Optimizing the classification of biological tissues using machine learning models based on polarized data
Corresponding Author
Carla Rodríguez
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Correspondence
Carla Rodríguez, Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra 08193, Spain.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorIrene Estévez
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Centre of Physics, Department of Physics, University of Minho, Guimarães, Portugal
Search for more papers by this authorEmilio González-Arnay
Servicio de Anatomía Patológica, Hospital Universitario de Canarias, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain
Departamento de Anatomía, Histología y Neurociencia, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorJuan Campos
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorAngel Lizana
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Carla Rodríguez
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Correspondence
Carla Rodríguez, Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra 08193, Spain.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorIrene Estévez
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Centre of Physics, Department of Physics, University of Minho, Guimarães, Portugal
Search for more papers by this authorEmilio González-Arnay
Servicio de Anatomía Patológica, Hospital Universitario de Canarias, Santa Cruz de Tenerife, Spain
Departamento de Anatomía, Histología y Neurociencia, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Madrid, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorJuan Campos
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorAngel Lizana
Optics Group, Physics Department, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona, Bellaterra, Spain
Search for more papers by this authorCarla Rodríguez and Irene Estévez have contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
Polarimetric data is nowadays used to build recognition models for the characterization of organic tissues or the early detection of some diseases. Different Mueller matrix-derived polarimetric observables, which allow a physical interpretation of a specific characteristic of samples, are proposed in literature to feed the required recognition algorithms. However, they are obtained through mathematical transformations of the Mueller matrix and this process may loss relevant sample information in search of physical interpretation. In this work, we present a thorough comparative between 12 classification models based on different polarimetric datasets to find the ideal polarimetric framework to construct tissues classification models. The study is conducted on the experimental Mueller matrices images measured on different tissues: muscle, tendon, myotendinous junction and bone; from a collection of 165 ex-vivo chicken thighs. Three polarimetric datasets are analyzed: (A) a selection of most representative metrics presented in literature; (B) Mueller matrix elements; and (C) the combination of (A) and (B) sets. Results highlight the importance of using raw Mueller matrix elements for the design of classification models.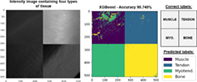
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| jbio202200308-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 1.6 MB | Data S1: Supplementary Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
REFERENCES
- 1V. N. Du Le, I. Saytashev, S. Saha, P. F. Lopez, M. Laughrey, J. C. Ramella-Roman, Biom. Opt. Express 2020, 11, 10.
- 2V. V. Tuchin, Tissue Optics: Light Scattering Methods and Instruments for Medical Diagnosis, SPIE Press, Bellingham, WA 2015.
10.1117/3.1003040 Google Scholar
- 3F. Vasefi, N. MacKinnon, R. Saager, A. J. Durkin, R. Chave, E. H. Lindsley, D. L. Farkas, Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4924.
- 4E. Gnanatheepam, U. Kanniyappan, K. Dornadula, A. Prakasarao, G. Singaravelu, Photodiag. Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101757.
- 5A. N. Yaroslavsky, X. Feng, A. Muzikansky, M. R. Hamblin, Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1.
- 6A. Patel, A. Khan, R. Quinlan, A. N. Yaroslavsky, Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 17.
- 7D. Ivanov, V. Dremin, A. Bykov, E. Borisova, T. Genova, A. Popov, R. Ossikovski, T. Novikova, I. Meglinski, J. Biophotonics 2020, 13, 8.
- 8D. L. Le, D. T. Nguyen, T. H. Le, Q. H. Phan, T. T. H. Pham, Opt. Commun. 2021, 480, 126460.
- 9C. Rodríguez, E. Garcia-Caurel, T. Garnatje, M. S. Ribas, J. Luque, J. Campos, A. Lizana, Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14743.
- 10T. H. Nguyen, M. E. Kandel, M. Rubessa, M. B. Wheeler, G. Popescu, Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 210.
- 11A. Van Eeckhout, E. Garcia-Caurel, T. Garnatje, J. C. Escalera, M. Durfort, J. Vidal, J. J. Gil, J. Campos, Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1.
- 12I. Ahmad, A. Khaliq, M. Iqbal, S. Khan, Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2020, 30, 101708.
- 13T. Novikova, I. Meglinski, J. C. Ramella-Roman, V. V. Tuchin, J. Biomed. Opt. 2016, 21, 7.
- 14J. Qi, D. S. Elson, J. Biophotonics 2017, 10, 8.
- 15S. A. Hall, M. A. Hoyle, J. S. Post, D. K. Hore, Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 15.
- 16Z. Kong, T. Ma, Y. Cheng, R. Fei, Z. Zhang, Y. Li, L. Mei, J. Quant. Rad. Trans. 2021, 271, 107747.
- 17J. L. Deuzé, F. M. Bréon, C. Devaux, P. Goloub, M. Herman, B. Lafrance, F. Maignan, A. Marchand, F. Nadal, G. Perry, D. Tanré, J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 4913.
- 18C. Rodríguez, A. Van Eeckhout, E. Garcia-Caurel, J. J. Gil, T. Garnatje, E. González-Arnay, J. Vidal, J. C. Escalera, I. Moreno, J. Campos, A. Lizana, Proc. SPIE 2021, 116460P.
- 19A. Van Eeckhout, A. Lizana, E. Garcia-Caurel, J. J. Gil, A. Sansa, C. Rodríguez, I. Estévez, E. González-Arnay, J. C. Escalera, I. Moreno, J. Campos, Proc. SPIE 2018, XVI, 104971V.
- 20A. Van Eeckhout, A. Lizana, E. Garcia-Caurel, J. J. Gil, A. Sansa, C. Rodríguez, I. Estévez, E. González-Arnay, J. C. Escalera, I. Moreno, J. Campos, J. Biophotonics 2017, 11, e201700189.
- 21P. Schucht, H. R. Lee, H. M. Mezouar, E. Hewer, A. Raabe, M. Murek, I. Zubak, J. Goldberg, E. Kövari, A. Pierangelo, T. Novikova, IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 12.
- 22A. Pierangelo, A. Benali, M. R. Antonelli, T. Novikova, P. Validire, B. Gayet, A. de Martino, Opt. Express 2011, 19, 2.
- 23M. Kupinski, M. Boffety, F. Goudail, R. Ossikovski, A. Pierangelo, J. Rehbinder, J. Vizet, T. Novikova, Biomed. Opt. Express 2018, 9, 11.
- 24C. He, H. He, J. Chang, Y. Dong, S. Liu, N. Zeng, Y. He, H. Ma, Biomed. Opt. Express 2015, 6, 8.
- 25A. A. Hyman, J. Cell, Biologia 1989, 9, 3.
- 26C. Rodríguez, A. Van Eeckhout, L. Ferrer, E. Garcia-Caurel, E. González-Arnay, J. Campos, A. Lizana, Biomed. Opt. Express 2021, 12, 4852.
- 27J. Wan, Y. Dong, J. H. Xue, L. Lin, S. Du, J. Dong, Y. Yao, C. Li, H. Ma, Biomed. Opt. Express 2022, 13, 3339.
- 28D. Ivanov, V. Dremin, T. Genova, A. Bykov, T. Novikova, R. Ossikovski, I. Meglinski, Front. Phys. 2022, 9, 814787.
- 29K. M. Sindhoora, K. U. Spandana, D. Ivanov, E. Borisova, U. Raghavendra, S. Rai, S. P. Kabenkkodu, K. K. Mahato, N. Mazumder, J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 2021, 1859, 012045.
10.1088/1742-6596/1859/1/012045 Google Scholar
- 30N. T. Luu, T. H. Le, Q. H. Phan, T. H. H. Pham, J. Biomed. Opt. 2021, 26, 7.
- 31I. Estévez, F. Oliveira, P. Braga-Fernandes, M. Oliveira, L. Rebouta, M. I. Vasilevskiy, Opt. Express 2022, 30, 28385.
- 32B. Liu, Y. Yao, R. Liu, H. Ma, L. Ma, Opt. Comm. 2019, 433, 60.
- 33D. Viktor, Z. Marcinkevics, E. Zherebtsov, A. Popov, A. Grabovskis, H. Kronberga, K. Geldnere, A. Doronin, I. Meglinski, A. Bykov, IEEE Trans. Med. Im. 2021, 40, 4.
10.1109/TMI.2020.3043708 Google Scholar
- 34C. He, H. He, J. Chang, B. Chen, H. Ma, M. J. Booth, Light Sci. Appl. 2021, 10, 194.
- 35J. J. Gil, R. Ossikovski, Polarized Light and the Mueller Matrix Approach, CRC Press, Boca Raton 2016.
- 36D. Goldstein, Polarized Light, 2nd ed., Marcel Dekker, New York 2003.
10.1201/9780203911587 Google Scholar
- 37R. A. Chipman, Polarimetry: Handbook of Optics, 2nd ed., McGraw Hill, New York 1995.
- 38J. J. Gil, I. San José, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 2022, 39, 3.
10.1364/JOSAA.448255 Google Scholar
- 39S. Jacquemoud, S. Ustin, Leaf Optical Properties, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge 2019.
10.1017/9781108686457 Google Scholar
- 40F. H. Mustafa, M. S. Jaafar, Indian J. Phys. 2013, 87, 3.
- 41J. S. Tyo, App. Opt. 2006, 45, 22.
- 42K. U. Spandana, K. K. Mahato, N. Mazumder, Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 34, 25.
- 43A. Peinado, A. Lizana, J. Vidal, C. Iemmi, J. Campos, Opt. Express 2010, 18, 9815.
- 44S. Y. Lu, R. A. Chipman, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 1996, 13, 5.
- 45R. Ossikovski, A. De Martino, S. Guyot, Opt. Lett. 2007, 32, 6.
- 46J. J. Gil, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 2013, 30, 4.
- 47R. Ossikovski, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 2009, 26, 5.
10.1364/JOSAA.26.001109 Google Scholar
- 48R. Ossikovski, J. Opt. Soc. Am. A. 2010, 27, 1.
- 49G. Nirmalya, M. F. G. Wood, A. Viktin, J. Biomed. Opt. 2008, 13, 4.
- 50S. Huard, Polarisation de la lumière, Elsevier-Masson, 1993.
- 51A. Van Eeckhout, E. Garcia-Caurel, T. Garnatje, M. Durfort, J. C. Escalera, J. Vidal, J. J. Gil, J. Campos, A. Lizana, PLoS One 2019, 14, 3.
- 52A. Van Eeckhout, E. Garcia-Caurel, R. Ossikovski, A. Lizana, C. Rodríguez, E. González-Arnay, J. Campos, J. Biophot. 2020, 13, e202000083.
- 53A. Van Eeckhout, A. Lizana, E. Garcia-Caurel, J. J. Gil, R. Ossikovski, J. Campos, Opt. Lett. 2017, 42, 20.
- 54A. Van Eeckhout, J. J. Gil, E. Garcia-Caurel, J. García Romero, R. Ossikovski, I. San José, I. Moreno, J. Campos, A. Lizana, Opt. Exp. 2021, 29, 38811.
- 55I. San José, J. J. Gil, Opt. Commun. 2011, 284, 1.
- 56J. Gil, Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 1.
- 57J. Gil, E. Bernabéu, Opt. Acta 1986, 33, 2.
10.1080/713821924 Google Scholar
- 58Y. Altun, K. Das, T. Mielikäinen, D. Malerba, J. Stefanowski, J. Read, M. Žitnik, M. Ceci, S. Džeroski, Machine Learning and Knowledge Discovery in Databases European Conference, ECML PKDD (2017).
- 59M. B. Kursa, W. R. Rudnicki, J. Stat. Soft. 2010, 36, 11.
- 60J. Schmidhuber, Neural Networks 2015, 61, 85.
- 61J. H. Friedman, Ann. Statist. 2001, 29, 5.
- 62G. Ke, Q. Meng, T. Finley, T. Wang, W. Chen, W. Ma, Q. Ye, T. Y. Liu, “LightGBM: A Highly Efficient Gradient Boosting Decision Tree,” Adv. in Neu. Info. Proc. Sys. 30 (2017).
- 63T. Chen, C. Guestrin, Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (KDD '16), Association for Computing Machinery, New York, 2016, pp. 785–794.
- 64P. Refaeilzadeh, L. Tang, H. Liu, Cross-Validation. Encyclopedia of Database Systems, Springer, Boston 2009.
- 65S. V. Stehman, Rem. Sens. Env. 1997, 62, 1.
- 66H. Asahara, M. Inui, M. K. Lotz, J. Bone, Miner. Res. 2017, 32, 9.
- 67B. Charvet, F. Ruggiero, D. le Guellec, Musc. Liga. Tend. J. 2012, 2, 2.
- 68D. L. Butler, E. S. Grood, F. R. Noyes, R. F. Zernucke, Exerc. Sports Sci. Rev. 1978, 6, 125.
- 69R. James, G. Kesturu, G. Balian, A. B. Chhabra, J. of Hand Surgery 2008, 33, 1.
- 70K. M. Ting, Confusion Matrix. Encyclopedia of Machine Learning and Data Mining, Springer, Boston 2017.
- 71U. Technau, C. B. Scholtz, Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2003, 47, 7.
10.1387/ijdb12 Google Scholar
- 72F. Soglia, S. Mudalal, E. Babini, M. D. Nunzio, M. Mazzoni, F. Sirri, C. Cavani, M. Petracci, Poult. Sci. 2015, 95, 3.




