Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
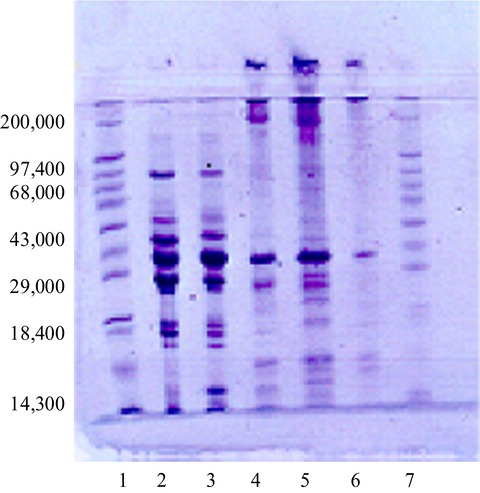
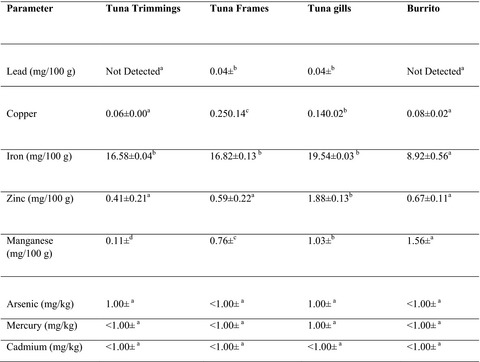
Proximate and biochemical characterization of burrito (Bachydeuterus auritus) and flying gurnard (Dactylopterus volitans)
- Pages: 369-373
- First Published: 21 June 2016
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Nutrient content of fish powder from low value fish and fish byproducts
- Pages: 374-379
- First Published: 05 July 2016
Hydroxycinnamic acids in cooked potato tubers from Solanum tuberosum group Phureja
- Pages: 380-389
- First Published: 12 July 2016
Migration of nonylphenol and plasticizers from polyvinyl chloride stretch film into food simulants, rapeseed oil, and foods
- Pages: 390-398
- First Published: 05 July 2016
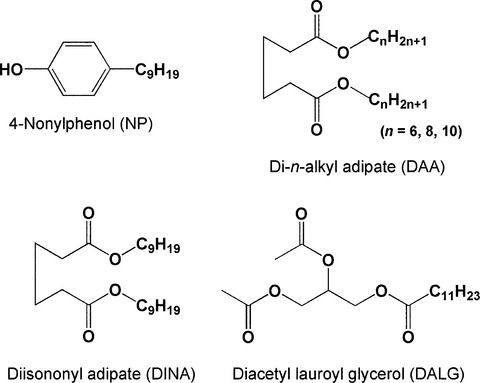
Nonylphenol (NP) more easily migrated from polyvinyl chloride (PVC) stretch film into aqueous foods than diisononyl adipate (DINA) and di-n-alkyl adipate (DAA). The migration ratio of NP, DINA, and DAA into fatty foods, such as minced tuna and pork, came to 15%–37% of their contents in PVC films at 5°C for 24 hr. The estimated daily intakes of NP and DINA for Japanese individuals around the year 2000 were 35 and 1,050 µg, respectively, and should be no safety concern.
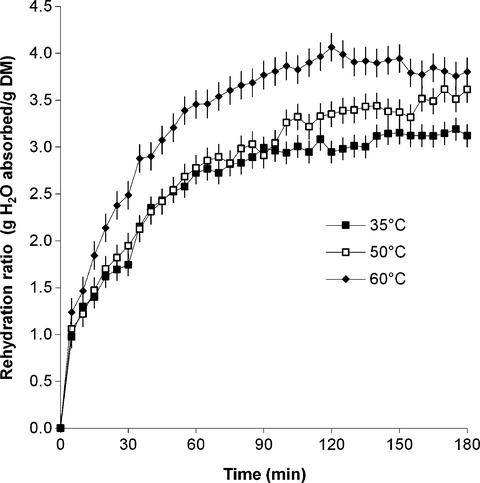
The rehydration behavior of microwave-dried amaranth (Amaranthus dubius) leaves
- Pages: 399-406
- First Published: 07 July 2016
Physicochemical, functional, and nutritional characteristics of stabilized rice bran form tarom cultivar
- Pages: 407-414
- First Published: 11 July 2016
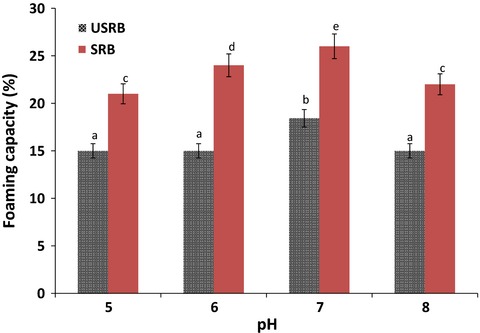
Indeed, many works have been accomplished on the stabilization of rice bran and the effect of extrusion on some functional properties of food has been studied, but there is still lack of knowledge concerning the evaluation of stabilized rice bran and surveying of its functional and nutritional properties. Therefore, the main aim of the current work is to compare the functional, nutritional and biophysical characteristics of rice bran before and after stabilization. Certainly, these evaluations can be vital to utilize rice bran as a food ingredient for the human diet. From a commercial perspective, when there is a growing market for rice bran with added value and more scientific information available about its benefits, industries are expected to show more interest in processing the product for human consumption besides its current use as animal feed.
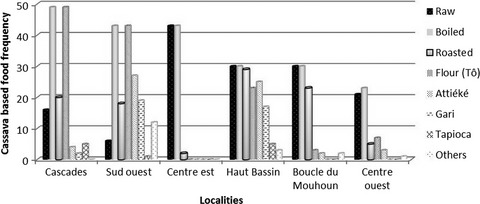
Origins, production, and utilization of cassava in Burkina Faso, a contribution of a neglected crop to household food security
- Pages: 415-423
- First Published: 20 July 2016
Evidence for decreased interaction and improved carotenoid bioavailability by sequential delivery of a supplement
- Pages: 424-433
- First Published: 28 July 2016
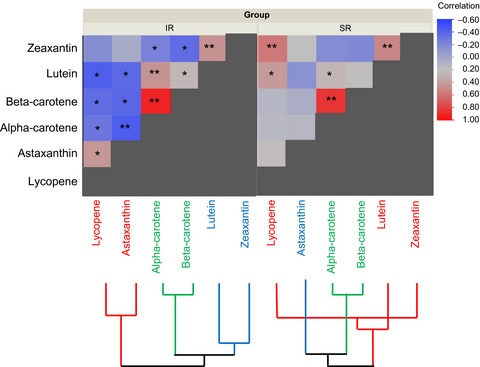
A randomized, double-blind, repeated-measure, cross-over study in adult humans evaluated the change of carotenoid levels in the plasma fraction for 8 hr after oral doses of a sequentially spaced carotenoid mix, in comparison to a nearly identical mix without sequential spacing. The carotenoid change from baseline, measured as area under the curve, is increased following consumption of the sequentially spaced mix over the change from baseline when carotenoids are delivered concomitantly. Spearman's correlation analysis also demonstrates less interaction and regulation between the sequentially spaced carotenoids, suggesting improved bioavailability from a novel sequential release mixed carotenoid formulation.
A sensory assessment of color and textural quality of refrigerated tomatoes preserved with different concentrations of potassium permanganate
- Pages: 434-438
- First Published: 01 August 2016
Effect of soy flour on nutritional, physicochemical, and sensory characteristics of gluten-free bread
- Pages: 439-445
- First Published: 01 August 2016
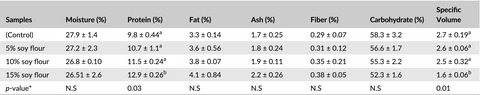
In this study, corn flour was replaced with soy flour at different levels 5%, 10% and 15% to producing a more nutritionally balanced GF bread.The results of evaluations showed that protein, fat, fiber, and ash contents of soy flour-supplemented GF bread increased with the incremental addition of soybean flour. The highest total score of sensory evaluation was for the bread sample containing 15% soybean flour. Adding higher levels of soybean flour into GF bread can improve bread quality, sensory characteristics and nutritional properties of bread.
Development and standardization of the “Let's Shop” questionnaire: an assessment of shopping habits and executive functions in people with obesity
- Pages: 446-453
- First Published: 05 August 2016

The article describes the development of the “Let's Shop” questionnaire as an assessment tool for shopping habits and executive functions among people with a range of BMI, and report on the respective reliability and validity measures obtained, specifically, factor analysis. This brief questionnaire will enable rapid administration by researchers and practitioners and will determine a potential association between executive functions in the supermarket arena and weight status.
Bacterial contaminants from frozen puff pastry production process and their growth inhibition by antimicrobial substances from lactic acid bacteria
- Pages: 454-465
- First Published: 05 August 2016
Modeling of drying kiwi slices and its sensory evaluation
- Pages: 466-473
- First Published: 13 August 2016
Comparison of phenolic content and antioxidant activities of millet varieties grown in different locations in Sri Lanka
- Pages: 474-485
- First Published: 24 August 2016
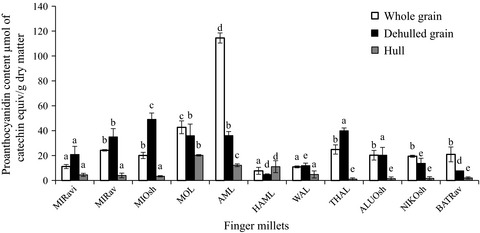
Soluble and bound phenolic content and their antioxidant activities of three millet varieties grown at different locations in Sri Lanka were reported. Results showed that variety, as well as cultivar had an effect in addition to the location of grown for the antioxidant activities of millet phenolics.
Anti-inflammatory and anti-insulin resistance activities of aqueous extract from Anoectochilus burmannicus
- Pages: 486-496
- First Published: 26 August 2016
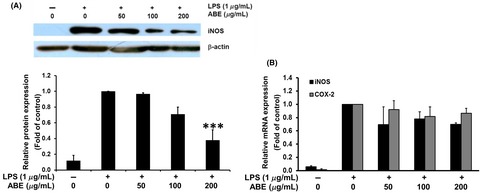
Anoectochilus burmannicus aqueous extract (ABE) showed anti-inflammatory activity by decreasing the level of inflammatory molecules including nitric oxide (NO), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), interleukin 6 (IL-6), IL-1β, and cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) in the LPS-treated RAW 264.7. Moreover, ABE exerted anti-insulin resistance activity as it significantly improved the glucose uptake in tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-treated 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The results of our study suggested the potential use of A. burmannicus as anti-inflammatory, anti-insulin resistance agents, or food supplement for prevention of chronic diseases.
Evaluation of different solvents to extract antibacterial compounds from jalapeño peppers
- Pages: 497-503
- First Published: 31 August 2016
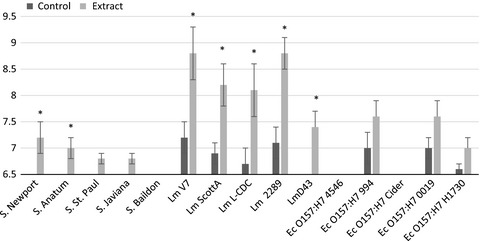
The purpose of this study was to identify which solvent is most successful at extracting compounds from jalapeño peppers that possess antibacterial activity against food-borne pathogens. There was greater bacterial inhibition from extracts created with methanol and ethanol than hot water. Listeria monocytogenes was significantly more susceptible to the extracts than E. coli or Salmonella isolates.
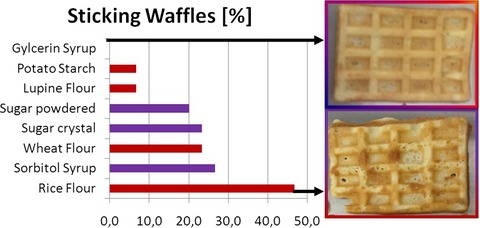
Waffle production: influence of batter ingredients on sticking of fresh egg waffles at baking plates—Part I: effect of starch and sugar components
- Pages: 504-512
- First Published: 20 September 2016
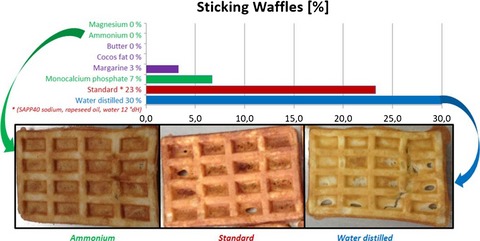
Waffle production: influence of batter ingredients on sticking of waffles at baking plates—Part II: effect of fat, leavening agent, and water
- Pages: 513-520
- First Published: 20 September 2016
Heat penetration attributes of milkfish (Chanos chanos) thermal processed in flexible pouches: a comparative study between steam application and water immersion
- Pages: 521-524
- First Published: 02 October 2016
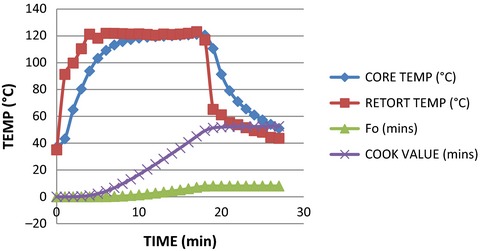
The difference in the heating penetration characteristics of product processed in retort by steam–air application and water immersion was studied. Fresh milkfish packed in dry pack and in oil medium, both in flexible pouches, was thermal processed to minimum F0 value of 7.77 at 121.1°C. Heat penetration data were recorded for every minute of processing using Ellab (TM 9608, Denmark) temperature recorder. Retort come up time to achieve 121.1°C was less in steam–air which led to a lower Ball's process time (B) and the total process time (T) observed in steam–air as compared to water immersion.
The effect of proteolytic activity of starter cultures on technologically important properties of yogurt
- Pages: 525-537
- First Published: 29 September 2016
In this study, the effects of proteolytic activity of yogurt starter bacteria on physicochemical and technological properties of yogurt were investigated. Results showed strains with high proteolytic activity had lower acidifying activity during fermentation and storage. Counts of starter cultures in samples produced using strains with high proteolytic activity were higher than other samples.
Effect of cooking and preservation on nutritional and phytochemical composition of the mushroom Amanita zambiana
- Pages: 538-544
- First Published: 28 September 2016
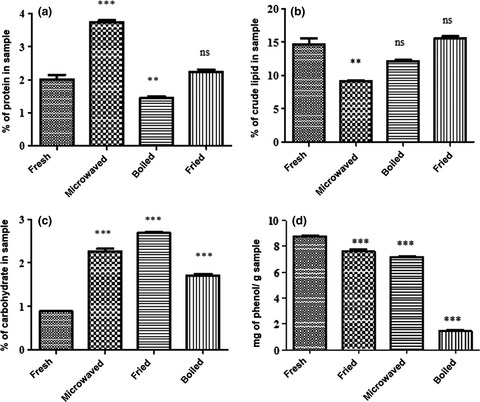
The article gives a summary on the impact that cooking and preservation has on the nutrient and phytochemical composition of the local mushroom Amanita zambiana. The findings highlight the fact that the choice of methods of cooking and preserving edible mushrooms play a significant role in the human diet. The data shown in this study provide information on the best cooking and preservation methods that retain most of the nutrients and phytochemicals in Amanita zambiana.
Influence of storage temperature and low-temperature conditioning on the levels of health-promoting compounds in Rio Red grapefruit
- Pages: 545-553
- First Published: 02 October 2016
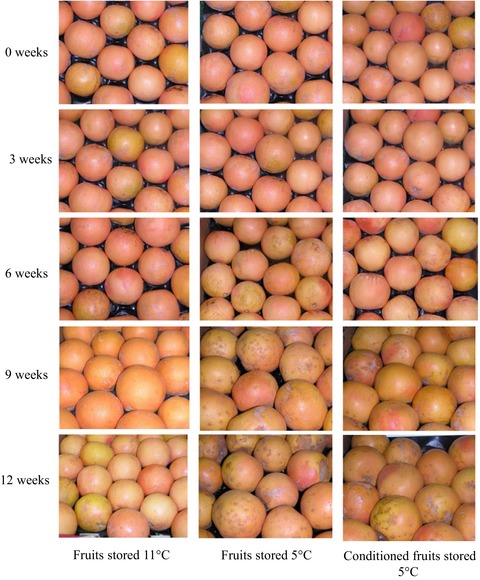

Rio Red grapefruits stored for 12 weeks at 11°C or 5°C and conditioned (CD) and levels of phytochemicals analyzed. Conditioning reduced chilling injury by 4.5- and 2.5-fold at 9 and 12 weeks. No effect of treatments seen on lycopene, narirutin, poncirin, and furocoumarin levels. CD fruits had similar or higher levels of most of the phytochemicals at 12 weeks.
Effect of psyllium and gum Arabic biopolymers on the survival rate and storage stability in yogurt of Enterococcus durans IW3 encapsulated in alginate
- Pages: 554-563
- First Published: 11 October 2016
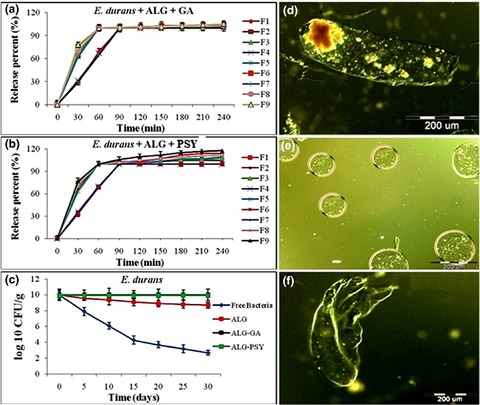
Herbal biopolymers, own prebiotic effects, can encapsulate Enterococcus durans cells. A hypothesis for bacteria protection by herbal biopolymers is proposed. Encapsulation of E. durans by the microbeads occurred by a partitioning process. Biopolymer-based encapsulation allows the oral administration of sensitive probiotics. Herbal biopolymers can protect bacteria in yogurt and release them in simulated intestine fluid.
Sensory optimization of crackers developed from high-quality cassava flour, starch, and prawn powder
- Pages: 564-569
- First Published: 26 September 2016
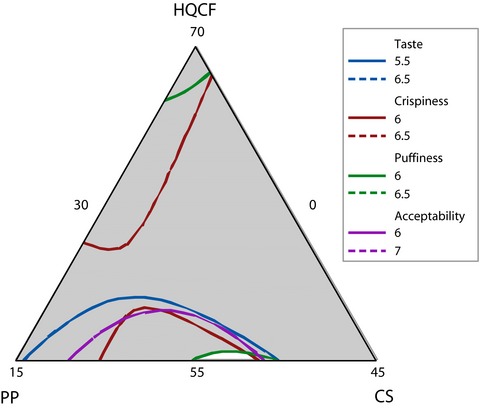
The suitability of high-quality cassava flour (HQCF) for processing value added snacks is demonstrated in this study. The crackers are developed and optimized using mixture design experiments. Preference test and consumer acceptability studies showed that the snack is highly acceptable to consumers.
Influence of low dose of gamma radiation and storage on some vitamins and mineral elements of dried oyster mushrooms (Pleurotus ostreatus)
- Pages: 570-578
- First Published: 11 October 2016
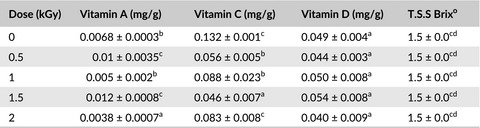
Pleurotus ostreatus showed appreciable levels of mineral elemental composition, essential vitamins A, C, and D, and can be endorsed as a natural medicinal food product in the food and pharmaceutical industries. The heavy metals detected were with also below the upper limits permissible by the WHO standards and is thus safe for human consumption.
A potential bioactive hard-stock fat replacer comprised of a molecular gel
- Pages: 579-587
- First Published: 23 October 2016
Packaging methods and storage duration affect essential oil content and composition of lemon verbena (Lippia citriodora Kunth.)
- Pages: 588-595
- First Published: 19 October 2016

Changes in essential oils (EOs) content and composition of lemon verbena leave at different packaging methods (packaged with air, nitrogen, or under vacuum) and during storage period (0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 months) were determined. Packaging of lemon verbena leaves with nitrogen preserved the highest EO content during 8 months of storage and achieved the desired amounts of citral, limonene, and 1,8-cineole.
Experimental and modeling investigation of mass transfer during combined infrared-vacuum drying of Hayward kiwifruits
- Pages: 596-601
- First Published: 25 October 2016
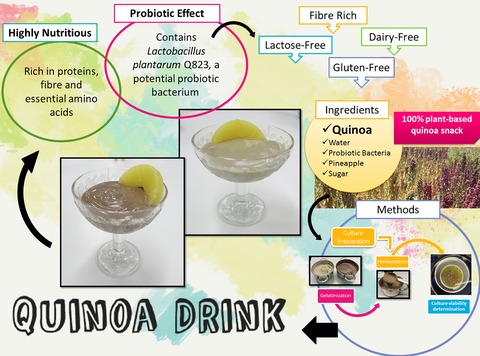
Development of a fermented quinoa-based beverage
- Pages: 602-608
- First Published: 28 October 2016
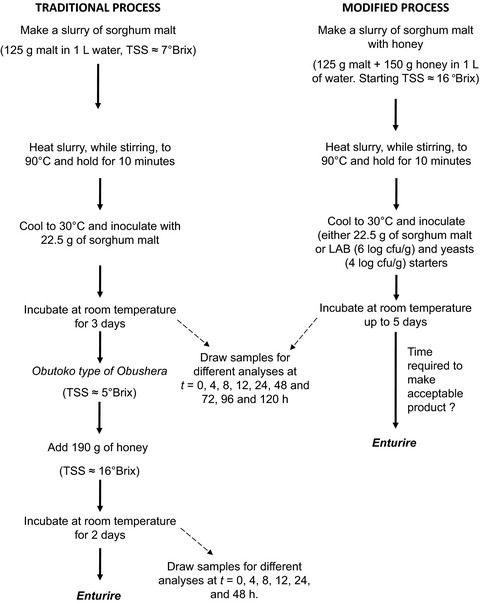
Application of starter cultures in the production of Enturire – a traditional sorghum-based alcoholic beverage
- Pages: 609-616
- First Published: 25 October 2016
Consumer knowledge, preference, and perceived quality of dried tomato products in Ghana
- Pages: 617-624
- First Published: 03 November 2016
Relative validation of a short questionnaire to assess the dietary habits of pregnant American Indian women
- Pages: 625-632
- First Published: 16 November 2016
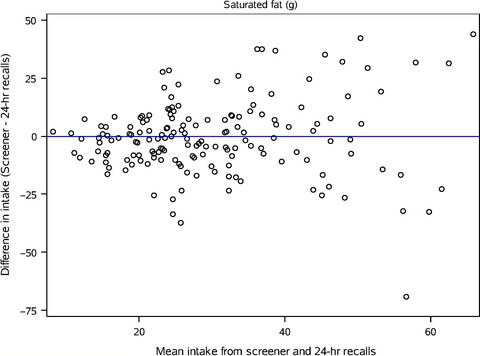
Our objective was to conduct a relative validation study comparing a short diet screening instrument to repeated 24-hour recalls data collected among pregnant American Indian women. Accurate dietary data collection instruments that are acceptable to respondents which can be administered fairly quickly in a public health setting will facilitate nutritional assessment in this population.
Value-added probiotic development by high-solid fermentation of sweet potato with Saccharomyces boulardii
- Pages: 633-638
- First Published: 09 December 2016
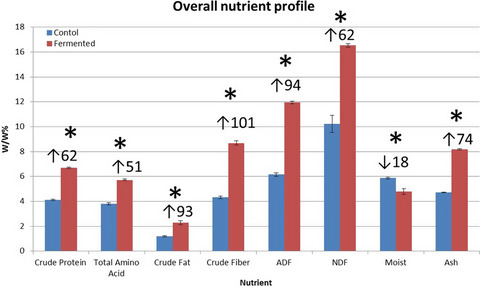
High solid submerged fermentation of sweet potato with Saccharomyces boulardii was successfully carried out with an end of fermentation viable live spore count of 8.0 × 1010 CFU/g. The freeze dried fermented product showed good stability with respect to CFU at 4°C for 12 months. The overall nutritional profile of the fermented product was positively changed with increased total protein, total amino acid, and neutral detergent fiber. The S. boulardii value-added sweet potato open up new opportunities for value-added probiotics for animal feed and human nutrition.
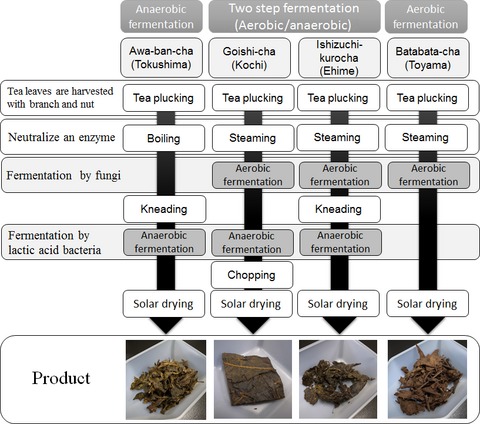
Comparison of antioxidant activities among four kinds of Japanese traditional fermented tea
- Pages: 639-645
- First Published: 22 November 2016
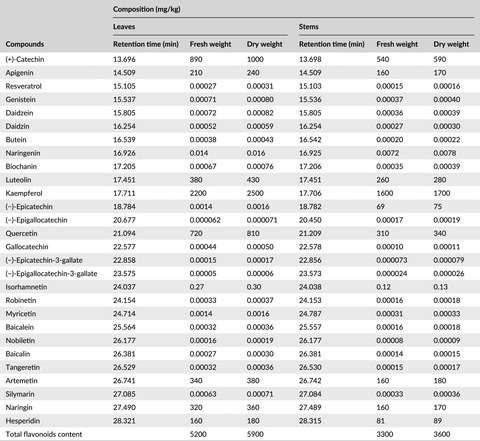
Investigation of the profile of phenolic compounds in the leaves and stems of Pandiaka heudelotii using gas chromatography coupled with flame ionization detector
- Pages: 646-652
- First Published: 23 November 2016
Effect of drying methods and blending ratios on dough rheological properties, physical and sensory properties of wheat–taro flour composite bread
- Pages: 653-661
- First Published: 02 December 2016
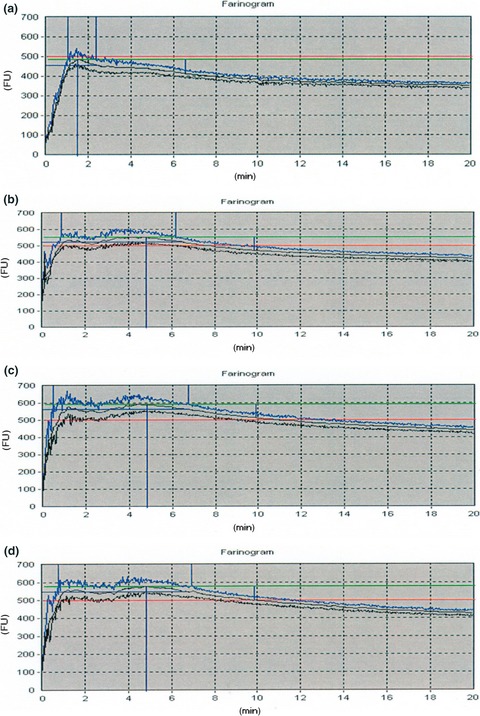
The study was conducted to evaluate the effect of taro drying methods and blending ratios on the physical quality attributes and sensory quality of taro–wheat bread. The study revealed that there is possibility of incorporating wheat flour up to 15 g per 100 g of wheat flour with acceptable sensory attributes of the composite bread.
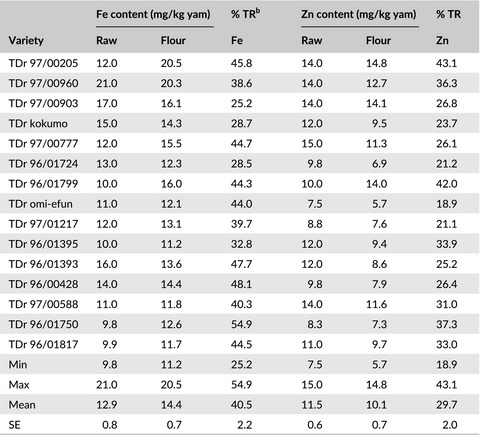
Retention of iron and zinc in yam flour and boiled yam processed from white yam (D. rotundata) varieties
- Pages: 662-668
- First Published: 05 December 2016
Effect of Persian and almond gums as fat replacers on the physicochemical, rheological, and microstructural attributes of low-fat Iranian White cheese
- Pages: 669-677
- First Published: 02 December 2016
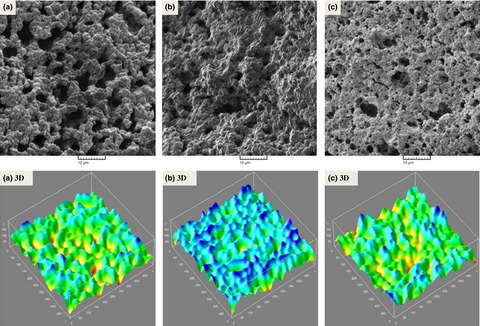
Awareness of the relationship between diet and health has stimulated interest in foods with less fat. However, low-fat foods including low-fat cheeses do not enjoy wide popularity mainly because of poor textural properties. The results of this study revealed that incorporating the optimum levels of Persian and almond gums into the formulation of low-fat Iranian white cheese makes it possible to develop a low-fat food with acceptable textural properties.
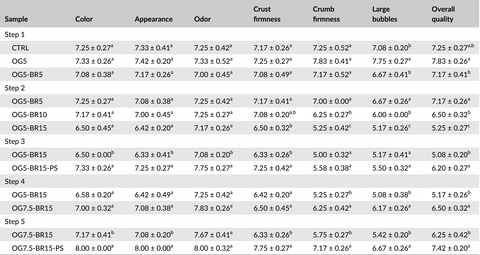
Effect of spices formulations on the physicochemical and sensory properties of Nnam gon, a Cameroonian dish prepared with cucurbitaceae seeds
- Pages: 678-688
- First Published: 23 November 2016
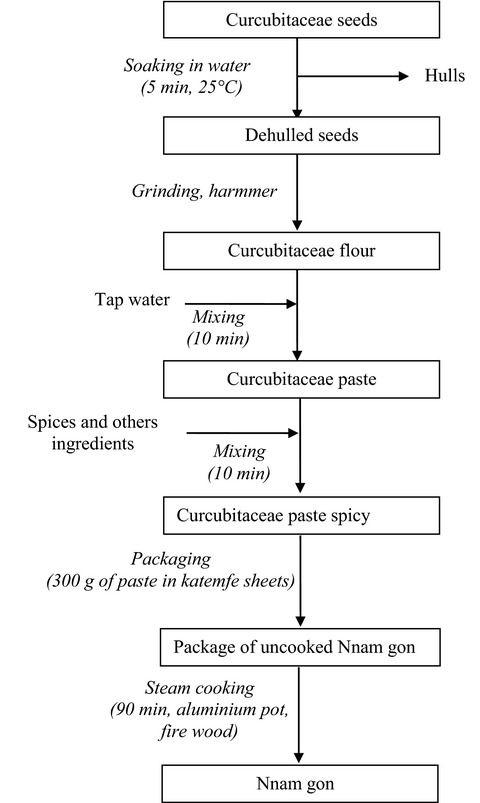
Cucurbitaceae seeds cakes (Nnam gon) were produced from four formulations including control formulation and three spicy formulations and their physicochemical characteristics and sensory profile (Quantitative Descriptive Analysis) were evaluated. The results revealed that proteins, total sugar, lipids, ash, and fibers levels increased significantly with spices adding. Spices adding appears to induce a decrease in hardness, cohesivity, elasticity, and granulous of cake, but it is responsible for enhanced oiliness.
Optimization of durum wheat bread enriched with bran
- Pages: 689-695
- First Published: 17 December 2016
In this work an attempt was made to optimize the formulation of durum wheat bread enriched with bran at high concentration. Organogel concentration and bran particle size were used as process variables to increase the sensory quality of bread. The addition of organogel and the decrease of bran particle size have improved the structural and sensory properties of bread.
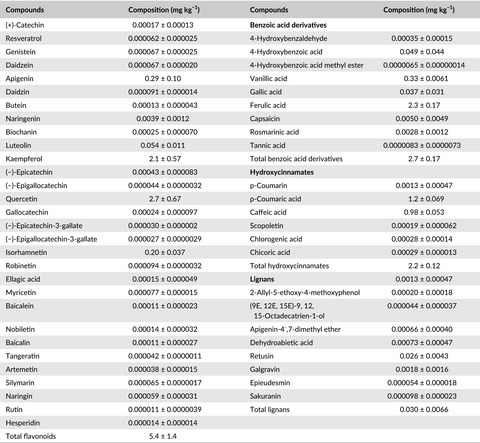
Bioactive phytochemicals in an aqueous extract of the leaves of Talinum triangulare
- Pages: 696-701
- First Published: 02 December 2016
Production of organic flavor compounds by dominant lactic acid bacteria and yeasts from Obushera, a traditional sorghum malt fermented beverage
- Pages: 702-712
- First Published: 05 December 2016
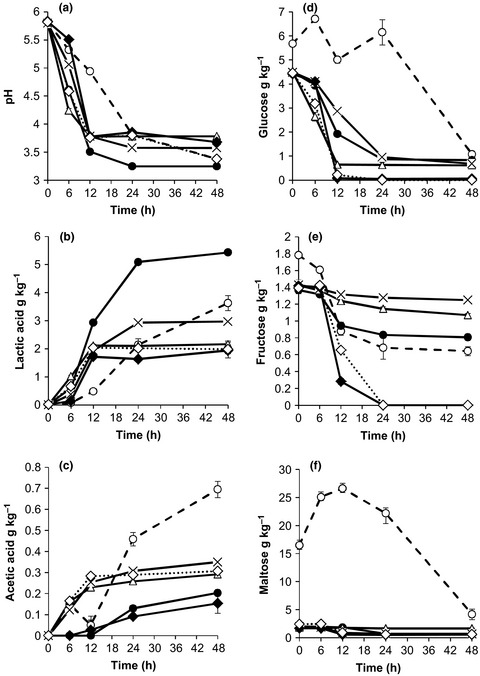
The study evaluated the contribution of dominant lactic acid bacteria (LAB) and yeasts in a sorghum malt fermented beverage (Obushera) toward its flavor profile. LAB contributed to production of lactic acid and some also produced acetate, ethanol, acetaldehyde, acetone, and acetoin while yeasts produced high amounts of acetaldehyde and methyl alcohols. Combinations of LAB with S. cerevisiae produced profile flavor compounds close to that of spontaneously fermented Obushera.
Development and evaluation of floating alginate microspheres for oral delivery of anthocyanins – A preliminary investigation
- Pages: 713-721
- First Published: 21 December 2016
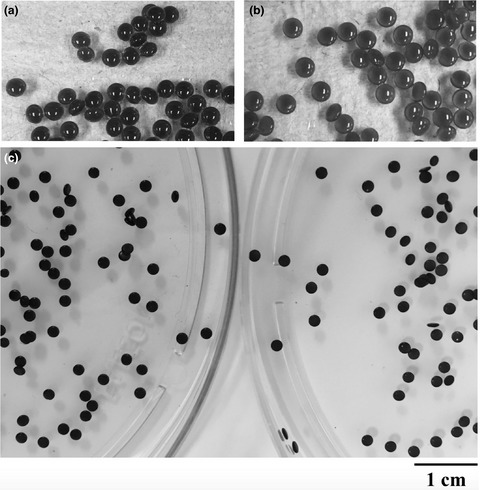
The objective of this study was to develop floating microspheres that could be used as gastroretentive systems for the delivery of anthocyanins. Increasing the carbonate:alginate weight ratio from 0 to 3:4 resulted in different degrees of floatability, larger particles, higher encapsulation efficiency, and lower amount of anthocyanins released.
Amino acid profile and protein quality in tuber and leaf of Coccnia abyssinica (Lam.) (Cogn.) accessions of Ethiopia
- Pages: 722-729
- First Published: 23 December 2016
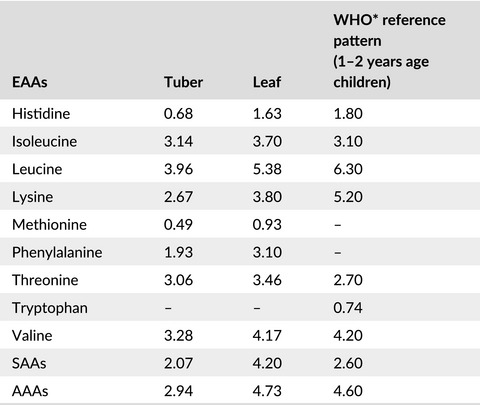
The amino acid profile of Coccinia abyssinica leaves and tubers were determined from ten different accessions taken from Debre Zeit Agricultural Research Center, Ethiopia. The amino acid profile was analyzed using performic acid oxidation and acid hydrolysis by ninhydrin-derivatized analysis with amino acid analyzer.
Antibacterial activity of jalapeño pepper (Capsicum annuum var. annuum) extract fractions against select foodborne pathogens
- Pages: 730-738
- First Published: 13 February 2017
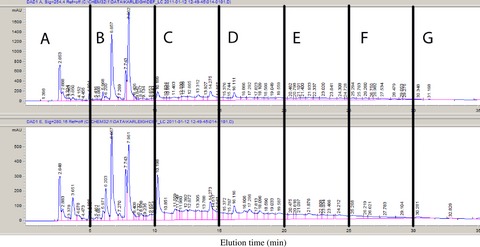
In this study, fractions were collected from jalapeño pepper extracts using reverse-phase HPLC and tested for antibacterial activity using the disk diffusion method. Following initial fractionation, two fractions (E and F) displayed antibacterial activity against all three pathogens (p > .05). The only fraction to display clear inhibition using both each was fraction E1, inhibiting the growth of L. monocytogenes, and was found to contain compounds belonging to a group of C. annuum-specific compounds called capsianosides.
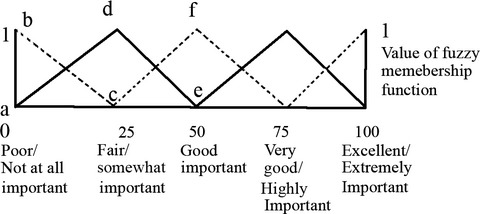
Sensory evaluation of selected formulated milk barberry drinks using the fuzzy approach
- Pages: 739-749
- First Published: 13 January 2017
Nutrient composition, functional, and pasting properties of unripe cooking banana, pigeon pea, and sweetpotato flour blends
- Pages: 750-762
- First Published: 12 January 2017

Some quality attributes of unripe cooking banana (UBF), pigeon pea (PPF), and sweetpotato (SPF) flour blends were investigated. There were significant (p < .05) differences in the nutrient composition, functional, and pasting properties of the blends. Cooking banana-pigeon pea-sweetpotato flour blends are desirable for alleviating malnutrition in Nigeria and developing new food products.
Effects of starch concentration on calcium-enhanced black bullhead catfish protein gels
- Pages: 763-769
- First Published: 22 January 2017
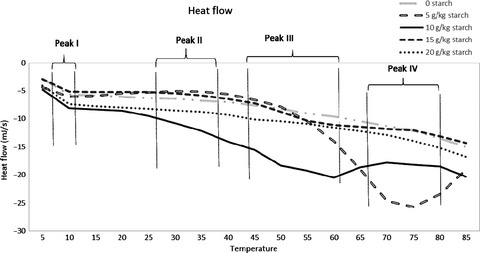
Protein gels were made that contained increasing amounts of potato starch (0, 5, 10, 15, 20 g/kg protein paste). Energy required to unfold protein groups increased with 5 g starch/kg paste. Protein gels got harder and darker with the added starch. Starch concentrations beyond 5 g starch/kg paste did not lead to further changes in textural properties.
Which product characteristics are preferred by Chinese consumers when choosing pork? A conjoint analysis on perceived quality of selected pork attributes
- Pages: 770-775
- First Published: 22 January 2017
Fresh preservation of alfalfa sprouts and mushroom slices by soaking with thymol and resveratrol solutions
- Pages: 776-783
- First Published: 09 February 2017
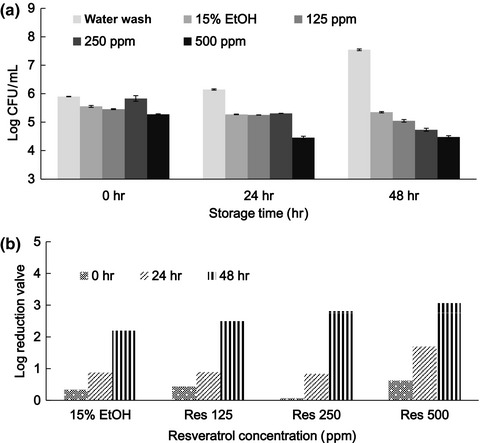
Thymol and resveratrol exhibited potent inhibitory activities against growth of Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. When cells of S. aureus were treated with thymol combined with resveratrol, both at 250 ppm, its 3LR value was <5 min. A synergistic antibacterial activity between thymol and resveratrol was apparent and known health beneficial activity of resveratrol is of virtue.
Optimization of the extraction of the p-menthadienol isomers and aristolone contained in the essential oil from Elyonurus hensii using a 23 full factorial design
- Pages: 784-792
- First Published: 09 February 2017
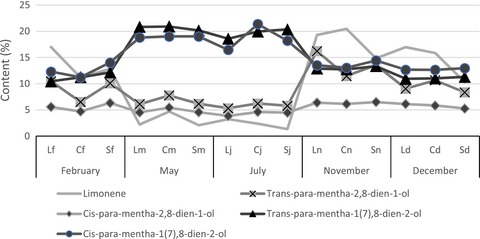
The residual water content is the most important factor which significantly influences the average yield of the essential oil and the content of the major constituents. Regarding the aerial part, a low residual water content of the plant material increases the essential oil yield and the content of cis and trans-p-mentha-2.8-dien-1-ol. To the roots, the samples which have a very low residual water content should provide extracts richer in aristolone.
Home-based preparation approaches altered the availability of health beneficial components from carrot and blueberry
- Pages: 793-804
- First Published: 18 March 2017
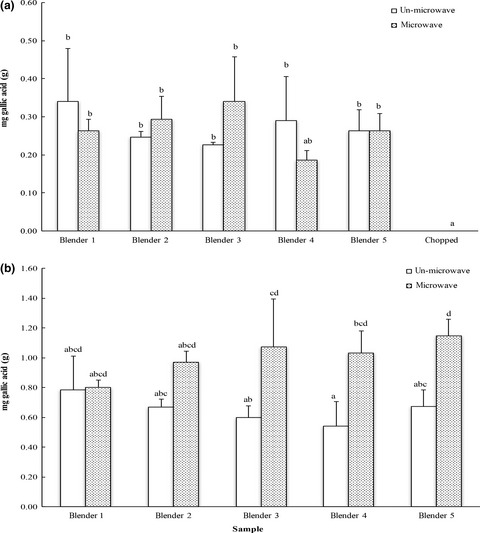
No difference among the commercial blenders/grinders on the extractable levels of health beneficial components including carotenoids, anthocyanins, free radical scavenging compounds and potential anti-inflammatory components and both particle size and inherent enzymes in the fruits and vegetables may alter the overall amount of available bioactives.
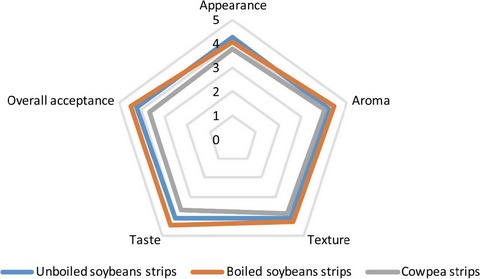
Nutritional and sensory properties: Snack food made from high-quality cassava flour and legume blend
- Pages: 805-811
- First Published: 01 March 2017
Effect of precooking and polyphosphate treatment on the quality of microwave cooked catfish fillets
- Pages: 812-819
- First Published: 22 February 2017
Spray drying of pomegranate juice using maltodextrin/cyclodextrin blends as the wall material
- Pages: 820-826
- First Published: 01 March 2017
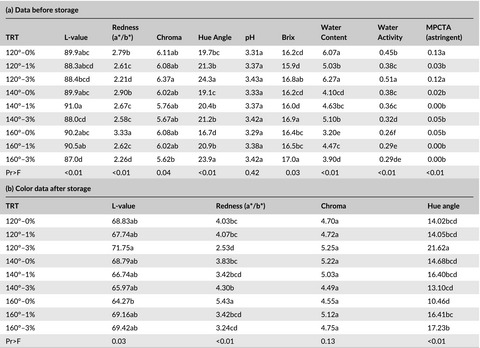
This work investigated the spray drying conditions and novel formulations with mixtures of maltodextrin with small amounts of γ-cyclodextrin. The results of spray drying fruit juice with a combination of γ-cyclodextrins and maltodextrins show how these parameters affect the physical properties such as powder color, water-holding capacity, and astringency index. The pH appears to affect the color of the powders. The drying temperature interacts with the γ-cyclodextrin/maltodextrin formulation. This information can extend to spray drying of other natural products and juices.
Nutritional advantages of sous-vide cooking compared to boiling on cereals and legumes: Determination of ashes and metals content in ready-to-eat products
- Pages: 827-833
- First Published: 01 March 2017
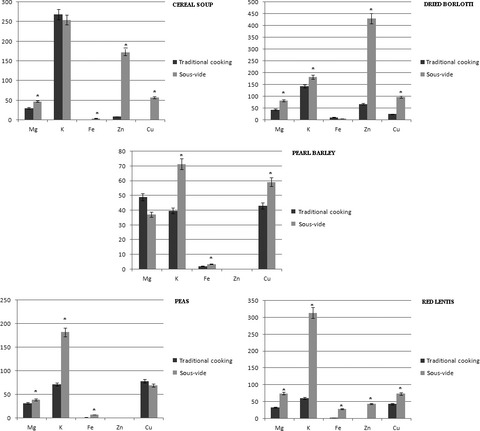
In order to guarantee the highest quality of ready-to-eat cereals and legumes, two different cooking methods have been applied: traditional cooking and sous-vide. Ashes and metals content (magnesium, potassium, iron, zinc, and copper) has been determined and compared in 50 samples of red lentils, peas, Borlotti beans, pearl barley, and cereals soup. All the samples cooked with sous-vide showed a significant increase in the content of minerals with the exception of potassium in cereal soup, iron in Borlotti beans, and magnesium in pearl barley. Ash content increased in legumes and in cereal soup cooked with sous-vide method. The higher different ashes concentration between total samples cooked with traditional cooking and with sous-vide was registered in zinc (+862 mg), iron (+314 mg), potassium (+109 mg), and copper (+95 mg). Sous-vide is preferred as it provides products with a higher concentration of metals compared to the ones cooked with traditional cooking.