Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
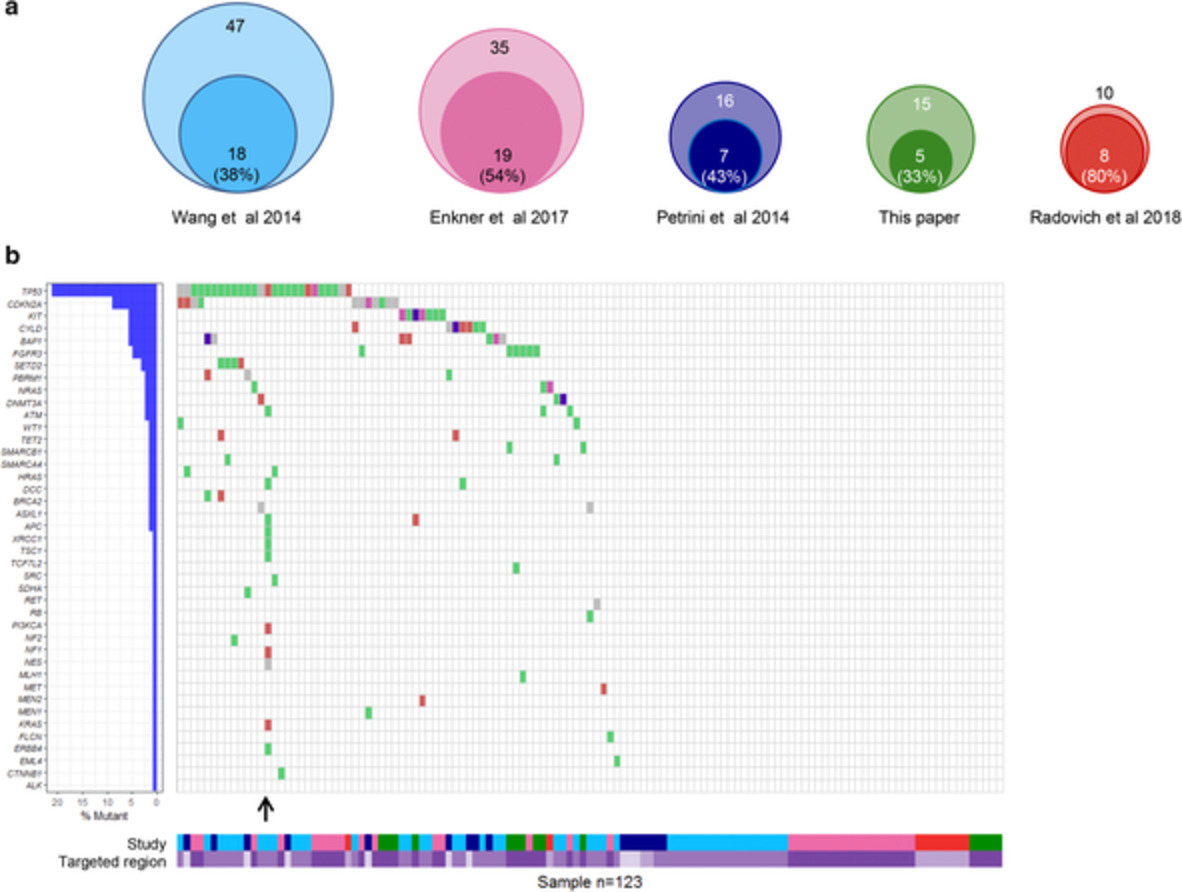
Mutation profile and immunoscore signature in thymic carcinomas: An exploratory study and review of the literature
- Pages: 1271-1278
- First Published: 11 March 2021
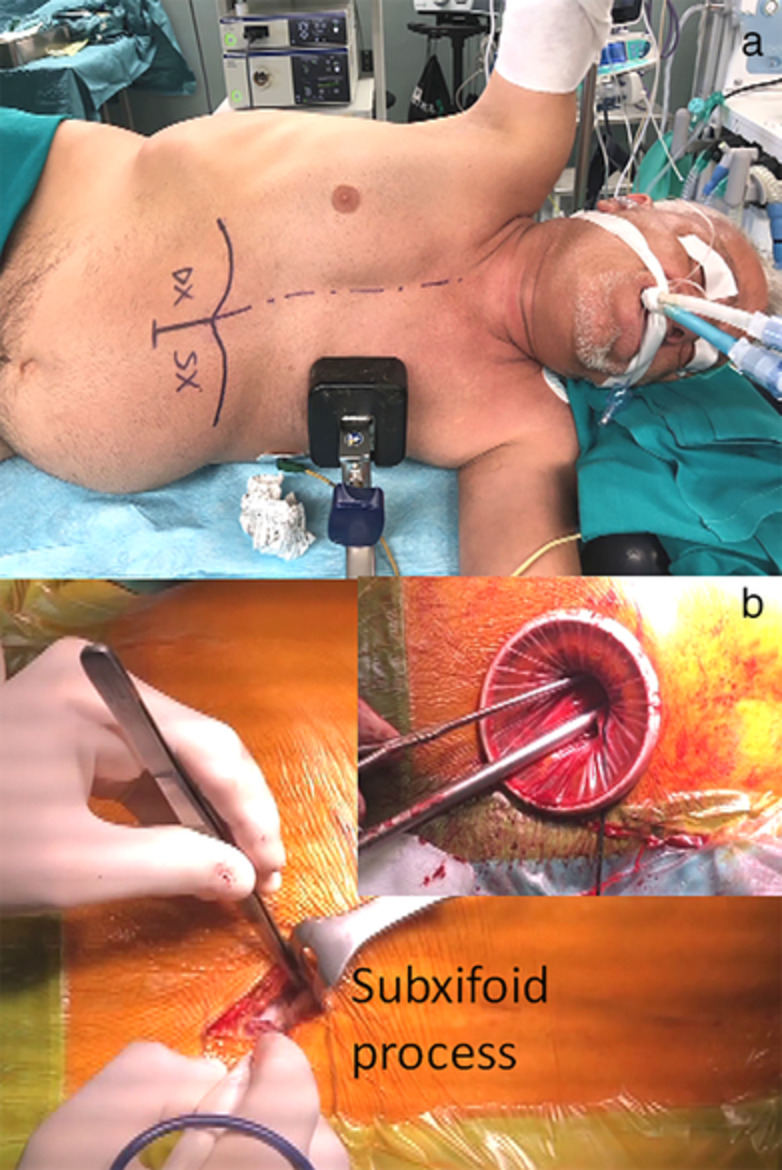
Subxifoid versus transthoracic thoracoscopic lobectomy: Results of a retrospective analysis before and after matching analysis
- Pages: 1279-1290
- First Published: 10 March 2021
CITED4 enhances the metastatic potential of lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 1291-1302
- First Published: 24 March 2021
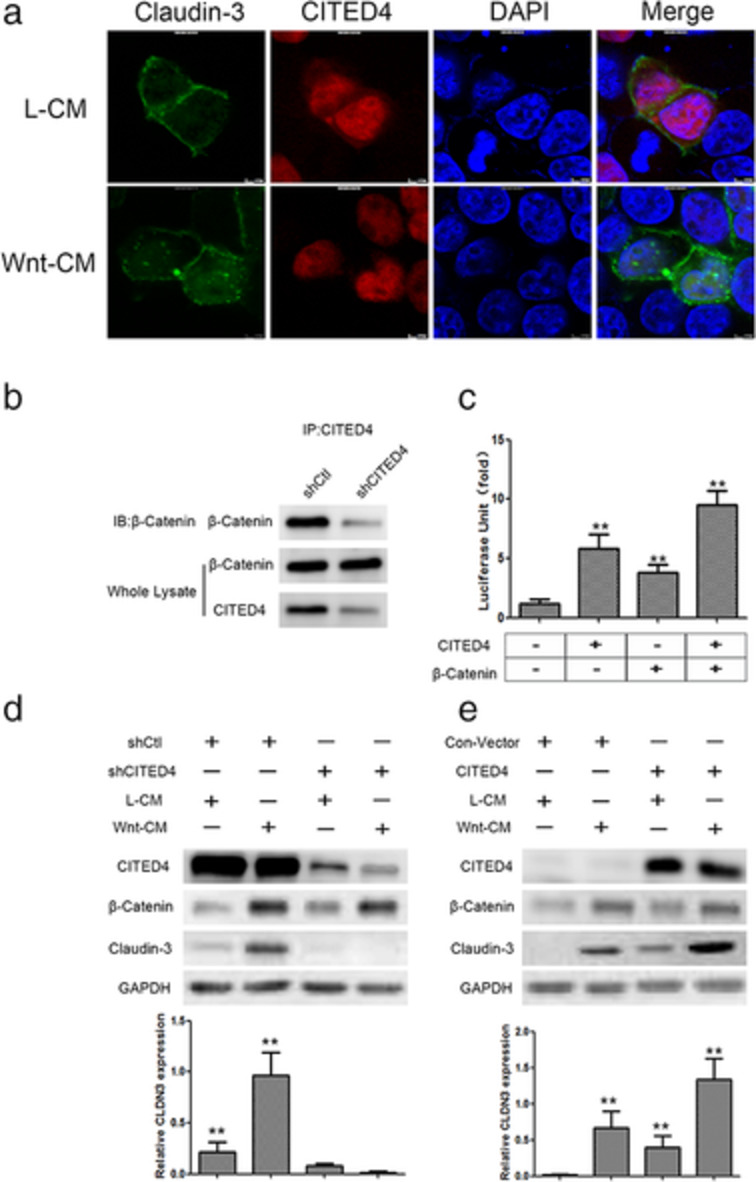
CITED4 expression is significantly upregulated in ADC tissues and cells. CITED4 interacted with CTNNB1 and functioned synergistically to enhance CLDN3 transcription. The CITED4-CTNNB1-CLDN3 axis plays a key role in the invasion and metastasis of ADC and provides a novel therapeutic target for lung cancer treatment.
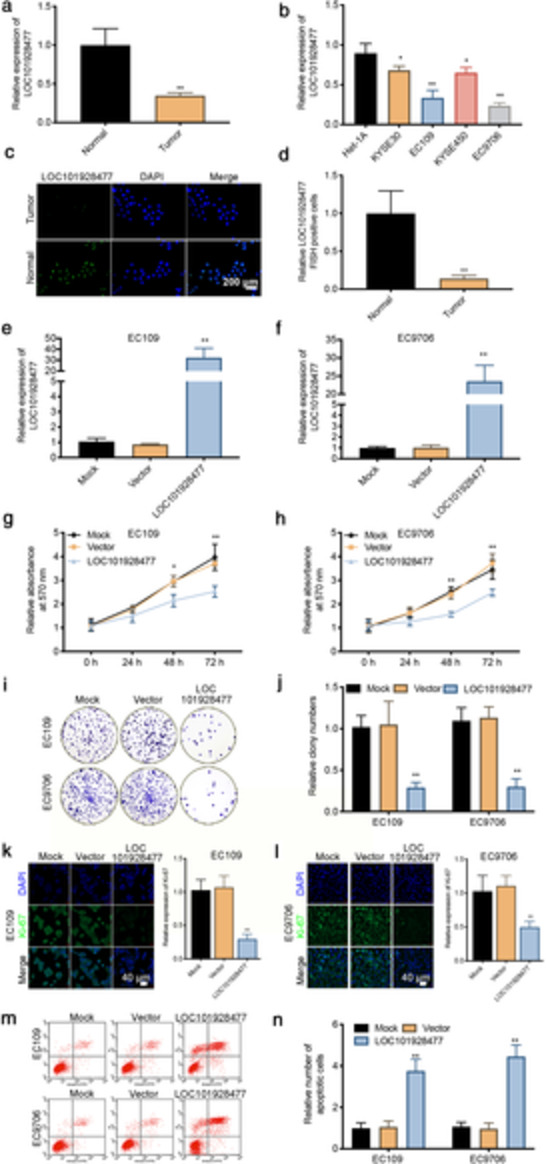
Downregulation of long non-coding RNA LOC101928477 correlates with tumor progression by regulating the epithelial-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- Pages: 1303-1311
- First Published: 13 March 2021
Identification of differentially expressed circular RNAs associated with thymoma
- Pages: 1312-1319
- First Published: 11 March 2021
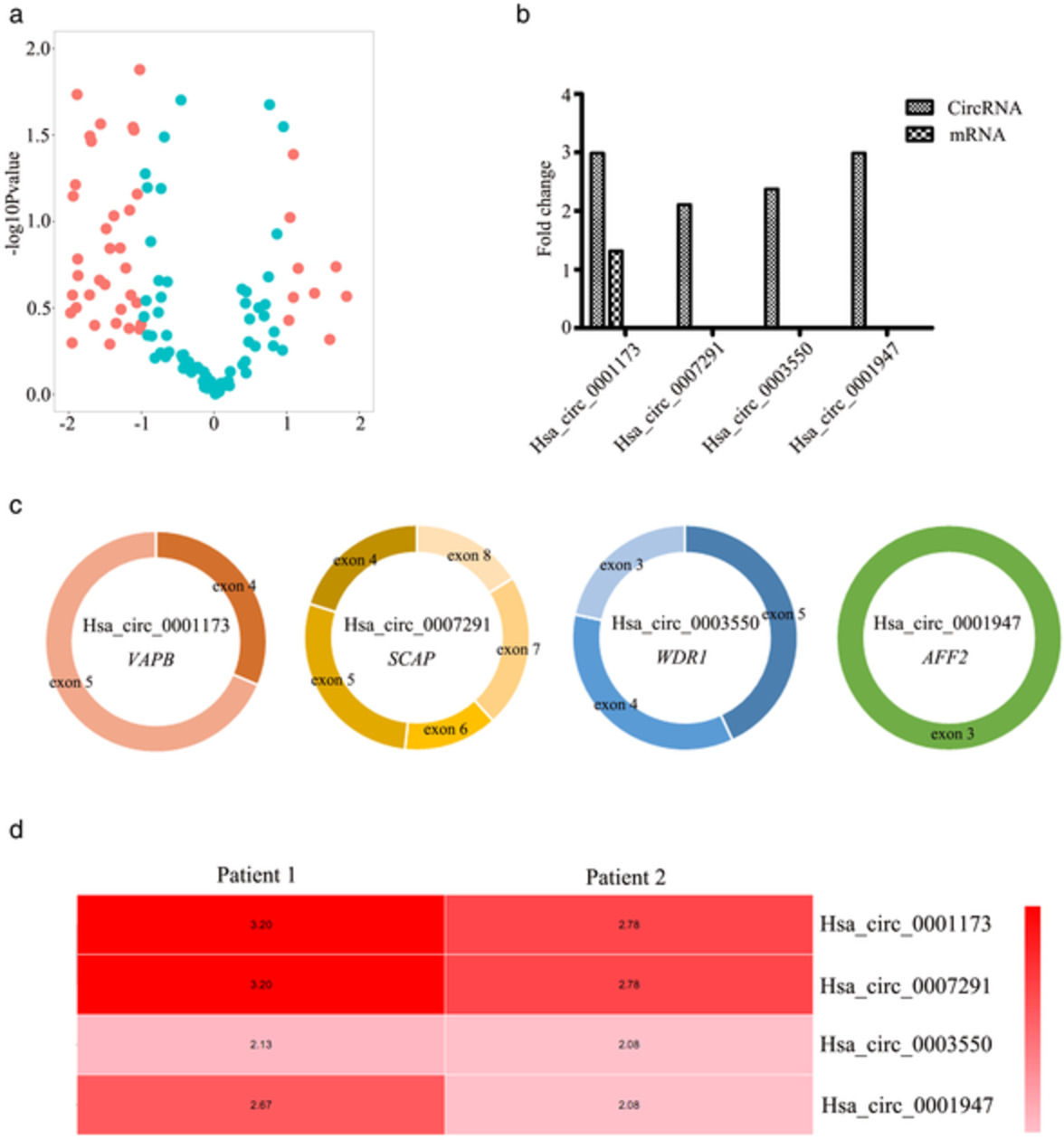
The expression levels of hsa_circ_0001173, hsa_circ_0007291, hsa_circ_0003550, and hsa_circ_0001947 were significantly upregulated and positively correlated with immune imbalance in thymoma patients. The discovery of new differentially expressed circRNAs can be used not only as a biomarker for diagnosis, but also as a potential target for the treatment of thymoma.
Long-term outcomes of high-dose (74 GyE) proton beam therapy with concurrent chemotherapy for stage III nonsmall-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 1320-1327
- First Published: 06 March 2021
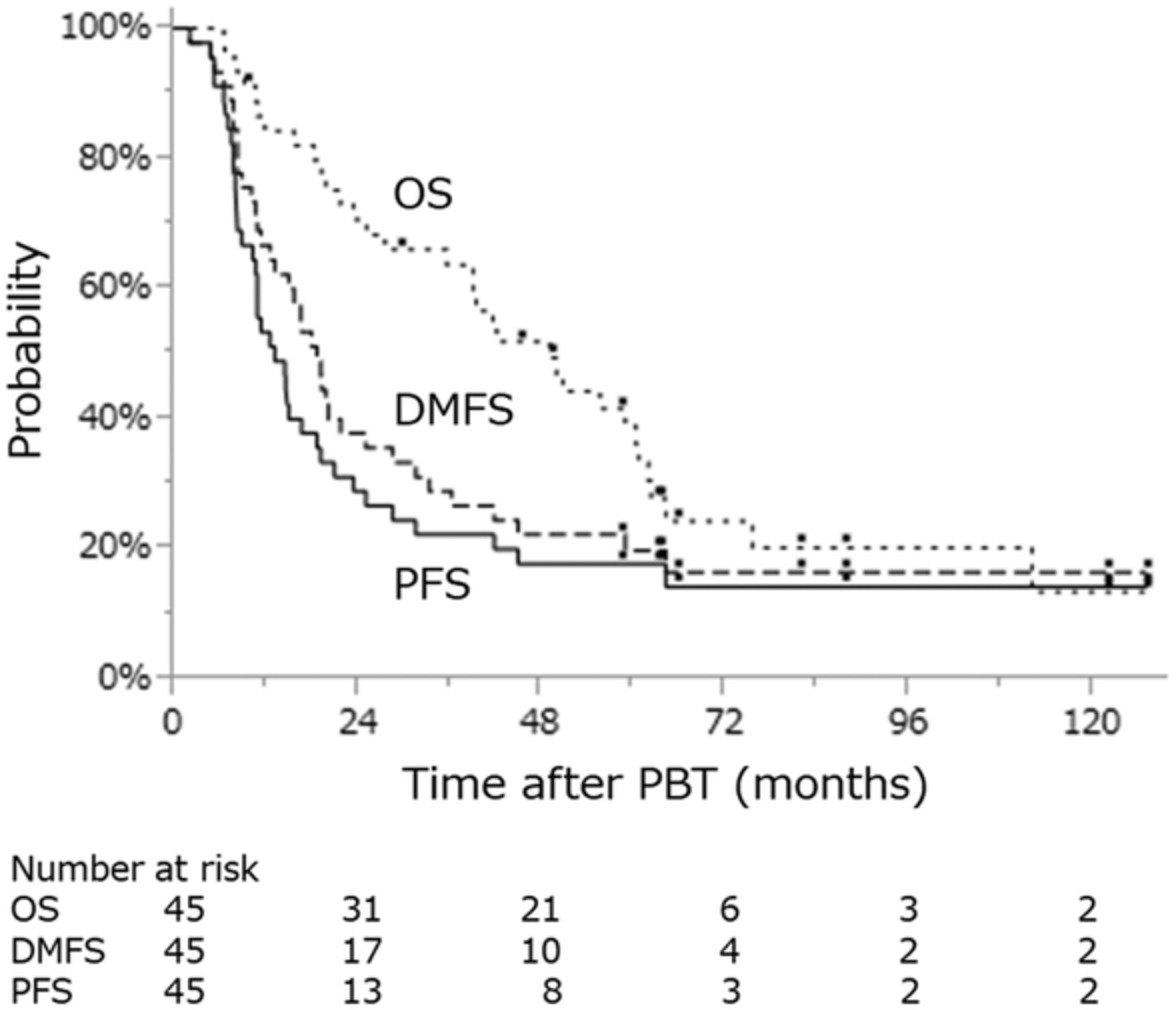
Forty-five patients with stage III non-small cell lung cancer (14 stage IIIA, 31 stage IIIB) who received high-dose (74 GyE) passive-scattering proton beam therapy (PBT) with concurrent chemotherapy were retrospectively reviewed to analyze survivals and toxicities. The 3- and 5-year overall survival rates were 63.7% and 38.8%, respectively, and the median overall survival was 49.1 months. Passive-scattering PBT of 74 GyE with chemotherapy showed favorable survival and a low incidence of severe adverse events in patients with stage III NSCLC.
Characteristics and outcomes of thymomas in Latin America: Results from over 10 years of experience (CLICaP-LATimus)
- Pages: 1328-1335
- First Published: 17 March 2021
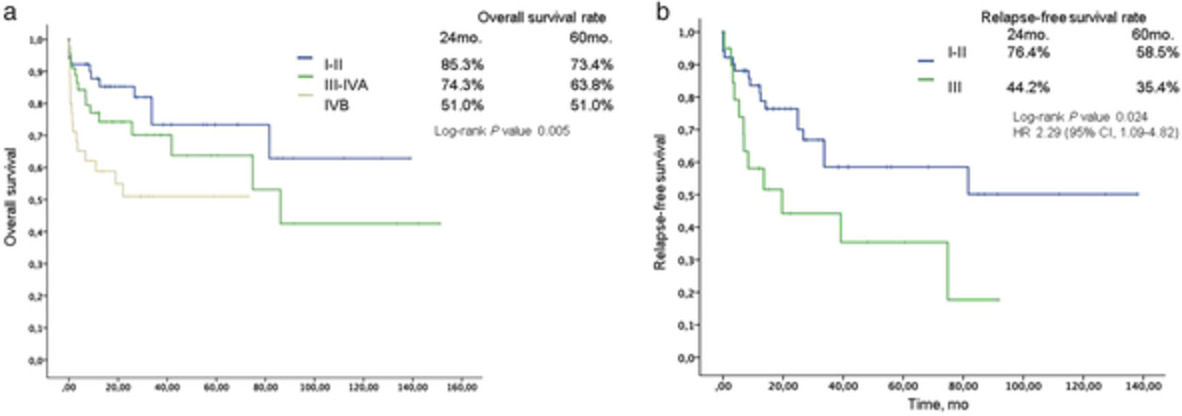
Here, we report the largest analysis of clinical characteristics of thymomas and outcomes in Latin American patients. Out of 135 patients included in the study, 21.5% (n = 29) concurrently presented myasthenia gravis. Relapse-free survival rates at five-years were 58.5% for stage I–II, and 35.4% for stage III. Five-year overall survival rates were 73.4%, 63.8% and 51%, at stages I–II, III–IVA and IVB, respectively.
Is major pathologic response sufficient to predict survival in resectable nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy?
- Pages: 1336-1346
- First Published: 10 March 2021
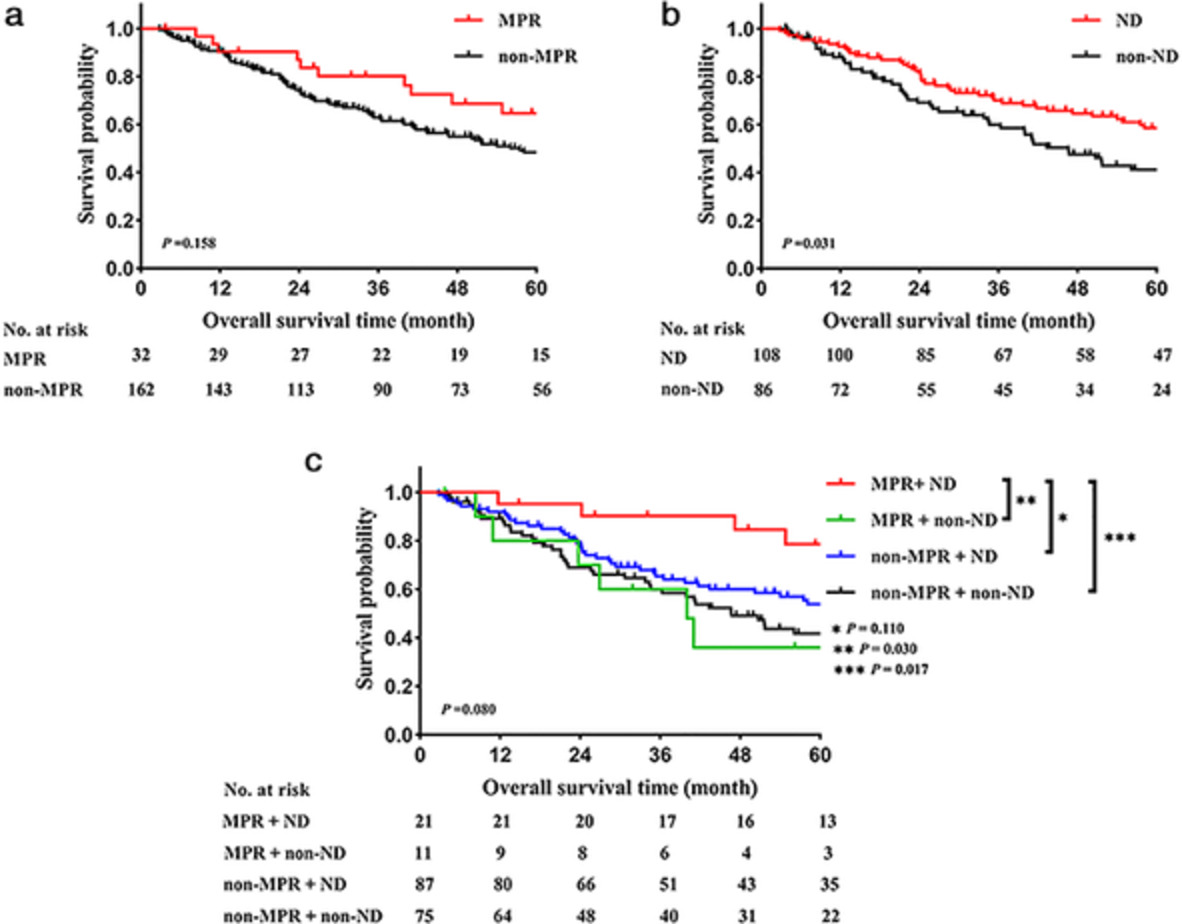
Pathologic response and nodal status of 194 nonsmall-cell lung cancer patients who received neoadjuvant chemotherapy and surgery were investigated. We demonstrated that major pathologic response was not adequate to predict survival, but when combined with nodal downstaging it could improve the efficacy of predicting survival in these patients. This helped to identify the population subset with the most favorable prognosis.
Biglycan, tumor endothelial cell secreting proteoglycan, as possible biomarker for lung cancer
- Pages: 1347-1357
- First Published: 11 March 2021

We found that biglycan (BGN) is expressed in tumor endothelial cells (TECs) and that BGN expression in TECs is associated with tumor progression and prognosis in lung cancer. Moreover, BGN expression in preoperative serum was significantly associated with BGN expression in TECs and with tumor malignancy.
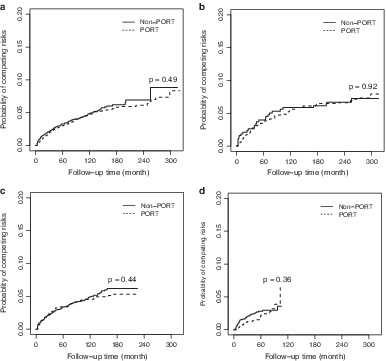
Risk of cardiac-related mortality in stage IIIA-N2 non-small cell lung cancer: Analysis of the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database
- Pages: 1358-1365
- First Published: 16 March 2021
Prognostic value of the geriatric nutritional risk index among patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer who subsequently underwent immunotherapy
- Pages: 1366-1372
- First Published: 12 March 2021
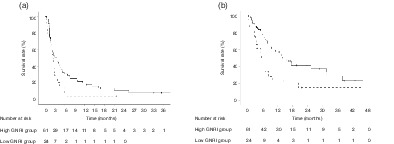
This retrospective study evaluated the prognostic value of the geriatric nutritional risk index (GNRI) among patients with previously treated advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who subsequently underwent immunotherapy. A high GNRI was associated with good outcome among patients with NSCLC. These results can be applied in clinical practice to evaluate patient prognosis and response to therapy.
SHR-1316, an anti-PD-L1 antibody, plus chemotherapy as the first-line treatment for advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: A multicentre, phase 2 study
- Pages: 1373-1381
- First Published: 24 March 2021
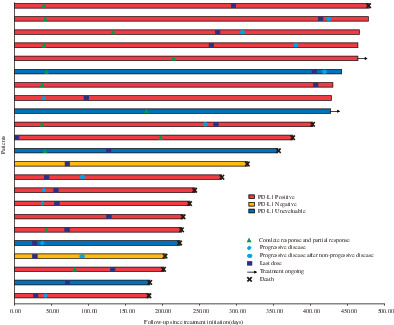
In this open-label, multicentre, phase 2 trial, anti-PD-L1 antibody (SHR-1316) plus liposomal irinotecan and 5-fluorouracil resulted in an impressive median progression-free survival of 8.5 months, median overall survival of 11.6 months, objective response rate of 52.2%, disease control rate of 73.9%, and median duration of response of 11.2 months. Adverse events were also manageable.
Management of chyle leakage after general thoracic surgery: Impact of thoracic duct embolization
- Pages: 1382-1386
- First Published: 30 March 2021
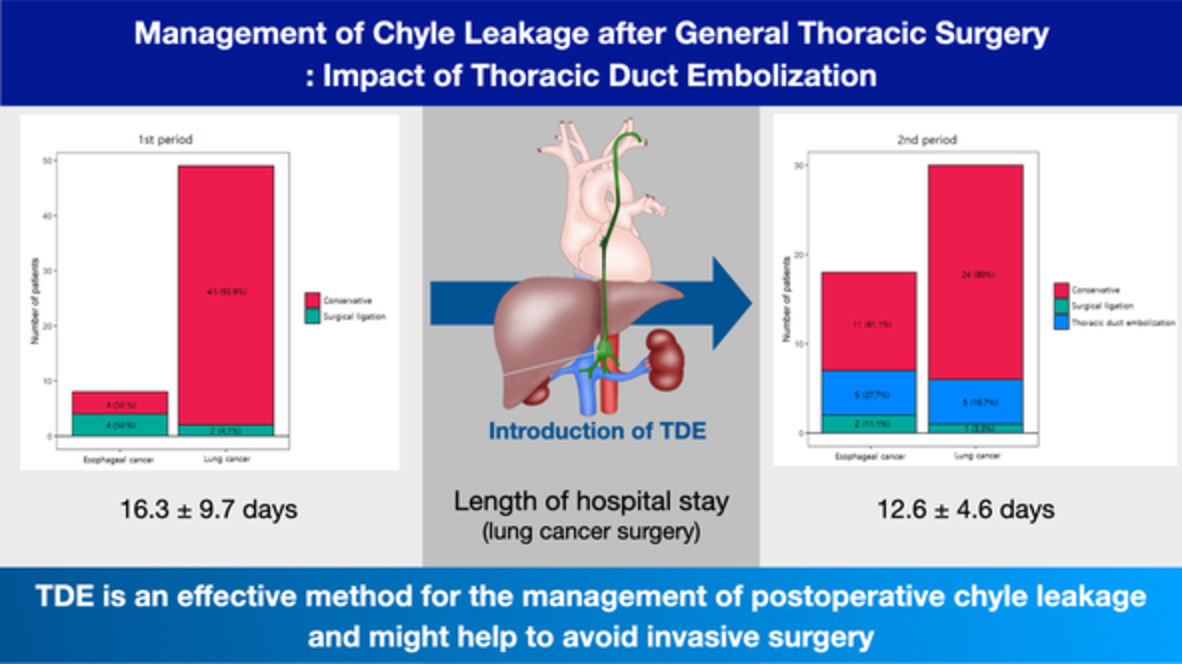
After the introduction of thoracic duct embolization (TDE), only three of 48 patients underwent surgical ligation of thoracic duct. The length of hospital stay of patients who underwent lung cancer surgery was shorter than that before the introduction of TDE. This study demonstrated that TDE is an effective method for the management of postoperative chyle leakage and can help avoid invasive surgery in this group of patients.
A retrospective analysis of pembrolizumab plus chemotherapy versus pembrolizumab monotherapy for advanced or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 1387-1397
- First Published: 12 March 2021
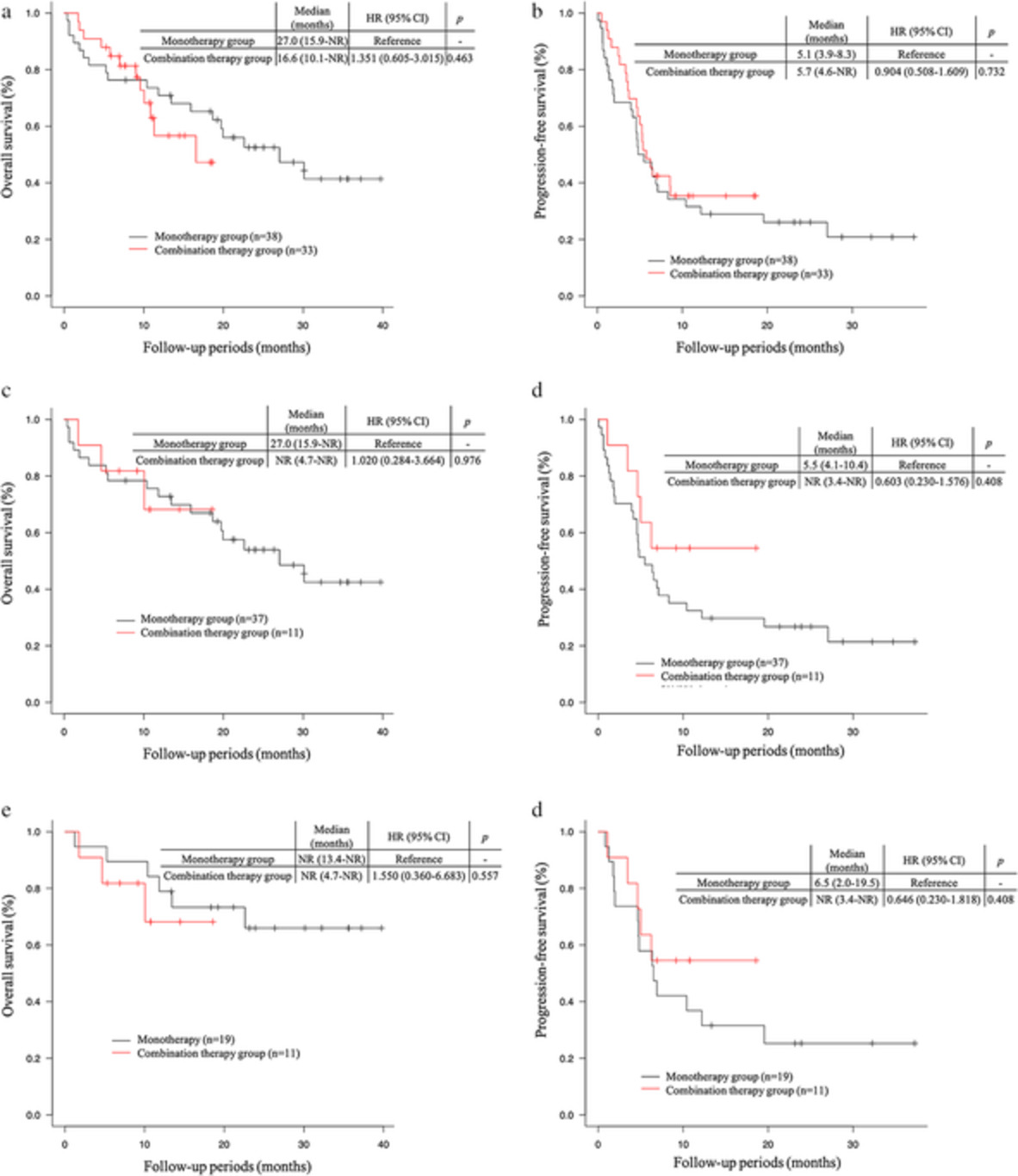
There was no significant difference in clinical response and prognosis between the combination therapy group and the monotherapy group. We think that the higher frequency of treatment discontinuation due to adverse events in the combination therapy group compared to the monotherapy group is one reason why there was no significant difference in prognosis between the two groups.
Combination of nitrous oxide and the modified inflation-deflation method for identifying the intersegmental plane in segmentectomy: A randomized controlled trial
- Pages: 1398-1406
- First Published: 04 April 2021
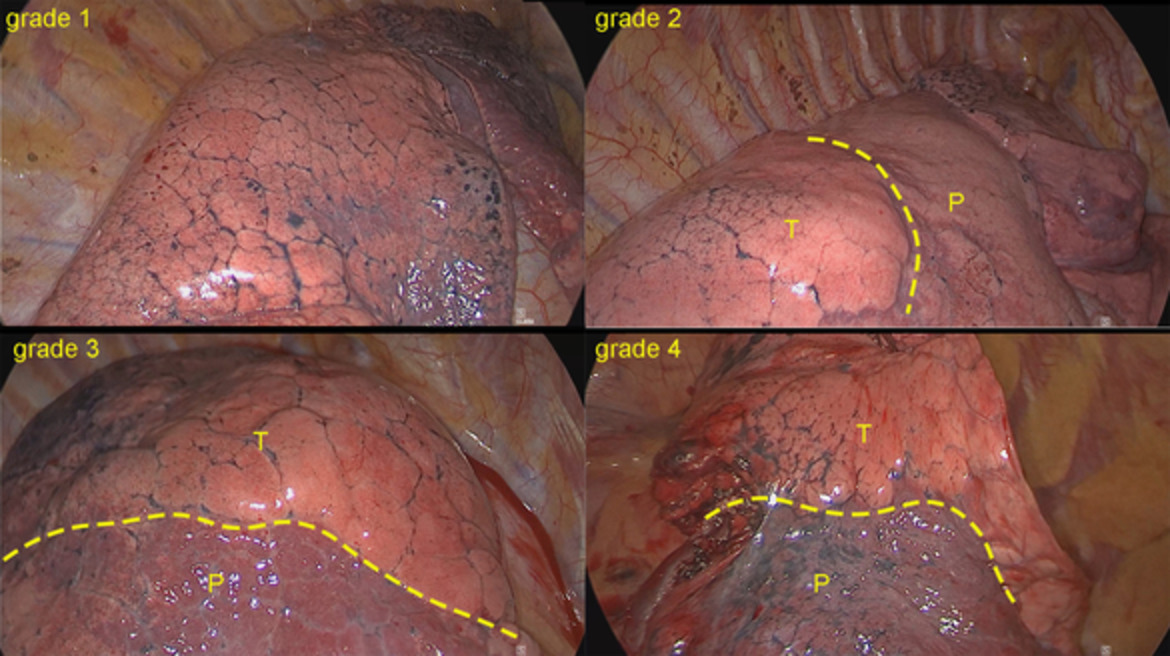
1. A modified inflation-deflation method is a simple technique for distinguishing the intersegmental demarcations. 2. Nitrous oxide is an inhaled anesthetic gas with high gas solubility, which could accelerate the process of lung collapse. 3. A combination of nitrous oxide and the modified inflation-deflation method can quickly and accurately identify lung resection borders.
Feasibility investigation of near-infrared fluorescence imaging with intravenous indocyanine green method in uniport video-assisted thoracoscopic anatomical segmentectomy for identifying the intersegmental boundary line
- Pages: 1407-1414
- First Published: 16 March 2021
Based on a large amount of clinical data, we found that the identification rate of IBL via ICGF-based method is comparable to the traditional MID method which is the globally accepted. Our study shows that the ICGF-based method can highly accurately identify the IBL and make anatomical segmentectomy easier and faster, and it helps to ensure sufficient resection margins, and therefore has the potential to be a feasible and effective technique to facilitate the quality of uniport VATS segmentectomy.
Quercetin induces pro-apoptotic autophagy via SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway in human lung cancer cell lines A549 and H1299 in vitro
- Pages: 1415-1422
- First Published: 11 March 2021
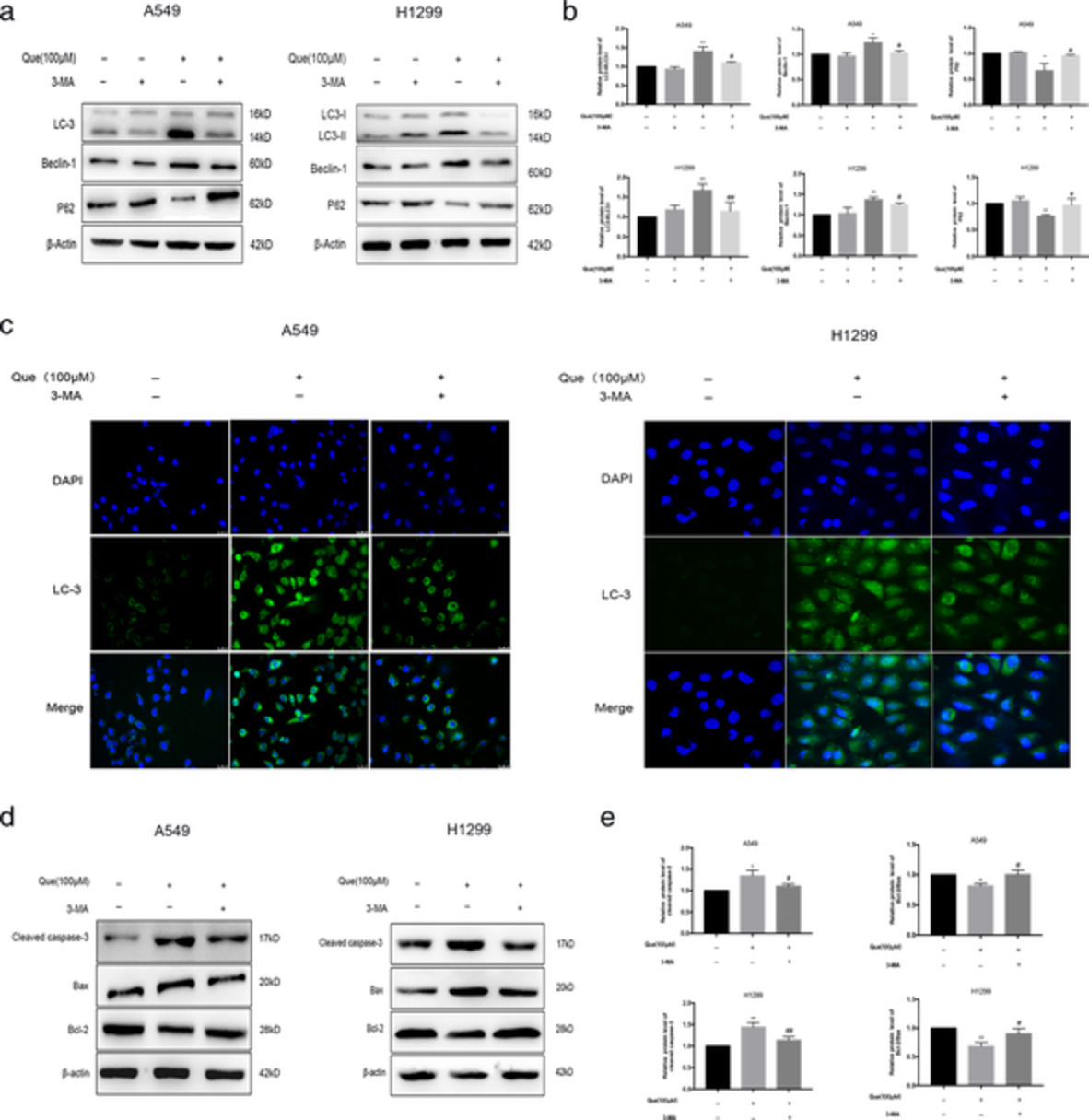
The present study substantiated that quercetin induces pro-apoptotic autophagy via SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway in human lung cancer cell line A549 in vitro. Furthermore, our study might provide a more effective therapeutic strategy for lung cancer by a combination treatment with quercetin and autophagy agonist.
Expanding TNM for lung cancer through machine learning
- Pages: 1423-1430
- First Published: 13 March 2021
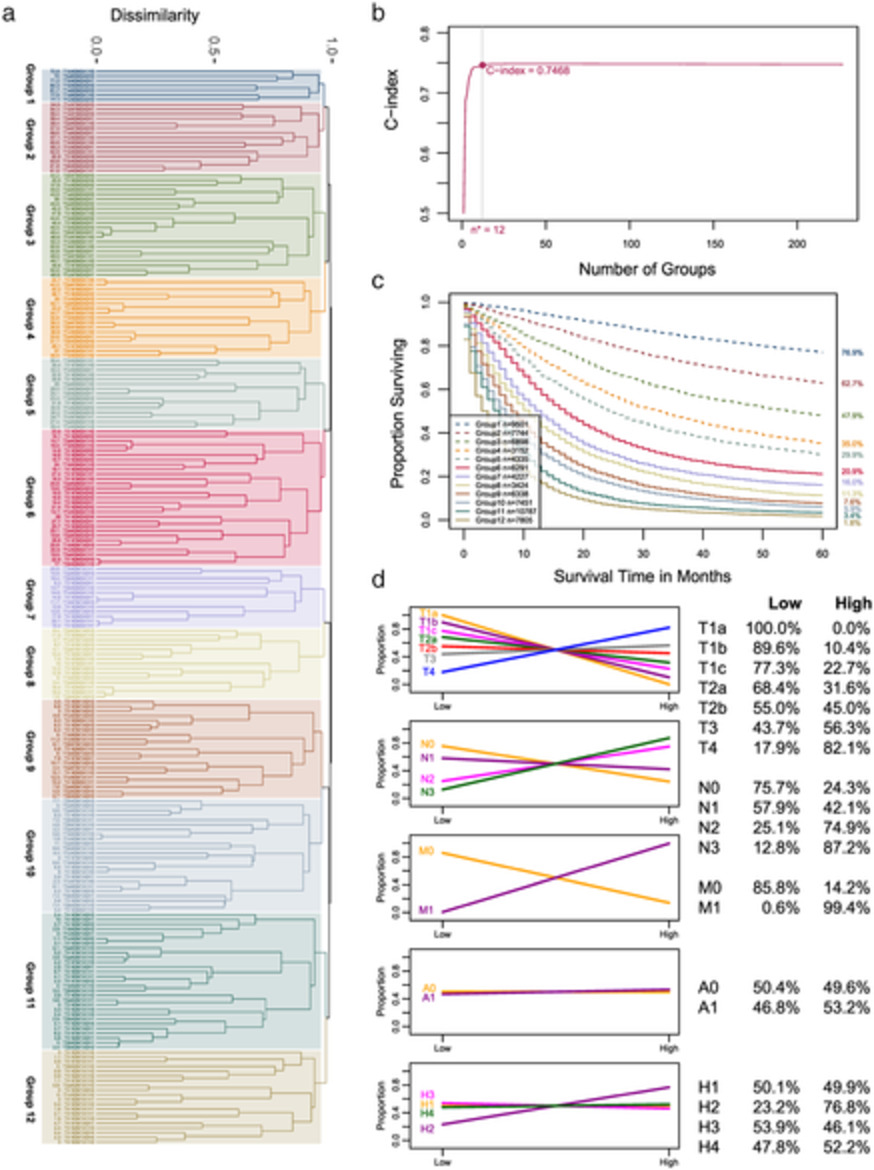
Expanding the TNM by integrating additional factors/variables is challenging. This study used machine learning to create prognostic systems that expand the TNM. On the basis of primary tumor, regional lymph nodes, metastasis, age, and histology type, a prognostic system for lung cancer was created to improve the patient stratification and survival prediction of the TNM.
Learning curve of robotic portal lobectomy for pulmonary neoplasms: A prospective observational study
- Pages: 1431-1440
- First Published: 11 March 2021
CASE REPORTS
EGFR-mutant lung adenocarcinoma associated with antisynthetase syndrome successfully treated with osimertinib
- Pages: 1441-1444
- First Published: 07 March 2021
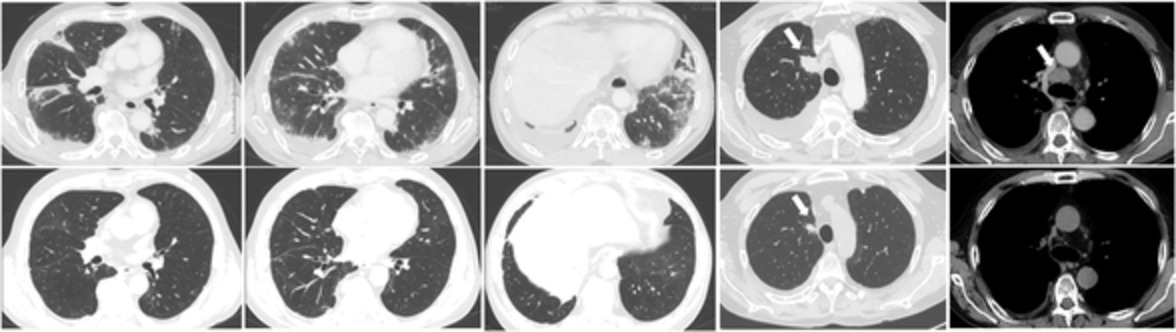
We report a case involving a patient with epidermal growth factor receptor-mutant lung adenocarcinoma and antisynthetase syndrome accompanied by interstitial lung disease (ILD), treated with osimertinib. After steroid pulse therapy, osimertinib was administered for the lung adenocarcinoma, without ILD exacerbation. Osimertinib could be a treatment option for EGFR-mutant lung cancer with paraneoplastic ILD.
Stereotactic body radiation therapy for an octogenarian with pulmonary carcinosarcoma
- Pages: 1445-1448
- First Published: 09 March 2021
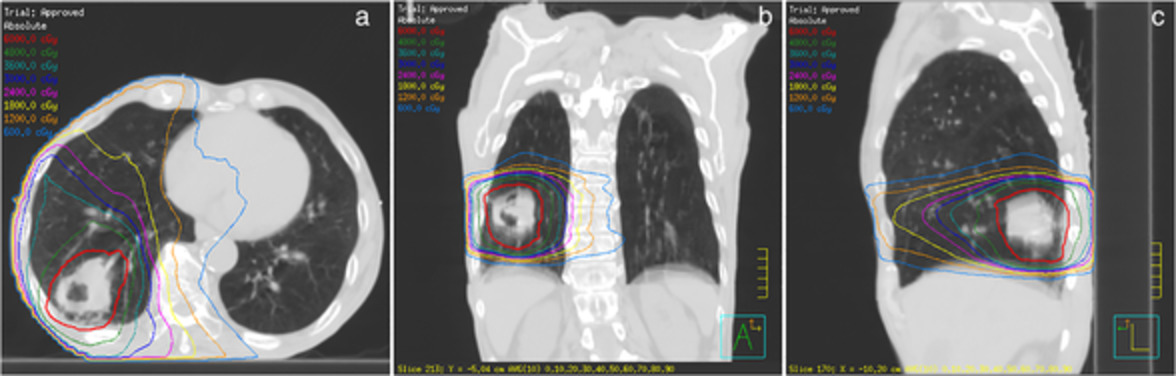
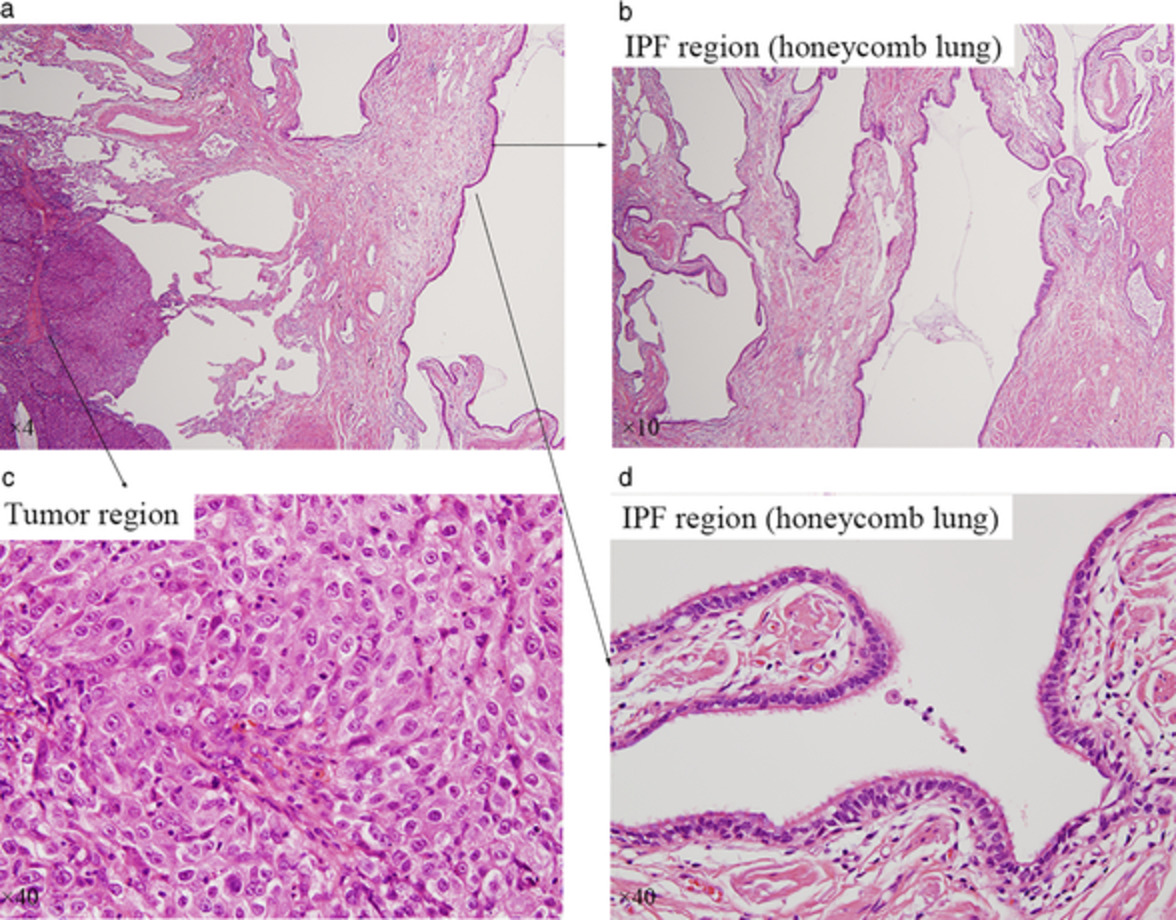
Genomic analysis between idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and associated lung cancer using laser-assisted microdissection: A case report
- Pages: 1449-1452
- First Published: 30 March 2021
Angiomatoid fibrosis histiocytoma in the pulmonary artery: A case report
- Pages: 1453-1456
- First Published: 13 March 2021
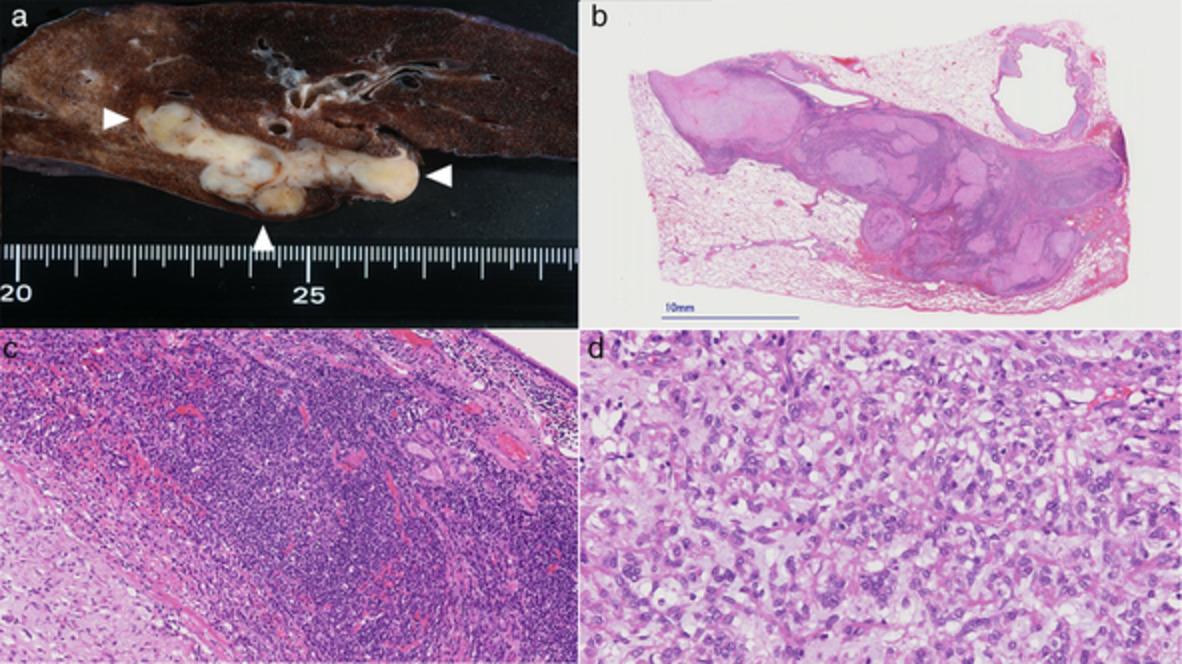
Angiomatoid fibrosis histiocytoma (AFH) is a rare neoplastic disease. Only one report has demonstrated an intraluminal tumor of the pulmonary artery trunk corresponding to AFH with ESWR1-ATF1 fusion to date. This is the first reported case of AFH occurring in the ascending artery with EWSR1-CREB1 fusion.
Remarkable response of non-small cell lung cancer to nintedanib treatment in a patient with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- Pages: 1457-1460
- First Published: 20 March 2021
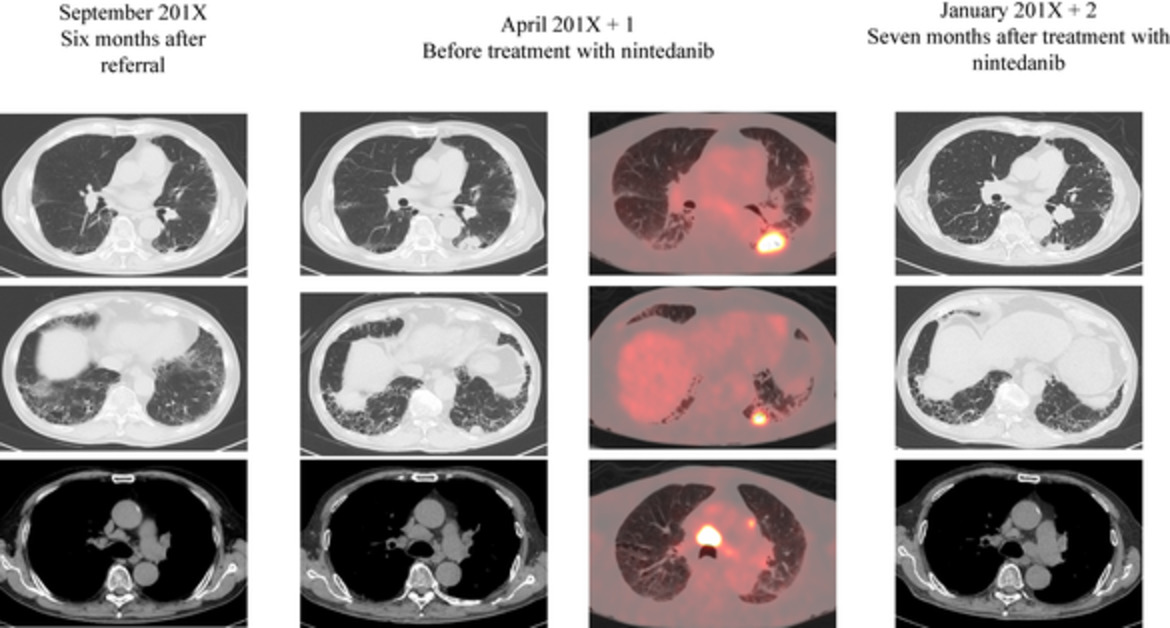
We present a case of an elderly patient with non-small cell carcinoma with underlying idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) who was treated with nintedanib. After seven months, partial remission of the lung cancer was observed without progression of IPF. This report indicates the possibility that nintedanib monotherapy could suppress lung cancer in patients with IPF.
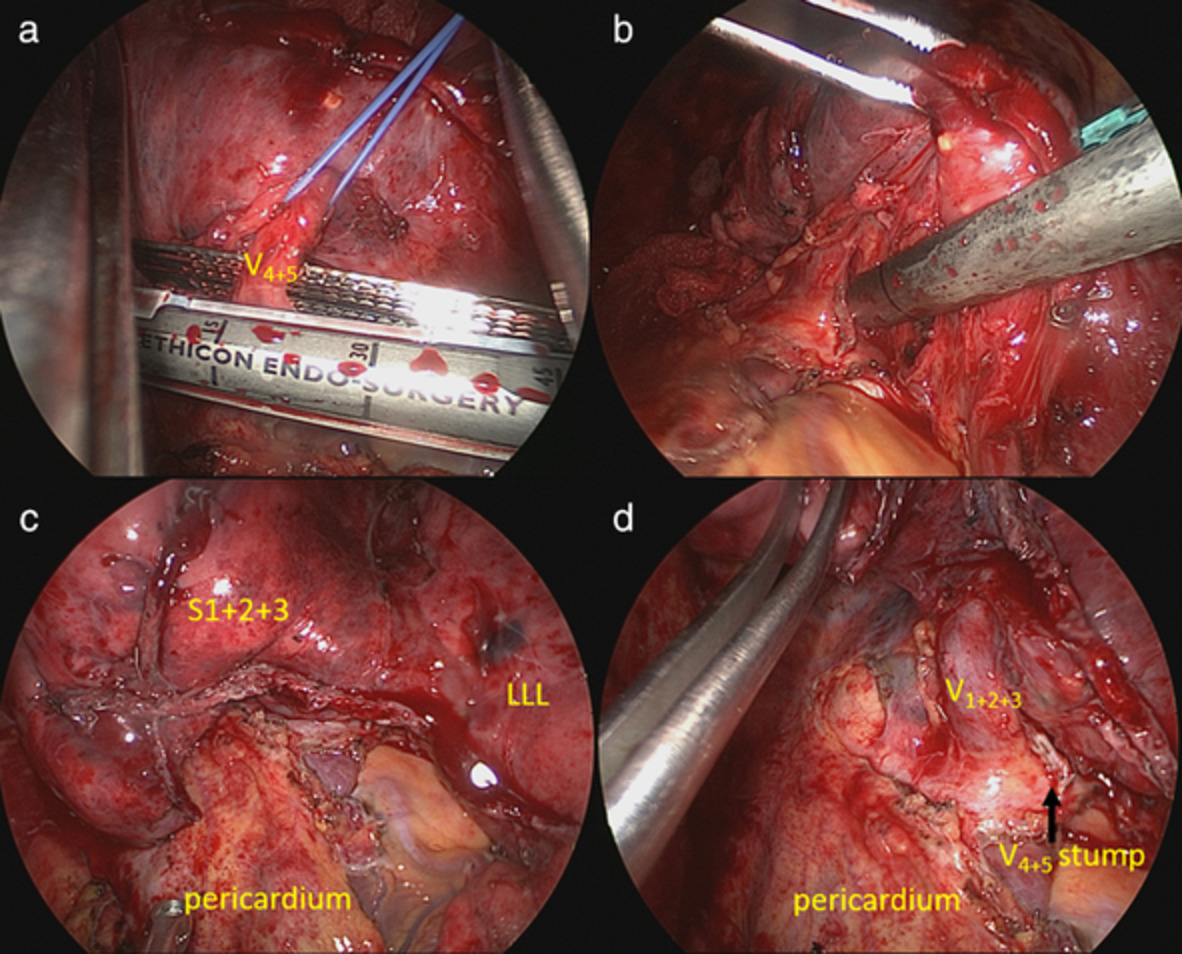
Thoracoscopic intrapericardial lingular segmentectomy for advanced lung cancer following immunotherapy
- Pages: 1461-1464
- First Published: 16 March 2021
IMAGING IN THORACIC CANCER
Pseudomesotheliomatous carcinoma of lung adenocarcinoma diagnosed using transesophageal ultrasound-guided bronchoscopic aspiration
- Pages: 1465-1466
- First Published: 10 March 2021
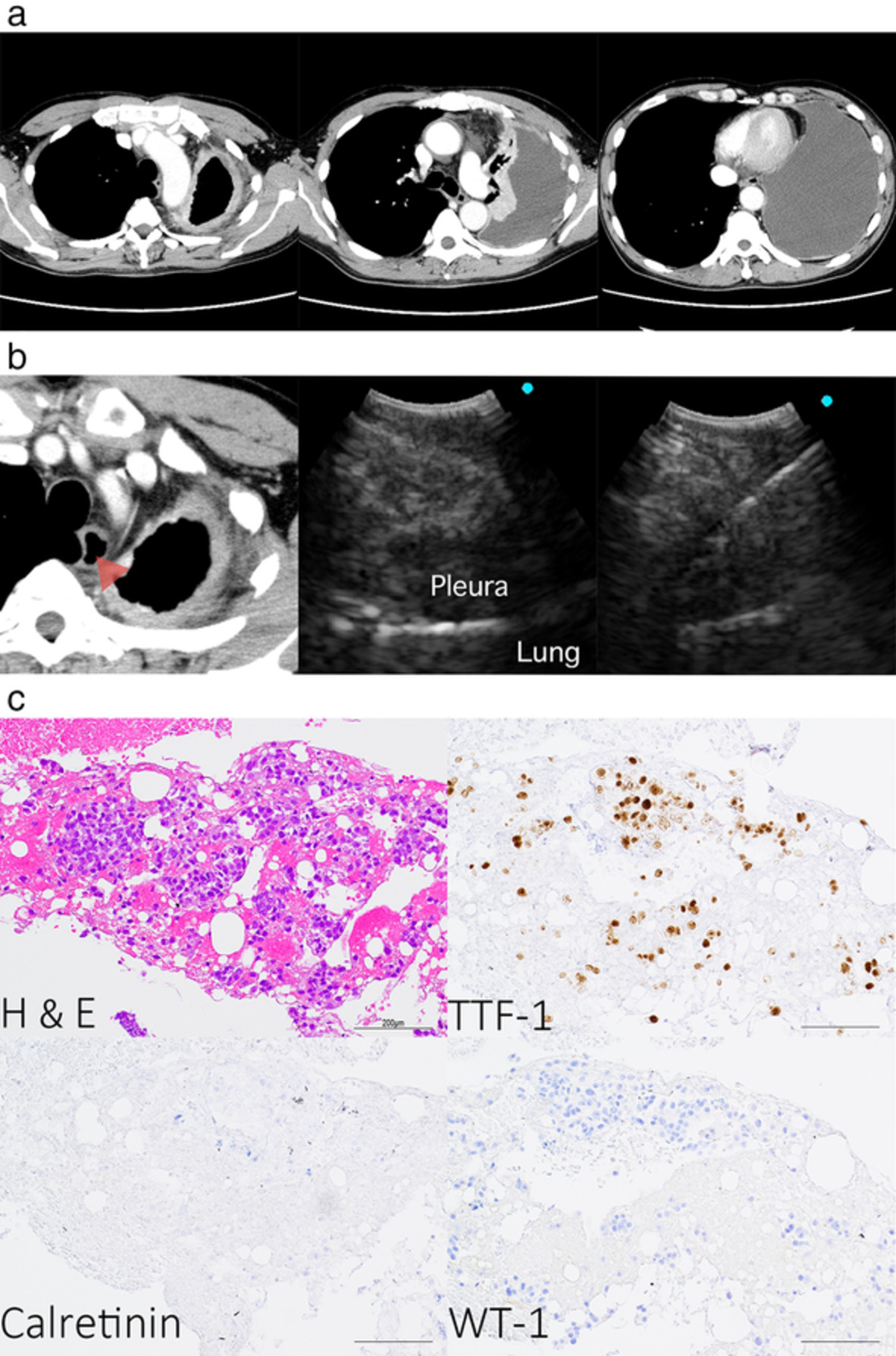
Endoscopic ultrasound with bronchoscope-guided fine-needle aspiration (EUS-B-FNA), a minimally invasive procedure, may be useful for the diagnosis of pseudomesotheliomatous (PMC) carcinoma because a sufficient amount of tissue can be obtained for diagnosis. This is the first report of PMC diagnosed using EUS-B-FNA. Our findings suggest that EUS-B-FNA may reduce the risk of dissemination for PMC.
Lung cancer metastasis to the pancreas mimicking autoimmune pancreatitis
- Pages: 1467-1468
- First Published: 03 April 2021
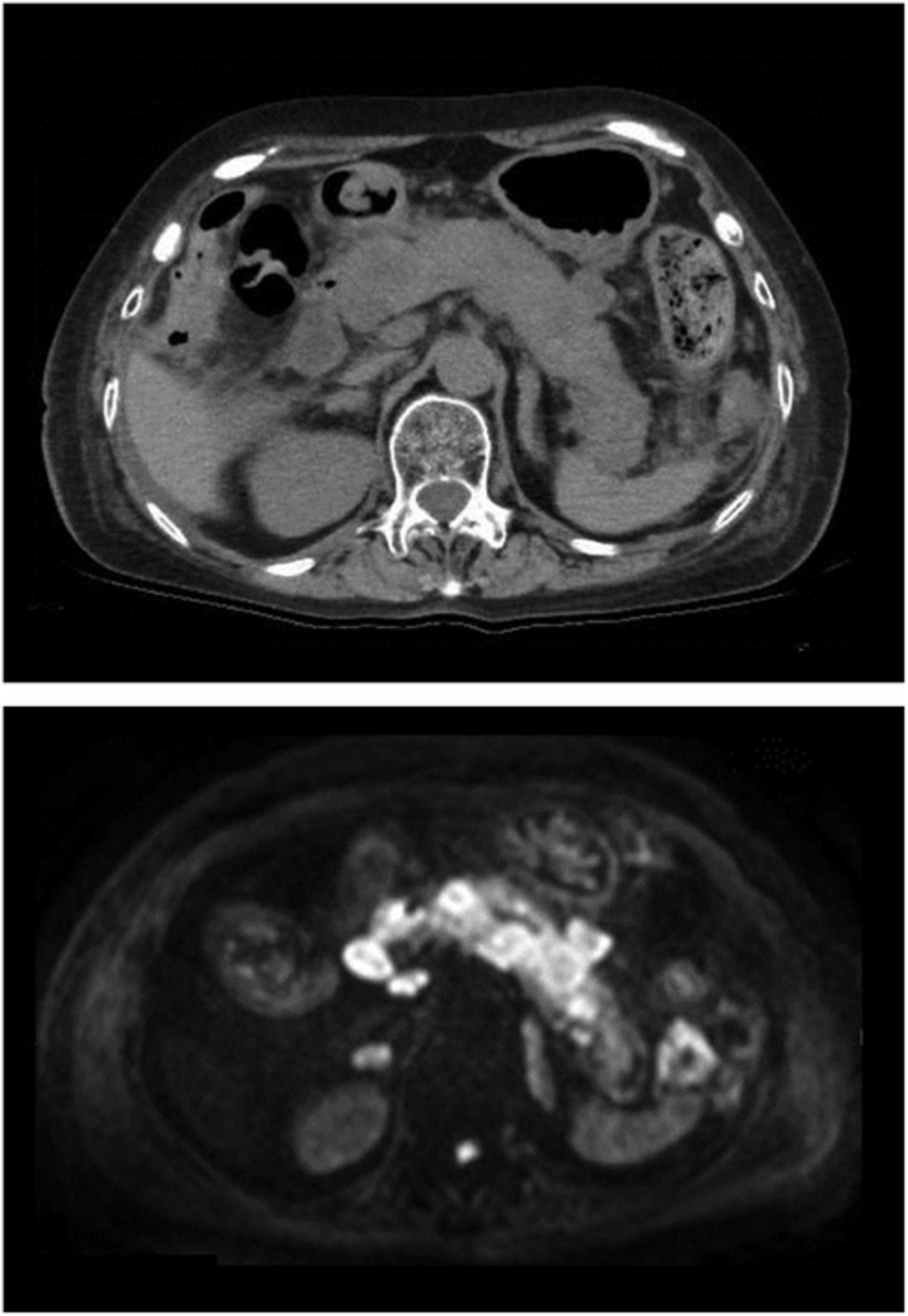
The unique radiological manifestation mimicking autoimmune pancreatitis caused by lung cancer metastasis to the pancreas has not previously been reported. The incidence of pancreatic secondary tumors has previously been reported to be approximately 15% in autopsy cases of malignant tumors, and it is unusual for thoracic oncologists to find that the second common primary tumor site of metastatic pancreas tumor is the lung.
CLINICAL GUIDELINE
Clinical recommendations for perioperative immunotherapy-induced adverse events in patients with non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 1469-1488
- First Published: 30 March 2021
TECHNICAL NOTE
Handling benign interlobar lymphadenopathy during thoracoscopic lobectomy
- Pages: 1489-1492
- First Published: 03 April 2021
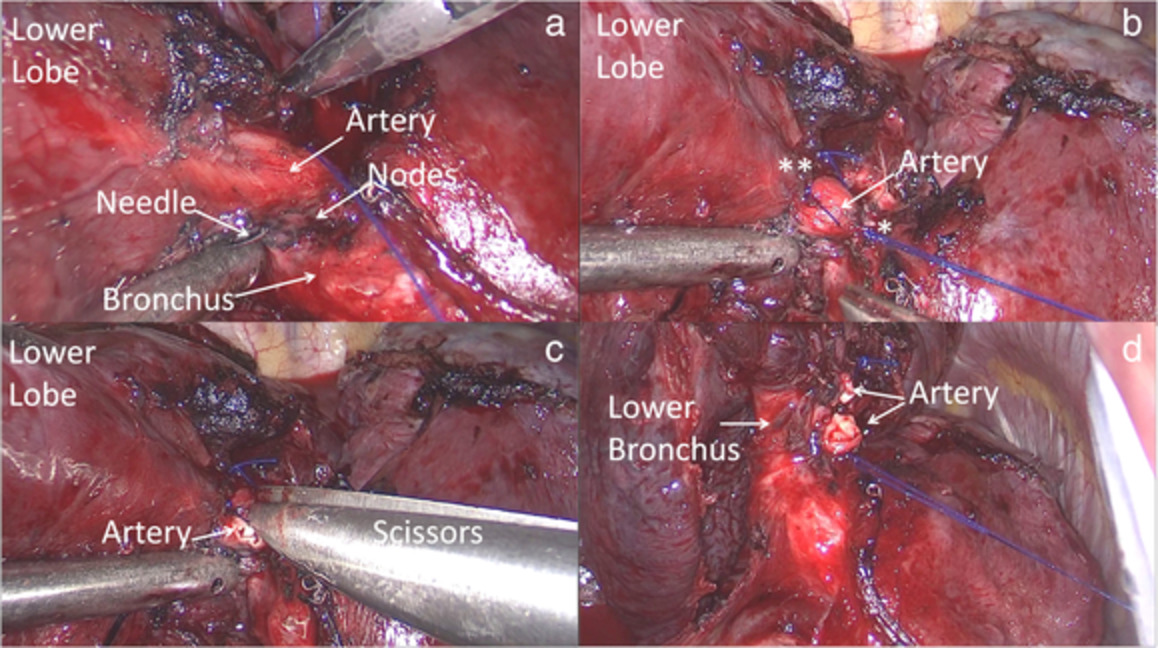
Calcified or inflammatory lymph nodes between the target bronchus and pulmonary artery is a huge challenge when performing thoracoscopic lobectomy. Here, we report a strategy to handle this clinical situation. A needle was passed across the nodes and the target vessel was closed with a proximal and distal suture, and then gradually transected with scissors. After dissection of adenopathies, the target bronchus was stapled.