Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARY
Surgery at the frontline at the time of the COVID-19 outbreak
- Pages: 3057-3059
- First Published: 16 September 2020
MINI REVIEW
Expression and role of p16 and GLUT1 in malignant diseases and lung cancer: A review
- Pages: 3060-3070
- First Published: 18 September 2020

This review highlights the role of p16 and GLUT-1 and GLUTs proteins in malignancies especially in lung cancer, focusing on the pathways activated leading to cell cycle dysregulation, cancer growth and migration. Since they have a clinical prognostic value, they may become targets for novel therapies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
HOXB7 mediates cisplatin resistance in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through involvement of DNA damage repair
- Pages: 3071-3085
- First Published: 30 September 2019
Prognostic and clinicopathological roles of programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) expression in thymic epithelial tumors: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 3086-3098
- First Published: 14 September 2020
Three dimensional texture analysis of noncontrast chest CT in differentiating solitary solid lung squamous cell carcinoma from adenocarcinoma and correlation to immunohistochemical markers
- Pages: 3099-3106
- First Published: 18 September 2020
Male breast cancer: A closer look at patient and tumor characteristics and factors associated with survival
- Pages: 3107-3116
- First Published: 15 September 2020
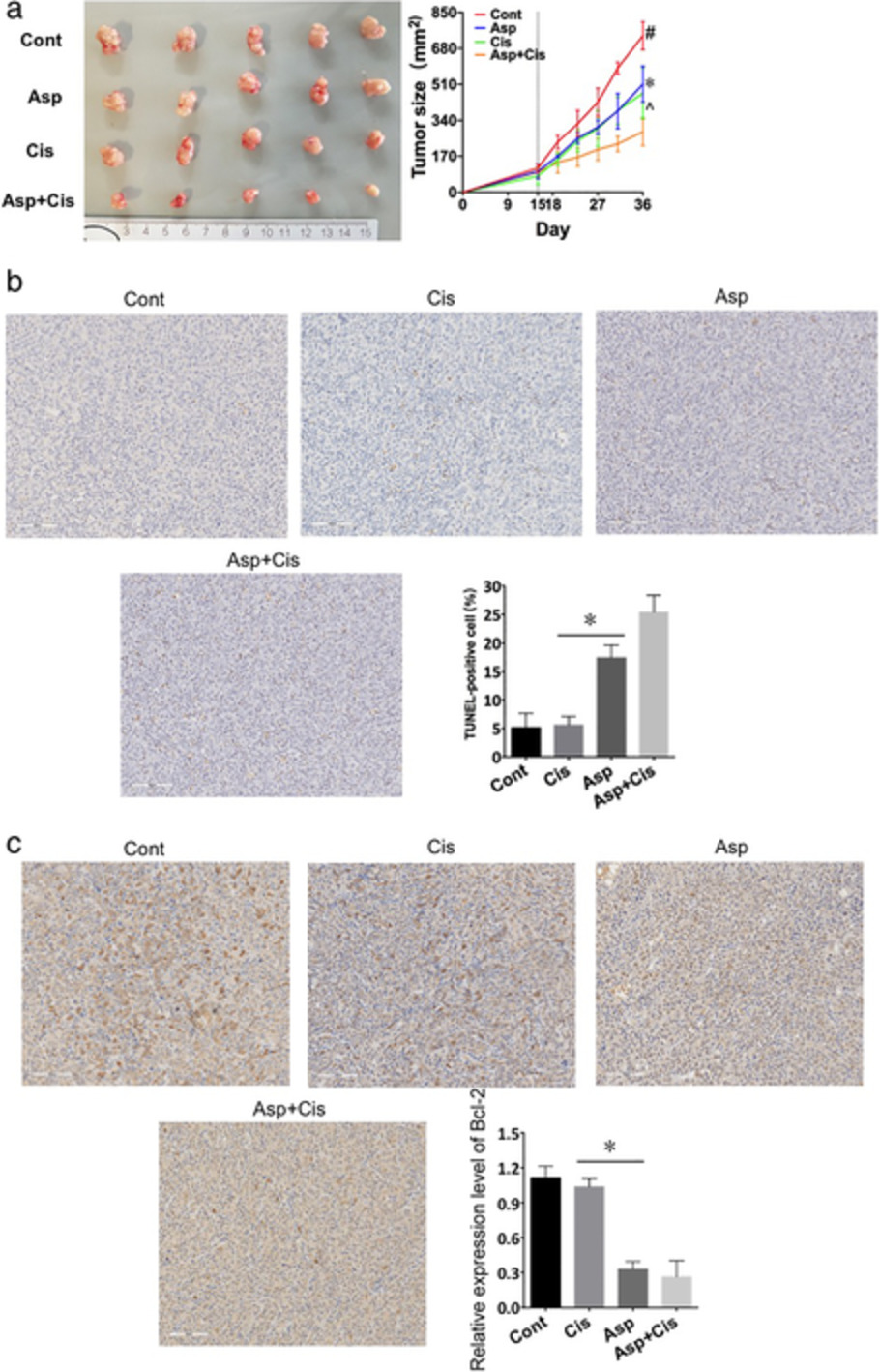
Aspirin overcomes cisplatin resistance in lung cancer by inhibiting cancer cell stemness
- Pages: 3117-3125
- First Published: 29 September 2020
MiR-429 suppresses proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
- Pages: 3126-3138
- First Published: 22 September 2020
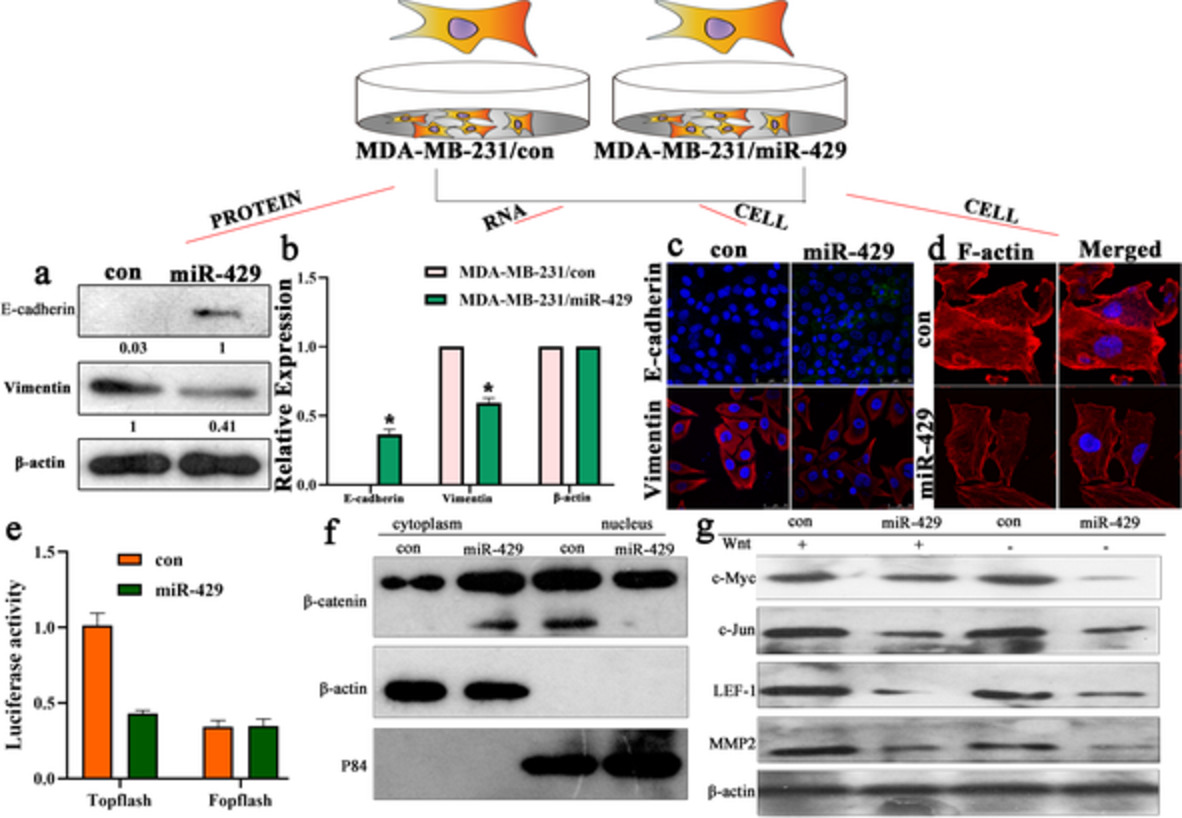
We report that increasing lines of evidence indicate the role of miRNAs in gene regulation in relation to tumor development. The aim of this study was to elucidate the undefined function and mechanism of miR-429 in the proliferation, metastasis, and invasion in breast cancer. Overexpression of miR-429 contributed to a notable impairment of proliferation, invasion, and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in vitro. miR-429 suppressed proliferation and invasion of breast cancer via inhibiting the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway.
Impacts of post-radiotherapy lymphocyte count on progression-free and overall survival in patients with stage III lung cancer
- Pages: 3139-3144
- First Published: 21 September 2020
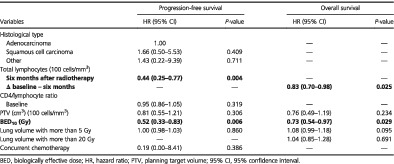
Radiation therapy is an essential local treatment for locally advanced lung cancer; however, the large fields of irradiation may have collateral effects. We revealed that lymphocyte counts decrease for a long time after irradiation, worsening OS and PFS. The other important issue is that low lymphocyte counts may affect the potential of immunotherapy. Immunotherapy at different time points and use of smaller radiation fields with high doses may be key issues for the future of lung cancer treatment.
Spread through air spaces (STAS) in invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma of the lung: Incidence, prognostic impact, and prediction based on clinicoradiologic factors
- Pages: 3145-3154
- First Published: 25 September 2020
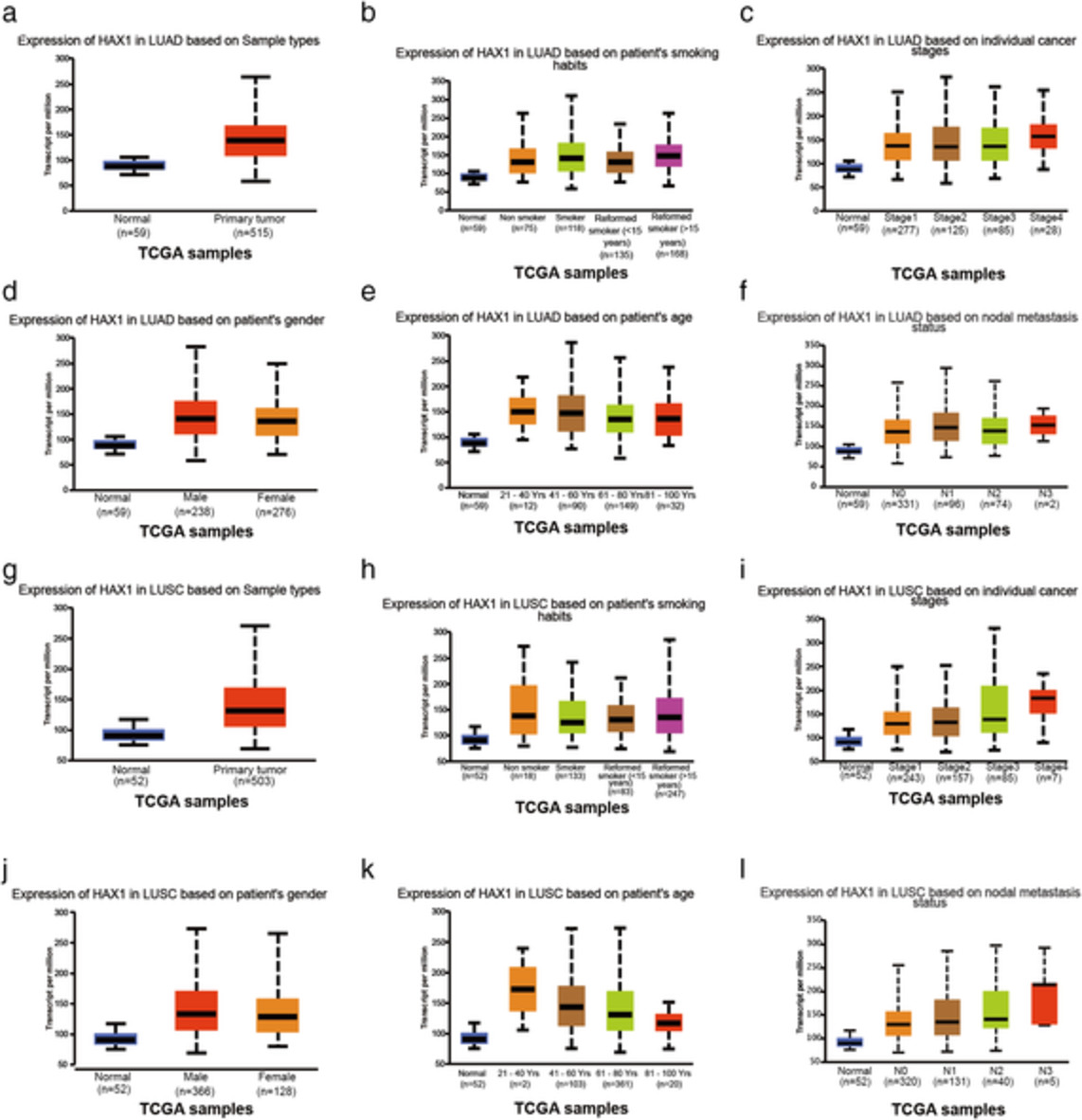
HAX1 enhances the survival and metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer through the AKT/mTOR and MDM2/p53 signaling pathway
- Pages: 3155-3167
- First Published: 14 September 2020
Matrix metalloproteinase-14 (MMP-14) downregulation inhibits esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cell migration, invasion, and proliferation
- Pages: 3168-3174
- First Published: 15 September 2020
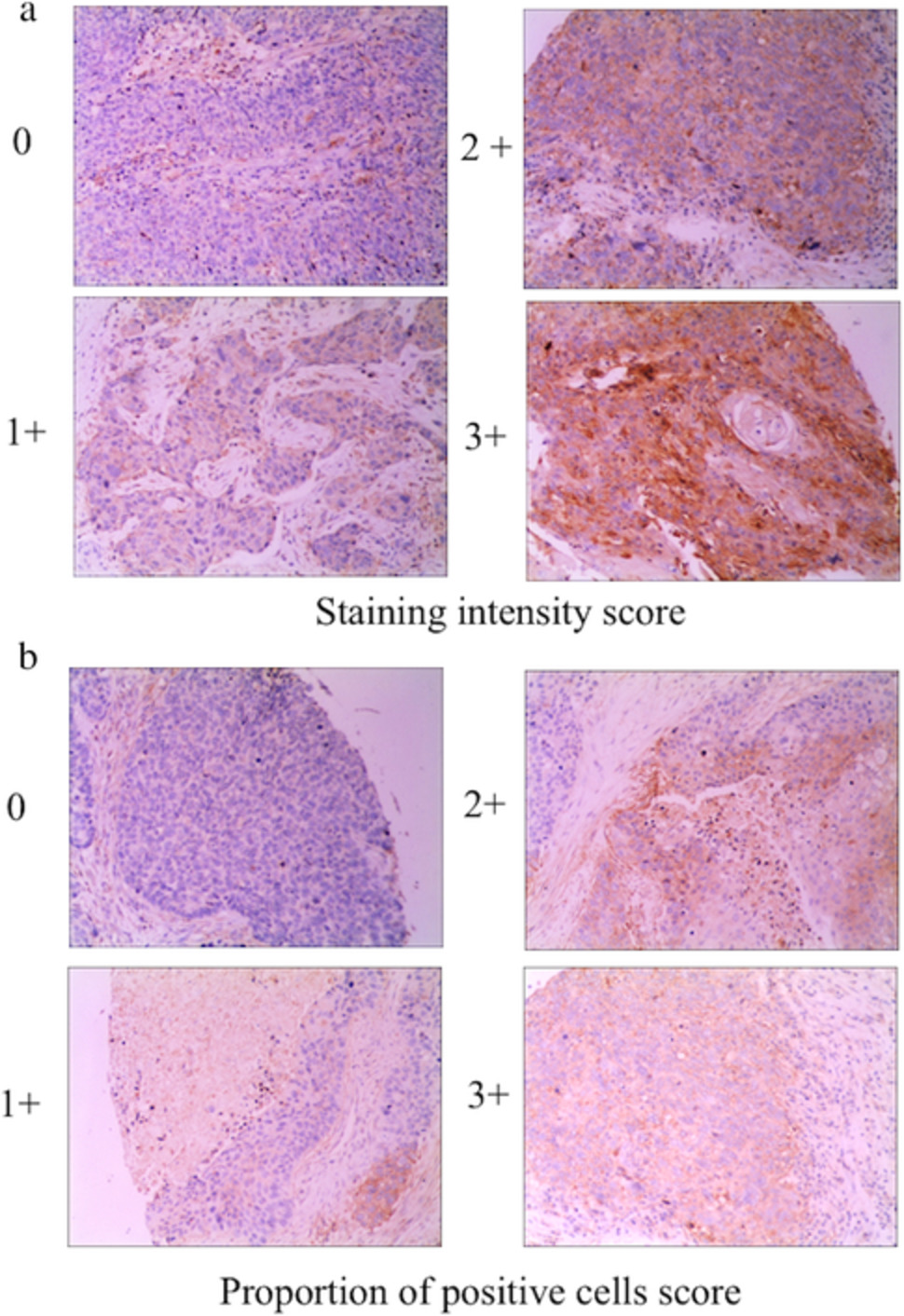
The results of this study indicate that MMP-14 upregulation commonly occurs in human ESCC and is correlated with to tumor T classification, N classification, degree of differentiation, and clinical stage of ESCC patients. MMP-14 knockdown can additionally compromise the proliferative and invasive activity of these tumor cells, suggesting that MMP-14 may be a viable therapeutic target for the treatment of ESCC, although further research will be needed to validate these findings. Furthermore, downregulation of the MMP-14 expression level decreased cell proliferation and invasion ability.
Human papillomavirus 16 (HPV 16) E6 but not E7 inhibits the antitumor activity of LKB1 in lung cancer cells by downregulating the expression of KIF7
- Pages: 3175-3180
- First Published: 18 September 2020
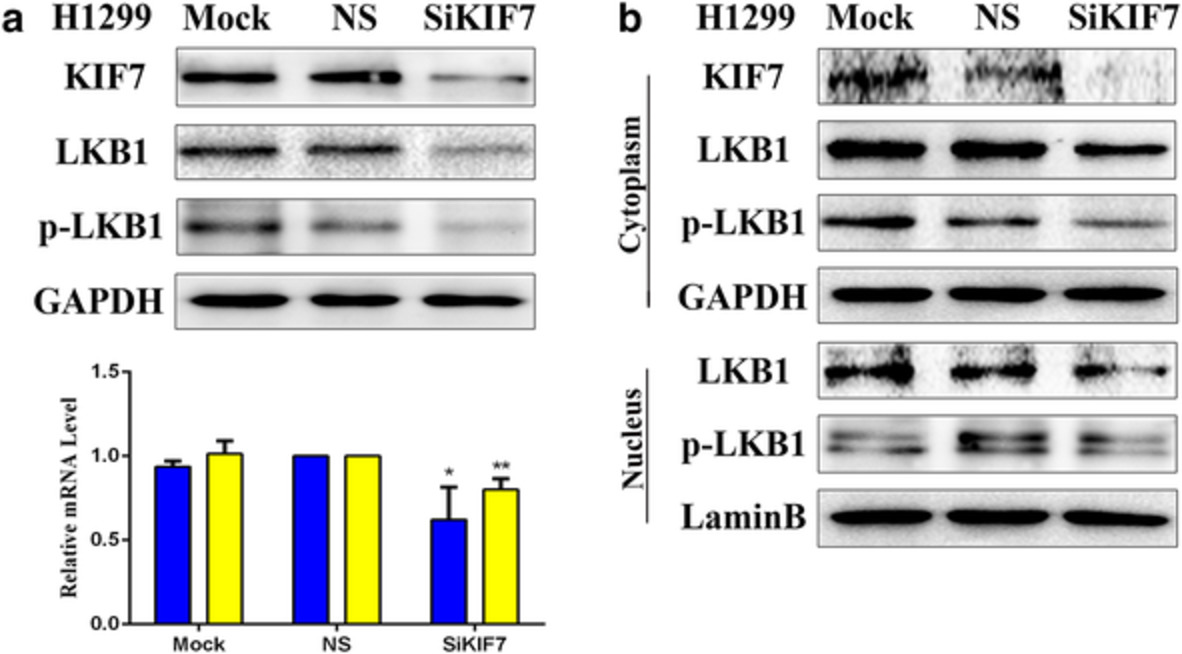
We demonstrated for the first time that E6 but not E7 inhibits the antitumor activity of LKB1 in lung cancer cells by downregulating the expression of KIF7 and the antitumor activity of LKB1 was determined by two factors, one was phosphorylation of LKB1, the other was that p-LKB1 must be located in the cytoplasm, both were indispensable.
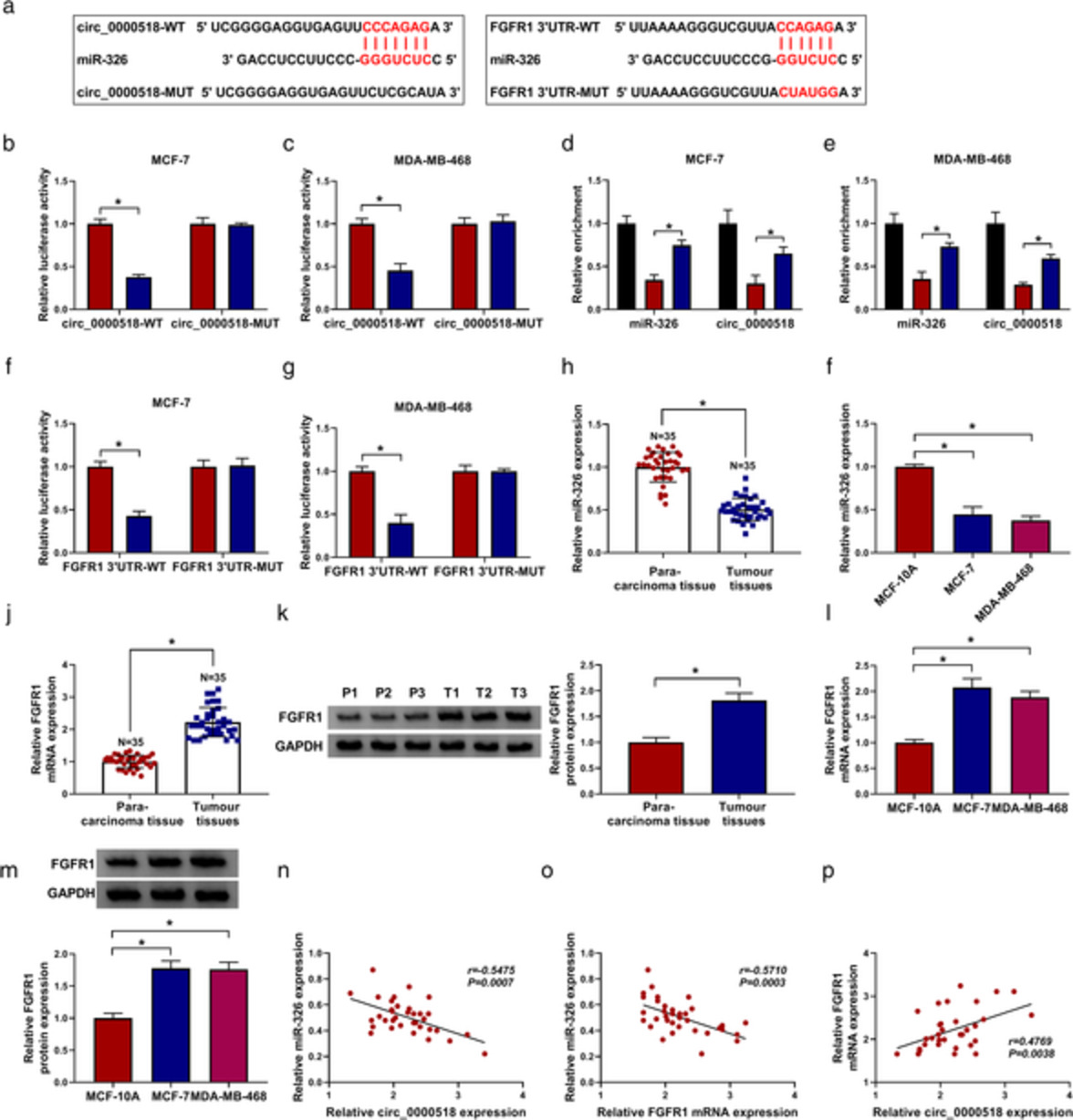
Hsa_circRNA_0000518 facilitates breast cancer development via regulation of the miR-326/FGFR1 axis
- Pages: 3181-3192
- First Published: 01 October 2020
Longitudinal analysis of complete blood count parameters in advanced-stage lung cancer patients
- Pages: 3193-3204
- First Published: 17 September 2020
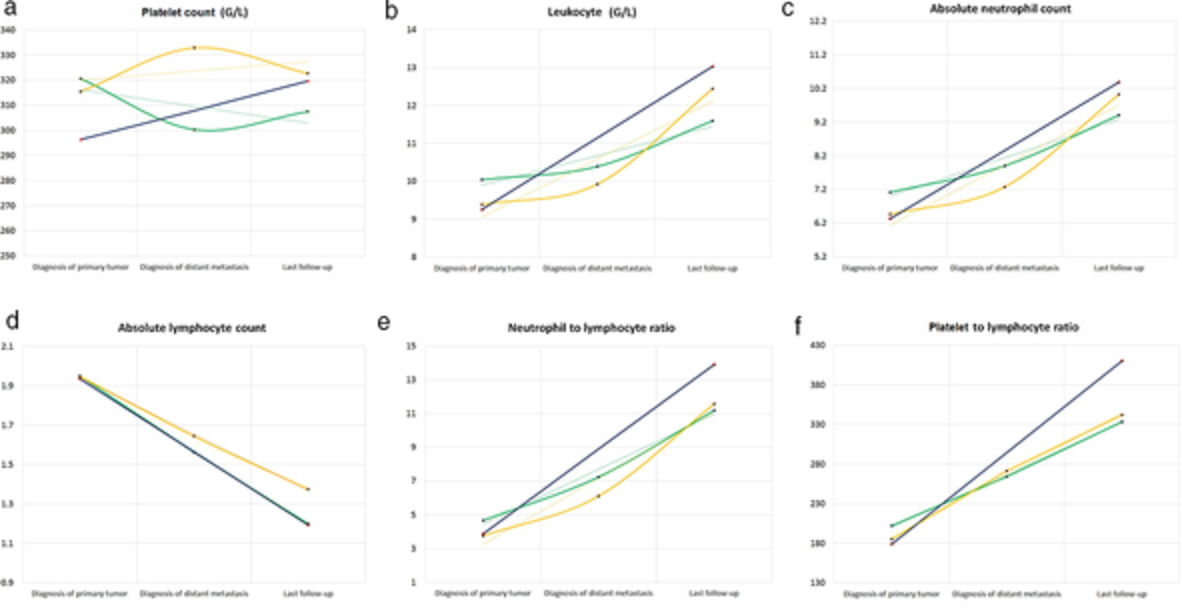
In our longitudinal analyses, we found significantly decreasing ALC, and significantly increasing ANC levels in advanced-stage lung cancer patients during disease progression. Interestingly, patients with brain metastases have descending-ascending PLT trendlines, while patients with bone metastases exhibit ascending-descending trendlines during disease progression. The current study might help to improve patient selection and treatment strategies for brain and bone metastatic lung cancer patients.
Clinicopathological characteristics of primary lung nuclear protein in testis carcinoma: A single-institute experience of 10 cases
- Pages: 3205-3212
- First Published: 03 October 2020
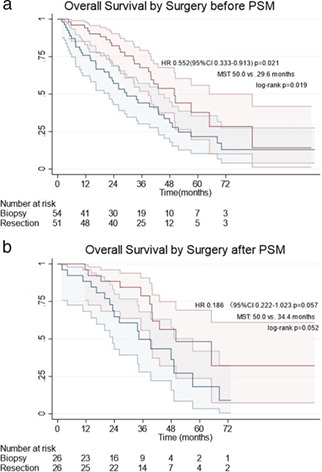
Primary tumor resection of non-small cell lung cancer patients with ipsilateral pleural dissemination (M1a) in the era of targeted therapy
- Pages: 3213-3222
- First Published: 18 September 2020
Serum immune modulators during the first cycle of anti-PD-1 antibody therapy in non-small cell lung cancer: Perforin as a biomarker
- Pages: 3223-3233
- First Published: 11 September 2020
Detection of circulating genetically abnormal cells in peripheral blood for early diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3234-3242
- First Published: 28 September 2020
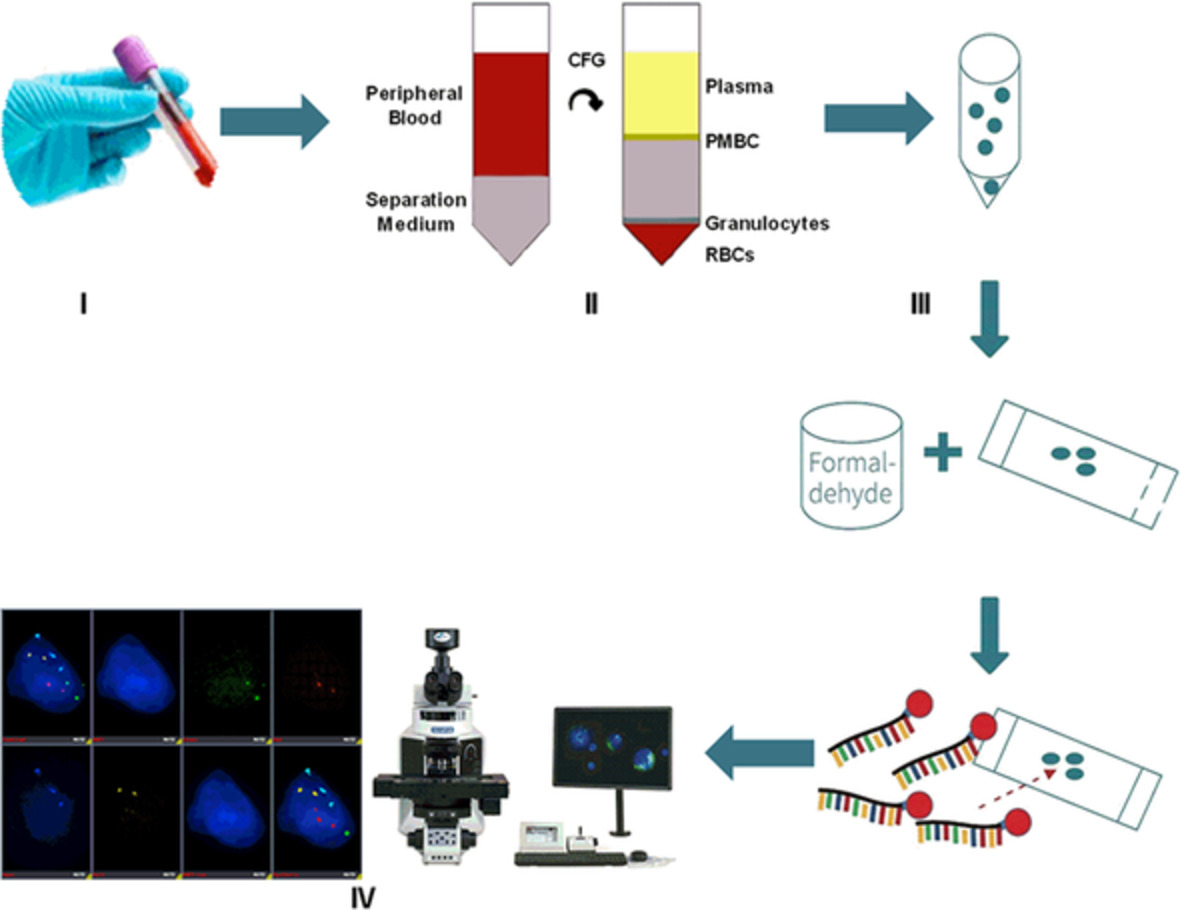
Workflow of circulating genetically abnormal cells enumeration.
Circulating genetically abnormal cell detection in early stage non-small-cell lung cancer was feasible.
Circulating genetically abnormal cell test has good stability and adaptability for different patient populations.
Circulating genetically abnormal cells could be used as a promising noninvasive biomarker for the early diagnosis of NSCLC.
Human skin biomarkers relationship to response to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors in advanced EGFR-mutated lung adenocarcinoma
- Pages: 3243-3251
- First Published: 05 October 2020

A total of 35 skin biopsies were obtained, of which 60% were female and 40% male, and the mean age of the participants was 60.6 ± 11.7 years. They were divided into three groups: pretreatment (12 patients: 34.3%); adequate response to treatment (12 patients: (34.3%); and no response to treatment (11 patients: 31.4%). We found that EGFR expression, STAT3, and the thickness of the stratum corneum (both in millimeters and in number of skin layers) had a statistically significant correlation with an adequate response to treatment with EGFR inhibitors in patients with stage IV lung adenocarcinoma. EGFR, p27 and the number of stratum corneum layers were related to better progression-free survival. The relationship between EGFR inhibition in skin and in the tumor explains the parallel biological effect.
Prognostic value of pretreatment smoking status for small cell lung cancer: A meta-analysis
- Pages: 3252-3259
- First Published: 22 September 2020
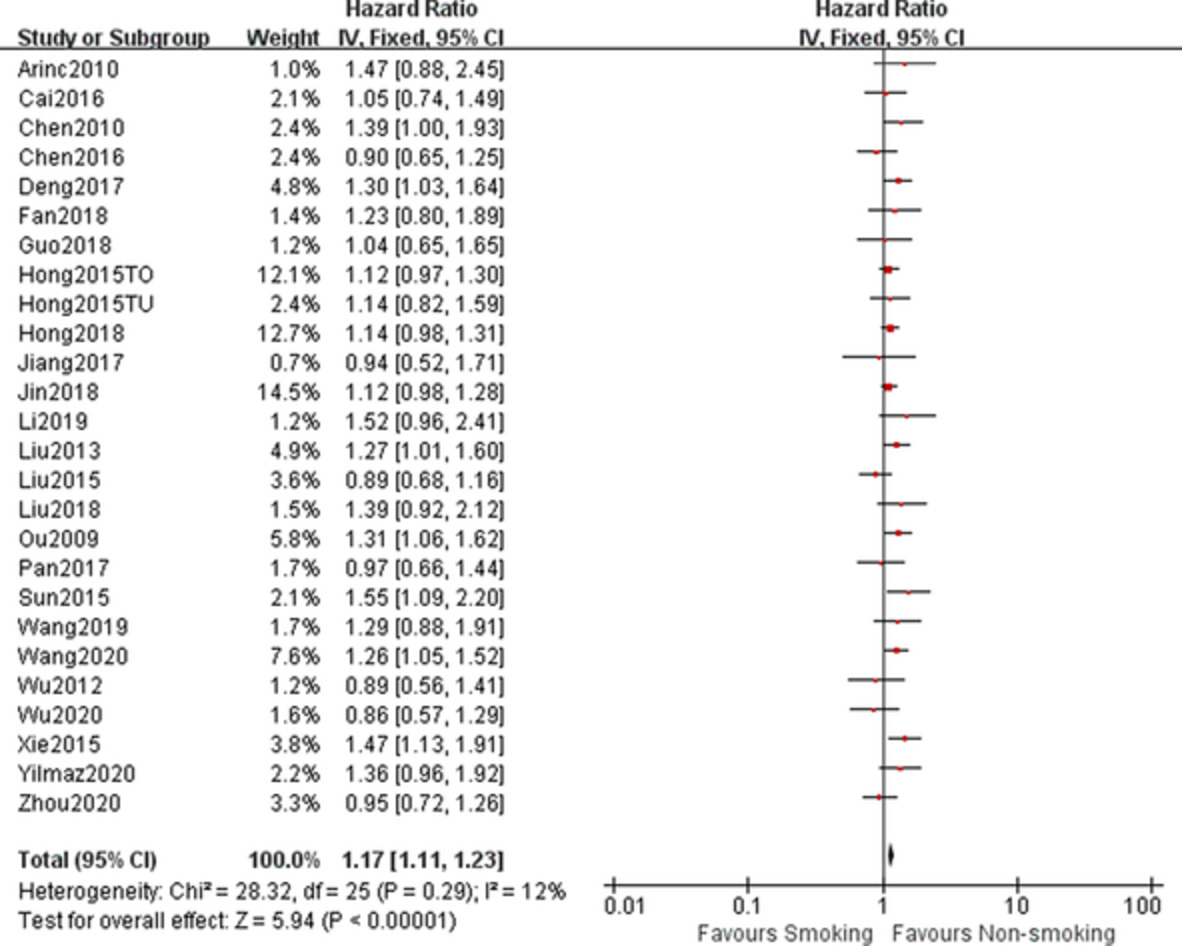
We conducted a meta-analysis of 27 studies involving 12047 patients to investigate the prognostic value of pretreatment smoking status for small cell lung cancer (SCLC), which demonstrated that smoking history was closely related to poorer survival outcome. Smoking history should be considered as an independent poor prognostic factor for patients with SCLC.
Predictive value of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography for PD-L1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Pages: 3260-3268
- First Published: 20 September 2020
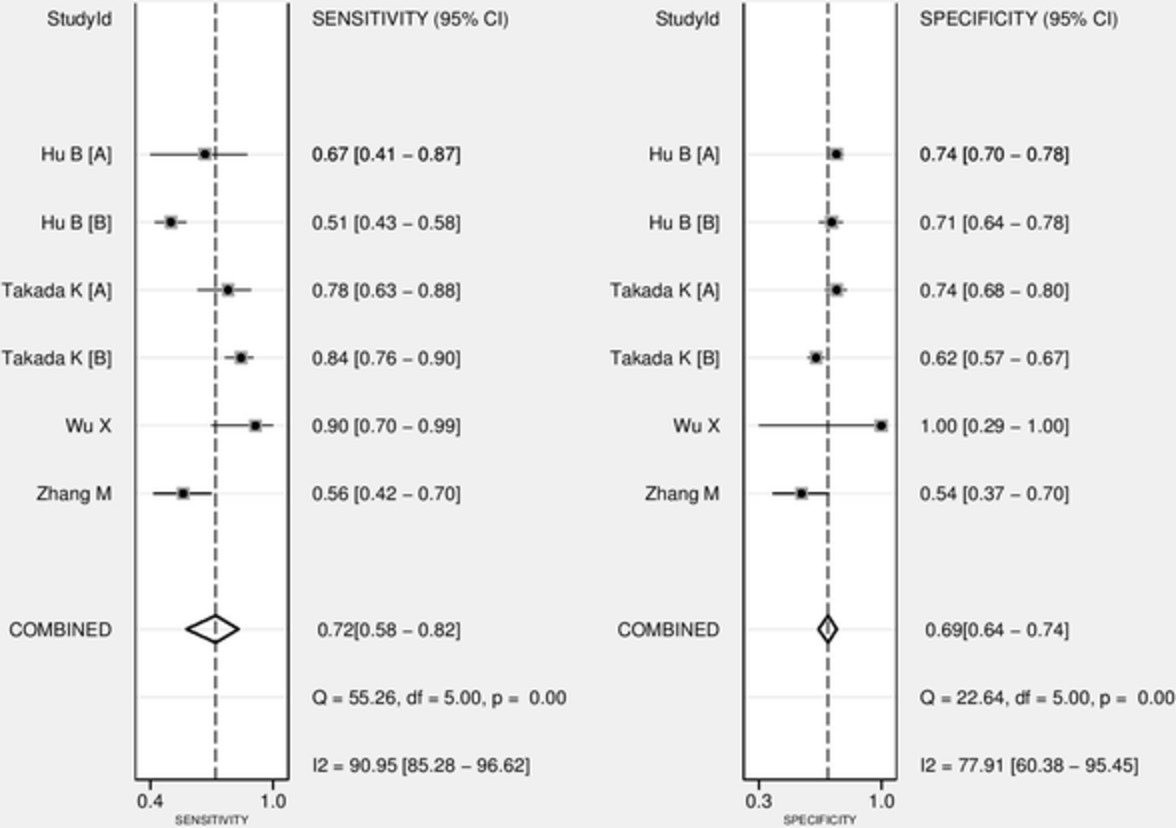
The current meta-analysis showed a moderate sensitivity and specificity of 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography/computed tomography (18F-FDG PET/CT) for the prediction of PD-L1 expression in NSCLC patients. The DOR was low and the likelihood ratio scattergram indicated that 18F-FDG PET/CT might not be useful for the prediction of PD-L1 expression in NSCLC patients or its exclusion. This study supports that the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT for predicting tumor expression of PD-L1 should be further elucidated.
Downregulation of m6A reader YTHDC2 promotes tumor progression and predicts poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3269-3279
- First Published: 21 September 2020
Characteristics of surgically resected non-small cell lung cancer patients with post-recurrence cure
- Pages: 3280-3288
- First Published: 22 September 2020
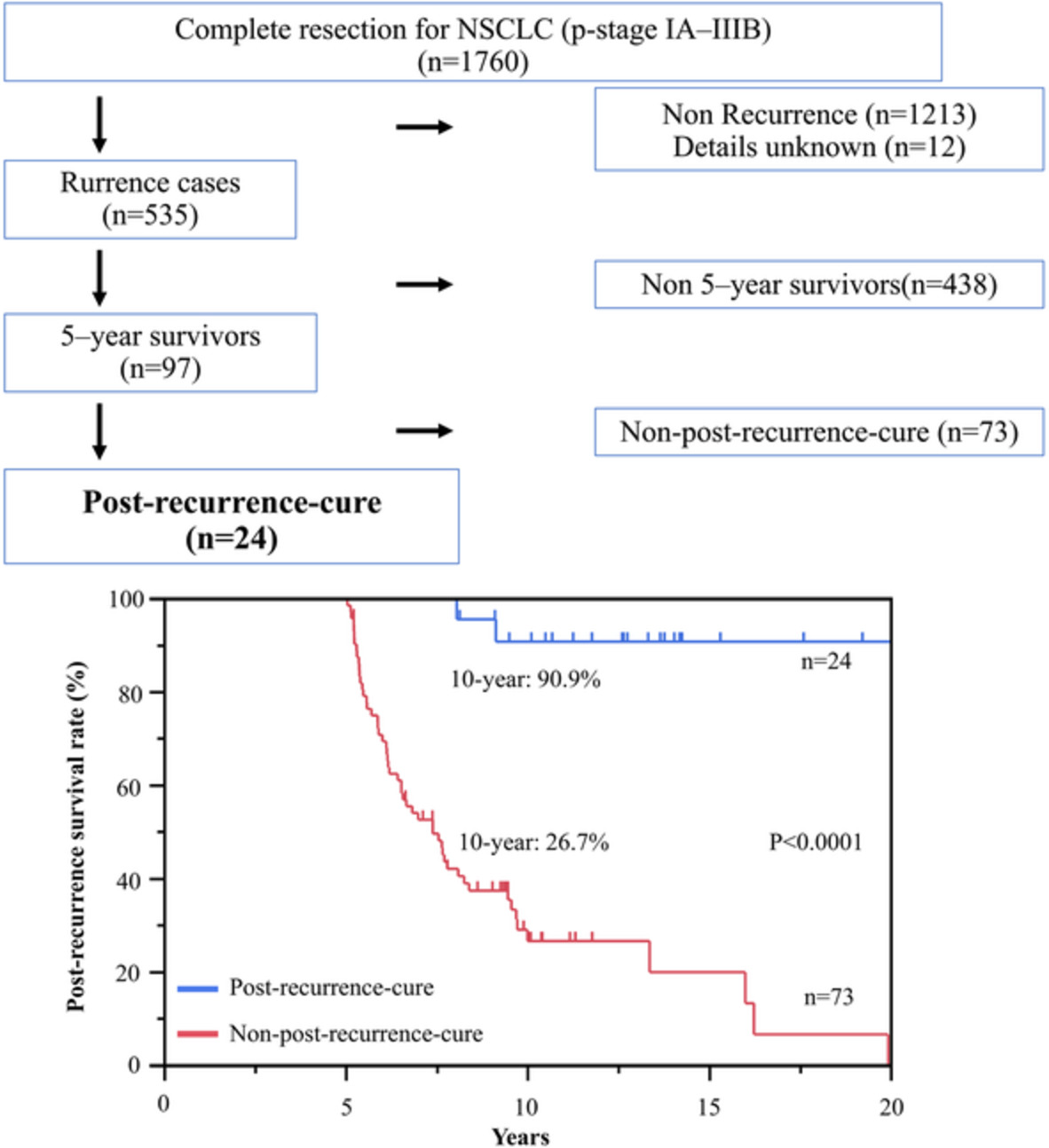
Among 535 patients who developed recurrence, 24 (4.5%) patients achieved post-recurrence cure. The post-recurrence cure patients who sustained cancer-free status for five years after treatment for recurrent lesions did not develop second recurrence. All post-recurrence cure patients received only local treatment, and the solitary recurrent lesions and local treatment at the initial recurrent sites were significantly associated with post-recurrence cure.
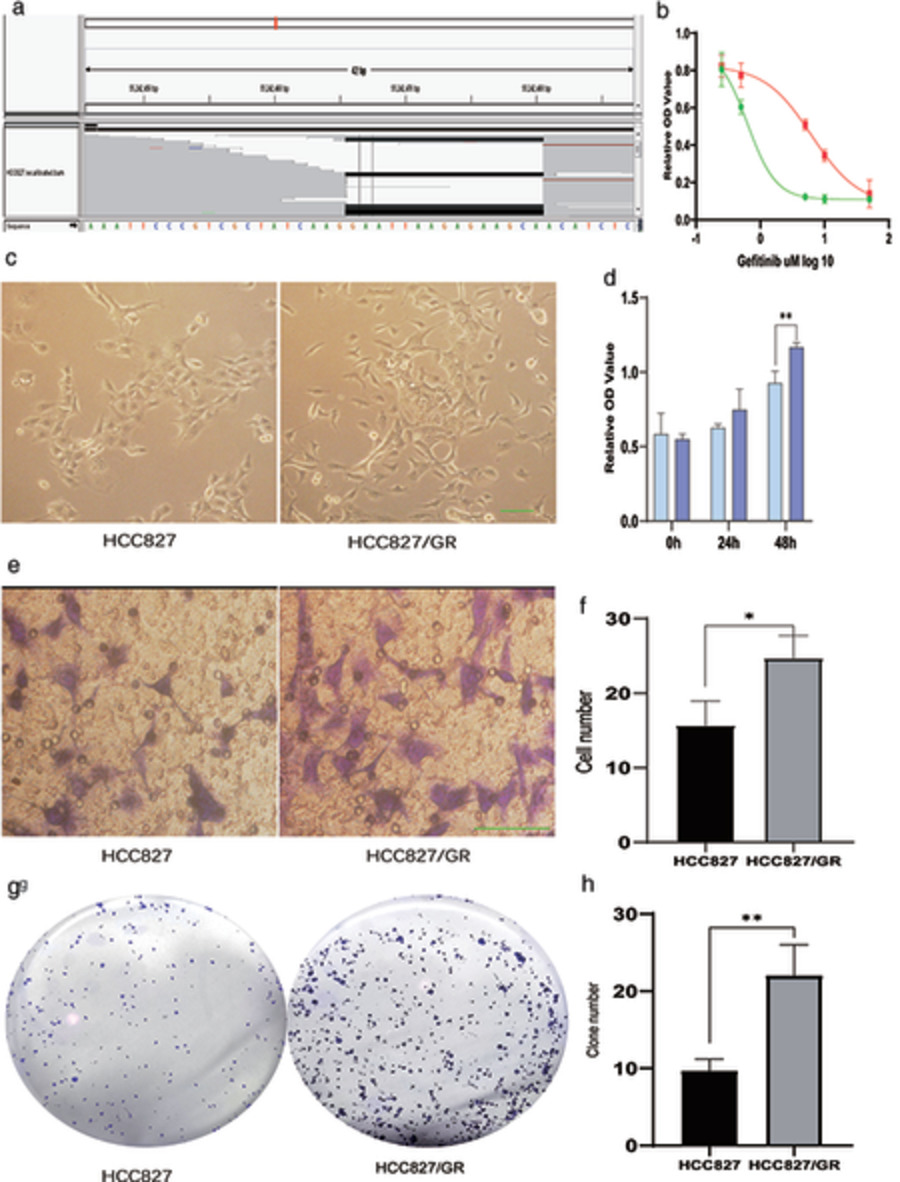
M2 macrophages reduce the effect of gefitinib by activating AKT/mTOR in gefitinib-resistant cell lines HCC827/GR
- Pages: 3289-3298
- First Published: 21 September 2020
GPX8 promotes migration and invasion by regulating epithelial characteristics in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3299-3308
- First Published: 25 September 2020
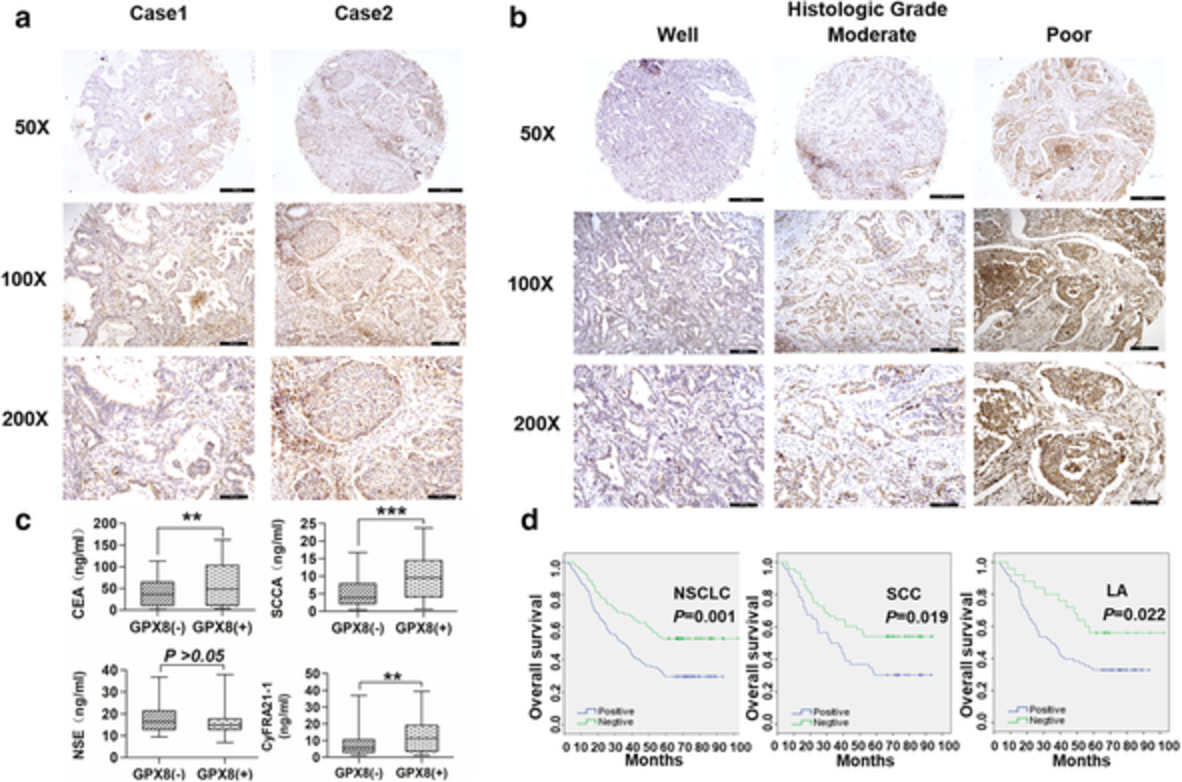
GPX8 is considered to play a crucial functional role in the GPX family, but few studies have shown the implications of GPX8 in cancer research, especially in lung cancer. In this study, we focus on exploring the function and clinical value of GPX8 in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). The results indicate that GPX8 could serve as a prognostic predictor and therapeutic target for NSCLC.
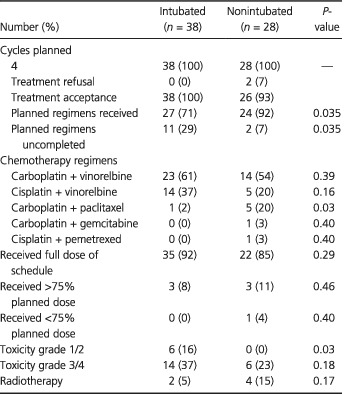
Oncological advantage of nonintubated thoracic surgery: Better compliance of adjuvant treatment after lung lobectomy
- Pages: 3309-3316
- First Published: 28 September 2020
Safety and effectiveness of pirfenidone combined with carboplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and non-small cell lung cancer: A retrospective cohort study
- Pages: 3317-3325
- First Published: 28 September 2020
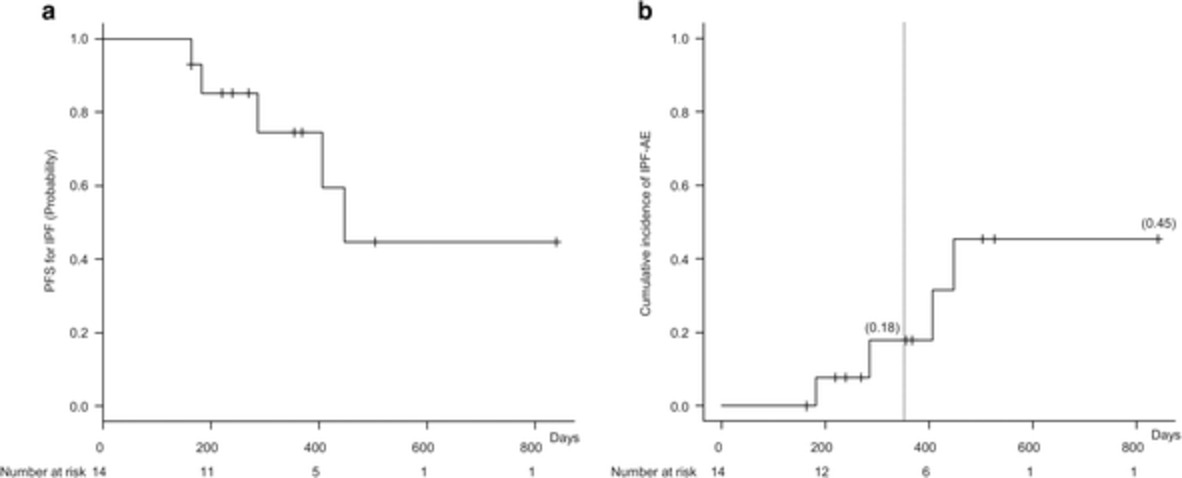
The safety and effectiveness of pirfenidone combined with cytotoxic agents or immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) have not been investigated. This study showed that pirfenidone combined with carboplatin-based chemotherapy or ICIs was safe for patients with IPF and NSCLC and did not induce acute exacerbations of IPF.
BCAR1 promotes proliferation and cell growth in lung adenocarcinoma via upregulation of POLR2A
- Pages: 3326-3336
- First Published: 01 October 2020
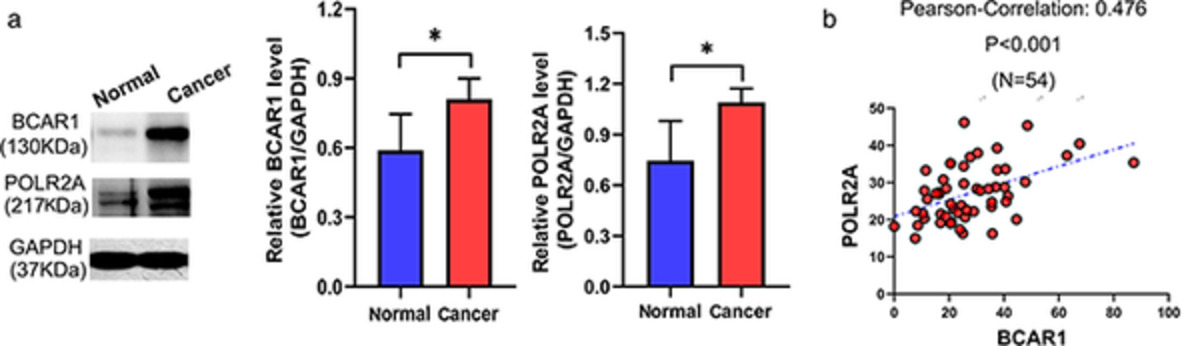
In this work, we elaborated the enhancement effect of a novel carcinogenetic molecule, ie, p130cas (breast cancer antiestrogen resistance 1, BCAR1) on proliferation and cell growth of lung cancer cells,and to explore the possible networks of interacting proteins of BCAR1. We found BCAR1 can promote proliferation and cell growth, probably via upregulation of POLR2A and subsequent enhancement of catalytic activity and transferase activity.
Efficacy of natural killer cell activity as a biomarker for predicting immunotherapy response in non-small cell lung cancer
- Pages: 3337-3345
- First Published: 05 October 2020
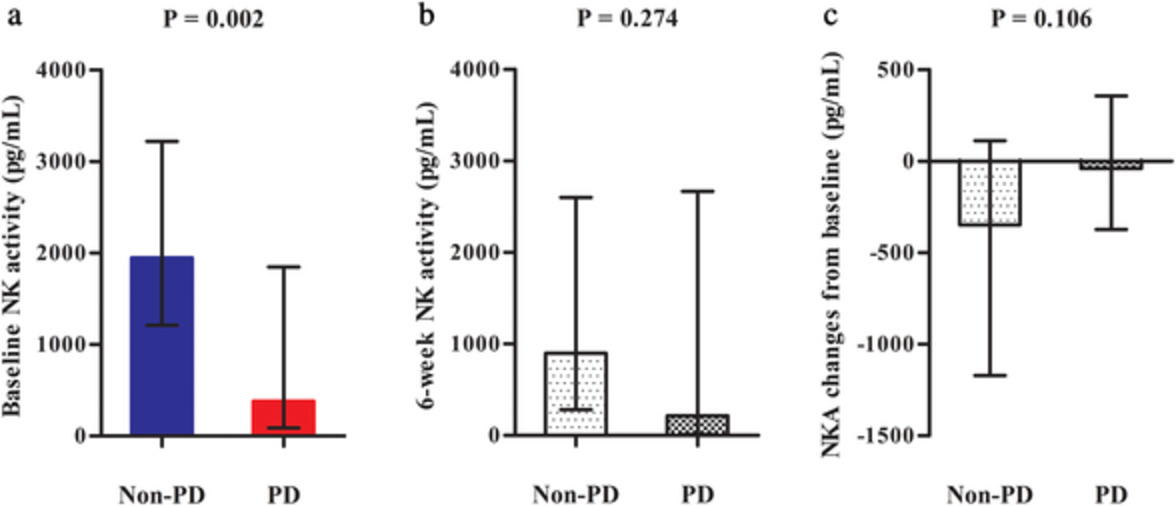
In this prospective observational study, patients with advanced NSCLC who were scheduled for immunotherapy from October 2018 to December 2019 were enrolled. The baseline NK cell activity was significantly higher in the non-PD group than in the PD group. NK cell activity from peripheral blood before immunotherapy is a non-invasive, simple, and novel way to predicting the treatment response in patients with NSCLC.
Real-life effectiveness of first-line anticancer treatments in stage IIIB/IV NSCLC patients: Data from the Czech TULUNG Registry
- Pages: 3346-3356
- First Published: 05 October 2020
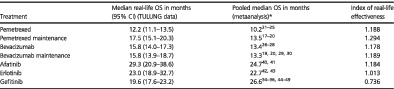
Comparison between our TULUNG data and pooled survival data from clinical trials showed higher real-life effectiveness for most of the studied first-line regimens. We found that lower ECOG PS, younger age, female sex and adverse events were associated with longer survival. We demonstrated that real-life effectiveness of certain treatments may strongly differ in various populations and health care systems.
Prognostic factors for survival in patients with metastatic lung adenocarcinoma: An analysis of the SEER database
- Pages: 3357-3364
- First Published: 28 September 2020
In this study we identified male sex, age = 65 years, lack of family support and liver and brain metastases as poor prognostic factors for overall survival (OS) in patients with stage IV lung ADC. The presence of liver metastases emerged as the worst prognostic factor. Consequently, it should be considered as a stratification factor for future studies evaluating new cancer treatments including immunotherapy.
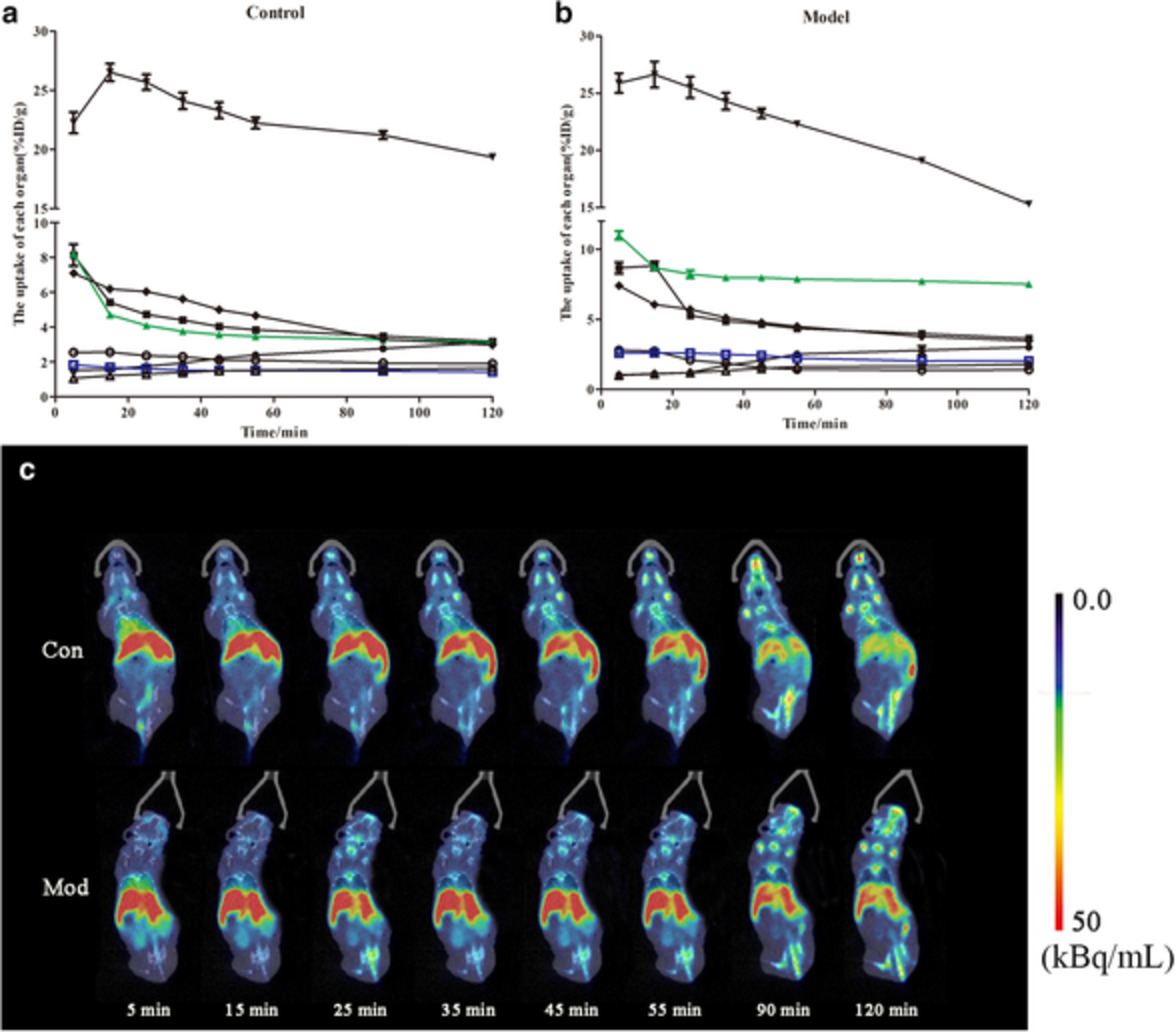
Biodistribution of andrographolide to assess the interior-exterior relationship between the lung and intestine using microPET
- Pages: 3365-3374
- First Published: 05 October 2020
CASE REPORTS
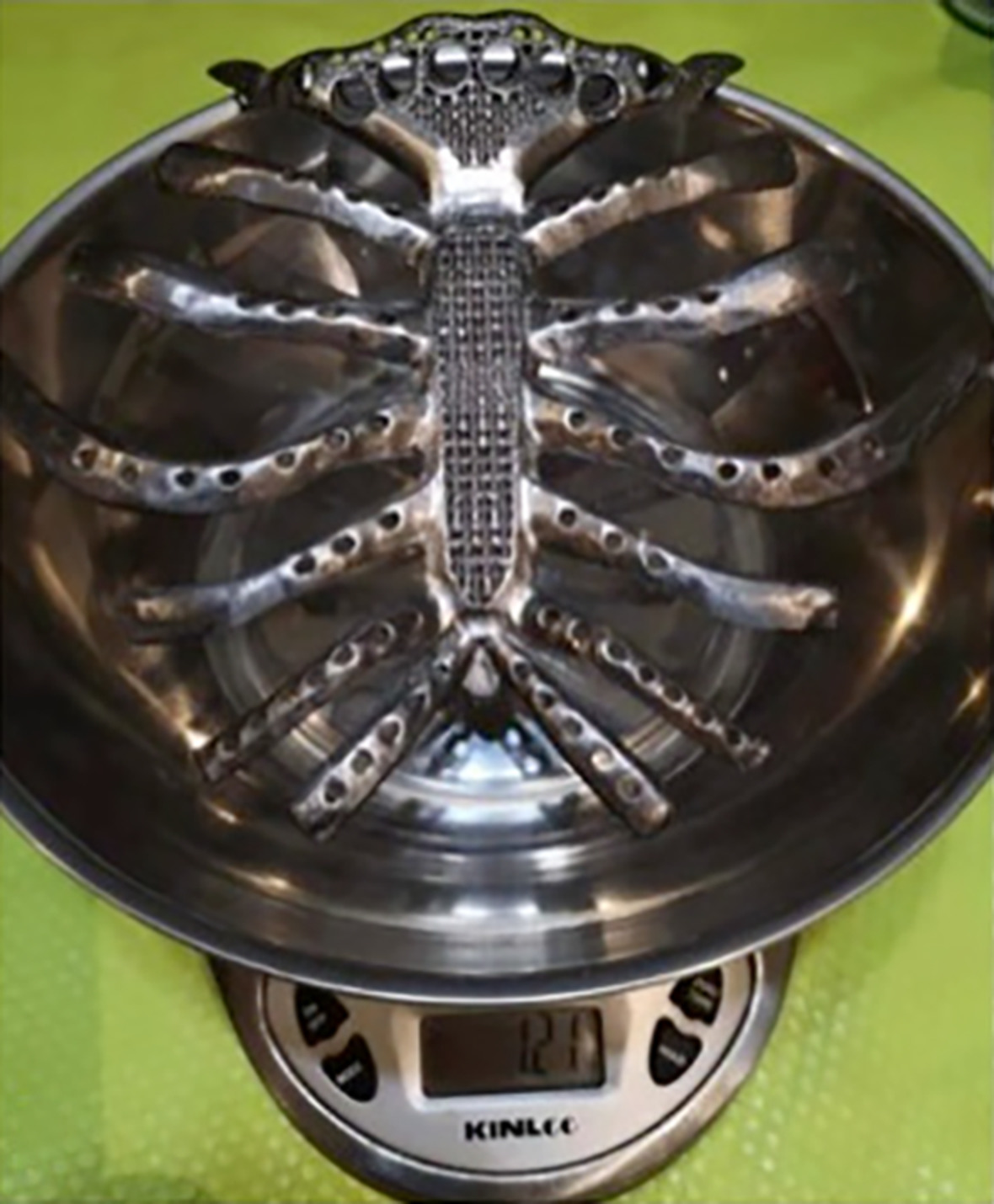
Three-dimensional (3D)-printed titanium sternum replacement: A case report
- Pages: 3375-3378
- First Published: 05 October 2020
Metastatic large cell carcinoma of the lung: A rare cause of acute small bowel obstruction
- Pages: 3379-3382
- First Published: 11 September 2020
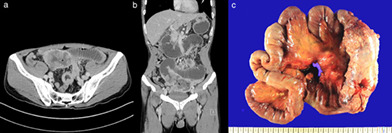
We report a case of acute intestinal obstruction as the initial presentation of primary lung cancer in a male patient. The patient underwent emergency surgery for multiple luminal malignancy with mesenteric masses, and immunohistochemical staining of the specimen revealed metastatic large cell carcinoma originating from the lung.
Durable efficacy of anlotinib in a patient with advanced thymic squamous cell carcinoma after multiline chemotherapy and apatinib: A case report and literature review
- Pages: 3383-3387
- First Published: 30 September 2020
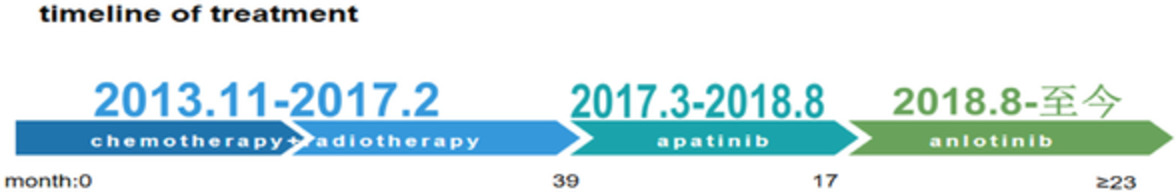
We present the case of a patient with an advanced TC harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion who successively benefited from two antiangiogenic agents after multiline therapy. After the failure of one tyrosine kinase inhibitor, the other was still active and effectively controlled the growth of the lesion.
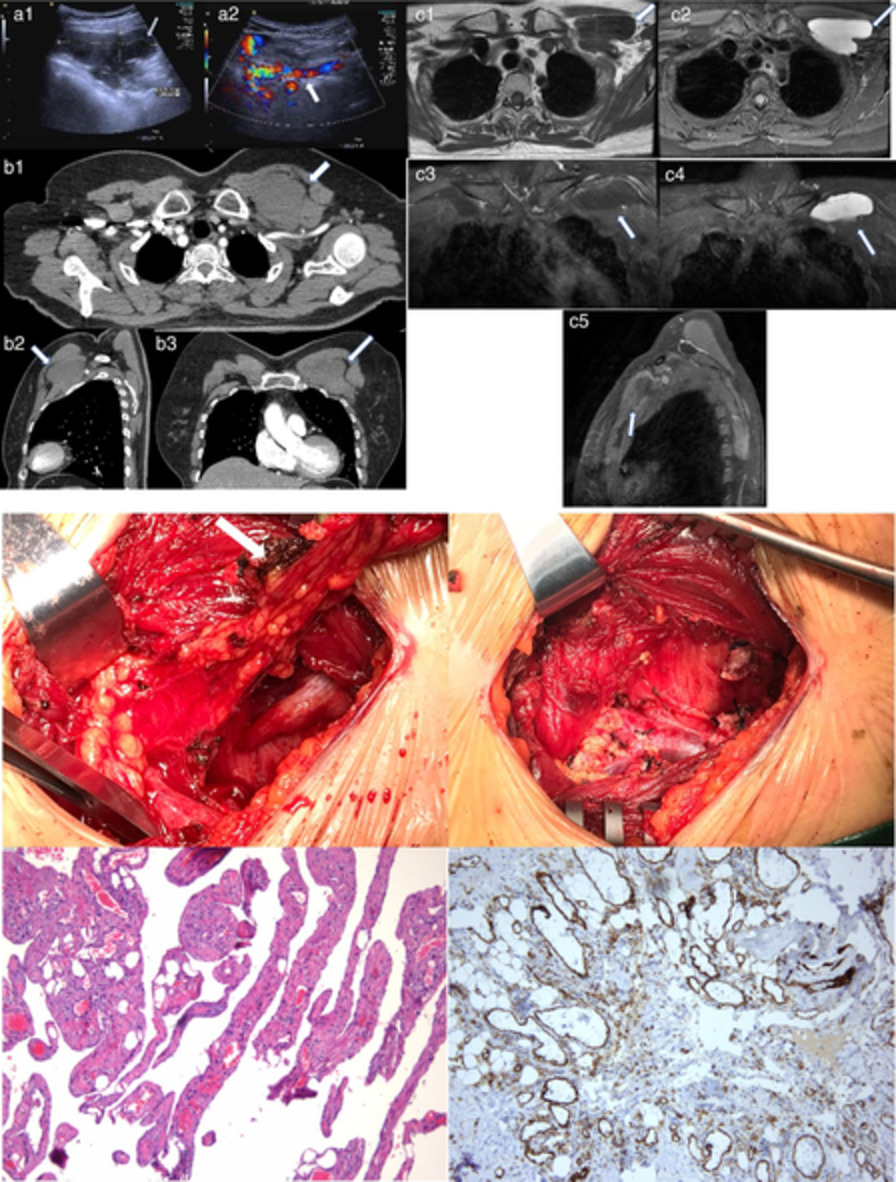
Rare cystic lymphangioma in the chest wall of an adult patient: A case report and comprehensive review of the literature
- Pages: 3388-3390
- First Published: 28 September 2020
Successful treatment with nivolumab in a patient with lung adenocarcinoma complicated by pulmonary aspergilloma
- Pages: 3391-3395
- First Published: 17 September 2020
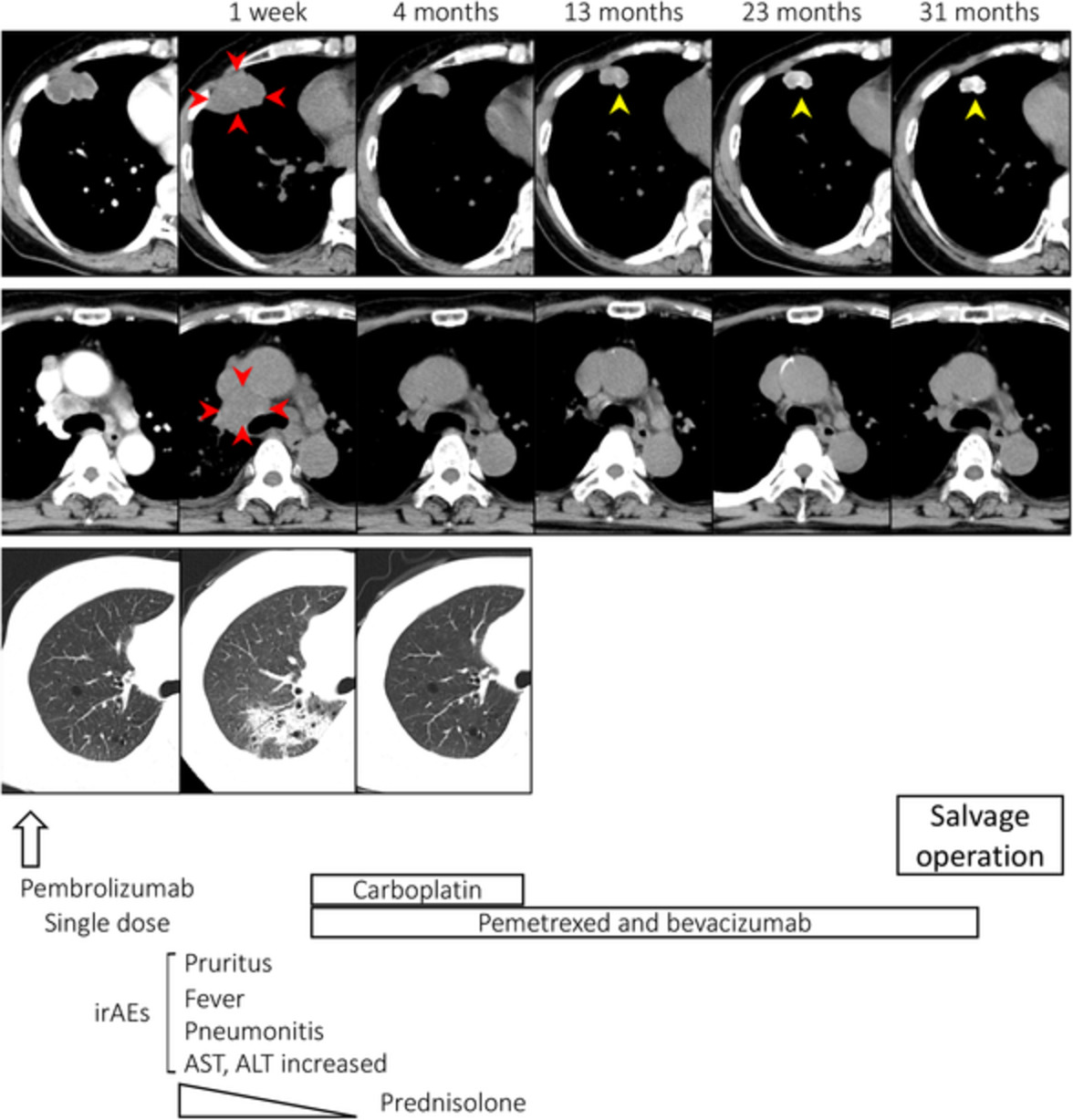
Lung adenocarcinoma with tumor resolution and dystrophic calcification after salvage surgery following immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A case report
- Pages: 3396-3400
- First Published: 15 September 2020
Potentially fatal complications of systemic air embolism after computed tomography-guided transthoracic needle biopsy in lung cancer harboring epithelial growth factor receptor mutation: A case report
- Pages: 3401-3406
- First Published: 02 October 2020
IMAGING IN THORACIC CANCERS
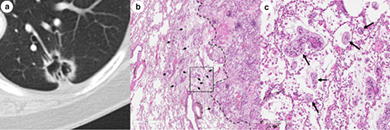
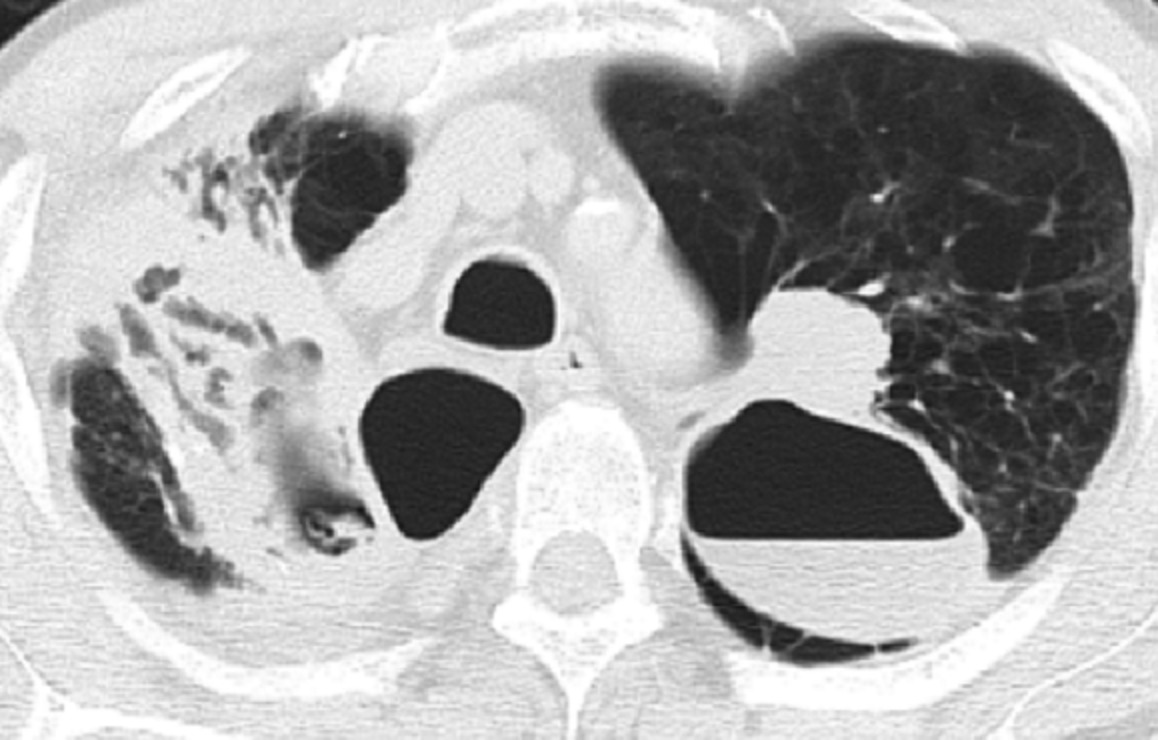
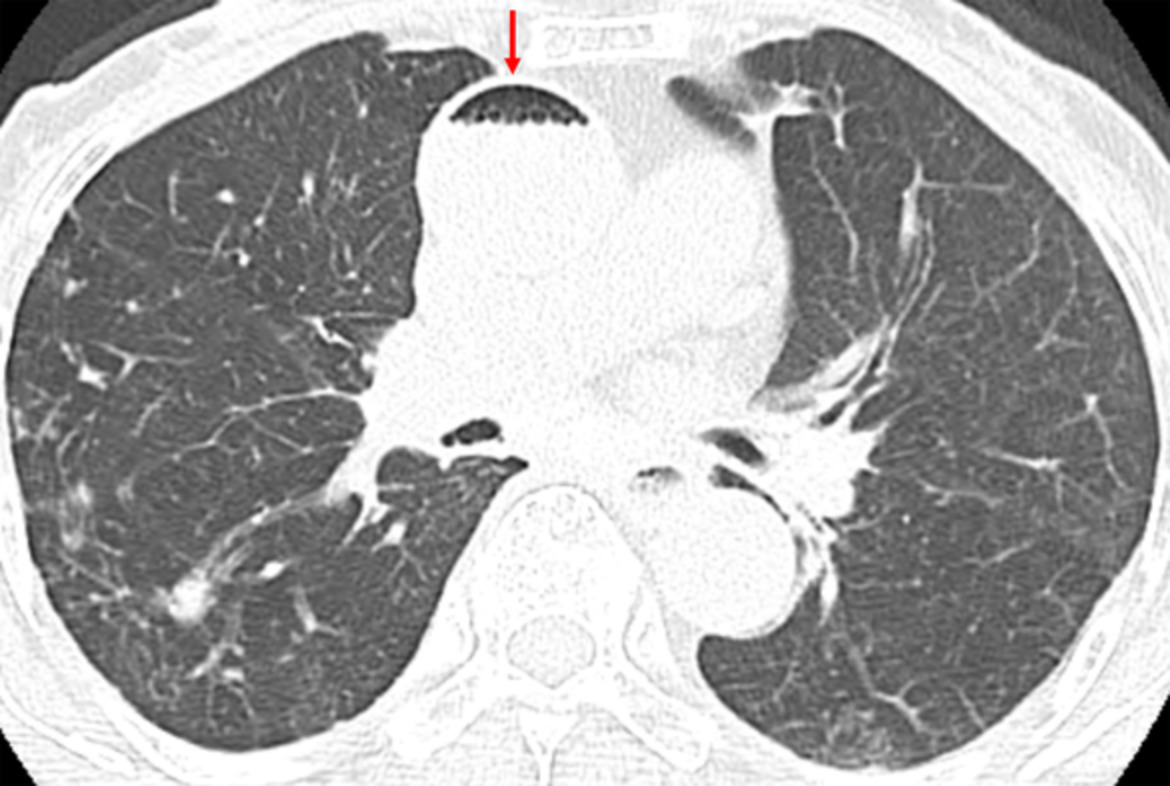
Unusual lung involvements of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma with chylothorax
- Pages: 3407-3408
- First Published: 18 September 2020
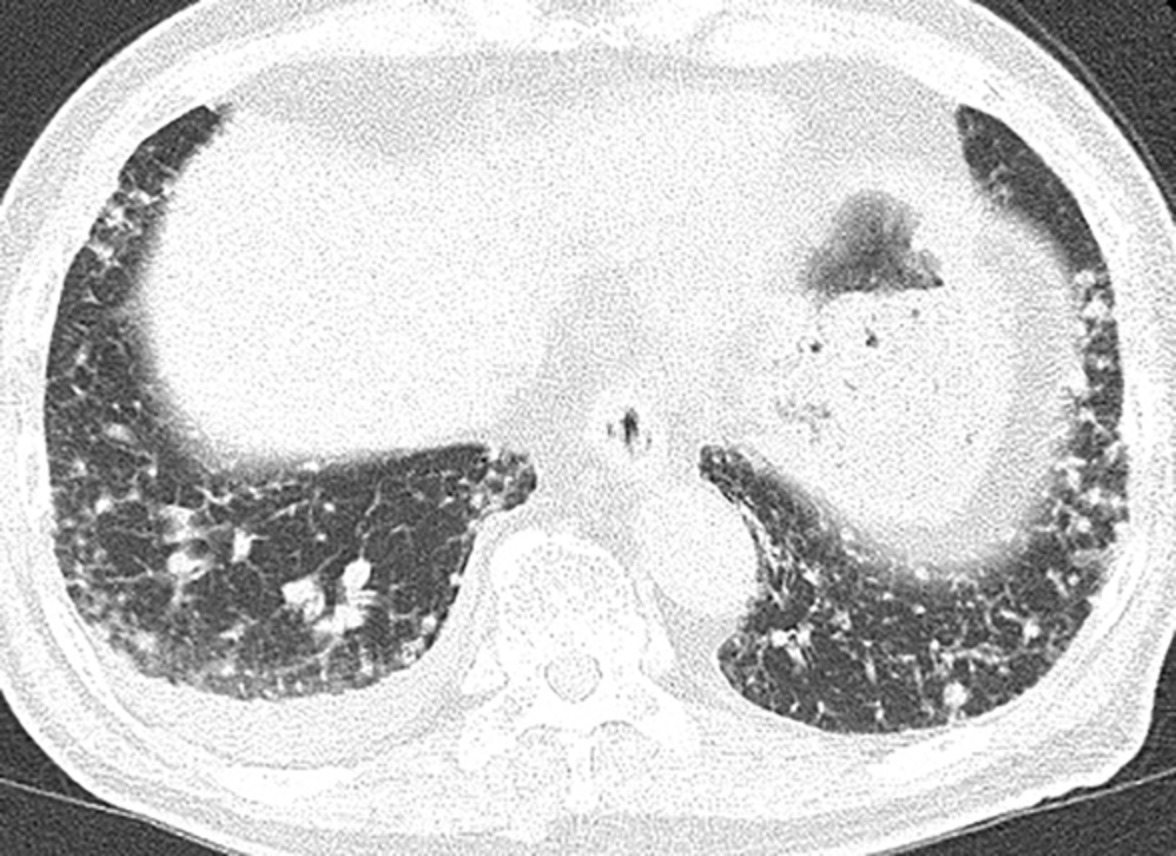
This case of invasive mucinous adenocarcinoma (IMA) showed subpleural micronodular opacities and chylothorax as unusual chest computed tomography (CT) patterns for IMA. IMA should be considered in the differential diagnosis of subpleural micronodular opacities accompanied by pleural effusion on chest CT.
TECHNOLOGICAL NOTE
Cloning short DNA into plasmids by one-step PCR
- Pages: 3409-3415
- First Published: 05 October 2020
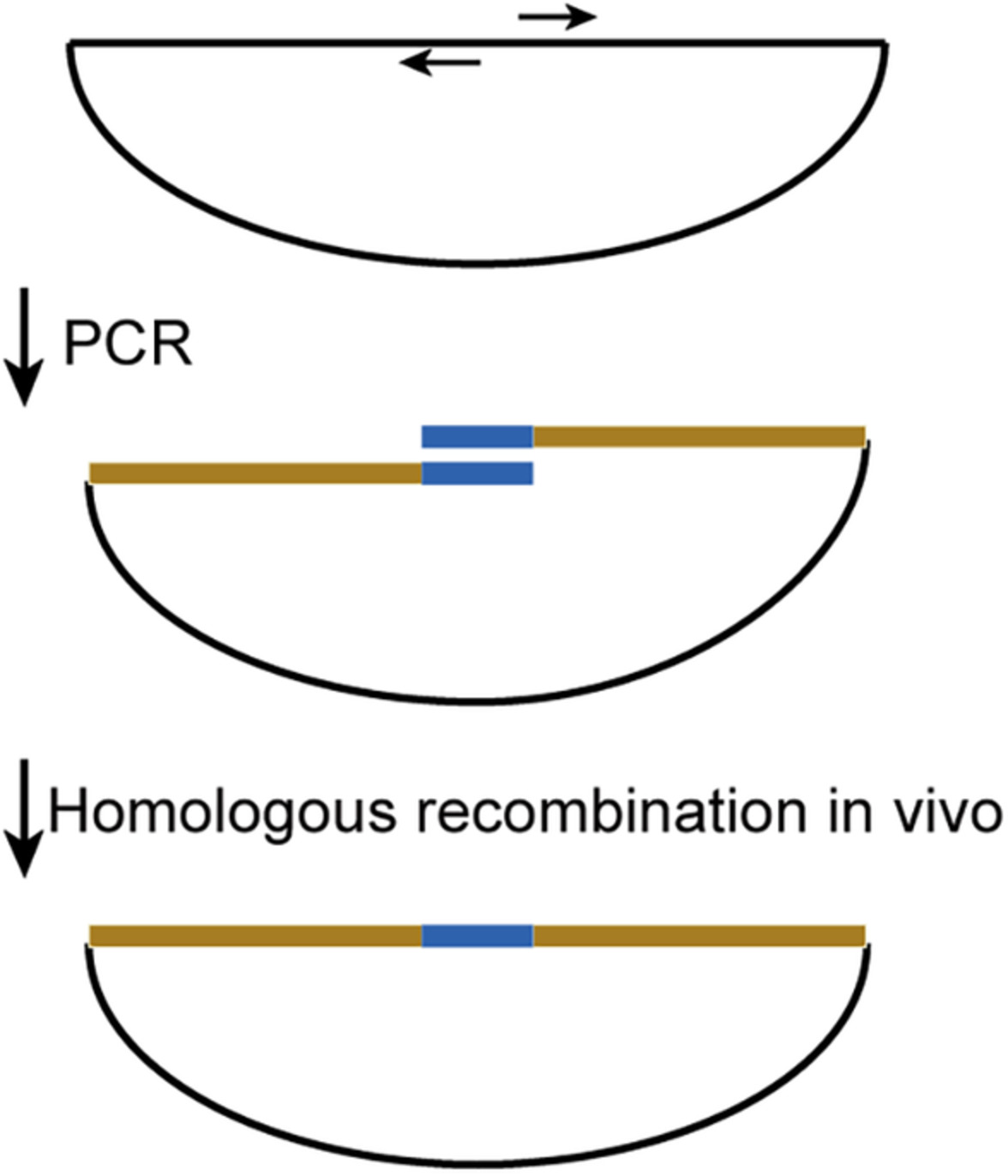
Our method uses one-step PCR to amplify the entire circular plasmid. The PCR products were transformed into E. coli and cyclized by homologous recombination in vivo. Free from the limitation of restriction enzyme sites and omitting the ligation process, our method offers a flexible and economical option of plasmid construction.