Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Diagnosis of malignant pleural disease: Ultrasound as “a detective probe”
- Pages: 223-230
- First Published: 22 November 2022
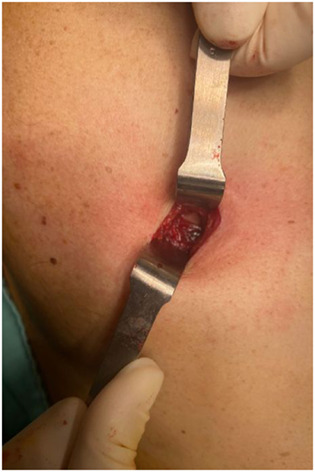
Chest ultrasound represents an important supplementary technique in the preoperative evaluation of the expansion of malignant pleural diseases. It allows to localize pleural tumors or pleural thickening and guide safe entry site for biopsy of the pleura, to assess the invasion of tumors to the pleura and chest wall, and guide biopsy of the tumors.
Safety of anti-SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccine in lung cancer patients undergoing anticancer chemotherapy: A multicenter, prospective, observational, patient-reported outcome study
- Pages: 231-236
- First Published: 20 November 2022
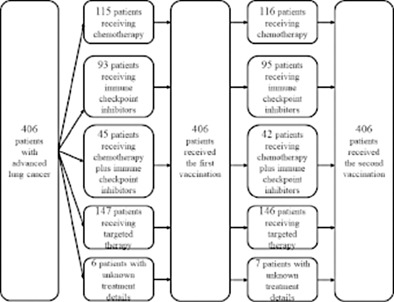
- Anti-SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccination is safe in patients with lung cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- Fever is more common in patients with lung cancer receiving chemotherapy.
- Vaccine-related side effects in these patients are comparable to those observed in healthy individuals.
Real-world treatment and prognostic factors for survival in ALK+ non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with brain metastases in China
- Pages: 237-245
- First Published: 21 November 2022

To explore the efficacy and prognostic factors of different treatment modalities on ALK+ NSCLC patients with brain metastases (BMs), 86 patients were retrospectively divided into two cohorts based on their history of treatment with ALK-TKIs prior to the incidence of BMs. Based on our results, the second-generation ALK- TKIs improved the duration of intracranial response and survival in ALK+ NSCLC patients with BMs in real world. Lower KPS (<80) had a negative impact on clinical outcomes (p < 0.0001) as an independent predictor.
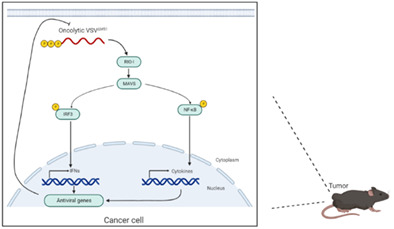
RIG-I-mediated innate immune signaling in tumors reduces the therapeutic effect of oncolytic vesicular stomatitis virus
- Pages: 246-253
- First Published: 29 November 2022
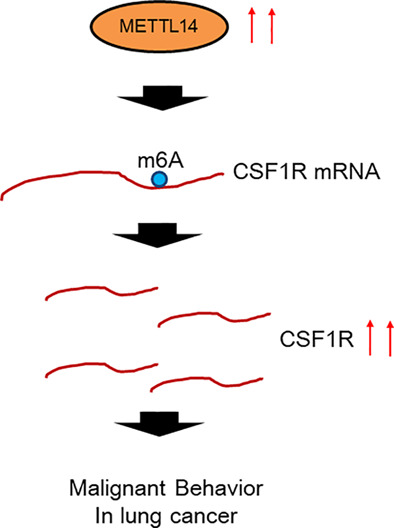
RNA m6A methyltransferase METTL14 promotes the procession of non-small cell lung cancer by targeted CSF1R
- Pages: 254-266
- First Published: 29 November 2022
Robot-assisted thymectomy in large anterior mediastinal tumors: A comparative study with video-assisted thymectomy and open surgery
- Pages: 267-273
- First Published: 25 November 2022
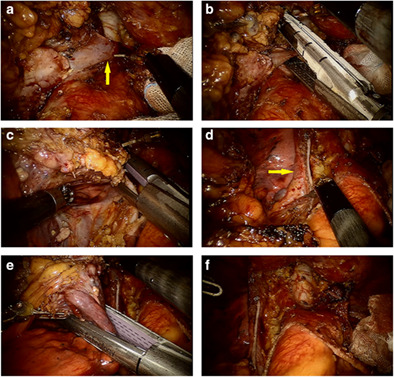
The robot-assisted thymectomy (RAT) can be performed using various approaches. The sub-xiphoid approach is routinely selected for centered and advanced large AMTs in our center; it can provide excellent visualization for exposing the proximal and distal ends of the innominate vein, which is convenient for resection of the invaded innominate vein, even for partial resection of the superior vena cava (SVC).
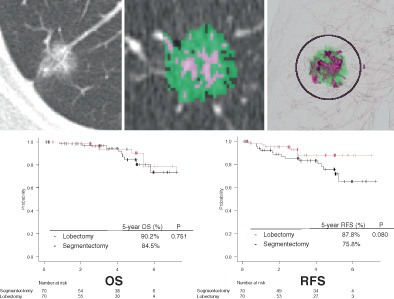
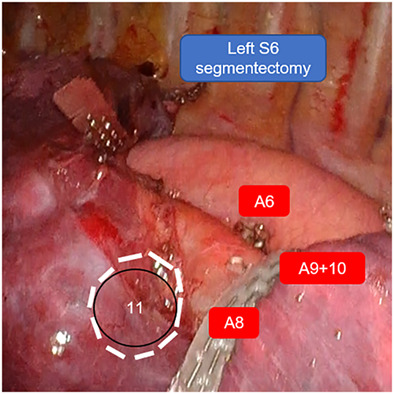
“Separated” precise subsegmentectomy: Single-port thoracoscopic noncombined subsegmentectomy in one lung lobe
- Pages: 274-280
- First Published: 24 November 2022
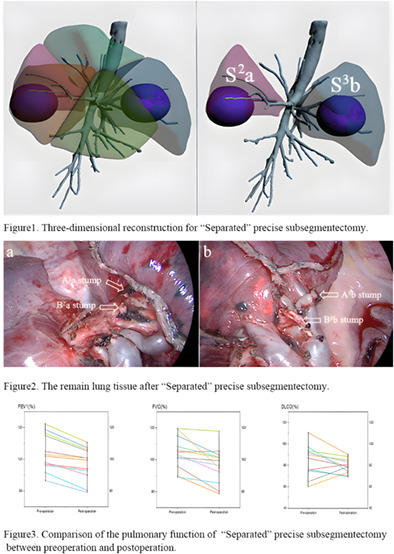
In clinical practice, when two or more distant lung segments or subsegments of the same lobe present with a ground glass opacity, lobectomy is performed in most of these patients. For these particular types of nodules, we perform “separated” precise subsegmentectomy to preserve more lung tissue. “Separated” precise subsegmentectomy is a novel and safe surgical method that could provide a more optimized way for patients with specific multiple nodules to preserve lung function.
One-lung ventilation in obese patients undergoing thoracoscopic lobectomy for lung cancer
- Pages: 281-288
- First Published: 07 December 2022
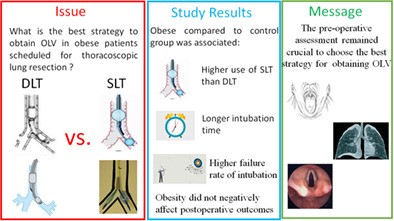
What is the best strategy to obtain one-lung ventilation (OLV) in obese patients scheduled for thoracoscopic lung resections? Double lumen tubes (DLTs), (i.e., Carlens tube, Robertshaw tube etc…) or single-lumen tube (SLT) with bronchial blockers (i.e., Univent, EZ blockers etc…)?Obese group compared to the control group was associated with: (i) higher use of a SLT with bronchial blockers than DLT; (ii) longer intubation time; and (iii) higher failure rate of intubation at the first attempt. No significant intergroup difference was found regarding intra-, peri- and postoperative complications and/or mortality.OLV was also safely performed in obese patients, and obesity did not negatively affect surgical outcomes. The preoperative evaluation of patients remains crucial when choosing the best strategy for obtaining OLV.
Pathologically noninvasive cancer predictors and surgical procedure for peripheral lung cancer
- Pages: 289-297
- First Published: 22 November 2022
Feasibility and safety of secondary video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery for ipsilateral lung cancer after prior pulmonary resection
- Pages: 298-303
- First Published: 30 November 2022
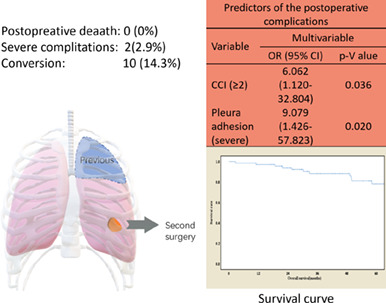
The increased survival of patients after a first operation has caused increases in the incidence of locoregional recurrence or second primary lung cancer and a concomitant increase in the number of patients who require secondary surgery. Ipsilateral secondary operation is also commonly practiced, albeit with enhanced difficulty. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the feasibility and safety of VATS for ipsilateral lung cancer after pulmonary resection.
Assessment of lymph node metastasis of ≤20 mm non-small cell lung cancer originating from superior segment compared to basal segment
- Pages: 304-308
- First Published: 09 December 2022
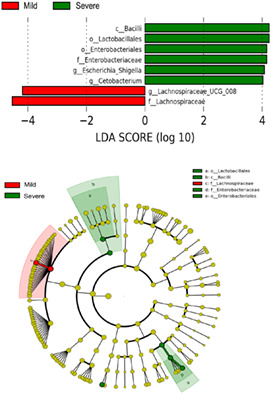
Diverse gut microbiota pattern between mild and severe cancer-related fatigue in lung cancer patients treated with first-line chemotherapy: A pilot study
- Pages: 309-319
- First Published: 11 December 2022
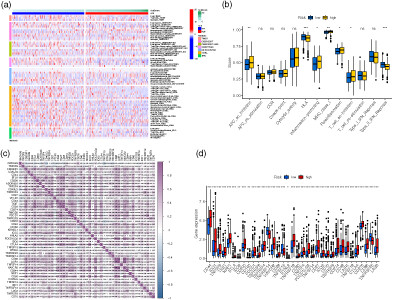
Identification of a novel anoikis-related gene signature to predict prognosis and tumor microenvironment in lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 320-330
- First Published: 11 December 2022
CASE REPORT
Primary lung sebaceous carcinoma successfully treated with radiotherapy and pembrolizumab: A case report
- Pages: 331-335
- First Published: 09 December 2022
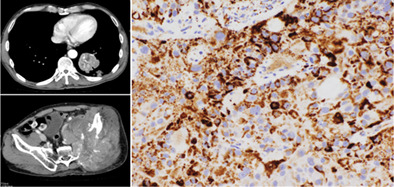
Primary sebaceous carcinoma of the lung is very rare, and no effective treatment has been yet established. We successfully treated lung sebaceous carcinoma with sequential treatment with radiotherapy and anti-PD-1 antibody therapy. The tumor had AKT1 mutation and was positive for PD-L1 expression, suggesting AKT-PD-L1 pathway may be implicated in the response to therapy.