Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER PICTURE
Front Cover
- First Published: 03 April 2023

Surface enhanced infrared spectroscopy (SEIRA) using resonant nanostructures can distinguish composition and constitution of label-free samples with low concentration. In this study, we designed a broadband dendric nanostructure and quantified the relationship between structure parameters and resonance. Precise tuning of structure parameters enables the detection of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein at the solution concentration of 40 μg/ml. This work represents a systematic approach for SEIRA toward biomolecular characterization.
Further details can be found in the article by Yupei Bian, Yang Li, Kang Liu, Houshu He, Yingmei Feng, and Xia Yu (e202200277).
Inside Cover
- First Published: 03 April 2023

A novel 0.9 mm-diameter intravascular photoacoustic catheter with coaxial excitation and detection was developed to overcome the limitation of imaging range. A miniature ring-shaped ultrasound transducer with a 0.18 mm-diameter orifice in the center was successfully fabricated. The results demonstrated that the coaxial catheter exhibited much better photoacoustic/ultrasound imaging performance from the intima to the adventitia.
Further details can be found in the article by Riqiang Lin, Qi Zhang, Shengmiao Lv, Jiaming Zhang, Xiatian Wang, Dongliang Shi, Xiaojing Gong, and Kwok-ho Lam (e202200269).
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEWS
The effectiveness of phototherapy for surface decontamination against SARS-Cov-2. A systematic review
- First Published: 22 December 2022
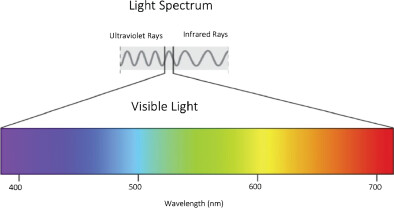
Light waves are featured according to their wave frequency and wavelength. Visible light has a wavelength range from 400 to 700 nanometers. Visible light comprises just a very restricted part of the full light wave spectrum. Light waves with lower frequencies and longer wavelengths include infrared light, microwaves and radio waves. Higher frequencies with shorter wavelengths with include ultraviolet light, gamma and X-rays.
Clinical applications of non-invasive multi and hyperspectral imaging of cell and tissue autofluorescence beyond oncology
- First Published: 05 January 2023
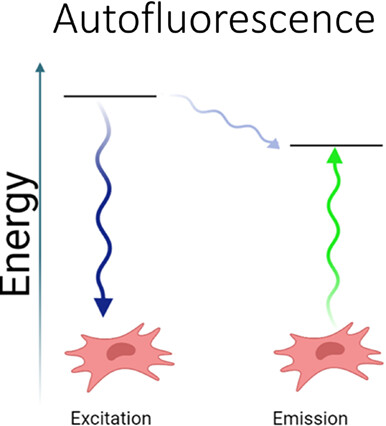
Fluorescence occurs when a material absorbs light (excitation) and subsequently relaxes to a lower energy state resulting in the emission of light. Due to the loss of vibrational energy when electrons go from an excited state to a ground state the emitted light has lower energy (longer wavelength). Numerous biological materials have native fluorescent properties and characteristic spectral profiles (autofluorescence). Although often treated as interference to staining methodologies that require tagging molecules with exogenous fluorophores, autofluorescence can enable non-invasive, direct assessment of cell and tissue characteristics.
Positive effects of low-dose photodynamic therapy with aminolevulinic acid or its methyl ester in skin rejuvenation and wound healing: An update
- First Published: 05 January 2023
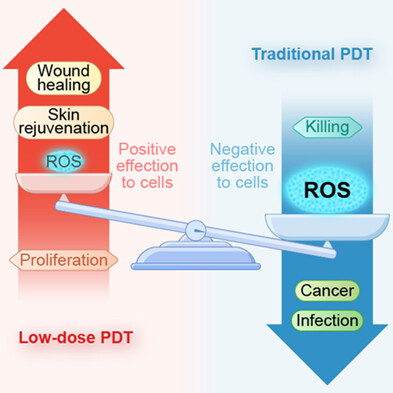
Traditional PDT can damage biological molecules and kill cells because of the production of highly cytotoxic ROS and has been clinically employed to treat skin tumors, infections, and other diseases. However, low-dose PDT leads to sufficiently low ROS level, which results in positive effects that are the exact opposite of the killing potency. Due to the favorable effects of low-dose PDT in cell proliferation, initiating the remodeling and regeneration processes, it has recently become a research hotspot. This article aims to review the basic and clinical research progresses of low-dose ALA/MAL-PDT in skin aging and wound healing.
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Dendric nanostructures for SARS-CoV-2 proteins detection based on surface enhanced infrared absorption spectroscopy
- First Published: 23 November 2022
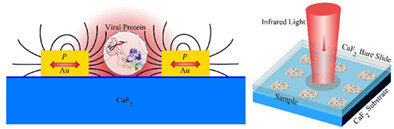
A surface enhanced infrared absorption (SEIRA) spectroscopy is proposed by deploying a novel nanostructure array as sample substrates. An array of gold dendric nanostructures are designed and fabricated with a precision resonance control to achieve surface enhancement covering a broadband molecular “finger-print” region. A low concentration detection of 40 μg/ml diluted SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein is experimentally demonstrated and the enhancement factor >3000 was achieved. This work represents a systematic approach for tailor-making polarization insensitive enhancement substrates toward biomolecular characterization.
Miniature intravascular photoacoustic endoscopy with coaxial excitation and detection
- First Published: 12 December 2022
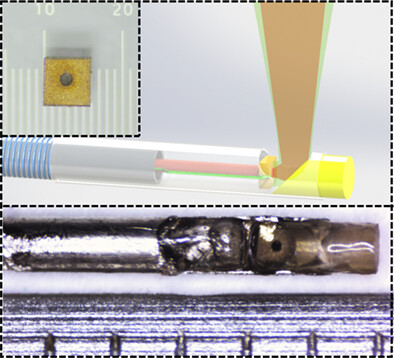
A miniature hollow ultrasound transducer was fabricated for photoacoustic endoscopic coaxial catheter. To demonstrate the significance and merits of this probe, phantom and ex vivo imaging experiments were conducted on both coaxial and noncoaxial catheters for comparison. The results demonstrated that the coaxial catheter exhibited much better photoacoustic/ultrasound imaging performance from the intima to the adventitia.
In vivo grading of lipids in fatty liver by near-infrared autofluorescence and reflectance
- First Published: 15 November 2022
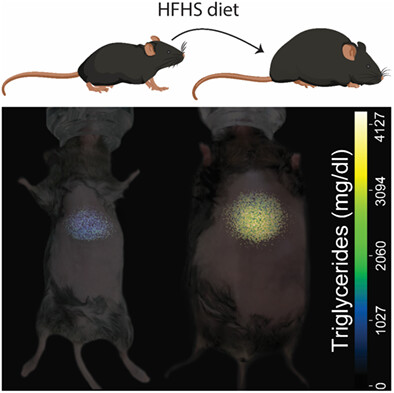
The absorption and reflection of near-infrared light by tissues affected by the nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as well as the tissues' autofluorescence can serve as indicators of its stage of development. In this work, we use them to build a regression model for the content of triglycerides in the liver of small animals going through a high-fat-high-sugar diet.
Diffuse optical detection of global cerebral ischemia in an adult porcine model
- First Published: 17 November 2022
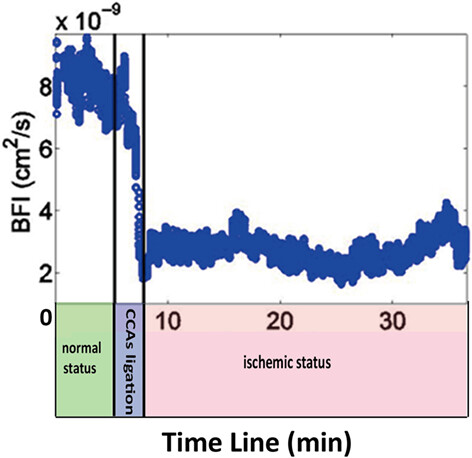
For rapid screening for acute ischemic stroke in prehospital settings, a hybrid diffuse optical device, which combines near-infrared spectroscopy and diffuse correlation spectroscopy is used to monitor cerebral hemodynamics before and after ischemic stroke in porcines. The results suggest that the diffuse optical method can detect the hemodynamic changes in porcines in the first few hours of ischemic stroke onset, and relative changes in the blood flow index may be a promising biomarker to identify acute ischemic stroke.
MCFSA-Net: A multi-scale channel fusion and spatial activation network for retinal vessel segmentation
- First Published: 22 November 2022
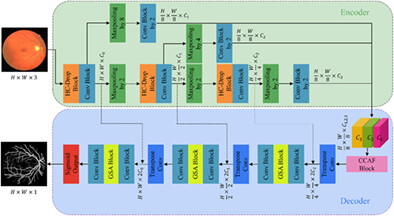
This article is a study for retinal vessel segmentation based on an end-to-end convolutional neural network. The Hybrid Convolution-DropBlock (HC-Drop) is first used in the encoder, and we then design the Channel Cooperative Attention Fusion (CCAF) module to fuse features of multiple scales and multiple channels to represent different morphological vessels. The Global Spatial Activation (GSA) module is adopted in the decoder to emphasize tiny vessels for their segmentation.
Detection of pathological response of axillary lymph node metastasis after neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer using multiphoton microscopy
- First Published: 12 December 2022
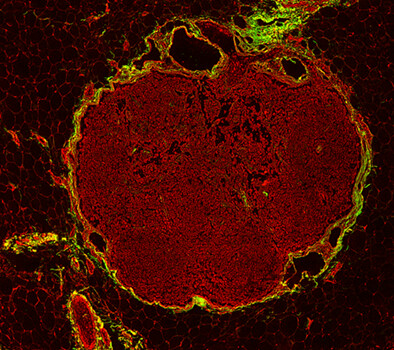
Here, we try to use multiphoton microscopy (MPM) to label-free assess the pathological changes of axillary lymph node metastasis induced by neoadjuvant chemotherapy, and also perform image analysis on multiphoton images to provide quantitative information to aid in monitoring the collagen changes between normal and abnormal lymph nodes as well as the diseased nodes with and without treatment response. We hope MPM will become an auxiliary diagnostic tool to help clinicians to rapidly conduct histopathologic examination without staining dye.
An optical system for noninvasive microscopy of psoriatic mice in vivo
- First Published: 14 December 2022
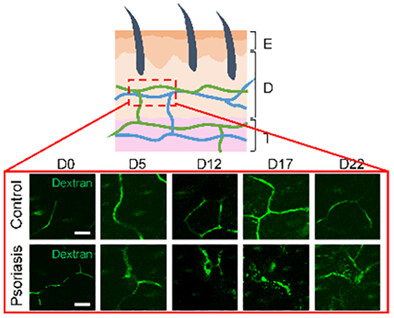
We developed a noninvasive microscopy scheme by combining in vivo fluorescent microscopy, optical clearing, and immune-labeling to enable real-time imaging of immune cells and cytokines in blood flow in psoriatic animal models through the thick opaque scales and inflammations. The vascular morphology and time-lapse kinetics of interleukin (IL)-23, IL-17, tumor necrosis factor-α, and CD4+ cells in blood are captured at submicron resolution through the thickening epidermis along the development of psoriasis in vivo.
Novel optical fiber Vernier immunosensor based on cascading Sagnac loops embedded with excessively tilted fiber grating for specific detection of canine distemper virus
- First Published: 17 December 2022
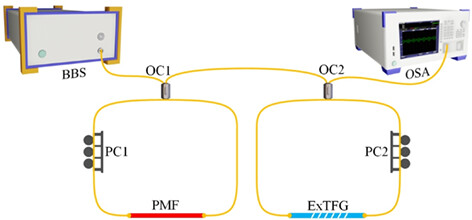
A novel fiber vernier biosensor based on excessively tilted fiber grating (ExTFG) was proposed for the specific detection of canine distemper virus (CDV). The RI sensitivity of normal ExTFG was largely improved by one order due to the magnification of vernier effect, making the sensor applicable for clinically monitoring the antigen content in CDV solution, especially for the early stage of diagnosis.
Intraoperative detection of IDH-mutant glioma using fluorescence lifetime imaging
- First Published: 12 December 2022
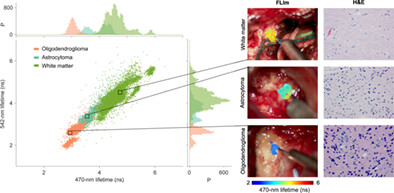
Identifying the glioma subtype during surgery can aid in modifying resection strategies, as each glioma subtype responds differently to post-surgical therapy. FLIm provides optical contrast between IDH-mutant astrocytoma and IDH-mutant oligodendroglioma, and between IDH-mutant tumor and surrounding white matter. This study supports the feasibility of fluorescence lifetime imaging (FLIm) to identify IDH-mutant glioma subtype intraoperatively.
Classification of pathogenic bacteria by Raman spectroscopy combined with variational auto-encoder and deep learning
- First Published: 15 December 2022
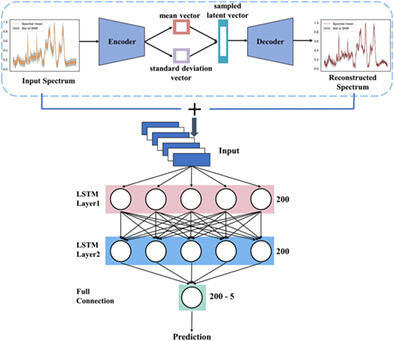
In this work, a pathogen detection method combining Raman spectroscopy, variational auto-encoder (VAE) and long short-term memory network is proposed. Experimental results show that this method not only improves the average accuracy of pathogen classification to 96.9%, but also reduces the number of Raman spectra collected from 1000 to 200. Our method can be applied to other spectral techniques (such as mass spectrometry and infrared spectroscopy) and material identification problems with only a slight adjustment.
Monitoring of microbial proteome dynamics using Raman stable isotope probing
- First Published: 17 December 2022
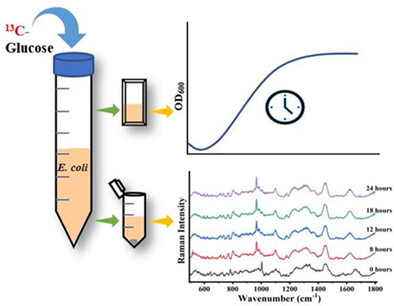
Raman stable isotope probing (Raman-SIP) is an efficient method for the qualitative and quantitative study of various metabolites. In this work, 13C-labeled glucose as the only carbon source in the growth medium is used for monitoring 13C incorporation in the microbial proteome and time dependet changes using Raman spectroscopy. This study demonstrates the utility of Raman-SIP as an adjunct tool for monitoring proteome-level changes at the community level.
The effects of transcranial laser photobiomodulation and neuromuscular electrical stimulation in the treatment of post-stroke dysfunctions
- First Published: 15 December 2022
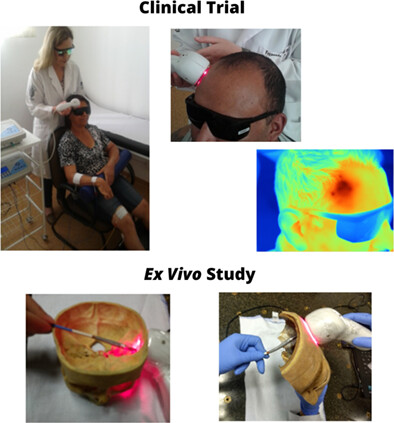
We performed a clinical trial and an ex vivo study. Transcranial laser photobiomodulation was applied together with neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) in post-stroke patients. There were improvement of cognitive function, pain relief, greater manual dexterity, enhancement of physical and social–emotional health which lead to better quality of life and well-being. Moreover, the distribution of infrared and red radiation after penetration through the cranium and hemihead of cadavers were showed.
Photothermal lipolysis accelerates ECM production via macrophage-derived ALOX15-mediated p38 MAPK activation in fibroblasts
- First Published: 18 December 2022
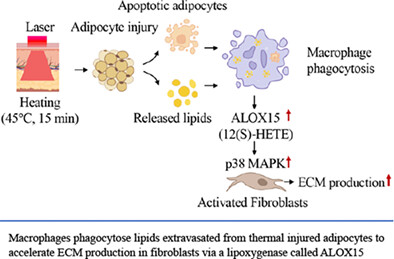
Skin and subcutaneous tissue tightening is usually treated by noninvasive photothermal treatment for medical esthetics purpose, while the underlying mechanism remains to be elucidated. Here, we hypothesized that adipocyte injury, as a stimulator, may regulate extracellular matrix production by increasing ALOX15 in macrophages, which could lead to fibroblast activation. The results of this study demonstrate that the mechanisms of adipose photothermal injury-induced skin and/or subcutaneous tissue tightening may have clinical relevance for noninvasive or minimally invasive photothermal therapeutics.
Optimizing the classification of biological tissues using machine learning models based on polarized data
- First Published: 15 December 2022
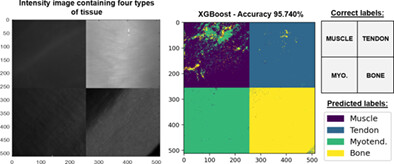
This work presents a thorough comparative between three polarimetric datasets composed by (A) a selection of most representative metrics presented in literature; (B) Mueller matrix elements; and (C) the combination of (A) and (B); to find the ideal polarimetric framework to construct organic tissue classification models. The best proposed models achieve global accuracy scores larger than 97% and classification rates superior to 99% for tendon, myotendinous junction and bone when using (B) and (C) datasets.
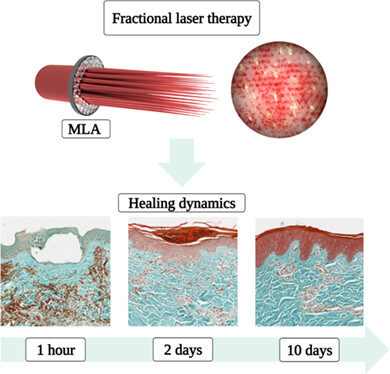
Microlesion healing dynamics in in vivo porcine skin after treatment with 1064 nm picosecond-domain Nd:YAG laser
- First Published: 06 January 2023
Label-free high-resolution white light quantitative phase nanoscopy system
- First Published: 05 January 2023
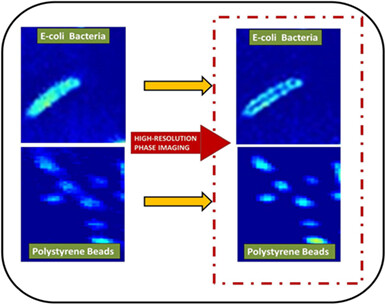
The white light quantitative phase nanoscopy (WLQPN) system is developed which offers super-resolution phase imaging. The Fourier-fringe analysis method limits the phase resolution below the actual diffraction limit of the system, whereas phase shifting approach provides full detector resolution. Then, the deconvolution approach further improves the phase resolution significantly. Therefore, five-phase shifting technique and deconvolution approach are used to obtain super-resolution in phase imaging. The high-resolution phase images of 200 nm polystyrene beads and subcellular features of the Escherichia coli bacteria are obtained with the present technique.
Use of photoacoustic imaging for monitoring vascular disrupting cancer treatments
- First Published: 05 September 2020
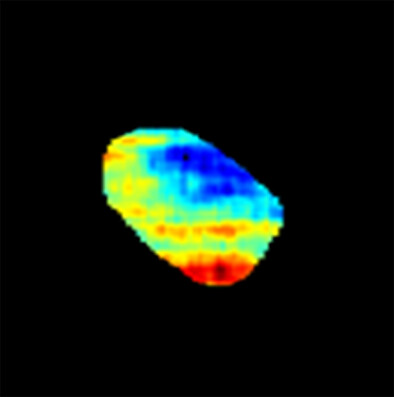
Monitoring microvessels damage has a huge application in the biomedical imaging field and especially for monitoring cancer therapy. Damaging the tumor microvessels is a class of cancer therapy which suspends the nutrition and oxygen delivered to tumor cells leading to its regression. Analysis of photoacoustic signals extract structural and functional information of the imaged tumor microvasculature which can be used for early assessing the cancer therapy.