Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 18 August 2024

Journal of Biophotonics focuses on the interdisciplinary field of biophotonics, publishing cutting-edge research on interactions between light and biological material. The journal covers photonics research in areas such as life sciences, medicine and biomedicine, environmental science, nutrition, biology, physics, and chemistry, ranging from fundamental research to the latest clinical applications.
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER
Virtual-point-based deconvolution for optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy
- First Published: 27 June 2024
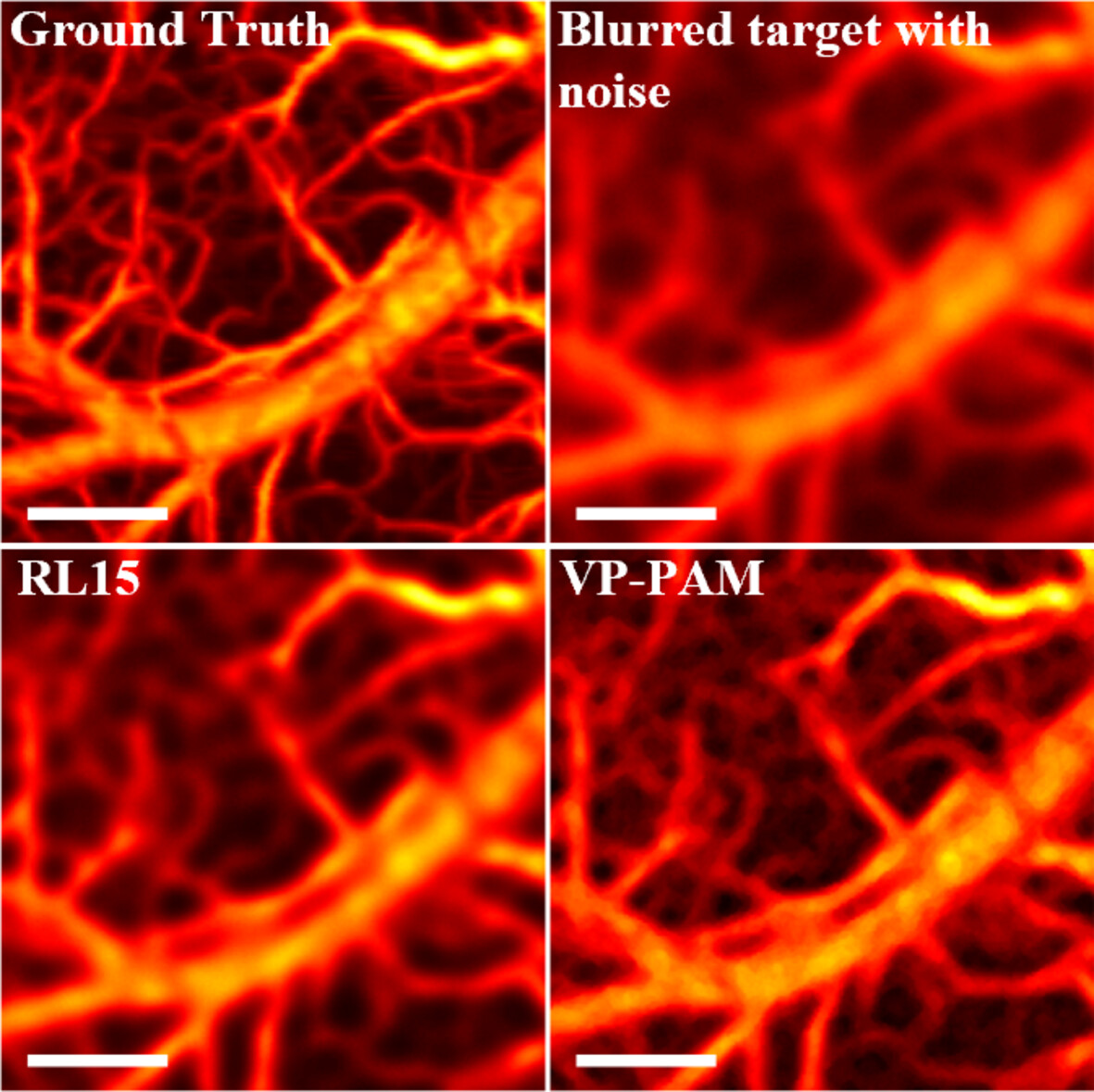
We introduce a virtual-point-based deconvolution technique designed to enhance the spatial resolution of OR-PAM images. This approach utilizes a novel genetic algorithm, combined with a pixel-level loss function and smoothness regularization, to iteratively refine the positioning of virtual point sources. The aim is to closely approximate the actual distribution of photoacoustic point sources.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Determining ideal offsets of spatially offset Raman spectroscopy for transcutaneous measurements—A Monte Carlo study
- First Published: 17 June 2024
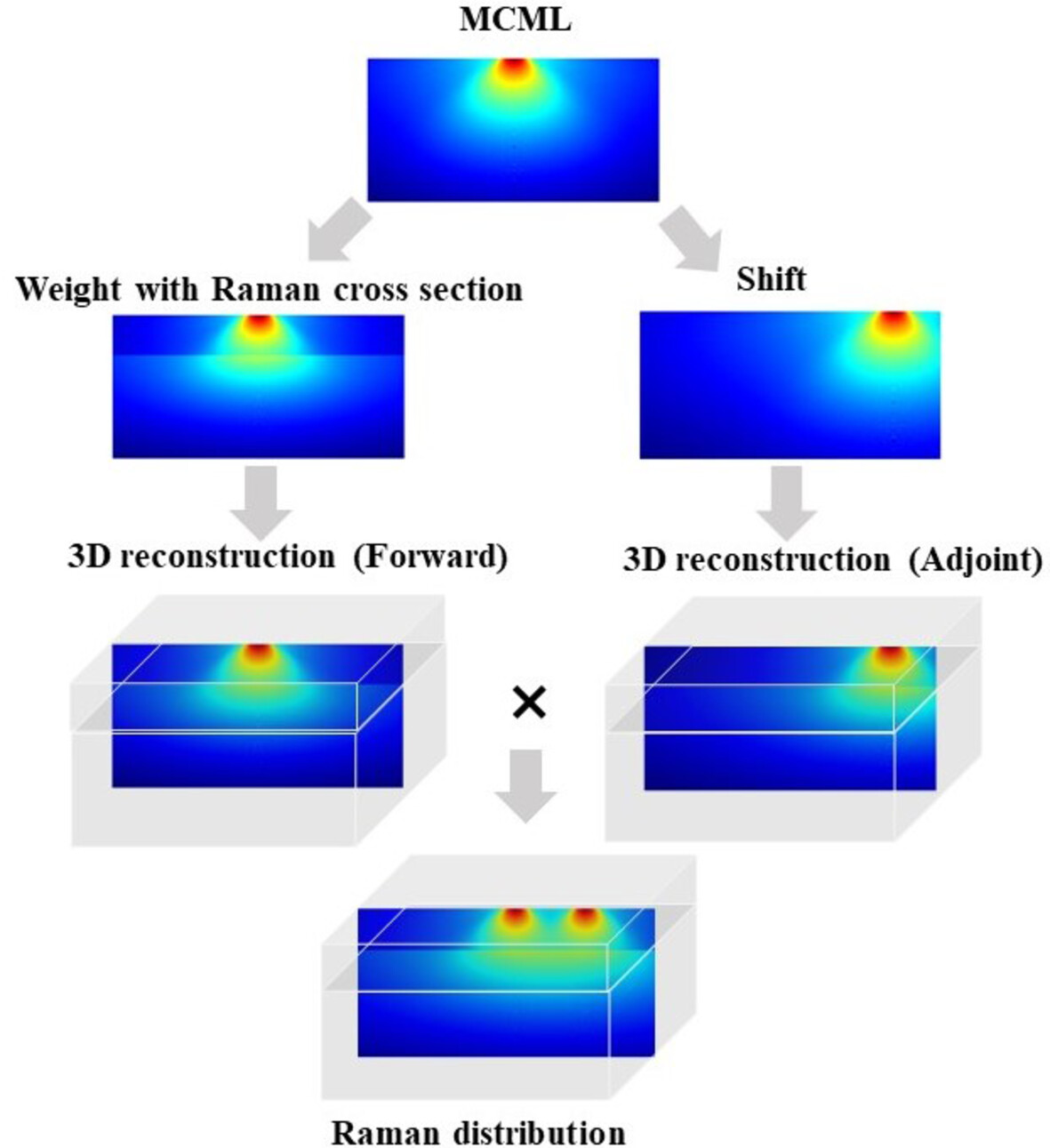
This study unveils the optimal spatial offsets for transcutaneous bone measurements using spatially offset Raman spectroscopy (SORS), employing a novel forward-adjoint Monte Carlo multi-layer (MCML) model to enhance noninvasive bone health diagnostics. Findings reveal that optimal offsets vary with tissue characteristics, promising significant advancements in medical applications.
Label-free imaging diagnosis and collagen-optical evaluation of endometrioid adenocarcinoma with multiphoton microscopy
- First Published: 17 June 2024
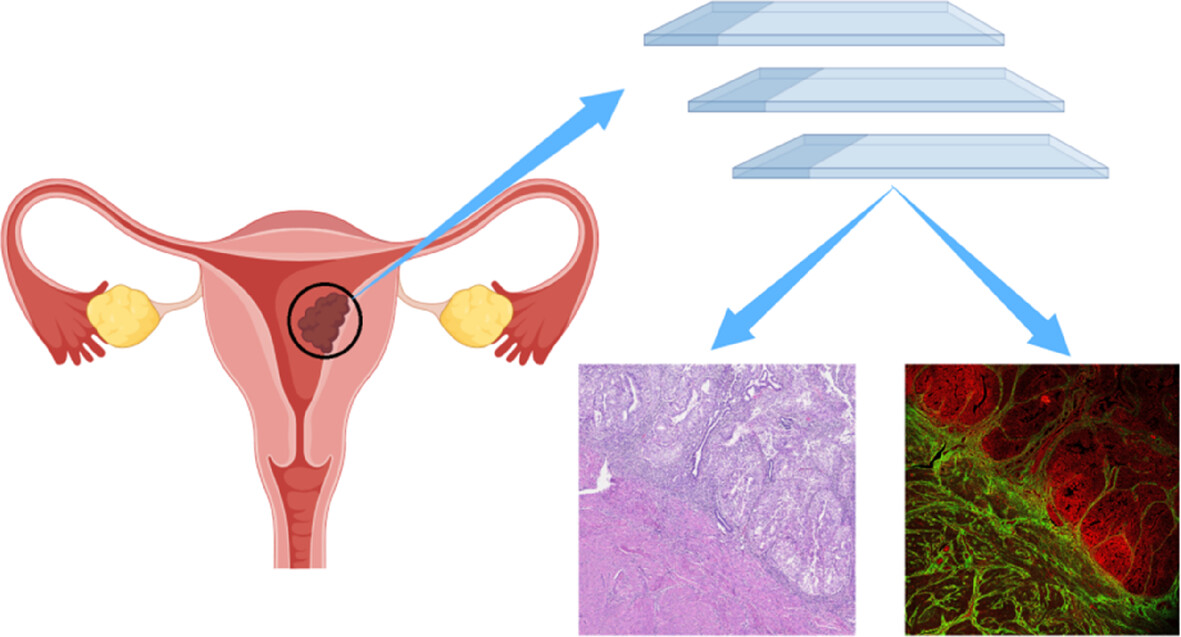
Our study employed multiphoton microscopy to establish the optical pathological characteristics of endometrioid adenocarcinoma, demonstrating its label-free ability to differentiate between benign endometrial hyperplasia and cancerosis. Furthermore, it enabled quantitative assessment of tumor microenvironment alterations by analyzing collagen signatures in endometrial stromal tissue.
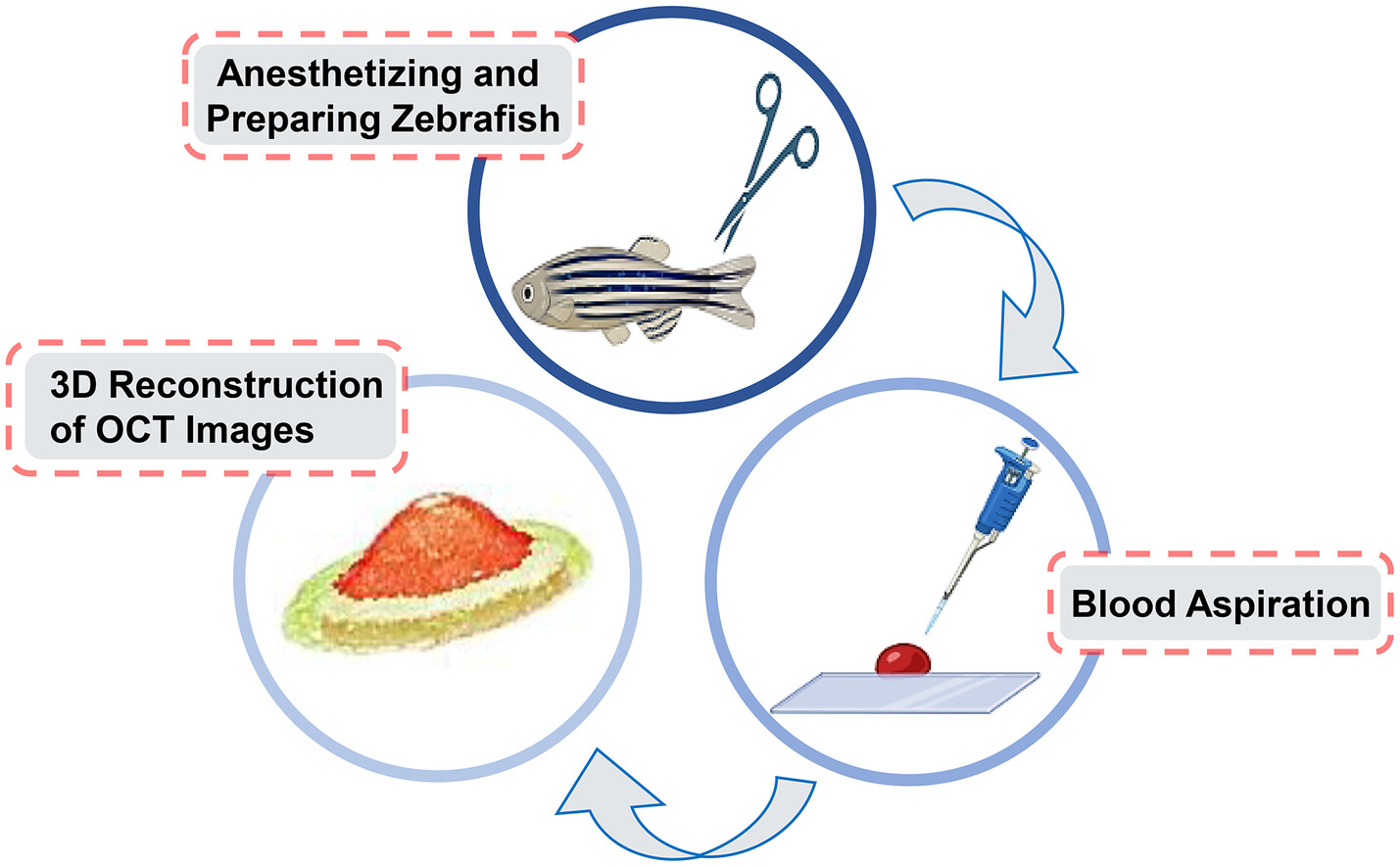
Three-dimensional morphological characterization of blood droplets during the dynamic coagulation process
- First Published: 17 June 2024
Raman spectroscopy with an improved support vector machine for discrimination of thyroid and parathyroid tissues
- First Published: 18 June 2024
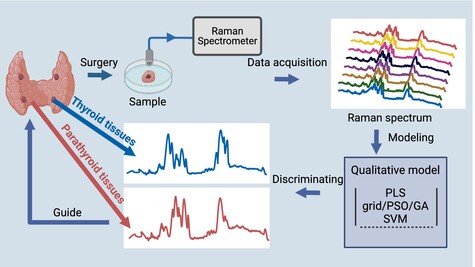
In thyroid surgery, there is a risk of inadvertently removing the parathyroid glands. At present, there is a lack of research on using Raman spectroscopy to discriminate parathyroid and thyroid tissues. The objective of this study is to discriminate thyroid and parathyroid tissues using Raman spectroscopy combined with an improved support vector machine (SVM) algorithm. The results show that the sensitivity of this algorithm is 94.67% and the accuracy is 94.44%.
Measurement of anisotropy factor of nanoparticle embedded tumor phantoms for plasmonic photothermal therapeutics
- First Published: 18 June 2024
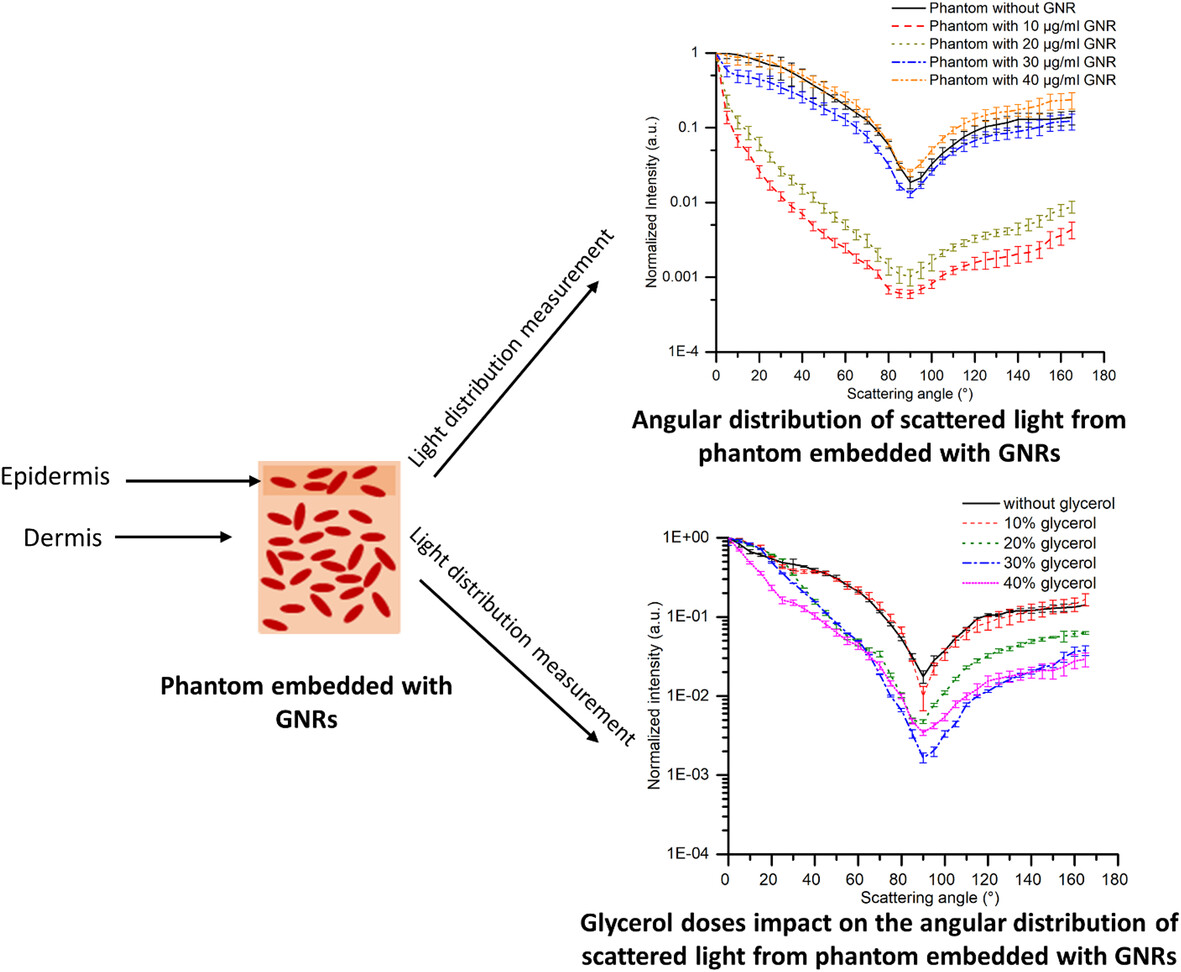
The anisotropy factor (g) of tumor phantom embedded with 40 μg/mL gold nanorods (GNRs) decreased by ~43% compared to the phantom with 10 μg/mL GNRs, which leads to a decrease in forward scattering and penetration of light. For the phantom incorporated with 40 μg/mL GNRs on increasing the phantom thickness from 600 to 1800 μm, the g is reduced by 47%. The glycerol doses ranging from 10% to 40% can increase the g of a tumor phantom embedded with GNRs by 44% and enhance the penetration of light.
An enhanced multimode phase imaging method based on the transport of intensity equation
- First Published: 18 June 2024
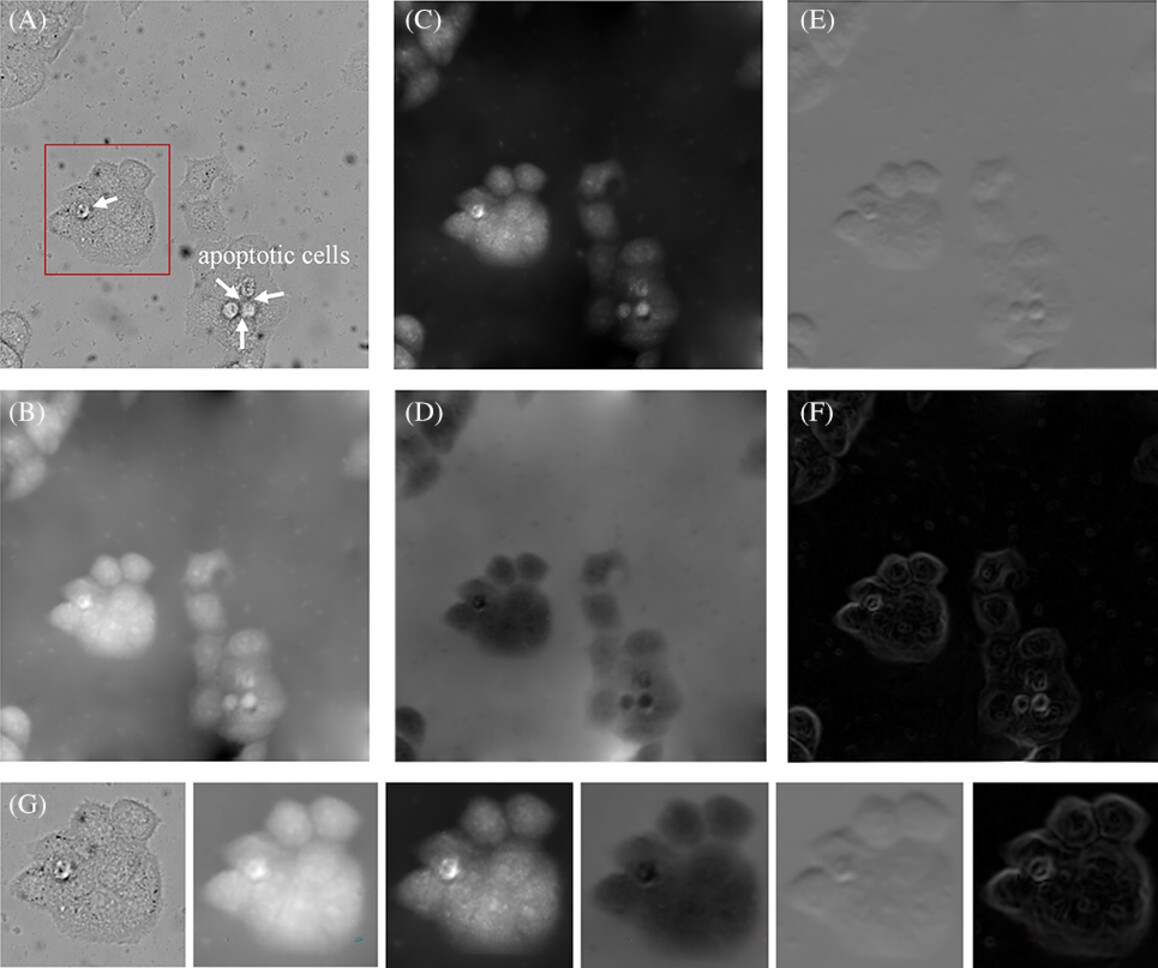
This paper proposes an enhanced multimode phase imaging method based on the TIE to perform multimode contrast-enhanced observation of unstained specimens. First, quantitative phase results of biological samples are obtained by solving the TIE, and then optimal ZPC and isotropic DIC images are obtained. Application of the algorithm to real and simulated objects shows significant feasibility and accuracy. Experiments on MCF-7 cells resulted in multimode images of cells with structures not visible in the raw intensity images. The algorithm is simple to implement and can be combined with traditional optical microscopy.
Optical-resolution photoacoustic microelastography system for elasticity mapping: Phantom study and practical application
- First Published: 18 June 2024
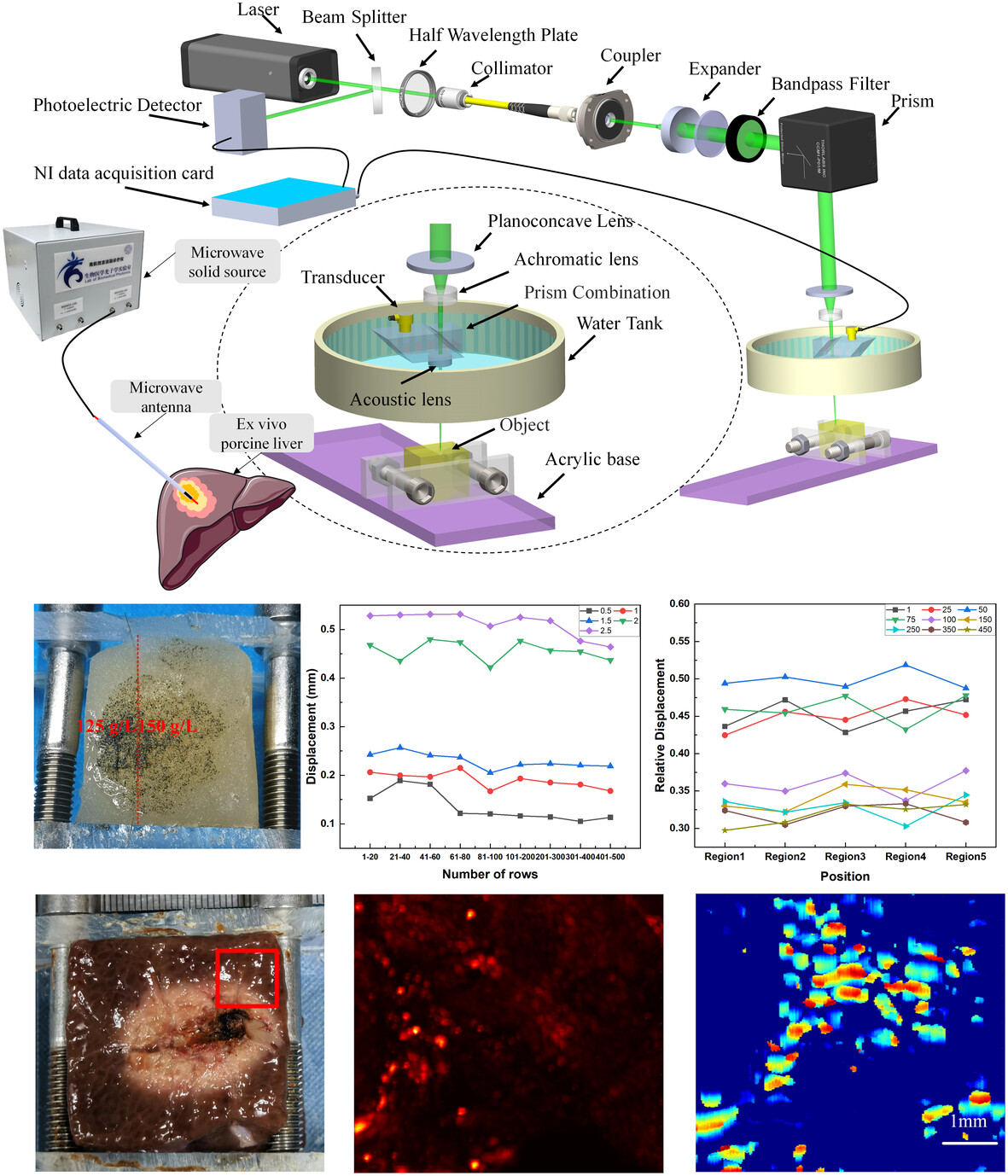
In this study, we utilized an optical-resolution photoacoustic microscopy imaging system to conduct photoacoustic imaging on an agar phantom with elastic differences and liver tissue after microwave ablation. By performing cross-correlation calculations, we obtained the distribution of elastic characteristics. The results highlight the potential of the photoacoustic system in investigating the elastic properties of microwave-ablated tissues, presenting a novel approach for disease diagnosis and pathological tissue analysis.
Compact Linnik-type hyperspectral quantitative phase microscope for advanced classification of cellular components
- First Published: 20 June 2024
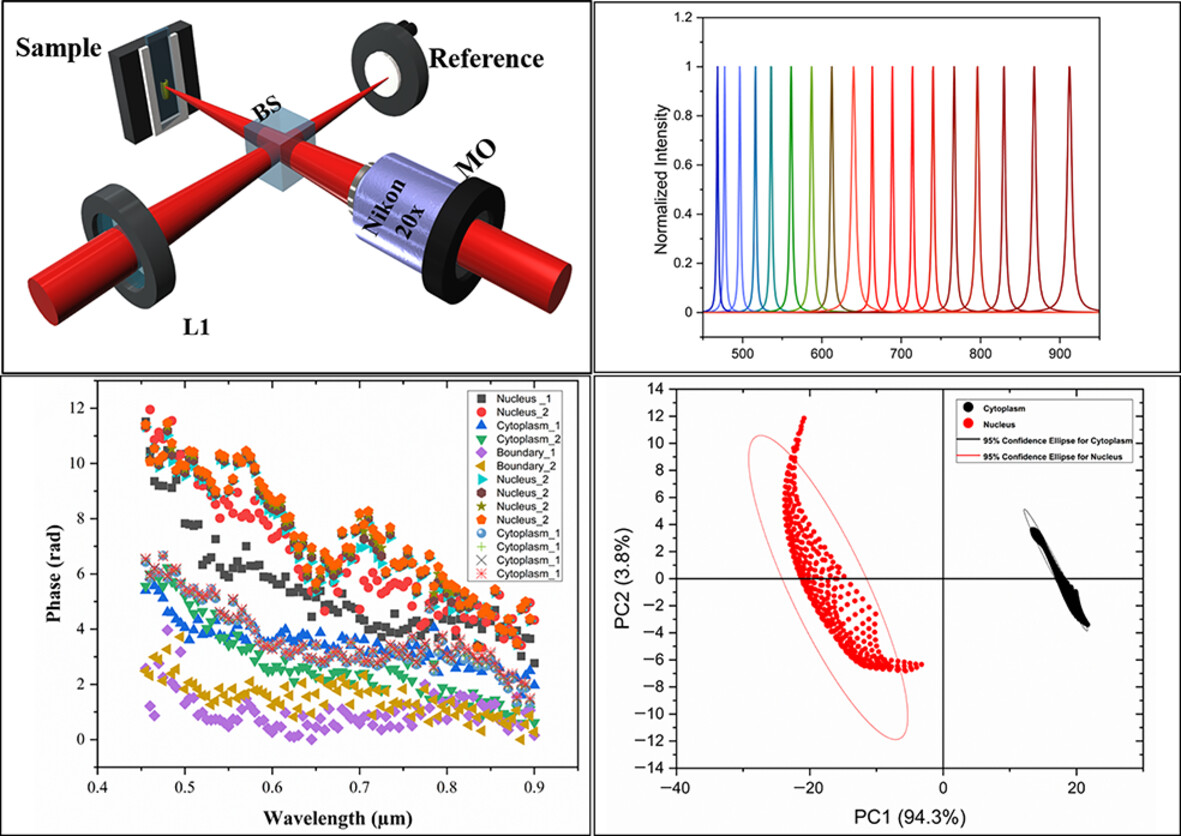
The challenges posed by using of two nonidentical microscope objective (MO) in two arms of a Linnik type interferometer are resolved by using a single MO based compact Linnik interferometer. Hyperspectral quantitative phase microscopy (QPM) is performed using the developed setup, which enables advanced classification of different cellular components.
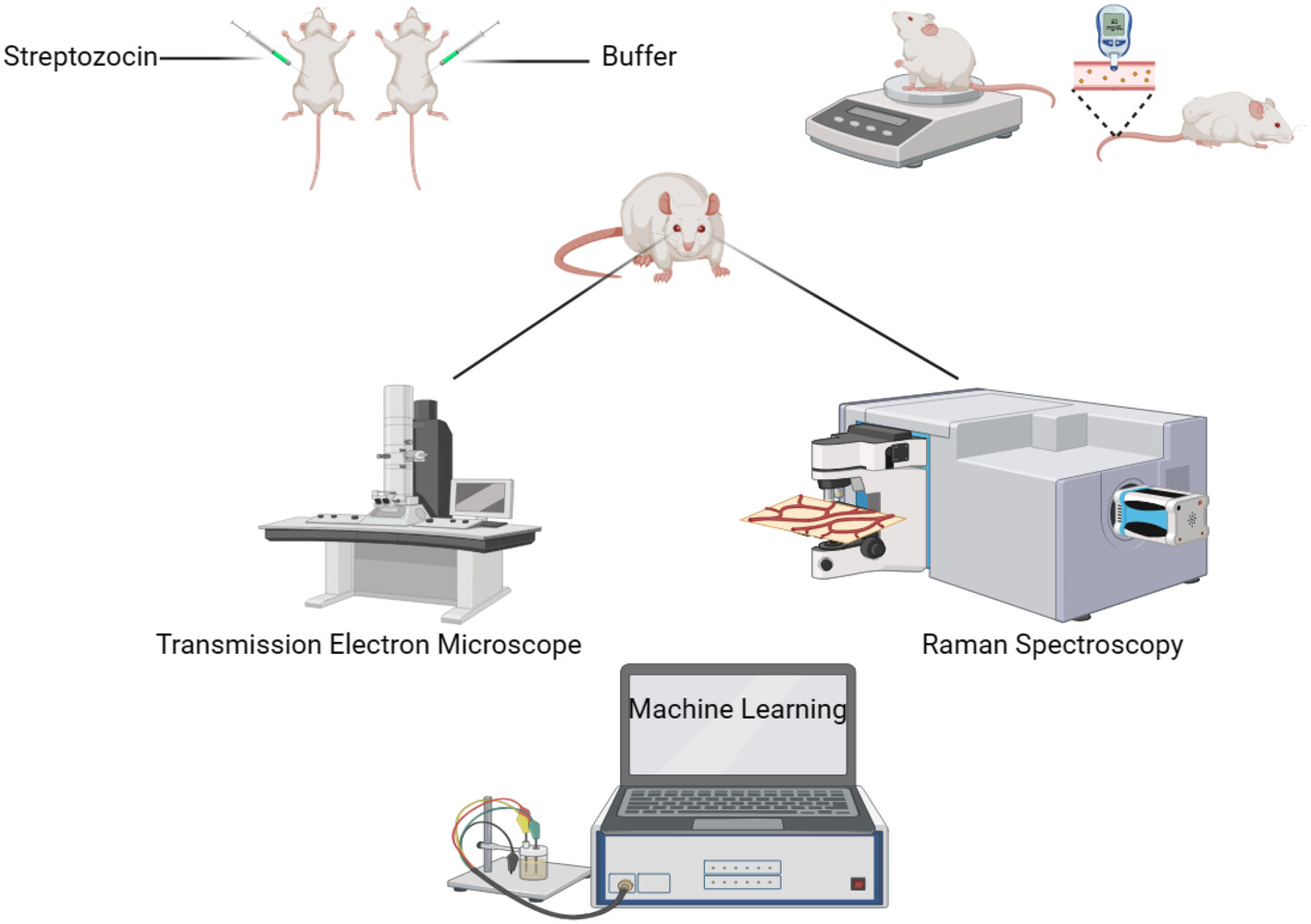
Diagnostic application in streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy rats: A study based on Raman spectroscopy and machine learning
- First Published: 21 June 2024
Selective induction of senescence in cancer cells through near-infrared light treatment via mitochondrial modulation
- First Published: 21 June 2024
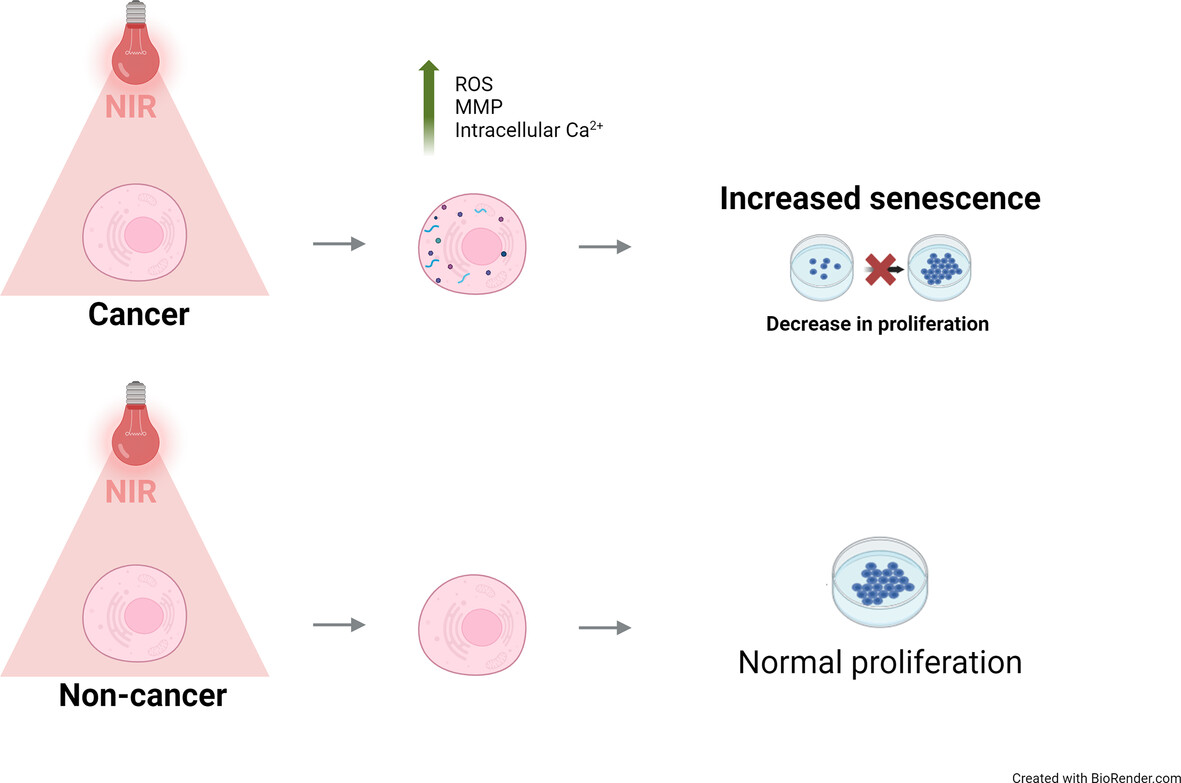
A total of 734 nm near-infrared (NIR) light induces senescence in cancer cells, accompanied by increased reactive oxygen species, mitochondrial membrane potential and intracellular calcium levels. Non-cancer cells show no senescence effect under similar conditions. This study highlights the potential of NIR light in selectively targeting cancer cells while sparing non-cancer ones.
Detecting emergence of ruptures in individual layers of the stretched intestinal wall using optical coherence elastography: A pilot study
- First Published: 25 June 2024
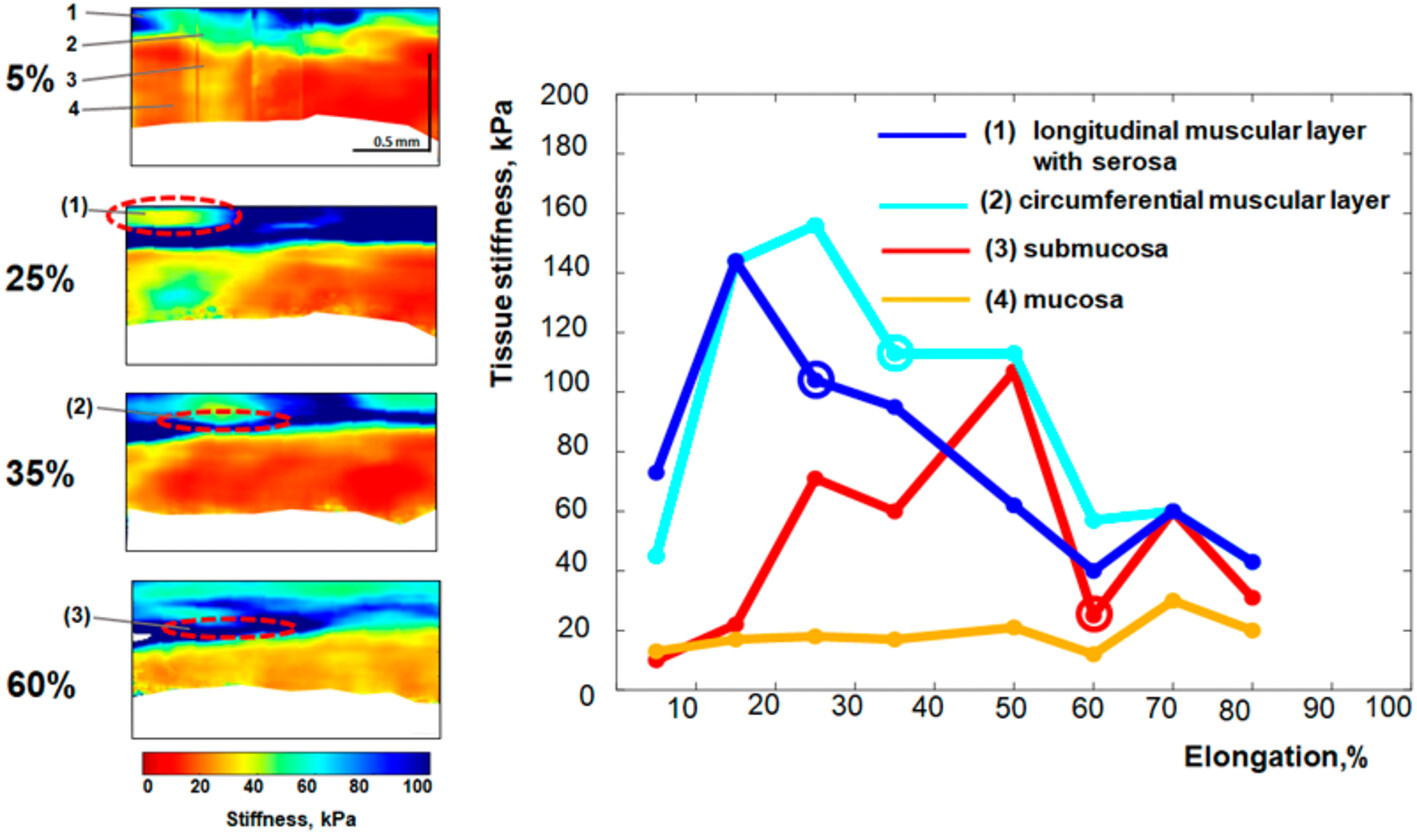
C-OCE allowed to establish that with longitudinal stretching of the small-intestine wall, ruptures appear first in the longitudinal muscle layer and then in the circumferential muscle layer, while submucosa and mucosa are more tolerant to stretching. A threshold of ~15%, defined for the longitudinal muscle layer, has been proposed as a practical safety criterion.
Optical parameters of healthy and tumor breast tissues in mice
- First Published: 26 June 2024
The study compares healthy and tumor breast tissue in mice using spectroscopy, refractometry, and Raman spectroscopy. The findings show that tumor tissue has lower scattering and refractive indices and altered molecular composition. The difference in the optical parameters of the tissues makes it possible to reliably differentiate them.
Noninvasive cardiac hemodynamics monitoring of acute myocardial ischemia in rats using near-infrared spectroscopy: A pilot study
- First Published: 27 June 2024
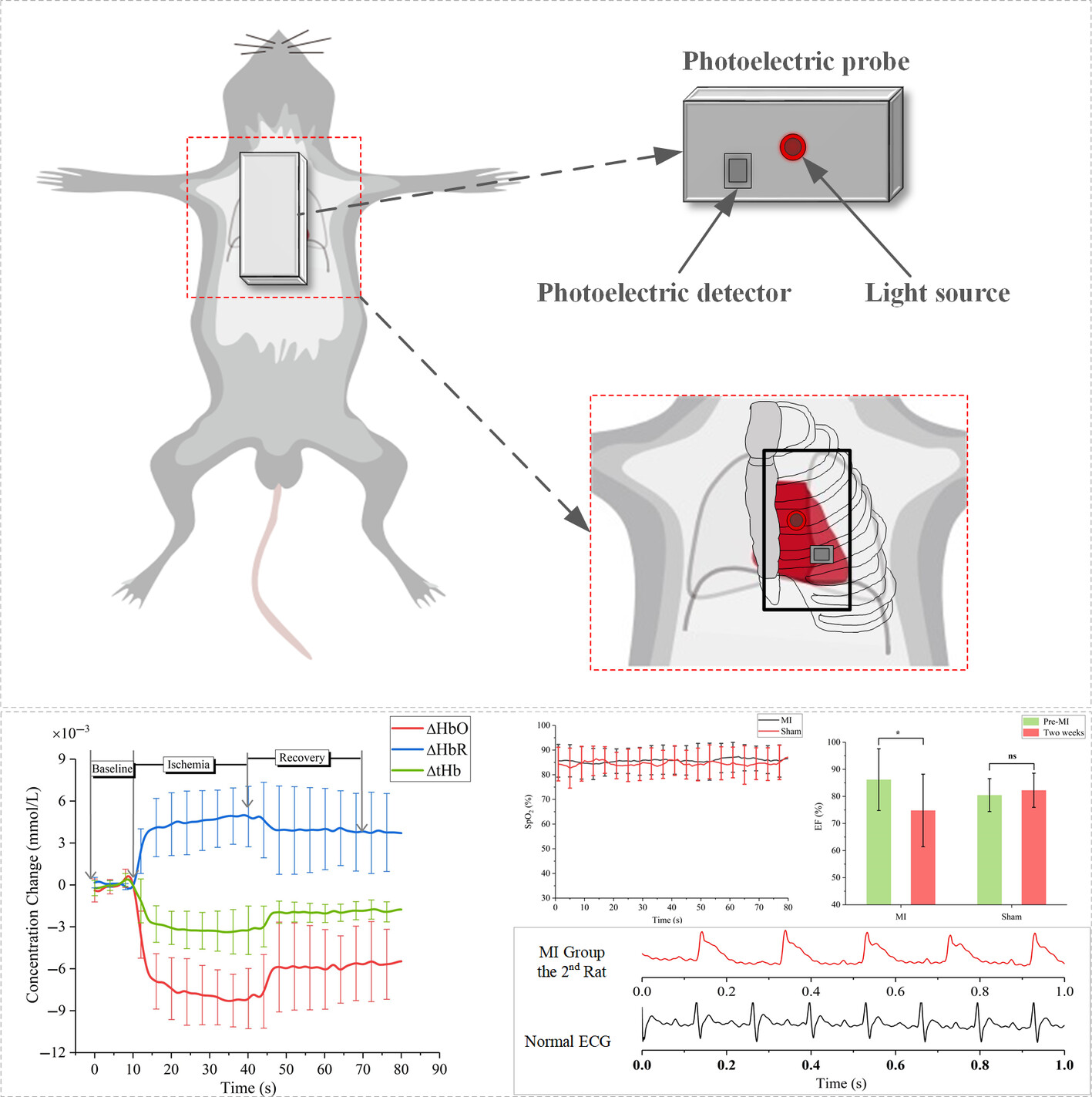
A near-infrared spectroscopic device was developed for the real-time monitoring of hemodynamic changes during coronary artery occlusion in the rat heart. This was evidenced by a rapid decrease in ΔHbO and a marked increase in ΔHbR when rats' myocardial ischemia occurred, accompanied by a significant elevation of the electrocardiographic ST segments. It has also yielded new insights for monitoring ischemic heart disease.
Combining red photobiomodulation therapy with polydioxanone threads for wrinkle reduction in the glabella region: A randomized, controlled, double-blind clinical trial
- First Published: 27 June 2024
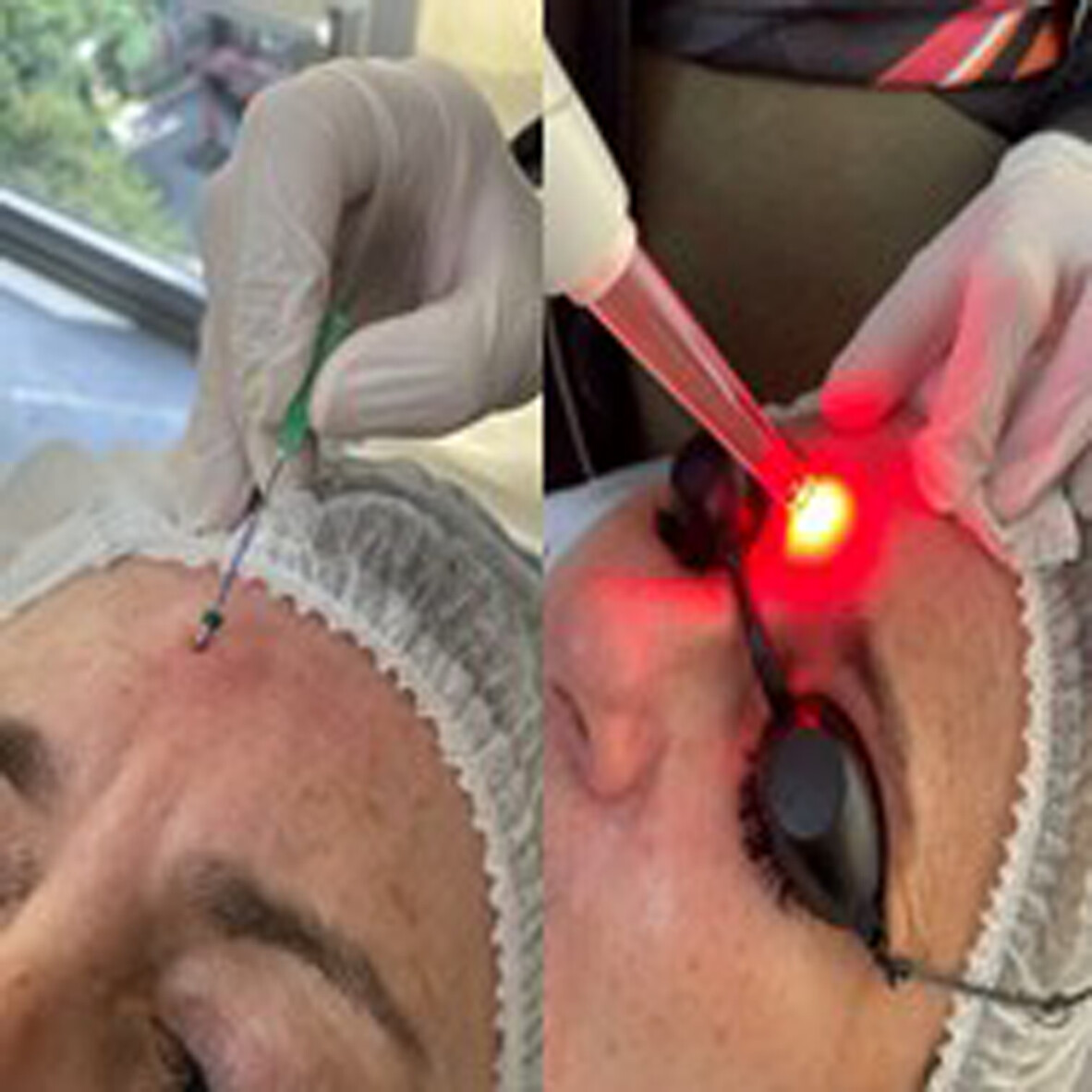
This study explores the combined use of polydioxanone threads and red LED photobiomodulation therapy (PBM) for reducing glabellar static wrinkles. Conducted on 40 individuals, the trial examines the effects one session on the control of post procedure swelling and also the effect of nine sessions over 30 days on the increase in dermal thickening provided by the thread. The PBM effect on thread hydrolysis was also evaluated.
Extraction of collagen morphological features from second-harmonic generation microscopy images via GLCM and CT analyses: A cross-laboratory study
- First Published: 27 June 2024

Collagen morphological features can be extracted from second-harmonic generation (SHG) images, but dependence to the experimental conditions represents a significant issue. This problem has been tackled by acquiring SHG images of the same collagenous sample in various laboratories, using different setups and conditions, and by comparing their extracted features. They strongly depend by specific experimental parameters; hence, a preprocessing method has been proposed and successfully tested for comparing results obtained in different labs.
Effects of solar radiations on stratum corneum hydration: Part II, protective action of solar filters
- First Published: 27 June 2024
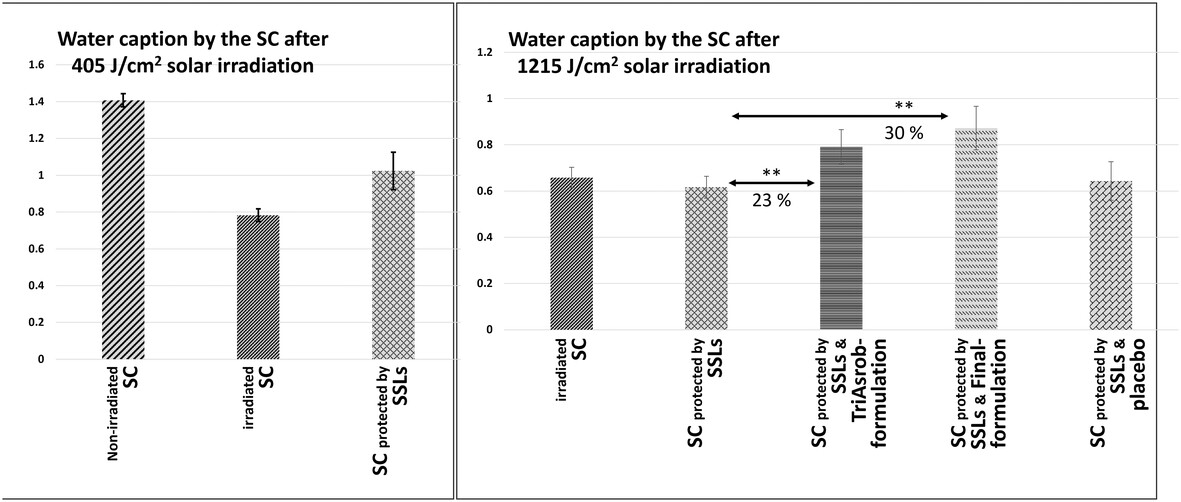
The study investigated the protective function of skin surface lipids (SSLs) against solar radiation and evaluated the effectiveness of a solar filter on SSLs composition and hydration kinetics in the stratum corneum. Results indicated that SSLs absorb solar light and help maintain water balance, but their protective function can be limited due to variation in distribution. Using a solar filter helped preserve SSLs and water balance, demonstrating the importance of supplementary measures for comprehensive skin protection.
Effect of 460 nm blue light PBM on human MeWo melanoma cells
- First Published: 27 June 2024
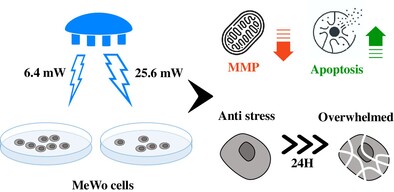
Photobiomodulation (PBM) using 460 nm blue light has been shown to have an inhibitory effect on skin cancer cells. We found that blue light inhibits these melanoma cells through oxidative stress and DNA damage, and this inhibition intensifies at higher irradiance levels. Although the cells initially attempt to resist the stress induced by the treatment, they eventually undergo apoptosis over time.
Raman spectroscopic analysis of human blood serum of glaucoma patients supplemented with macular pigment carotenoids
- First Published: 27 June 2024
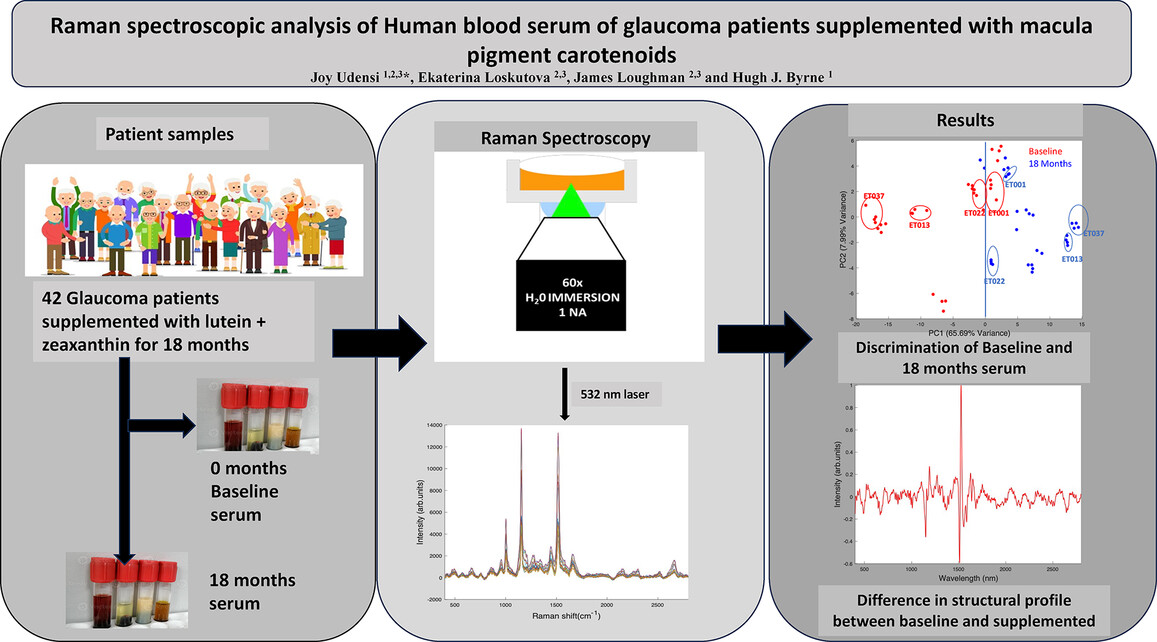
Supplementation with macular pigment carotenoids increased overall serum carotenoids content and this increase was highest in patients with initial high baseline carotenoid content. Clear distinction in structural profile of serum carotenoids pre and post supplementation was noted, indicating Raman spectroscopy can potentially differentiate and quantify carotenoids in blood.
In vivo Raman spectroscopic and fluorescence study of suspected melanocytic lesions and surrounding healthy skin
- First Published: 27 June 2024
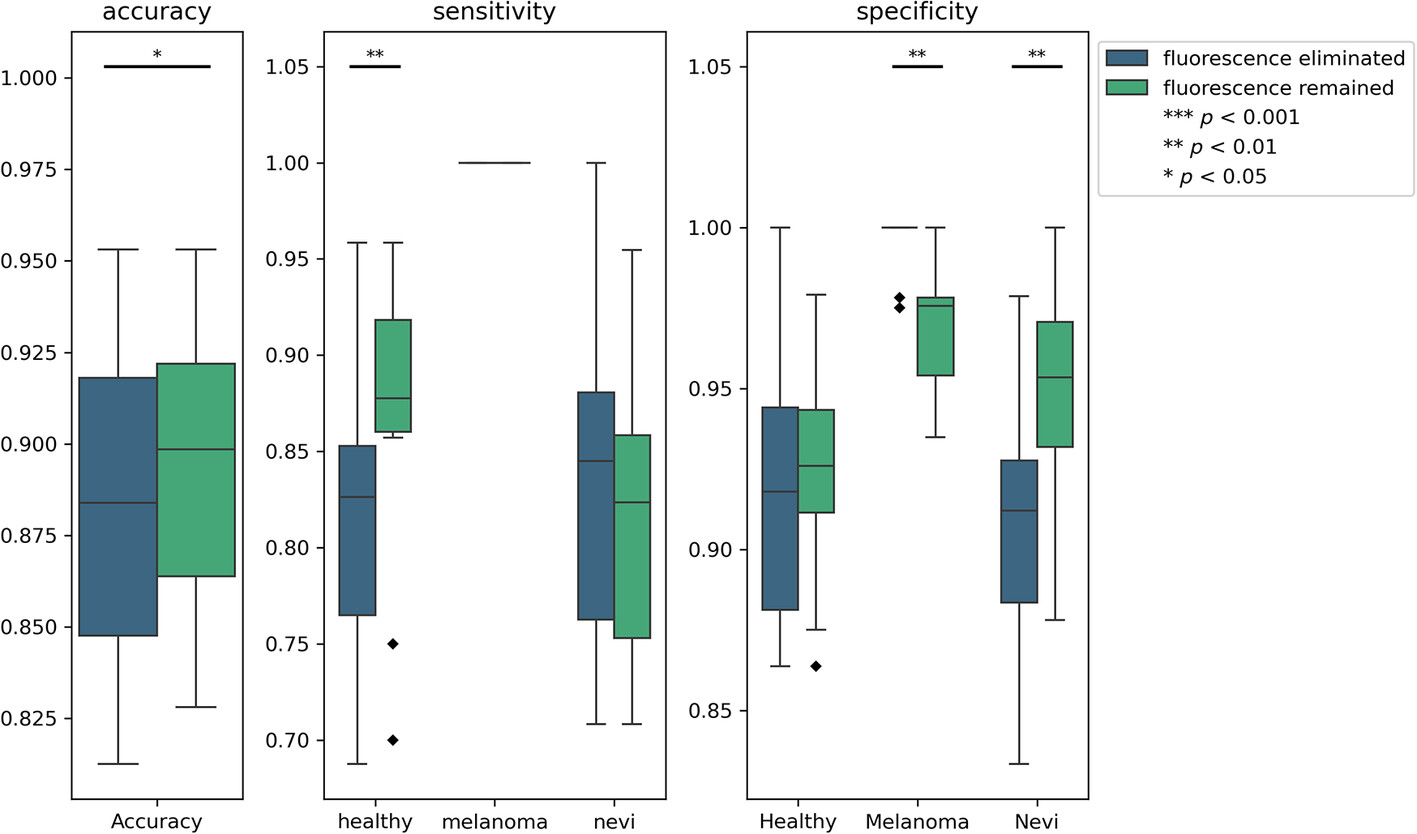
Raman spectroscopy was used for noninvasive diagnosis of skin melanoma. With spectra data containing autofluorescence, machine learning obtained higher accuracy to classify different skin lesions compared to the pure Raman spectra data without autofluorescence. This demonstrates that the autofluorescence background in Raman spectra holds diagnostic value.