Noninvasive cardiac hemodynamics monitoring of acute myocardial ischemia in rats using near-infrared spectroscopy: A pilot study
Sifan Chen
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorQiao Li
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorQinyu Pan
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorQiuyan Yin
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorLiang Yue
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorPeng Zhang
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Gong Chen
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Department of Cardiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Correspondence
Gong Chen and Weichao Liu, Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Weichao Liu
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Correspondence
Gong Chen and Weichao Liu, Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorSifan Chen
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorQiao Li
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorQinyu Pan
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorQiuyan Yin
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorLiang Yue
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorPeng Zhang
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Gong Chen
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Department of Cardiology, The Affiliated Hospital of Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Correspondence
Gong Chen and Weichao Liu, Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Weichao Liu
Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan, China
Correspondence
Gong Chen and Weichao Liu, Key Laboratory of Medical Electrophysiology, Ministry of Education & Medical Electrophysiological Key Laboratory of Sichuan Province (Collaborative Innovation Center for Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases), Institute of Cardiovascular Research, Southwest Medical University, Luzhou, Sichuan 646000, China.
Email: [email protected] and [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorSifan Chen and Qiao Li contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Noninvasive and real-time optical detection of cardiac hemodynamics dysfunction during myocardial ischemia remains challenging. In this study, we developed a near-infrared spectroscopy device to monitor rats' myocardial hemodynamics. The well-designed system can accurately reflect the hemodynamics changes by the classic upper limb ischemia test. Systemic hypoxia by disconnecting to the ventilator and cardiac ischemia by coronary artery slipknot ligation was conducted to monitor myocardial hemodynamics. When systemic hypoxia occurred, ΔHbR and ΔtHb increased significantly, whereas ΔHbO decreased rapidly. When coronary blood flow was obstructed by slipknots, cardiothoracic ΔHbO immediately begins to decline, while ΔHbR also significantly increases. Simultaneously, SpO2 did not show any obvious changes during myocardial ischemia, while SpO2 decreased significantly during systemic hypoxia. These results demonstrated that cardiothoracic hemodynamics stemmed from myocardial ischemia. This pilot study demonstrated the practicality of noninvasive, low-cost optical monitoring for cardiac oxygenation dysfunction in rats.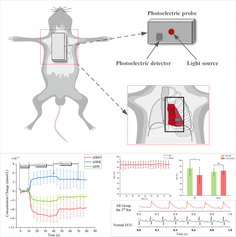
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
REFERENCES
- 1P. Libby, J. E. Buring, L. Badimon, G. K. Hansson, J. Deanfield, M. S. Bittencourt, L. Tokgözoğlu, E. F. Lewis, Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 56.
- 2W. Wang, M. Hu, H. Liu, X. Zhang, H. Li, F. Zhou, Y. M. Liu, F. Lei, J. J. Qin, Y. C. Zhao, Z. Chen, W. Liu, X. Song, X. Huang, L. Zhu, Y. X. Ji, P. Zhang, X. J. Zhang, Z. G. She, J. Yang, H. Yang, J. Cai, H. Li, Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1943.
- 3J. A. Purcell, L. Haynes, Am. J. Nurs. 1984, 84, 627.
- 4L. Tang, X. Q. Hu, S. H. Zhou, Acta Cardiol. Sin. 2014, 30, 493.
- 5I. Asouhidou, T. Asteri, BMC Res. Notes 2009, 2, 25.
- 6T. Durduran, R. Choe, W. B. Baker, A. G. Yodh, Rep. Prog. Phys. 2010, 73, 076701.
- 7F. F. Jöbsis, Science 1977, 198, 1264.
- 8Y. Yu, K. Zhang, L. Zhang, H. Zong, L. Meng, R. Han, Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2018, 1, CD010947.
- 9B. Pan, C. Huang, X. Fang, X. Huang, T. Li, J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201800240.
- 10G. Jia, G. Liu, H. Niu, Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 784821.
- 11L. Katus, A. Blasi, S. McCann, L. Mason, E. Mbye, E. Touray, M. Ceesay, M. de Haan, S. E. Moore, C. E. Elwell, S. Lloyd-Fox, NeuroImage 2023, 274, 120153.
- 12S. Marcolini, I. Frentz, C. A. Sanchez-Catasus, J. D. Mondragon, P. K. Feltes, A. van der Hoorn, R. J. H. Borra, M. A. Ikram, R. Dierckx, P. P. De Deyn, Ageing Res. Rev. 2022, 79, 101661.
- 13J. Carr, J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3795.
- 14U. Sigwart, M. Grbic, M. Payot, J.-J. Goy, A. Essinger, A. Fischer, Ischemic events during coronary artery balloon obstruction, Springer, Berlin Heidelberg 1984, p. 29.
10.1007/978-3-642-69589-6_6 Google Scholar
- 15D. Contini, L. Spinelli, A. Torricelli, A. Pifferi, R. Cubeddu, L. Ascari, L. Potí, M. G. Trivella, A. L'Abbate, Biomedical Optics and 3-D Imaging (Miami, Florida United States) 2010, p. BTuD98.
- 16M. G. Trivella, A. Piersigilli, F. Bernini, G. Pelosi, S. Burchielli, S. Puzzuoli, C. Kusmic, A. L'Abbate, Int. J. Artif. Organs 2017, 40, 338.
- 17E. Gussakovsky, Y. Yang, J. Rendell, O. Jilkina, V. Kupriyanov, Anal. Biochem. 2010, 407, 120.
- 18E. Gussakovsky, Y. Yang, J. Rendell, O. Jilkina, V. Kupriyanov, J. Biophotonics 2012, 5, 128.
- 19R. Honikman, A. A. Pawale, S. Itagaki, H.-M. Lin, C. Rodriguez-Diaz, A. J. Weiss, G. W. Fischer, M. M. Weiner, J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2021, 35, 1367.
- 20W. Liu, W. Chen, X. Fang, Y. Li, T. Li, J. Biophotonics 2019, 12, e201900148.
- 21R. K. Almajidy, K. Mankodiya, M. Abtahi, U. G. Hofmann, IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 13, 292.
- 22C. S. Gary, A. Iskandarova, A. I. Abadeer, G. J. Yohe, A. M. Giladi, J. Hand Surg. Am. 2023, 23, 326.
- 23R. N. Soares, D. N. Proctor, G. V. de Oliveira, T. S. Alvares, J. M. Murias, Microcirculation 2020, 27, e12599.
- 24M. Katayama, P. Jiamsripong, E. M. McMahon, T. R. Lombari, A. E. Bukatina, Q. Wu, R. J. Marler, M. Belohlavek, Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2012, 38, 1662.
- 25E. Gao, Y. H. Lei, X. Shang, Z. M. Huang, L. Zuo, M. Boucher, Q. Fan, J. K. Chuprun, X. L. Ma, W. J. Koch, Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 1445.
- 26X. Sun, H. Chen, R. Gao, Y. Qu, Y. Huang, N. Zhang, S. Hu, F. Fan, Y. Zou, K. Hu, Z. Chen, J. Ge, A. Sun, ACS Nano 2023, 17, 896.
- 27K. Zhao, N. Li, B. Pan, T. Li, Microelectron. Reliab. 2018, 87, 188.
- 28A. Cheung, L. Tu, A. Macnab, B. K. Kwon, B. Shadgan, J. Biomed. Opt. 2022, 27, 077001.
- 29T. W. Scheeren, P. Schober, L. A. Schwarte, J. Clin. Monit. Comput. 2012, 26, 279.




