Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
Compliance of clinical microbiology laboratories with recommendations for the diagnosis of bloodstream infections: Data from a nationwide survey in Italy
- First Published: 03 February 2020
We present the result of national survey during which microbiologists from 204 Italian hospitals have been interviewed on the application of guidelines concerning the proper use of blood cultures. Although the study showed some positive aspects, a full compliance with the guidelines is still far away, and more surveys will be needed to monitor the situation in the future.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Transposon mutagenesis in Mycobacterium kansasii links a small RNA gene to colony morphology and biofilm formation and identifies 9,885 intragenic insertions that do not compromise colony outgrowth
- First Published: 21 February 2020
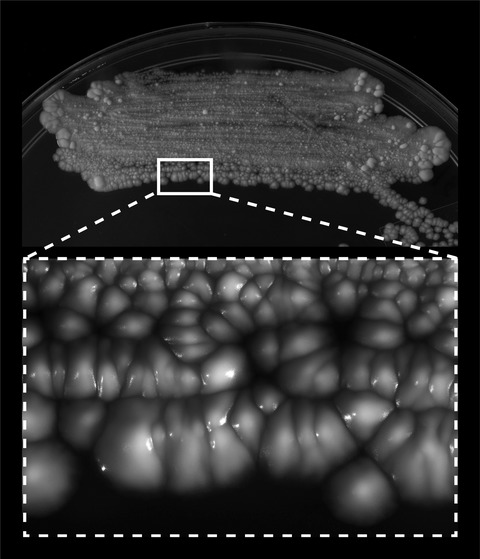
The study validated the functionality of a powerful transposon mutagenesis tool in the poorly studied Mycobacterium kansasii pathogen and used this tool to reveal the role of a small RNA gene in colony morphology and biofilm formation and to identify ≈12,000 insertions that do not compromise viability. The study also demonstrated the susceptibility of the Galleria mellonella larva to Mk, setting the stage for further exploration of this infection model to study this resilient nontuberculous mycobacterial pathogen.
Recombinant spider silk coatings functionalized with enzymes targeting bacteria and biofilms
- First Published: 07 February 2020
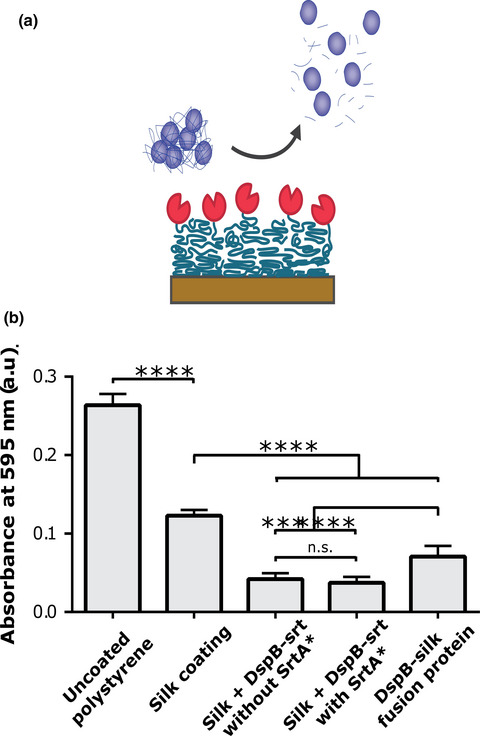
Surgical implants could potentially be protected from colonization of bacteria by having a protective coating with antibacterial properties. Herein, we investigate strategies to use assembly of silk functionalized with antibacterial enzymes to prepare such coatings. Both the peptidoglycan degrading enzyme SAL-1 and the biofilm-matrix degrading enzyme Dispersin B were shown effective when immobilized using a silk coating.
Cabbage looper (Trichoplusia ni Hübner) labial glands contain unique bacterial flora in contrast with their alimentary canal, mandibular glands, and Malpighian tubules
- First Published: 28 January 2020
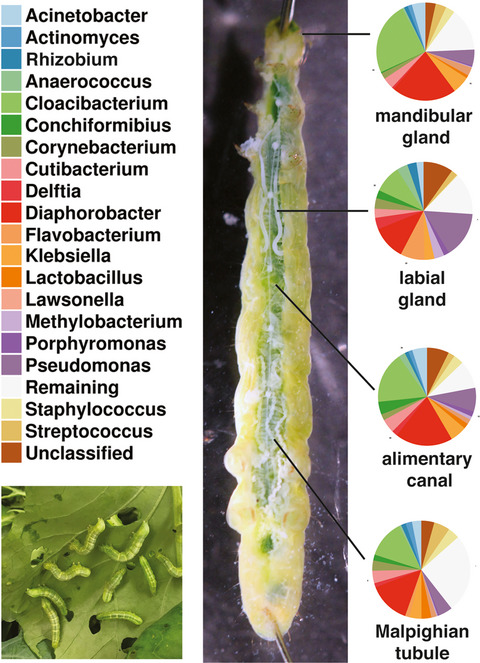
Labial gland secretions and the gut microbiota of insects affect defense responses of plants to herbivory. However, the microbiome of the labial gland has not been investigated. This work using cabbage looper, a serious pest of cole crops, demonstrates that the labial glands possess a community of bacteria that is distinct from the gut and other associated organs. This discovery warrants additional research to determine what role the labial gland microbiota has on the plant response to insect pests.
Rapid high resolution melting assay to differentiate Streptococcus suis serotypes 2, 1/2, 1, and 14
- First Published: 22 January 2020
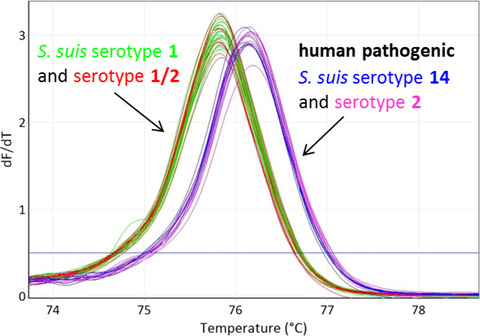
The designed high resolution melting assay allows to correctly differentiate Streptococcus suis serotype pair 2 and 1/2 or 1 and 14, respectively. The assay is based on a single-nucleotide polymorphism within the capsular polysaccharide synthesis gene cluster K and enables a rapid identification of potential zoonotic serotypes.
Bacterioplankton community variation in Bohai Bay (China) is explained by joint effects of environmental and spatial factors
- First Published: 05 February 2020
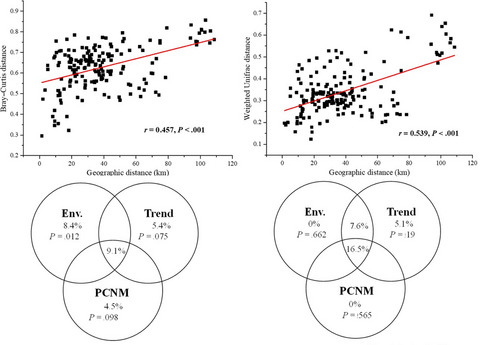
Parsing the relative importance of environmental and spatial factors in determining community structure in anthropogenic disturbed semi-enclosed bay environment is rarely few. This study found that the joint effects of environmental and spatial factors contributed to the explained variation of bacterioplankton community composition in Bohai Bay (China), in which stronger spatial effects on bacterial beta diversity than those of local environmental factors were detected, which indicated that dispersal limitation accounted more for the bacterial community variation than environmental heterogeneity.
Burkholderia cenocepacia–host cell contact controls the transcription activity of the trimeric autotransporter adhesin BCAM2418 gene
- First Published: 25 February 2020
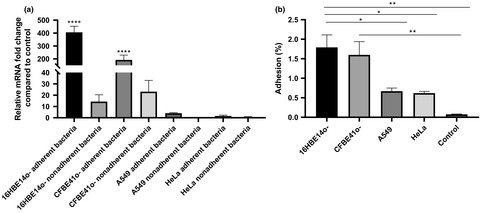
Burkholderia cenocepacia adheres to the respiratory epithelium of cystic fibrosis patients and causes chronic inflammation and disease. Our findings uncover the transcriptional alteration of BCAM2418 gene induced by the physical contact of the bacterium with bronchial epithelial cells. We found that overexpression of BCAM2418 gene augmented the bacterial cell adhesion to host cells, and it is dependent on recognition of O-linked glycans from the host cell membranes.
Spo0J and SMC are required for normal chromosome segregation in Staphylococcus aureus
- First Published: 28 January 2020
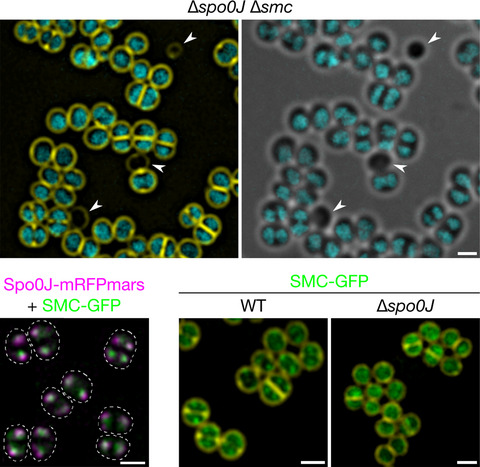
Chromosome segregation is an essential but poorly understood process in spherical bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus. Here, we show that the staphylococcal ParB homologue, Spo0J, and the structural maintenance of chromosomes (SMC) protein act in concert to achieve efficient chromosome segregation in S. aureus. We demonstrate that Spo0J and SMC form a complex that is dependent on correct localization of Spo0J and propose that additional mechanisms are likely involved in accurate staphylococcal chromosome segregation.
Streamlined production, purification, and characterization of recombinant extracellular polyhydroxybutyrate depolymerases
- First Published: 22 February 2020

A rapid, efficient approach for the expression of active recombinant extracellular polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) depolymerases originating from various bacterial strains. It enables the characterization of new PHB depolymerases and the direct comparison of activity between enzymes and conditions; as an example, the activity of five PHB depolymerases is evaluated and compared at different pH and temperatures. This approach can accelerate the investigation and development of applications based on the degradation of biopolymers.
Identification of an anaerobic bacterial consortium that degrades roxarsone
- First Published: 13 February 2020
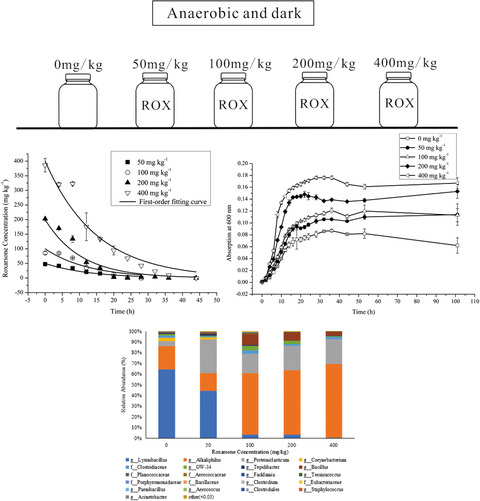
Roxarsone (ROX) is an organoarsenic animal drug used in production as a feed additive to increase weight gain and improve feed efficiency. This study revealed the close relationship between ROX and microbial growth. A stable anaerobic bacterial consortium that effectively degraded ROX was identified. The bacterial community, growth curve, and degradation ability at different ROX concentrations were assessed.
Changes in the community structure of the symbiotic microbes of wild amphibians from the eastern edge of the Tibetan Plateau
- First Published: 11 February 2020
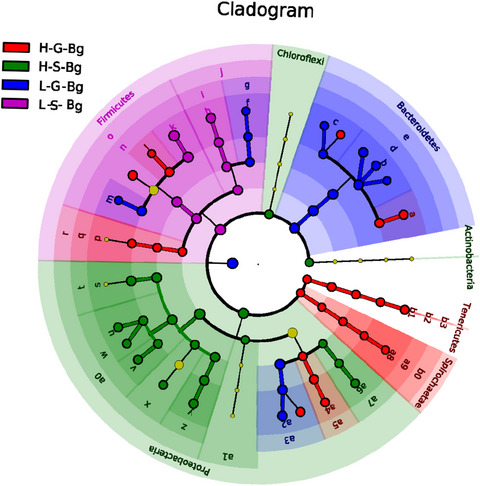
Altitude has a potential effect on the animal symbiotic microbiome. Here, we provided an example of this effect in the wild amphibians. High relative abundance of Caulobacteraceae and Sphingomonadaceae was found in skin samples from both Bufo gargarizans and the other high-altitude amphibians (nine species combined). High relative abundance of Coxiellaceae and Mycoplasmataceae was found in gut samples from both B. gargarizans and the other high-altitude amphibians.
Fitness costs associated with carriage of a large staphylococcal plasmid are reduced by subinhibitory concentrations of antiseptics
- First Published: 13 February 2020
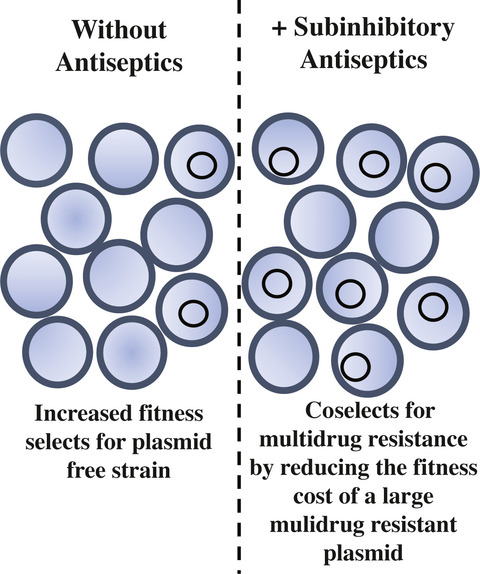
Pathogenic bacteria often carry large plasmids that contain multiple resistance genes; individually, these elements coselect for additional resistance genes that are genetically linked by the plasmid. In this short communication, we demonstrate increased triclosan resistance can be conjugatively transferred in Staphylococcus aureus. Furthermore, in a competition assay, we show subinhibitory concentrations of antiseptics abrogate the fitness cost of a large multidrug resistance plasmid in S. aureus, thus coselecting for the numerous antimicrobial resistance genes present on the plasmid.
A novel way to synthesize pantothenate in bacteria involves β-alanine synthase present in uracil degradation pathway
- First Published: 29 February 2020
The production of isoprene from cellulose using recombinant Clostridium cellulolyticum strains expressing isoprene synthase
- First Published: 28 February 2020
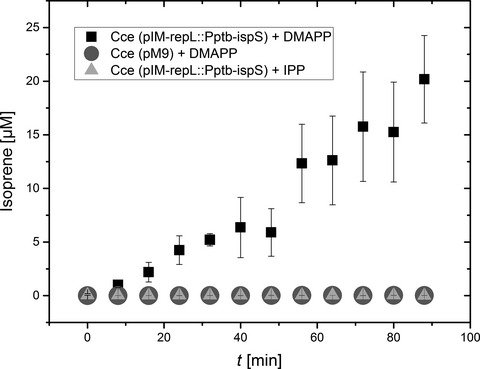
We engineered the mesophilic prokaryote Clostridium cellulolyticum, which can degrade cellulosic biomass, to utilize the resulting glucose monomers as a feedstock for the production of isoprene. We have shown for the first time that engineered C. cellulolyticum can be used as a metabolic chassis for the sustainable production of isoprene.
Bacterial community dynamics in spontaneous sourdoughs made from wheat, spelt, and rye wholemeal flour
- First Published: 11 February 2020
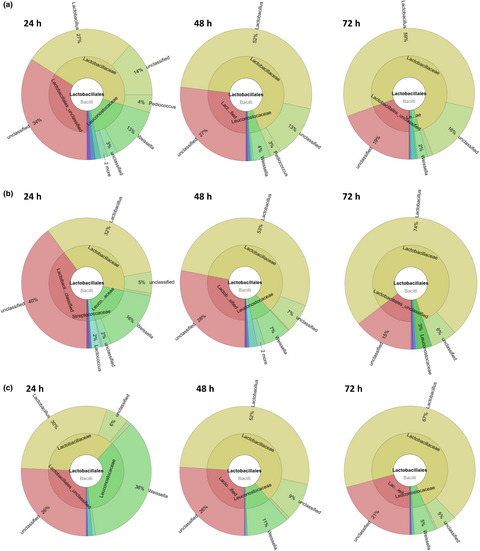
This work was carried out to determine the microbial biodiversity of spontaneous sourdoughs that are made from wheat, spelt, and rye wholemeal flour on an industrial scale. The culture-independent approach demonstrated how the microbial ecology changed during 72 hr of fermentation. The Weissella was the most abundant genus after a 24 hr of fermentation of the rye sourdough, but as the process progressed, its abundance decreased in favor of the Lactobacillus genus similarly as in wheat and spelt sourdoughs.