Measurement of anisotropy factor of nanoparticle embedded tumor phantoms for plasmonic photothermal therapeutics
Abstract
Measurement of anisotropy factor (g) in the presence of nanoparticles (NPs) is important for understanding light distribution for plasmonic photothermal cancer therapeutics. Here, anisotropy factor is investigated through bilayer phantoms (epidermal and dermal) of various thicknesses incorporated with gold nanorods (GNRs) concentrations of 10–40 μg/mL by using in-house developed goniometric setup. Results show that 10 μg/mL GNRs in the phantom increase g by ~50% (g = 0.9471) w.r.t. phantom without NPs. Higher concentrations (40 μg/mL) of GNRs decrease g by ~43% (g = 0.5341) w.r.t. phantom with 10 μg/mL GNRs. For 40 μg/mL GNRs phantom, the anisotropy factor reduces by 47% for phantom thickness from 600 to 1800 μm. Anisotropy factor of GNR embedded phantom increased by 44% by using glycerol (10%–40%). Incorporation of NPs in a tumor significantly affects g, a major parameter for light distribution. These measurements provide insights for light scattering based on nanoparticle doses for plasmonic photothermal therapeutics.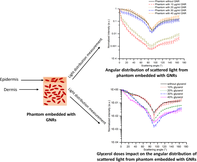
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data sharing is not applicable to this article as no new data were created or analyzed in this study.




