Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
Clinical Cancer Research
EDITORIAL
Compassion is a key quality for palliative care teams
- Pages: 5325-5326
- First Published: 10 October 2018
Multidisciplinary team members including doctors, nurses, and chaplains, and social workers involve palliative. Therefore, it is not easy to define palliative care in a word. We are convinced that compassion is at the core of palliative care.
REVIEW
The role of tissue and serum carcinoembryonic antigen in stages I to III of colorectal cancer—A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 5327-5338
- First Published: 09 October 2018
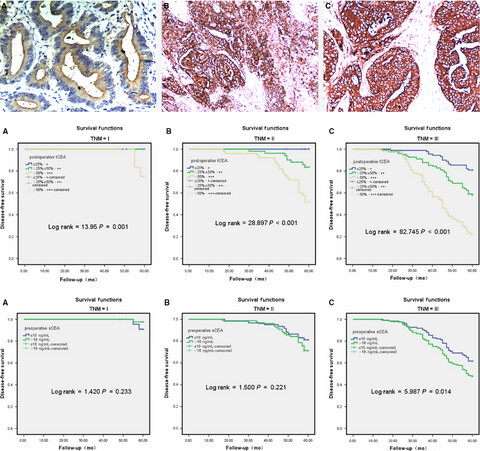
Tissue carcinoembryonic antigen (t-CEA)expression and serum carcinoembryonic antigen (s-CEA) expression of colorectal carcinoma (CRC) are the most useful tumor markers for the diagnosis and evaluation of prognosis, but the role remains controversial. The objective of this study was to compare the prognostic value of CEA both in serum and tumor tissue in CRC.
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
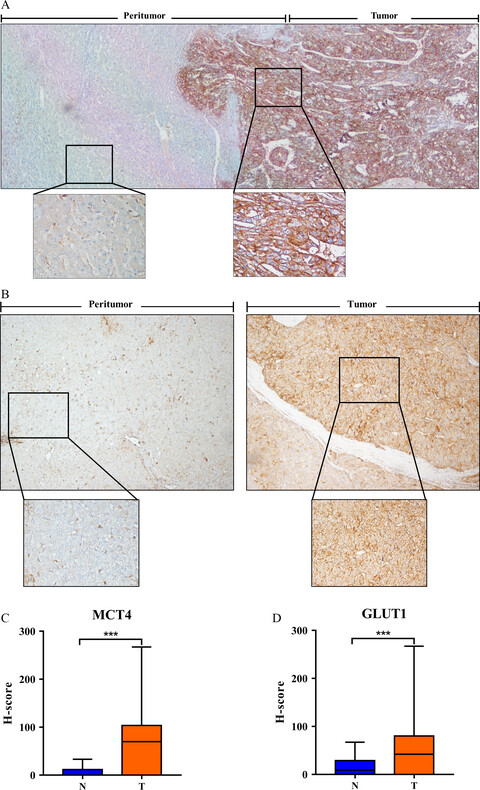
Aberrant MCT4 and GLUT1 expression is correlated with early recurrence and poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after hepatectomy
- Pages: 5339-5350
- First Published: 10 October 2018
Adherence to postresection colorectal cancer surveillance at National Cancer Institute-designated Comprehensive Cancer Centers
- Pages: 5351-5358
- First Published: 18 October 2018
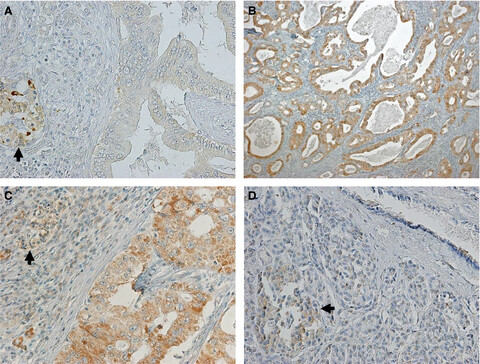
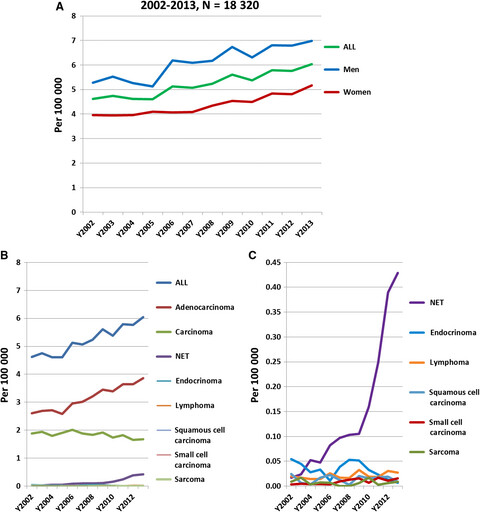
Clinicopathological features and prognosis of patients with gastric neuroendocrine tumors: A population-based study
- Pages: 5359-5369
- First Published: 11 October 2018
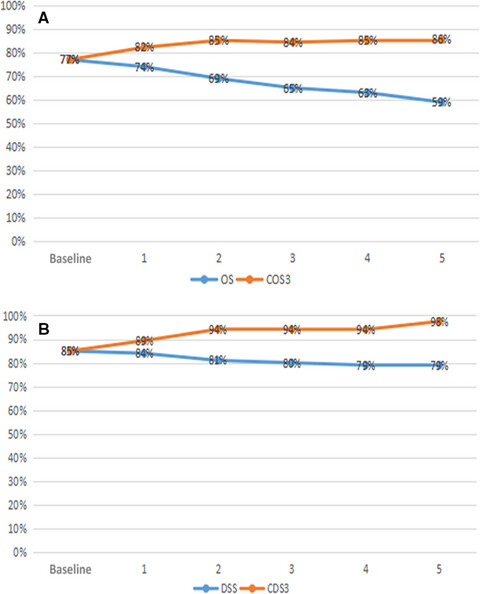
Our study showed that age, tumor grade, T stage, and N stage were the prognostic factors of patients with G-NETs, whose survival improves gradually with each year of survival after surgery. The patients with poorer initial prognosis, the gap between the actual DSS and CDS3 or OS and COS, become increasingly significant.
National Cancer Database Comparison of Radical Cystectomy vs Chemoradiotherapy for Muscle-Invasive Bladder Cancer: Implications of Using Clinical vs Pathologic Staging
- Pages: 5370-5381
- First Published: 10 October 2018
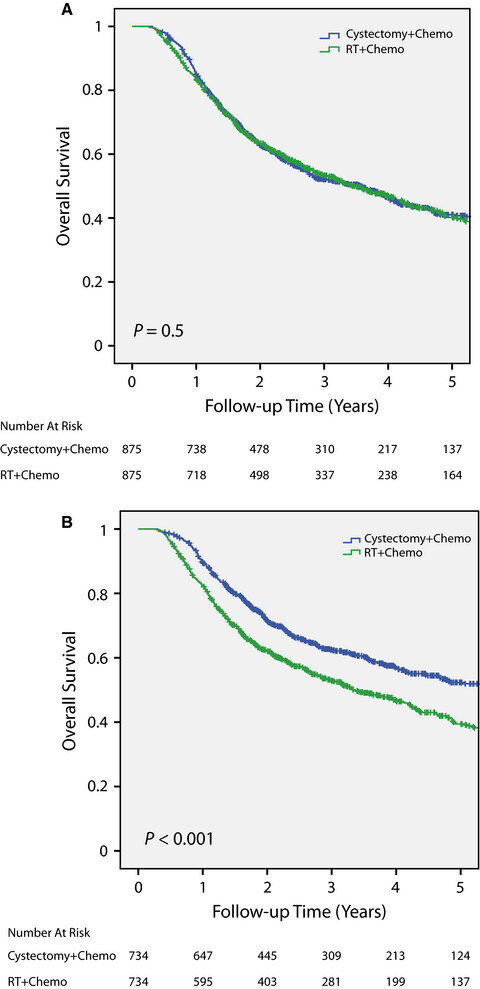
Previous publications have shown better overall survival for muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients treated with radical cystectomy compared to definitive chemoradiotherapy, but those studies were complicated by imbalance in patient characteristics or matching the pathologic stage of cystectomy patients to the clinical stage of chemoRT. In this study, matched pair analyses using clinical stage showed similar overall survival between radical cystectomy/chemotherapy and definitive chemoradiotherapy.
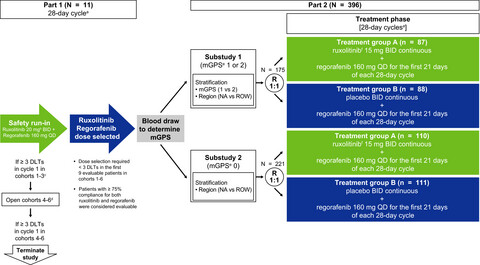
Randomized, double-blind, phase two study of ruxolitinib plus regorafenib in patients with relapsed/refractory metastatic colorectal cancer
- Pages: 5382-5393
- First Published: 19 August 2018
Integrated analysis of long noncoding RNA interactions reveals the potential role in progression of human papillary thyroid cancer
- Pages: 5394-5410
- First Published: 14 October 2018
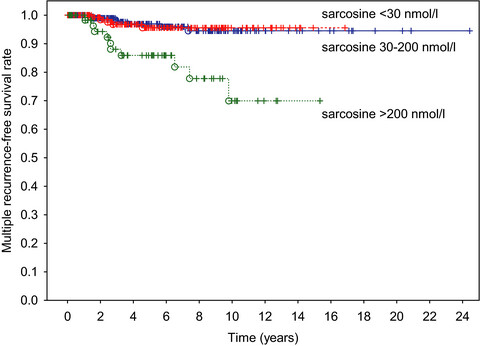
Post-treatment urinary sarcosine as a predictor of recurrent relapses in patients with prostate cancer
- Pages: 5411-5419
- First Published: 12 September 2018
Would 1.0 cm be a more suitable cutoff to subdivide pT1 tumors in hormone receptor-negative and HER2-positive breast cancer?
- Pages: 5420-5430
- First Published: 01 October 2018
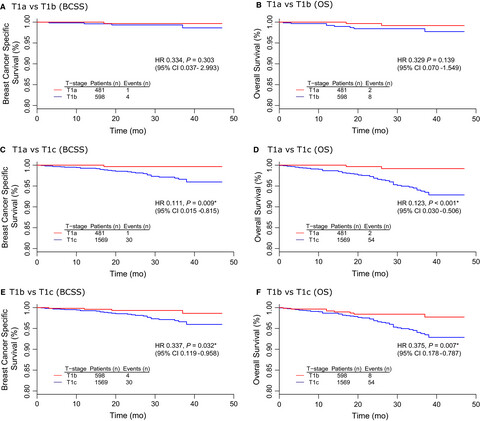
The present study retrospectively analyzed the prognosis of T1a-T1c HER2+/Hormone Receptor-negative (HoR-) breast cancer. T1a and T1b HER2+/HoR- breast cancer had great homogeneity in that these two subgroups had comparable survival and both showed no significant survival difference with its counterpart of HER2-/HoR+subtype. Conversely, T1c HER2+/HoR- breast cancers revealed worse prognosis than T1a/T1b HER2+/HoR- and T1c HER2-/HoR+tumors. Hence, compared to T1c, T1a and T1b HER2+/HoR- breast cancer had favorable prognosis and great homogeneity, indicating 1.0 cm may be a suitable cutoff for subclassification of T1 cancer.
Modification of American Joint Committee on cancer prognostic groups for renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 5431-5438
- First Published: 10 October 2018
Analysis of solid tumor mutation profiles in liquid biopsy
- Pages: 5439-5447
- First Published: 27 September 2018
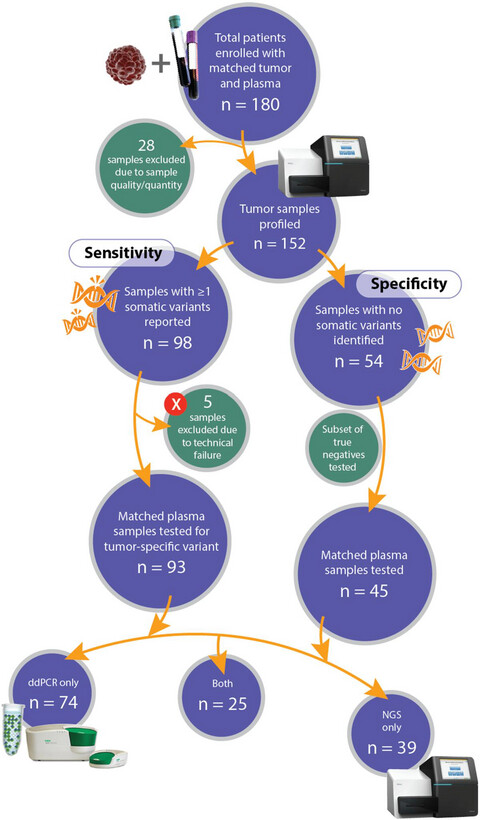
This study examines the tumor-plasma concordance in seven cancer types across stages. A concordance of 82% and 32% was observed in advanced (Stage IIB and above) and early (Stage I to Stage IIA) stage samples, respectively. Overall survival outcomes correlated well to presurgical/at-biopsy ctDNA levels.
Radioiodine refractoriness score: A multivariable prediction model for postoperative radioiodine-refractory differentiated thyroid carcinomas
- Pages: 5448-5456
- First Published: 27 September 2018
A prospective analysis of symptom burden for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase treated with frontline second- and third-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors
- Pages: 5457-5469
- First Published: 14 October 2018
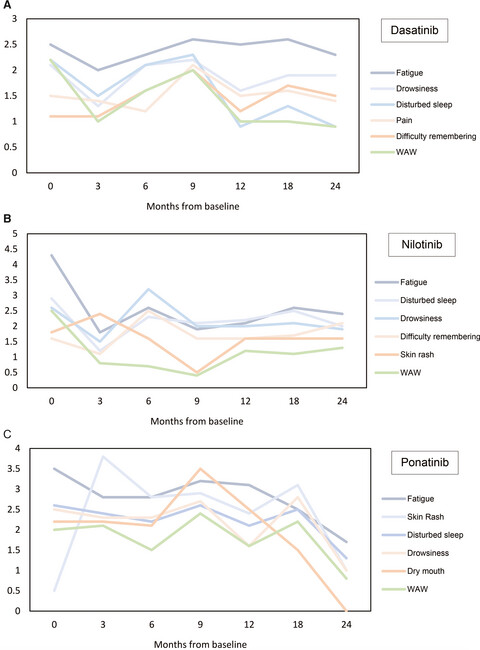
We prospectively measured the symptom burden of 219 patients with chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia (CML-CP) enrolled on frontline tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI) trials with dasatinib, nilotinib, or ponatinib using a previously validated questionnaire. Overall, patients tolerated therapy well with improvement of their symptoms from baseline, with few dose reductions related to toxicity or symptomatology, and nearly 90% experienced persistent mild symptoms. Side effects related to TKIs may impact the quality of life in patients with CML-CP.
Early PET-CT in patients with pathological stage III colon cancer may improve their outcome: Results from a large retrospective study
- Pages: 5470-5477
- First Published: 22 October 2018
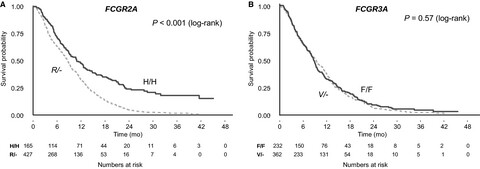
Fc-gamma receptor polymorphisms, cetuximab therapy, and overall survival in the CCTG CO.20 trial of metastatic colorectal cancer
- Pages: 5478-5487
- First Published: 14 October 2018
Postoperative chemotherapy had no prognostic effect on early-staged young ovarian cancer with unilateral resection
- Pages: 5488-5496
- First Published: 10 October 2018
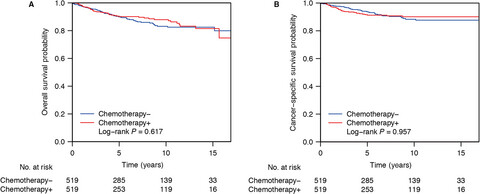
Postoperative chemotherapy has been widely used in the treatment of early-staged ovarian cancer patients undergoing unilateral resection, but the clinical decision mainly depends on the doctor’s experience without a well-defined guideline. Our study suggested that postoperative chemotherapy is not necessary for early-staged young ovarian cancer patients with unilateral resection, as indicated by both the overall survival and cancer-specific survival.
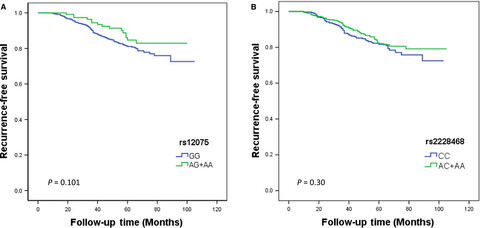
Effect of functional genetic variants in chemokine decoy receptors on the recurrence risk of breast cancer
- Pages: 5497-5504
- First Published: 24 October 2018
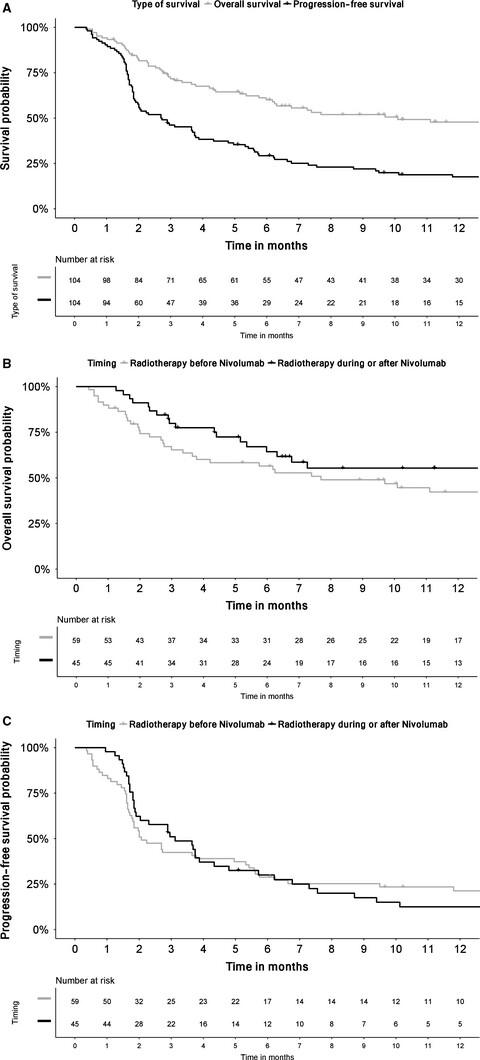
Safety of combined PD-1 pathway inhibition and radiation therapy for non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicentric retrospective study from the GFPC
- Pages: 5505-5513
- First Published: 11 October 2018
Clinical implication of subcategorizing T2 category into T2a and T2b in TNM staging of breast cancer
- Pages: 5514-5524
- First Published: 12 October 2018
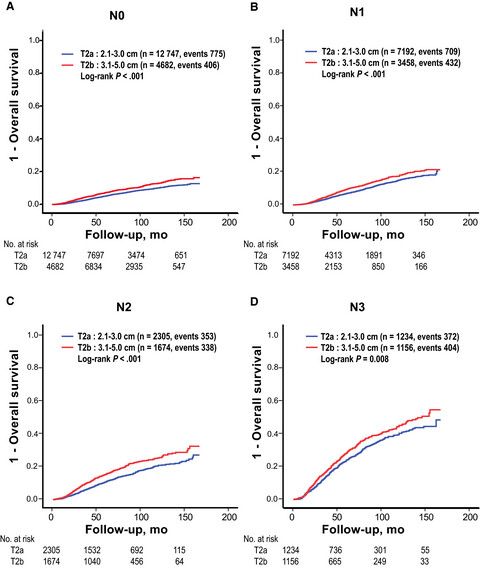
Regarding TNM staging in breast cancer (BC), T2 category is currently not divided into subcategories even though it covers a wider range of tumor sizes than T1 category. In analyses of 34,528 Korean T2 BC patients, we show that T2 category of BC could be subcategorized into T2a (2-3cm) and T2b (3-5cm) with a cutoff value of 3 cm. The survival difference between the two T2 subcategories is not fully explained by the model after adjusted for biologic risk factors incorporated into the 8th edition AJCC cancer staging for BC. More detailed anatomic classification might help us predict prognosis more accurately.
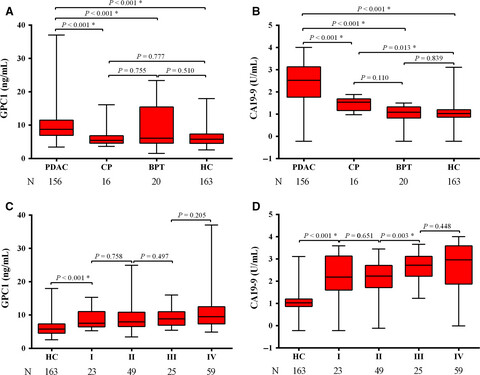
High levels of serum glypican-1 indicate poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 5525-5533
- First Published: 24 October 2018
Clinical landscape of cancer metastases
- Pages: 5534-5542
- First Published: 16 October 2018
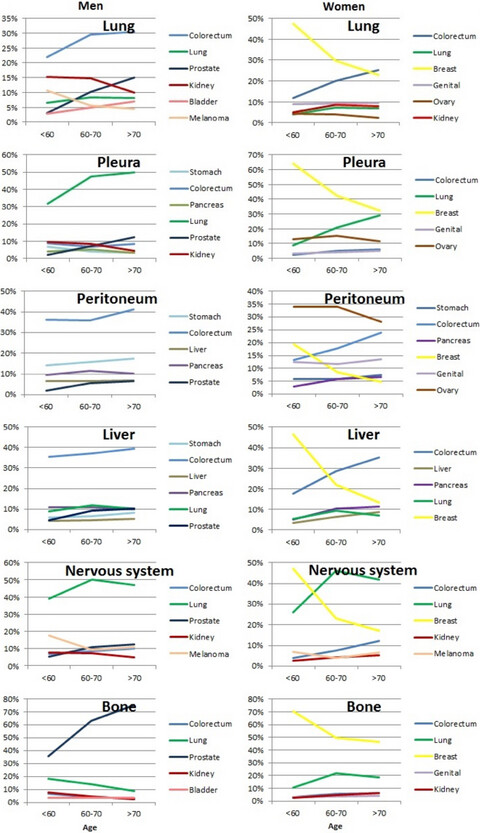
This study uses a novel population-based approach to identify metastases and describes metastatic pathways from 14 common primary cancers to 12 specific metastatic sites. The present achievement was to implement the first nationwide description of clinical landscape of cancer metastases, with an aim to serve as a reliable source for clinicians and researchers.
Cancer Biology
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
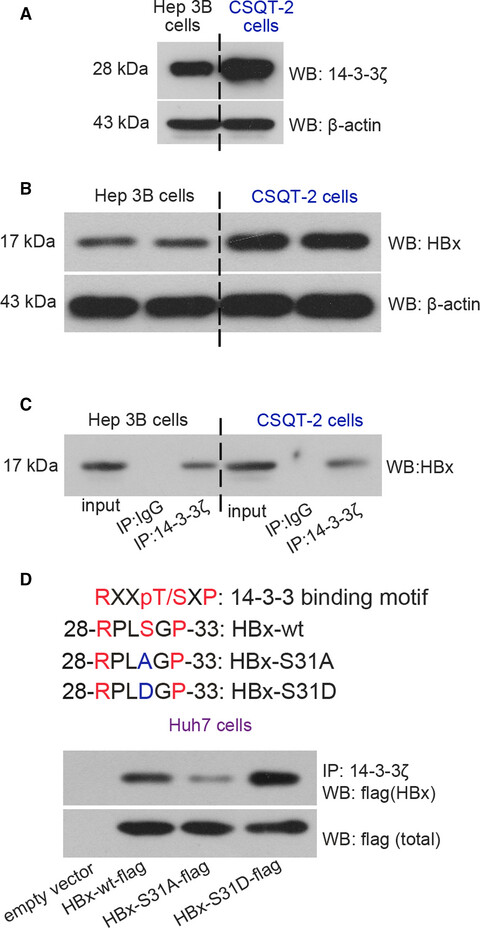
14-3-3ζ binds to hepatitis B virus protein X and maintains its protein stability in hepatocellular carcinoma cells
- Pages: 5543-5553
- First Published: 24 October 2018
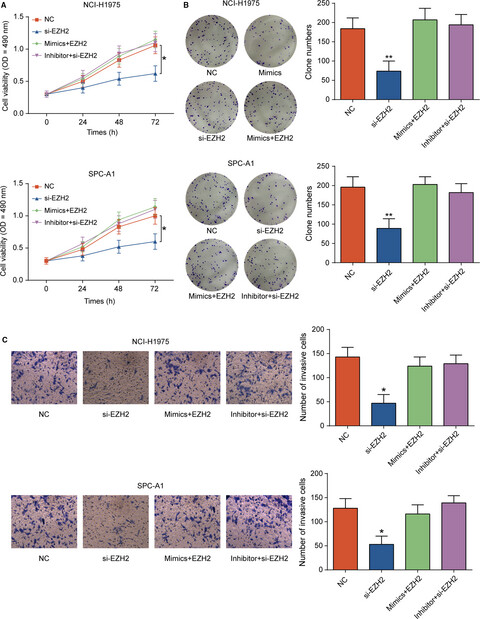
Downregulated miR-144-3p contributes to progression of lung adenocarcinoma through elevating the expression of EZH2
- Pages: 5554-5566
- First Published: 02 October 2018
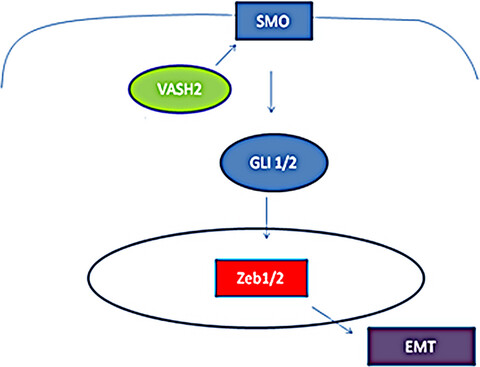
Vasohibin 2 promotes malignant behaviors of pancreatic cancer cells by inducing epithelial-mesenchymal transition via Hedgehog signaling pathway
- Pages: 5567-5576
- First Published: 14 October 2018
USP14 as a novel prognostic marker promotes cisplatin resistance via Akt/ERK signaling pathways in gastric cancer
- Pages: 5577-5588
- First Published: 17 September 2018
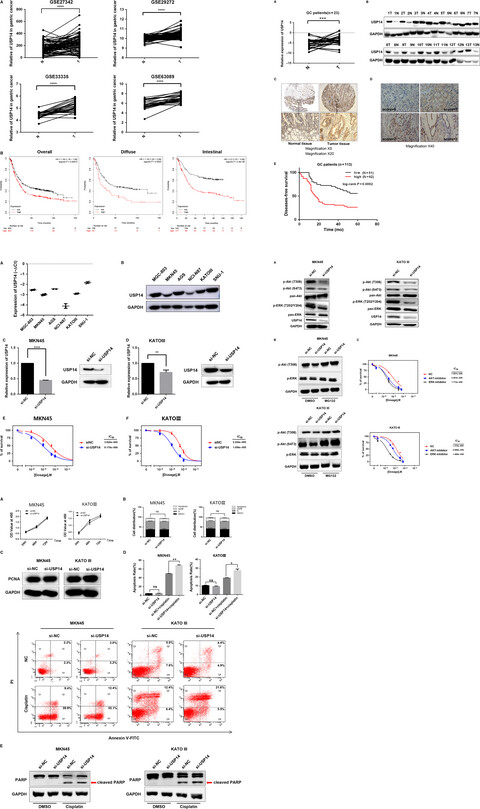
USP14 levels were significantly increased in gastric cancer (GC) tissues compared to the paired normal tissues. USP14 level was an independent prognostic factor for DFS in GC patients. Knockdown of USP14 sensitized GC cells to cisplatin by triggering cisplatin-induced apoptosis via impeding Akt and ERK signaling pathways.
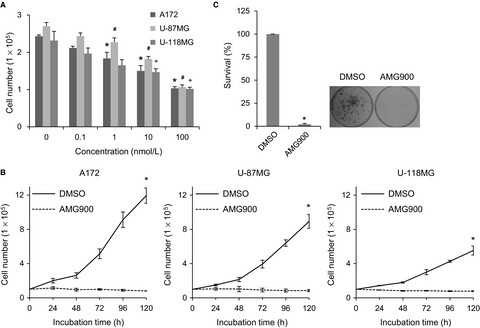
An Aurora kinase inhibitor, AMG900, inhibits glioblastoma cell proliferation by disrupting mitotic progression
- Pages: 5589-5603
- First Published: 17 September 2018
Strong impact of sulfotransferases on DNA adduct formation by 4-aminobiphenyl in bladder and liver in mice
- Pages: 5604-5610
- First Published: 10 October 2018
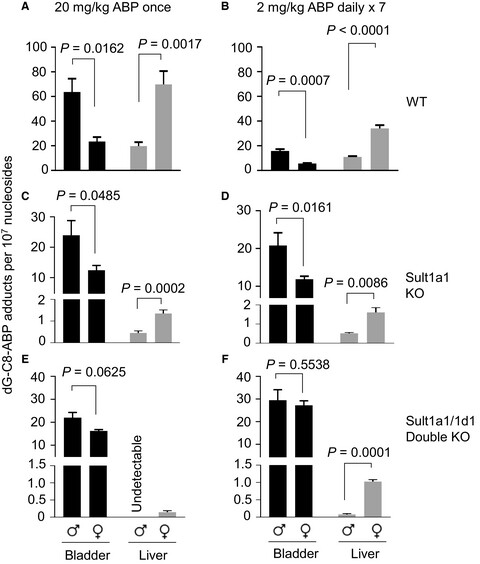
Liver sulfotransferases may decrease bladder exposure to carcinogens by generating unstable metabolites that cause toxicity locally. This study shows that sulfotransferases 1a1 and 1d1, whose expression in male mouse liver is suppressed by androgen, promotes 4-aminobiphenyl (ABP) genotoxicity in hepatic cells, whereas eliminating them in mice greatly protects liver against 4-aminobiphenyl and decreases excess male bladder susceptibility to 4-aminobiphenyl. Our results reveal the strong impact of sulfotransferases on bladder and liver susceptibility to a human carcinogen.
THIS ARTICLE HAS BEEN RETRACTED
Retracted: GNA13 promotes tumor growth and angiogenesis by upregulating CXC chemokines via the NF-κB signaling pathway in colorectal cancer cells
- Pages: 5611-5620
- First Published: 28 September 2018
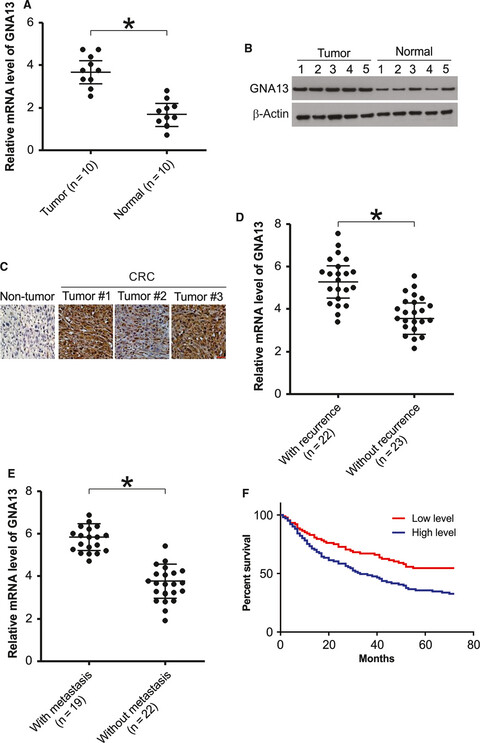
Increased expression levels of GNA13 promoted cell growth, migration, invasion, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, whereas GNA13 silencing abrogated these malignant phenotypes. In addition, overexpressing GNA13 in cancer cells increased the levels of the chemokines CXCL1, CXCL2, and CXCL4 via NF-kB signaling pathway, which contributed to colorectal cancer (CRC) proliferation and colony formation.
Cancer Biology
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
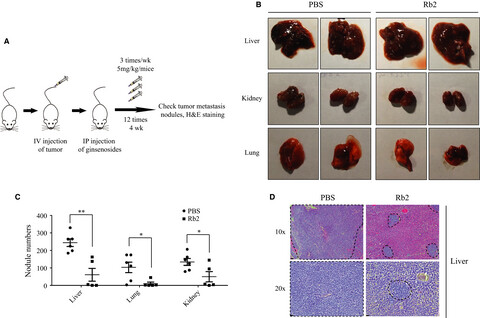
The anti-metastatic effect of ginsenoside Rb2 in colorectal cancer in an EGFR/SOX2-dependent manner
- Pages: 5621-5631
- First Published: 27 September 2018
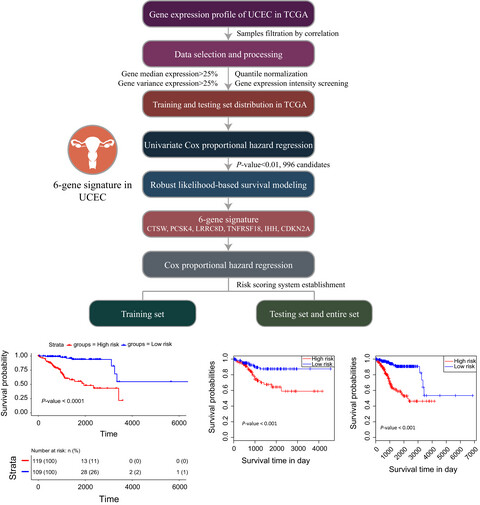
Identification of a six-gene signature with prognostic value for patients with endometrial carcinoma
- Pages: 5632-5642
- First Published: 10 October 2018
CTHRC1 overexpression predicts poor survival and enhances epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer
- Pages: 5643-5654
- First Published: 09 October 2018
Profiling of serum antibodies against human papillomavirus antigens in Korean women with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer
- Pages: 5655-5664
- First Published: 23 October 2018
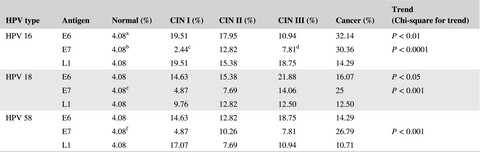
In the present study, the prevalences of nine types of anti-HPV antibodies (anti-E6, E7, and L1 antibodies of HPV types 16, 18, and 58) were evaluated in normal (control), CIN I, CIN II, CIN III, and cervical cancer. The frequencies of nine types of anti-HPV antibodies were higher in the CIN stages and cervical cancer than in normal women. It appeared that the frequencies of anti-HPV16 E6 and E7, anti-HPV18 E6 and E7, and anti-HPV58 E7 antibodies were higher in the cervical cancer group than in the CIN stages. However, there were few differences in the frequencies of anti-HPV 16, 18, and 58 L1 antibodies in cervical cancer vs CIN stages.
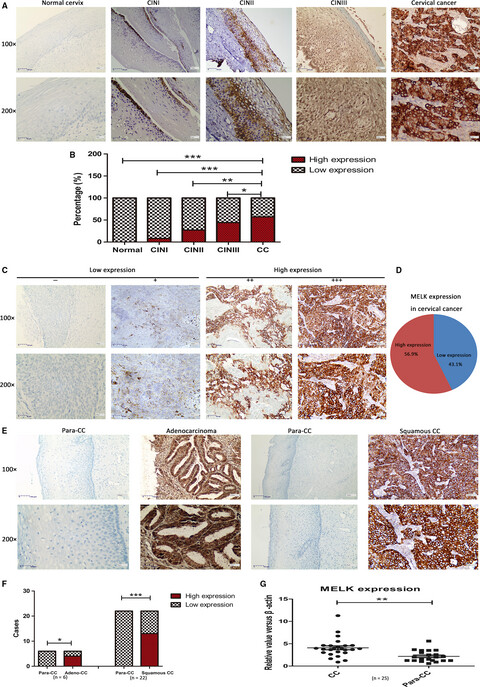
Maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase: A novel biomarker and a potential therapeutic target of cervical cancer
- Pages: 5665-5678
- First Published: 18 October 2018
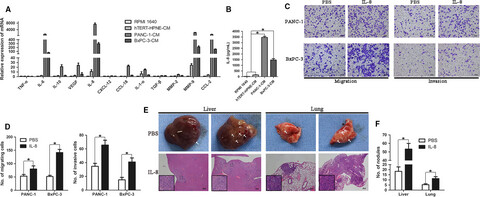
Tumor-driven like macrophages induced by conditioned media from pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma promote tumor metastasis via secreting IL-8
- Pages: 5679-5690
- First Published: 12 October 2018
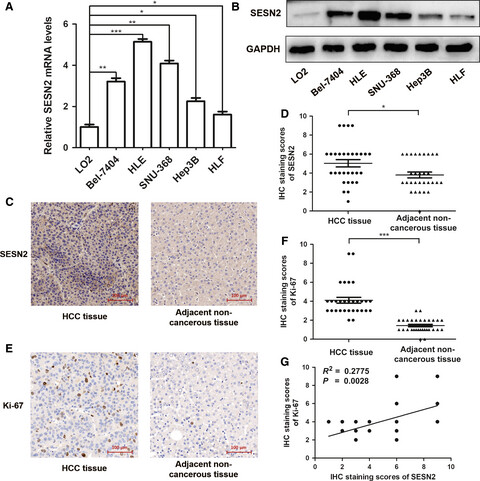
Sestrin 2 confers primary resistance to sorafenib by simultaneously activating AKT and AMPK in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 5691-5703
- First Published: 11 October 2018
Dihydroartemisinin induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer via inhibition of the hedgehog signaling pathway
- Pages: 5704-5715
- First Published: 18 October 2018
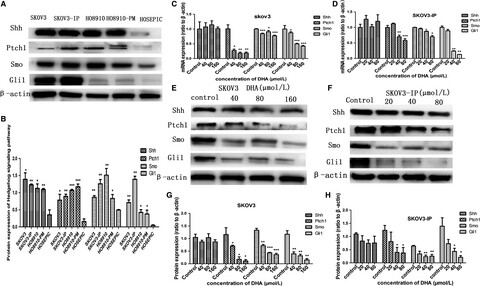
Dihydroartemisinin (DHA), the main active products of artemisinin extracted from traditional Chinese medicine Artemisia annua, has been used as an anti-malarial drug since ancient China. In recent years, DHA has also been shown to exert anticancer effects in certain types of cancer, including ovarian cancer. However, the precise molecular mechanisms of DHA exerts anti-cancer effects in ovarian cancer are still unclear. The present study demonstrates that DHA induces apoptosis and inhibits proliferation, migration, and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer via inhibiting the hedgehog signaling pathway.
Aberrant CpG-methylation affects genes expression predicting survival in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 5716-5726
- First Published: 23 October 2018
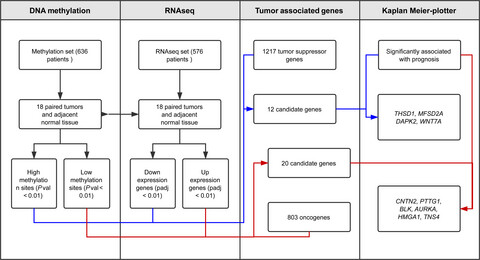
We analyzed methylation status of 485 578 CpG sites and RNA-seq transcriptomes of 20 532 genes for 1095 LUAD samples in TCGA database. Methylation aberrances regulate gene expression level during tumorigenesis and influence prognosis of LUAD patients. Integrating knowledge of epigenetics and expression of genes can be useful for an in-depth understanding of cancer mechanism.
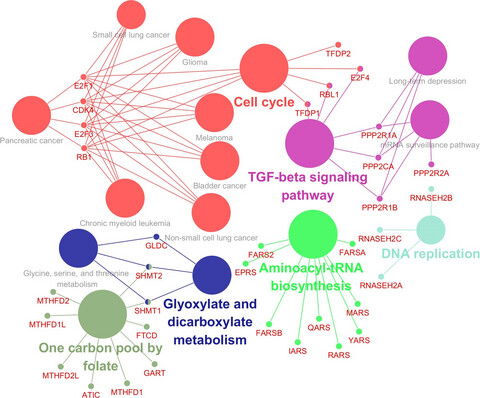
Transcriptome-wide association study identifies multiple genes and pathways associated with pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 5727-5732
- First Published: 18 October 2018
WAVE2 is associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic cancers and promotes cell motility and invasiveness via binding to ACTN4
- Pages: 5733-5751
- First Published: 23 October 2018
Cancer Prevention
ORIGINAL RESEARCH
Prostate cancer survivors: Risk and mortality in second primary cancers
- Pages: 5752-5759
- First Published: 01 October 2018
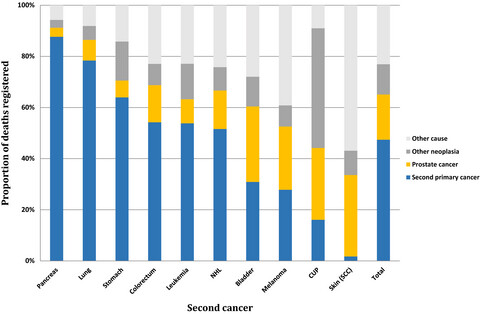
Second primary cancers although appear autonomously among prostate cancer patients owing to the same risk factors as observed for first cancers, they are responsible for almost half of the fatalities. For improved survival of men with prostate cancer, prevention and early detection of second primary cancers is urgent.
Role of serum EBV-VCA IgG detection in assessing gastric cancer risk and prognosis in Northern Chinese population
- Pages: 5760-5774
- First Published: 10 October 2018
This is an innovative report about the role of serum EBV-VCA IgG detection in assessing the risk of gastric cancer (GC) and its precursor as well as GC prognosis. And this is the first report about the relationship between EBV-VCA IgG serology assay and gastric function status. Our study provides theoretical and experimental basis for evaluating the potential of serum EBV-VCA IgG as a biomarker in prediction of GC risk and prognosis.
The incidence and survival of pancreatic cancer by histology, including rare subtypes: a nation-wide cancer registry-based study from Taiwan
- Pages: 5775-5788
- First Published: 27 September 2018
Retinal vein thrombosis and risk of occult cancer: A nationwide cohort study
- Pages: 5789-5795
- First Published: 27 September 2018
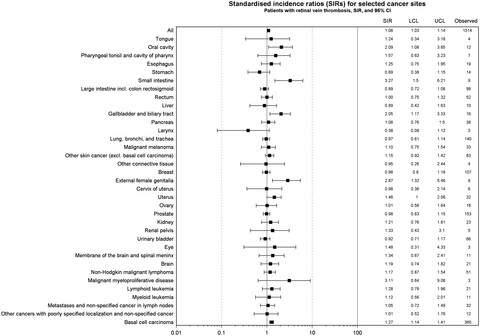
In this Danish nationwide cohort study on 9589 patients with retinal vein thrombosis, we found that the risk of any cancer was 1.2% <6 months and 28.8% >5 years. We compared the observed cancer risk to that expected in the general population of the same age and found that the <6 months’ standardized incidence rate (SIR) was 1.20 (95% CI 0.99-1.44), the 6-12 months’ SIR was 1.15 (95% CI 0.94-1.39), and >5 years, the SIR was 1.08 (95% CI 1.03-1.14). Retinal vein thrombosis was not an important clinical marker for occult cancer, and an extensive diagnostic cancer workup does not appear warranted for retinal vein thrombosis patients.
Smoking is associated with increased risk of myeloproliferative neoplasms: A general population-based cohort study
- Pages: 5796-5802
- First Published: 14 October 2018
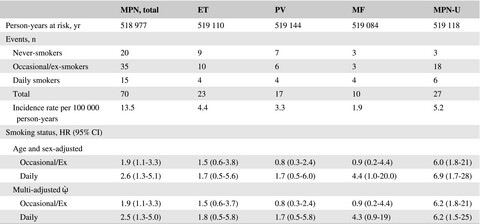
In a general population-based cohort study on 75,896 participants from Denmark, we found that smoking was a significant risk factor for the development of chronic myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN). These results support the existing and growing evidence of smoking as one of many inflammatory stimuli driving the MPN clone.
Health-related quality of life of esophageal cancer patients in daily life after treatment: A multicenter cross-sectional study in China
- Pages: 5803-5811
- First Published: 22 October 2018
Determinants of mobile technology use and smartphone application interest in cancer patients
- Pages: 5812-5819
- First Published: 02 October 2018
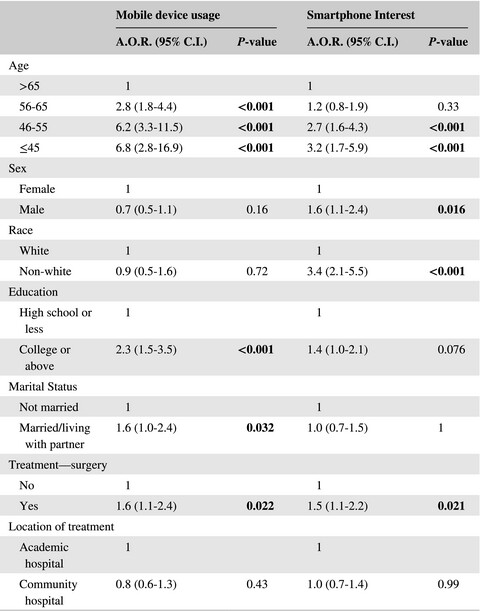
This study assesses the demographic and treatment-related characteristics associated with mobile technology use and smartphone application interest in a mixed patient population from academic and community settings. It was found that age and race impact mobile technology use and interest in smartphone applications with younger and non-white populations expressing an interest in smartphones at three times the reference group.
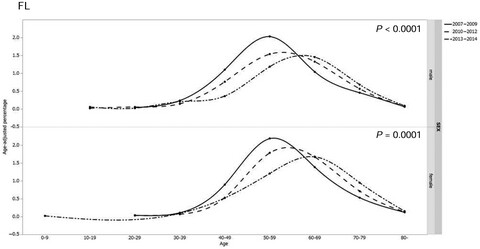
Subtype-specific epidemiology of lymphoid malignancies in Taiwan compared to Japan and the United States, 2002-2012
- Pages: 5820-5831
- First Published: 09 October 2018
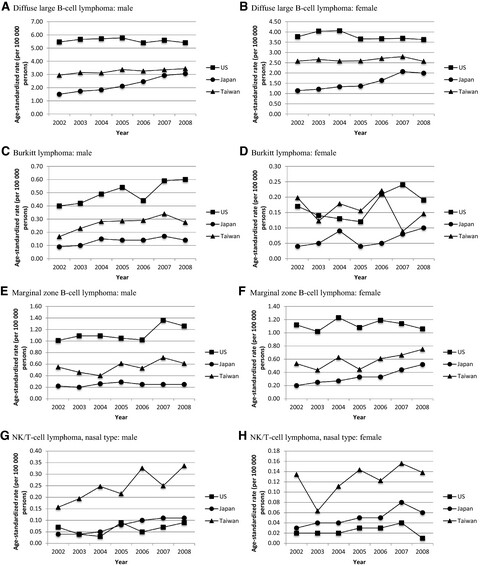
This study aims to provide epidemiological information on lymphoma within Taiwanese and to compare the data with that in Japan and the United States. We used Taiwan Cancer Registry Database as our data source and patients with lymphoma were identified through the ICD-O-3 codes and those with non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) were categorized into three major types and 13 subtypes according to 2008 WHO Classification. The incidence rates of lymphoma in Taiwan are mostly lower than those in the United States and higher or comparable to those in Japan except for NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, whose age-adjusted incidence in Taiwan is the highest.
Factors contributing to disparities in mortality among patients with non–small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 5832-5842
- First Published: 28 September 2018
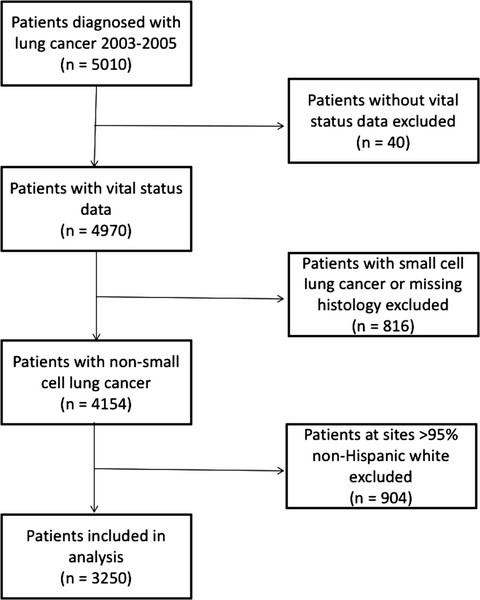
Using data from the Cancer Care Outcomes Research and Surveillance (CanCORS) consortium, a large, multi-regional observational study of newly diagnosed cancer patients, we documented higher unadjusted mortality for NSCLC among patients who were black, have lower income, less well-educated, and with non-private insurance. We used a series of Cox proportional hazards model to estimate the increased risk of death associated with sociodemographic factors, clinical characteristics, and treatments received to determine what accounted for the disparities. We found that patients’ clinical characteristics and treatments received primarily contributed to the mortality disparities that we observed in patients with NSCLC.
Epidemiology and secular trends of malignant lymphoma in Japan: Analysis of 9426 cases according to the World Health Organization classification
- Pages: 5843-5858
- First Published: 11 October 2018
CORRIGENDUM
The current state and future perspectives of cannabinoids in cancer biology
- Page: 5859
- First Published: 21 November 2018