Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
Application of a novel prognostic invasive lesion index in ductal carcinoma in situ with minimal invasion of the breast
- Pages: 2489-2496
- First Published: 04 October 2017
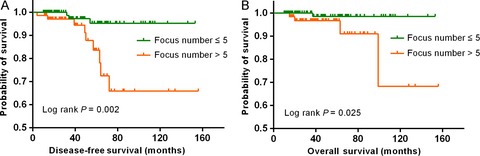
Multiple invasive foci has been shown to increase the risk of lymph node metastasis (LNM) in early breast cancer, but its prognostic implication remains unknown. In this study, we found that more than five invasive foci is an independent predictor for LNM and an unfavorable prognostic parameter. Furthermore, the invasive lesion index, established by the number of invasive foci and the invasive component size, could potentially be used to predict survival prognosis in patients with DCIS-MI.
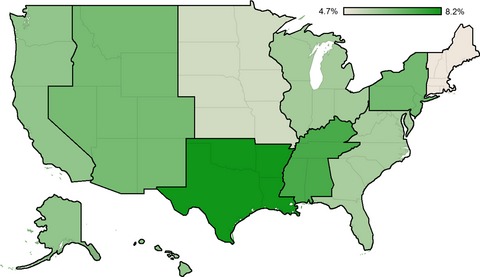
Social determinants of stage IV anal cancer and the impact of pelvic radiotherapy in the metastatic setting
- Pages: 2497-2506
- First Published: 04 October 2017
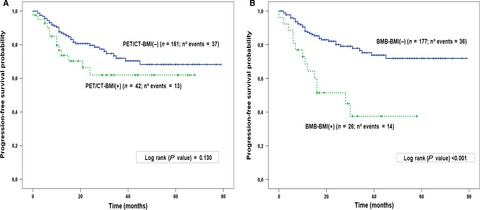
Bone marrow biopsy superiority over PET/CT in predicting progression-free survival in a homogeneously-treated cohort of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
- Pages: 2507-2514
- First Published: 27 September 2017
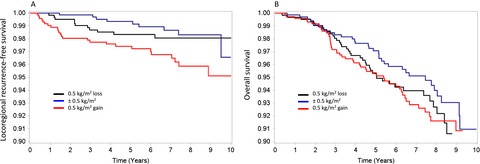
Association between weight gain during adjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage breast cancer and survival outcomes
- Pages: 2515-2522
- First Published: 10 October 2017
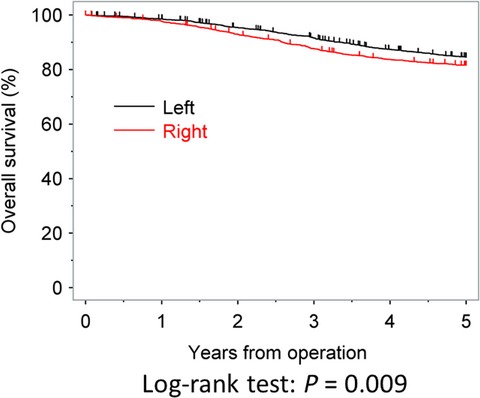
Clinical impact of tumor location on the colon cancer survival and recurrence: analyses of pooled data from three large phase III randomized clinical trials
- Pages: 2523-2530
- First Published: 25 September 2017
Identification of keratin 19-positive cancer stem cells associating human hepatocellular carcinoma using CYFRA 21-1
- Pages: 2531-2540
- First Published: 30 September 2017
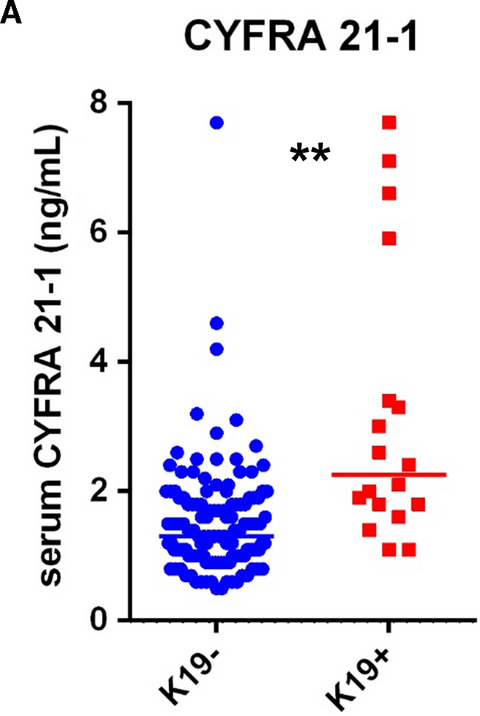
Keratin 19 (K19) is known to be a cancer stem cells (CSCs) marker in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, easily-measurable surrogate marker of K19 + HCC-CSCs has not been identified. This study showed that serum CYFRA 21-1 is the significant predictor of K19 expression in human HCC, and that CYFRA 21-1 levels reflect K19 function and TGFβ receptor 1 inhibitor treatment efficacy in HCC cells.
Expression profiling of long noncoding RNA identifies lnc-MMP3-1 as a prognostic biomarker in external auditory canal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 2541-2551
- First Published: 29 September 2017
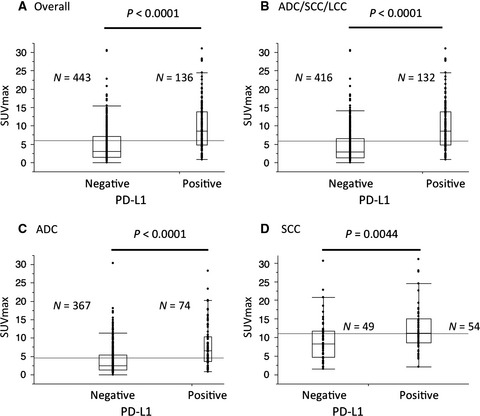
Metabolic characteristics of programmed cell death-ligand 1-expressing lung cancer on 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography
- Pages: 2552-2561
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Identifying patterns of adaptation in breast cancer patients with cancer-related fatigue using response shift analyses at subgroup level
- Pages: 2562-2575
- First Published: 10 October 2017
Fatigue might be perceived differently among breast cancer patients over time as a consequence of patients’ adaptation and psychological adjustment to their cancer experience which can be related to response shift. Several response shift effects were evidenced in different groups and women seemed to adapt differently to their treatment and breast cancer experience possibly indicating differing needs for medical/psychological support.
High frequency of brain metastases after adjuvant therapy for high-risk melanoma
- Pages: 2576-2585
- First Published: 10 October 2017
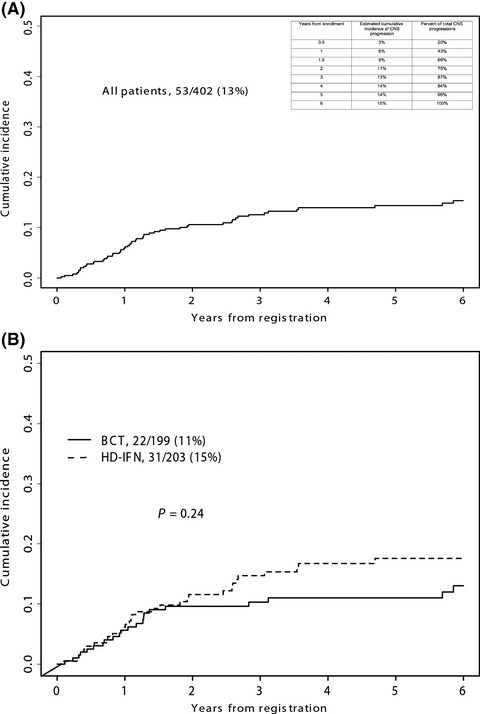
The frequency of brain metastases developing in advanced regional melanoma (Stage IIIB and C) remains poorly defined. We performed a retrospective analysis of a large patient sample that were staged and managed using contemporary techniques from the intergroup trial SWOG 0008 to provide an estimate of the risk of CNS relapse. Difference between treatment arms was not expected. This data provides a basis for design of future studies for surveillance and treatment of early brain metastases.
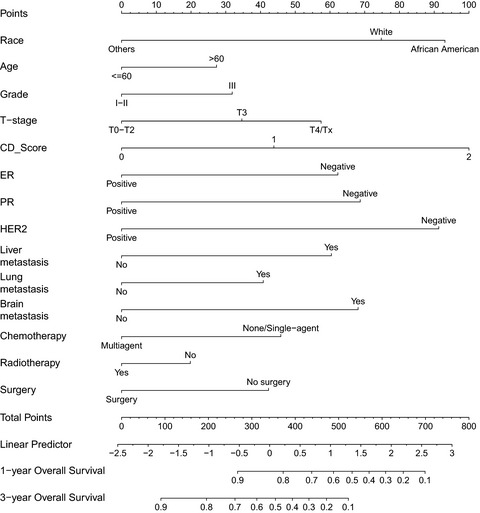
Development and validation of a nomogram predicting the overall survival of stage IV breast cancer patients
- Pages: 2586-2594
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Reviews
The application of crowdsourcing approaches to cancer research: a systematic review
- Pages: 2595-2605
- First Published: 29 September 2017
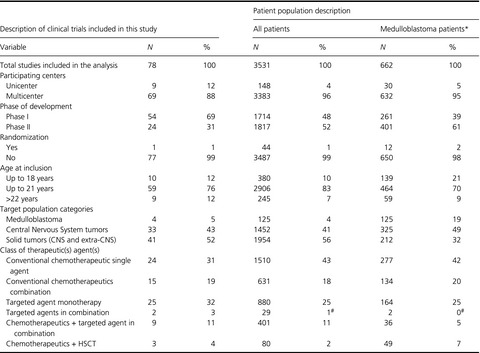
Medulloblastoma in children and adolescents: a systematic review of contemporary phase I and II clinical trials and biology update
- Pages: 2606-2624
- First Published: 04 October 2017
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Crizotinib targets in glioblastoma stem cells
- Pages: 2625-2634
- First Published: 27 September 2017
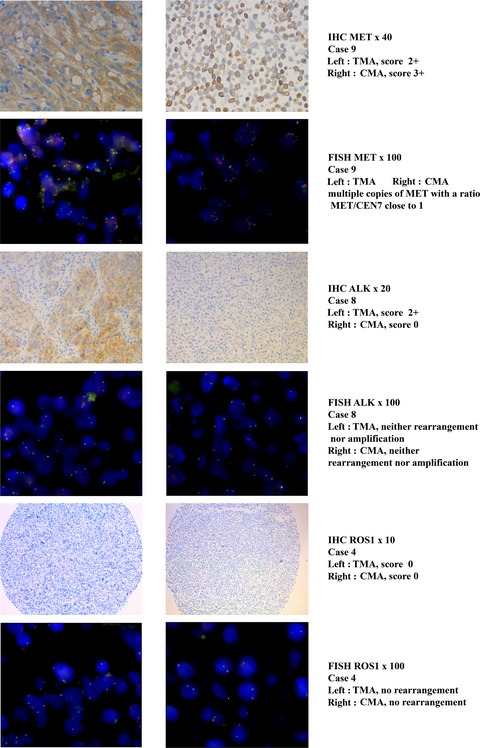
Tissue and stem cells microarrays from nine glioblastomas samples were used to evaluate expression and chromosomal abnormalities of ALK, ROS1, and MET. No molecular rearrangement of these three important genes was observed but rather an overexpression of ALK and MET in some of the glioblastoma stem cell samples, supporting the role of these two genes in tumorigenicity.
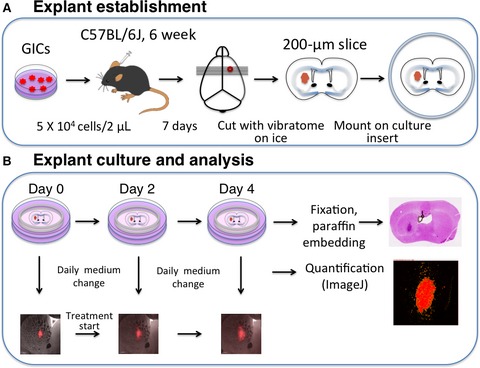
Organotypic brain explant culture as a drug evaluation system for malignant brain tumors
- Pages: 2635-2645
- First Published: 04 October 2017
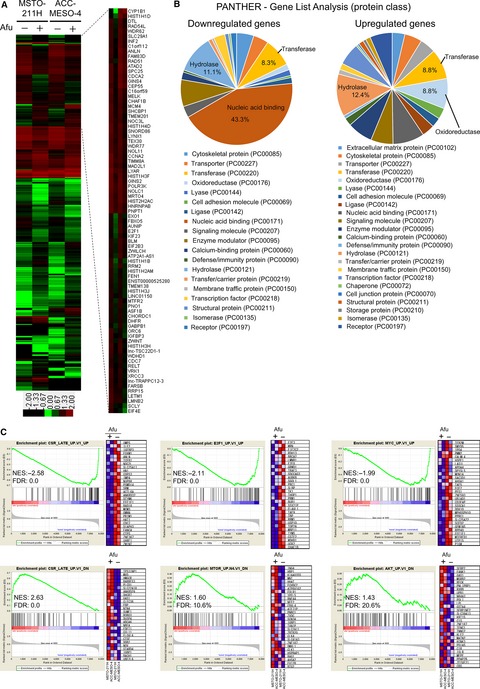
Novel ATP-competitive Akt inhibitor afuresertib suppresses the proliferation of malignant pleural mesothelioma cells
- Pages: 2646-2659
- First Published: 27 September 2017
NLRC and NLRX gene family mRNA expression and prognostic value in hepatocellular carcinoma
- Pages: 2660-2672
- First Published: 29 September 2017
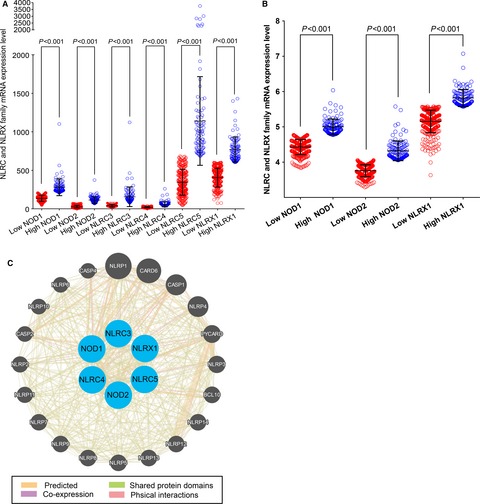
Nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain (NOD)-like receptor (NLR)C and NLRX family proteins play a key role in the innate immune response. The relationship between these proteins and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) remains unclear. This study investigated the prognostic significance of NLRC and NLRX family protein levels in HCC patients.
Targeting MTA1/HIF-1α signaling by pterostilbene in combination with histone deacetylase inhibitor attenuates prostate cancer progression
- Pages: 2673-2685
- First Published: 10 October 2017
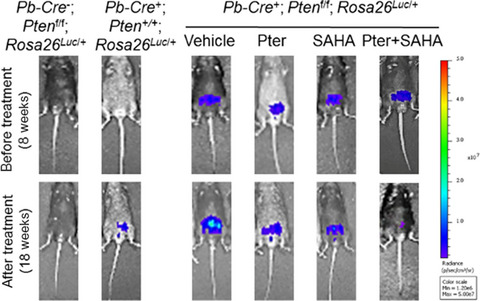
Utilization of dietary bioactive molecules as chemo-sensitizers is an emerging approach in developing combination strategies that can potentially provide more efficacy and less toxicity for anticancer treatments. Our study offers preclinical proof for combinatorial strategy using natural product, pterostilbene, with histone deacetylase inhibitor, SAHA, as a MTA1-targeted interventional therapy to abrogate prostate cancer. Changes in MTA1-associated proangiogenic factors in serum may be used as molecular response biomarkers for such therapy.
Grainyhead-like 2 (GRHL2) regulates epithelial plasticity in pancreatic cancer progression
- Pages: 2686-2696
- First Published: 29 September 2017
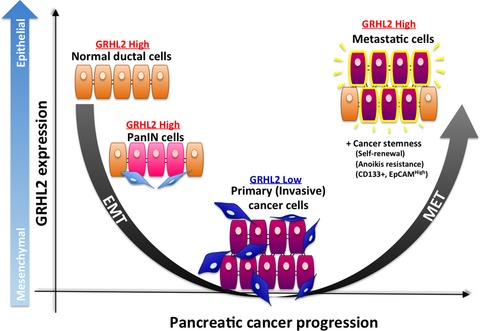
GRHL2 has a significantly positive correlation with E-cadherin and CD133 in 155 resected human primary PDAC tissues. GRHL2 is highly expressed in liver metastatic cells than in primary invasive cells of both human and mouse PDAC, accompanied by a positive correlation with E-cadherin expression. Knockdown studies followed by flow cytometry analysis for a subpopulation of CD133+ showed that GRHL2 facilitates CFPAC-1 cells to maintain stem-like characters including self-renewal capacity and anoikis resistance.
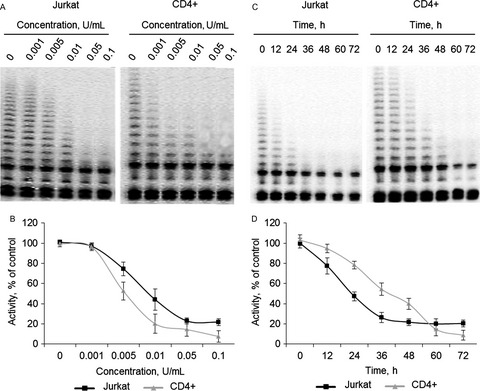
Inhibition of telomerase activity and induction of apoptosis by Rhodospirillum rubrum L-asparaginase in cancer Jurkat cell line and normal human CD4+ T lymphocytes
- Pages: 2697-2712
- First Published: 05 October 2017
Dynamic changes of urine proteome in a Walker 256 tumor-bearing rat model
- Pages: 2713-2722
- First Published: 04 October 2017

Urine is a noninvasive and attractive biofluid for biomarker research, and has the potential to reflect early and small pathological changes in the body. Urine proteins changed significantly with cancer development in a tumor-bearing rat model. Our results indicate that urine proteins could enable early detection of cancer at an early onset of tumor growth and monitoring of cancer progression.
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Ten-year immune persistence and safety of the HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine in females vaccinated at 15–55 years of age
- Pages: 2723-2731
- First Published: 05 October 2017
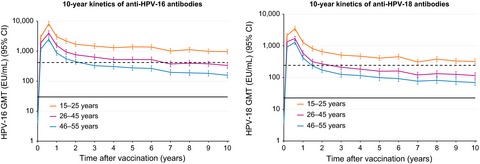
The HPV-16/18 AS04-adjuvanted vaccine produced a sustained immune response in women aged 15–55 years at vaccination for up to 10 years, with an acceptable safety profile. Study results suggest that women in age groups not targeted by adolescent immunization and catch-up programs may still individually benefit from HPV vaccination.
Incidence, risk factors, and outcomes of central venous catheter-related thromboembolism in breast cancer patients: the CAVECCAS study
- Pages: 2732-2744
- First Published: 04 October 2017
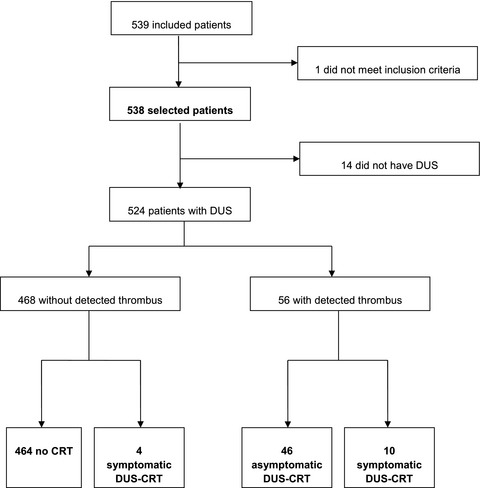
Data regarding central venous catheter-related thrombosis (CRT) in breast cancer (BC) patients are limited, although CVC placement for chemotherapy is common in this population and BC is the first cause of cancer in women worldwide. We conducted a large prospective multicentre study (9 cancer hospitals, 524 patients). The 6-months cumulative probability of symptomatic and asymptomatic CRT was 11.5%. BMI >30 kg/m² and lobular carcinoma histology were the main risk factors for CRT.
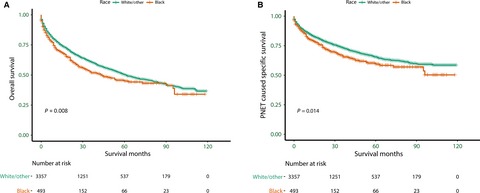
Racial disparities in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors survival: a SEER study
- Pages: 2745-2756
- First Published: 04 October 2017