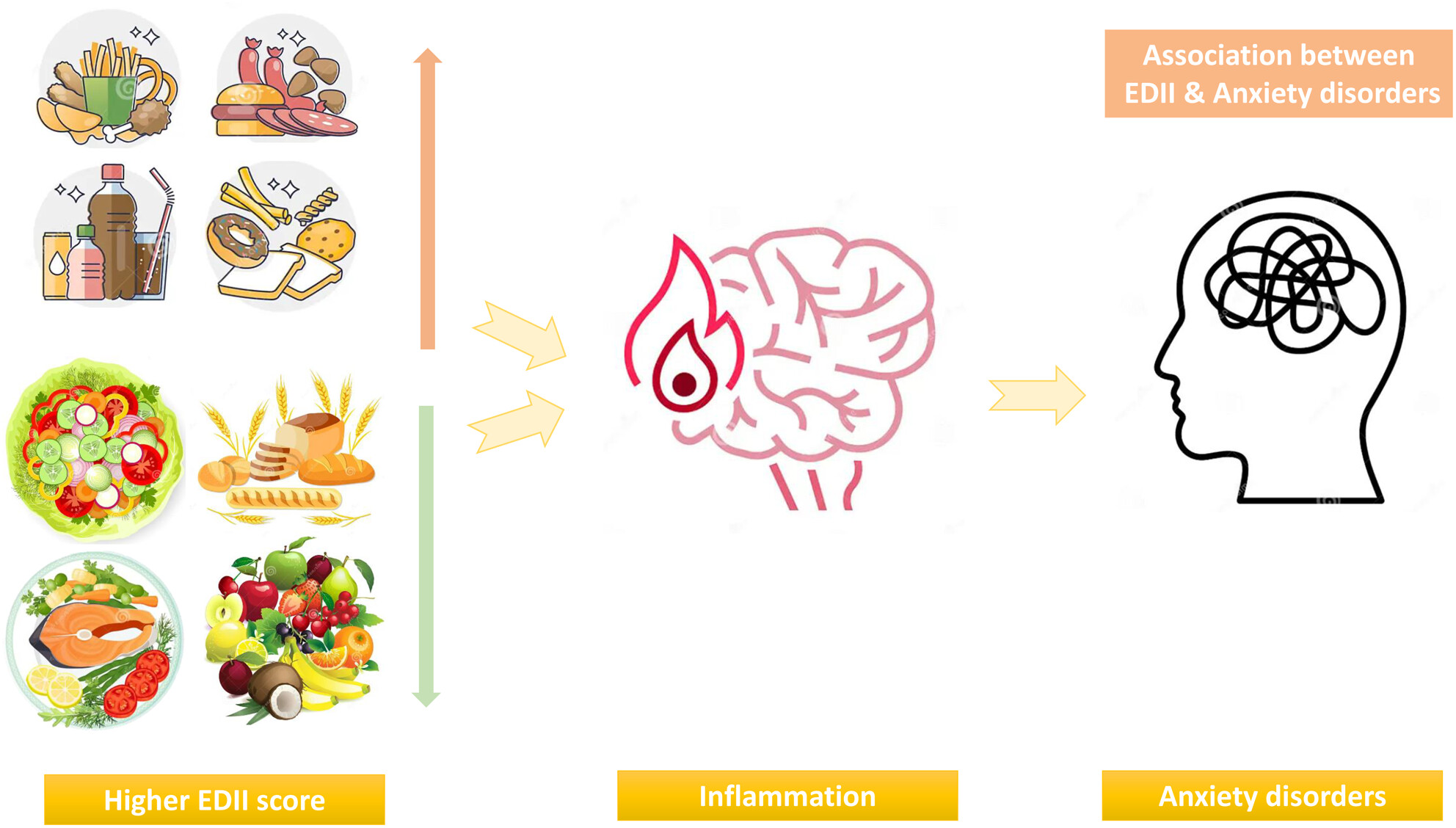
Diet may be a modifiable factor in the prevention of psychiatric disorders by modulating inflammation. We observed that after adjusting for confounders, individuals in the top category of EDII score were 2.09 fold more likely to have AD compared with those in the bottom category. Also, higher EDII contributed to a higher GAD-7 score.
Fabrication of green colorimetric smart packaging based on basil seed gum/chitosan/red cabbage anthocyanin for real-time monitoring of fish freshness
- Pages: 6360-6375
- First Published: 23 July 2023
Smart films based on basil seed gum/chitosan/red cabbage anthocyanin (RCA) fabricated. RCA concentration significantly affected the antioxidant activity of composite films. Ten-percent RCA indicated obvious color changes against different pH and ammonia gas levels. Fabricated smart films successfully monitored fish freshness during the storage time.
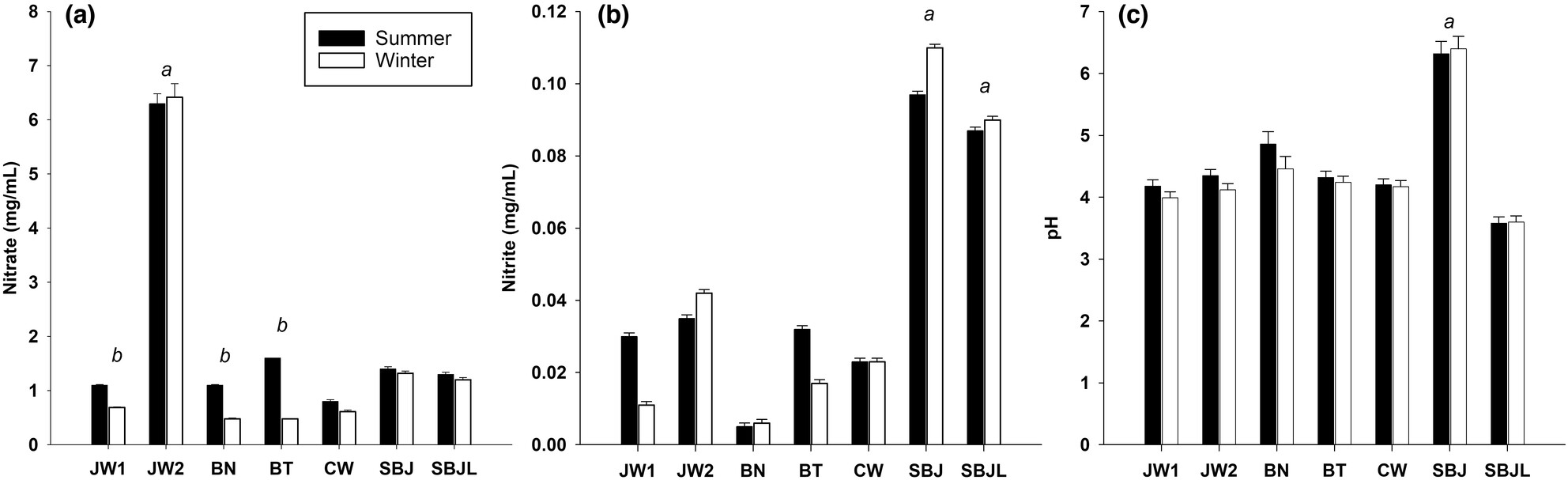
Content of nitrate and nitrite in commercial and self-made beetroot juices and the effect of storage temperature
- Pages: 6376-6383
- First Published: 23 July 2023
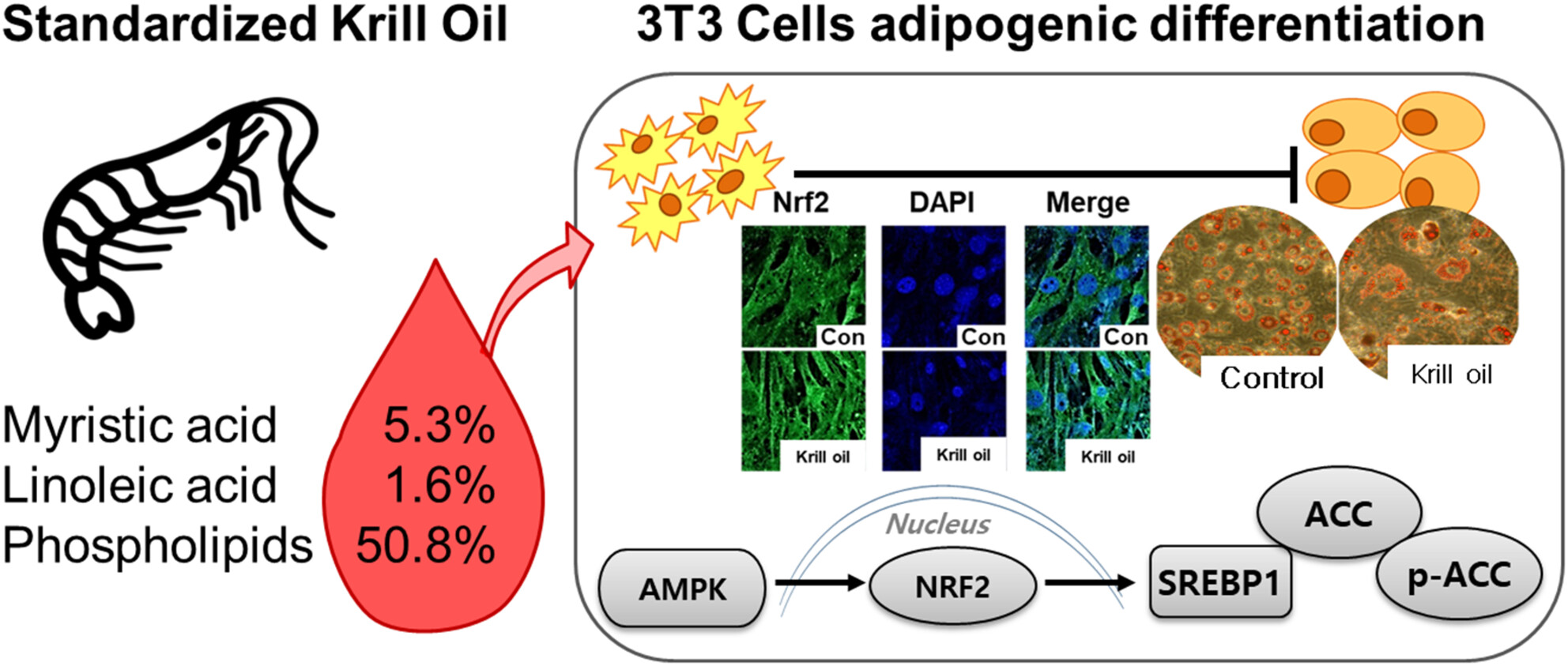
Krill oil inhibited adipogenic differentiation by inducing the nuclear Nrf2 expression and the AMPK activity
- Pages: 6384-6392
- First Published: 21 July 2023
Anticancer assessment and antibiofilm potential of Laetiporus sulphureus mushroom originated from Serbia
- Pages: 6393-6402
- First Published: 30 July 2023
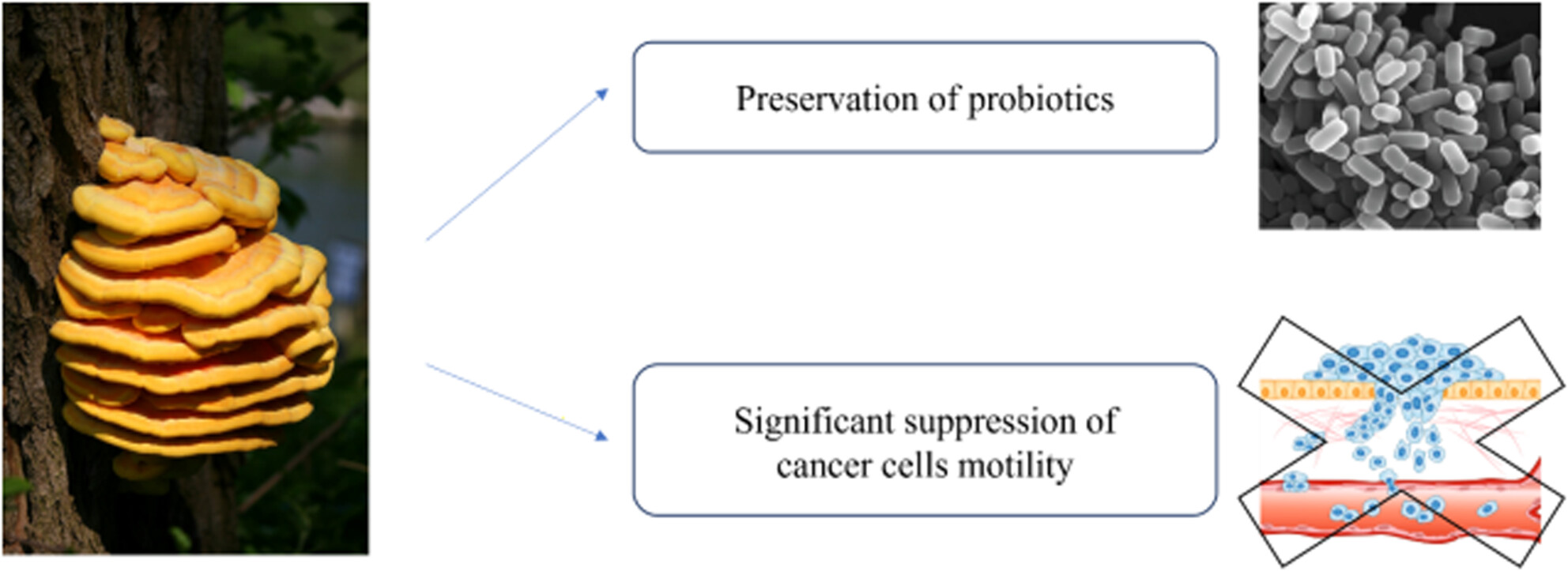
Rosmarinic acid is the main component in Laetiporus sulphureus ethanolic extract. Prooxidative and antimigratory effects were observed on tested cancer cells. Low doses of our extract showed promising results on tested model systems regarding significant antimigratory capacity for cancer cells without effect on planktonic and probiotic cultures in biofilm.
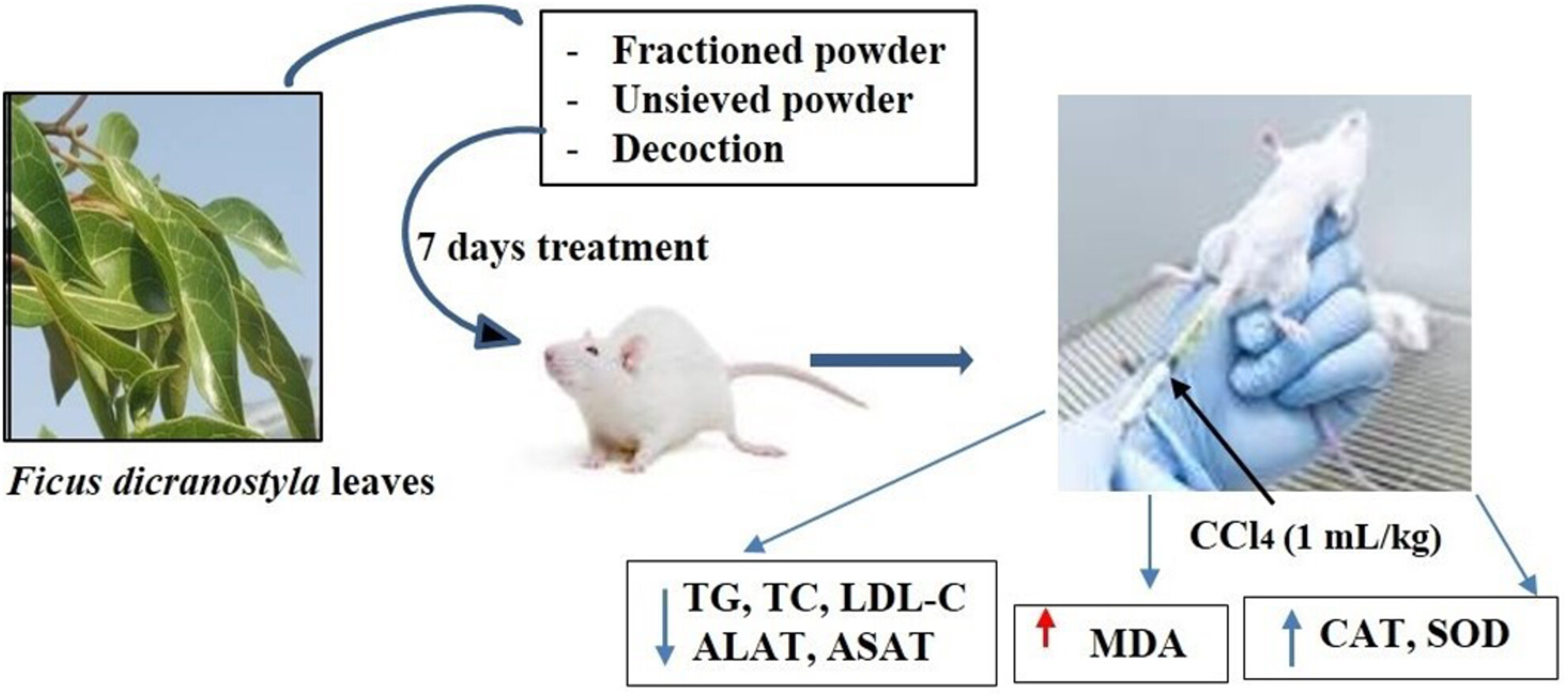
Hepatoprotective and in vivo antioxidant effects of granulometric classes and decoction of Ficus dicranostyla Mildbread leaves powders against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity in Wistar rats
- Pages: 6403-6412
- First Published: 23 August 2023
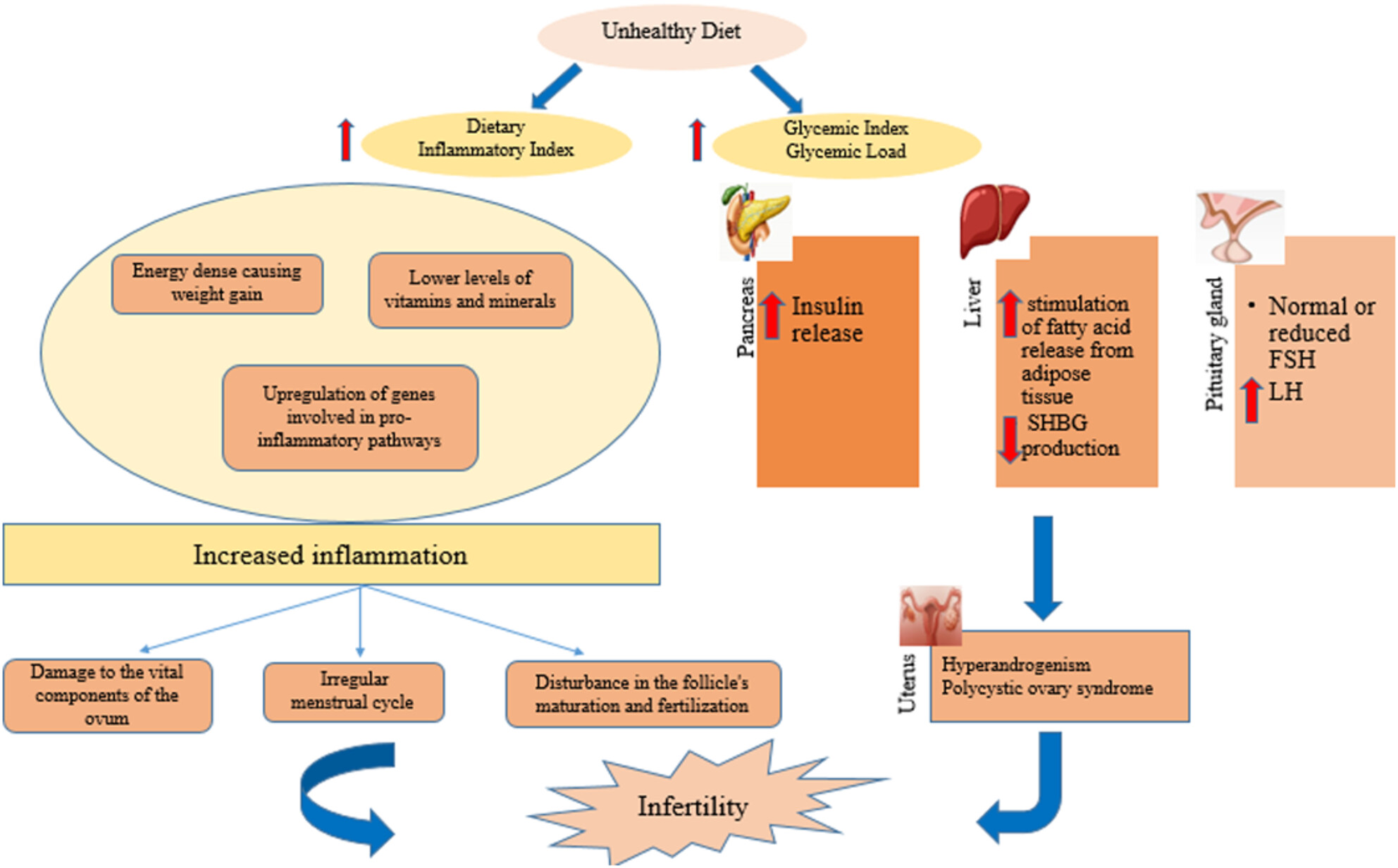
Glycemic index, glycemic load, dietary inflammatory index, and risk of infertility in women
- Pages: 6413-6424
- First Published: 09 August 2023
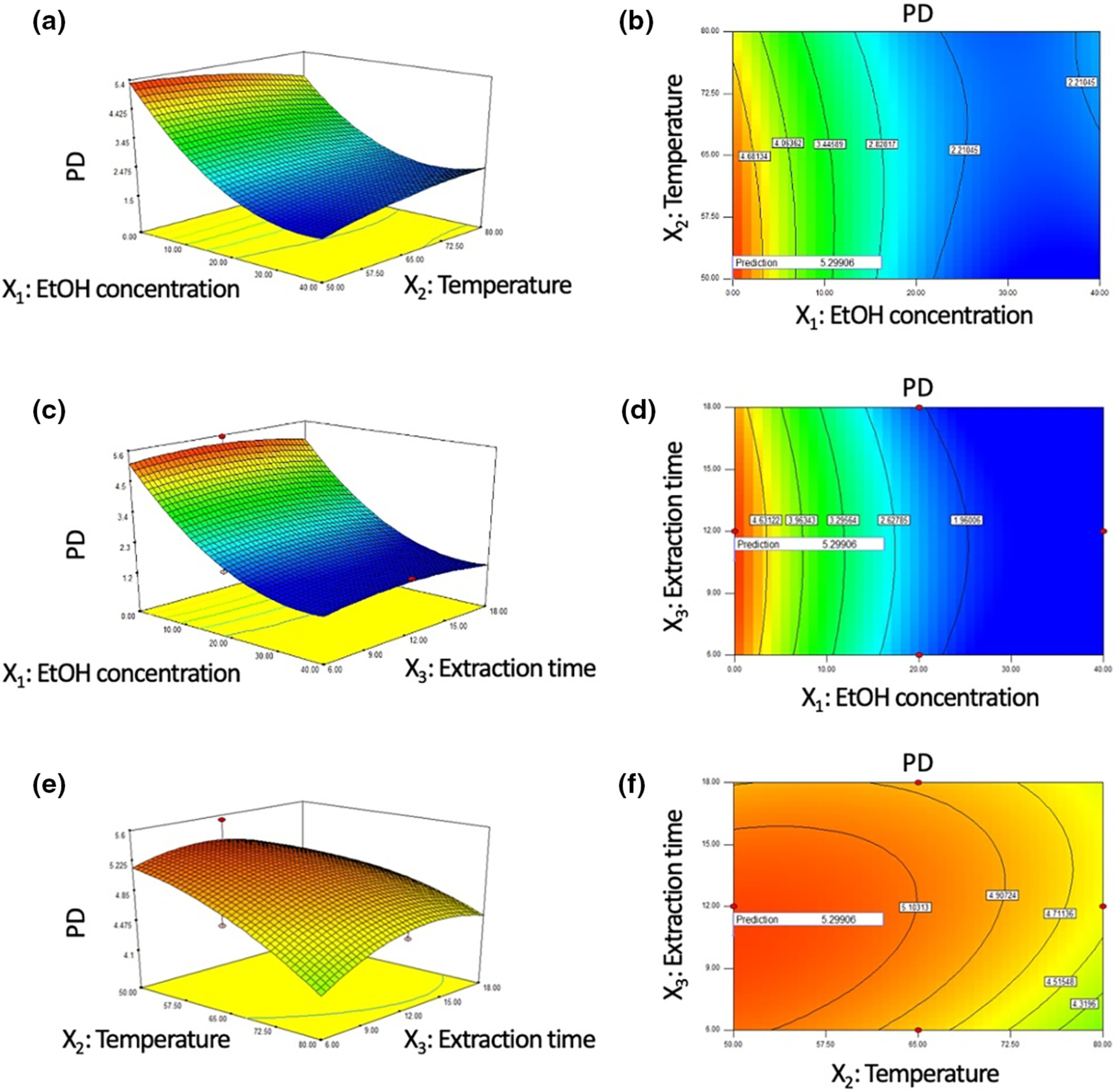
Optimization of extraction condition for platycodin D from Platycodon grandiflorum root and verification of its biological activity
- Pages: 6425-6434
- First Published: 30 July 2023
Mineral composition, the profile of phenolic compounds, organic acids, sugar and in vitro antioxidant capacity, and antimicrobial activity of organic extracts of Juniperus drupacea fruits
- Pages: 6435-6446
- First Published: 30 July 2023
This study was carried out to evaluate the phenolic components, organic acid, sugar, and macro- and micromineral distributions of methanol, and water extracts of Juniperus drupacea fruit, as well as their antioxidant and antimicrobial potential. Among the individual phenolic compounds, catechin, a flavonoid that was the highest in both extractions, was determined as 300.49 μg/g in methanol extract and 314.88 μg/g in water extract. DPPH scavenging activity was higher in methanol extracts. While the methanol extract of J. drupacea had no-inhibitory effect on the gram-negative bacteria tested, it exhibited a strong inhibition on the gram-positive bacteria Listeria innocua, Listeria.
Food safety knowledge among 7th-grade middle school students: A report of a Brazilian municipal school using workshop-based educational strategies
- Pages: 6447-6458
- First Published: 06 August 2023
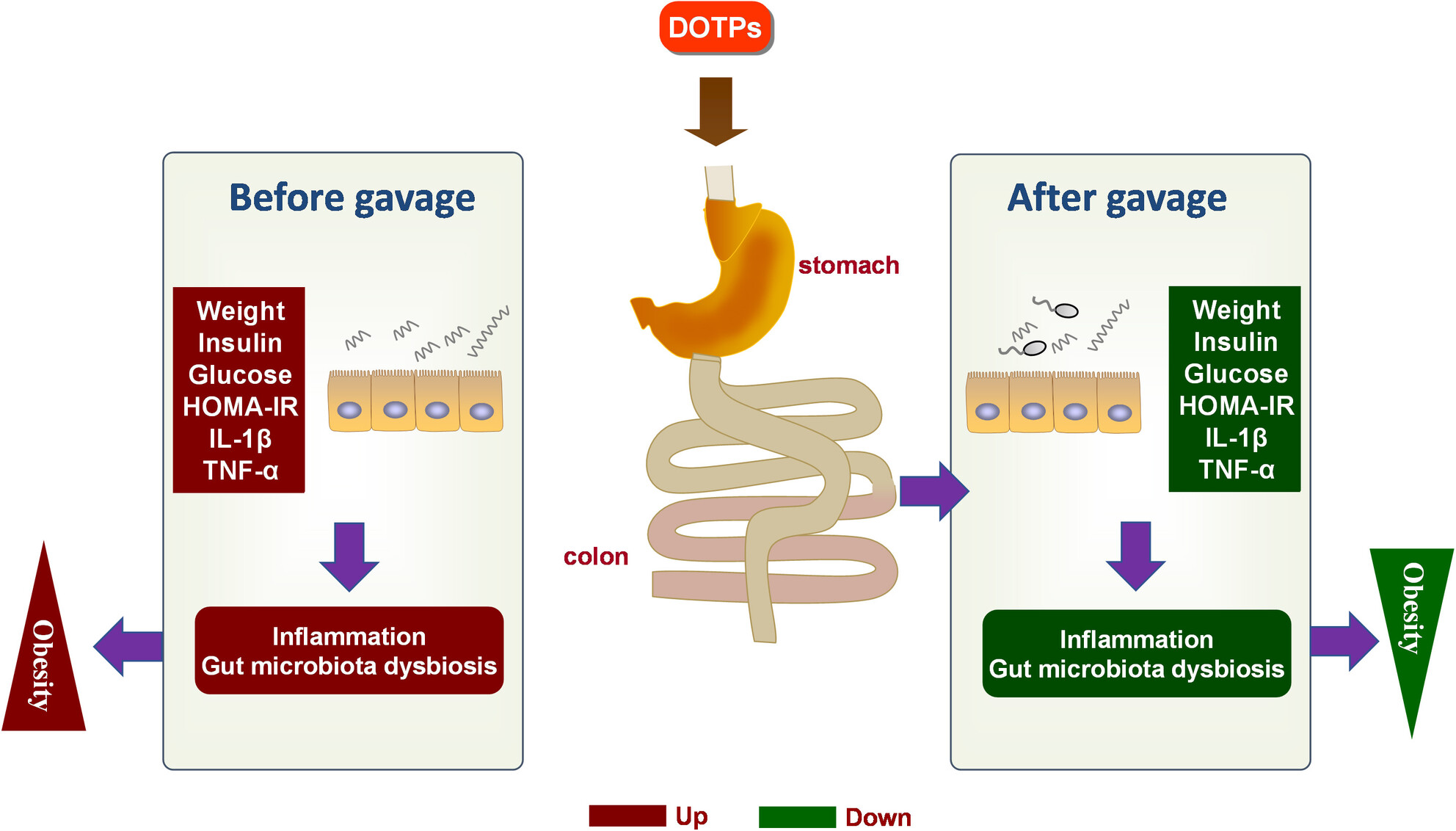
Anti-obesity effects exerted by Dioscorea opposita Thunb. polysaccharides in diet-induced obese mice
- Pages: 6459-6469
- First Published: 06 August 2023
Oyster-derived dipeptides RI, IR, and VR promote testosterone synthesis by reducing oxidative stress in TM3 cells
- Pages: 6470-6482
- First Published: 06 August 2023
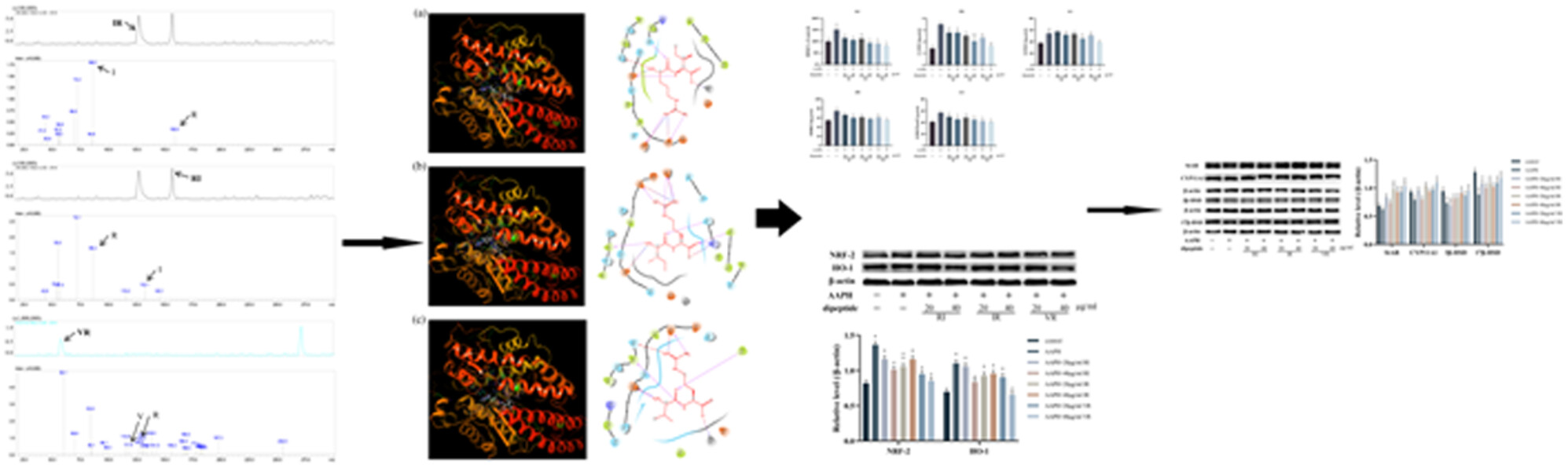
This study reports on three oyster-derived dipeptides with antioxidant activity, RI, IR, and VR. The results of this study suggest that these dipeptides may promote testosterone biosynthesis by alleviating oxidative stress in TM3 cells, thereby increasing the expression of critical enzymes in the testosterone synthesis pathway. In addition, these three dipeptides may alleviate the oxidative stress state of cells by directly scavenging excess ROS from cells rather than increasing the activity of antioxidant enzymes in cells.
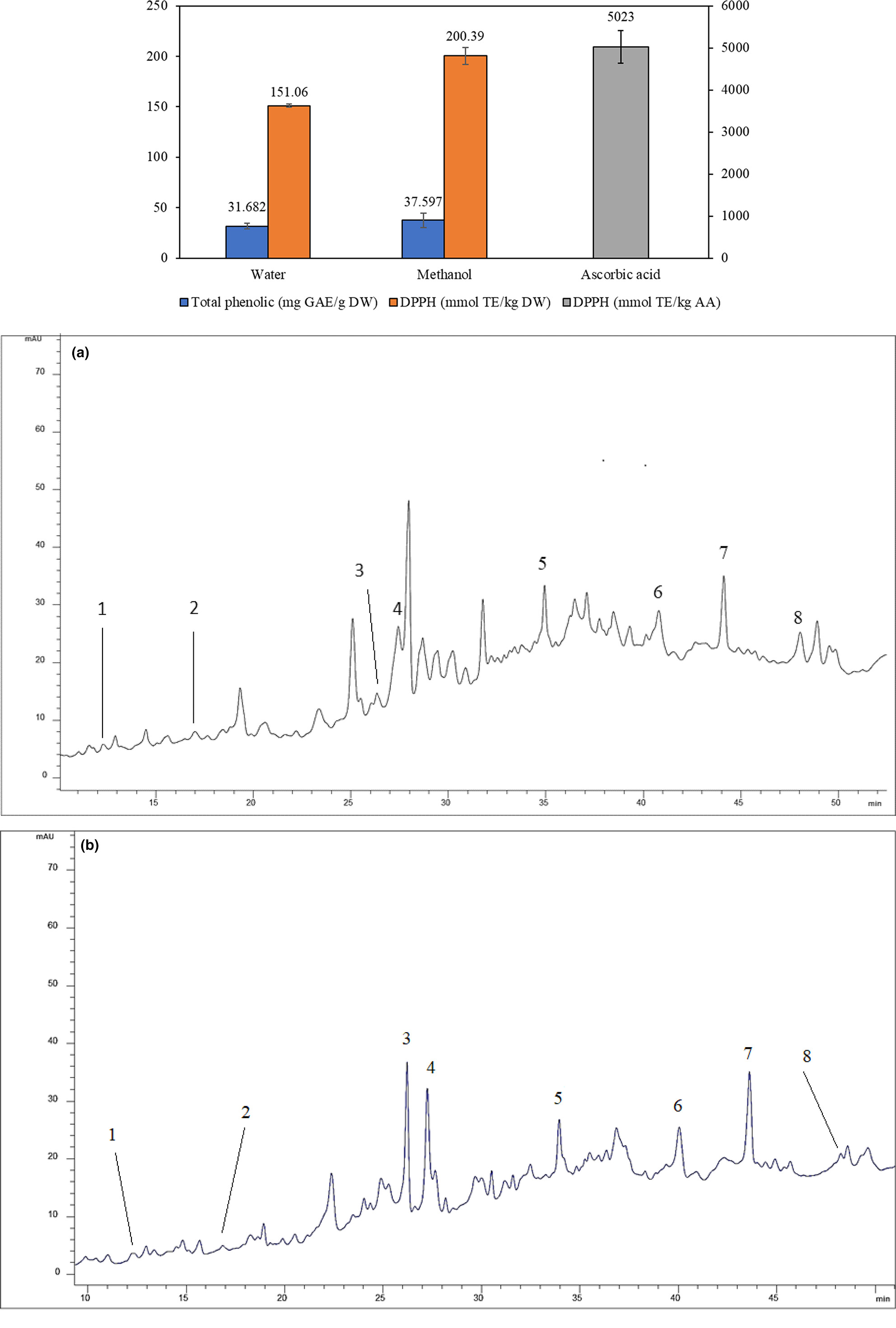
The combined anticancer of peanut skin procyanidins and resveratrol to CACO-2 colorectal cancer cells
- Pages: 6483-6497
- First Published: 03 August 2023
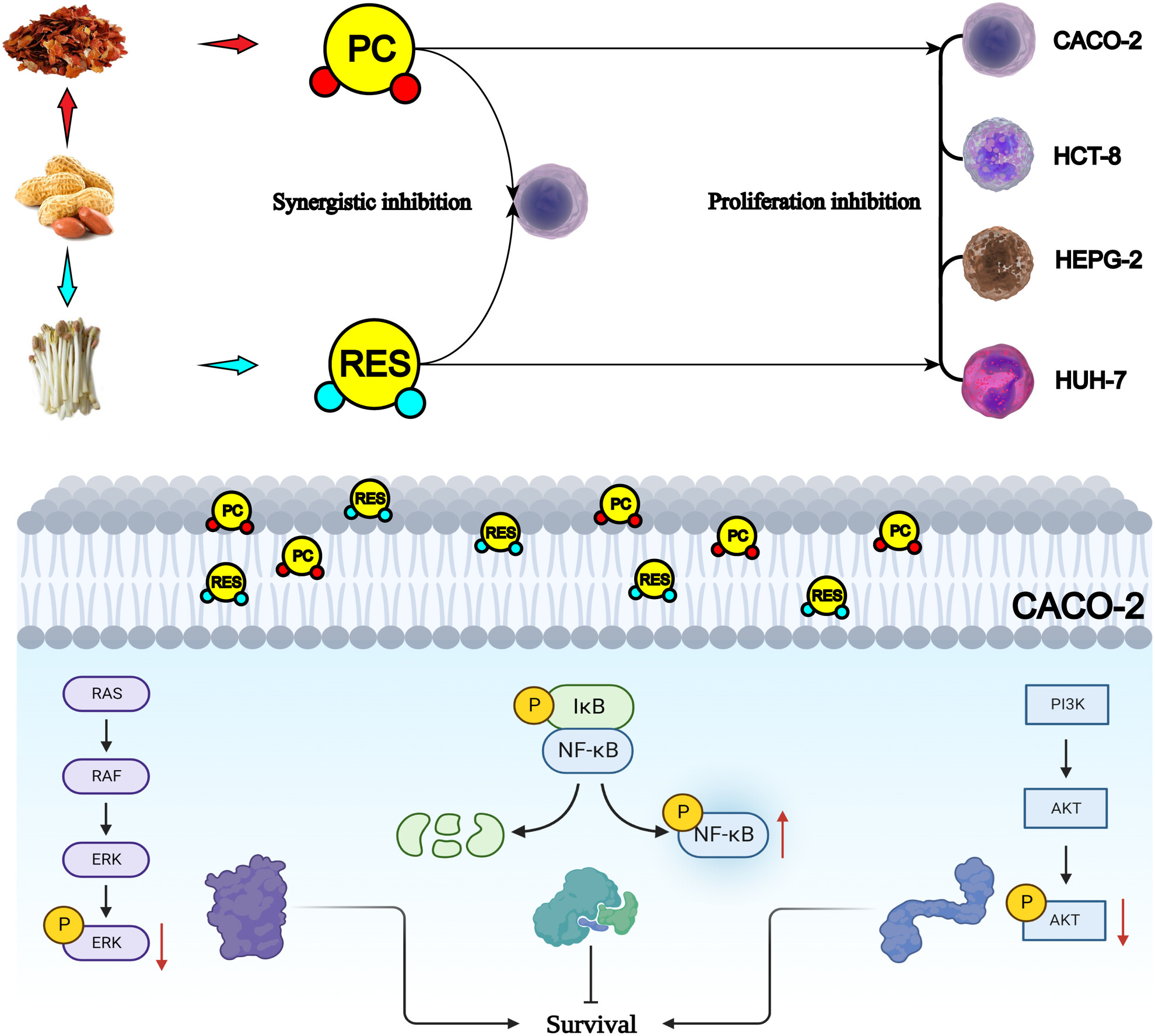
In the present study, the synergistic anticancer potential of procyanidins (PC) and resveratrol (RES) extracted from peanut skin and peanut buds, respectively, was investigated, when applied in combination. CACO-2 and HCT-8 cells as colorectal cancer models and HEPG-2 and HUH-7 cells as liver cancer models were used to observe the effects of PC and RES alone or in combination on the growth and proliferation of these four types of cancer cells.
Effects of superfine grinding sweet potato leaf powders on physicochemical and structure properties of sweet potato starch noodles
- Pages: 6498-6508
- First Published: 02 August 2023
A high-performance method for quantitation of aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, G2: Full validation for raisin, peanut matrices, and survey of related products at Ho Chi Minh City
- Pages: 6509-6521
- First Published: 15 August 2023
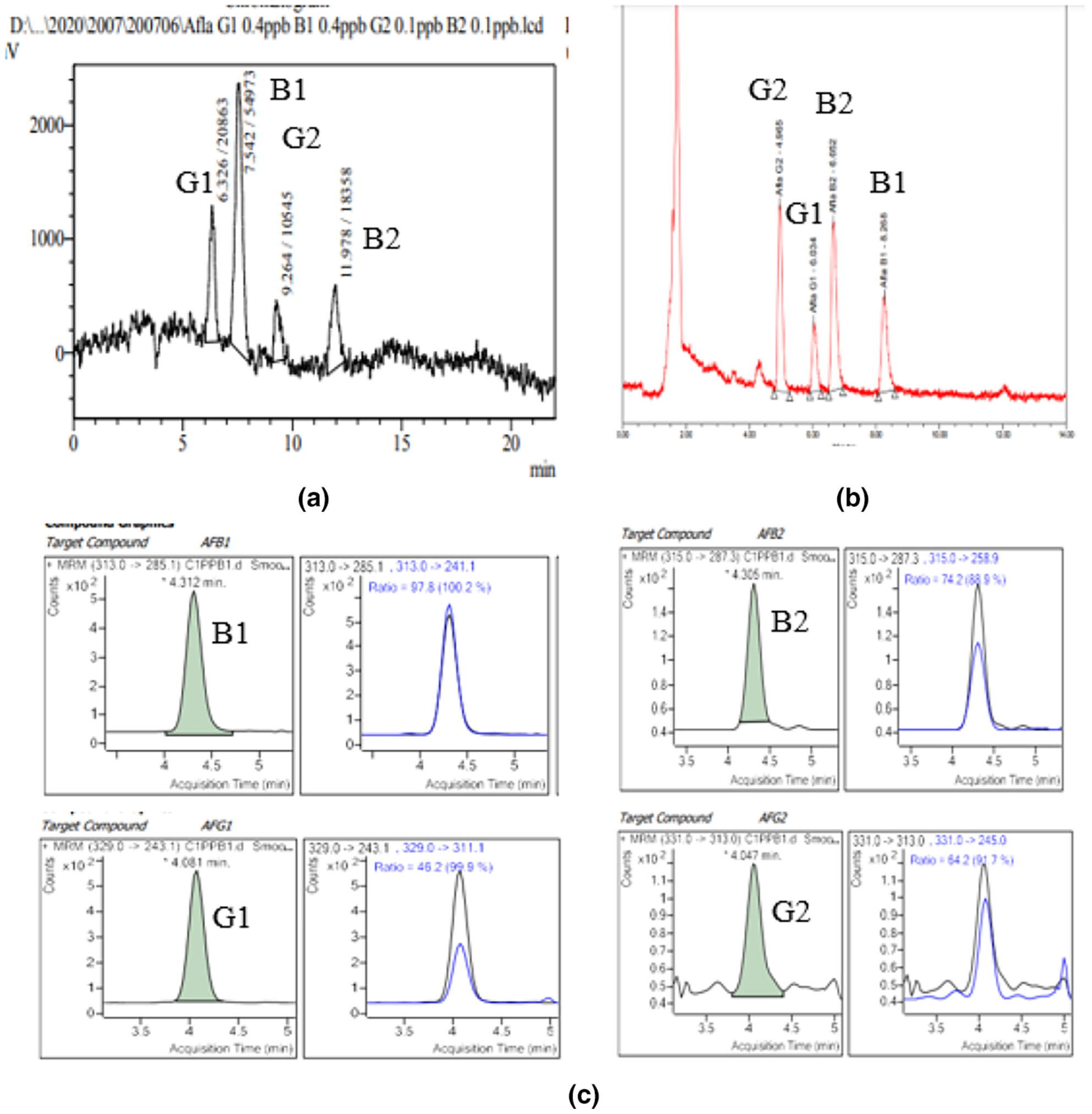
Optimization and validation for simultaneous quantitation of four aflatoxins B1, B2, G1, and G2 in peanuts and raisins were performed on ultra-performance liquid chromatography in a combination of fluorescence detector, without derivatization. And investigations of 350 peanut and raisin samples collected at Markets in the central districts of HCM city were done.
Evaluating the effect of food components on the digestion of dietary nucleic acids in human gastric juice in vitro
- Pages: 6522-6531
- First Published: 06 August 2023
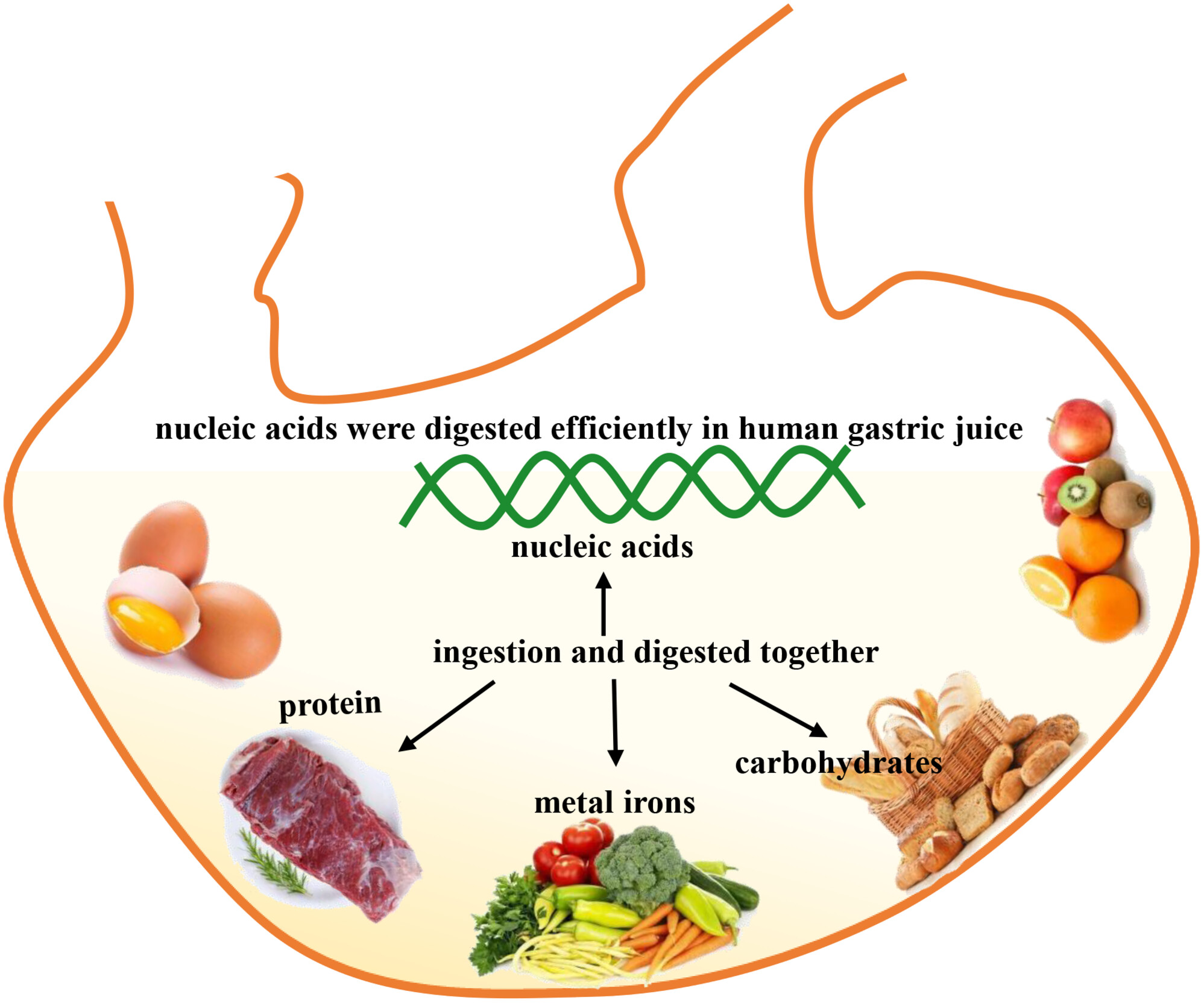
Long-stranded DNA was degraded efficiently in human gastric juice in vitro. Food components in the recommended dietary range levels had little effect on DNA digestion, and high concentration of divalent ion (e.g., Mg2+) could accelerate DNA digestion. Short-stranded DNA and miRNAs could not be degraded in human gastric juice in vitro.
Changes in flavor substances during the processing of boneless cold-eating rabbit meat
- Pages: 6532-6543
- First Published: 06 August 2023
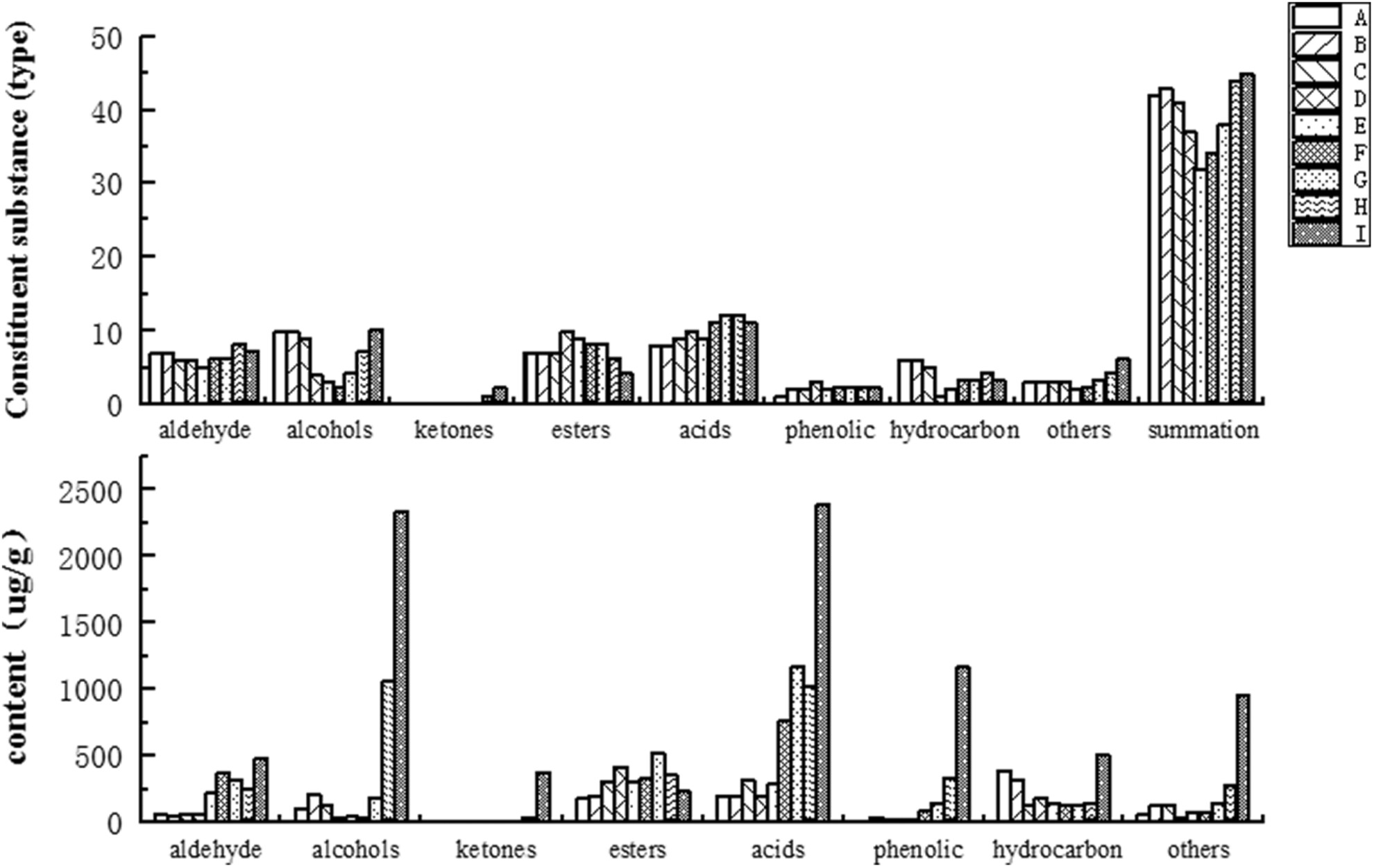
A total of 77 volatile flavors was detected. The types of volatile flavor substances were mainly alcohols, esters, and hydrocarbons that were transformed gradually into alcohols, acids, and others. Esters and acid compounds were the main flavor substances during the entire processing of cold-eating rabbits. The 15 min stage of frying was the pivotal point for boneless, cold-eating rabbits to produce volatile flavor substances.
Suckling or non-suckling? Sensory characterization of commercialized lamb meat according to feeding
- Pages: 6544-6559
- First Published: 25 August 2023
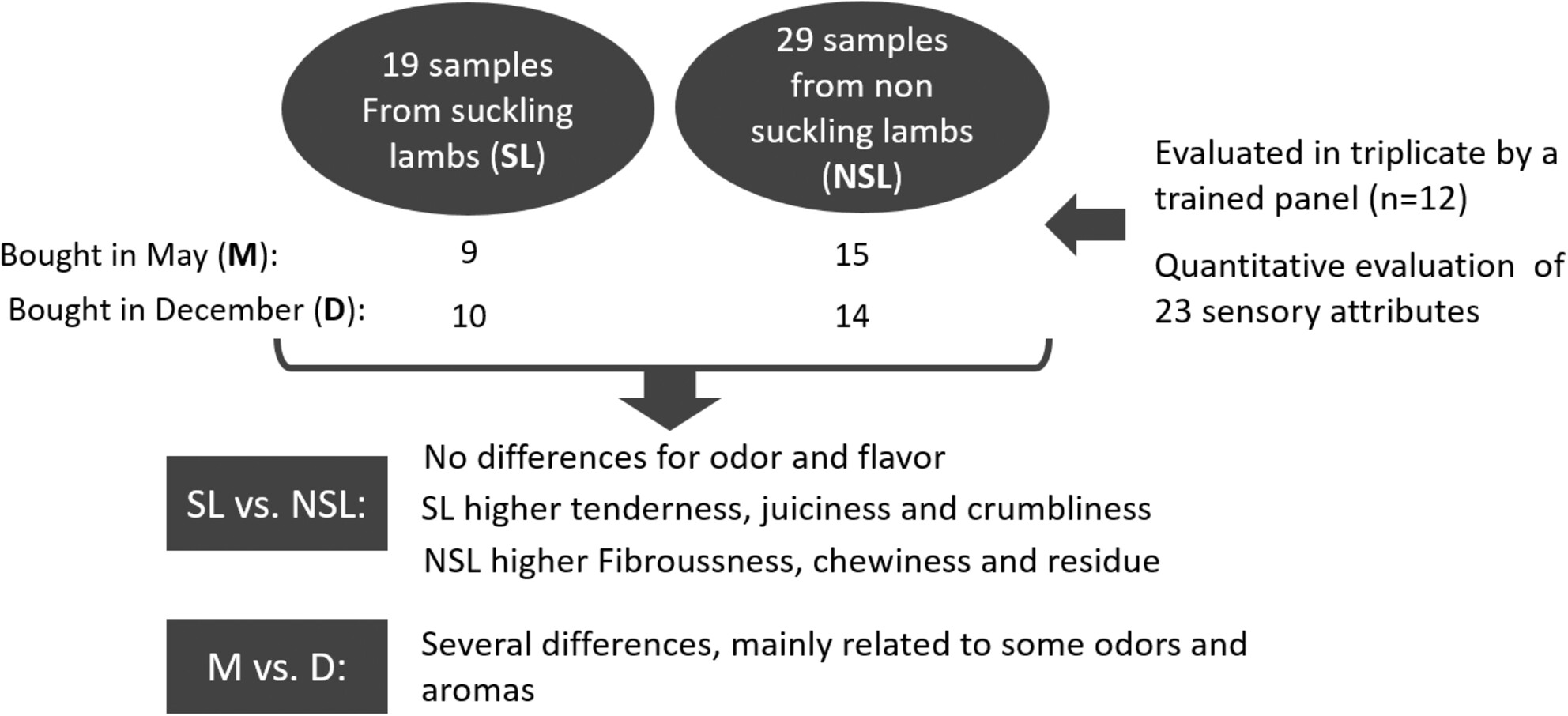
- Representative lamb meat samples commercialized as “suckling lamb” and without this indication were collected in 23 stores in two different seasons (May and December).
- A method (including sensory references) was developed for the sensory description of the samples, and a panel was trained to evaluate them.
- Several sensory differences were found according to the feeding and to the season.
Immunostimulatory effects of marine algae extracts on in vitro antigen-presenting cell activation and in vivo immune cell recruitment
- Pages: 6560-6570
- First Published: 21 August 2023
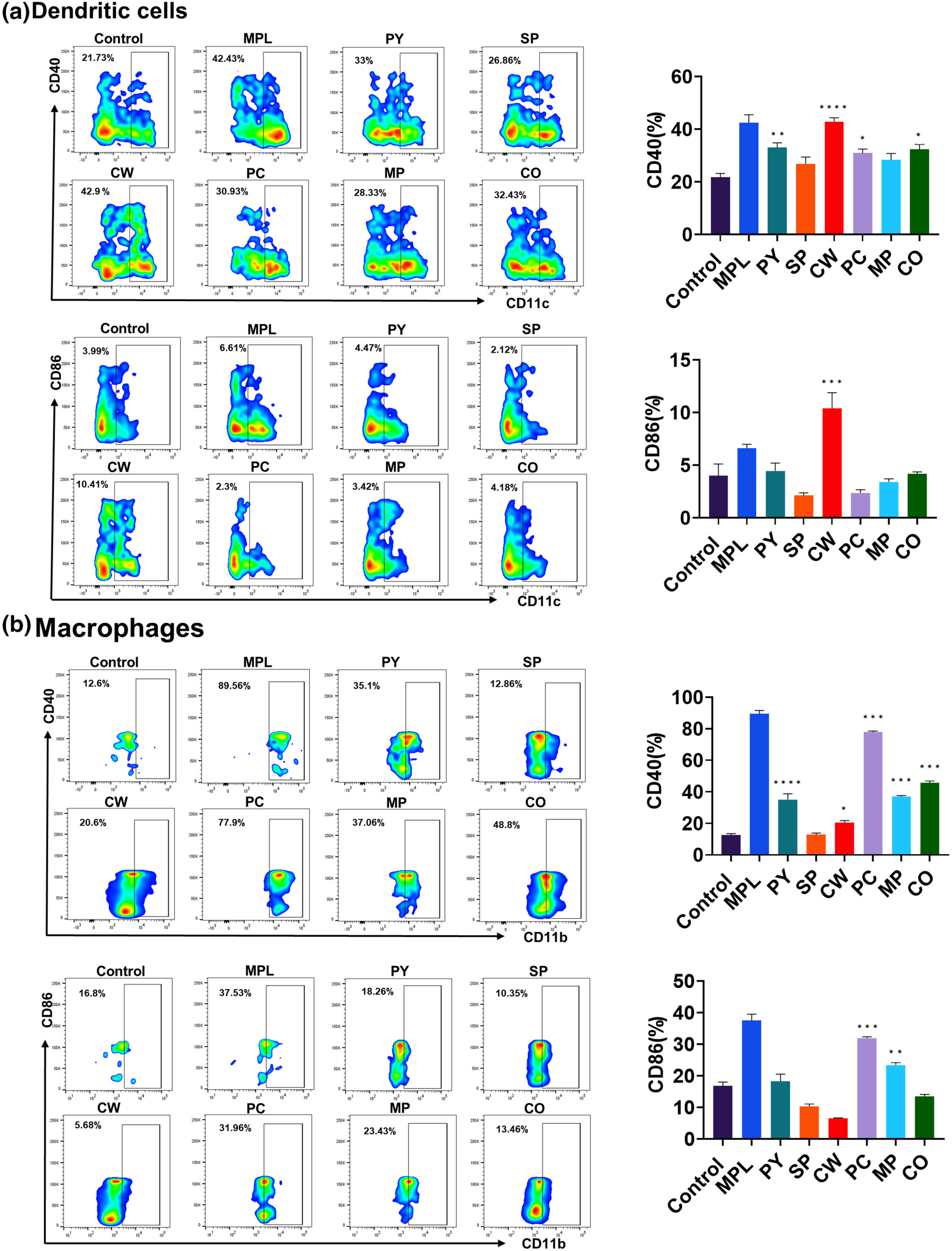
Six different marine algae extracts (MAEs) activated bone marrow-derived dendritic cells and bone marrow-derived macrophages by upregulating activation marker expressions and producing cytokines. In addition, the mice injected with MAEs exhibited higher cytokine production as well as enhanced innate immune cell recruitment capacities. This study can unravel the immunological activity of MAEs and broaden their applications in food and pharmaceutical fields.
Characterization and valorization of soybean residue (okara) for the development of synbiotic ice cream
- Pages: 6571-6581
- First Published: 07 August 2023
Tibetan tea reduces obesity brought on by a high-fat diet and modulates gut flora in mice
- Pages: 6582-6595
- First Published: 07 August 2023

We were able to demonstrate that Tibetan tea (TT) dramatically inhibited high-fat diet-induced weight gain, fat accumulation, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia in mice, as well as control the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism. The way that TT controls the gut microbiota produces short-chain fatty acids and controls the expression of genes involved in lipid synthesis may be responsible for its positive effects on obesity. Our research gave TT's potential as a functional beverage for the prevention and treatment of obesity a new direction.
Effects of sesame dehulling on physicochemical and sensorial properties of its oil
- Pages: 6596-6603
- First Published: 29 August 2023
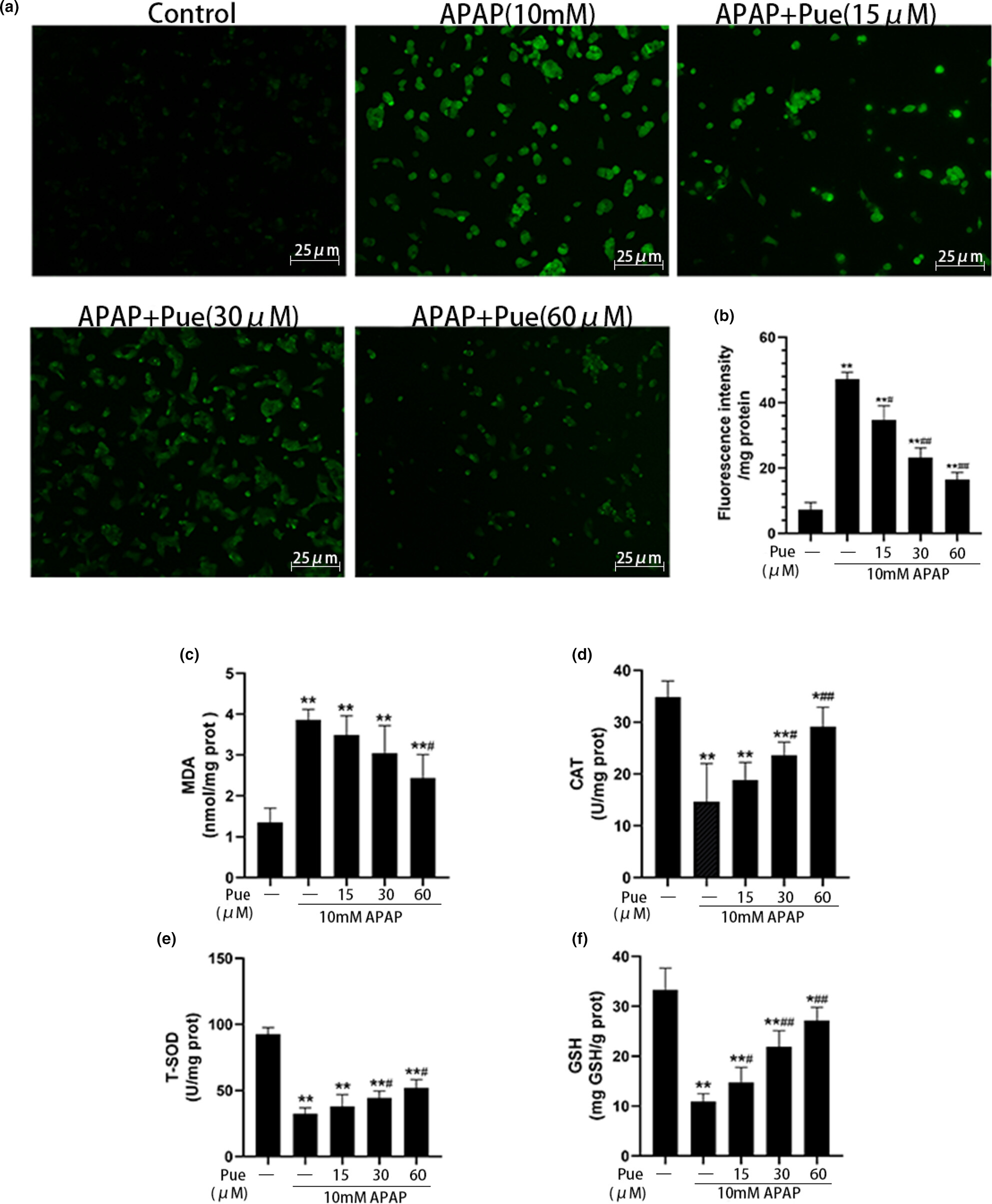
Puerarin protects against acetaminophen-induced oxidative damage in liver through activation of the Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway
- Pages: 6604-6615
- First Published: 11 August 2023
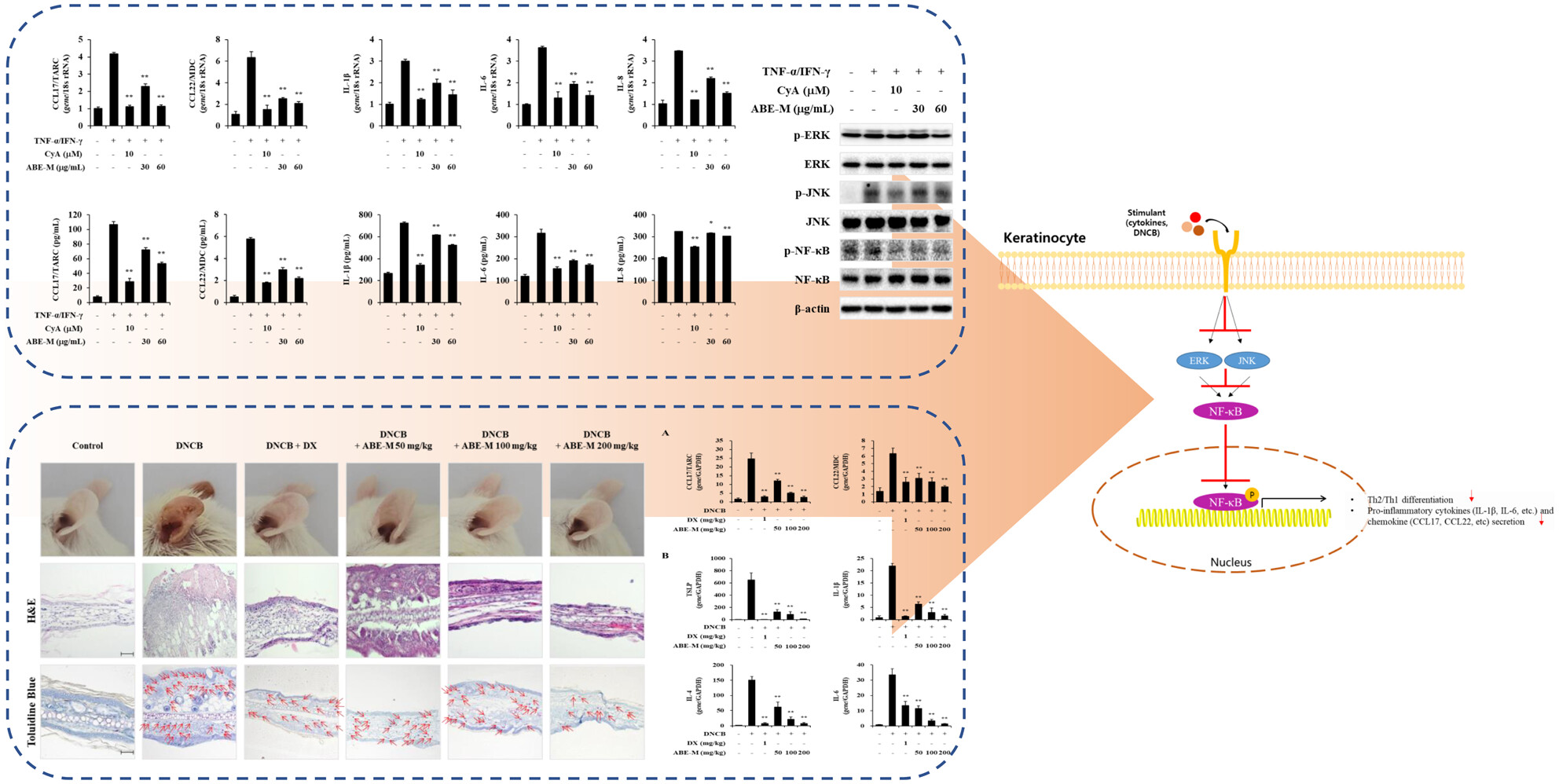
Effect of Ampelopsis brevipedunculata (Maxim.) Trautv extract on a model of atopic dermatitis in HaCaT cells and mice
- Pages: 6616-6625
- First Published: 17 August 2023
Relationship between one-carbon metabolism and fetal growth in twins: A cohort study
- Pages: 6626-6633
- First Published: 11 August 2023
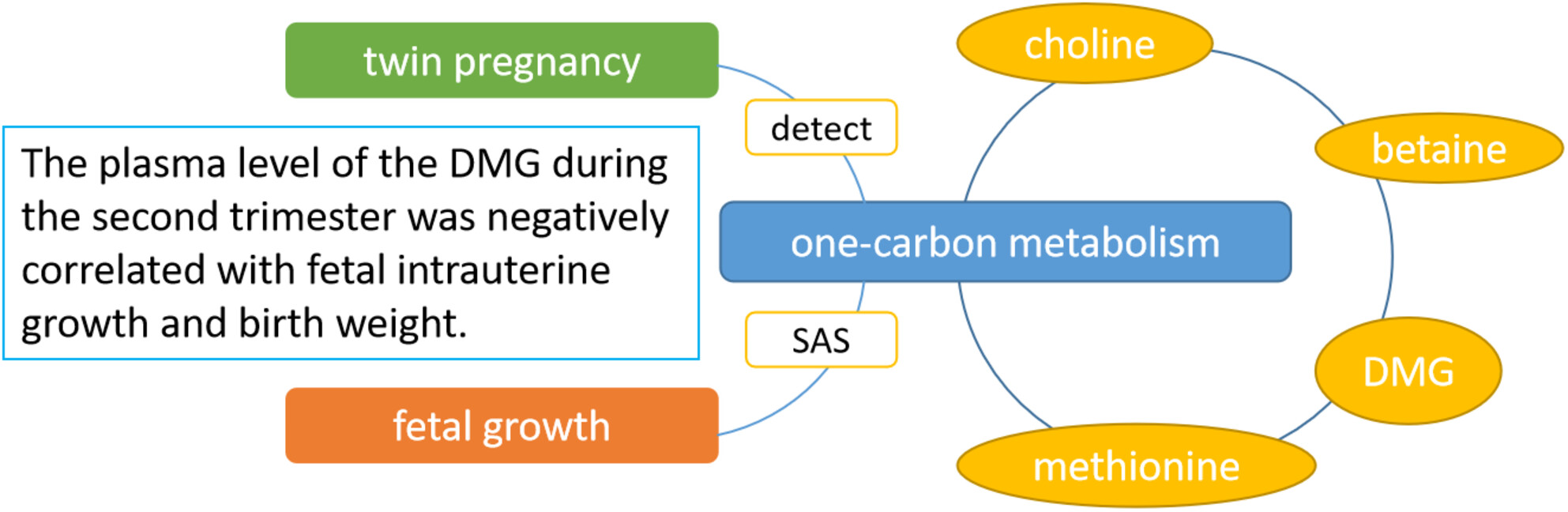
We investigated the associations of one-carbon metabolism-related metabolites, including choline, betaine, dimethylglycine (DMG), and methionine with fetal growth of twins. The plasma level of the DMG during the second trimester was negatively correlated with fetal intrauterine growth and birth weight.
Study on the antioxidant activity of peptides from soybean meal by fermentation based on the chemical method and AAPH-induced oxidative stress
- Pages: 6634-6647
- First Published: 28 August 2023
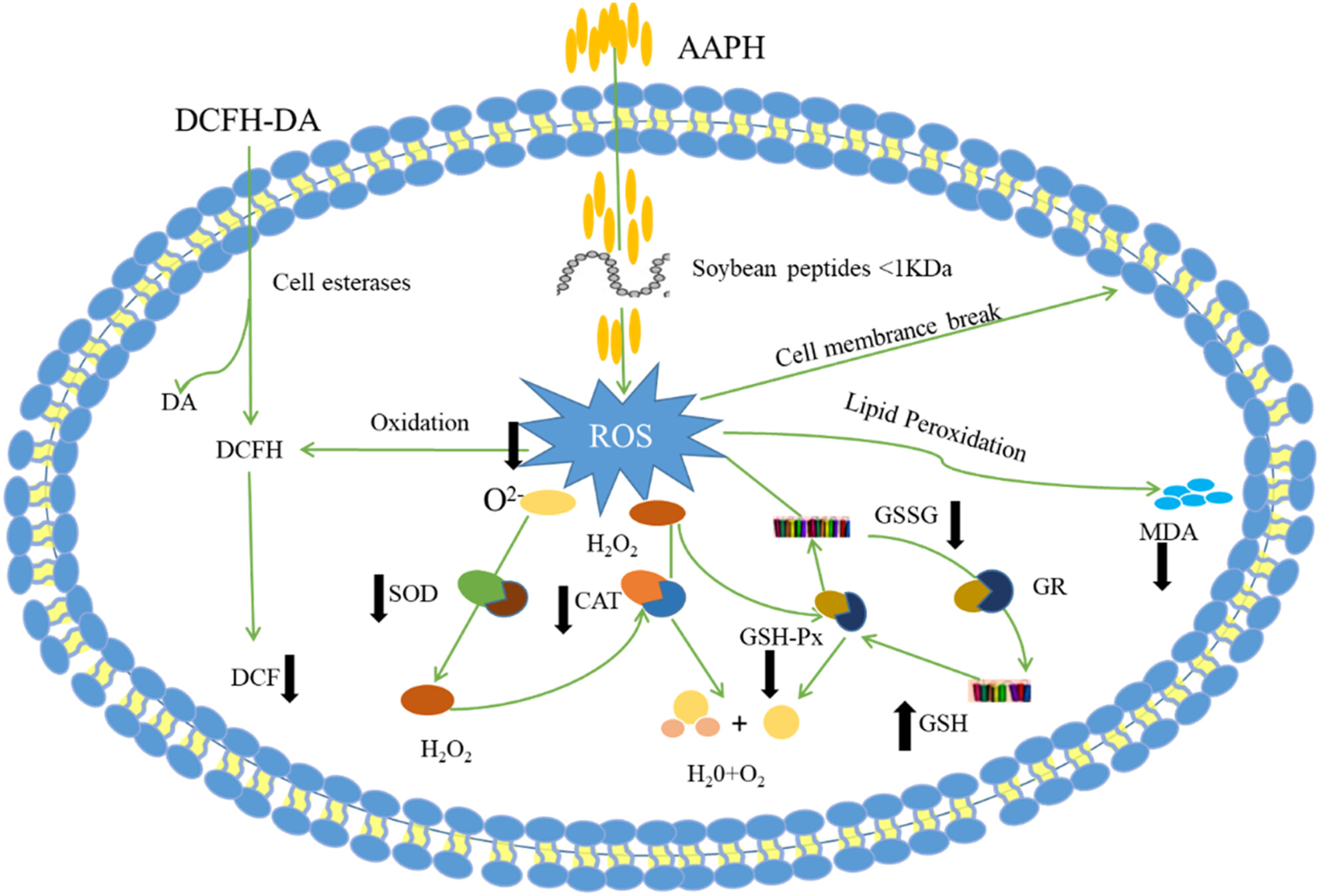
Soybean peptides were prepared by fermentation with mixed Lactic acid bacteria and Aspergillus oryzae from soybean meal, meanwhile degrading the macromolecule protein and some antinutritional factors in soybean meal. The soybean peptides expressed the strong antioxidant activity in vitro and intracellular., which can developed as the additive of functional foods, medicines and cosmetic.
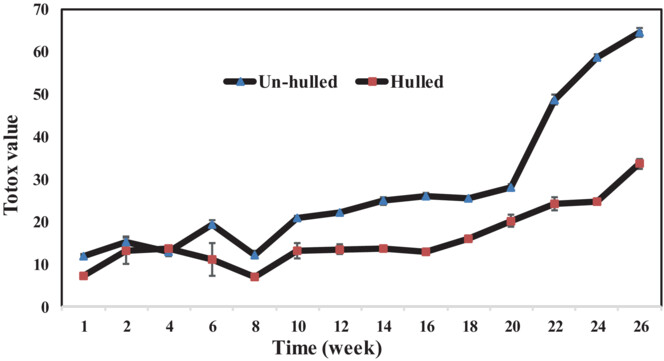
How storage time affects sensory, chemical, and physical characteristics of flavored olive oil
- Pages: 6648-6659
- First Published: 11 August 2023
The objectives of this study were to evaluate the changes of sensory, chemical, and physical characteristics of flavored olive oils during storage. The changes during storage time were analyzed to evaluate its influence on the quality of flavored olive oil. Each flavored olive oil was prepared by three flavoring methods and selected sensory, chemical, and color parameters were monitored based on international standards.
Effects of diets containing grape pomace on the growth, nutrition indices, and the quality traits of common carp (Cyprinus carpio)
- Pages: 6660-6669
- First Published: 10 August 2023
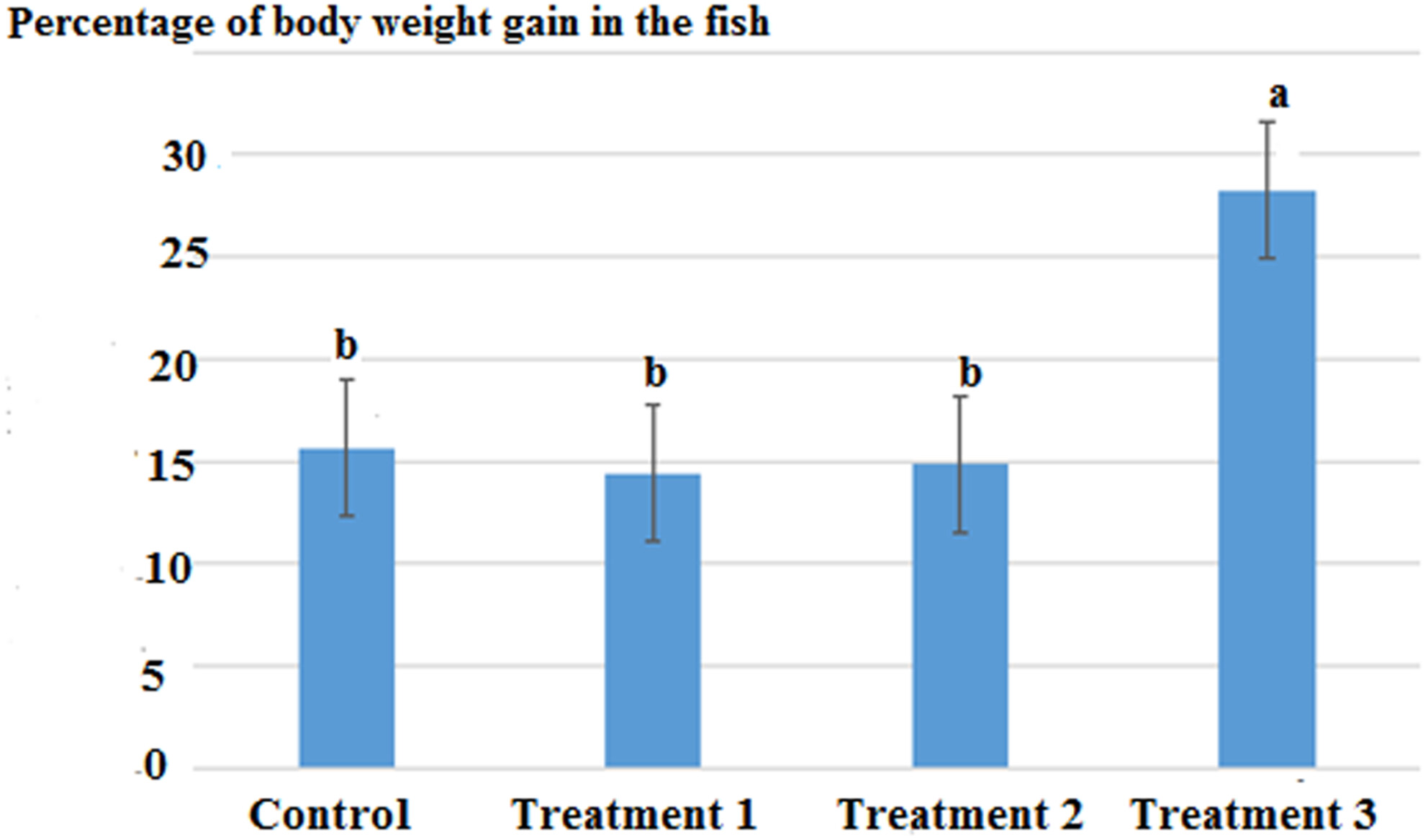
The average daily weight gain (g), weight gain (g), and specific growth rate (%) were significantly higher (p < .05) in T3 as compared to T1 and T2 groups. The lowest feed conversion ratio was recorded in T3 group. The morphological indices, condition factors, viscerosomatic index, and hepatosomatic index were significantly higher in T3 group as compared to other treatments. The protein, fat, moisture, and ash contents of the whole fillets of the Cyprinus carpio were significantly influenced by feeding rate. The results showed that grape pomace had a positive effect on growth, survival, and nutritional indices in the carp fish. According to the obtained results, grape pomace (150 g/kg food) can be considered as the diet component for the carp fish. The percentage of body weight gain of common carp under the influence of different amounts of grape pomace (control treatment), T1 (5% treatment), T2 (10% treatment), T3 (15% treatment). Results shown that grape pomace 15% concentration found highest of effect on the fish growth.
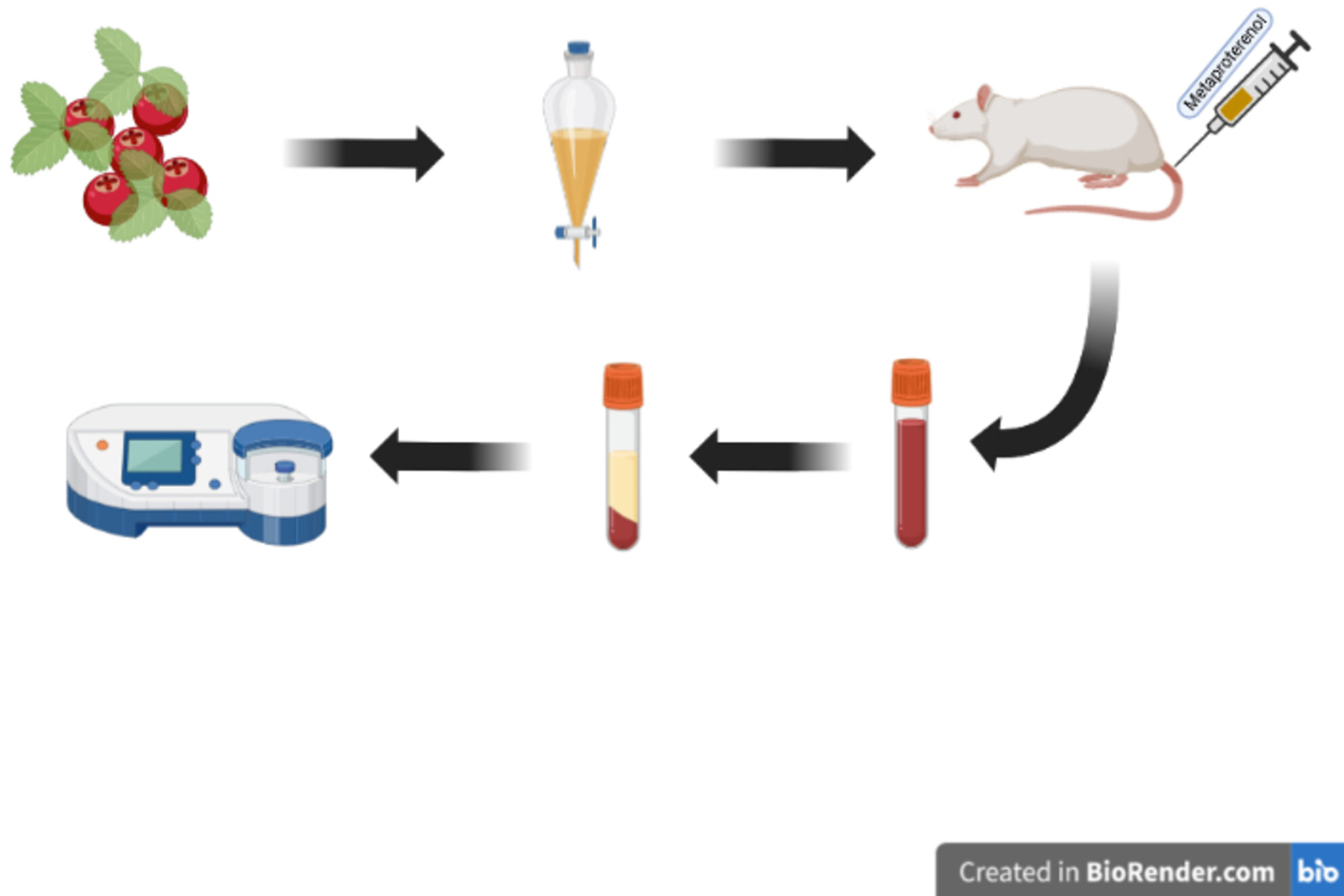
The role of alcohol extract of cranberry in improving serum indices of experimental metaproterenol-induced heart damage in rats
- Pages: 6670-6675
- First Published: 09 August 2023
Comparative study of conventional frying and air frying on the quality of potatoes (Solanum tuberosum L.)
- Pages: 6676-6685
- First Published: 09 August 2023
Effect of vitamin D3 on lipid droplet growth in adipocytes of mice with HFD-induced obesity
- Pages: 6686-6697
- First Published: 24 August 2023
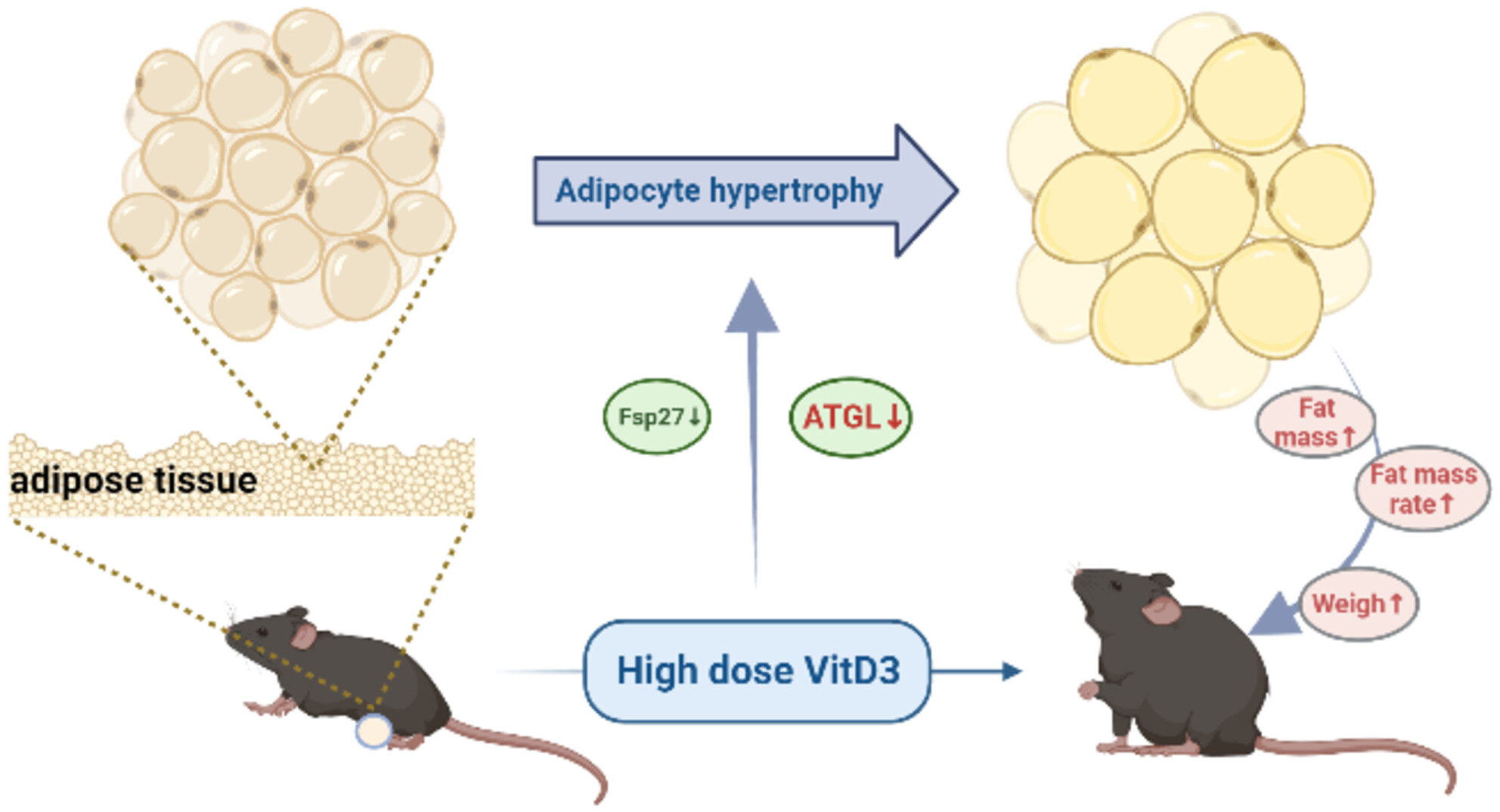
High-dose VitD3 possibly via inhibiting the ATGL expression, thereby inhibiting lipolysis, increasing the volume of adipocytes, and decreasing their fat-storing ability resulted in decreased Fsp27 expression. Therefore, long-term high-dose oral VitD3 may not necessarily improve obesity, the intervention dose and duration of VitD3 in the treatment of VitD3 deficiency in obese patients are the key points.
CORRECTION
Correction to bacteriophages and food safety: An updated overview
- Page: 6698
- First Published: 04 September 2023
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: Connexin 43 upregulation by dioscin-inhibited gastric cancer metastasis by suppressing PI3K/Akt pathway
- Pages: 6699-6707
- First Published: 17 August 2022