Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
A “water”-based educational intervention to increase the public's utilization of low-dose computed tomography-based lung-cancer screening services
- Pages: 3083-3084
- First Published: 24 October 2021
COMMENTARY
Pembrolizumab provides long-term survival benefits in advanced non-small cell lung cancer: The 5-year outcomes of the KEYNOTE-024 trial
- Pages: 3085-3087
- First Published: 13 October 2021
REVIEW
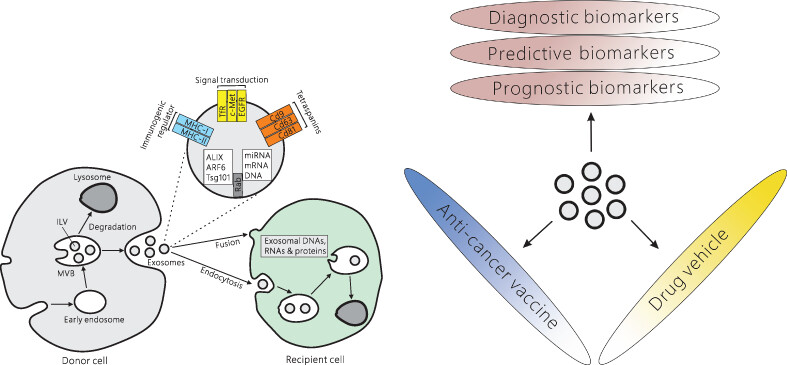
Formation, contents, functions of exosomes and their potential in lung cancer diagnostics and therapeutics
- Pages: 3088-3100
- First Published: 04 November 2021
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Value of pretreatment serum lactate dehydrogenase as a prognostic and predictive factor for small-cell lung cancer patients treated with first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy
- Pages: 3101-3109
- First Published: 01 November 2021
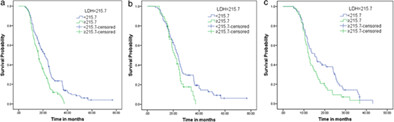
The current study aimed to evaluate the serum pretreatment lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and overall survival (OS) in small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) patients who received first-line platinum-containing chemotherapy. A total of 234 SCLC patients, who received first-line platinum-based chemotherapy between 2013 and 2018, were retrospectively analyzed. Age <65 years old, ECOG score <2 points, LD-SCLC, and pretreatment LDH <215.70 U/L are the positive independent prognostic factors for SCLC patients.
Development and validation of a prognostic nomogram for malignant esophageal fistula based on radiomics and clinical factors
- Pages: 3110-3120
- First Published: 14 October 2021
Trimodality therapy for esophageal cancer: The role of surgical and radiation treatment parameters in the development of anastomotic complications
- Pages: 3121-3129
- First Published: 15 October 2021
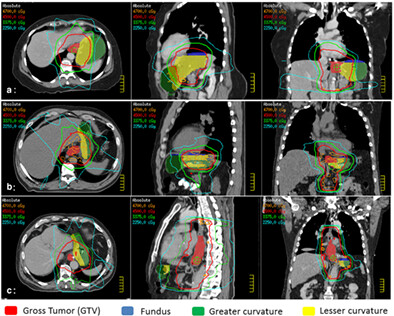
In trimodality therapy for esophageal cancer, radiation dose to any individual gastric substructure was not associated with anastomotic complications but anastomotic location (cervical vs. thoracic) is more closely associated with whether patients will experience anastomotic complications than neoadjuvant radiation treatment parameters. These data support the safety of neoadjuvant chemoradiation prior to esophagectomy for patients with esophageal cancers.
Predictive value of a novel Asian lung cancer screening nomogram based on artificial intelligence and epidemiological characteristics
- Pages: 3130-3140
- First Published: 28 October 2021

A novel AI model was developed for LDCT detection specifically. Our study showed that epidemiological characteristics should be considered in lung cancer screening, which can significantly improve the efficiency of AI model alone. We combined the CNN model score with Asian lung cancer epidemiological characteristics to develop a new Nomogram to facilitate and accurately perform individualized lung cancer screening, especially for Asians.
Pathological high malignant grade is higher risk of recurrence in pN0M0 invasive lung adenocarcinoma, even with small invasive size
- Pages: 3141-3149
- First Published: 12 October 2021

Invasive tumor size and pathological malignant grade overlap in invasive adenocarcinoma. Distribution of the 576 patients according to invasive tumor size and pathological malignant grading. A total of 563 patients (surrounded by red squares) were evaluated (a). Bar graph indicating the percentage of each pathological grade according to invasive tumor size (b).
A cross-sectional study of psychological burden in Chinese patients with pulmonary nodules: Prevalence and impact on the management of nodules
- Pages: 3150-3156
- First Published: 15 October 2021

Almost one fifth of the patients with pulmonary nodules (PNs) screened positive for anxiety. Patients with positive HADS anxiety screening results were more likely to adopt more aggressive PN management which meant higher rates of benign or precursor disease resected and/or more radiation absorbed. This study alerts clinicians to the need to assess and possibly treat emotional responses after PN detection.
Value and significance of brain radiation therapy during first-line EGFR-TKI treatment in lung adenocarcinoma with EGFR sensitive mutation and synchronous brain metastasis: Appropriate timing and technique
- Pages: 3157-3168
- First Published: 14 October 2021
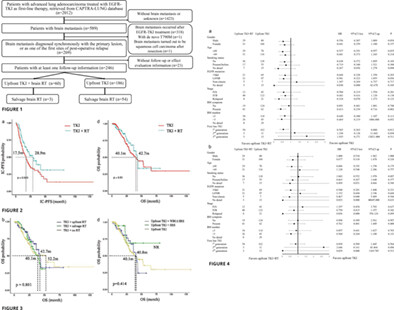
To our best knowledge, this is the most extensive multicenter real-world study (Fig.1) on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutant lung adenocarcinoma with synchronous brain metastasis (BM) and treated with first-line EGFR targeting tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI). On the basis of first-line EGFR-TKI therapy, additional upfront brain radiation therapy (RT) could improve intracranial progression free survival (PFS) (Fig.2a), particularly for patients with BM symptom and 1st-generation EGFR-TKI (Fig.4a). With no OS improvement (Fig.2d, Fig.3b, Fig.4b), upfront whole-brain irradiation could be deferred during the first-line EGFR-TKI treatment; however, upfront brain stereotactic radio-surgery (SRS) might have potential OS benefit (Fig.3d).
Thoracic mesenchymal malignant tumors and programed cell death ligand-1 status: Clinicopathologic and prognostic analysis of eight pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas and eight malignant mesotheliomas
- Pages: 3169-3176
- First Published: 15 October 2021
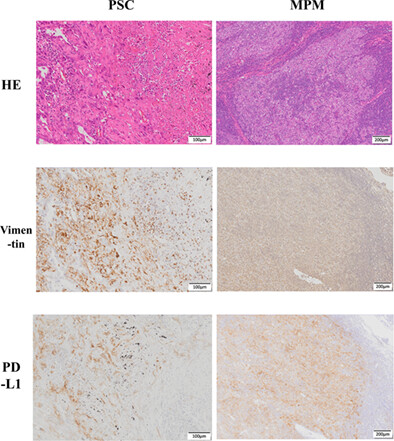
In malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM) and pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma (PSC), which are thoracic mesenchymal malignant tumors, programed cell death ligand-1 (PD-L1) was positive in the vimentin-positive part or the sarcomatoid area, found to be clinicopathologically significant. In MPM, the effectiveness of immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) has been shown, especially in nonepithelioid type. Our results support the possibility that ICIs will work as well as MPM if PSC is also positive for PD-L1 and has mesenchymal features such as vimentin-positive or sarcomatoid compartments.
Response and safety of whole-brain radiotherapy plus temozolomide for patients with brain metastases of non-small-cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 3177-3183
- First Published: 26 October 2021
Hexokinases II-mediated glycolysis governs susceptibility to crizotinib in ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3184-3193
- First Published: 02 November 2021
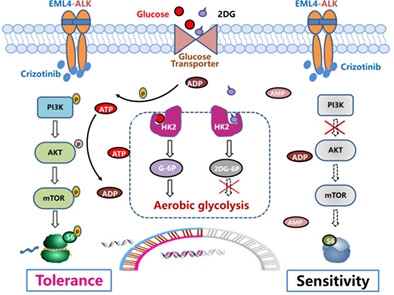
This study found that ALK+ NSCLC cells have higher glycolysis levels than ALK− NSCLC Cells. HK2 plays a crux role in the high level of glycolysis and HK2-mediated aerobic glycolysis probably governs susceptibility to crizotinib in ALK+ NSCLC cells. Glycolysis inhibitor 2DG sensitizes ALK+ NSCLC cells to crizotinib by inhibiting HK2-mediated glycolysis and P-ALK/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway.
MGMT gene promoter methylation in humoral tissue as biomarker for lung cancer diagnosis: An update meta-analysis
- Pages: 3194-3200
- First Published: 15 October 2021
Diagnostic performance of dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging for breast cancer detection: An update meta-analysis
- Pages: 3201-3207
- First Published: 20 October 2021
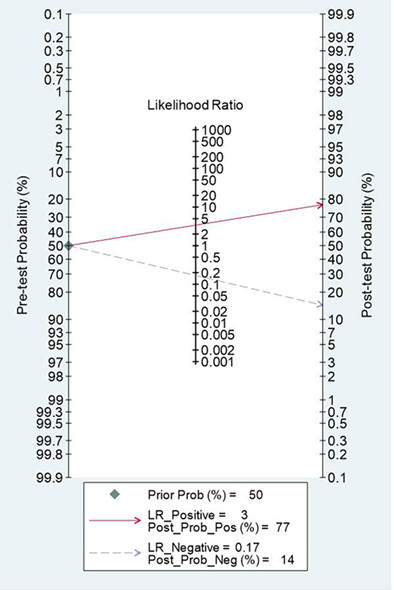
Likelihood ratio and post-test probability are important indexes of diagnostic tests. In our meta-analysis, both the positive and negative likelihood ratio and post-test probability were moderate. Given a pretest probability of 50%, the positive post-test probability is 77% and the negative post-test probability is 14%.
Endostar (rh-endostatin) improves efficacy of concurrent chemoradiotherapy for locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 3208-3215
- First Published: 21 October 2021
In our meta-analysis of 716 patients, endostar combined with CCRT significantly improved ORR and DCR compared with CCRT. Endostar combination treatments had similar incidences of main adverse events compared with CCRT (p > 0.05). Therefore, we concluded that endostar combined with CCRT is associated with significantly higher ORR and DCR than CCRT with similar incidences of main adverse events in NSCLC.
Synchronous microwave ablation followed by core-needle biopsy via a coaxial cannula for highly suspected malignant lung ground-glass opacities: A single-center, single-arm retrospective study
- Pages: 3216-3222
- First Published: 20 October 2021
Circ_0016760 accelerates non-small-cell lung cancer progression through miR-646/AKT3 signaling in vivo and in vitro
- Pages: 3223-3235
- First Published: 17 October 2021
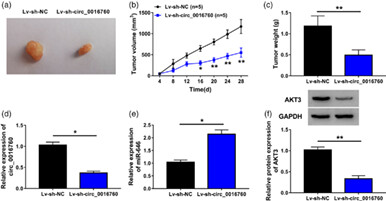
Circ_0016760 silencing blocks NSCLC progression in vivo. BALB/c mice were arbitrarily divided into two groups (n = 5). A total of 2.7 × 106 A549 cells stably expressing Lv-sh-NC or Lv-sh-circ_0016760 were subcutaneously injected into the mice. (A) The representative images of tumors in the Lv-sh-NC group and the Lv-sh-circ_0016760 group are shown. (B) Tumor volume was recorded every 4 days as length × width2 × 0.5. (C) Tumors were weighed after 28-day inoculation. (D and E) The expression of circ_0016760 and miR-646 was determined by qRT-PCR. (F) Western blot assay was implemented to measure the protein level of AKT3 in tumor tissues. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.
Identification and validation of an individualized prognostic signature of lung squamous cell carcinoma based on ferroptosis-related genes
- Pages: 3236-3247
- First Published: 20 October 2021
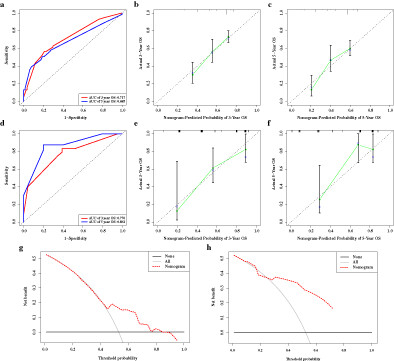
We developed a nomogram to predict the overall survival of lung squamous cell carcinoma patients using the risk score calculated from the ferroptosis-related gene-based signature and the T stage. The nomogram showed satisfactory discrimination power, calibration, and clinical usefulness in both the TCGA and GEO cohort.
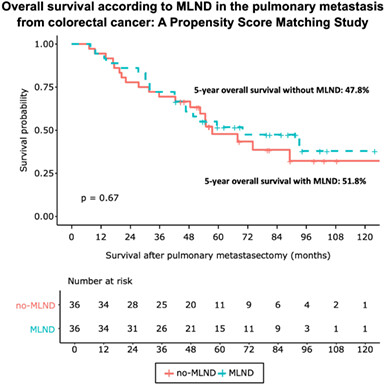
Effects of mediastinal lymph node dissection in colorectal cancer-related pulmonary metastasectomy
- Pages: 3248-3254
- First Published: 30 October 2021
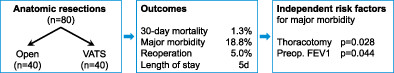
Risk factors for surgical complications after anatomic lung resections in the era of VATS and ERAS
- Pages: 3255-3262
- First Published: 24 October 2021
Comparing survival and treatment response of patients with acquired T790M mutation second-line osimertinib versus sequential treatment of chemotherapy followed by osimertinib: A real-world study
- Pages: 3263-3272
- First Published: 26 October 2021
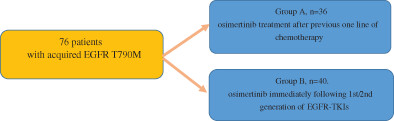
Osimertinib treatment after one line of chemotherapy (group A) had a better response rate and a better PFS than osimertinib treatment immediately following treatment with first/second generation EGFR-TKIs (group B). COPD tended to a poor prognostic factor for PFS and OS2 in patients with osimertinib use.
CASE REPORTS
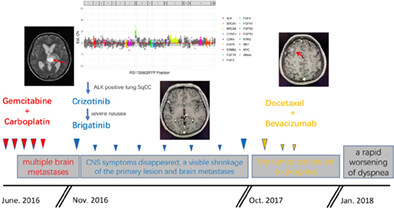
Brigatinib treated ALK positive lung squamous cell carcinoma after failed chemotherapy: A case report
- Pages: 3273-3276
- First Published: 13 October 2021
Ureteral metastasis from pulmonary adenocarcinoma: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 3277-3280
- First Published: 20 October 2021
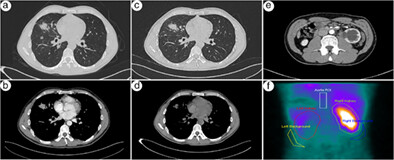
A patient with lumbago and left hydronephrosis was diagnosed with left ureteral metastasis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma after a CT-guided percutaneous transthoracic needle biopsy of the lung and retroperitoneal laparoscopic left nephroureterectomy. Although rare, our case has demonstrated that pulmonary adenocarcinoma has the possibility of metastasizing to the ureter, a risk that should be considered in some lung cancer patients.
Diagnostic utility of transbronchial biopsy for Hodgkin's lymphoma: A case study
- Pages: 3281-3285
- First Published: 25 October 2021
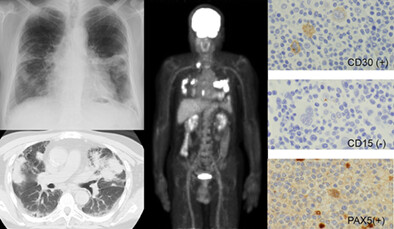
Here, we report a case of undiagnosed HL with lung lesions despite multiple TBBs. Our literature review indicated that the diagnostic success rate of TBB was low (18.5%) in cases of lung lesions in HL. Surgical biopsy should be considered early to avoid a delay in diagnosis because the diagnostic ability of TBB for HL patients with lung lesions is limited.
Successful treatment of locally advanced lung cancer using late concurrent chemoradiation therapy administered after immune checkpoint inhibitor plus platinum chemotherapy
- Pages: 3286-3289
- First Published: 24 October 2021