Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Issue Information
Clinical Cancer Research
Original Research
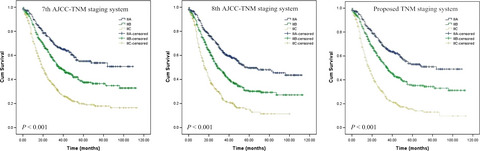
Validation of the American Joint Commission on Cancer (8th edition) changes for patients with stage III gastric cancer: survival analysis of a large series from a Specialized Eastern Center
- Pages: 2179-2187
- First Published: 14 September 2017
Cytoreductive nephrectomy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: inequities in access exist despite improved survival
- Pages: 2188-2193
- First Published: 22 August 2017
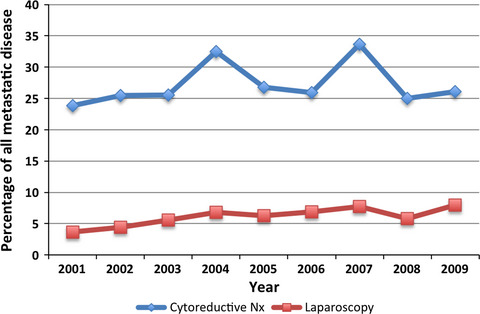
Cytoreductive nephrectomy is commonly used in conjunction with systemic therapy to treat advanced renal cell carcinoma. Despite a strong association with improved survival, individuals who are elderly, female, have treatment in a nonteaching facility or do not have private insurance have a reduced likelihood of receiving this surgery.
Digital PCR analysis of circulating tumor DNA: a biomarker for chondrosarcoma diagnosis, prognostication, and residual disease detection
- Pages: 2194-2202
- First Published: 23 August 2017

Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is emerging as a powerful biomarker for a range of cancers. The authors of this study have used digital PCR to assess the ability to detect ctDNA for the first time in patients with chondrosarcoma. ctDNA was detectable in 14 of 29 patients and its detection was associated with high-grade disease and a significantly poorer prognosis compared to those patients in whom mutant IDH1 was not detected in cell free DNA.
Survival of cutaneous melanoma based on sex, age, and stage in the United States, 1992–2011
- Pages: 2203-2212
- First Published: 06 September 2017
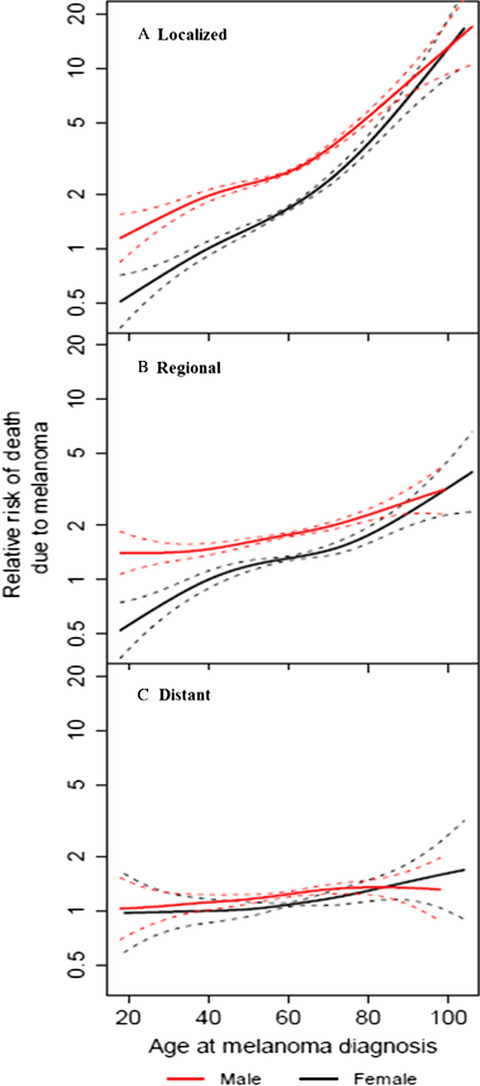
In local and regional cutaneous melanoma, women of all ages have a significant survival benefit over men. However, data from the SEER registry indicate that this female survival advantage is decreased when the disease is metastatic, suggesting an unknown protective biology is lost in distant disease.
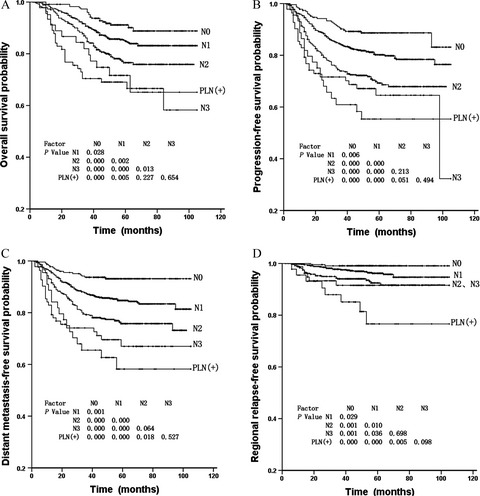
Prognostic effect of parotid area lymph node metastases after preliminary diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma: a propensity score matching study
- Pages: 2213-2221
- First Published: 06 September 2017
Efficacy of biological response modifier lentinan with chemotherapy for advanced cancer: a meta-analysis
- Pages: 2222-2233
- First Published: 21 September 2017
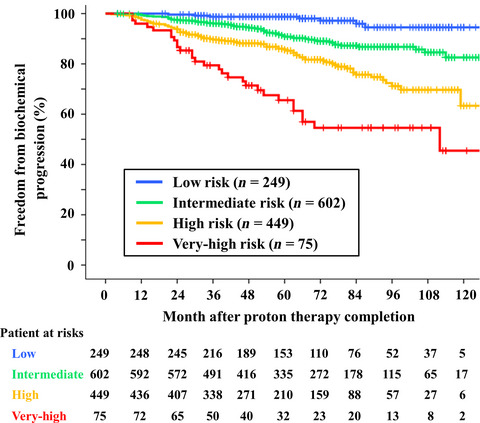
Long-term outcomes in patients treated with proton therapy for localized prostate cancer
- Pages: 2234-2243
- First Published: 06 September 2017
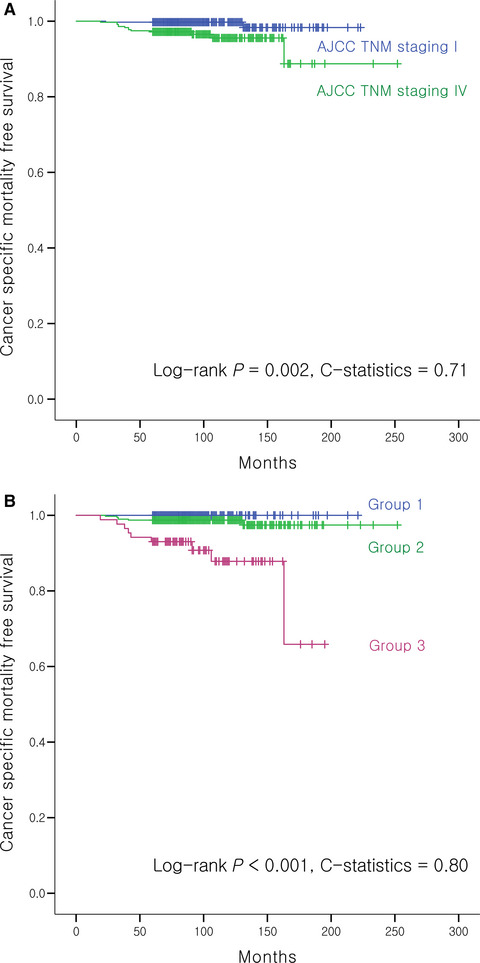
Restratification of survival prognosis of N1b papillary thyroid cancer by lateral lymph node ratio and largest lymph node size
- Pages: 2244-2251
- First Published: 31 August 2017
miR-199a-3p and miR-214-3p improve the overall survival prediction of muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients after radical cystectomy
- Pages: 2252-2262
- First Published: 06 September 2017
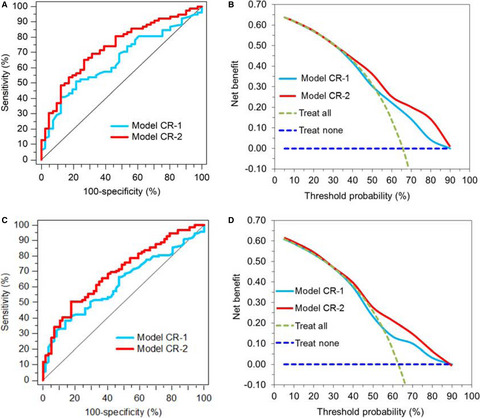
This study demonstrated the usefulness of the microRNAs miR-199a-3p and miR-214-3p in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissue samples from patients with muscle-invasive bladder cancer after radical cystectomy as predictive biomarkers of overall survival. In this aspect, the miRNAs combined with traditional clinicopathological factors improved the prediction accuracy for overall survival and could be useful to facilitate clinical decision making for further treatment strategies.
Prognostic role of stereotactic body radiation therapy for elderly patients with advanced and medically inoperable pancreatic cancer
- Pages: 2263-2270
- First Published: 23 August 2017
Osteonecrosis of the jaw and survival of patients with cancer: a nationwide cohort study in Denmark
- Pages: 2271-2277
- First Published: 21 September 2017
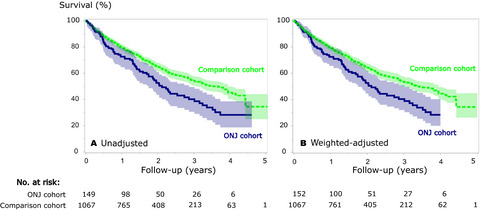
In this nationwide cohort study, the authors examined the association between osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) and survival among cancer patients treated with bone-targeted agents. ONJ was associated with reduced survival. The reason for the association is likely ONJ being a marker of advanced disease or of survival-related lifestyle characteristics.
Clinical predictive factors of long-term survival after curative resection of pancreatic cancer: a retrospective study
- Pages: 2278-2286
- First Published: 18 September 2017
Prognostic and predictive role of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) treated with up-front pemetrexed-based chemotherapy
- Pages: 2287-2296
- First Published: 21 September 2017
![Prognostic and predictive role of [18F]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG-PET) in patients with unresectable malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) treated with up-front pemetrexed-based chemotherapy](/cms/asset/2b9fad61-701a-4092-a986-92c091c05508/cam41182-toc-0001-m.jpg)
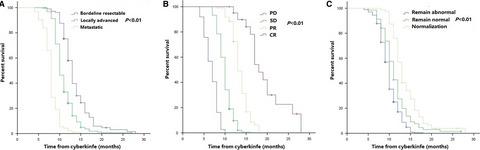
Our data confirmed the prognostic role of baseline FDG-PET in a large series of MPM patients: baseline SUVmax and TLG statistically significantly correlate with PFS and OS in all population. In patients without pleurodesis, the FDG-PET is able to predict treatment response: both ∆SUV ≥ 25% and ∆TLG ≥ 30% responses have a statistically significant lower risk of PD and death.
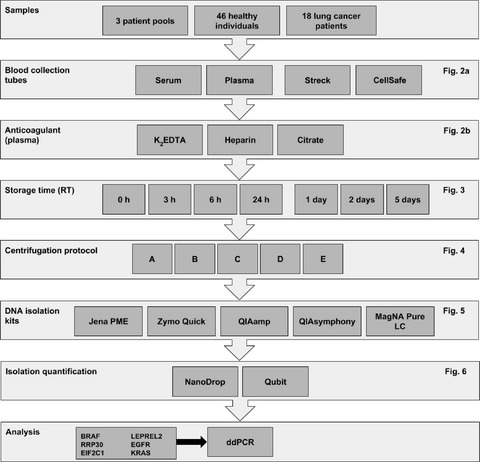
Preanalytical blood sample workup for cell-free DNA analysis using Droplet Digital PCR for future molecular cancer diagnostics
- Pages: 2297-2307
- First Published: 21 September 2017
Cancer Biology
Original Research
Combination therapy using molecular-targeted drugs modulates tumor microenvironment and impairs tumor growth in renal cell carcinoma
- Pages: 2308-2320
- First Published: 23 August 2017
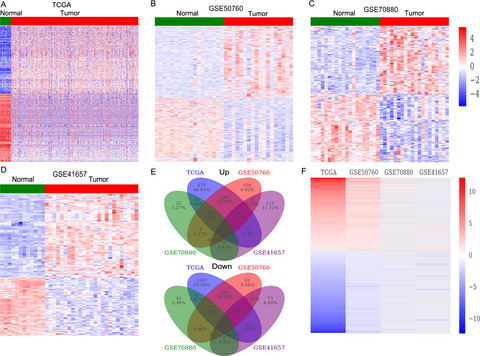
Identification of dysregulated lncRNAs profiling and metastasis-associated lncRNAs in colorectal cancer by genome-wide analysis
- Pages: 2321-2330
- First Published: 31 August 2017
CISD2 enhances the chemosensitivity of gastric cancer through the enhancement of 5-FU-induced apoptosis and the inhibition of autophagy by AKT/mTOR pathway
- Pages: 2331-2346
- First Published: 31 August 2017
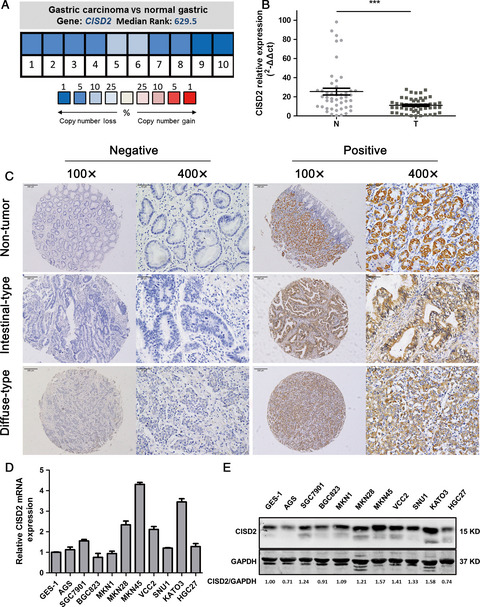
This study showed that CISD2 is down-regulated in gastric cancer tissues, and significantly correlated with age, Lauren's classification, and differentiation. The inhibitory effect of CISD2 on gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration invasion, and increase chemotherapy sensitivity are mediated by enhancing 5-FU-induced apoptosis and inhibiting autophagy through AKT/mTOR pathway. The results elucidate a potential mechanism underlying the tumor-suppressor role of CISD2 and it is expected that screening CISD2 expression combined chemotherapy drugs will become the new therapy strategy for gastric cancer.
Relationship of tumor PD-L1 (CD274) expression with lower mortality in lung high-grade neuroendocrine tumor
- Pages: 2347-2356
- First Published: 18 September 2017
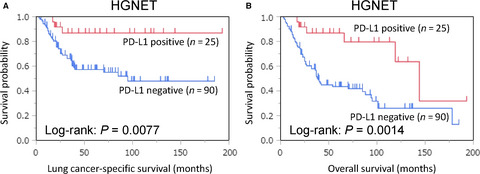
High-grade neuroendocrine tumor (HGNET) (small cell lung carcinoma and large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma) is the most aggressive histological subtype of lung cancer, and immunotherapies, including anti-PD-1/Programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) therapy, are emerging and promising. The prevalence of PD-L1 positivity in lung HGNET is shown. PD-L1 positivity is associated with lower mortality in lung HGNET.
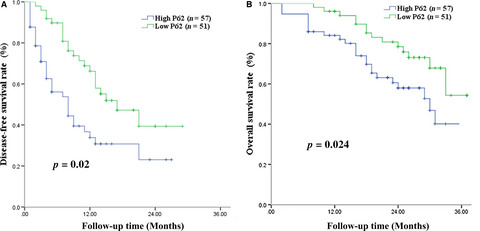
Expression of P62 in hepatocellular carcinoma involving hepatitis B virus infection and aflatoxin B1 exposure
- Pages: 2357-2369
- First Published: 21 September 2017
Metabolomic and transcriptomic profiling of hepatocellular carcinomas in Hras12V transgenic mice
- Pages: 2370-2384
- First Published: 21 September 2017
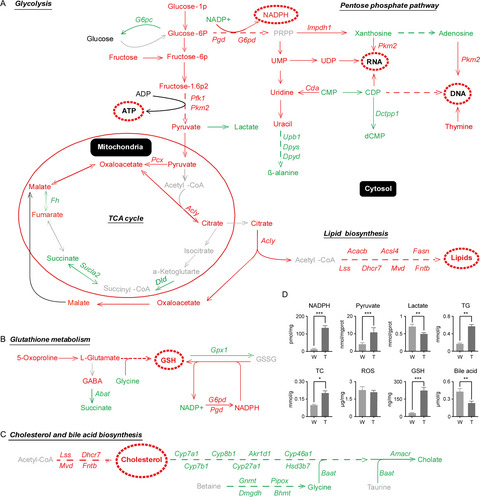
This study provides integrative analysis of metabolomics and transcriptomics data for mouse HCC induced by the ras oncogene. The enhanced glycolysis, citrate shuttle, pentose phosphate pathway, and expression of lipid biosynthesis-associated key enzymes play central roles in the accumulation of lipid droplets in HCC. Enhanced cholesterol biosynthesis and attenuated bile acid biosynthesis play important roles in cholesterol accumulation in HCC. High levels of GSH and elevated Bcl2 and Ucp2 expression may contribute to a normal level of ROS in HCC.
Strong antitumor efficacy of a pancreatic tumor-targeting oncolytic adenovirus for neuroendocrine tumors
- Pages: 2385-2397
- First Published: 21 September 2017
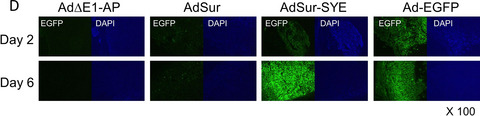
We have previously identified a pancreatic cancer-targeting peptide ligand and demonstrated that a survivin promoter-regulated adenovirus, displaying the ligand, provided effective oncolysis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in a preclinical study. In this study, we found that this adenovirus showed an even higher gene transduction efficiency and oncolytic potency for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in vitro, in a mouse model, and using clinical specimens of various human cancers. The data suggest that the virus, AdSur-SYE, is a promising next-generation therapy agent for pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors.
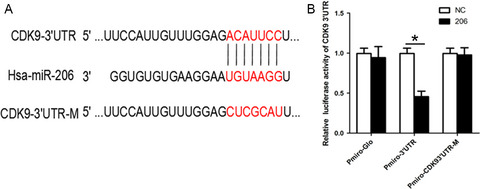
miR-206 inhibits the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via targeting CDK9
- Pages: 2398-2409
- First Published: 21 September 2017
Cancer Prevention
Original Research
Trends in active surveillance for very low-risk prostate cancer: do guidelines influence modern practice?
- Pages: 2410-2418
- First Published: 18 September 2017
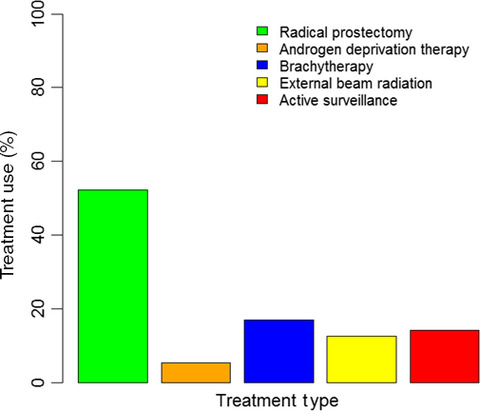
This article demonstrates one of the largest series examining the role of active surveillance in patients with very low-risk prostate cancer. Our results in disparities and trends in recommendations for active surveillance reveal an important aspect of cancer care in the management of this disease entity.
Effects of low-to-moderate alcohol supplementation on urinary estrogen metabolites in postmenopausal women in a controlled feeding study
- Pages: 2419-2423
- First Published: 06 September 2017
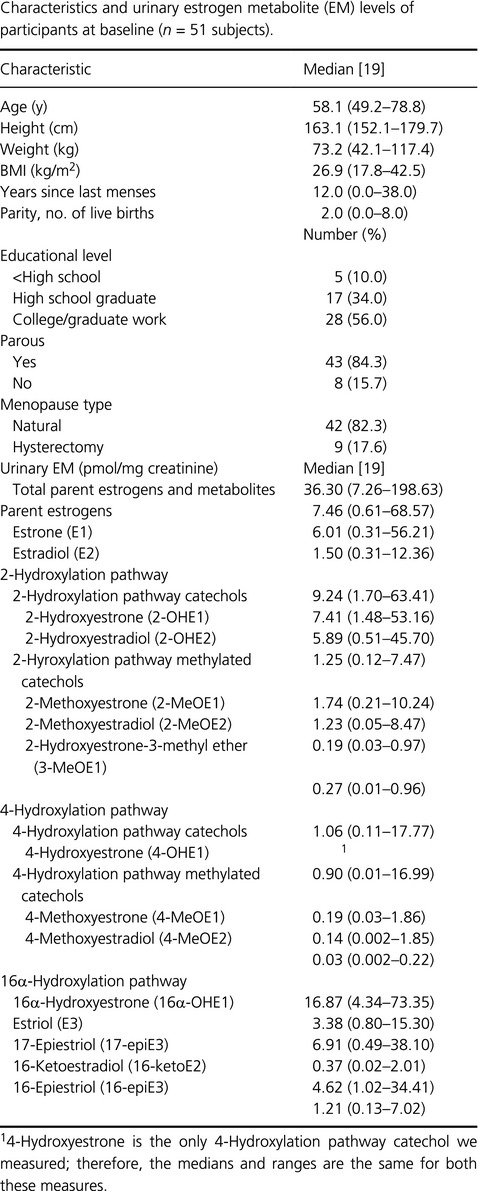
Recent evidence indicates that postmenopausal breast cancer risk increases with higher levels of 16-EpiE3 and decreases with lower levels of 2-OHE1 in different prospective cohorts. Since moderate alcohol consumption in our study of postmenopausal women increased 16-EpiE3 and lowered 2-OHE1, these results imply that moderate drinking may have dual effects on later breast cancer development, but this finding needs confirmation.
Promotion of cell proliferation by the proto-oncogene DEK enhances oral squamous cell carcinogenesis through field cancerization
- Pages: 2424-2439
- First Published: 23 August 2017
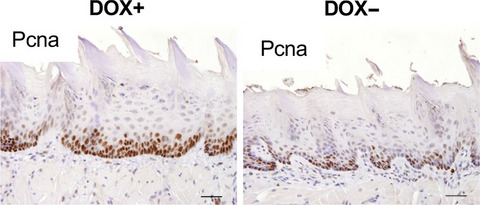
Representative images of IHC analysis for detection of PCNA in the tongues of 4NQO-treated mice with or without DOX (DOX+ and DOX- respectively). Scale bars, 40 μm. PCNA-positive cells in DOX+ iDek mice were spread to the upper layer of the epithelium and the PCNA-positive index in DOX+ iDek mice was significantly higher than that in DOX- iDek mice.
Effect of socioeconomic status on stage at diagnosis of lung cancer in a hospital-based multicenter retrospective clinical epidemiological study in China, 2005–2014
- Pages: 2440-2452
- First Published: 21 September 2017
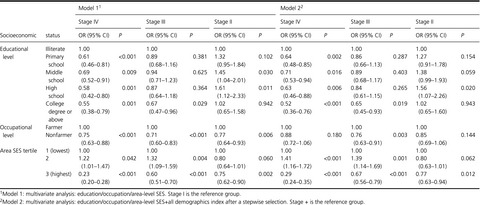
To date, the role of socioeconomic status (SES), either at the individual or community level, in shaping lung cancer risk has been only measured in non-Chinese populations, and the association is inconsistent. This is the first study to consider, simultaneously, measures of SES at the individual and area levels in China, in which the most socioeconomically deprived areas is associated with a higher risk of advanced-stage lung cancer compared with the least deprived areas.
Evaluation of a prediction model for colorectal cancer: retrospective analysis of 2.5 million patient records
- Pages: 2453-2460
- First Published: 21 September 2017
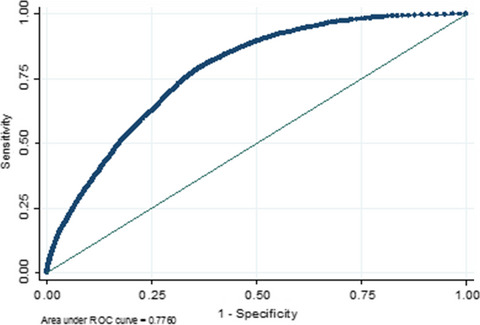
Early detection of colorectal cancer is associated with improved survival, but patients are often diagnosed at a stage beyond surgical cure. We have validated in UK primary care a new risk algorithm for colorectal cancer that draws on full blood count data. Changes in full blood count indices enable identification of patients at risk, offering a new approach to support early detection.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and prostate cancer risk: results from the EPICAP study
- Pages: 2461-2470
- First Published: 21 September 2017
Our results showed a decreased risk of prostate cancer in men using NSAIDs, especially with frequent, current, and chronic use. This effect is particularly observed in men using nonaspirin NSAIDs, and especially with preferential anti-COX-2 activity. Protective effect of NSAIDs seemed to be more pronounced in aggressive prostate cancer and in situation of chronic inflammation mediated by a personal history of prostatitis.
Review
Personal use of hair dyes and risk of leukemia: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 2471-2486
- First Published: 18 September 2017

The purpose of this study was to synthesize and examine the evidence on the relative risk of leukemia among hair dye users under various exposure scenarios. Findings suggest that personal hair dye use is not a significant risk factor for leukemia when data from all studies were combined. Upon stratification, permanent hair dye use, dark hair dye use, hair dye use pre-1980, hair dye use among males, and hair dye use for ≥15 years were associated with a statistically significant increased risk of leukemia. Further research is required to determine whether these associations truly reflect a risk of leukemia due to methodological limitations in the underlying studies.