Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Intestinal flora characteristics of advanced non-small cell lung cancer in China and their role in chemotherapy based on metagenomics: A prospective exploratory cohort study
- Pages: 3293-3303
- First Published: 24 October 2021
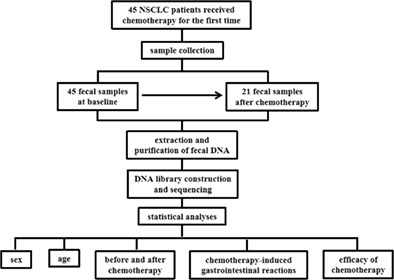
Significant differences in the intestinal flora of patients with advanced NSCLC were found according to sex and age. The abundances of Streptococcaceae, Lactobacillaceae, and Leuconostocaceae after platinum-containing dual-drug chemotherapy were significantly higher compared to those before chemotherapy at the family level. Advanced NSCLC patients with gastrointestinal reactions had higher metabolism, human diseases, cellular processes, and environmental information processing than those who did not. Nonresponders had higher levels of the six major metabolic pathways compared to responders.
Prediction modeling using routine clinical parameters to stratify survival in malignant pleural mesothelioma patients complicated with malignant pleural effusion
- Pages: 3304-3309
- First Published: 26 October 2021
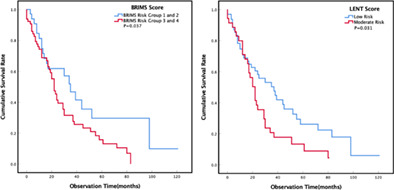
The individual survival of patients with MPM combined with MPE varied greatly in this study. Both LENT and BRIMS scores could help stratify the survival risk of patients with MPM complicated by MPE with fair-to-good performance. More effective predictive models should be established in adequately designed prospective studies.
Impact of tumor size and location on lung dose difference between stereotactic body radiation therapy techniques for non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3310-3318
- First Published: 24 October 2021
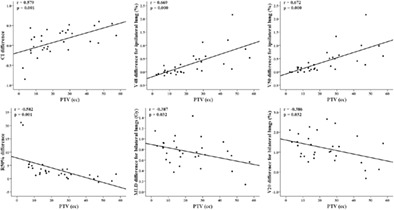
The dosimetric differences between 3D-CRT and IMRT were mainly correlated with the PTV rather than location-related parameters, with positive and negative correlations with the high-dose and intermediate-dose parameters, respectively. Together with the dosimetric benefit in high-dose lung regions of IMRT for larger tumors, the relative increases in the MLD and V20 for small-sized tumors could be reduced by applying a more rapid dose fall-off outside the PTV.
Prognostic factors of T2aN0M0 (T3-4cmN0M0, stage IB) non-small-cell lung cancer after surgery: Single-center real-world research
- Pages: 3319-3326
- First Published: 03 November 2021
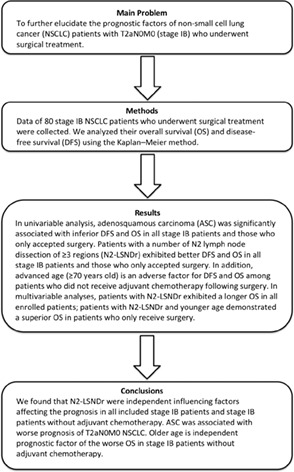
To further elucidate the prognostic factors of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with T2aN0M0 (stage IB) who underwent surgical treatment. We retrospectively analyzed the data of stage IB NSCLC patients who underwent surgical treatment at our center from October 2013 to September 2016 and 80 patients were enrolled. We analyzed their overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) using the Kaplan–Meier method. In univariable analysis, adenosquamous carcinoma (ASC) was significantly associated with inferior DFS (p = 0.036, p = 0.037) and OS (p = 0.001, p = 0.003) in all stage IB patients and those who only accepted surgery. Patients with a number of N2 lymph node dissection of ≥3 regions (N2-LSNDr) exhibited better DFS (p = 0.020, p = 0.005) and OS (p = 0.003, p = 0.001) in all stage IB patients and those who only accepted surgery. In addition, advanced age (≥70 years old) is an adverse factor for DFS (p = 0.049) and OS (p = 0.018) among patients who did not receive adjuvant chemotherapy following surgery. In multivariable analyses, patients with N2-LSNDr exhibited a longer OS (p = 0.045) in all enrolled patients; patients with N2-LSNDr (p = 0.016) and younger age (p = 0.021) demonstrated a superior OS in patients who only receive surgery. We found that N2-LSNDr were independent influencing factors affecting the prognosis in all included stage IB patients and stage IB patients without adjuvant chemotherapy. ASC was associated with worse prognosis of T2aN0M0 NSCLC. Older age is independent prognostic factor of the worse OS in stage IB patients without adjuvant chemotherapy.
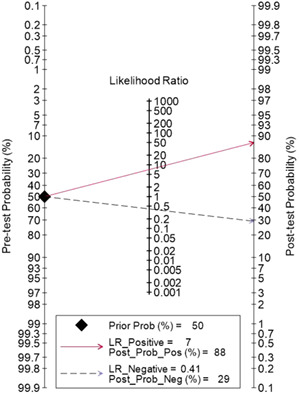
Diagnostic performance of SHOX2 promoter methylation as biomarker for lung cancer identification: A meta-analysis update
- Pages: 3327-3332
- First Published: 05 November 2021
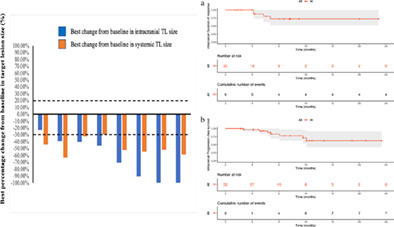
Heterogeneous radiological response to chemotherapy is associated with poor prognosis in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3333-3339
- First Published: 24 October 2021
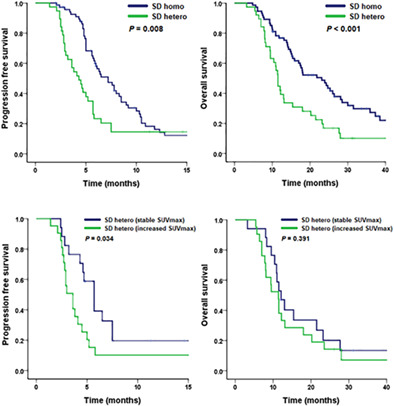
Patients with heterogeneous radiological responses in the SD group had a shorter PFS and OS. In particular, patients with increased SUVmax in lesions with heterogeneous radiological responses had a shorter PFS than patients with a stable SUVmax. The presence of lesions with radiological heterogeneity was associated with disease progression and poor prognosis in the SD group.
The reversal of drug resistance by two-dimensional titanium carbide Ti2C (2D Ti2C) in non-small-cell lung cancer via the depletion of intracellular antioxidant reserves
- Pages: 3340-3355
- First Published: 05 November 2021
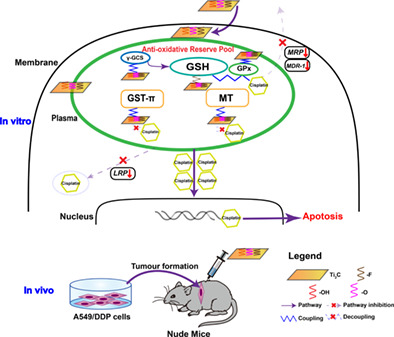
Two-dimensional titanium carbide (2D Ti2C) can reduce the glutathione (GSH) content through reactive oxygen species generation or direct binding to GSH, and 2D Ti2C can also reduce the level of γ-glutamylcysteine (γ-GCS) synthetase, which mediates GSH production, and glutathione peroxidase (GPx), which enables GSH to react with hydrogen peroxide. In addition, 2D Ti2C can reduce the expression of the antioxidant genes glutathione-S-transferase-Pi (GST-π) and metallothionein (MT). It is also possible that the 2D Ti2C surface reactive groups can bind to the thiol groups in a cysteine-rich protein such as metallothionein to alter its structure and function. Furthermore, 2D Ti2C can decrease the expression of drug resistance genes including lung resistance protein (LRP), multidrug resistant protein (MRP), and multidrug resistance-1 (MDR-1), which would normally contribute to cisplatin efflux. Hence, downregulation of these genes can also increase the effective accumulation of cisplatin in cells and promote its entry into the nucleus.
Circular RNA circCPA4 promotes tumorigenesis by regulating miR-214-3p/TGIF2 in lung cancer
- Pages: 3356-3369
- First Published: 05 November 2021
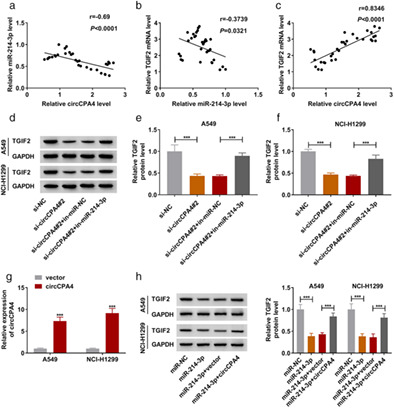
Lung cancer is the most prevalent malignancy in adults, and circular RNA (circRNA) circCPA4 (hsa_circ_0082374) is highly expressed in non-small cell lung cancer. In this paper, our results suggested that circCPA4 deficiency could inhibit the progression of lung cancer cells by regulating the miR-214-3p/ TGIF2 axis. These findings suggested underlying therapeutic targets for the treatment of lung cancer.
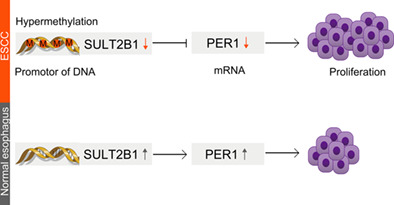
The promoter hypermethylation of SULT2B1 accelerates esophagus tumorigenesis via downregulated PER1
- Pages: 3370-3379
- First Published: 02 November 2021
CT-guided microwave ablation in patients with lung metastases from breast cancer
- Pages: 3380-3386
- First Published: 02 November 2021
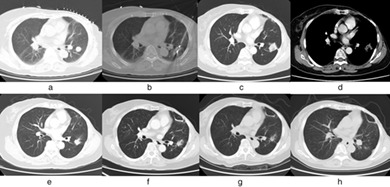
Most patients with lung metastases from breast cancer, especially those with multiple metastases, are ineligible for operation. Thirty-two patients who underwent microwave ablation (MWA) for lung metastases from breast cancer over a 6-year period were examined. Computed tomography-guided percutaneous MWA may be safe and effective for treating lung metastases from breast cancer.
Lung cancer risk following previous abnormal chest radiographs: A 27-year follow-up study of a Chinese lung screening cohort
- Pages: 3387-3395
- First Published: 09 November 2021
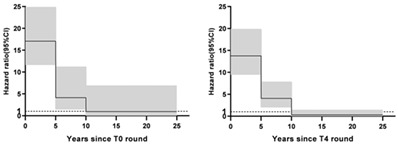
Abnormal imaging results might be useful to lung cancer risk stratification. We investigated the long-term lung cancer risk following abnormal CXR findings based on the extended follow-up of an occupational screening cohort in Yunnan, China. Although decreased over time, an increased lung cancer risk relative to abnormal CXR findings can continue for 10 years.
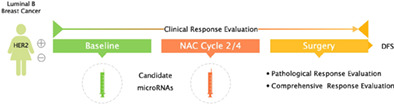
Circulating microRNAs as indicators in the prediction of neoadjuvant chemotherapy response in luminal B breast cancer
- Pages: 3396-3406
- First Published: 09 November 2021
Efficacy of dacomitinib in patients with EGFR-mutated NSCLC and brain metastases
- Pages: 3407-3415
- First Published: 09 November 2021
Intrapleural treatment in patients with non-small cell lung cancer with malignant pleural effusions in the real world
- Pages: 3416-3425
- First Published: 06 November 2021
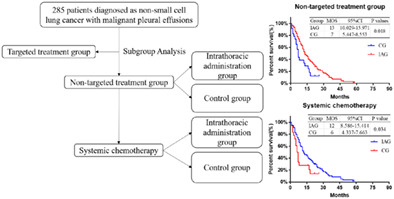
There is a debate about a malignant pleural effusion (MPE) necessitates intrapleural treatment. 285 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with MPEs were included in the cohort. Among patients who received only chemotherapy as systemic therapy or who don't receive targeted treatment, the median overall survival of patients of intrathoracic administration group (IAG; intrapleural treatment with drugs) was longer than that of control group (CG; no drug treatment in the pleural cavity). Intrapleural treatment can prolong the survival of NSCLC patients with MPEs who don't receive targeted treatment or who receive only chemotherapy.
CASE REPORTS
Capmatinib successfully overcomes tepotinib-induced intolerable peripheral edema
- Pages: 3426-3428
- First Published: 25 October 2021
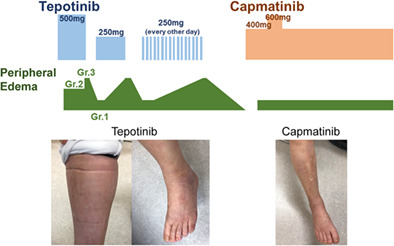
Peripheral edema has been identified as one of the most common adverse events in capmatinib and tepotinib; however, there is no unified management for this side effect. This is the first report that two MET inhibitors have different effects on the development of peripheral edema, and that the MET inhibitors can be continued by switching these drugs.
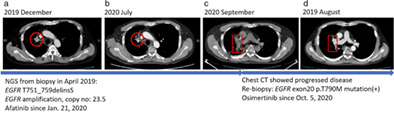
Afatinib and osimertinib in lung adenocarcinoma harbored EGFR T751_I759delinsS mutation: A case report
- Pages: 3429-3432
- First Published: 02 November 2021
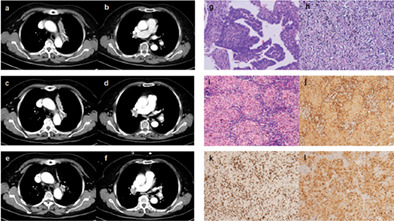
Sarcoidosis-like reaction after neoadjuvant pembrolizumab combined with chemotherapy mimicking disease progression of NSCLC induced encouraging discovery of pathological complete response
- Pages: 3433-3436
- First Published: 11 November 2021