Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The 340B Drug Pricing Program and Management of Advanced Prostate Cancer
- First Published: 30 December 2024
Activin A promoted the anti-tumor effect of ActRIIA high CD8+ T cells in mouse hepatoma
- First Published: 27 December 2024
Prognostic factors in patients with localized and metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma. A report from two studies and two registries of the Cooperative Weichteilsarkom Studiengruppe CWS
- First Published: 09 January 2025
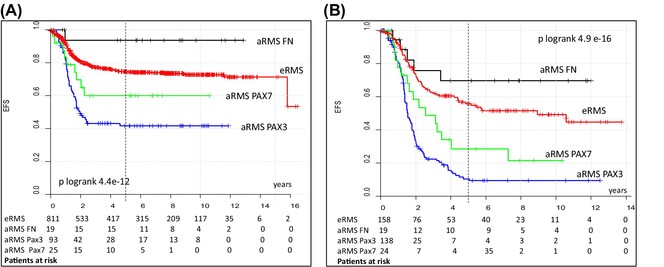
PAX3::FOXO1 fusion should replace FOXO1 fusion as an adverse prognostic factor in risk stratification of patients with rhabdomyosarcoma. The prognostic relevance of PAX7::FOXO1-positive and FN alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (aRMS), along with the clinical factors described in this report, allows further refinement of risk assessment of patients with localized and metastatic (aRMS).
Phase 3 Study of Talazoparib Plus Enzalutamide Versus Placebo Plus Enzalutamide as First-Line Treatment in Patients With Metastatic Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer: TALAPRO-2 Japanese Subgroup Analysis
- First Published: 31 December 2024
Pretreatment Fatigue in Breast Cancer Patients: Comparison With Healthy Controls and Associations With Biopsychosocial Variables
- First Published: 09 January 2025
Diagnostic Performance and Safety of Ultrasound-Guided Core Needle Biopsy for Diagnosing Lymphoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- First Published: 06 January 2025
Enrichment of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts, Macrophages, and Up-Regulated TNF-α Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment of CMS4 Colorectal Peritoneal Metastasis
- First Published: 30 December 2024
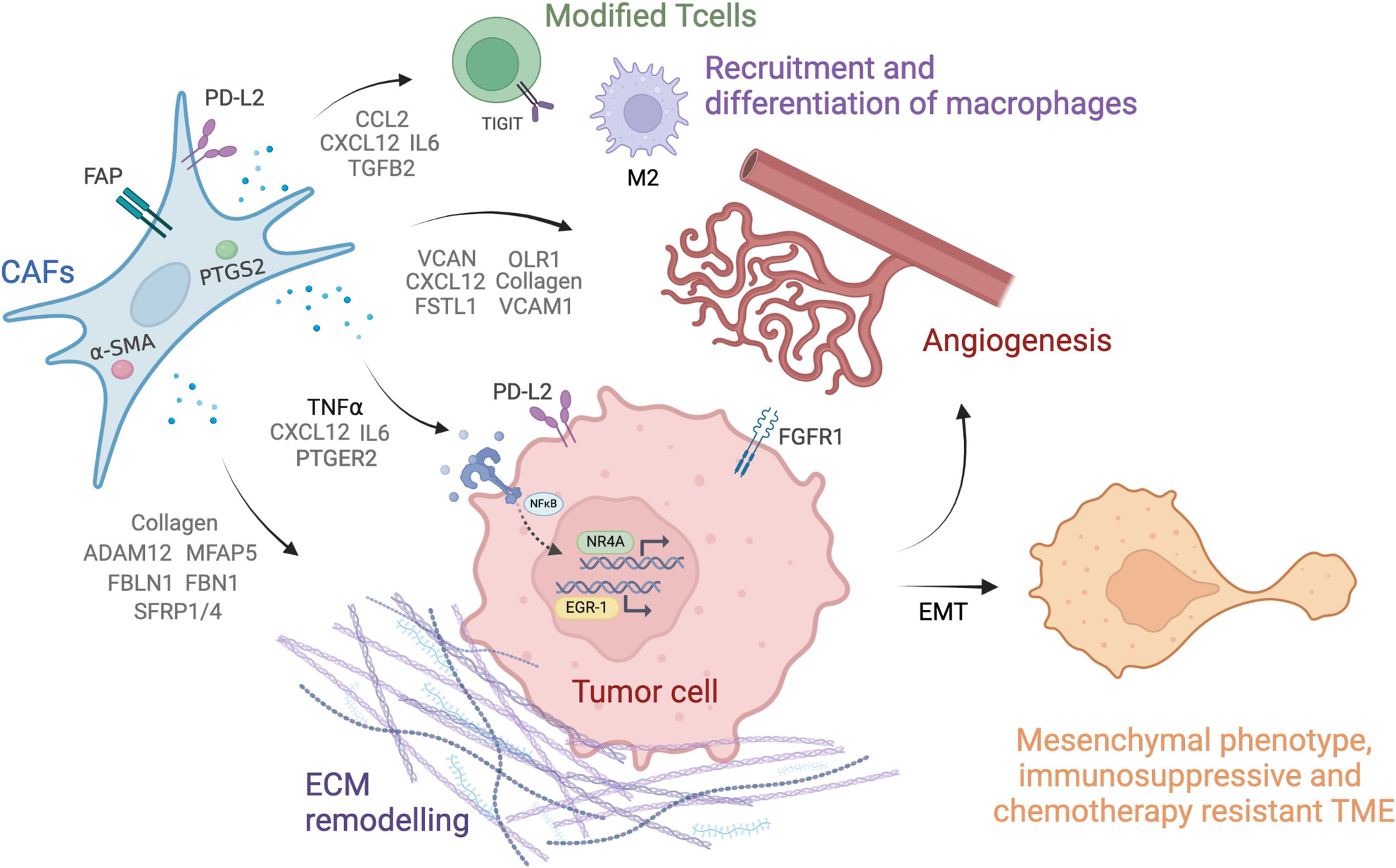
Immunotherapy is ineffective in mCRC; however, the efficacy could be significantly enhanced by modifying the tumor immune microenvironment. Comparison of immune cell populations and cell signaling in colorectal liver, lung, and peritoneal (PM) metastases using immune cell deconvolution tools and transcriptomic data, revealed enrichment of CAFs and CAF-related secreting factors in the CMS4 PM microenvironment, that could facilitate intraperitoneal spread, immune suppression, and chemotherapy resistance. Targeting CAF-associated pathways, M2 macrophages, and TNF-⍺ signaling could be novel therapeutic strategies for CMS4 PM-CRC, as they might alter the tumor immune interplay and improve immunotherapy response.
The Multi-Kinase Inhibitor GZD824 (Olverembatinib) Shows Pre-Clinical Efficacy in Endometrial Cancer
- First Published: 30 December 2024
REVIEW
DNA Methylation in Prostate Cancer: Clinical Implications and Potential Applications
- First Published: 09 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Guiding Sole Intraoperative Radiotherapy in Breast Cancer According to ASTRO Guidelines: Mitigating Adverse Outcomes in a Taiwan Single-Center
- First Published: 30 December 2024
Efficacy and Safety of Chemotherapy or EGFR-TKIs as First-Line Therapy in NSCLC Patients Harboring Non-Ex 20 Ins Uncommon EGFR Mutations: A Retrospective Study in China
- First Published: 30 December 2024
A Clinical Prediction Model for Pathologic Upgrade to Invasive Carcinoma Following Conization of Cervical High-Grade Squamous Intraepithelial Lesions
- First Published: 30 December 2024
CORRECTION
Correction to ‘MUC1 as a Target for CAR-T Therapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma’
- First Published: 30 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
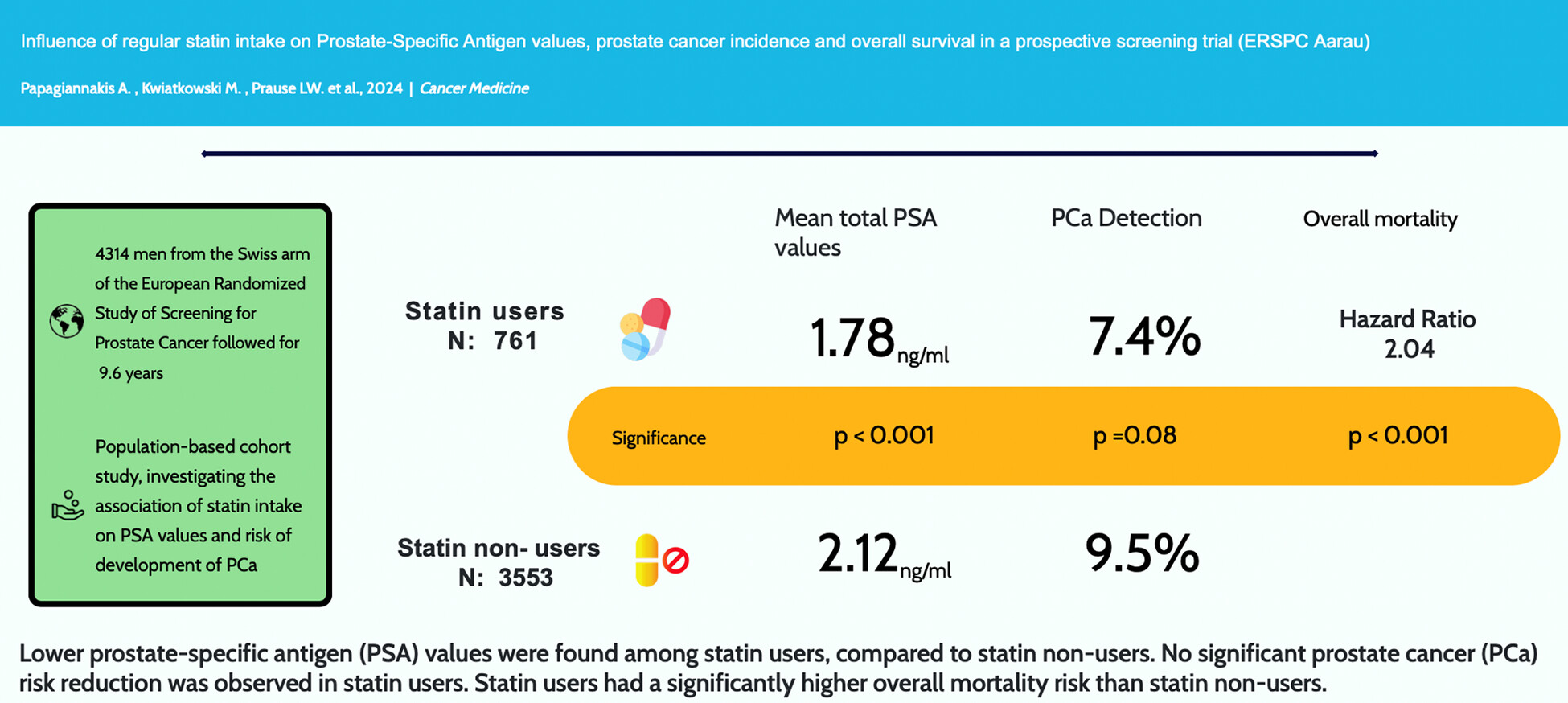
Influence of Regular Statin Intake on Prostate-Specific Antigen Values, Prostate Cancer Incidence and Overall Survival in a Prospective Screening Trial (ERSPC Aarau)
- First Published: 06 January 2025
A Nationwide Exploration of Social Inequalities in Cancer Mortality Amidst the COVID-19 Pandemic in Belgium
- First Published: 08 January 2025

We analyzed nationwide Belgian data to assess changes in cancer mortality during the early stages of the COVID-19 pandemic (March–December 2020) compared to the same period in 2019, focusing on potential shifts in social disparities. Our findings showed decreases in reported cancer deaths, particularly among individuals aged 75 and older, without significant alterations in existing socioeconomic patterns. These reductions may reflect the prioritization of COVID-19 in cause-of-death coding and its role as a competing risk, highlighting the need for continued policy and healthcare efforts to address persistent educational inequalities.
Patient and Caregiver Perceptions of Caregiving Contributions During Cancer Clinical Trials: A Mixed-Methods Study
- First Published: 09 January 2025
Cancer Incidence Among People With a Prior Hospital Record of Depression in Scotland, 1991–2019: A Cohort Study
- First Published: 08 January 2025
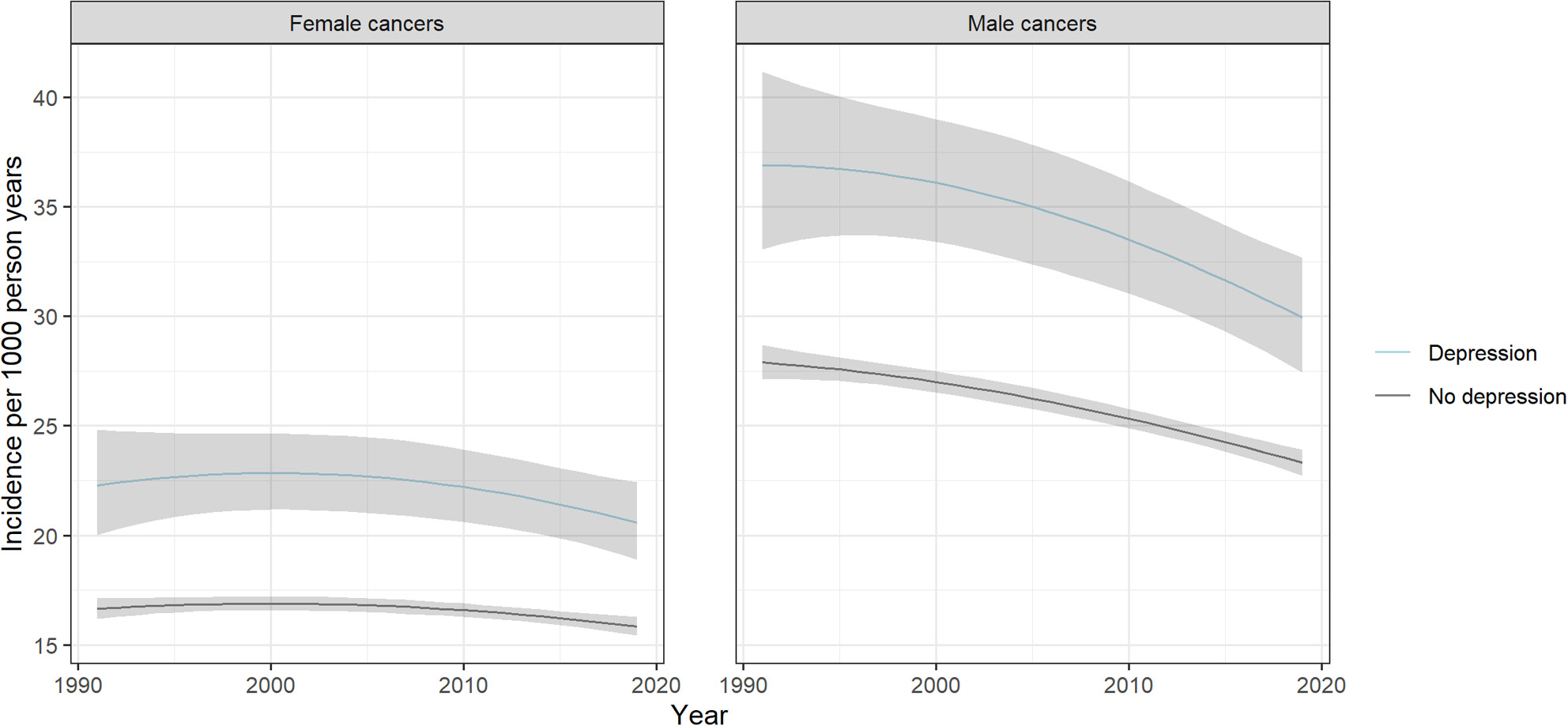
Existing evidence on depression and cancer risk is conflicting, likely reflecting differences in methodology, as well as study limitations, such as small study population and short follow-up periods. Moreover, there has been almost no investigation of how any mental health disparity in cancer risk has changed over time or differs by population sub-group. We therefore addressed these gaps in a cohort study using Scottish linked administrative healthcare data to compare cancer incidence (all cancers and common cancer subtypes) in those with versus without a hospital admission record for depression, over a 29-year study period.
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
CD4+ T Cells Mediate Dendritic Cell Licensing to Promote Multi-Antigen Anti-Leukemic Immune Response
- First Published: 27 December 2024
CD4+ T cell-mediated mechanism of DC licensing can promote multi-Ag immune responses that may augment current targeted immunotherapies.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Phase I Trial of Upamostat Combined With Gemcitabine in Locally Unresectable or Metastatic Pancreatic Cancer: Safety and Preliminary Efficacy Assessment
- First Published: 30 December 2024
REVIEW
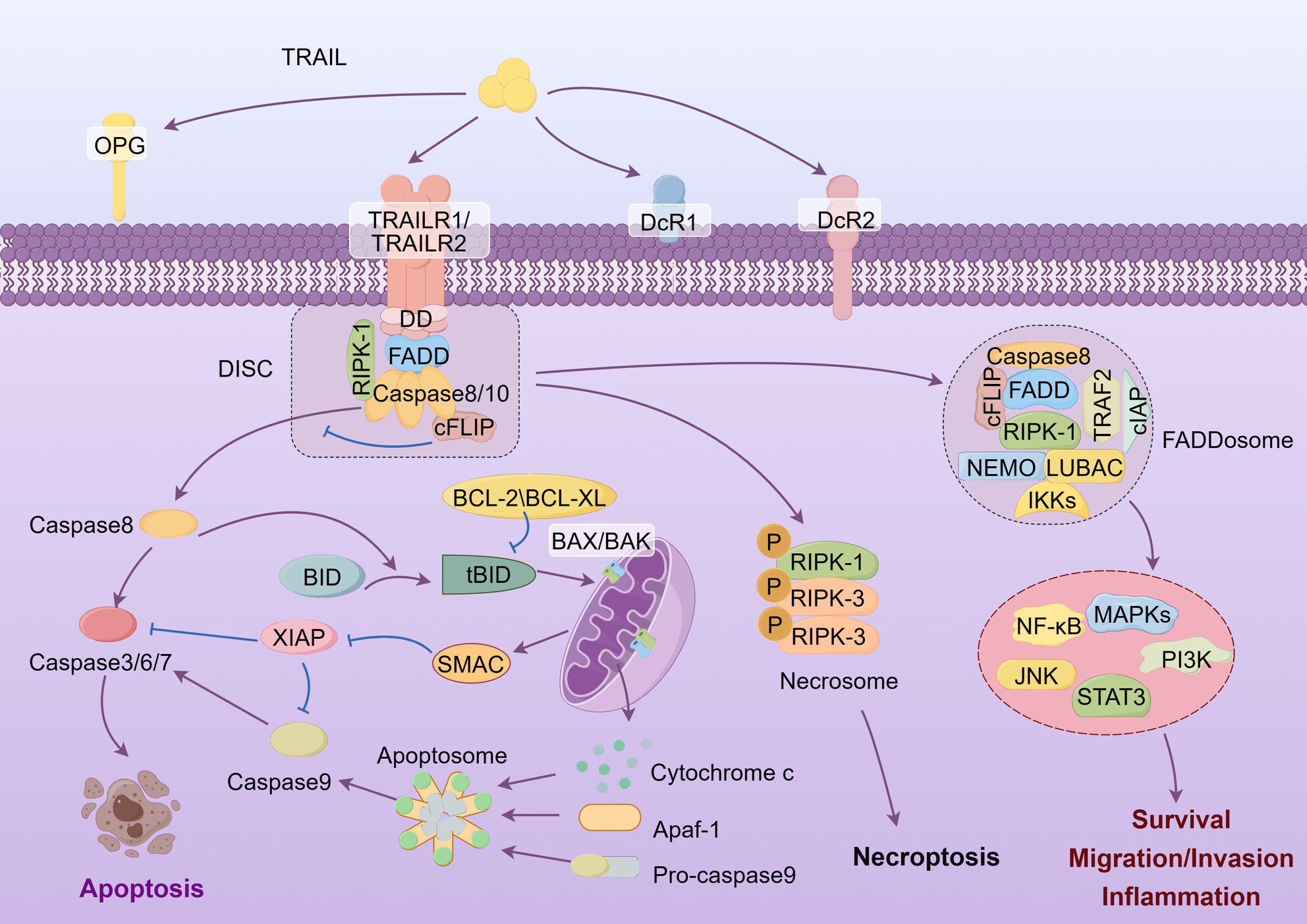
Turn TRAIL Into Better Anticancer Therapeutic Through TRAIL Fusion Proteins
- First Published: 30 December 2024
RESEARCH ARTICLE
The Impact of Chemotherapy and Body Mass Index on Cancer-Related Fatigue in Colon Cancer Patients: A PROFILES-Registry Study
- First Published: 06 January 2025
Differentiating Pulmonary Nodule Malignancy Using Exhaled Volatile Organic Compounds: A Prospective Observational Study
- First Published: 07 January 2025
Does Asthma Affect the Risk of Developing Breast Cancer?
- First Published: 31 December 2024
Influence of Organ-Specific Extranodal Involvement on Survival Outcomes in Stage IV Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- First Published: 31 December 2024
Prostate Cancer Patients' Perceptions Regarding the Relevance of a Digital Rectal Examination During Their Follow-Up After Radiation Therapy
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Immune Cell Profiling Reveals a Common Pattern in Premetastatic Niche Formation Across Various Cancer Types
- First Published: 30 December 2024
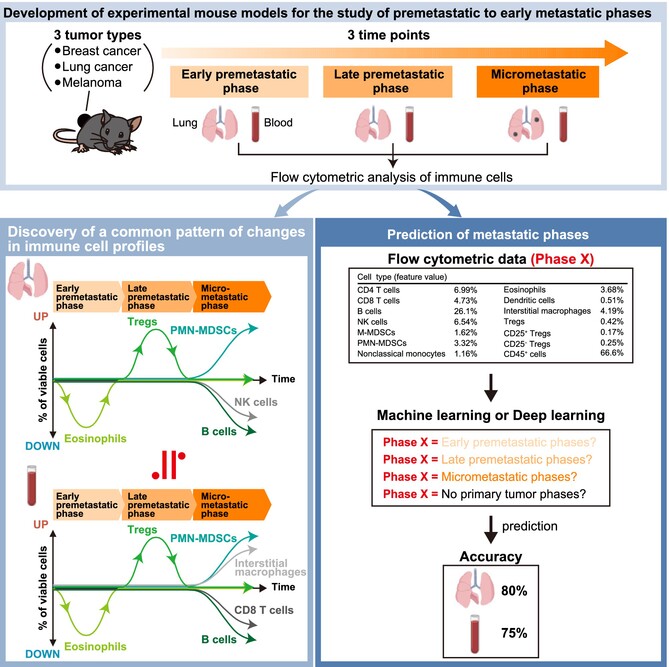
Summary of the dynamics of immune cell types in peripheral blood showing a decrease in the number of eosinophils in the early premetastatic phase, an increase in Tregs in the late premetastatic phase, and an increase in PMN-MDSCs and interstitial macrophages and a decrease in B cells and CD8 T cells in the micrometastatic phase.
Tandem Versus Single Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation for High-Risk Multiple Myeloma in the Era of Novel Agents: A Real-World Study of China
- First Published: 02 January 2025
Combination of Hotspot Mutations With Methylation and Fragmentomic Profiles to Enhance Multi-Cancer Early Detection
- First Published: 03 January 2025
Circulating CD3+CD8+ T Lymphocytes as Indicators of Disease Status in Patients With Early Breast Cancer
- First Published: 03 January 2025
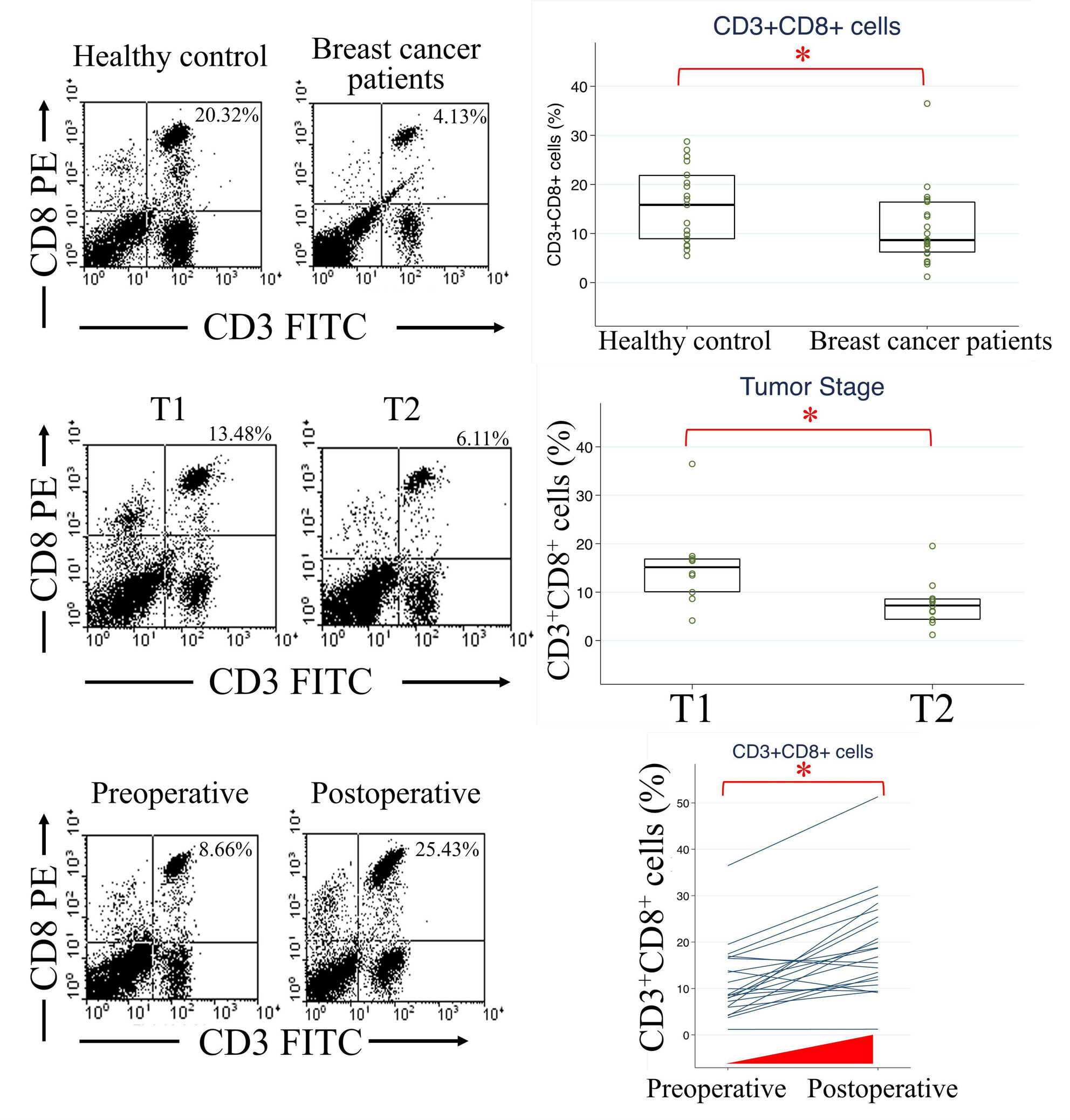
Circulating CD3+CD8+ cell levels were lower in breast cancer patients, elevated posttreatment, and subsequently declining upon recurrence. Elevated plasma chemokine (C–C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) levels distinguished patients with breast cancer from healthy controls. In summary, circulating CD3+CD8+ CTL and plasma CCL2 levels emerged as promising dual-purpose biomarkers and therapeutic targets in breast cancer management.
REVIEW
Effectiveness and Safety of Treatments for Early-Stage Merkel Cell Carcinoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized and Non-Randomized Studies
- First Published: 03 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Levels and Survival Outcomes in Advanced Biliary Tract Cancer: Results From the NIFTY Trial
- First Published: 03 January 2025
Molecular Mechanisms of Synergistic Effect of PRIMA-1met and Oxaliplatin in Colorectal Cancer With Different p53 Status
- First Published: 05 January 2025
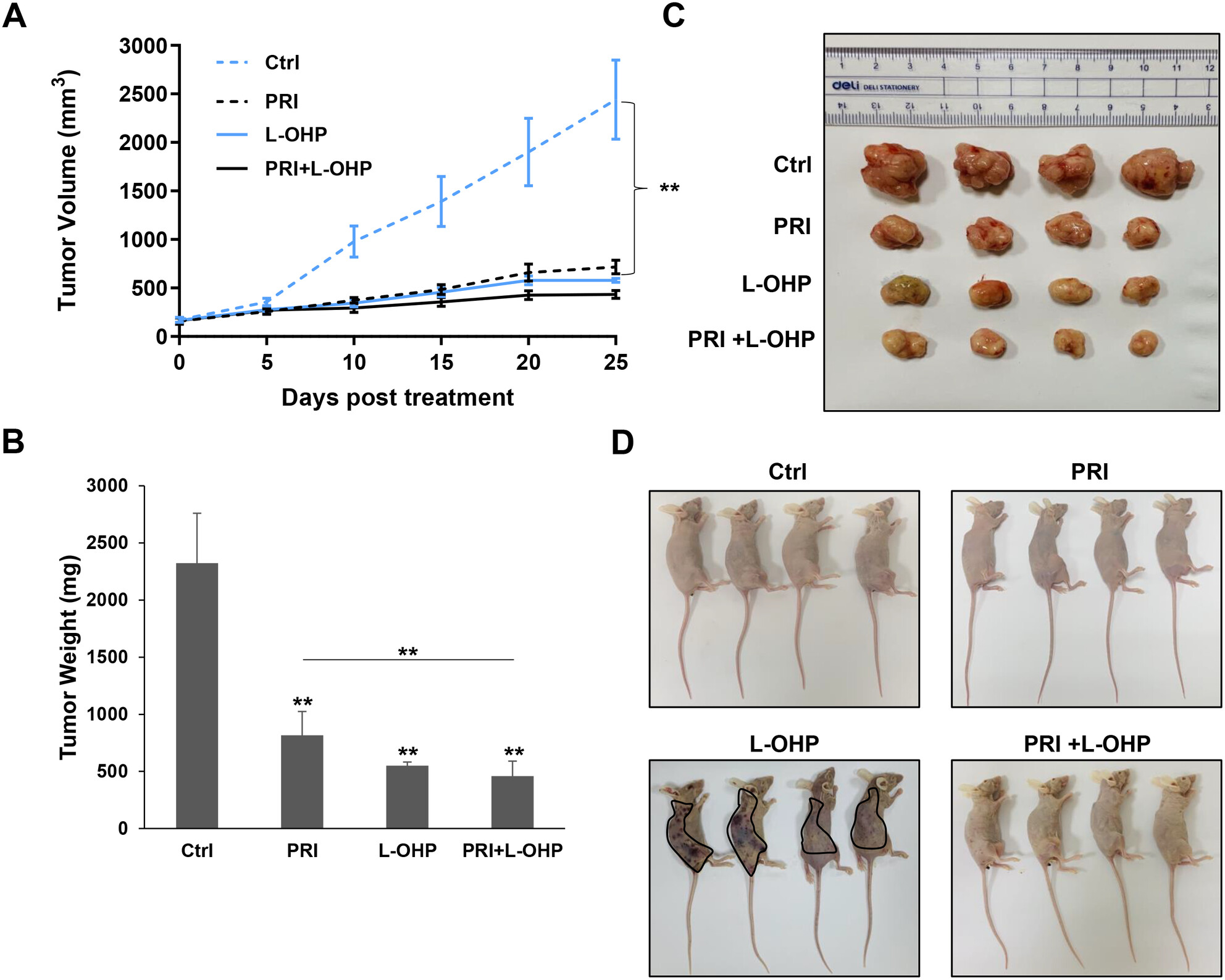
We report differential molecular mechanisms including pathways, key modules, and hub genes, induced by combination of oxaliplatin (L-OHP) and PRIMA-1met (APR-246, eprenetapopt) in p53-wild type vs. p53-mutant colorectal cancer. Our in vivo studies show that the additional of PRIMA-1met offers a threefold advantage: enhanced therapeutic effects, reduced L-OHP resistance, and prevention of L-OHP-related side effects.
Repurposing of Metformin to Improve Survival Outcomes in Patients With Upper Tract Urothelial Carcinoma
- First Published: 05 January 2025
REVIEW
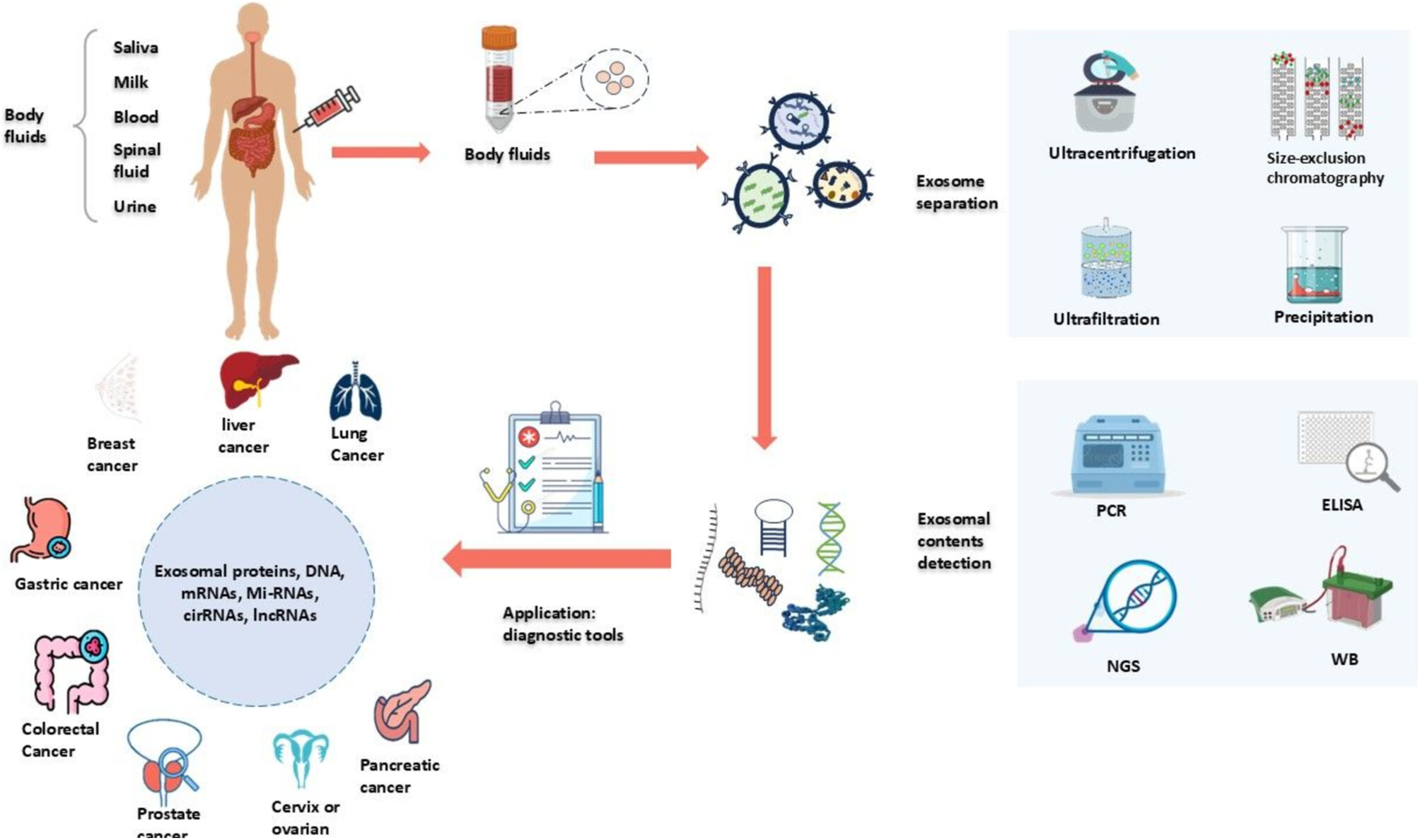
Diagnostic and Prognostic Significance of Exosomes and Their Components in Patients With Cancers
- First Published: 06 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
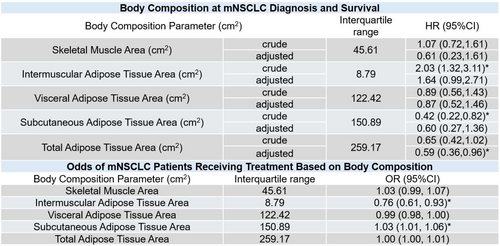
The Association Between Body Composition, Overall Survival, Treatment Decisions, and Patient-Reported Outcomes in Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- First Published: 07 January 2025
Findings support adiposity as a protective factor for mNSCLC survival and higher odds of receiving cancer treatment. This study supports future work aimed at utilizing multiple clinical factors (e.g., body composition and PROs), along with ECOG Performance Status, to identify a more refined method to dictate treatment decisions and prognostic information.
Assessing the Causal Effect of Circulating Protein-To-Protein Ratio on the Risk of Morbidity of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- First Published: 07 January 2025
REVIEW
Exploring Multiplex Immunohistochemistry (mIHC) Techniques and Histopathology Image Analysis: Current Practice and Potential for Clinical Incorporation
- First Published: 07 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Can Large Language Models Aid Caregivers of Pediatric Cancer Patients in Information Seeking? A Cross-Sectional Investigation
- First Published: 07 January 2025
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Frequency of Missing TNM Stage Data for Adults With Intellectual or Developmental Disabilities in a Provincial Cancer Registry—A Brief Report
- First Published: 07 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) due to Breast, Cervical, Colorectal and Oral Cancers in Taiwan Regions
- First Published: 07 January 2025
FXYD3 Is Frequently Expressed in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma but Does Not Predict Survival
- First Published: 09 January 2025
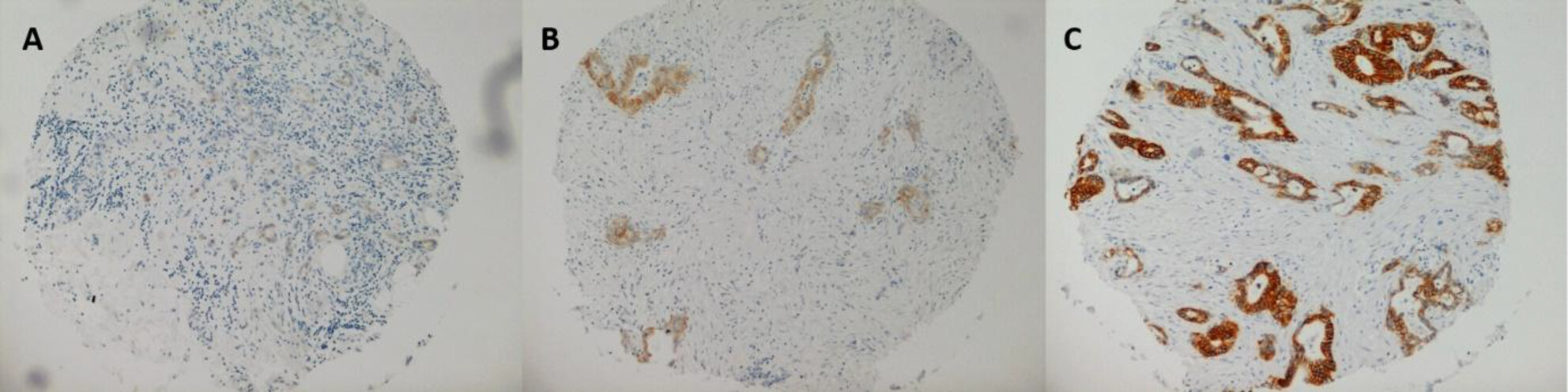
Pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) remains one of the world's deadliest cancers, and there is significant imperative to develop novel prognostic biomarkers to guide our limited therapeutic options. FXYD3 is a transmembrane protein overexpressed in numerous cancers including pancreatic cancer and, like other seven members of the FXYD family, is known to modulate Na/K-ATPase activity. However, despite knowledge of its upregulation, the role of FXYD3 in pancreatic cancer survival has not yet been assessed on a larger scale. Herein, we present a study establishing the rate of immunohistochemically-evaluated FXYD3 expression in chemotherapy-naïve resected PDAC tumours. Furthermore, we demonstrate that FXYD3 expression does not correlate with survival in these patients.
Baseline FIB-4 May Be a Risk Factor of Recurrence After SBRT in Patients With HBV-Related Small HCC
- First Published: 09 January 2025
Prognostic Features and Potential for Immune Therapy in Metastatic Mismatch Repair-Deficient Colorectal Cancer: A Retrospective Analysis of a Large Consecutive Population-Based Patient Series
- First Published: 09 January 2025
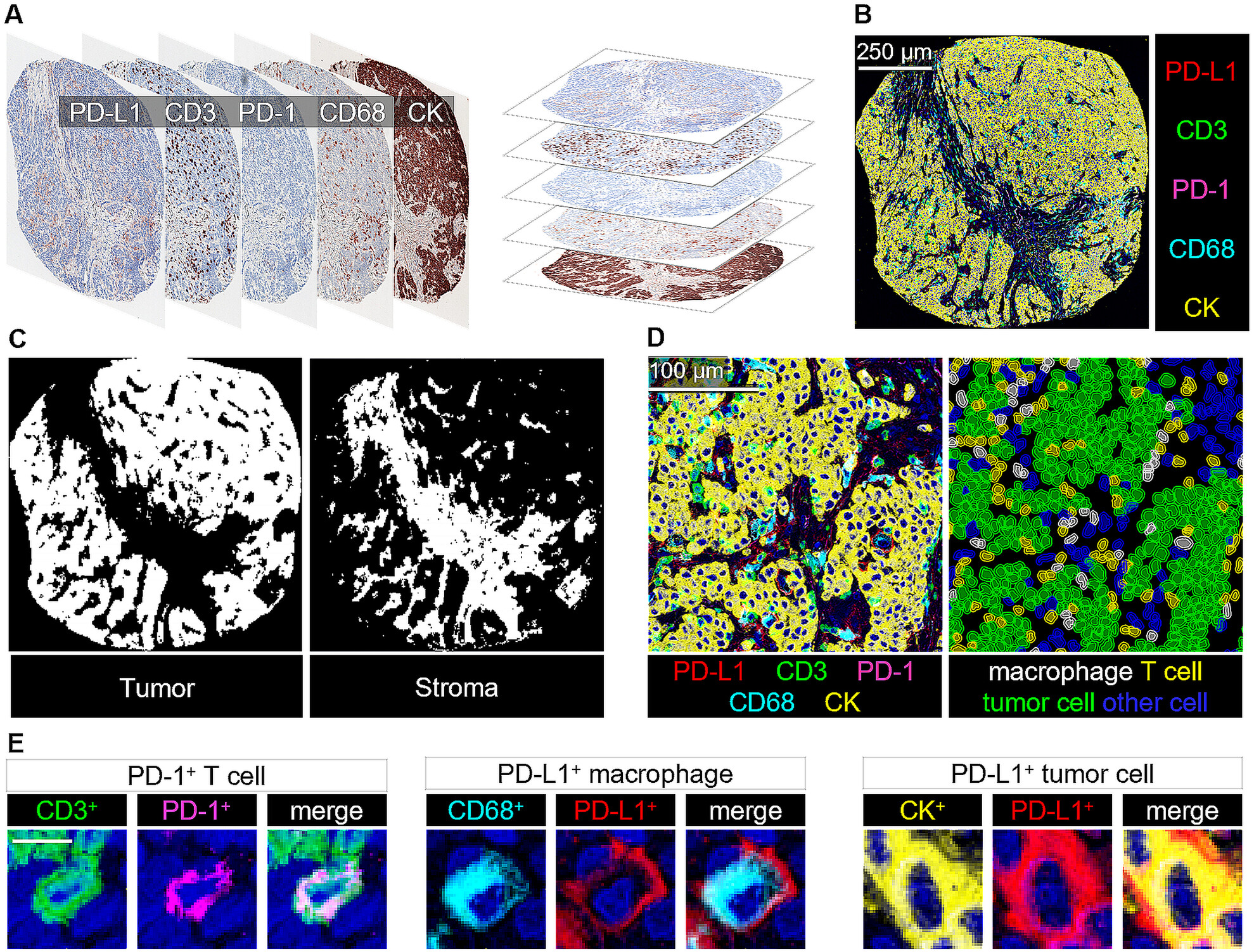
Mismatch repair–deficient colorectal cancer patients are generally older, with often significant comorbidities, and only a limited portion of patients with metastatic tumors underwent oncological treatments. Many of the metastatic tumors present features that may impair response to PD-1 blockade therapy. High proportions of necrosis and stroma were common in metastatic tumors and were associated with worse survival; however, high Crohn's-like reaction density, T-cell proximity score, and CD68+/PD-L1+ cell number in the tumor center and invasive margin were independent prognostic immune factors for improved survival.
Arterial Thromboembolism in Patients With Advanced Lung Cancer: Secondary Analyses of the Rising-VTE/NEJ037 Study
- First Published: 09 January 2025
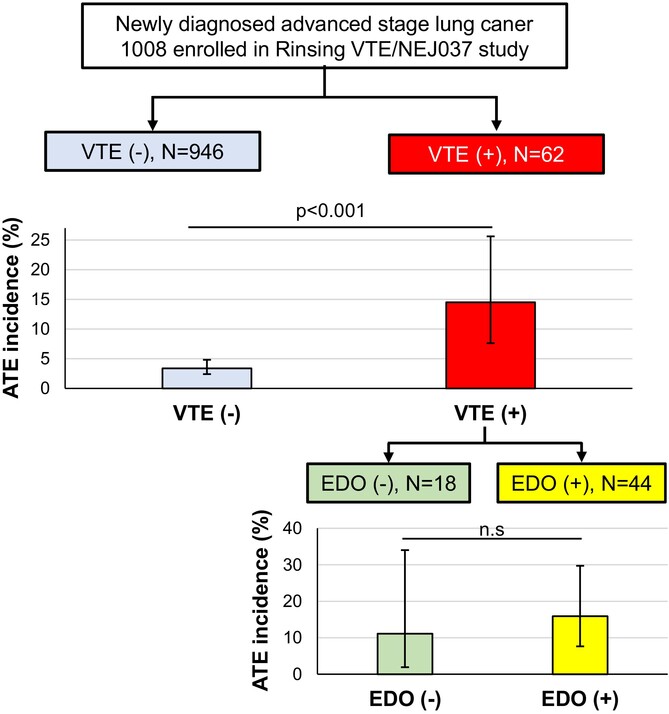
The incidence rate of arterial thromboembolism (ATE) was 4.1% over a 2-year follow-up in advanced lung cancer patients. Venous thromboembolism (VTE) was further identified as an independent risk factor for ATE, while intervention with direct oral anticoagulants was seen as less effective for the prevention of ATE in advanced lung cancer patients with VTE.
The Effect of Expressive Writing on the Experiences of Head and Neck Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Pages: 1-12
- First Published: 09 January 2025
BRIEF COMMUNICATION
Inhibiting H3K27 Demethylases Downregulates CREB-CREBBP, Overcoming Resistance in Relapsed Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
- Pages: 1-7
- First Published: 10 January 2025
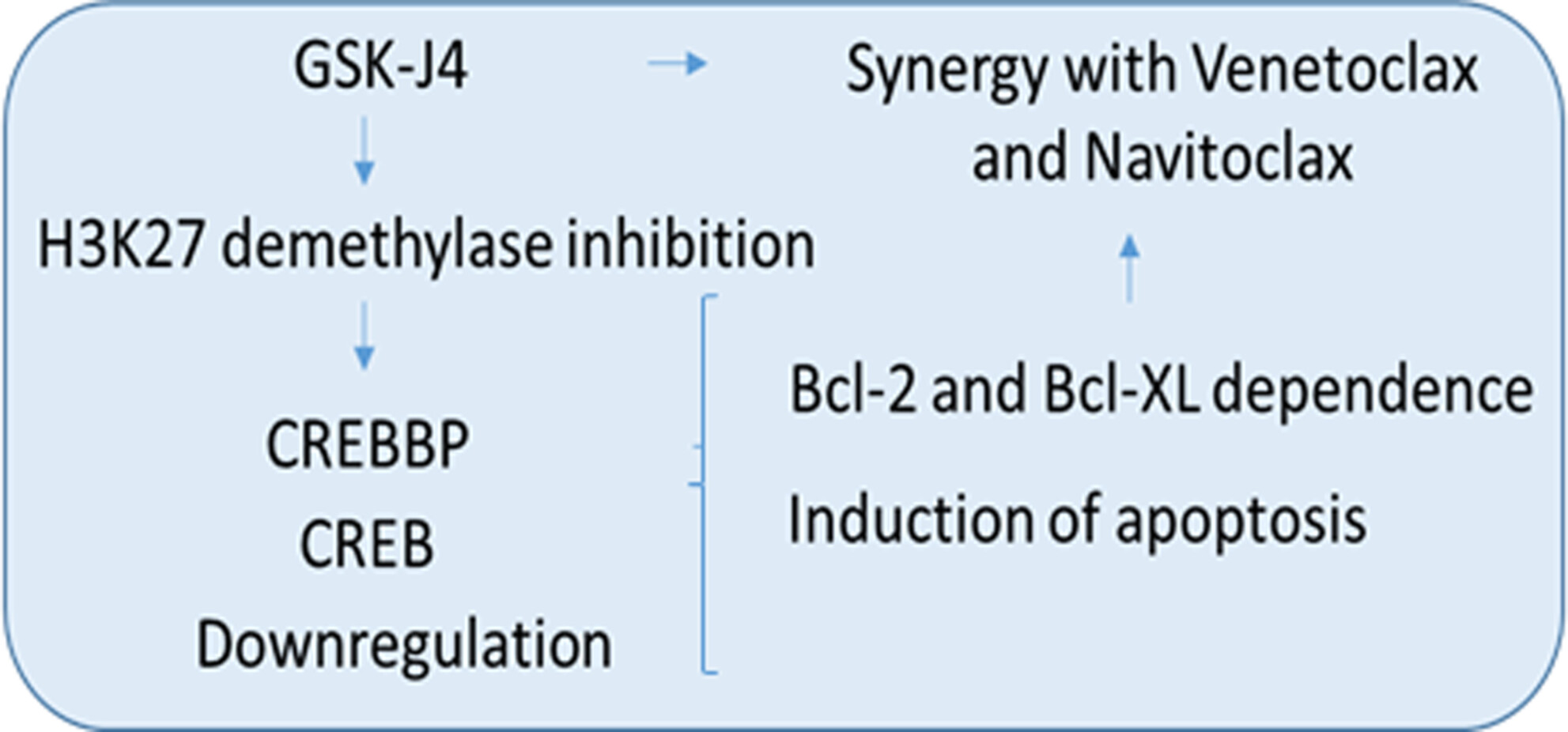
This study investigates the effect of epigenetic regulator GSK-J4 in the downregulation of CREB and CREBBP in acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cell lines and relapsed patient samples, leading to apoptosis induction and cell cycle arrest. We propose H3K27 demethylase inhibition as a potential treatment strategy for patients with treatment-resistant ALL, using CREBBP as a biomarker for drug response and combining GSK-J4 with venetoclax and navitoclax as synergistic partners.
REVIEW
Insights Into the Role of Bmi-1 Deregulation in Promoting Stemness and Therapy Resistance in Glioblastoma: A Narrative Review
- First Published: 10 January 2025
CORRECTION
Correction to “ARHGAP42 Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion Involving PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathway in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma”
- First Published: 10 January 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Concomitant Usage of H1-Antihistamines and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors on Cancer Patient Survival
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Mutation in CDC42 Gene Set as a Response Biomarker for Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Metagenomic Profiling of Oral Microbiome Dynamics During Chemoradiotherapy in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Patients
- First Published: 13 January 2025