Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Atomistic Understanding of the Ferroelectric Properties of a Wurtzite-Structure (AlN)n/(ScN)m Superlattice
- First Published: 17 May 2021

In article number 2100009, the ab initio calculations by Cheol Seong Hwang, Jung-Hae Choi, and co-workers show that wurtzite-type AlN can have a suitable range of ferroelectric switching barrier (Ea) and spontaneous polarization (Ps) by forming superlattice structures with ScN. The Ea is dominated by the local structure instability, while the Ps is significantly affected by the structural parameters and the Born effective charge.
Inside Front Cover
Low-Thermal-Budget Fluorite-Structure Ferroelectrics for Future Electronic Device Applications
- First Published: 17 May 2021

In article number 2100028, Jiyoung Kim, Si Joon Kim, and co-workers comprehensively review the various factors such as doping effects, deposition method, annealing method and conditions, and substrate material for obtaining fluorite-structure ferroelectrics with low-thermal-budget processes (400 °C or less). These low-thermal-budget processes facilitate not only the integration of ferroelectric circuits in the back-end-of-line, but also the applications to flexible and wearable electronics.
Masthead
Inside Back Cover
On the Origin of Wake-Up and Antiferroelectric-Like Behavior in Ferroelectric Hafnium Oxide
- First Published: 17 May 2021

With the help of transmission Kikuchi diffraction the major physical mechanism of antiferroelectric-like behavior as well as of the wake-up effect is determined by Maximilian Lederer, Konrad Seidel, and co-workers in article number 2100086. Furthermore, guidelines on how to influence this behavior by crystallographic texture and adjacent layers, as well as process conditions are identified. Finally, electric-field-induced crystallization is discovered as a new effect in hafnium oxide thin films.
Back Cover
Electric-Field-Induced Ferroelectricity in 5%Y-doped Hf0.5Zr0.5O2: Transformation from the Paraelectric Tetragonal Phase to the Ferroelectric Orthorhombic Phase
- First Published: 17 May 2021

Ferroelectricity facilitated by field-induced phase transition is demonstrated by Takao Shimizu, Hiroshi Funakubo, and co-workers in article number 2000589. Their X-ray diffraction and scanning transparent electron microscopy studies show the as-deposited paraelectric tetragonal phase transforms to the ferroelectric orthorhombic phase in the Y-doped Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 film by applying a strong electric field.
Guest Editorials
Emerging Fluorite- and Wurtzite-Type Ferroelectrics: From (Hf,Zr)O2 to AlN and Related Materials
- First Published: 17 May 2021
Review@RRL
Reviews
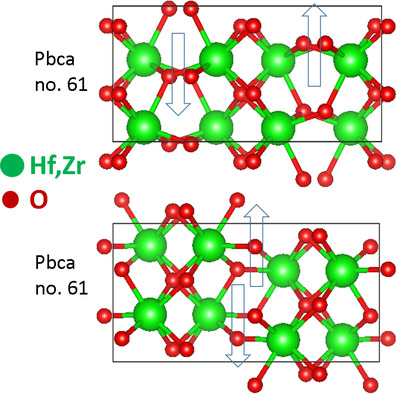
An Overview of Ferroelectric Hafnia and Epitaxial Growth
- First Published: 26 March 2021
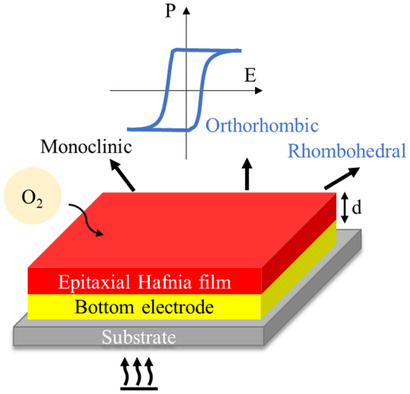
Epitaxial control of hafnia thin films can be effective while mediating the phase competition of monoclinic, orthorhombic, and rhombohedral phases. Therefore, the effects of growth temperature, epitaxial strain from substrate and bottom electrode, oxygen content, and film thickness variations are reviewed. Subsequent influences on ferroelectricity such as wake-up effect, imprint, and retention are also discussed.
Low-Thermal-Budget Fluorite-Structure Ferroelectrics for Future Electronic Device Applications
- First Published: 05 February 2021
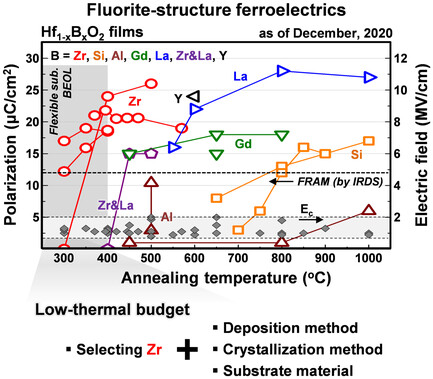
The various factors such as doping effects, deposition method, annealing method and conditions, and substrate material for obtaining fluorite-structure ferroelectrics with low-thermal-budget (400 °C or less) processes are reviewed. These low-thermal-budget processes facilitate not only the integration of ferroelectric circuits in the back-end-of-line but also applications for flexible and wearable electronics.
Rapid Research Letters
Ferroelectric, Analog Resistive Switching in Back-End-of-Line Compatible TiN/HfZrO4/TiOx Junctions
- First Published: 18 December 2020
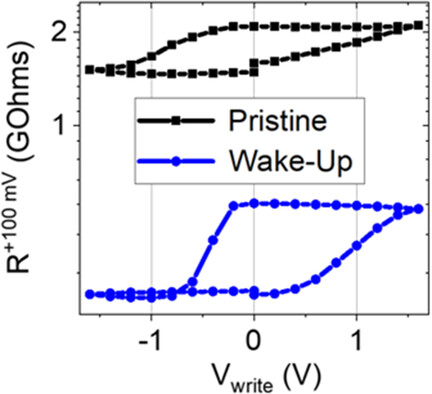
An analog resistive memory device is fabricated with a back-end-of-line compatible process. Two TiN electrodes are separated by a ferroelectric, 4.5 nm-thick HfZrO4 (HZO) layer, and a semiconducting TiOx interlayer. Synaptic functionality is obtained, in the pristine state as well as after wake-up, and originates from the ferroelectric properties of the HZO layer.
Impact of Iridium Oxide Electrodes on the Ferroelectric Phase of Thin Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 Films
- First Published: 26 February 2021
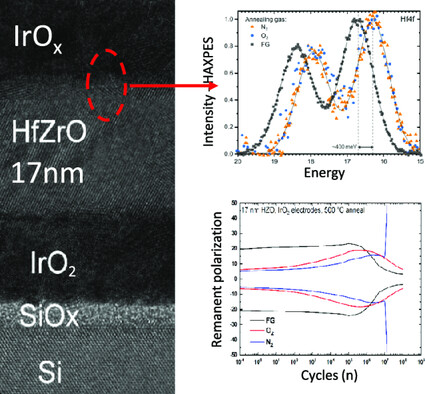
The influence of the oxygen concentration in the IrOx electrodes during crystallization anneal on the ferroelectric properties is characterized by electrical, chemical, and structural methods. A significant change in the ferroelectric properties after annealing in forming gas, O2, and N2 atmospheres is found as a result of the interaction of the top electrode with the dielectric layer.
Research Articles
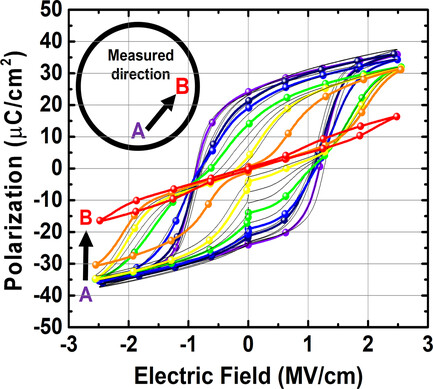
Sub-Microsecond Polarization Switching in (Al,Sc)N Ferroelectric Capacitors Grown on Complementary Metal–Oxide–Semiconductor-Compatible Aluminum Electrodes
- First Published: 05 February 2021
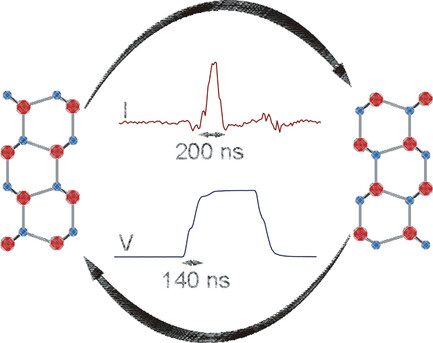
Rapid ferroelectric switching, within 200 ns and no obvious loss of polarization for over 8000 cycles are observed in 45 nm-thick (Al,Sc)N thin films deposited by reactive sputtering. This newly discovered nitride ferroelectric material offers large and stable remanent polarizations of 115 μC cm−2 and compatibility with complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS) transistor processing.
Electric-Field-Induced Ferroelectricity in 5%Y-doped Hf0.5Zr0.5O2: Transformation from the Paraelectric Tetragonal Phase to the Ferroelectric Orthorhombic Phase
- First Published: 10 February 2021
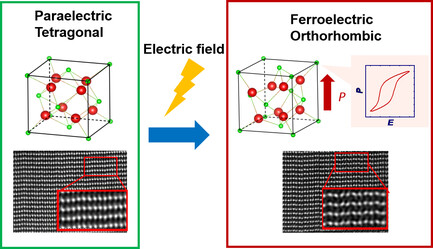
The phase transition in ferroelectric Y-doped Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 epitaxial thin film induced by an electric field is demonstrated, which triggers the emergence of ferroelectric characteristics from the nonpolar tetragonal phase to the polar orthorhombic phase. This ferroelectricity induced by the electric-field-induced phase transition is quite an important mechanism by which ferroelectricity is exhibited in flurorite-oxides ferroelectrics.
In Situ Characterization of Ferroelectric HfO2 During Rapid Thermal Annealing
- First Published: 08 February 2021
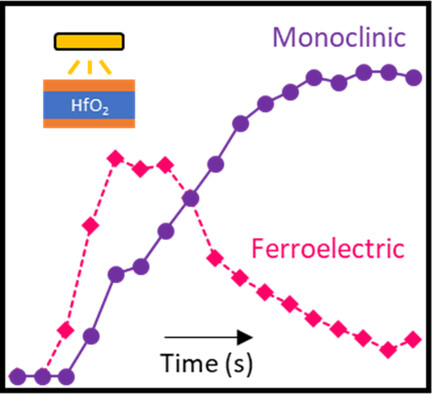
During annealing, thin-film HfO2 in capacitors initially crystallizes into a ferroelectric phase but then transforms to a monoclinic structure within seconds. The kinetic barrier to this conversion is above 1 eV f.u.−1 Fast temperature ramp rates (which minimize the time above the crystallization temperature) can boost remanent polarization more than twofold.
Atomistic Understanding of the Ferroelectric Properties of a Wurtzite-Structure (AlN)n/(ScN)m Superlattice
- First Published: 13 February 2021
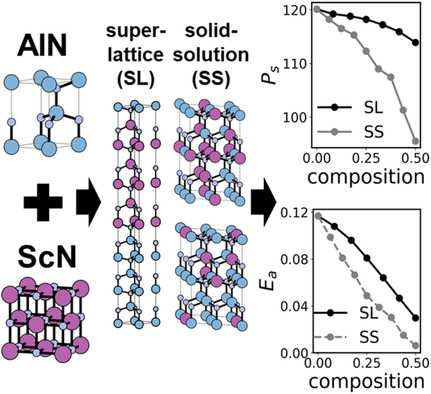
The ferroelectric properties (switching barrier [Ea] and spontaneous polarization [Ps]) of (AlN)n/(ScN)m superlattice structures are investigated and compared with those of (Al,Sc)N solid solutions, based on density functional theory calculations. The Ea and Ps values decrease as the ScN fraction increases, which are attributed to the structural parameters and local structural instability.
High-Performance and High-Endurance HfO2-Based Ferroelectric Field-Effect Transistor Memory with a Spherical Recess Channel
- First Published: 03 March 2021
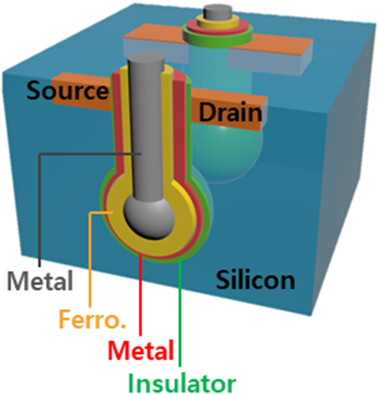
The spherical recess channel transistor structure is applied to metal–ferroelectric–metal–insulator–semiconductor ferroelectric field-effect transistors (FeFETs), and through numerical simulation based on various materials and device design parameters, the direction of high-performance FeFETs is presented.
Effect of Hydrogen on Hafnium Zirconium Oxide Fabricated by Atomic Layer Deposition Using H2O2 Oxidant
- First Published: 01 April 2021
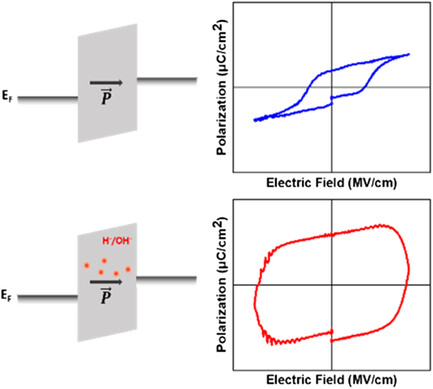
The behavior of hydrogen-incorporated hafnium zirconium oxide (HZO) and the effect of post O2 plasma treatment are presented. HZO thin film fabricated by H2O2 oxidants shows a leaky electrical property resulting from hydrogen-related trap sites. O2 plasma treatment is proposed to reduce the leakage current by reducing the degree of hydrogen incorporation and oxygen vacancies inside the film.
Aging in Ferroelectric Si-Doped Hafnium Oxide Thin Films
- First Published: 18 March 2021
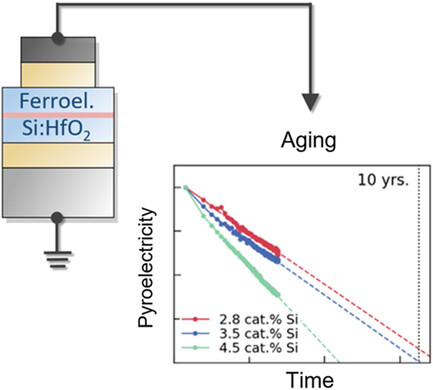
The ferroelectric hafnium oxide material system offers a unique combination of physical properties, enabling novel sensor applications and nanoelectromechanical systems, for which long-term stability is an essential concern. In this work, aging effects in polycrystalline, Si-doped HfO2 thin films are assessed, which are found to be accelerated by temperature, low film thickness, and high dopant content.
Chemical Stability of IrO2 Top Electrodes in Ferroelectric Hf0.5Zr0.5O2-Based Metal–Insulator–Metal Structures: The Impact of Annealing Gas
- First Published: 23 February 2021
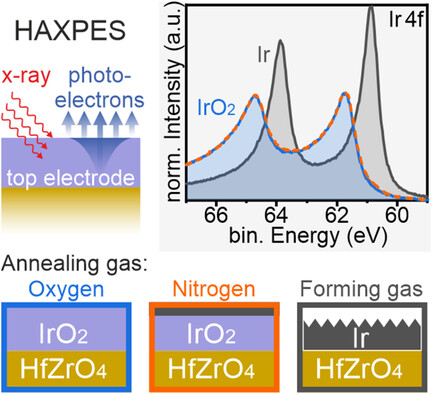
The choice of gas atmosphere during rapid thermal annealing (RTA) impacts the chemistry of top electrode and interface of ferroelectric IrO2/Hf0.5Zr0.5O2/IrO2 capacitors. Strongly modified chemical states are observed for RTA in forming gas, where a reduction to metallic Ir with incorporated and possibly mobile oxygen is found—which may affect the metal–insulator–metal (MIM)'s performance instabilities.
Ferroelectric La-Doped ZrO2/HfxZr1−xO2 Bilayer Stacks with Enhanced Endurance
- First Published: 13 February 2021
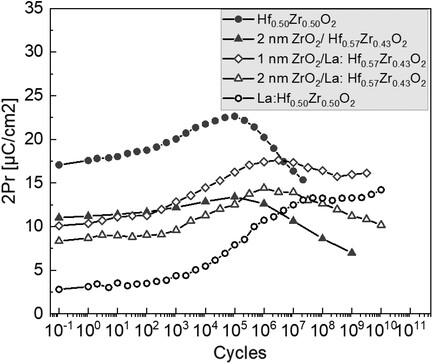
Enhanced endurance (1010 cycles) of Hf-rich hafnium zirconate using 1.6% La dopant is reported. Faster wake-up behavior is promoted by stacking the ferroelectric layer with ZrO2. A correlation of ferroelectric characteristics (remanent polarization and endurance) with the initial content of the phase extracted by Rietveld refinement of the X-ray diffraction spectra brings new insights into modalities to control the ferroelectric behavior of 10 nm hafnium zirconate films grown by atomic layer deposition, with potential application in ferroelectric random-access memory.
Ferroelectric Aluminum Scandium Nitride Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Resonators with Polarization-Dependent Operating States
- First Published: 23 April 2021
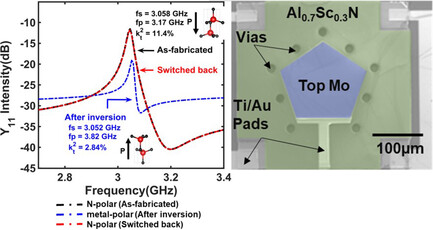
Ferroelectric aluminum scandium nitride film bulk acoustic resonators (FBARs), with a quality factor of 572, electromechanical coupling coefficient of 11.4%, and operating at 3.17 GHz, are demonstrated. The operations of such ferroelectric FBARs are studied at the two polarization states (i.e., nitrogen polar and metal-polar). Such devices are used in tunable filters in the super-high-frequency range.
Understanding Reproducibility of Sputter-Deposited Metastable Ferroelectric Wurtzite Al0.6Sc0.4N Films Using In Situ Optical Emission Spectrometry
- First Published: 20 March 2021
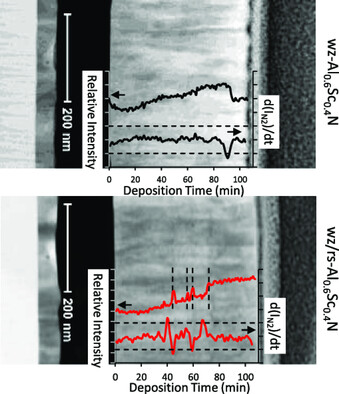
In situ monitoring with glow discharge optical emission spectroscopy during growth of Al0.6Sc0.4N films reveals a connection between target mode and film properties. Poisoned target mode favors synthesis of ferroelectric (0002) textured wurtzite films, whereas metallic target mode favors (111) rocksalt growth and leads to clear microstructure heterogeneities, degradation of wurtzite phase purity, and nonferroelectric films.
A Novel Combinatorial Approach to the Ferroelectric Properties in HfxZr1−xO2 Deposited by Atomic Layer Deposition
- First Published: 01 April 2021
A novel combinatorial approach to investigate the ferroelectricity of HfxZr1−xO2 thin films via a saturated/non-saturated atomic layer deposition (ALD) technique is proposed. Detailed observation of continuous variation of the ferroelectric–antiferroelectric transition is successfully applied. It is possible to achieve a higher efficiency method for studying ferroelectricity change in terms of the doping and composition of HfO2-based ferroelectric thin films through this combinatorial approach.
Ferroelectric Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 Thin Films Crystallized by Pulsed Laser Annealing
- First Published: 17 March 2021
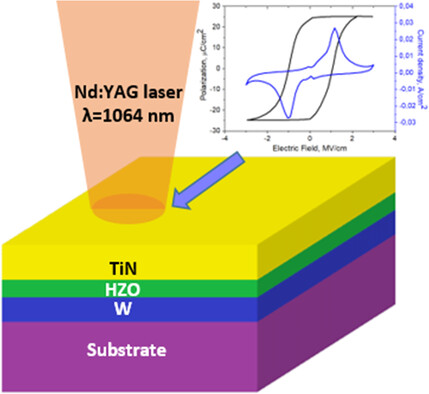
Pulsed laser irradiation of a solid substrate results in extremely fast heating and cooling rates of a subsurface region, which gives rise to quenching of metastable phases during crystallization. The possibility of forming a ferroelectric phase in Hf0.5Zr0.5O2 (HZO) thin films by their crystallization with laser pulses of millisecond and nanosecond duration is demonstrated.
On the Origin of Wake-Up and Antiferroelectric-Like Behavior in Ferroelectric Hafnium Oxide
- First Published: 03 April 2021
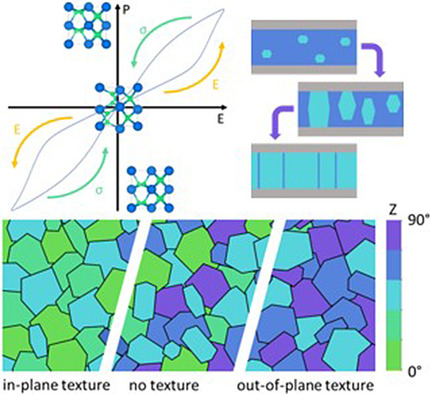
Antiferroelectricity in hafnium oxide is caused by ferroelastic switching due to the in-plane stress σ of the thin film. In addition, electric field–induced crystallization into the ferroelectric phase and the crystallographic texture affect the ferroelectric response over field cycling. Multiple process parameters, such as annealing temperature, influence this behavior.
A Segmented-Target Sputtering Process for Growth of Sub-50 nm Ferroelectric Scandium–Aluminum–Nitride Films with Composition and Stress Tuning
- First Published: 12 April 2021
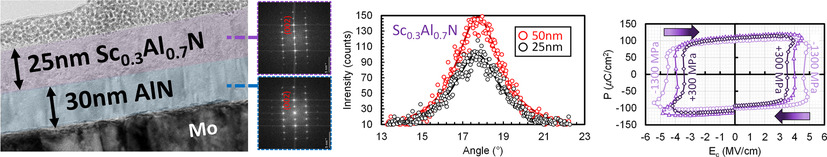
A reactive magnetron sputtering process, based on segmented aluminum–scandium targets, is developed for growth of ferroelectric scandium–aluminum–nitride (ScxAl1−xN) films. ScxAl1−xN films as thin as 25 nm with full width at half maximum better than 2.8° are achieved. The process provides large tuning of scandium content over and residual stress, enabling coercive field scaling for integrated device applications.