Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Review Article
Current concepts in the management of diabetic polyneuropathy
- Pages: 464-475
- First Published: 12 September 2020
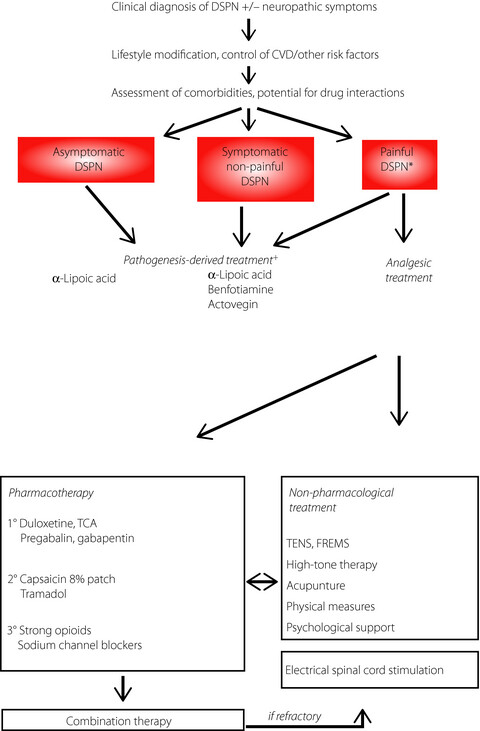
Approximately one of three people with diabetes is affected by diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy, which is associated with marked impairment in quality of life primarily as a result of neuropathic pain and foot ulcers, but still remains underdiagnosed and undertreated. The management of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy includes three cornerstones: (i) lifestyle modification, causal treatment aimed at near-normoglycemia and multifactorial cardiovascular risk intervention; (ii) pathogenesis-derived pharmacotherapy; and (iii) symptomatic treatment of neuropathic pain using analgesic compounds (combinations, if required) and non-pharmacological options.
Commentaries
Microbe-associated metabolites as targets for incident type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 476-478
- First Published: 02 October 2020
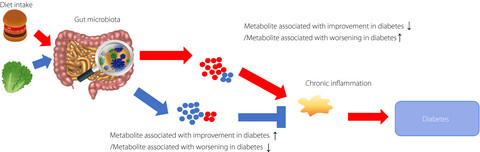
Metabolites produced by gut microbiota could be pathogenic or beneficial to the host. Gut microbiota varies among countries, age and sex, there is a possibility that the microbe-associated metabolites might vary among countries, age and sex. Further studies are required to clarify the relationship among diet, gut microbiota, gut microbiota-related metabolites and development of type 2 diabetes.
Is metformin a miracle or a menace in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes?
- Pages: 479-481
- First Published: 17 December 2020
JDI Updates
In search of the optimal management strategy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 482-484
- First Published: 19 August 2020
Articles
Basic Science and Research
Growth arrest-specific 6 modulates adiponectin expression and insulin resistance in adipose tissue
- Pages: 485-492
- First Published: 24 September 2020
Calcium signaling in endocardial and epicardial ventricular myocytes from streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
- Pages: 493-500
- First Published: 28 October 2020
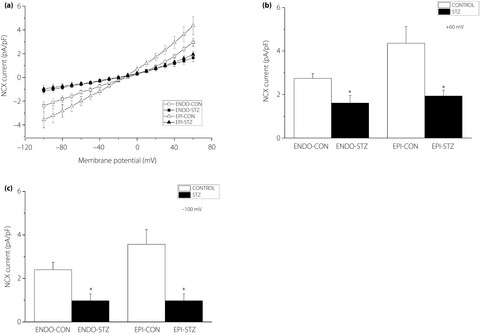
This is the first report to investigate the effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on L-type Ca2+ current simultaneously measured with Ca2+ transients in epicardial and endocardial left ventricular myocytes isolated from rats 5–6 months after the induction of diabetes. Streptozotocin-induced diabetes causes a progressive increase in the amplitude of endocardial and epicardial myocyte Ca2+ transients that is independent of the L-type Ca2+ current. The effect of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on Ca2+ handling might be attributed, at least in part, to the dysfunction of the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger.
Clinical Science and Care
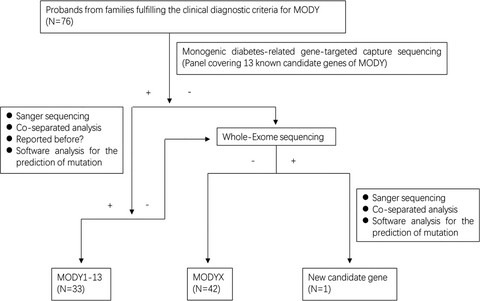
Recognition of maturity-onset diabetes of the young in China
- Pages: 501-509
- First Published: 02 August 2020
Different interaction of onset age and duration of type 1 diabetes on the dynamics of autoantibodies to insulinoma-associated antigen-2 and zinc transporter 8
- Pages: 510-515
- First Published: 22 July 2020
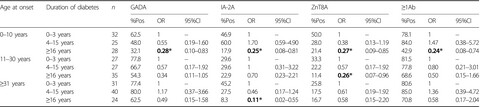
In the present study, we showed that there was a significant interaction between the onset age and duration of diabetes in patients diagnosed when aged ≤10 years regarding all of the autoantibodies to insulinoma-associated antigen-2, zinc transporter 8 and glutamic acid decarboxylase (P < 0.05). However, in patients diagnosed in the middle tertile (11–30 years), the interaction was significant only for zinc transporter 8 autoantibodies, in those with late-onset diabetes (aged ≥31 years) only for insulinoma-associated antigen-2 autoantibodies.
Type 1 diabetes management and outcomes: A multicenter study in Thailand
- Pages: 516-526
- First Published: 19 August 2020
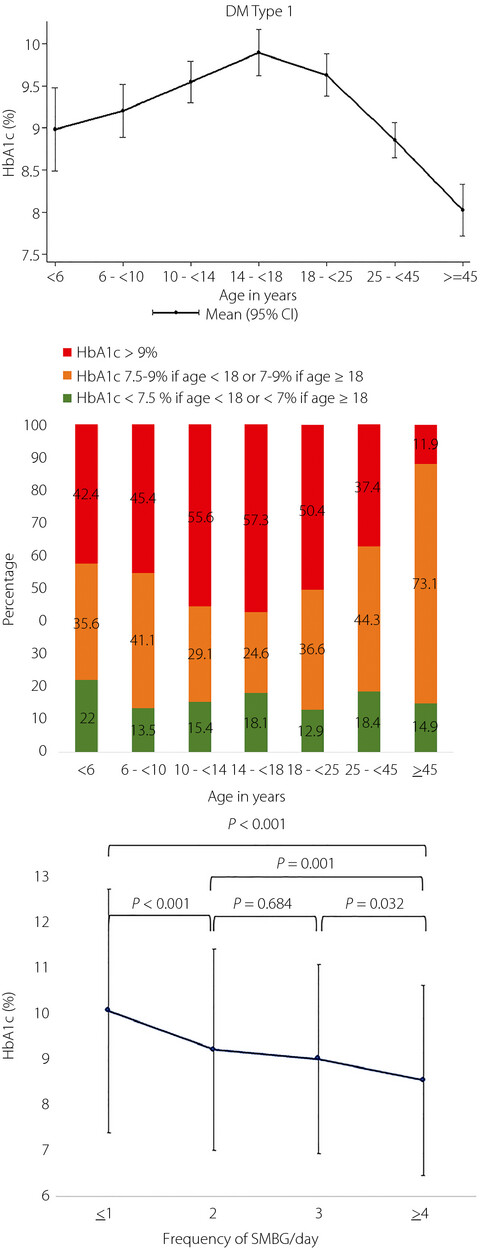
This study reflects a nationwide snapshot of the management and outcomes of 1,907 patients with type 1 diabetes in Thailand. A total of 43% of patients were found to be receiving conventional insulin treatment, and 57% were receiving intensive insulin treatment. Most of the Thai type 1 diabetes patients that we enrolled in this study were not meeting their recommended glycemic target. Good glycemic control was achieved by just 13% of patients receiving conventional insulin treatment, and by just 19% of patients receiving intensive insulin treatment. Multivariate analysis showed good glycemic control to be significantly associated with the 25 to <45 years age group, intensive insulin therapy with self-monitoring of blood glucose three or more times daily and duration of disease of 1 to <5 years.
Dietary fiber intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in a general Japanese population: The Hisayama Study
- Pages: 527-536
- First Published: 01 August 2020
Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of teneligliptin monotherapy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise
- Pages: 537-545
- First Published: 18 August 2020
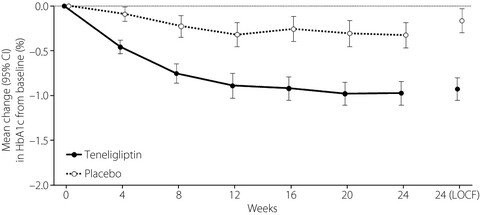
This multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study evaluated the efficacy and safety of teneligliptin monotherapy compared with a placebo in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise. To assess efficacy (primary efficacy end-point: glycosylated hemoglobin from baseline to week 24) and safety (incidence of adverse events and adverse drug reactions), eligible type 2 diabetes patients were assigned in a 1:1 ratio to treatment with teneligliptin 20 mg or a placebo, administered orally once daily before breakfast for 24 weeks. The least square mean change in glycosylated hemoglobin from baseline to week 24 was −0.95% with teneligliptin versus −0.14% with a placebo, and the least square mean change in fasting plasma glucose from baseline to week 24 was −21.9 mg/dL with teneligliptin versus −1.4 mg/dL with a placebo, with the incidence rates of adverse events and adverse drug reactions being similar in both groups, showing that teneligliptin was effective and generally well tolerated at 24 weeks among Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with diet and exercise.
Sodium–glucose cotransporter inhibitors as add-on therapy in addition to insulin for type 1 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Pages: 546-556
- First Published: 15 August 2020
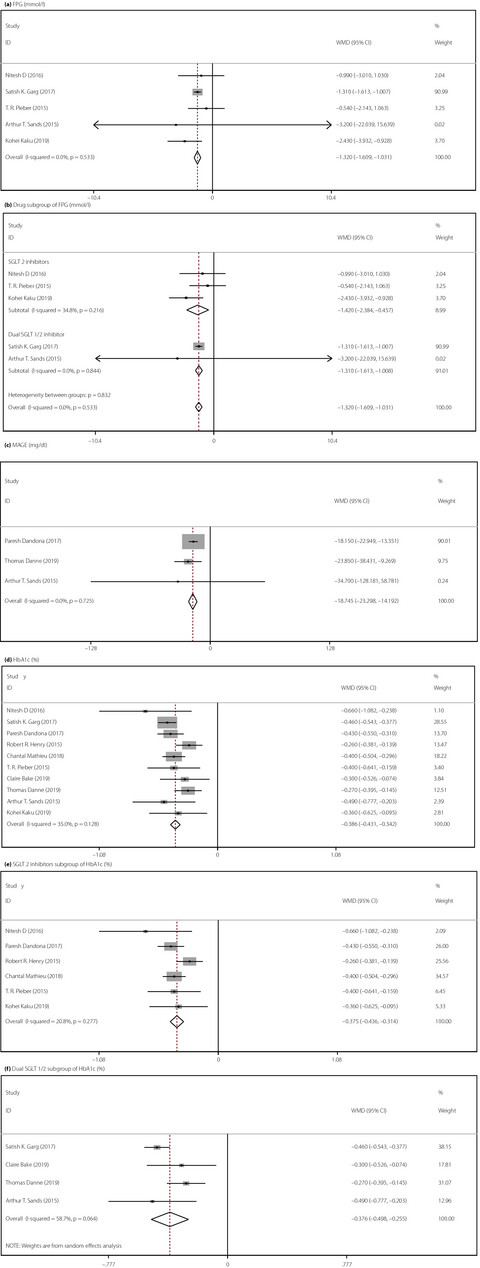
The present meta-analysis analyzed the efficacy and safety of sodium–glucose co-transporter (SGLT) 2 inhibitors and dual SGLT1/2 inhibitors added to insulin for patients with type 1 diabetes, and carried out a subgroup analysis between SGLT2 inhibitors and dual SGLT1/2 inhibitors. Our results showed that SGLT inhibitors as add-on therapy is associated with improved glycemic control, but increased risk for urinary tract infections and diabetic ketoacidosis, proving the potential benefits of SGLT inhibitors with careful use for type 1 diabetes patients.
Association between the triglyceride–glucose index and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- Pages: 557-565
- First Published: 22 July 2020
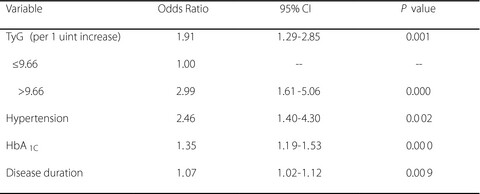
The triglyceride–glucose index provides an affordable and easily interpreted biomarker for monitoring the degree of insulin resistance, and was independently associated with diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. It was a better marker than homeostasis model assessment for insulin resistance for identification of diabetic nephropathy in type 2 diabetes patients.
Serum vaspin levels are positively associated with diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 566-573
- First Published: 14 August 2020
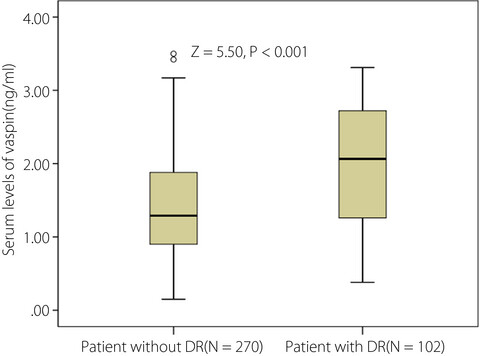
The regulation of vaspin serum concentrations in diabetic retinopathy is unknown. This study showed that higher vaspin serum levels were associated with increased risk of diabetic retinopathy and vision-threatening diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes, which showed that vaspin is an important indicator factor for diabetic retinopathy.
Diagnostic utility of corneal confocal microscopy in type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Pages: 574-582
- First Published: 03 August 2020

The early pathological changes of diabetic peripheral neuropathy are mainly small nerve fiber injuries. Corneal confocal microscopy is a simple, non-invasive and repeatable technique to detect the damage of small nerve fibers. The purpose of this study was to explore the application of corneal confocal microscopy in diabetic peripheral neuropathy and other chronic complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Point-of-care nerve conduction device predicts the severity of diabetic polyneuropathy: A quantitative, but easy-to-use, prediction model
- Pages: 583-591
- First Published: 16 August 2020
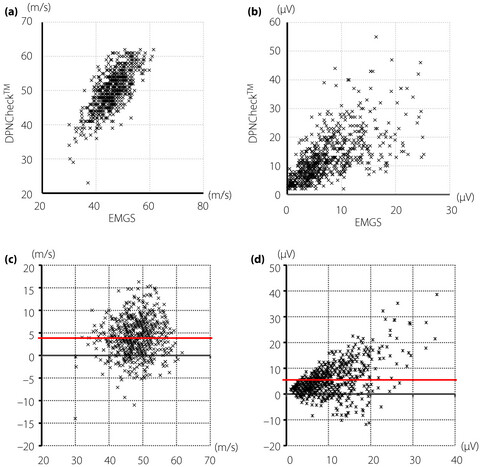
Currently, most diagnostic criteria for diabetic polyneuropathy consist of physical examinations; for example, Achilles tendon reflex or vibration sensation with a tuning fork. Therefore, the low diagnostic sensitivity of these criteria should be improved. Although the gold standard for quantitative evaluation of diabetic polyneuropathy is an electromyography system, these have not become widely used due to their high cost and necessity of an advanced examination technique. The current work verified the efficacy of a handheld nerve conduction device. If clinicians recognize the validity and reliability of the device, this simplified nerve conduction study could be carried out in various clinical settings, including clinics or hospitals in developing or developed countries. The worldwide utilization of the device would improve diagnostic sensitivity for diabetic polyneuropathy in the future.
Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic neuropathy and painful diabetic neuropathy in primary and secondary healthcare in Qatar
- Pages: 592-600
- First Published: 16 August 2020
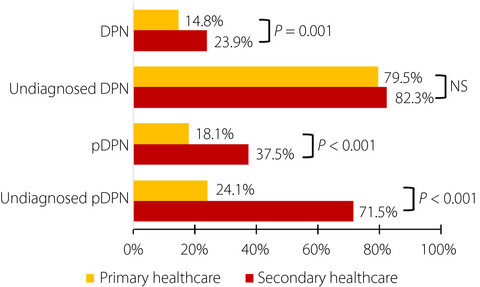
The prevalence of diabetic neuropathy and painful diabetic neuropathy is lower in primary healthcare, and is attributed to better control of risk factors for diabetic peripheral neuropathy. However, approximately 80% of patients with diabetic neuropathy were undiagnosed in both primary and secondary healthcare. Diabetic neuropathy is associated with poor glycemic control, hyperlipidemia and hypertension, whereas painful neuropathy is associated with obesity and reduced physical activity.
Associations between urinary 6-sulfatoxymelatonin excretion and diabetic vascular complications or arteriosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Pages: 601-609
- First Published: 23 July 2020
Development of a clinical risk score for incident diabetes: A 10-year prospective cohort study
- Pages: 610-618
- First Published: 04 August 2020
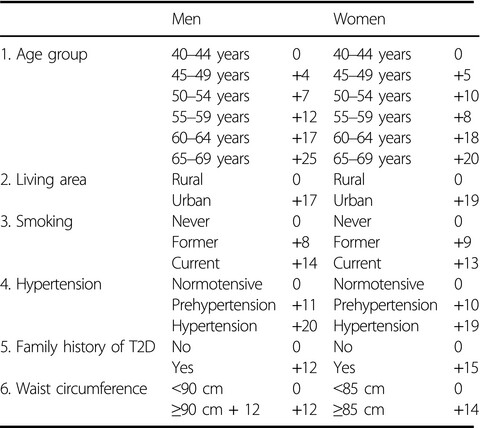
Age, living location (rural or urban), smoking, hypertension, family history of type 2 diabetes and waist circumference were key risk factors of new-onset type 2 diabetes in Korean individuals. A self-assessable Korean Diabetes Risk score composed with non-laboratory variables provided better accurate prediction of 10-year risk of new-onset type 2 diabetes compared with a Western study or a previously developed Korean Diabetes Score.
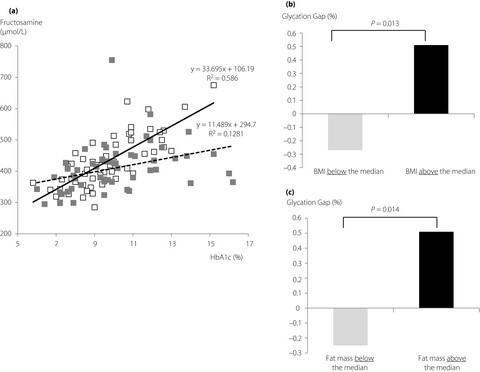
Increased body fat mass reduces the association between fructosamine and glycated hemoglobin in obese type 2 diabetes patients
- Pages: 619-624
- First Published: 07 August 2020
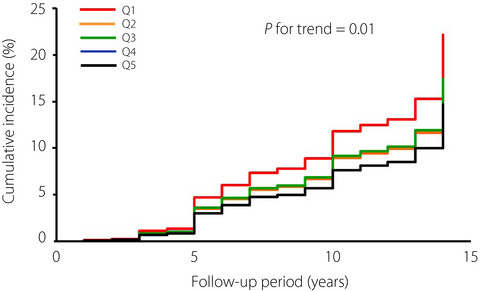
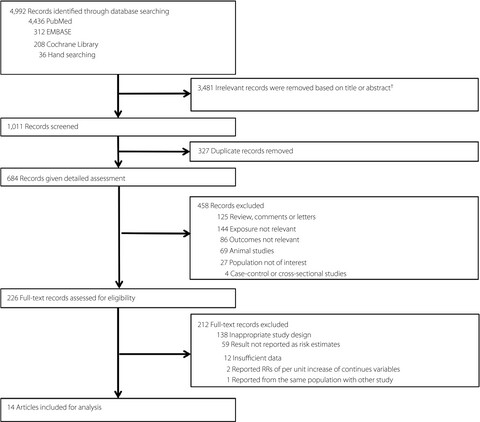
Association between weight cycling and risk of developing diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 625-632
- First Published: 03 August 2020
Associations between sarcopenia and white matter alterations in older adults with diabetes mellitus: A diffusion tensor imaging study
- Pages: 633-640
- First Published: 04 August 2020
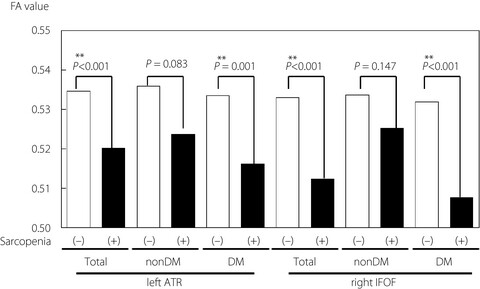
Older adults with diabetes mellitus are susceptible to sarcopenia and altered white matter integrity. Using diffusion tensor imaging technique, we found alterations in left anterior thalamic radiation and right inferior fronto-occipital fasciculus are associated with sarcopenia in patients with diabetes.
Relationships between gut microbiota, plasma glucose and gestational diabetes mellitus
- Pages: 641-650
- First Published: 23 July 2020
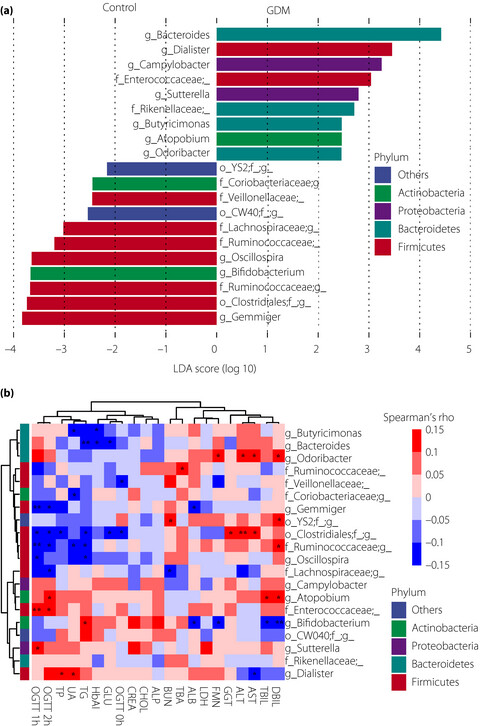
A significantly lower α-diversity and changed microbial communities were identified in the gestational diabetes mellitus group compared with the normal pregnancy group. Changed microbiome composition is associated with fasting serum levels of metabolites, especially glucose. Microbial gene functions related to glycan biosynthesis and metabolism are found to be enriched in gestational diabetes mellitus patients.
Combination of alcohol and glucose consumption as a risk to induce reactive hypoglycemia
- Pages: 651-657
- First Published: 29 July 2020
Potassium supplementation blunts the effects of high salt intake on serum retinol-binding protein 4 levels in healthy individuals
- Pages: 658-663
- First Published: 29 July 2020
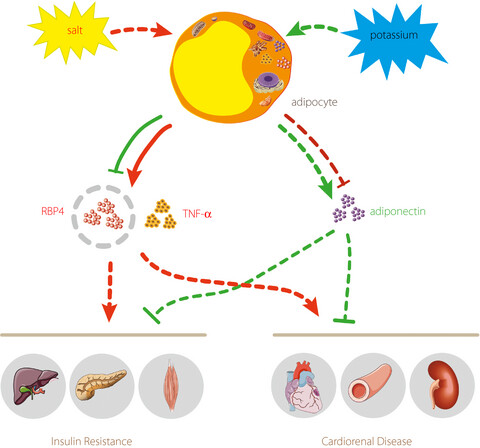
Excess dietary salt and low potassium intake are strongly correlated with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Retinol-binding protein 4, termed “adipokines”, is associated with insulin resistance or type 2 diabetes mellitus. Our study found salt loading can enhance the production of circulating retinol-binding protein 4; inversely, potassium supplementation can blunt the effects of excessive retinol-binding protein 4.
Early detection of euglycemic ketoacidosis during thoracic surgery associated with empagliflozin in a patient with type 2 diabetes: A case report
- Pages: 664-667
- First Published: 19 July 2020
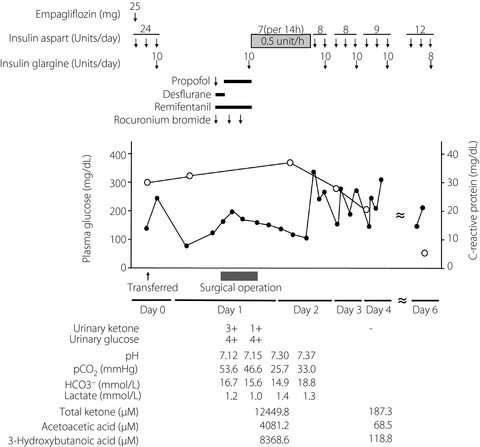
Surgery is a known risk factor of diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) for patients with an insufficient withdrawal period of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors. Although there are the cases of DKA associated with sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors after surgery, we report the first case of euglycemic DKA associated with empagliflozin detected during thoracic surgery. Awareness of the risk of euglycemic DKA is critical for early identification, management and even prevention when patients are treated with sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors.
Rapid and dramatic glucose-lowering effect of bromocriptine in an inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes patient with prolactinoma
- Pages: 668-671
- First Published: 24 July 2020