Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 29 August 2024

Cover image: The cover image is based on the article Unveiling the shield: Troglitazone's impact on epilepsy-induced nerve injury through ferroptosis inhibition by Zhi-Bin Wang et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.14911.
ISSUE INFORMATION
META ANALYSIS
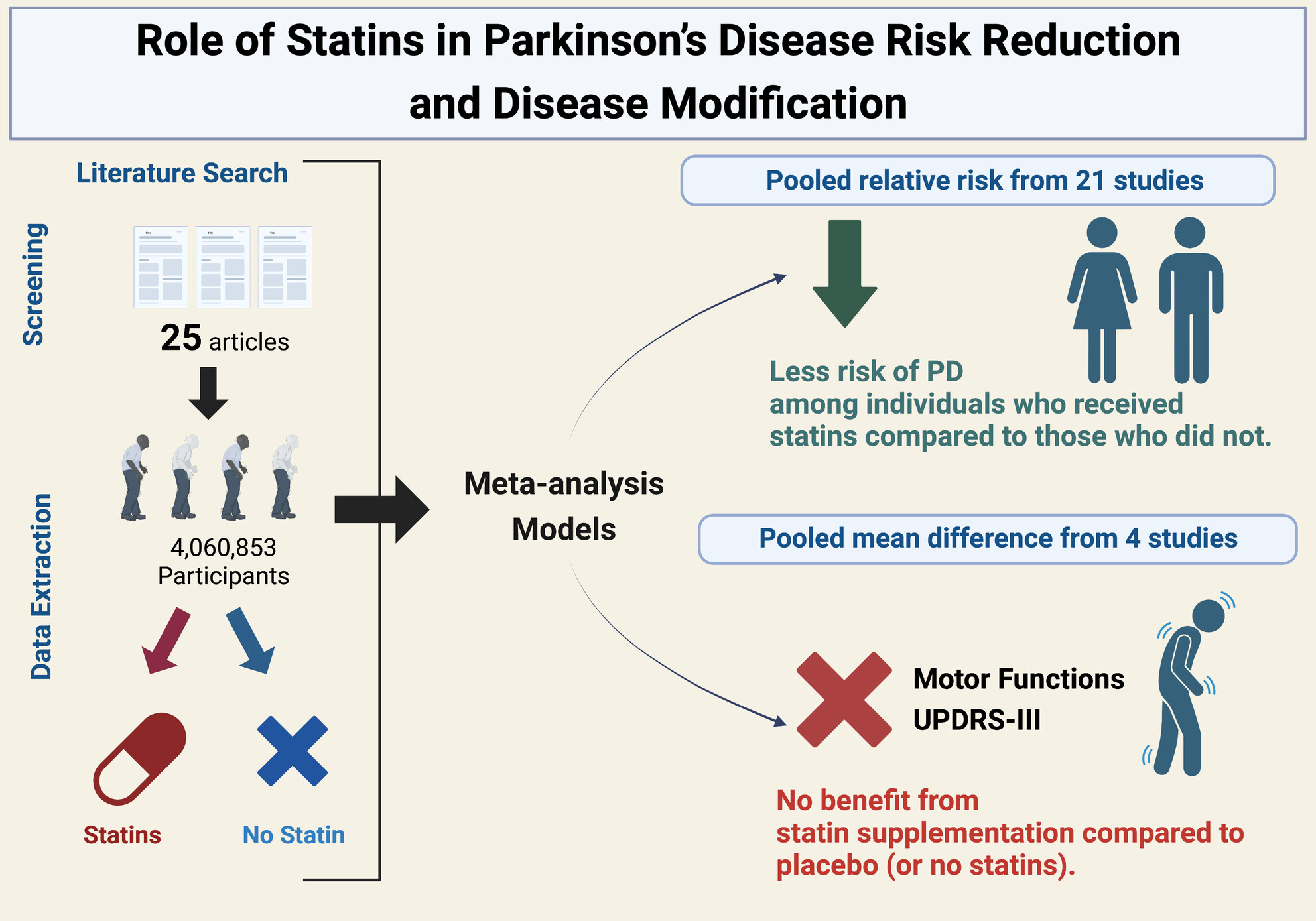
Determining the role of statins in Parkinson's disease risk reduction and disease modification: A comprehensive meta-analysis of 4 million participants' data
- First Published: 04 August 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Serotonin (5-HT)2A/2C receptor agonist 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane hydrochloride improves detrusor sphincter dyssynergia by inhibiting L-type voltage-gated calcium channels in spinal cord injured rats
- First Published: 04 August 2024
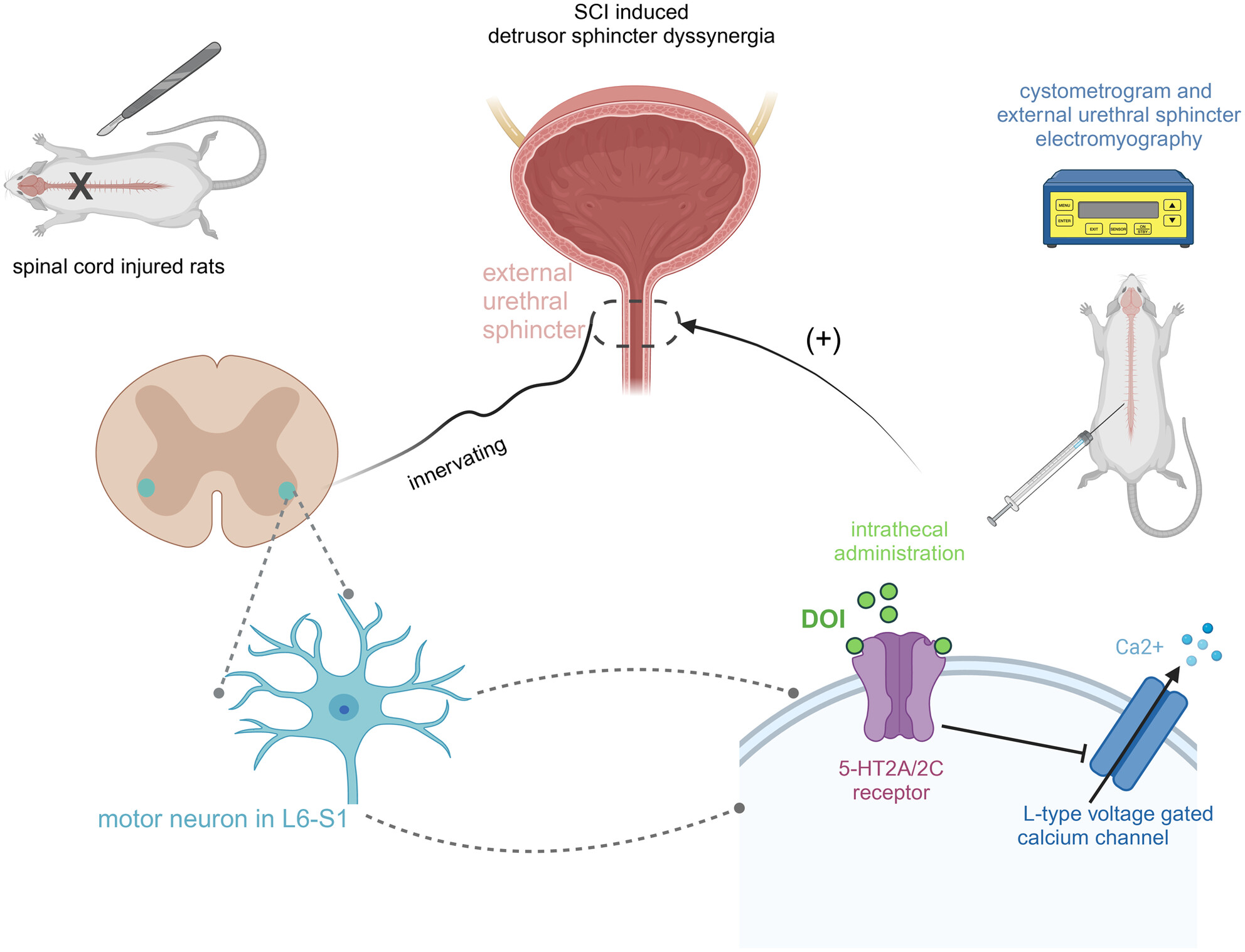
L-type voltage-gated calcium channel blocker, nifedipine, could improve spinal cord injury-induced detrusor sphincter dyssynergia. 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodophenyl-2-aminopropane hydrochloride may improve SCI-induced DSD by inhibiting the L-type voltage-gated calcium channel in lumbosacral cord motoneurons.
REVIEW
Progress and recognition of idiopathic intracranial hypertension: A narrative review
- First Published: 04 August 2024
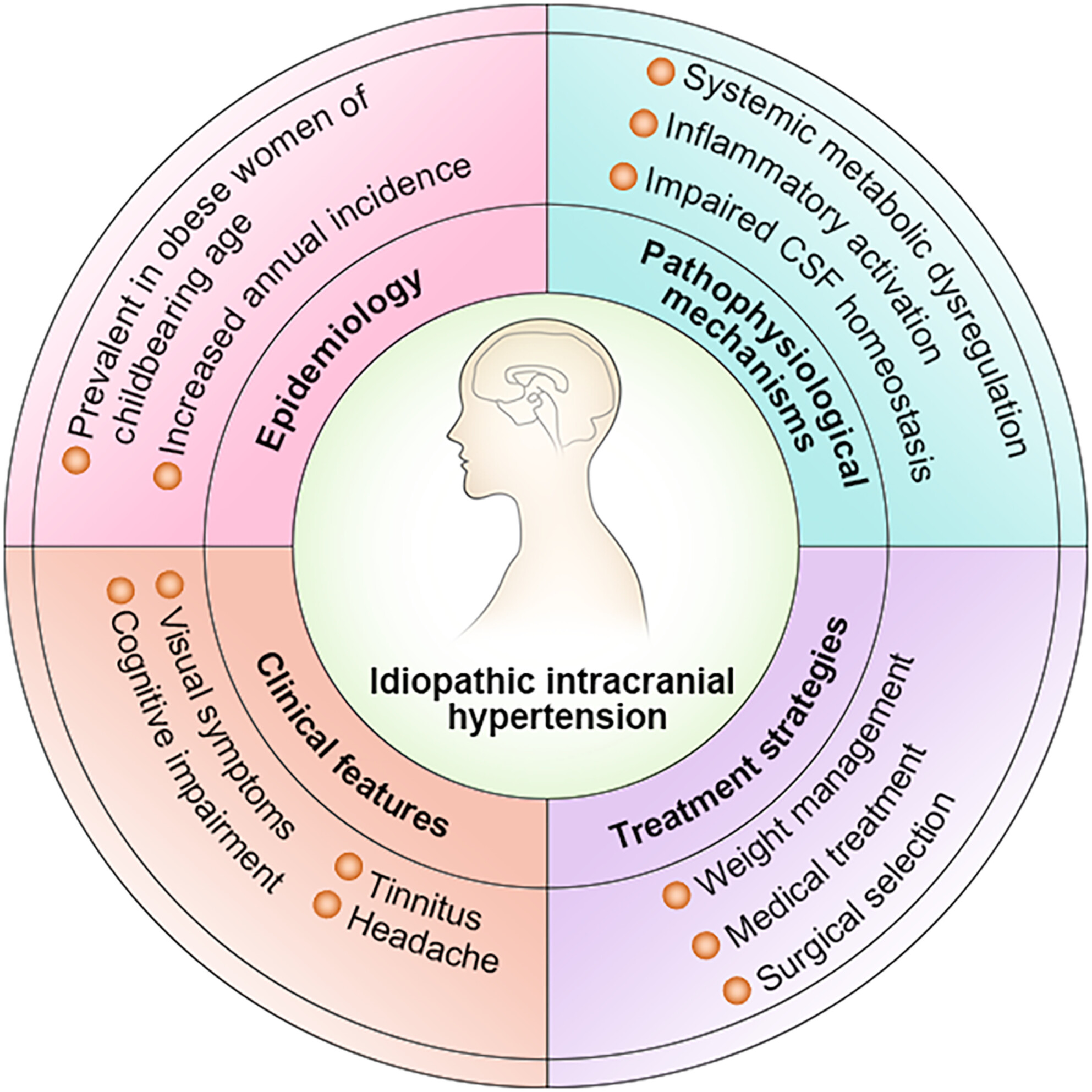
We integrate recent studies and findings to provide a thorough and detailed exploration of various facets of idiopathic intracranial hypertension, including its epidemiology, pathophysiological mechanisms, clinical features, and treatment strategies. This contributes to a better understanding of the disease and potential therapeutic targets.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Effects of batroxobin on the antithrombotic system in patients with cerebral venous thrombosis: Clues to mechanisms
- First Published: 04 August 2024
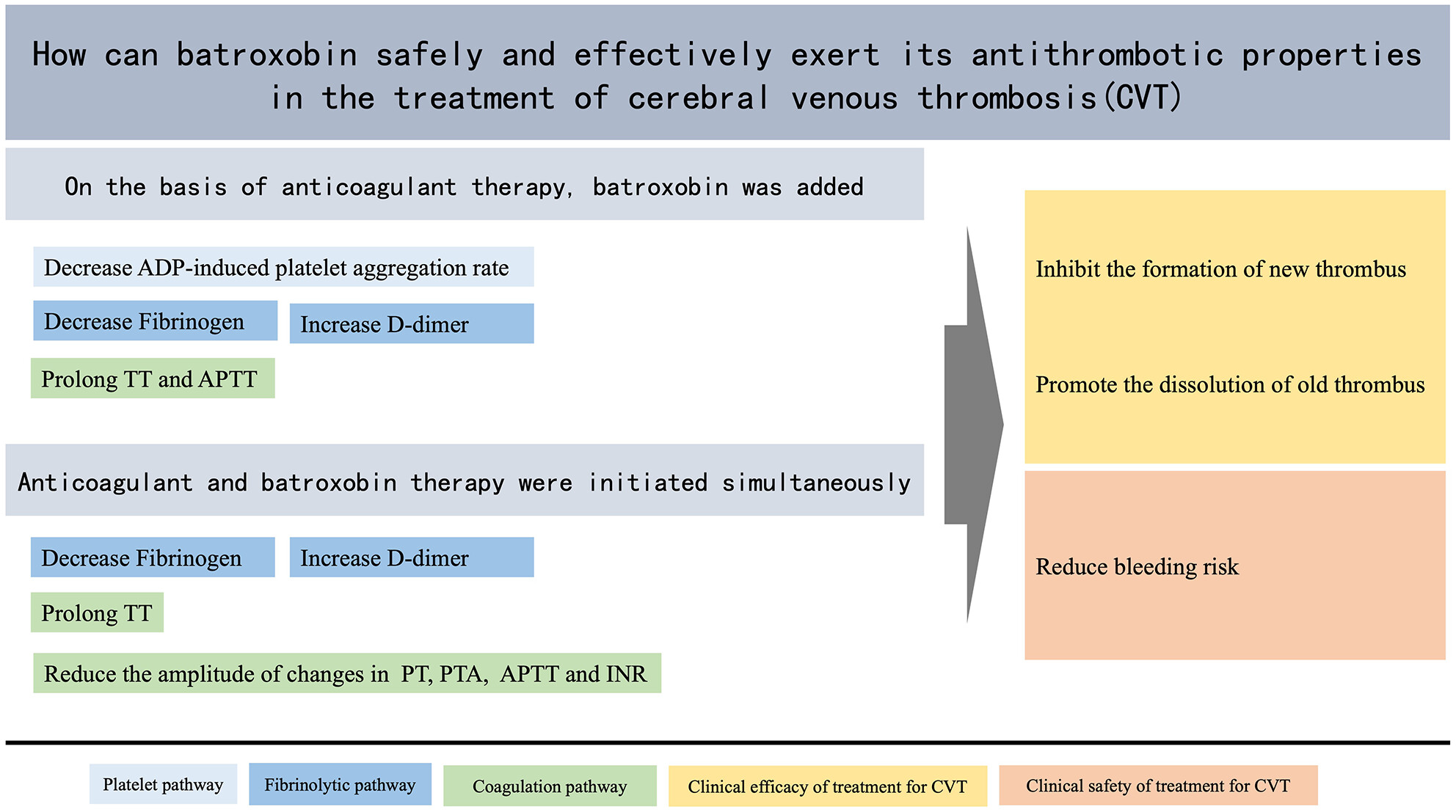
Batroxobin can inhibit platelet aggregation, degrade insoluble fibrinogen, dissolve soluble fibrin, and prolong TT and APTT which makes it play a stable role in the effective treatment of CVT. Batroxobin can slow down the changes in coagulation indicators, which makes it not increase the risk of adverse events, especially bleeding.
Increased opioid consumption in neoadjuvant immunotherapy plus chemotherapy for patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: A multicenter, prospective cohort study
- First Published: 04 August 2024
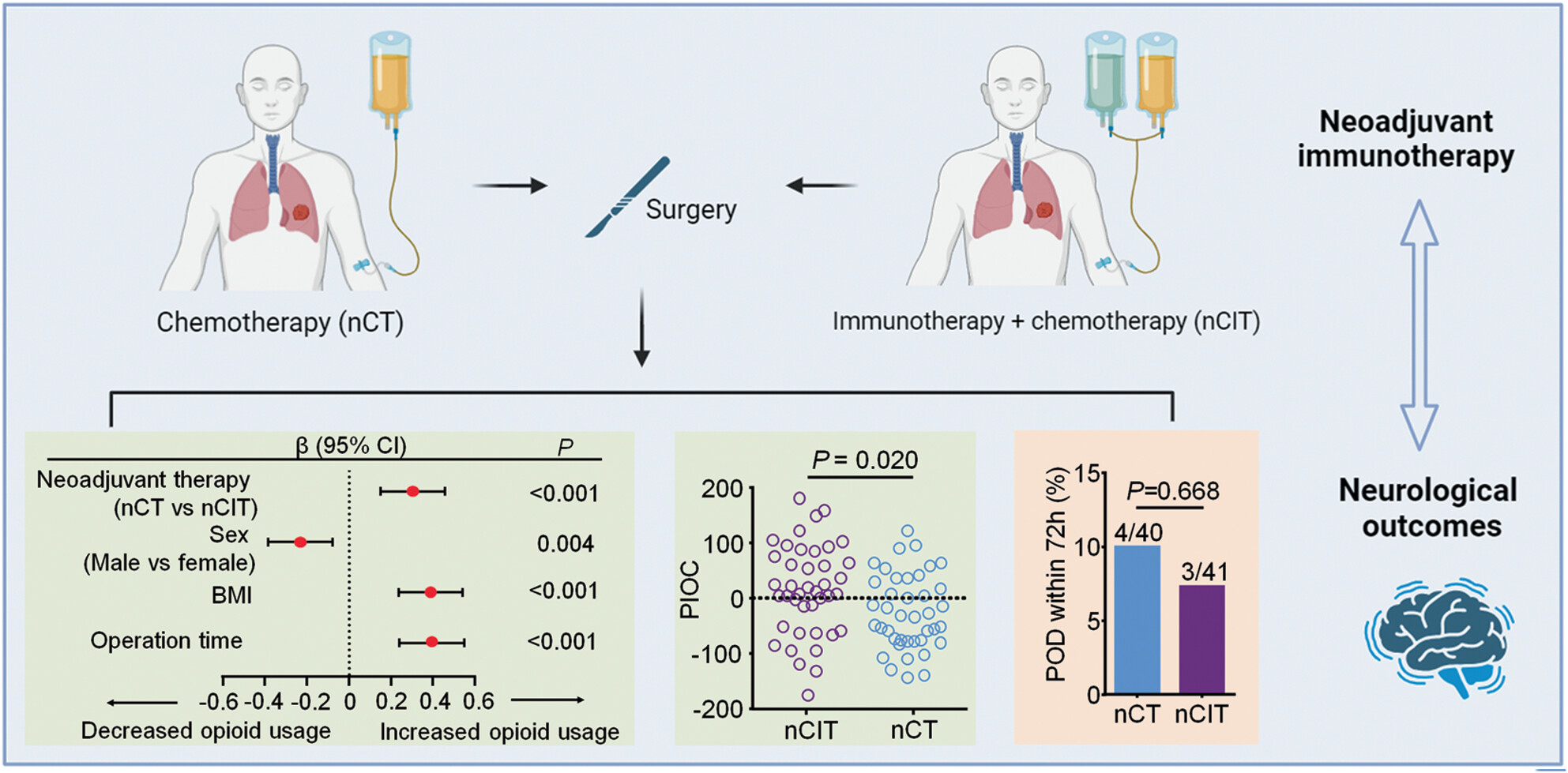
Patients with non-small-cell lung cancer receiving neoadjuvant chemoimmunotherapy warrant increased opioid consumption perioperatively and suffered from more postoperative pain compared with patients receiving neoadjuvant chemotherapy alone. However, there is no statistical difference in incidence of postoperative delirium (POD) between groups within 72 h after surgery.
Efficacy and safety of batroxobin in patients with acute ischemic stroke: A multicenter retrospective analysis
- First Published: 04 August 2024

Intravenous batroxobin treatment was found to significantly reduce the risk of stroke recurrence and improve functional outcomes for patients with acute ischemic stroke beyond the thrombolytic therapy time window. Additionally, the treatment did not lead to an increase in moderate-to-severe bleeding events.
Clinico-sero-pathological profiles and risk prediction model of idiopathic inflammatory myopathy (IIM) patients with different perifascicular changes
- First Published: 04 August 2024
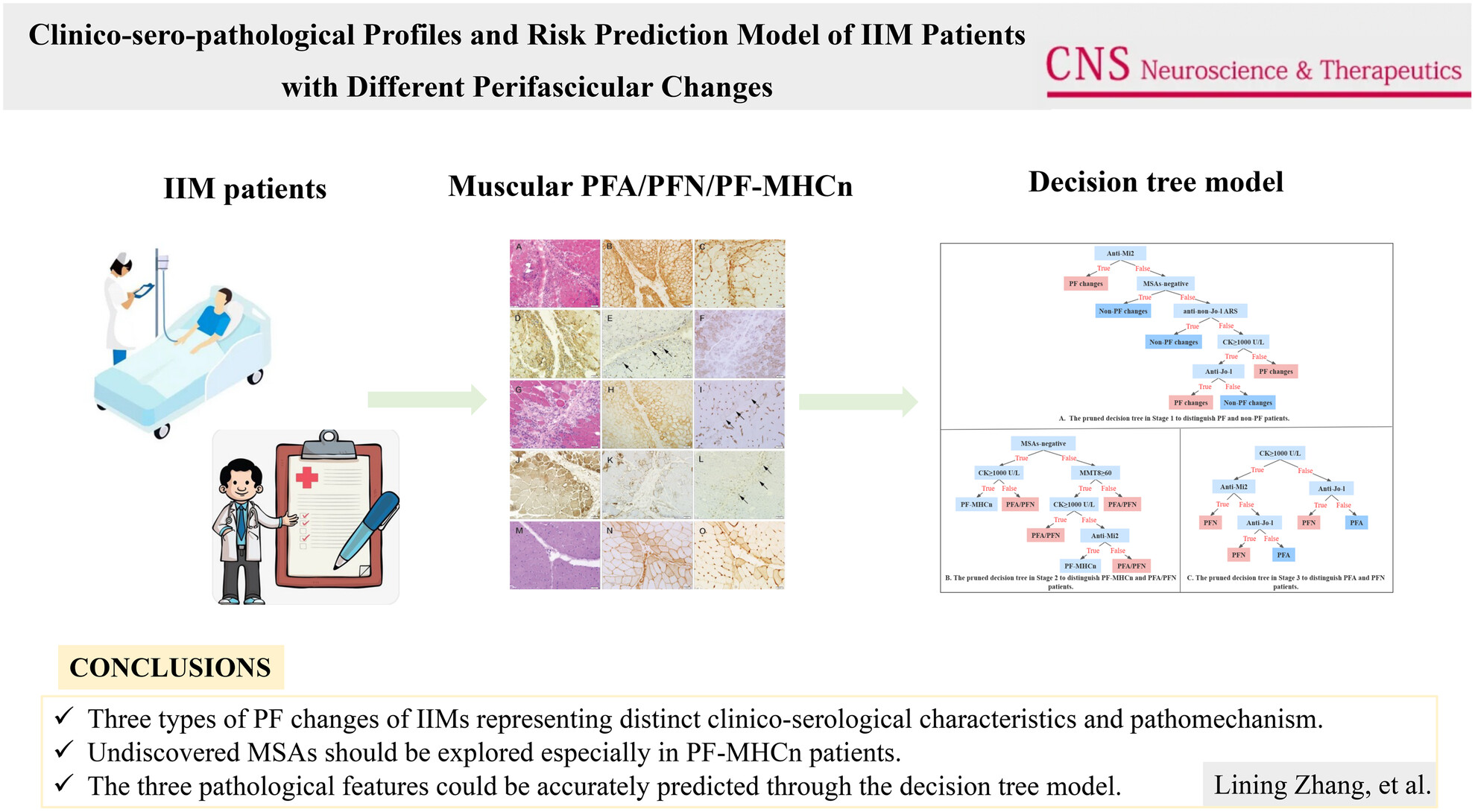
There are three kind of PF changes on muscle pathology of IIM patients, including PFA, PFN, and PF-MHCn, each referring to different clinico-sero-pathological characteristics and distinct pathogenic mechanism. The tree-based three-stage clinico-serological machine learning model could accurately predict which kind of PF changes an IIM patient would develop.
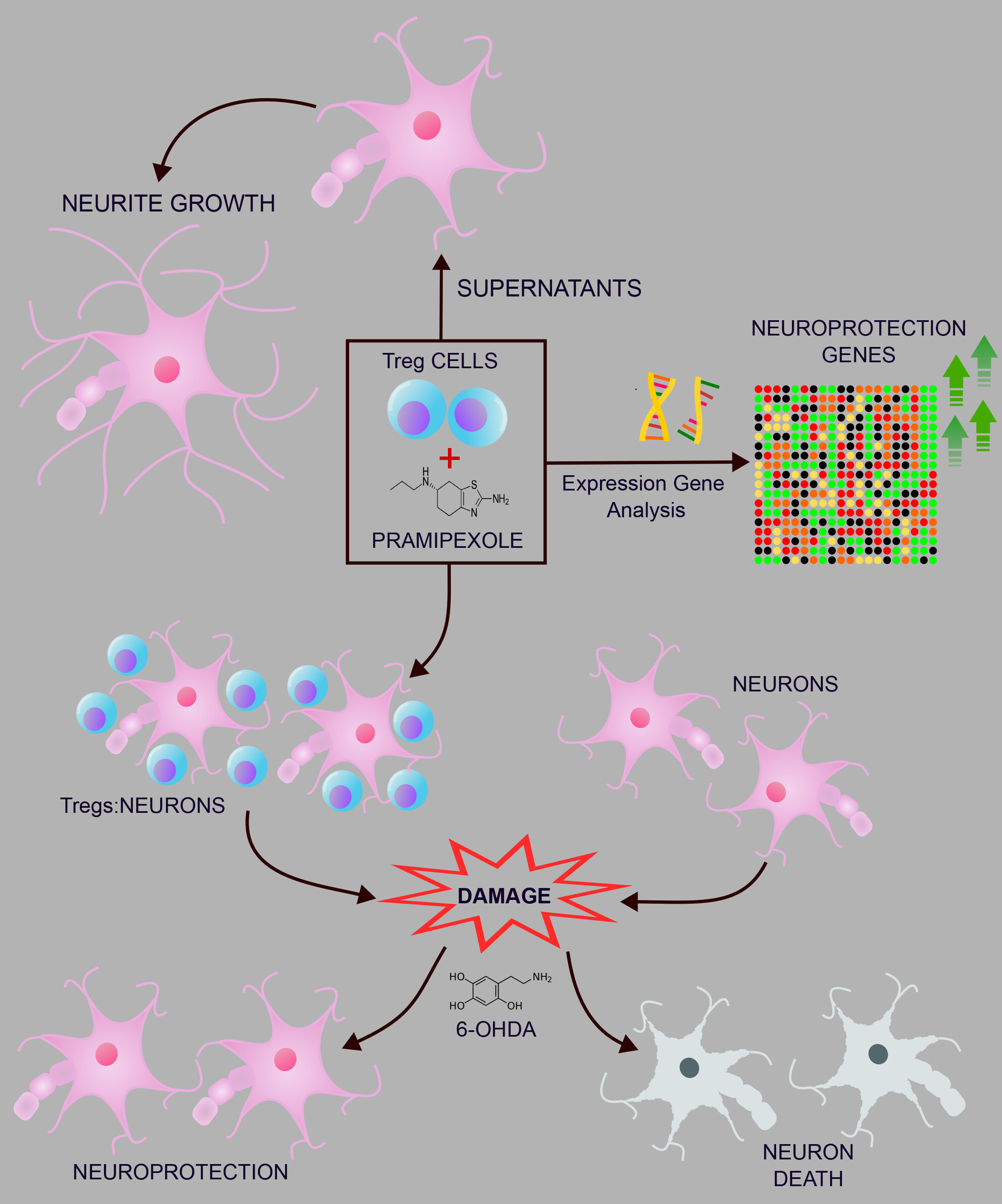
Treating activated regulatory T cells with pramipexole protects human dopaminergic neurons from 6-OHDA-induced degeneration
- First Published: 04 August 2024
Nesfatin-1 inhibits cerebral aneurysms by activating Nrf2 and inhibiting NF-κB signaling
- First Published: 04 August 2024
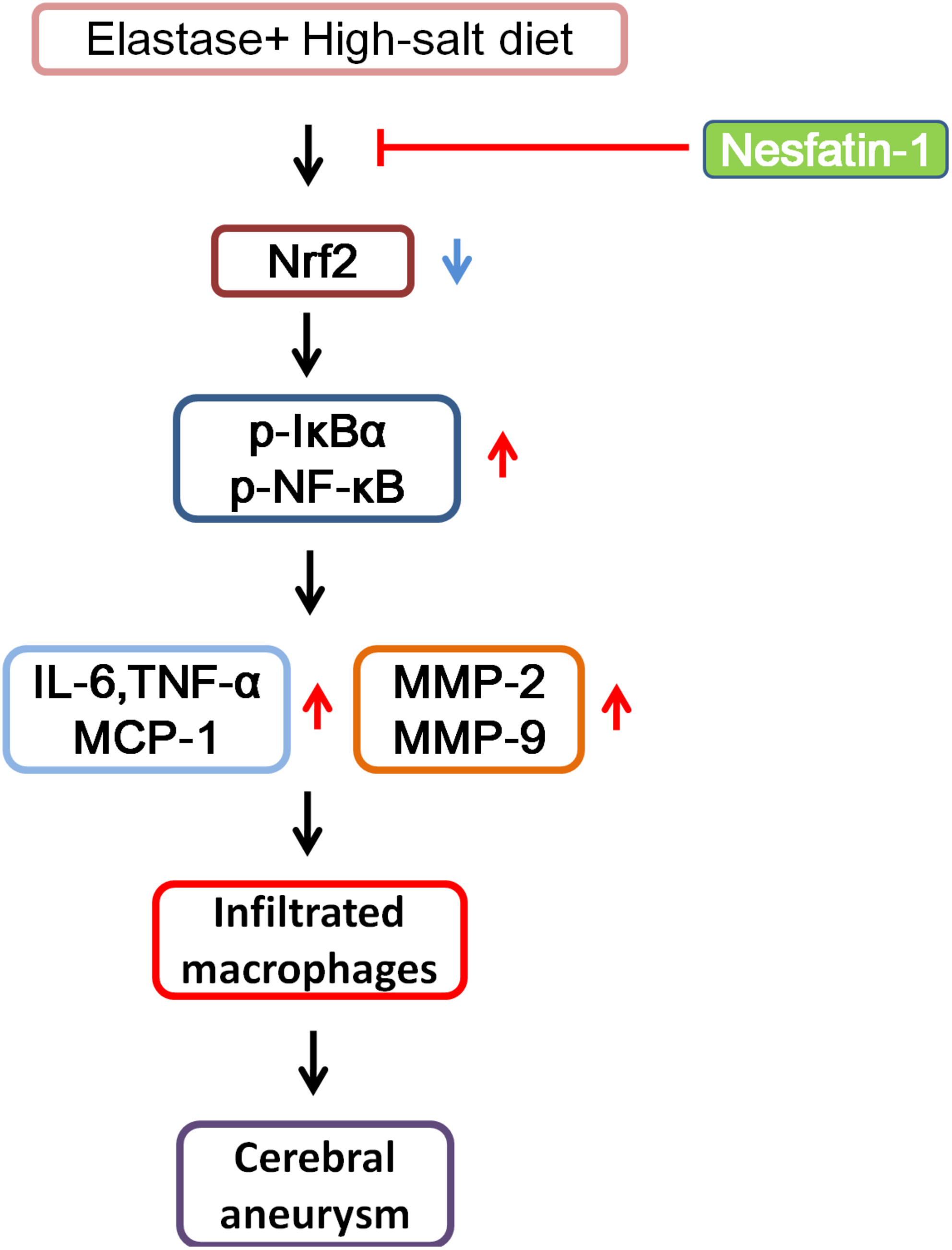
This study shows that Nes-1 activated Nrf-2 by promoting its nuclear translocation but prevented the activation of the IκBα/NF-κB signaling pathway to inhibit the expression of pro-inflammatory mediators such as IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, MMP-2, and MMP-9. Subsequently, Nes-1 suppressed the invasion of macrophages and CA formation.
Deciphering the neuroprotective mechanisms of RACK1 in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury: Pioneering insights into mitochondrial autophagy and the PINK1/Parkin axis
- First Published: 04 August 2024
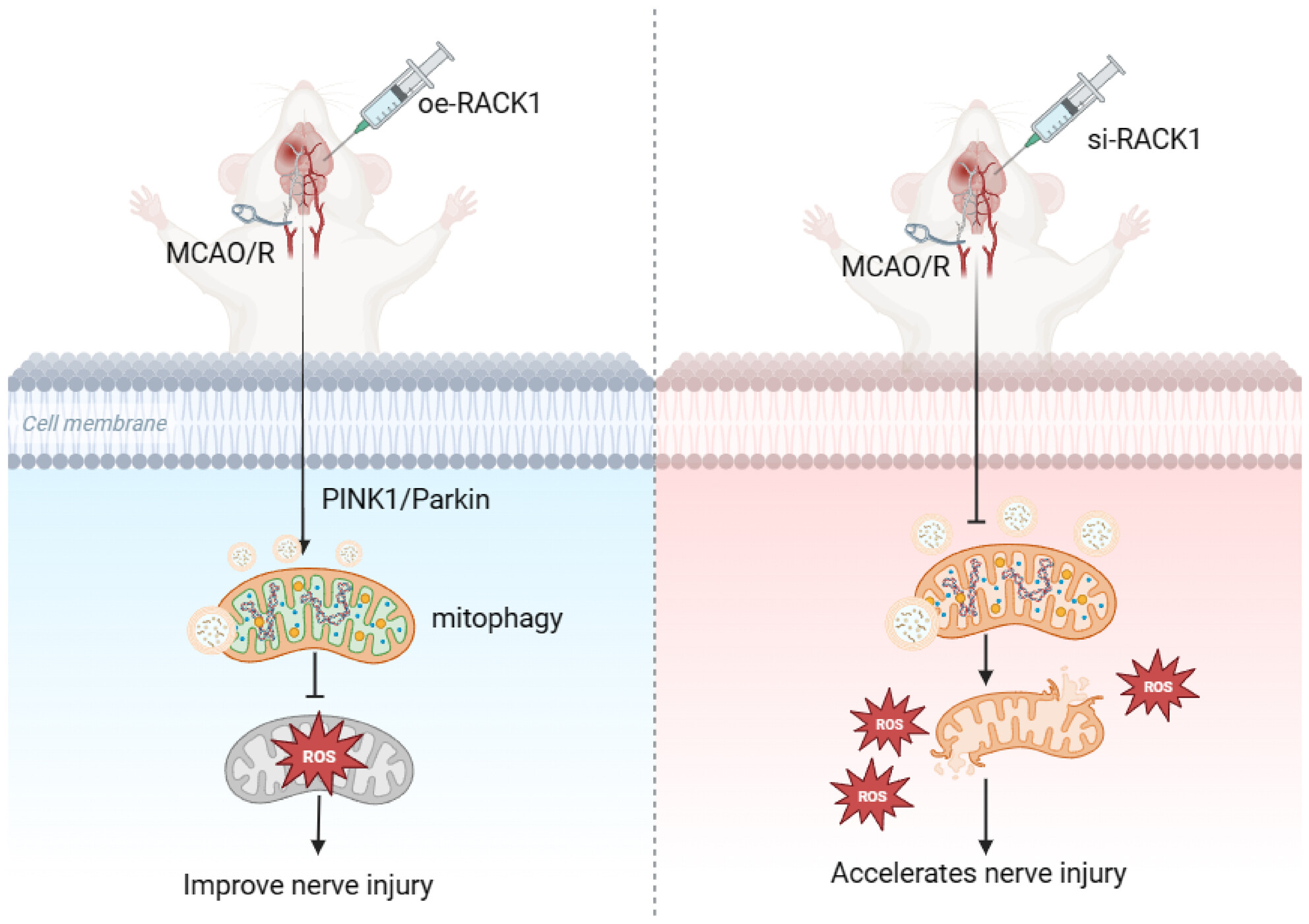
This study reveals the key role of RACK1 in CIRI. The study finds that RACK1 regulates mitochondrial function and autophagy. The study confirms the centrality of the PINK1/Parkin pathway. The study offers new strategies for treating CIRI. The study provides comprehensive in vitro and in vivo evidence.
REVIEW
Mitochondrial plasticity and synaptic plasticity crosstalk; in health and Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 04 August 2024
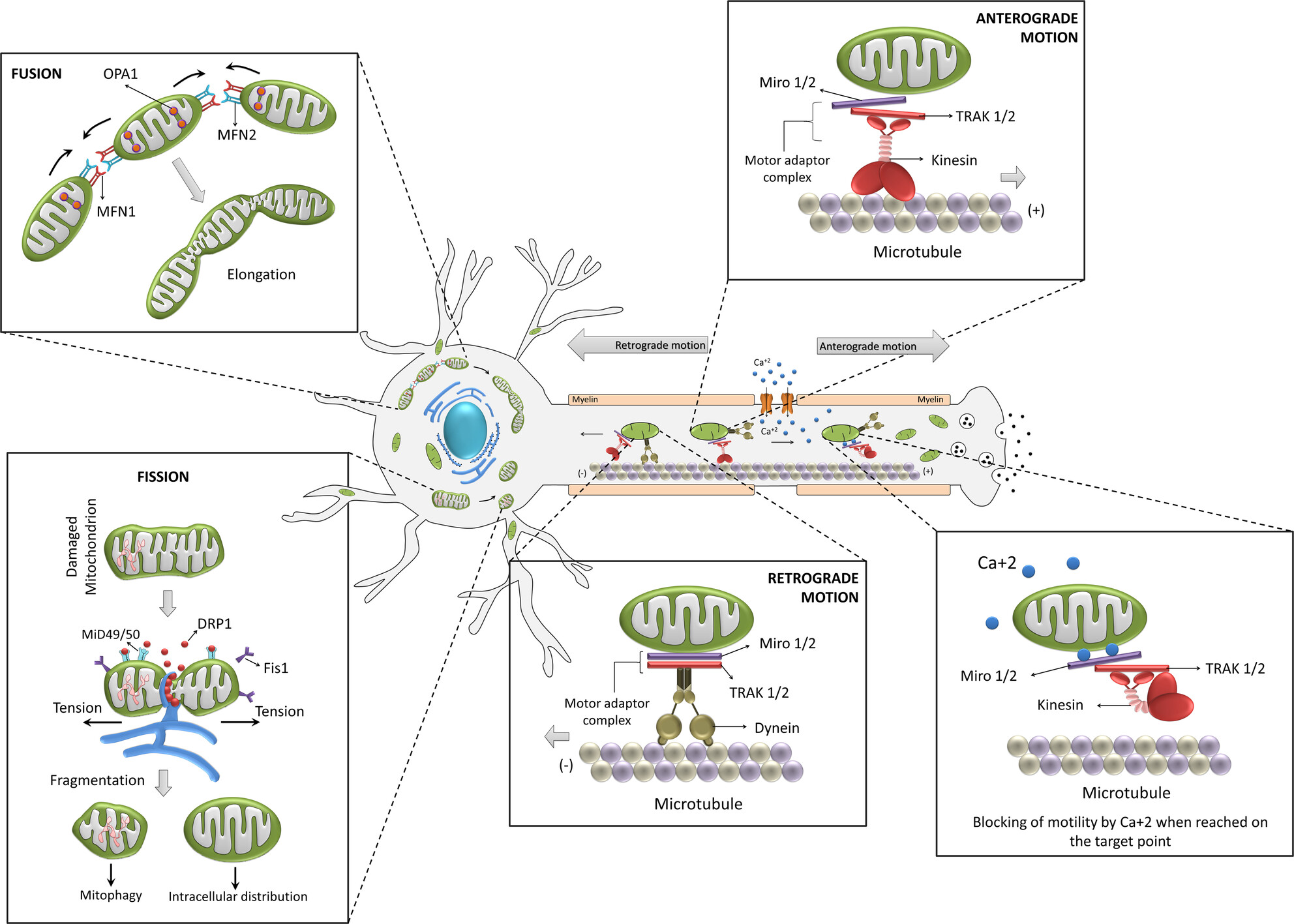
The mechanism of mitochondrial transport within the neuron is mediated on the cytoskeleton. The retrograde (−) motion deployed the movement of mitochondria toward the cell body with the help of dynein, TRAK1/2, and Mrio1/2 protein. While anterograde (+) motion causes the movement toward the axon with the assistance of kinesin, TRAK1/2, and Miro1/2 proteins. At the axon terminal, the mitochondrion is separated due to the influx of calcium, which destabilizes its complex with kinesin protein. In the cell body, mitochondria undergo fission and fusion process in order to remove its damaged portion or to conserve it, respectively.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
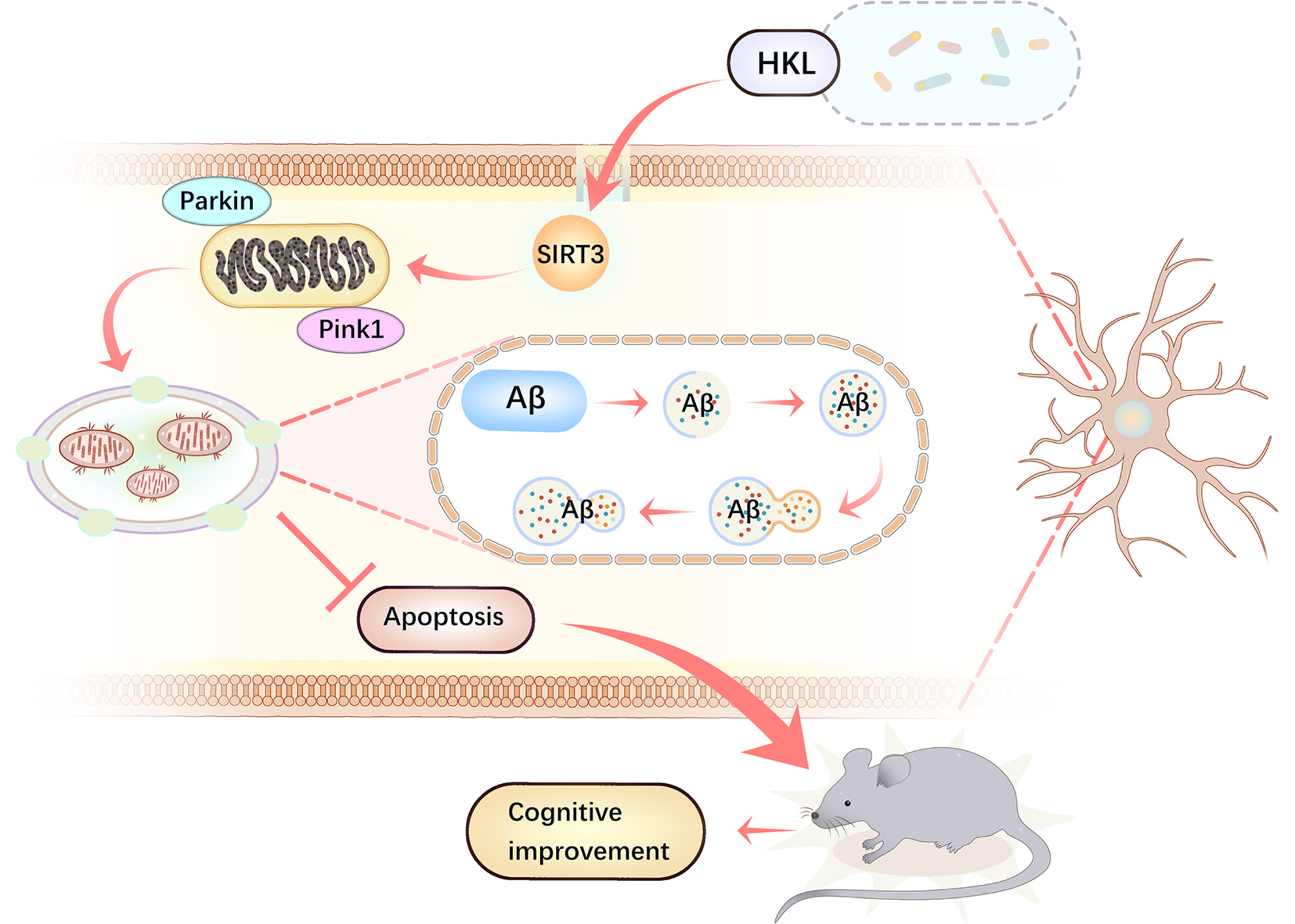
Honokiol relieves hippocampal neuronal damage in Alzheimer's disease by activating the SIRT3-mediated mitochondrial autophagy
- First Published: 04 August 2024
Transcriptional expression patterns of the cortical morphometric similarity network in progressive supranuclear palsy
- First Published: 04 August 2024
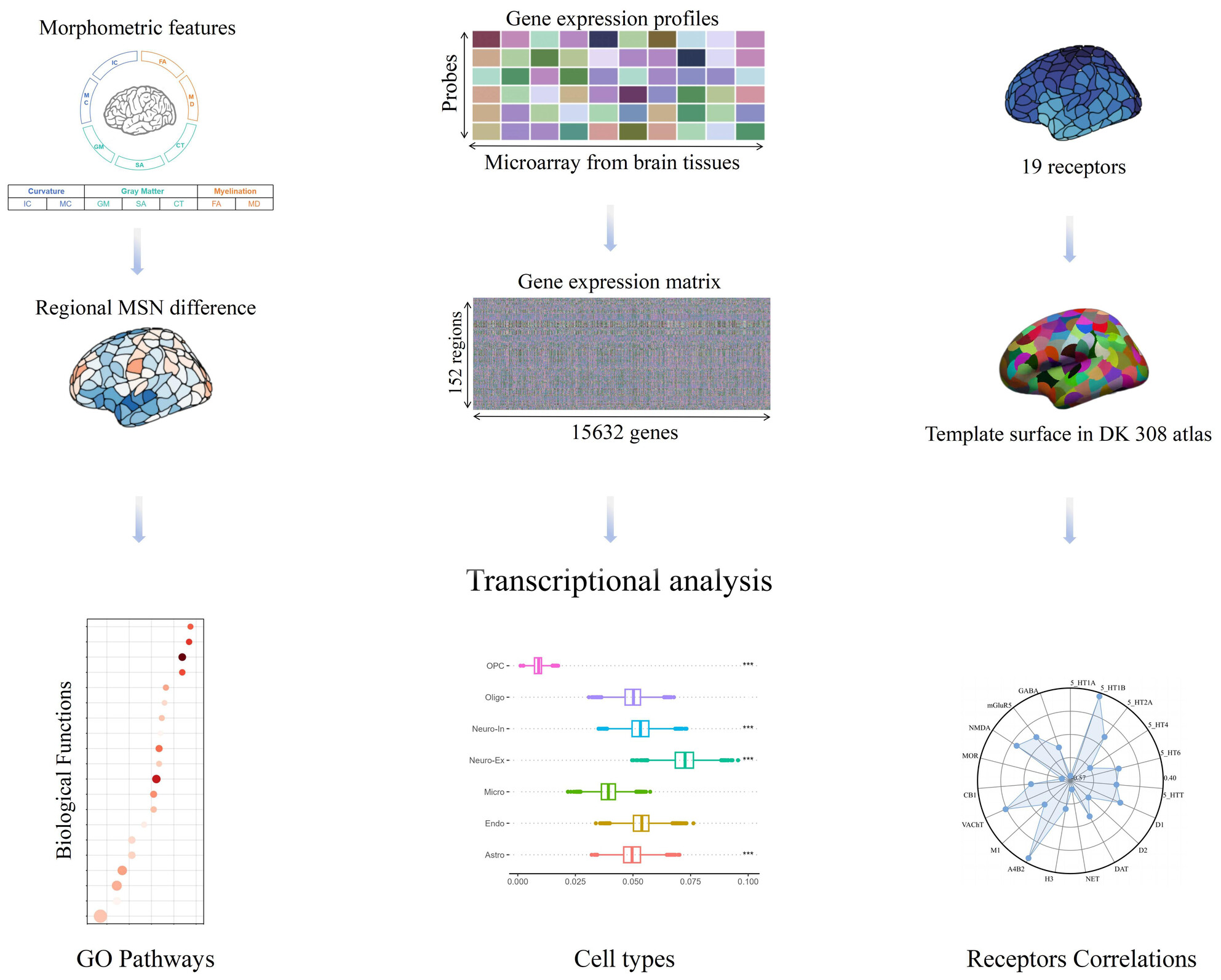
MSN in PSP patients was mainly decreased in frontal and temporal cortex but increased in occipital cortex. In longitudinal studies, these are mainly in frontal and parietal regions. The expression pattern associated with MSN changes in PSP involves genes implicated in astrocytes, excitatory, and inhibitory neurons and is functionally enriched in neuron-specific biological processes. MSN were negatively correlated with the levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and opioid receptors.
Abnormal large-scale brain functional network dynamics in social anxiety disorder
- First Published: 06 August 2024
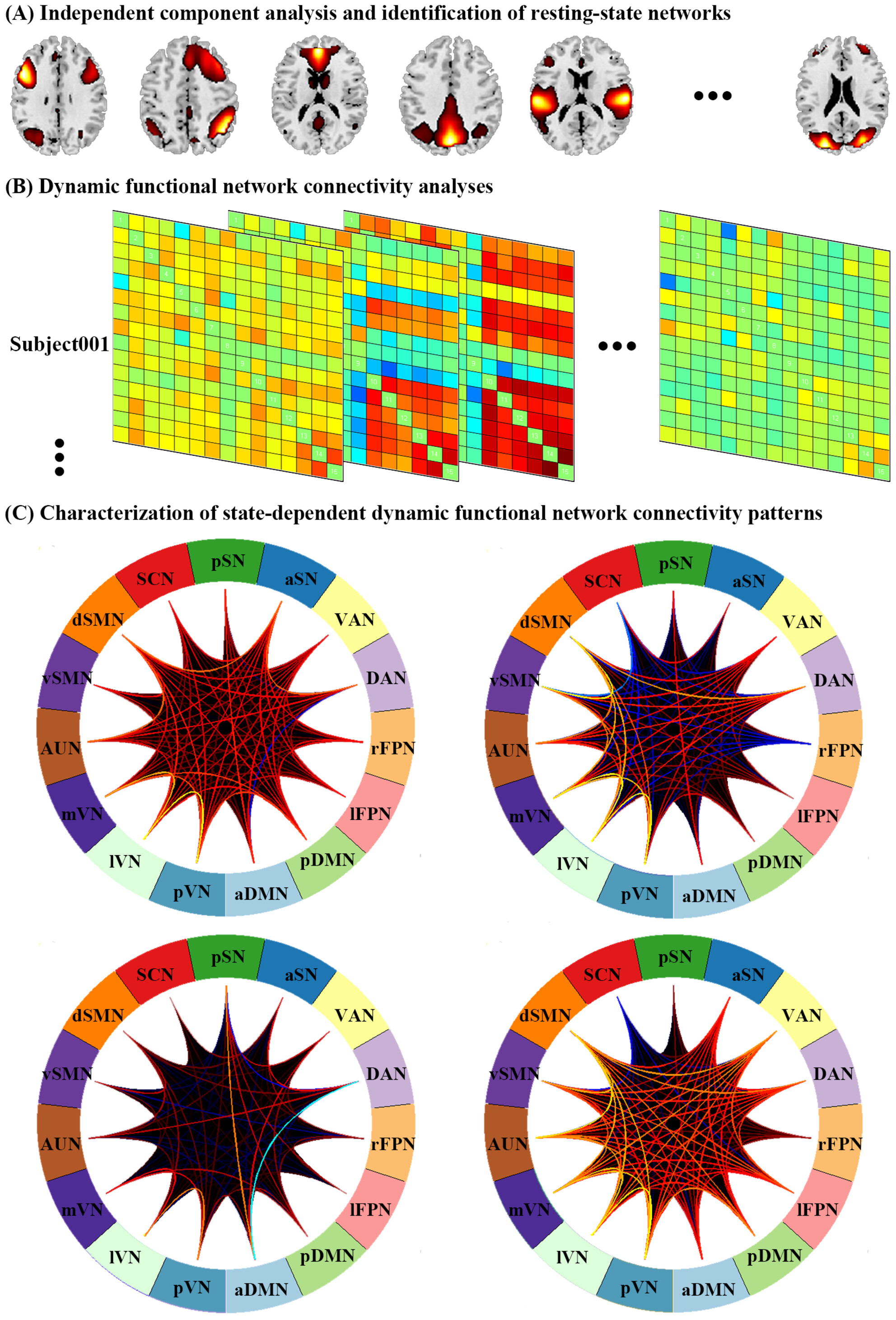
Four distinct recurring states were identified, including (in order of decreasing frequency) state with “widely weak” FNC, state with “widely moderate” FNC, state with “locally strong” FNC (mainly involving perceptual networks), and state with “widely strong” FNC. SAD patients significantly spent more time in a “weakly connected” state and less time in “strongly connected” states and demonstrated decreased FNC mainly within/between the default mode network, the attention network, and perceptual networks.
Electroencephalography microstate alterations reflect potential double-edged cognitive adaptation in Ménière's disease
- First Published: 06 August 2024

We identified several EEG microstate characteristics in MD patients, which facilitate postural control yet exacerbate subjective symptoms and effectively discriminate MD from HC. Microstate features may serve as a new avenue for optimizing cognitive compensation strategies and exploring potential neurobiological markers in MD.
S100A9 deletion in microglia/macrophages ameliorates brain injury through the STAT6/PPARγ pathway in ischemic stroke
- First Published: 06 August 2024
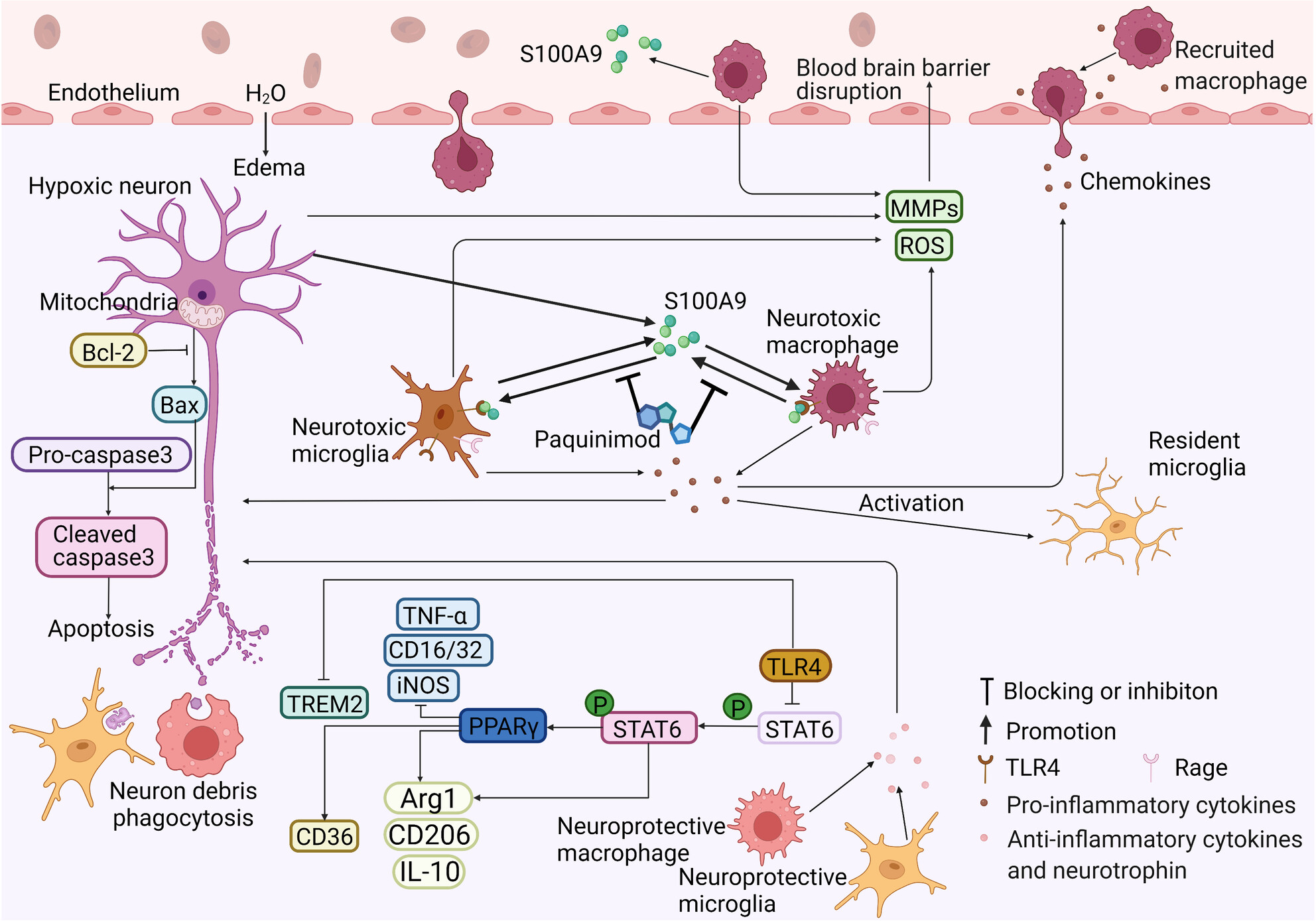
The polarization imbalance between the M1/M2-like phenotype exacerbates inflammatory response and neuronal death. By inhibiting or blocking the binding of S100A9 to TLR4, neuronal death can be reduced through modulation of inflammatory molecules. STAT6 and PPARγ, the downstream targets of TLR4, can be regulated by inhibiting or blocking S100A9.
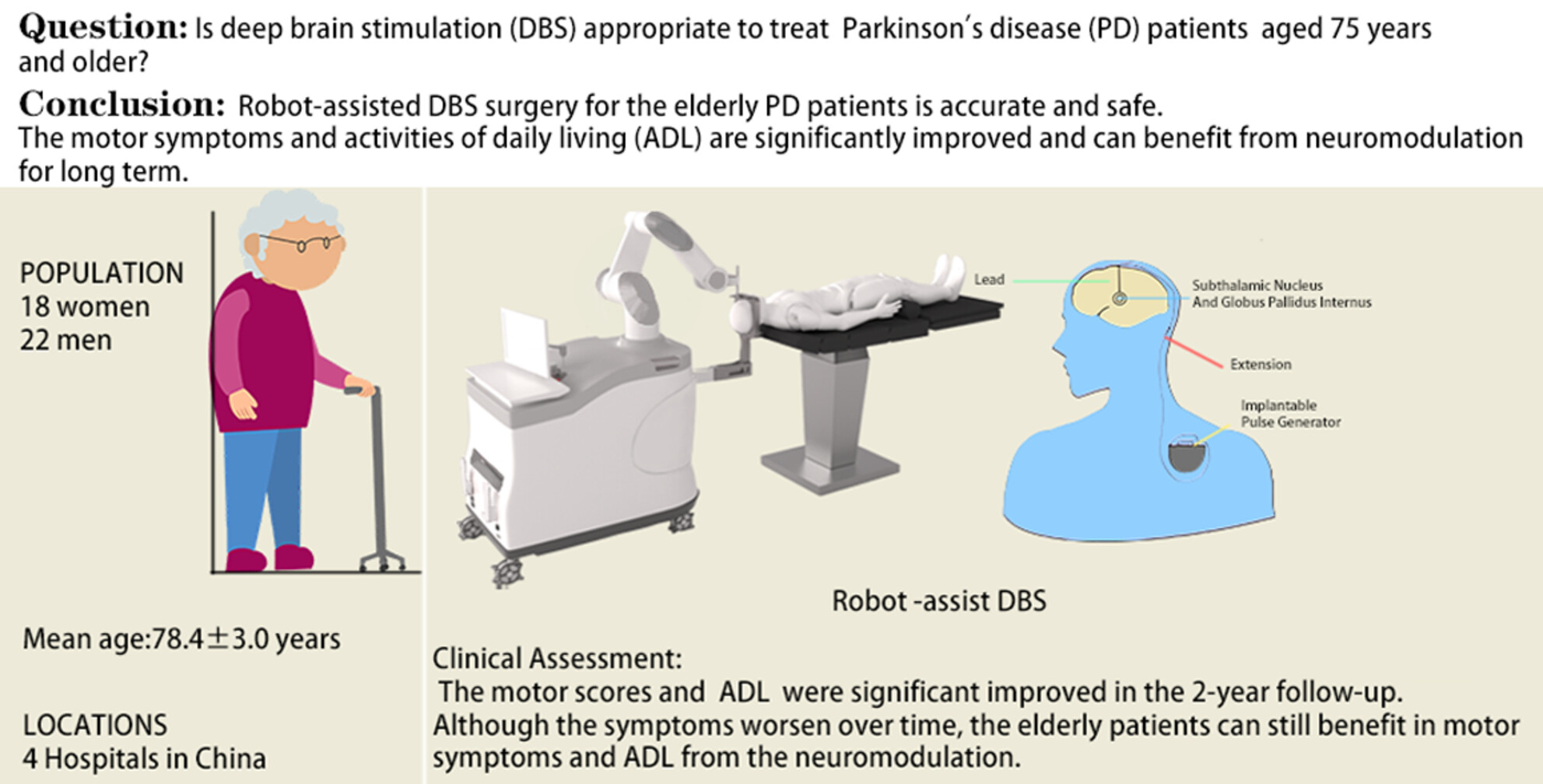
Safety and efficiency of deep brain stimulation in the elderly patients with Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 06 August 2024
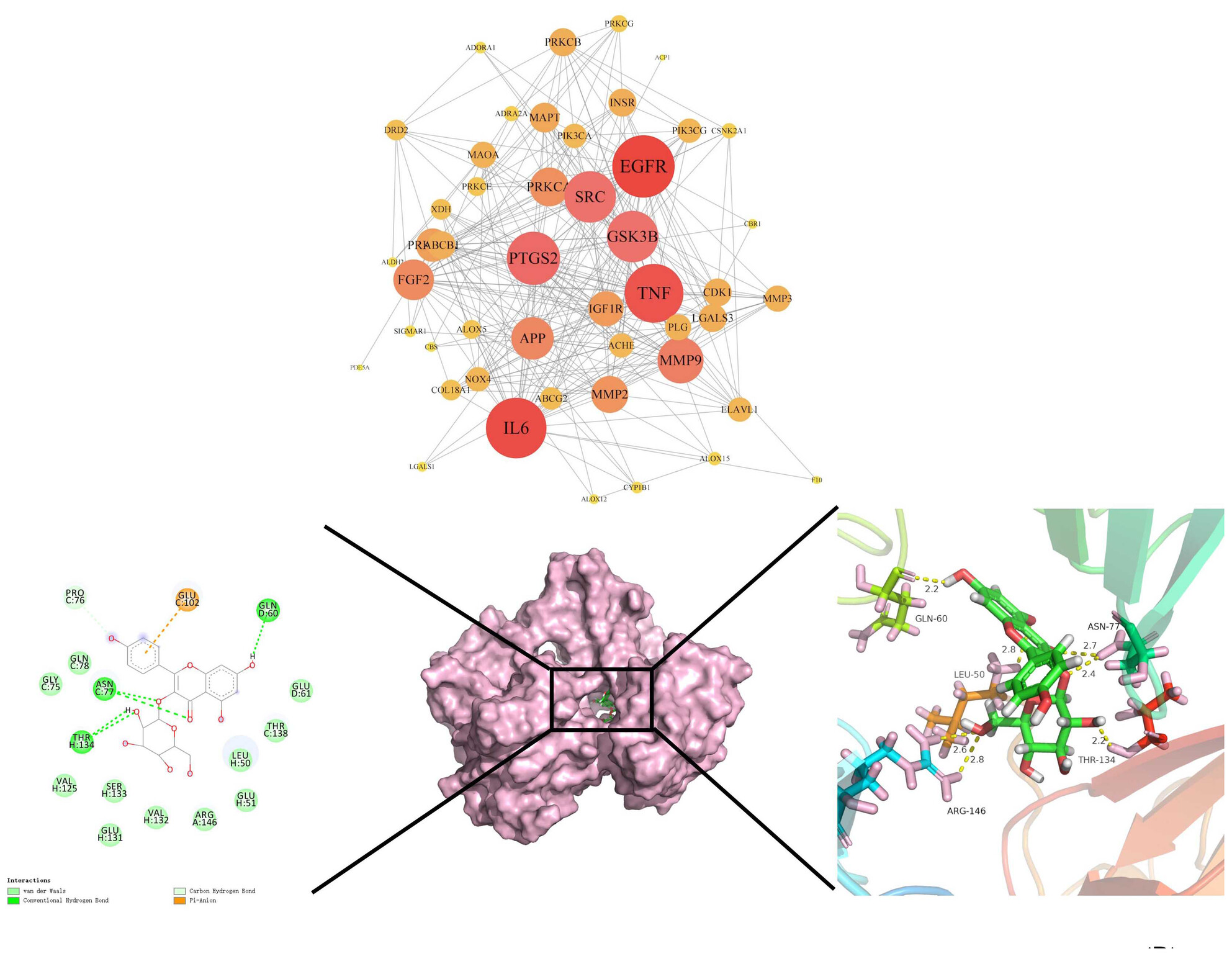
Astragalin improves cognitive disorder in Alzheimer's disease: Based on network pharmacology and molecular docking simulation
- First Published: 06 August 2024
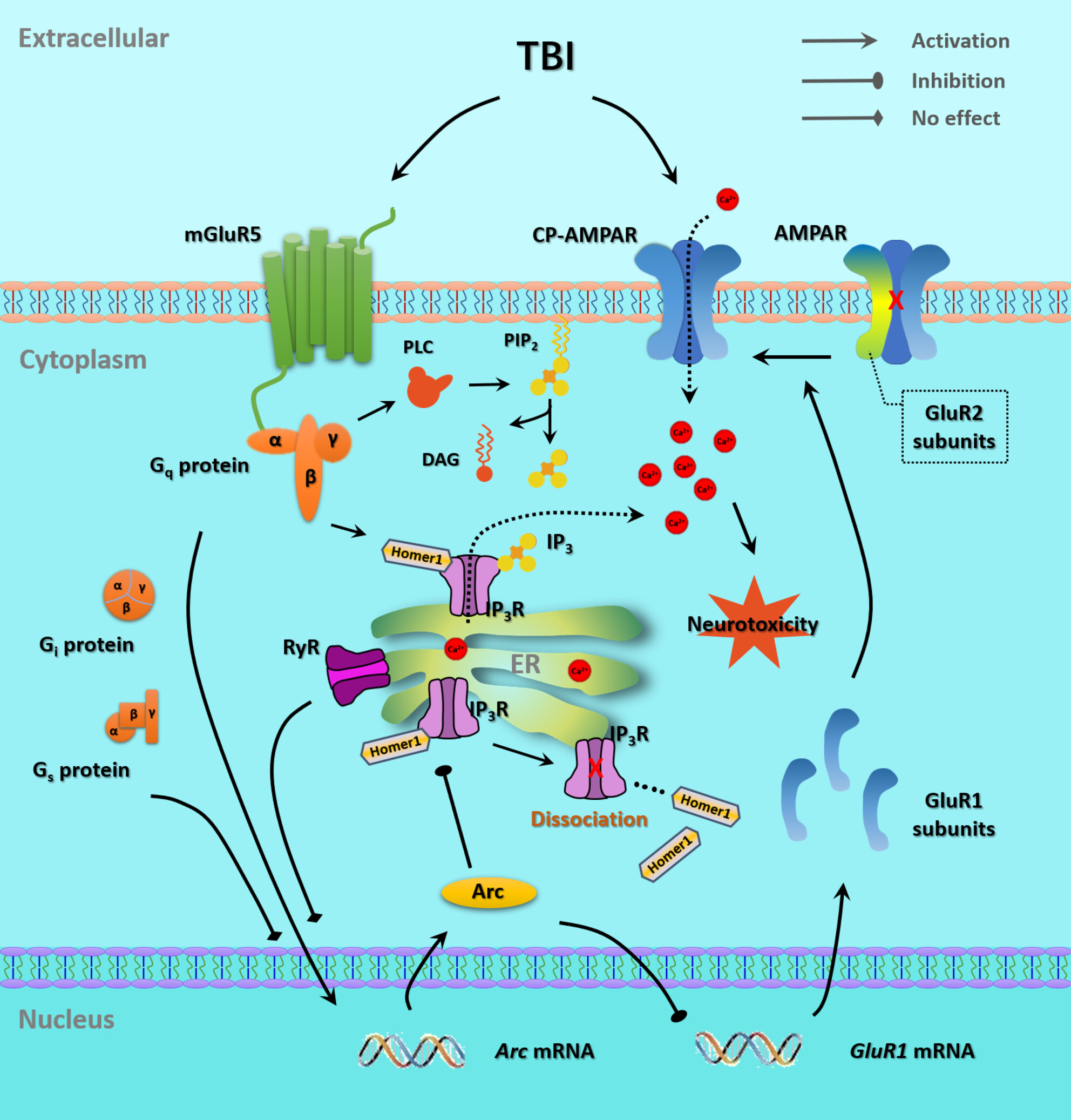
The mGluR5-mediated Arc activation protects against experimental traumatic brain injury in rats
- First Published: 06 August 2024
Fucoidan improving spinal cord injury recovery: Modulating microenvironment and promoting remyelination
- First Published: 14 August 2024
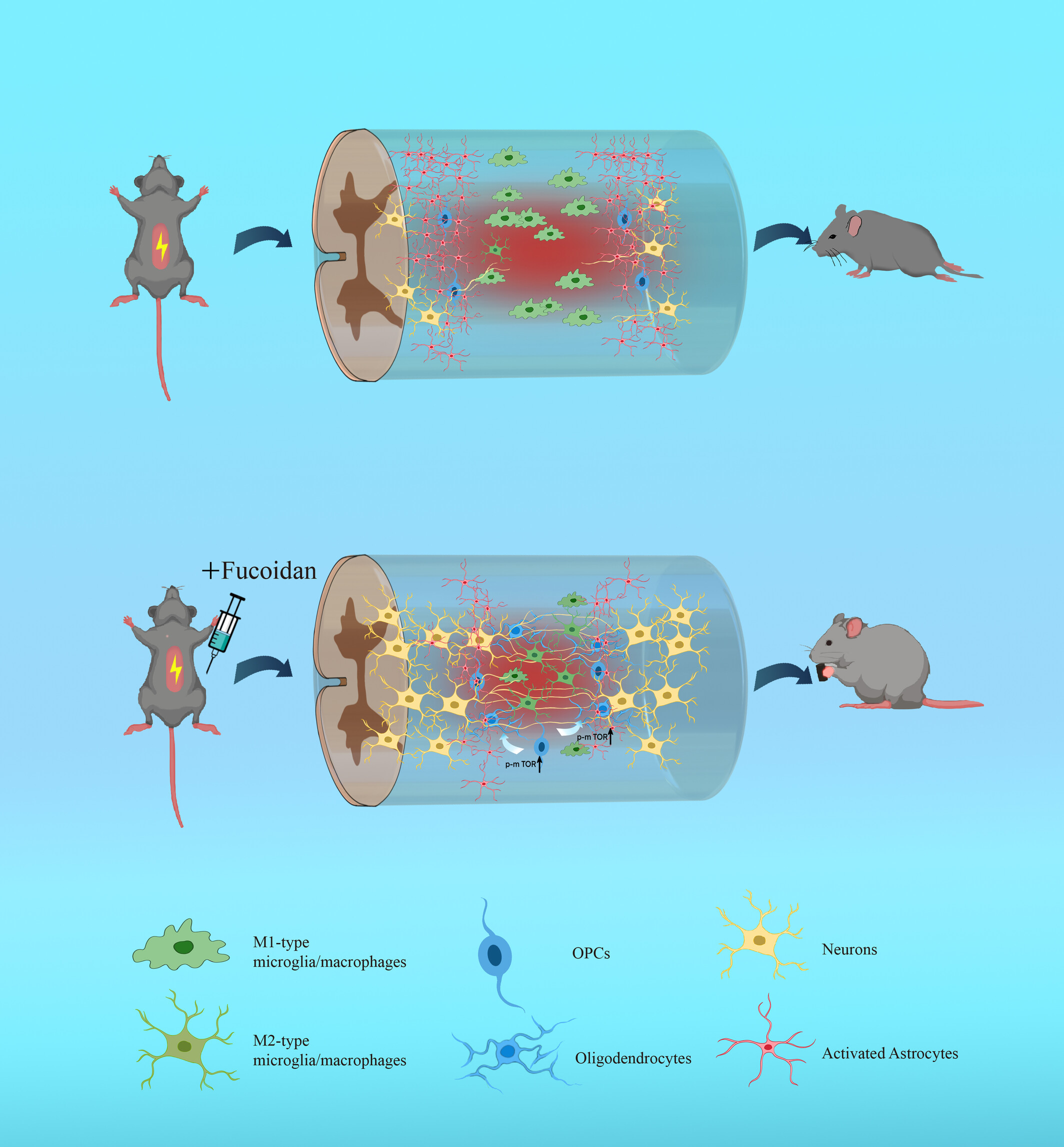
Our results indicate that in the SCI model, fucoidan exhibits significant anti-inflammatory effects and promotes the transformation of pro-inflammatory M1-type microglia/macrophages into anti-inflammatory M2-type ones. Fucoidan enhances the survival of neurons and axons in the injury area and improves remyelination. Additionally, fucoidan promotes OPC differentiation into mature oligodendrocytes by activating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. These findings suggest that fucoidan improves SCI repair by modulating the microenvironment and promoting remyelination.
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
Reduced risk tolerance and cortical excitability following COVID-19 infection
- First Published: 06 August 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Gender-specific prognosis models reveal differences in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients between sexes
- First Published: 06 August 2024
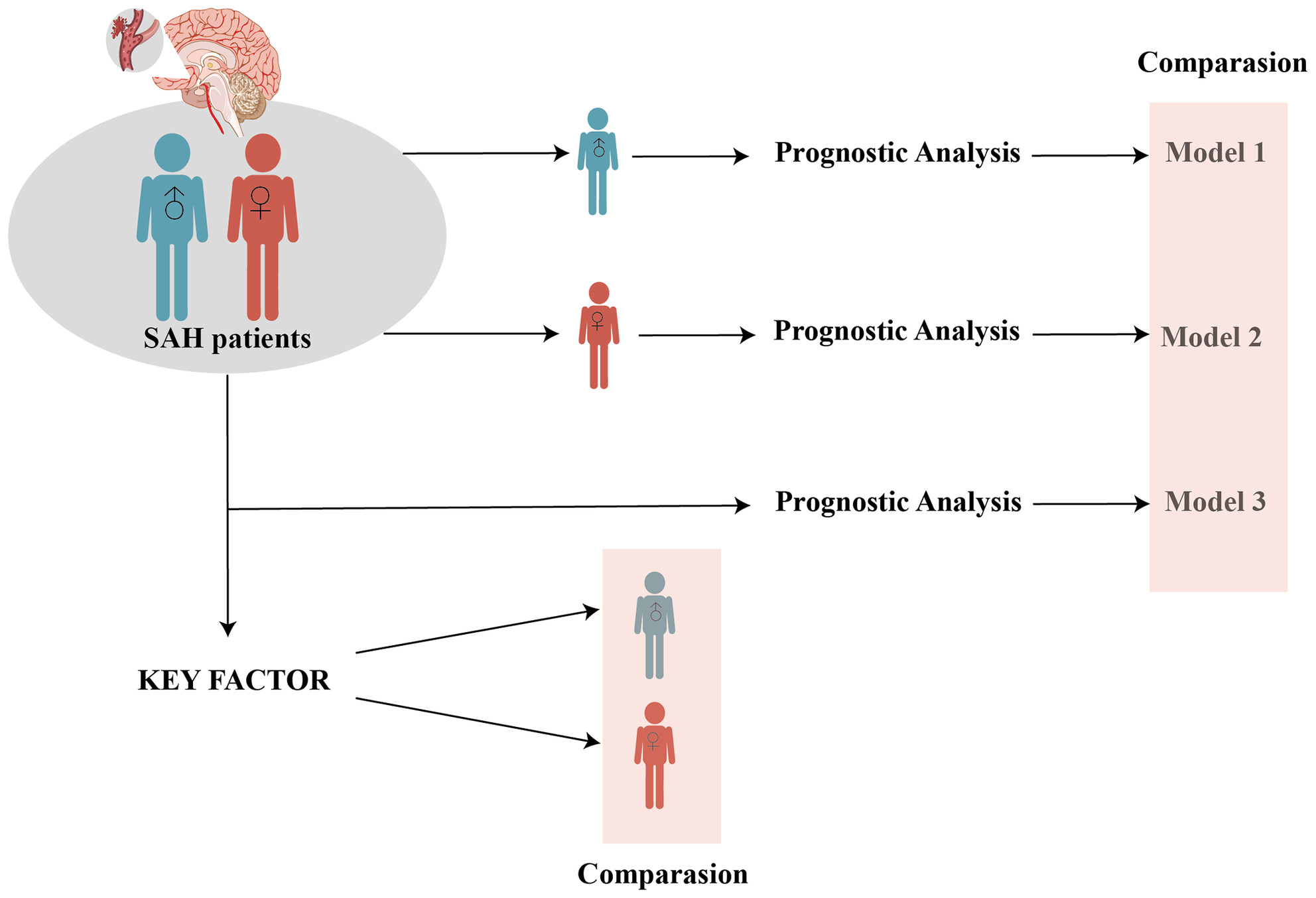
Gender-specific prognostic models were developed based on distinct factors among SAH patients. Variations in baseline characteristics and treatments partially contribute to gender-based prognosis differences. Independent prognostic factors vary by gender. Gender-specific prognostic models demonstrated robust discriminative ability, highlighting the importance of considering gender-specific factors in SAH prognosis.
Unraveling multi-scale neuroimaging biomarkers and molecular foundations for schizophrenia: A combined multivariate pattern analysis and transcriptome-neuroimaging association study
- First Published: 08 August 2024
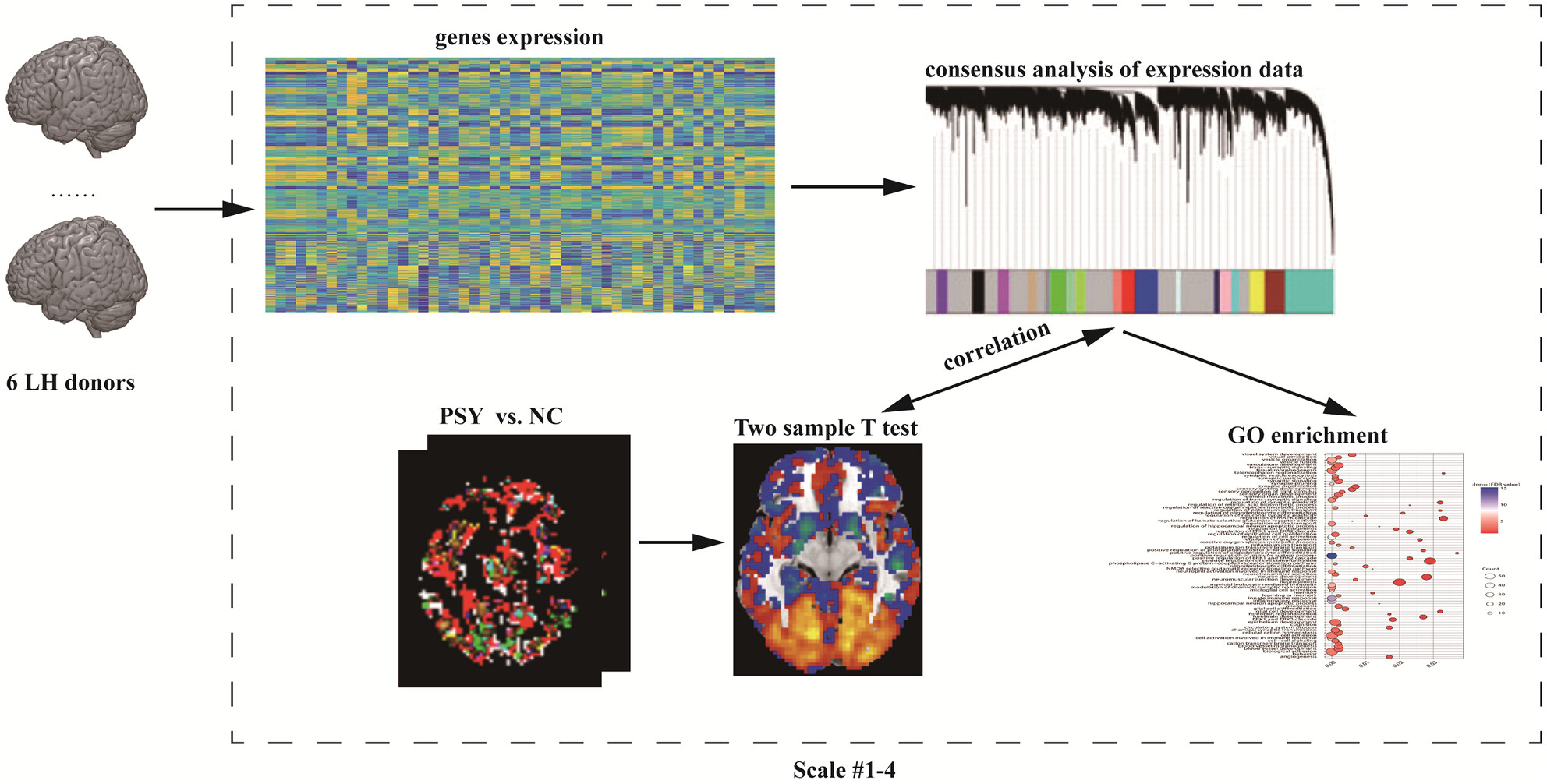
Our study highlights the potential of multi-scale ReHo analysis as a valuable neuroimaging biomarker in the diagnosis of schizophrenia. Furthermore, we observed spatial scale-dependent differences in enriched biological processes in the brain associated with schizophrenia. These related genes were mainly linked to immune responses, inflammation, synaptic signaling, ion channels, cellular development, myelination, and transporter activity.
REVIEW
Blood pressure management after endovascular thrombectomy: Insights of recent randomized controlled trials
- First Published: 08 August 2024
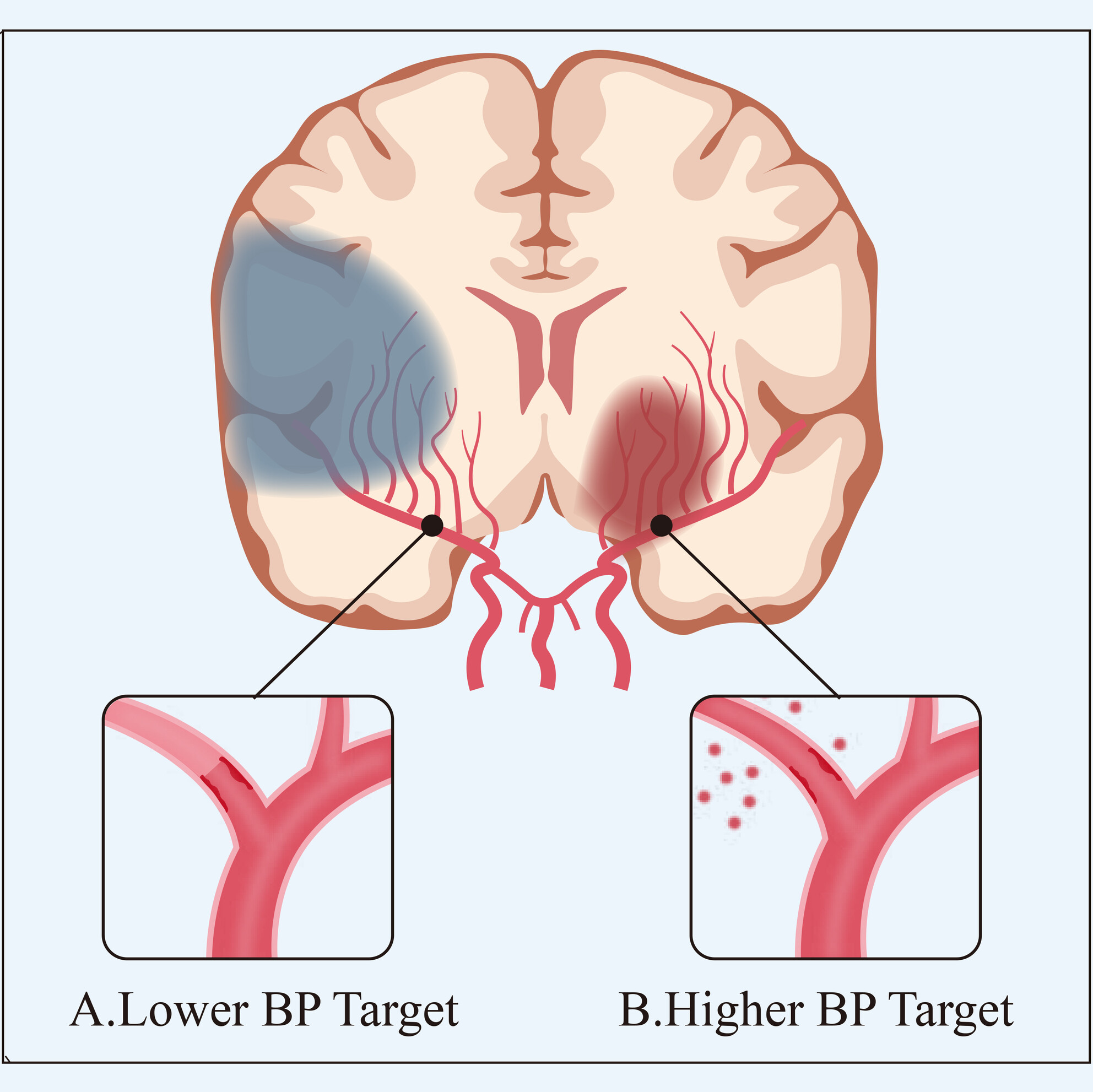
The ideal systolic blood pressure target following successful endovascular thrombectomy remains unclear. This article summarizes and analyzes the key conclusions and implications of recent randomized controlled trials, while also exploring the innovative directions for optimizing blood pressure control following endovascular thrombectomy. The recently completed randomized controlled trials failed to demonstrate the beneficial effect of intensive blood pressure control on both the functional outcome and reduction of the risk of intraparenchymal hemorrhage. Future research should place greater emphasis on individualized blood pressure management strategies, minimizing blood pressure variability, and implementing multi-stage BP management protocols in this field.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Impact of peripheral lymphocyte subsets on prognosis for patients after acute ischemic stroke: A potential disease prediction model approach
- First Published: 28 August 2024
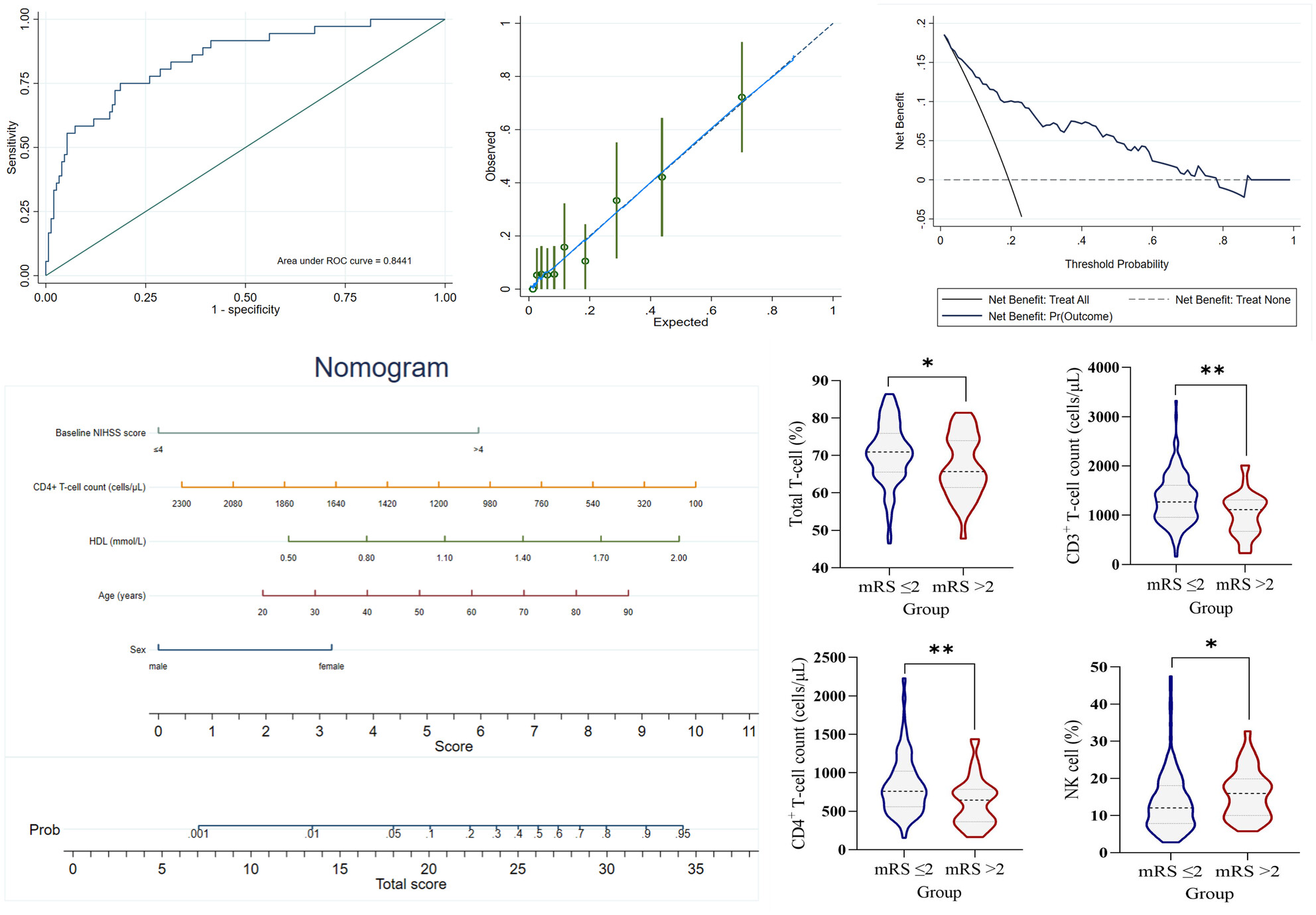
This analysis demonstrates that peripheral T lymphocyte counts in patients with acute ischemic stroke (AIS) are negatively correlated with the 3-month prognosis. The correlation analysis, stratified by onset days, indicates that this conclusion is most significant in the 1–3 days post-stroke group. Furthermore, an individualized predictive model based on CD4+ T-cell count shows high accuracy, suggesting its potential as a target for interventions to improve the prognosis of patients with AIS.
Hyperglycemia-induced Sirt3 downregulation increases microglial aerobic glycolysis and inflammation in diabetic neuropathic pain pathogenesis
- First Published: 09 August 2024
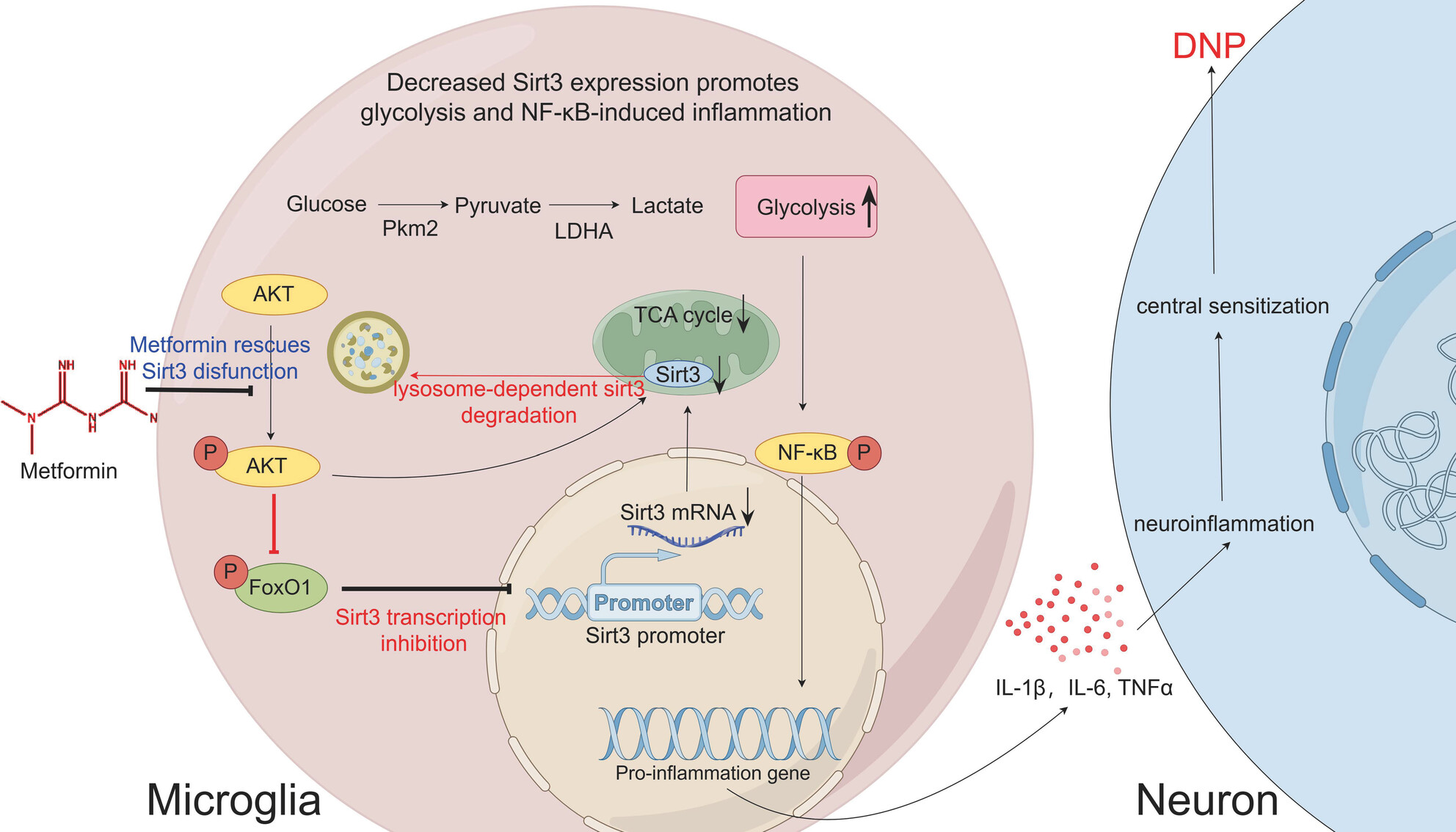
Li et al. have addressed the critical role of hyperglycemia-induced neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathic pain (DNP), a significant and growing global health concern due to the rising prevalence of diabetes. Metformin can decrease neuroinflammation and DNP, and this effect depends on its regulation of Sirt3 protein level.
Evaluation of neuroretina following i.v. or intra-CSF AAV9 gene replacement in mice with MPS IIIA, a childhood dementia
- First Published: 09 August 2024
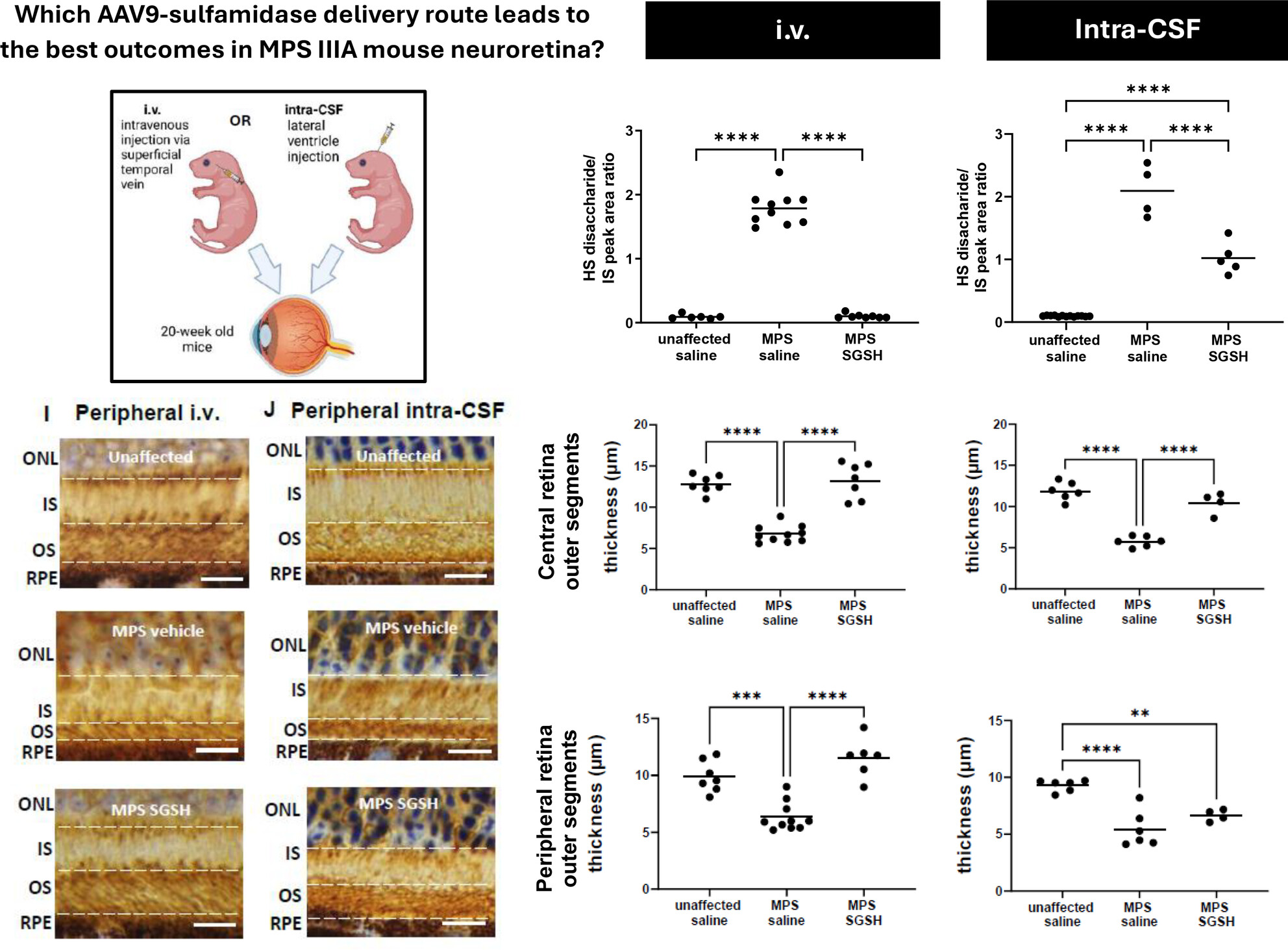
Beard, Hemsley and colleagues compared the efficacy of neonatal AAV9-based gene replacement via intravenous or cerebrospinal fluid injection routes, on retinal degeneration in a mouse model of childhood dementia caused by Sanfilippo syndrome. Intravenous AAV9-CMV-human sulfamidase resulted in superior therapeutic efficacy, compared with cerebrospinal fluid infusions of the same viral vector. Created with BioRender.com.
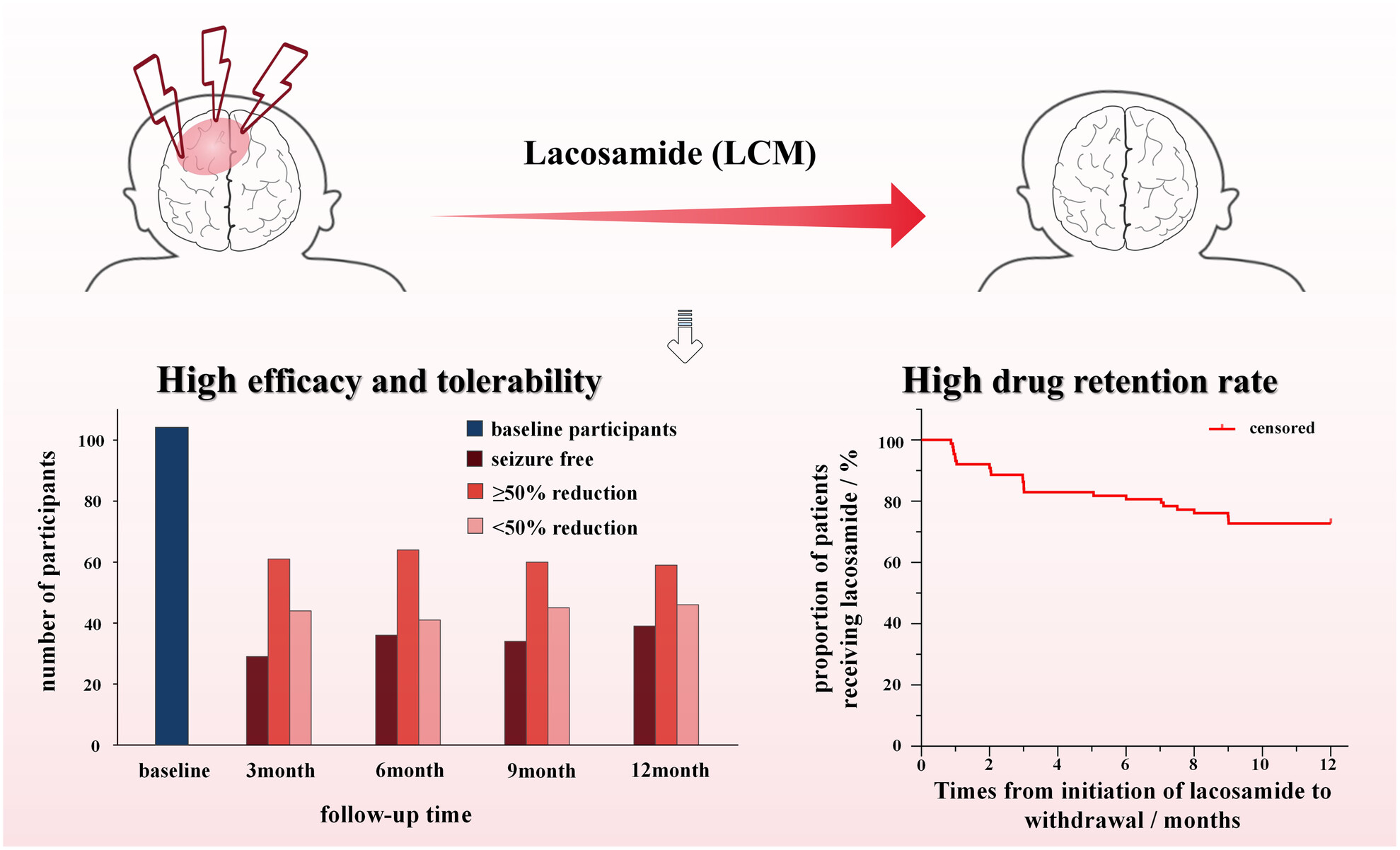
Efficacy, safety, and tolerability of adjunctive Lacosamide therapy for focal seizures in young children aged ≥1 month to ≤4 years: A real-world study
- First Published: 09 August 2024
REVIEW
Natural compounds from herbs and nutraceuticals as glycogen synthase kinase-3β inhibitors in Alzheimer's disease treatment
- First Published: 11 August 2024
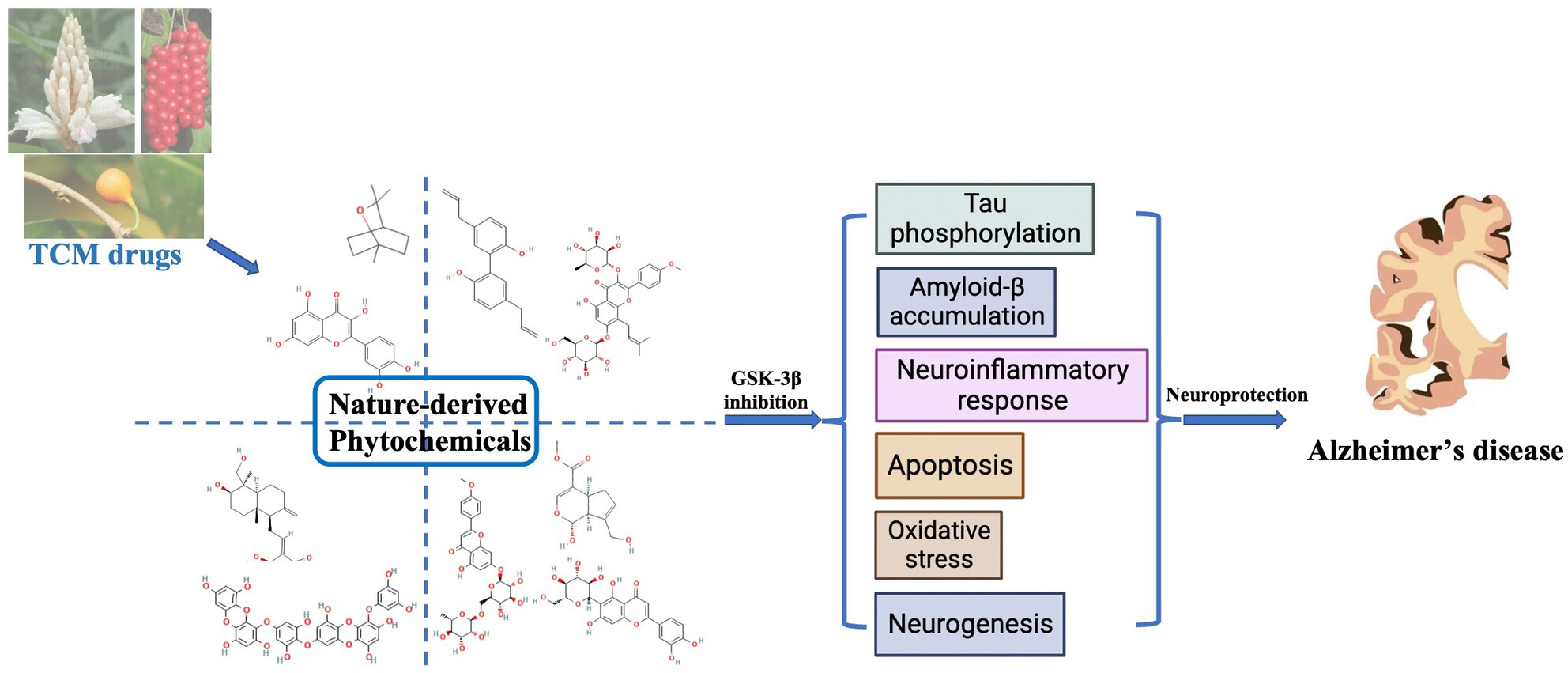
GSK-3β kinase dysregulation aggregates Aβ production and accumulation in Alzheimer's disease (AD). Hyperactive GSK-3β promotes phosphorylation and formation of toxic tau species. GSK-3β represents a promising therapeutic target against AD. Nature-derived phytochemicals inhibiting GSK-3β activity provided novel therapeutic strategy for AD.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Motor progression trajectories and risk of mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson's disease: A latent class trajectory model from PPMI cohort
- First Published: 12 August 2024
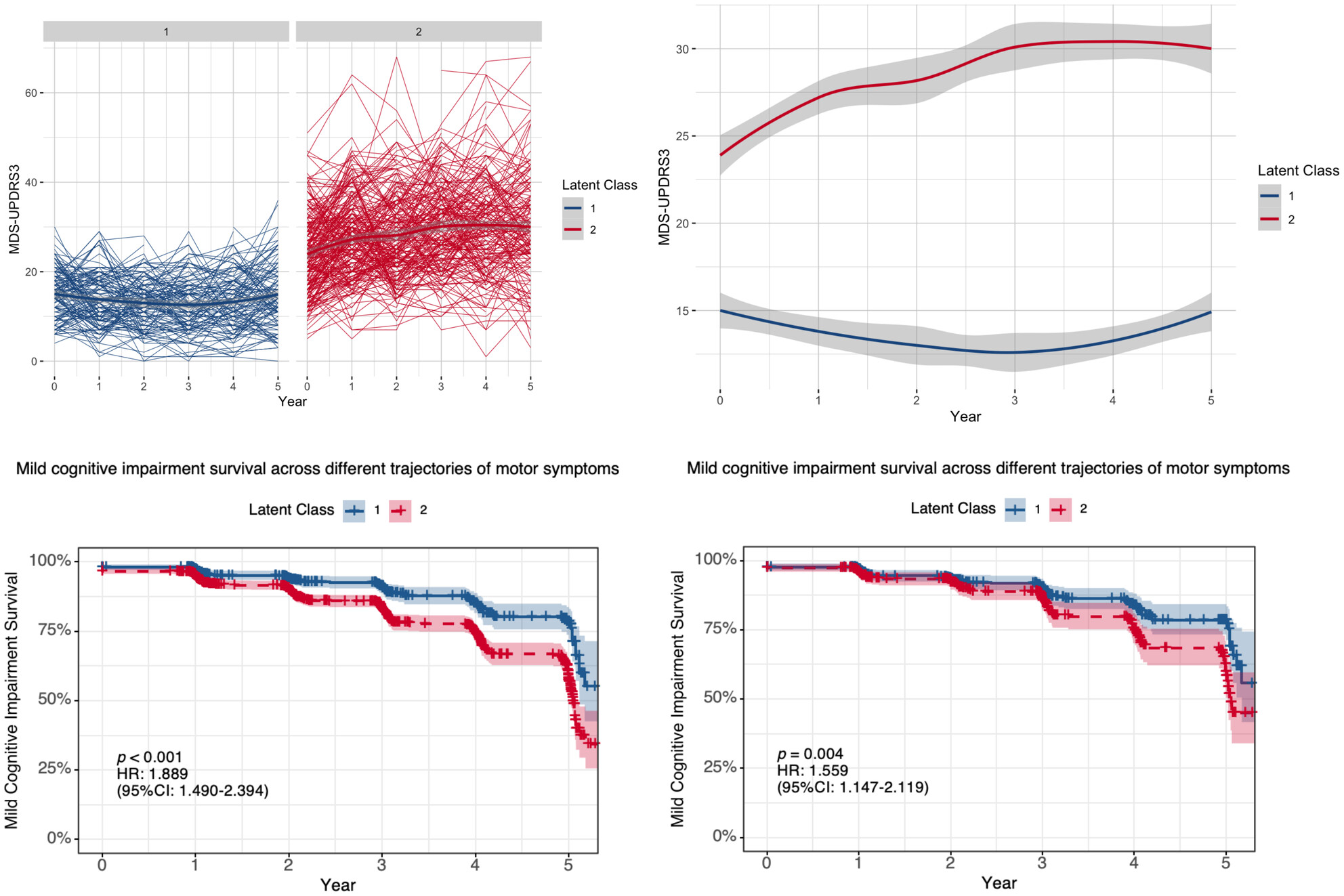
The heterogeneity of motor progression in Parkinson's disease (PD) may serve as a predictive factor for early cognitive decline. This study indicates that PD patients with severe and progressive motor symptoms are at a higher risk of developing mild cognitive impairment than those with mild and stable motor symptoms.
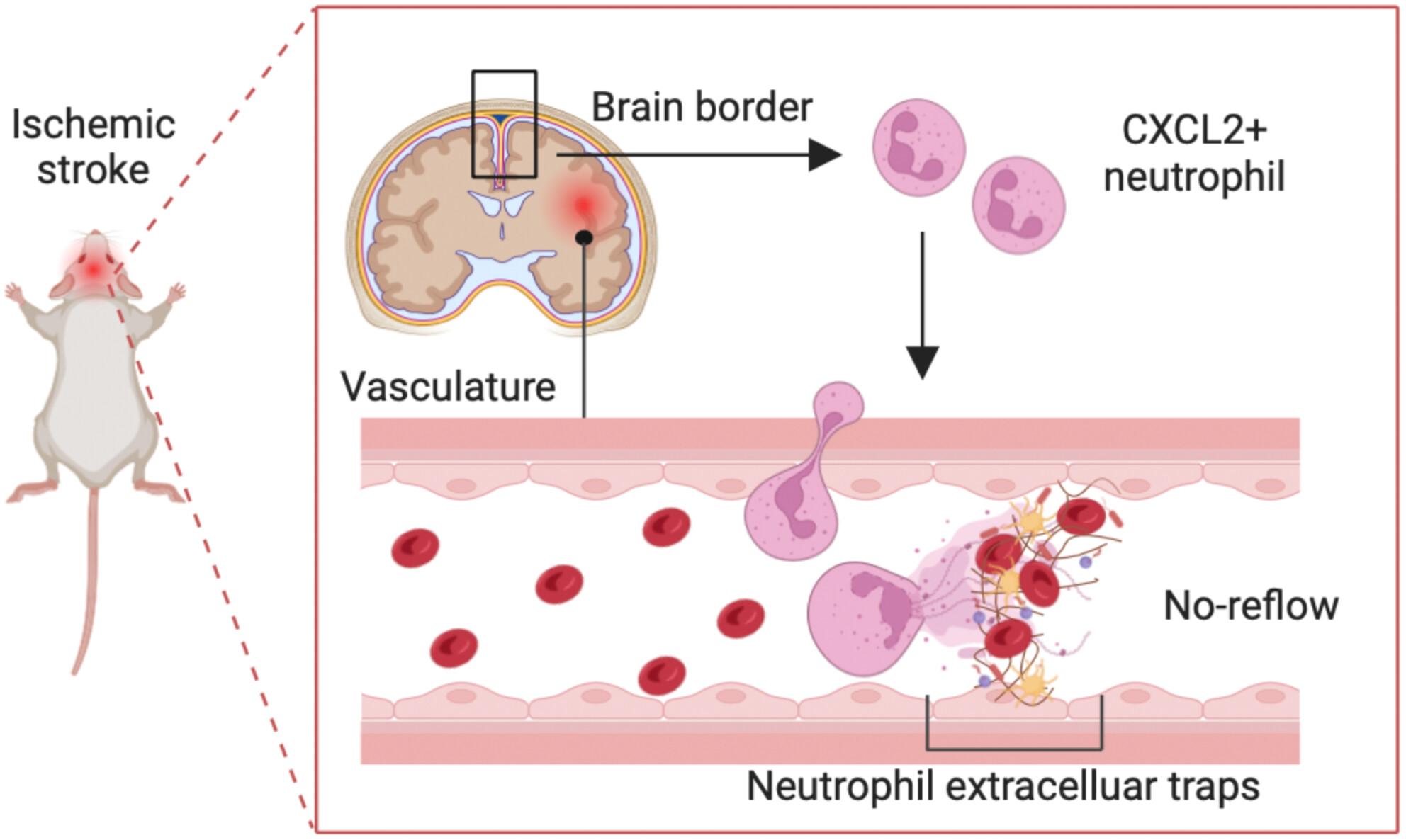
Brain border-derived CXCL2+ neutrophils drive NET formation and impair vascular reperfusion following ischemic stroke
- First Published: 12 August 2024
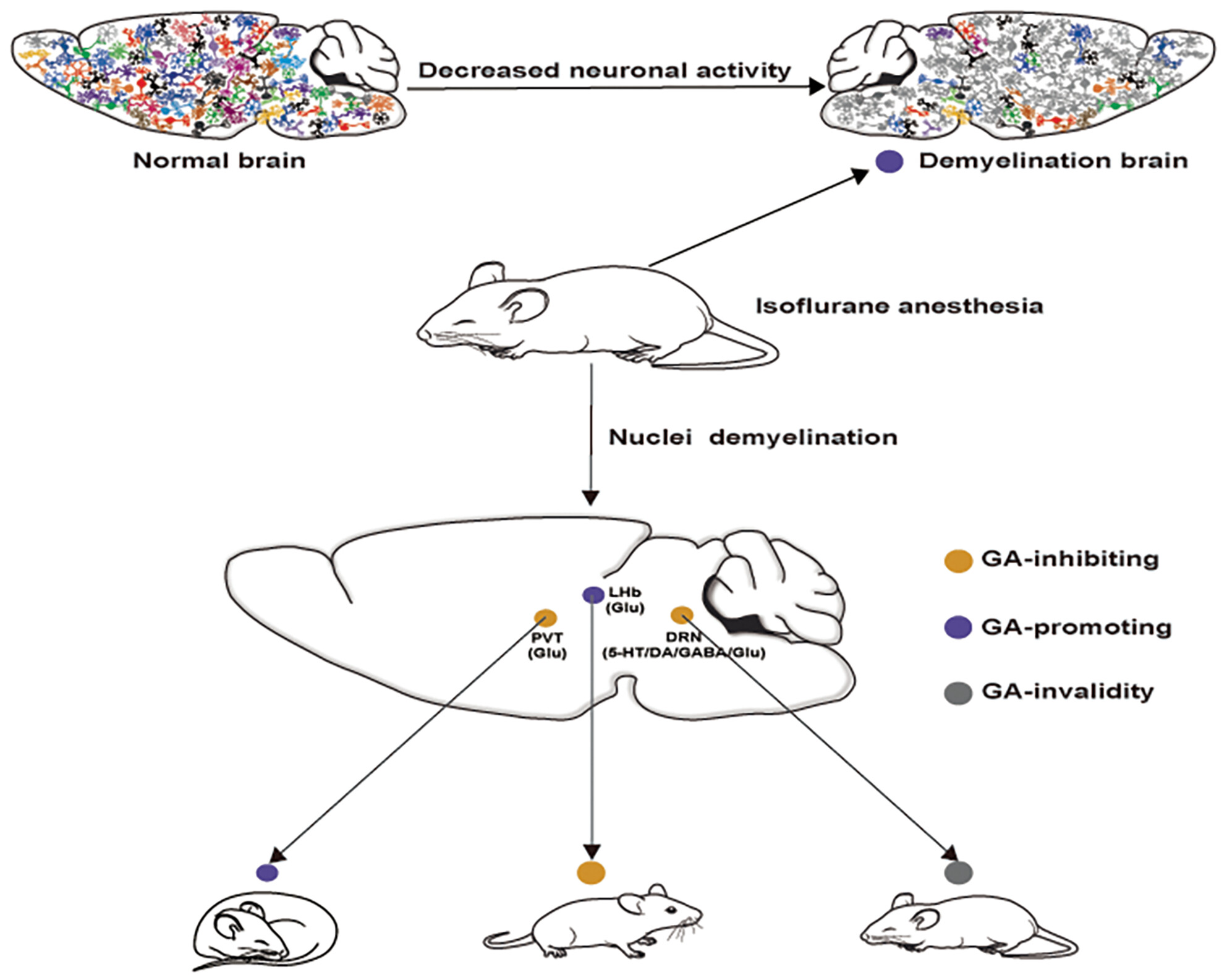
Myelin modulates the process of isoflurane anesthesia through the regulation of neural activity
- First Published: 13 August 2024
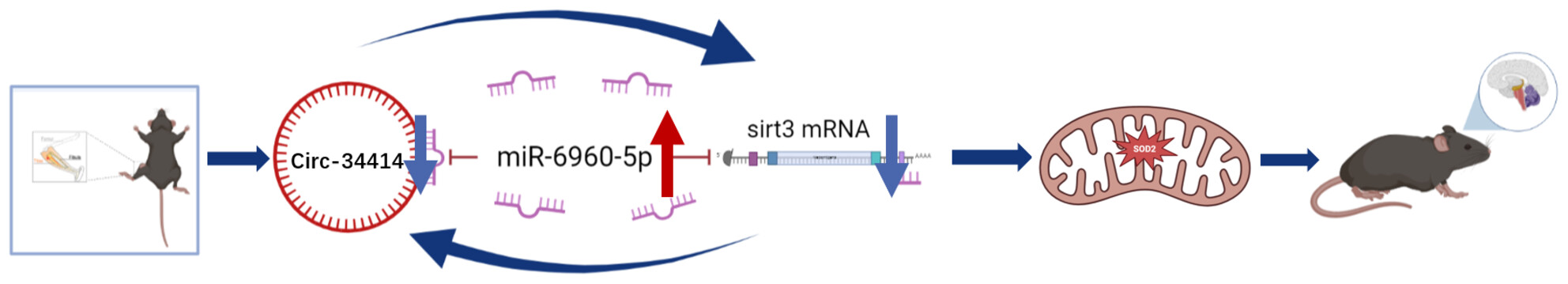
Role of the circRNA_34414/miR-6960a-5p/SIRT3 axis in postoperative delirium via CA1 Vglut1+ neurons in older mice
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Modulating neuroinflammation and cognitive function in postoperative cognitive dysfunction via CCR5-GPCRs-Ras-MAPK pathway targeting with microglial EVs
- First Published: 14 August 2024
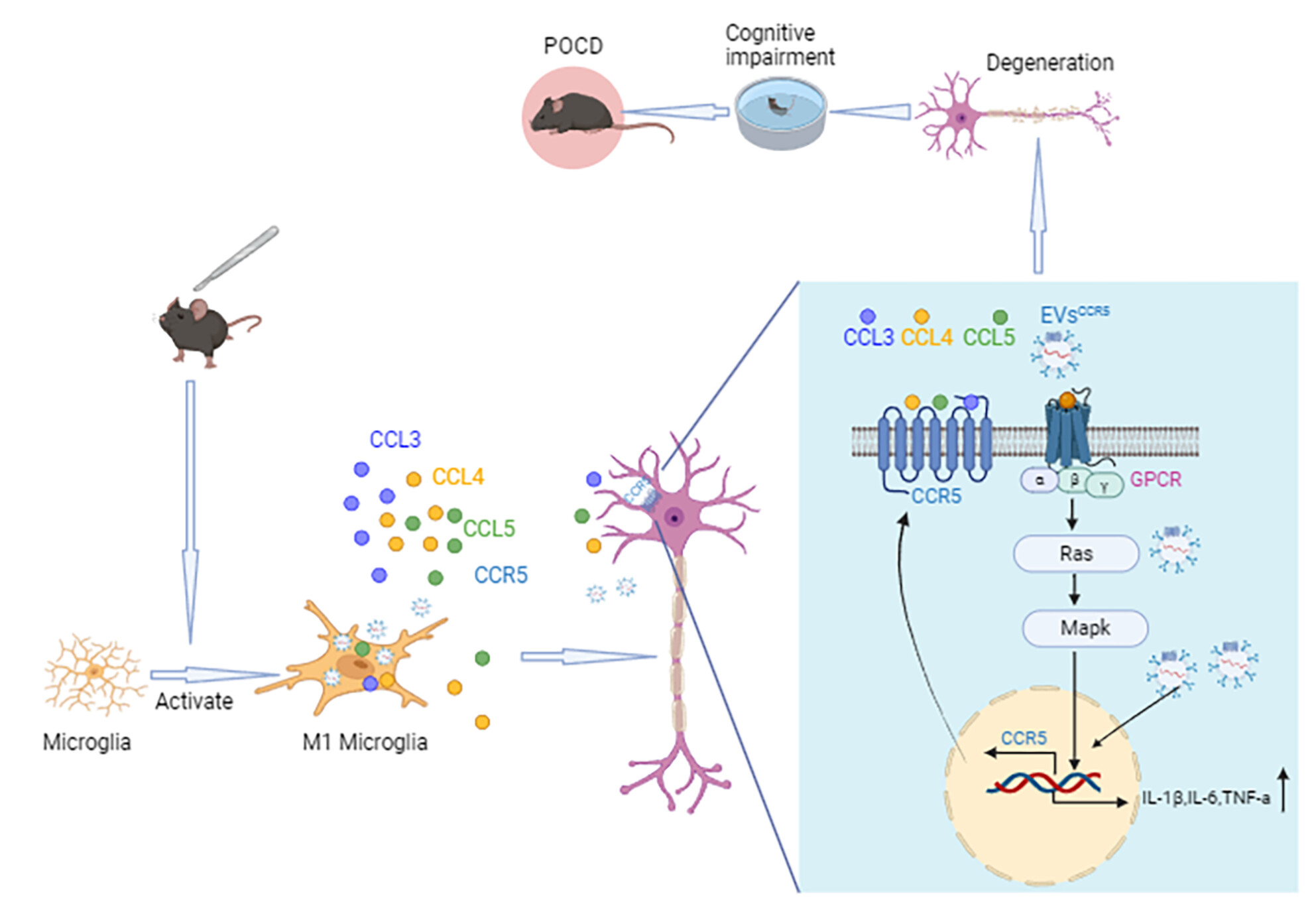
Administer anesthesia and perform surgery to promote M1 polarization of microglia and the release of EVsM1 with high CCR5 expression. EVsM1 promotes CCR5 expression on the neuronal surface, which triggered activation of the GPCRs-Ras-Mapk signaling pathway by the binding of CCL3/4/5 to their receptor CCR5 on neurons, causing neuronal degeneration, synaptic loss, and ultimately POCD.
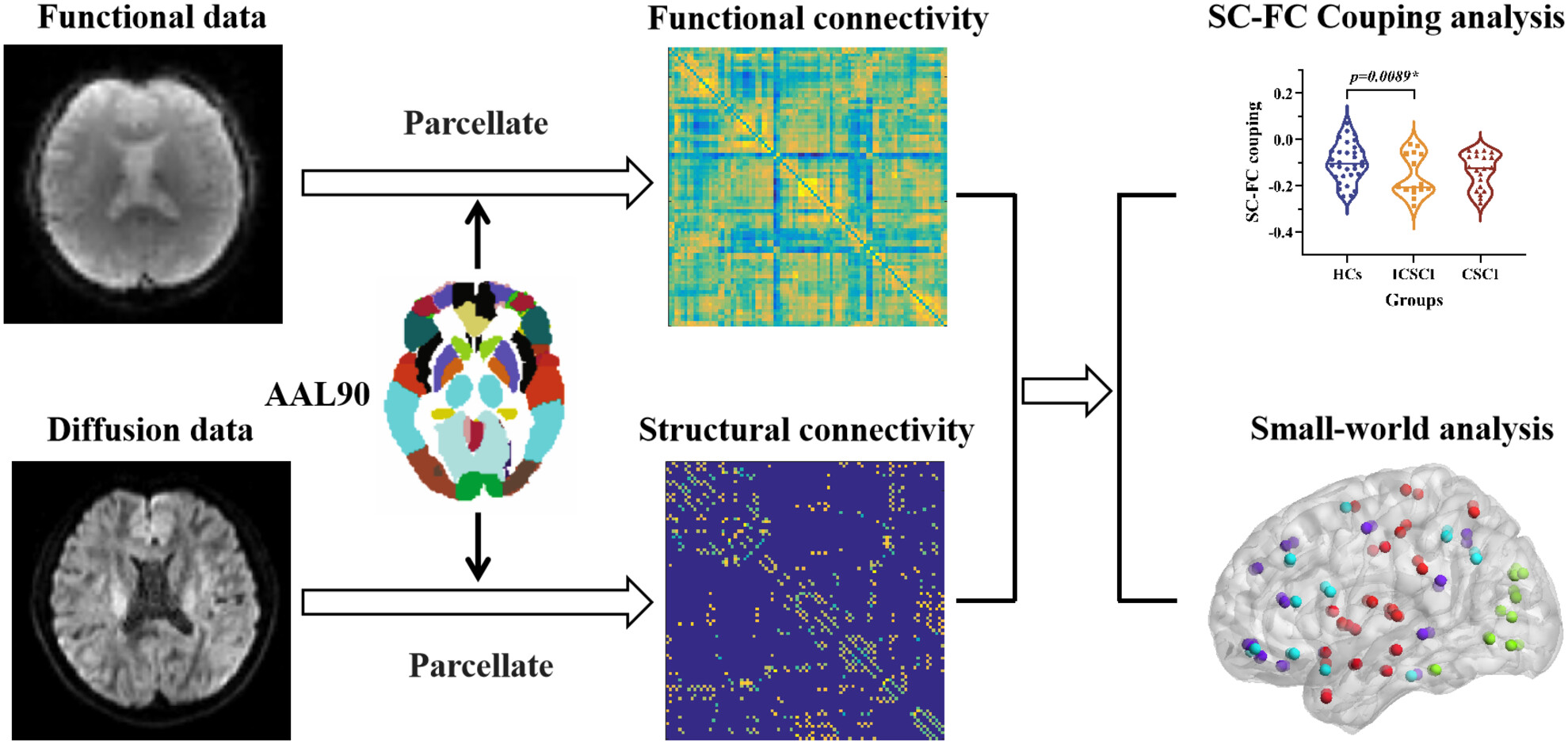
Distinct brain network patterns in complete and incomplete spinal cord injury patients based on graph theory analysis
- First Published: 26 August 2024
Unveiling the shield: Troglitazone's impact on epilepsy-induced nerve injury through ferroptosis inhibition
- First Published: 15 August 2024
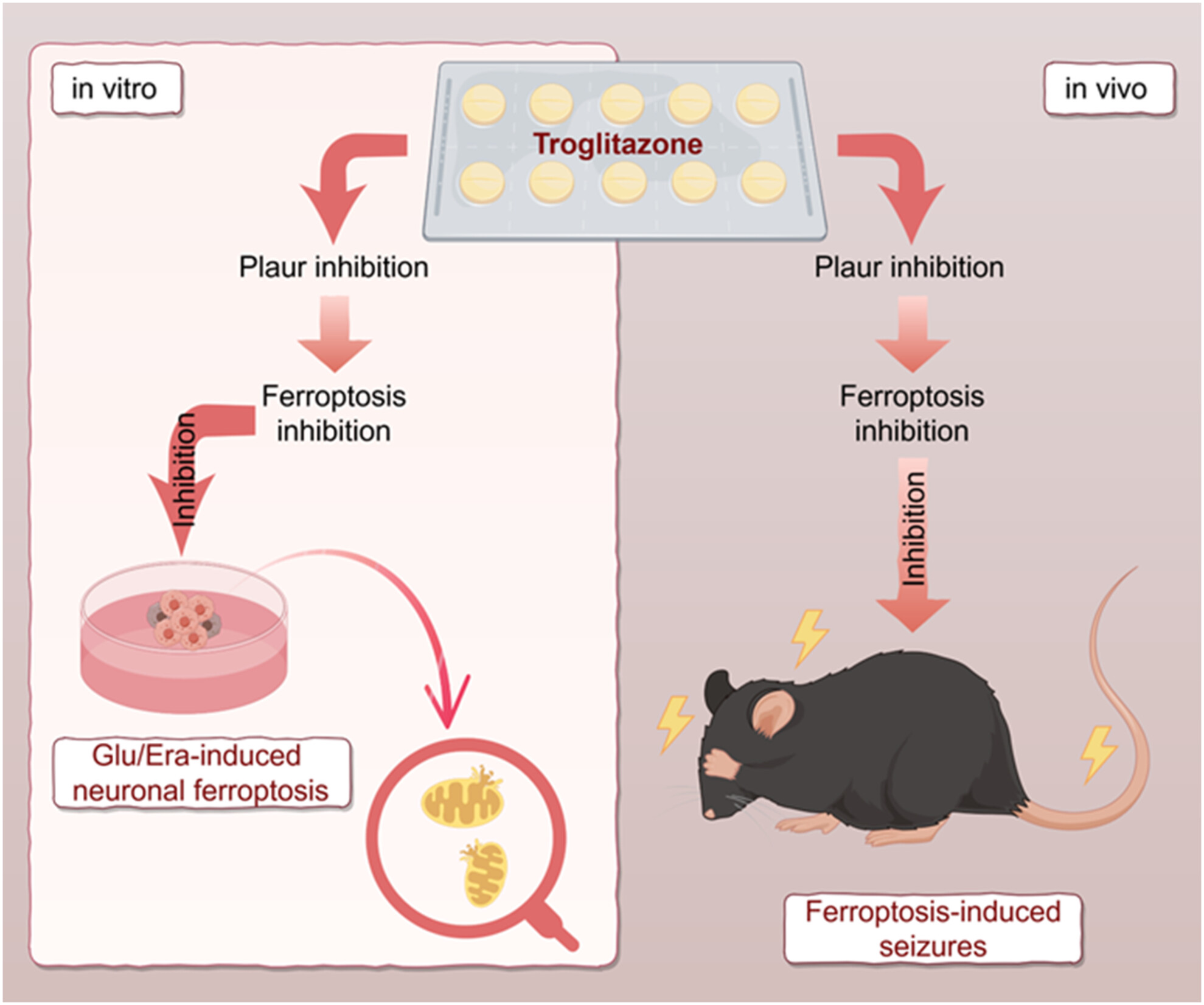
Troglitazone can provide significant neuroprotection against neuronal damage. Troglitazone demonstrates remarkable therapeutic efficacy in alleviating seizure occurrence in mice with an epileptic model. The neuroprotective action of troglitazone is mediated through the inhibition of Plaur, and downregulation of Plaur can mimic this protective effect. Drawn by Figdraw (www.figdraw.com)
Interference of default mode on attention networks in adults with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder and its association with genetic variants and treatment outcomes
- First Published: 15 August 2024
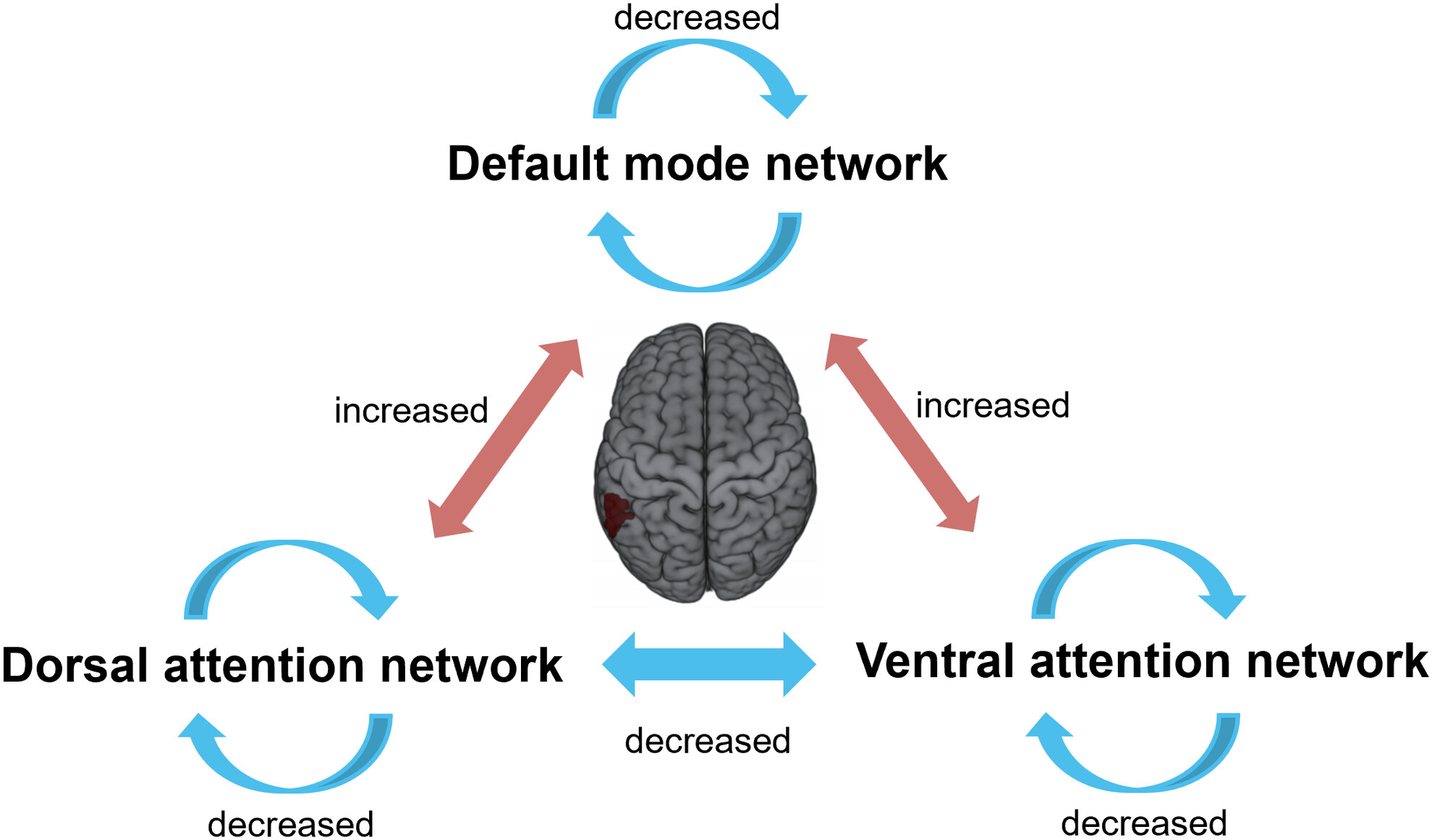
Our voxel-based connectome analyses indicated hypoconnectivity within the DMN (the connectivity between the precuneus with other DMN components) and attentional networks (the connectivity between the left middle temporal cluster and other DAN/VAN components) and hyperconnectivity between these networks (the connectivity between the left middle temporal and DMN components) in adults with ADHD, with the middle temporal gyrus as a key ‘bridge’ region.
Parabrachial nucleus Vglut2 expressing neurons projection to the extended amygdala involved in the regulation of wakefulness during sevoflurane anesthesia in mice
- First Published: 18 August 2024
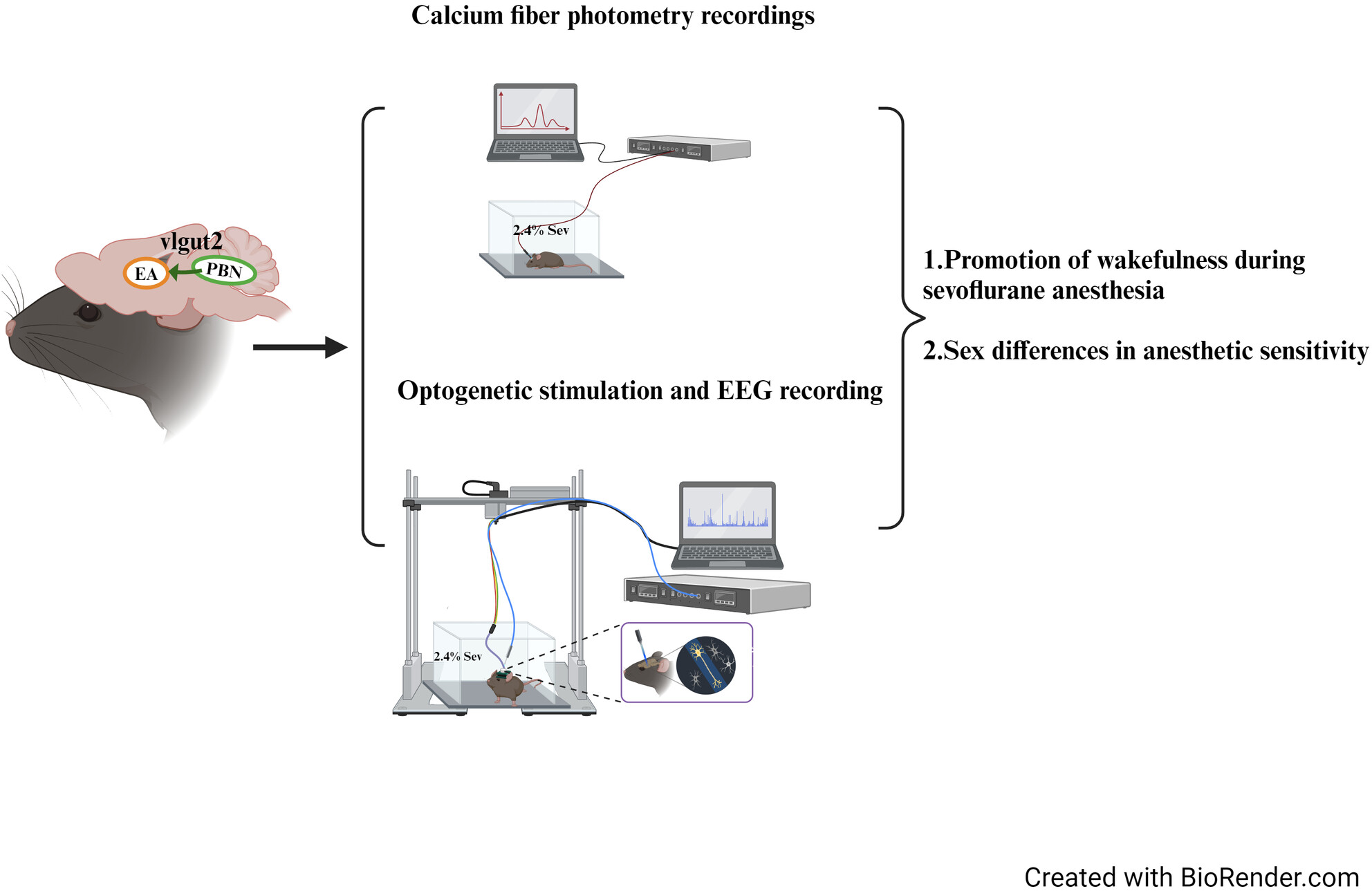
The PBNvglut2-EA is involved in the modulation of awakening during sevoflurane anesthesia. The PBNvglut2-EA exhibited sexually dimorphic activity patterns under general anesthesia. The activation of the PBNvglut2-EA reduced sensitivity to sevoflurane in males and resulted in enhanced arousal states and EEG changes.
Physical function is associated with cognitive status, brain amyloid-beta deposition, and blood biomarkers in Chinese Han population
- First Published: 18 August 2024
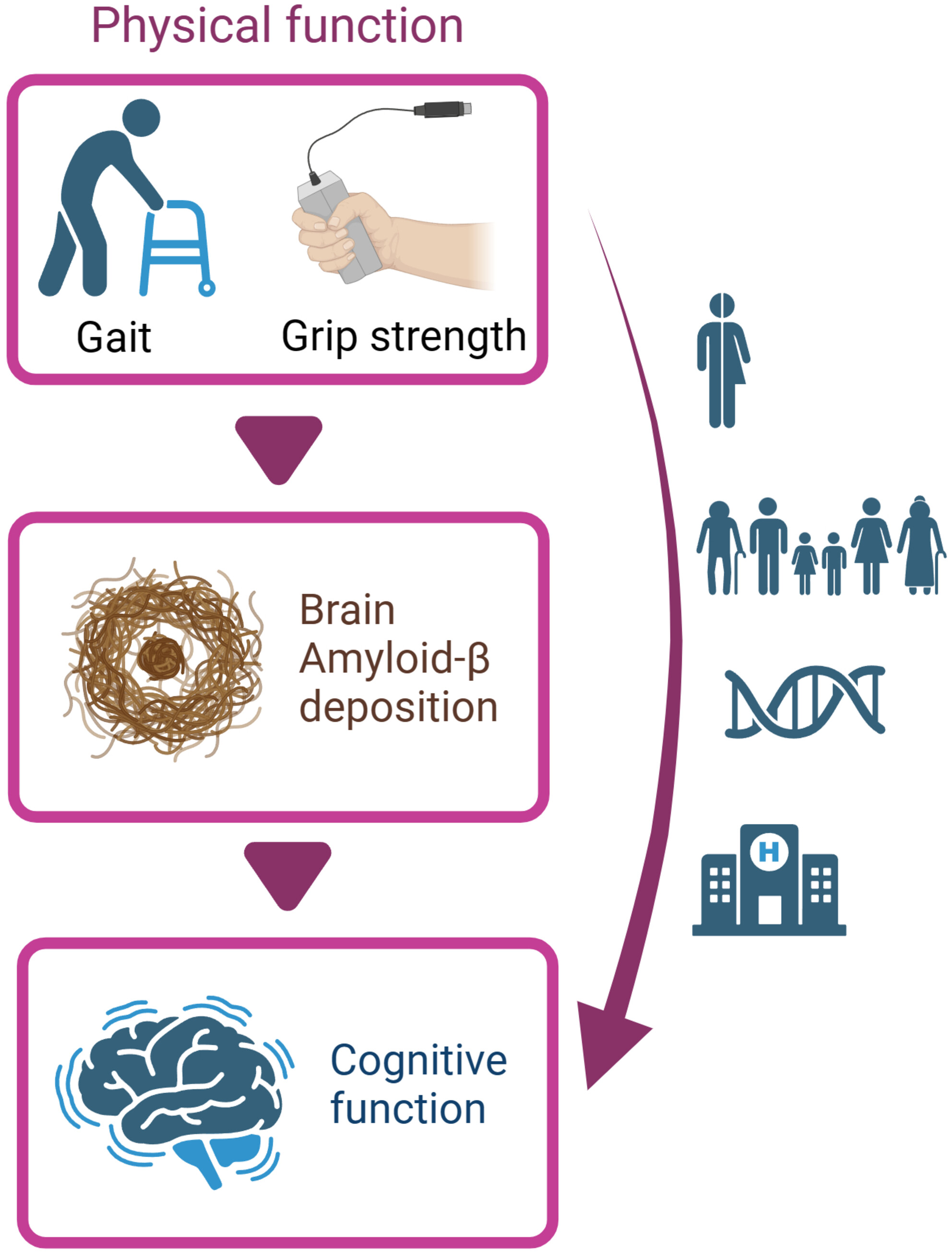
The physical function represented by grip strength and gait is significantly associated with cognitive function, and this relationship is not influenced by gender, age, genetic factors, or dementia severity. This connection allows us to distinguish whether a person's cognition is impaired based on their physical abilities. The brain Aβ deposition serves as an intermediate factor that partially mediates the relationship between physical function and cognitive function, and this mediating effect is particularly pronounced in the female population.
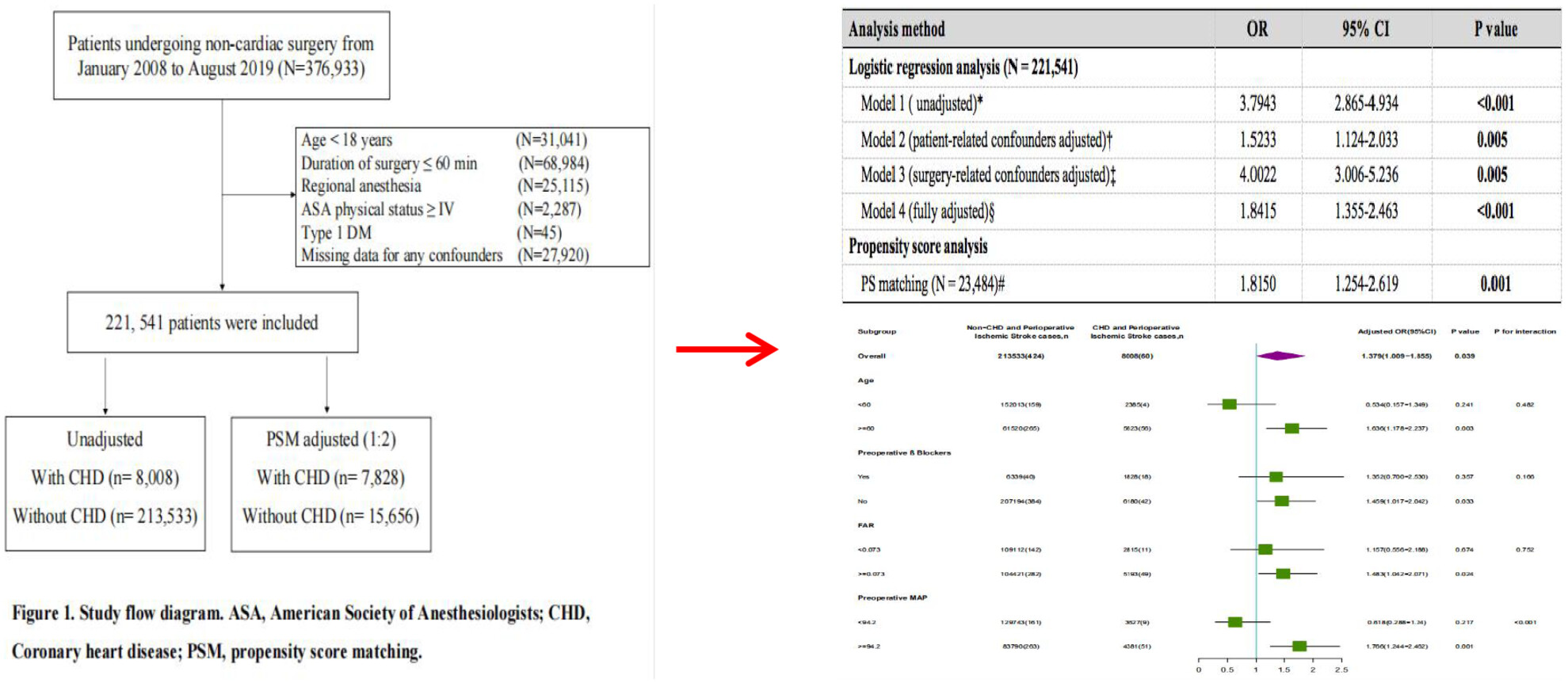
Coronary heart disease increases the risk of perioperative ischemic stroke after noncardiac surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 26 August 2024
Unveiling the interoception impairment in various major depressive disorder stages
- First Published: 18 August 2024
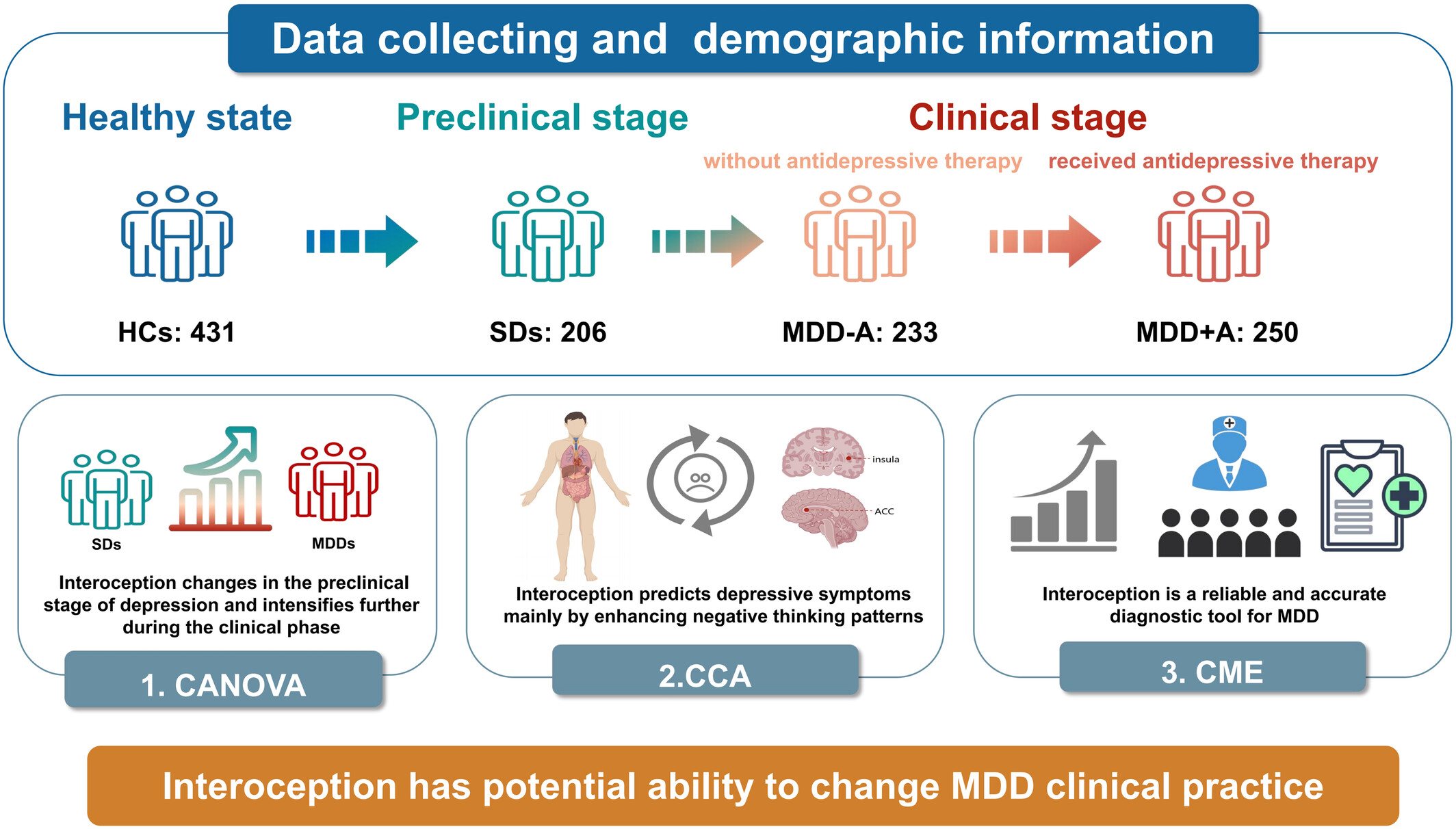
In this study, interoception impairments, beginning in MDD's preclinical phase and escalating during its clinical stage, were found to predictively impact all primary symptom clusters, particularly emotional symptoms. Internal validation underscored their significant role in improving diagnostic accuracy and predictive capabilities for MDD, which offers discriminative and predictive utility for MDD clinical practice.
Myelin endocytosis by brain endothelial cells causes endothelial iron overload and oligodendroglial iron hunger in hypoperfusion-induced white matter injury
- First Published: 19 August 2024
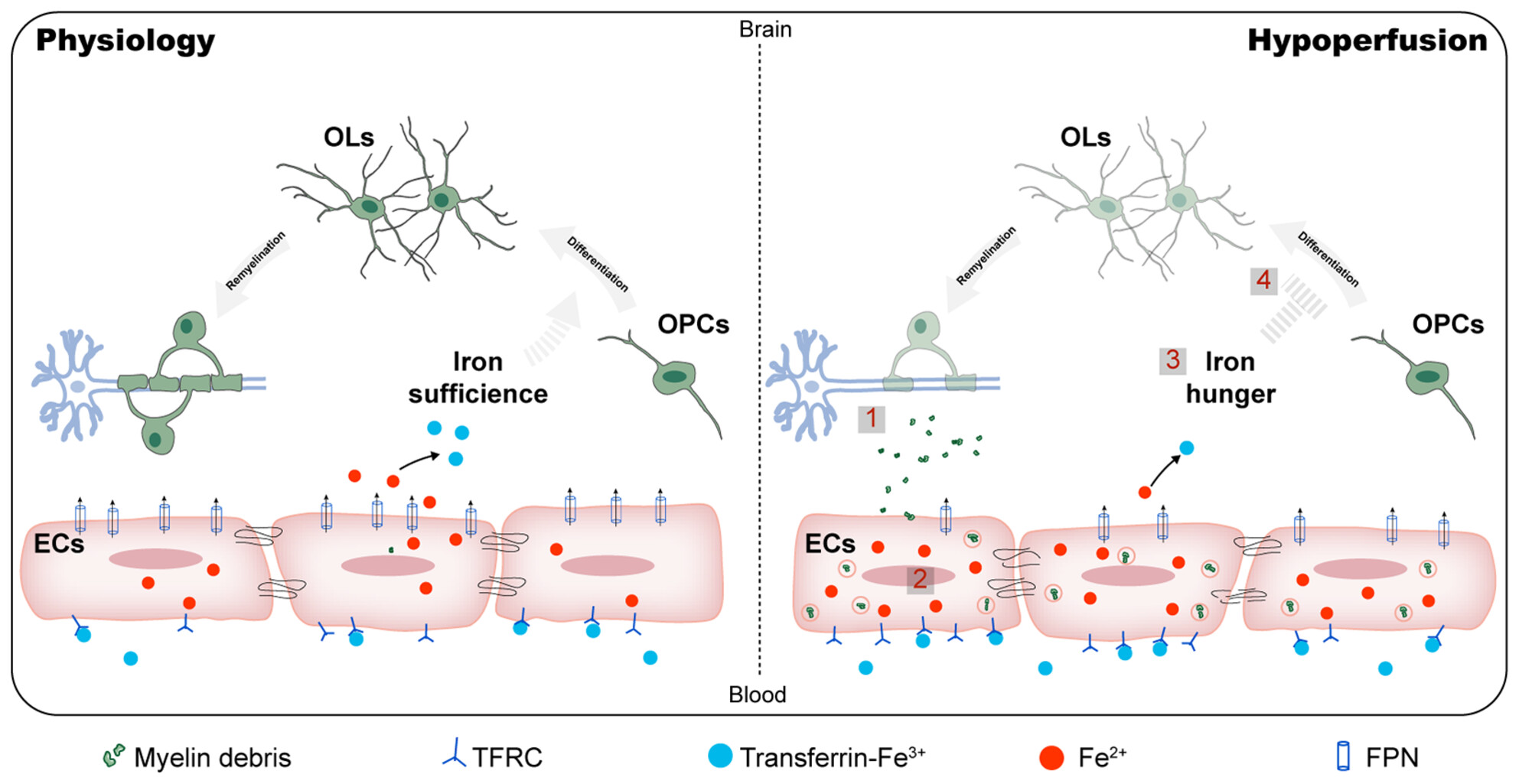
After hypoperfusion injury, brain endothelial cells experience intracellular iron overload due to endocytosis of excessive myelin sheaths, leading to ferroptosis and impaired iron transport. Iron retention in brain endothelial cells results in oligodendroglial iron hunger and remyelination failure. Intranasal iron supplementation to brain parenchyma bypassing blood–brain barrier promotes myelin regeneration in hypoperfusion-induced white matter injury.
Long noncoding RNA H19 knockdown promotes angiogenesis via IMP2 after ischemic stroke
- First Published: 19 August 2024
Fecal microbiota from patients with Parkinson's disease intensifies inflammation and neurodegeneration in A53T mice
- First Published: 19 August 2024
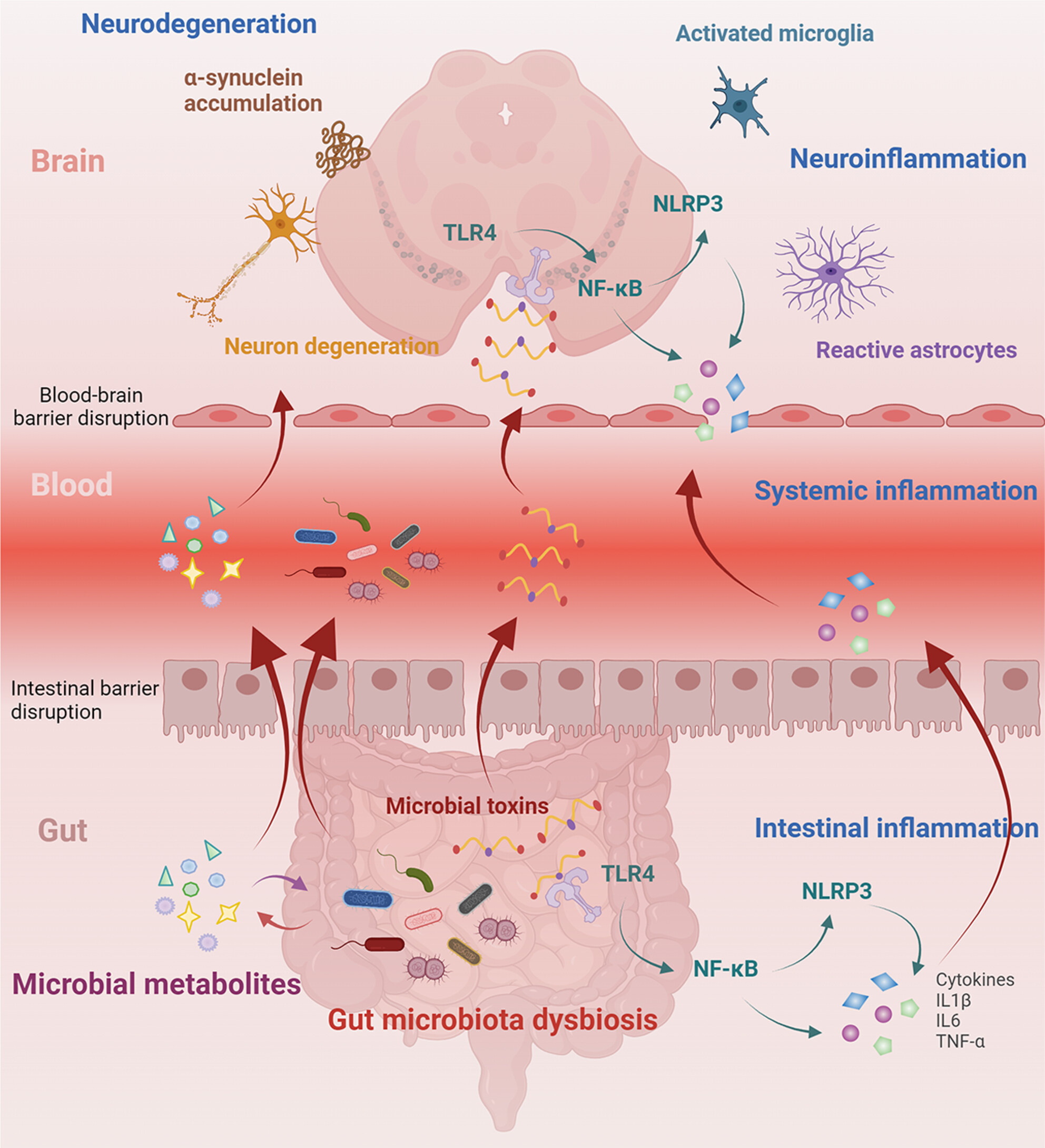
FMT from PD patients altered the structure and composition of the gut microbiota in recipient mice and significantly altered the metabolic profiles, which collectively may aggravate intestinal and systemic inflammation, cause BBB damage, and eventually lead to dopaminergic neurodegeneration. In conclusion, our results suggest that gut microbiota and intestinal ecological disorders are important driving factors for the progression of PD.
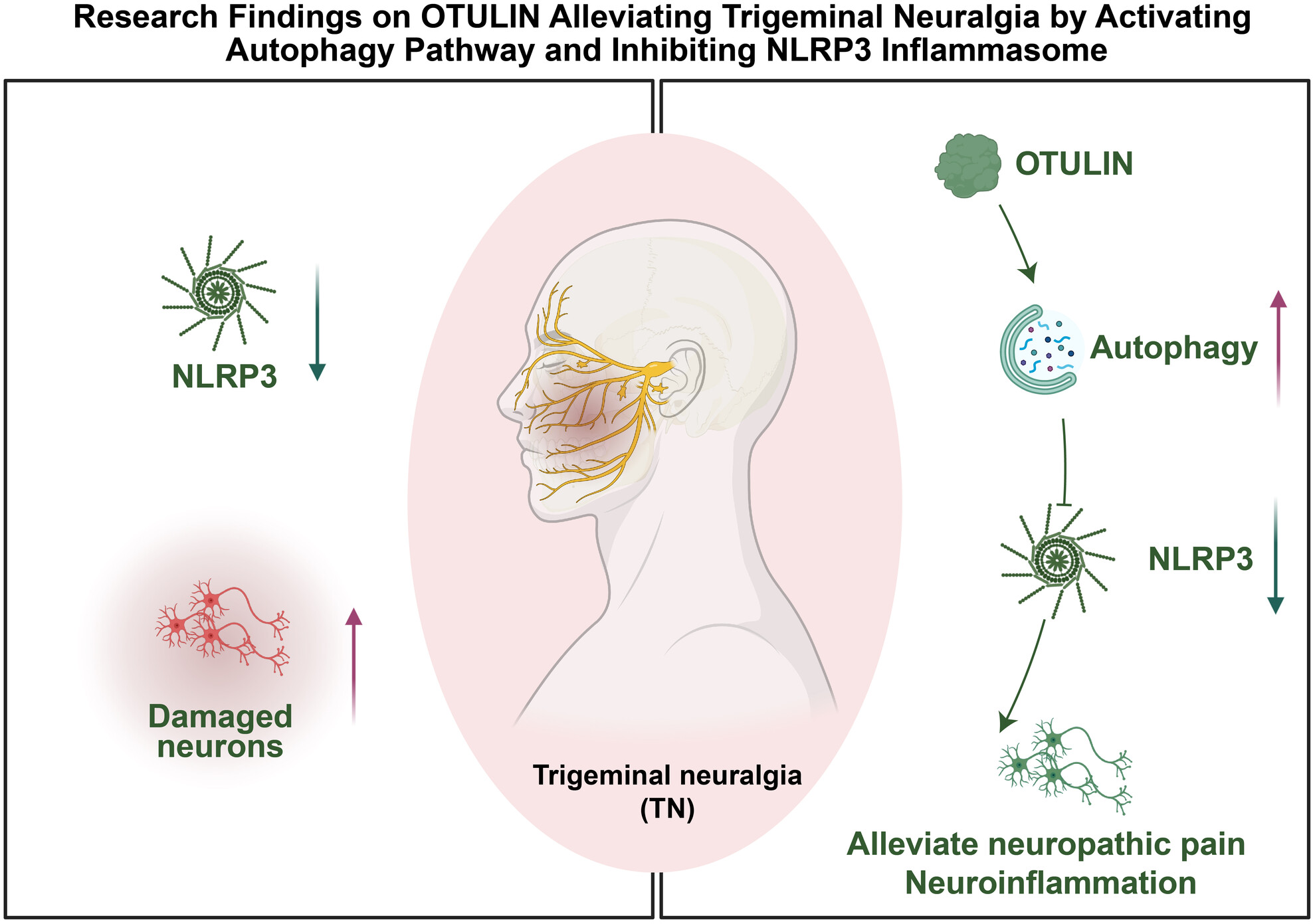
OTULIN's influence on neuroinflammation and pain modulation in trigeminal neuralgia
- First Published: 22 August 2024
Effectiveness of metformin pretreatment for stroke severity: A propensity score matching study
- First Published: 21 August 2024
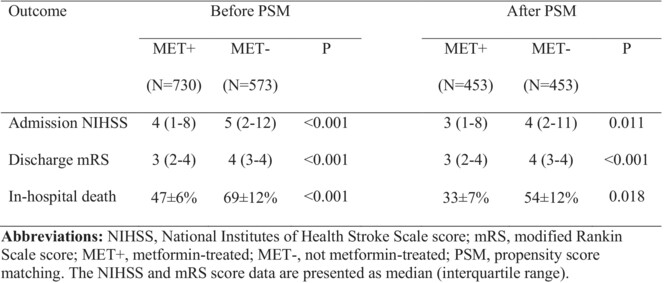
This propensity score matching analysis of our stroke dataset found that diabetics being treated with metformin had milder clinical stroke severity, less in-hospital mortality, and better functional outcomes compared to those who were treated with alternative antidiabetic medications at the time of their ischemic stroke. Among diabetic patients with acute ischemic stroke, metformin appears to confer neuroprotection.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
From hearing loss to neurological complications: Is there an “ear glymphatic system”?
- First Published: 21 August 2024
CASE REPORT
A rare case of acute meningitis caused by Moraxella osloensis
- First Published: 23 August 2024
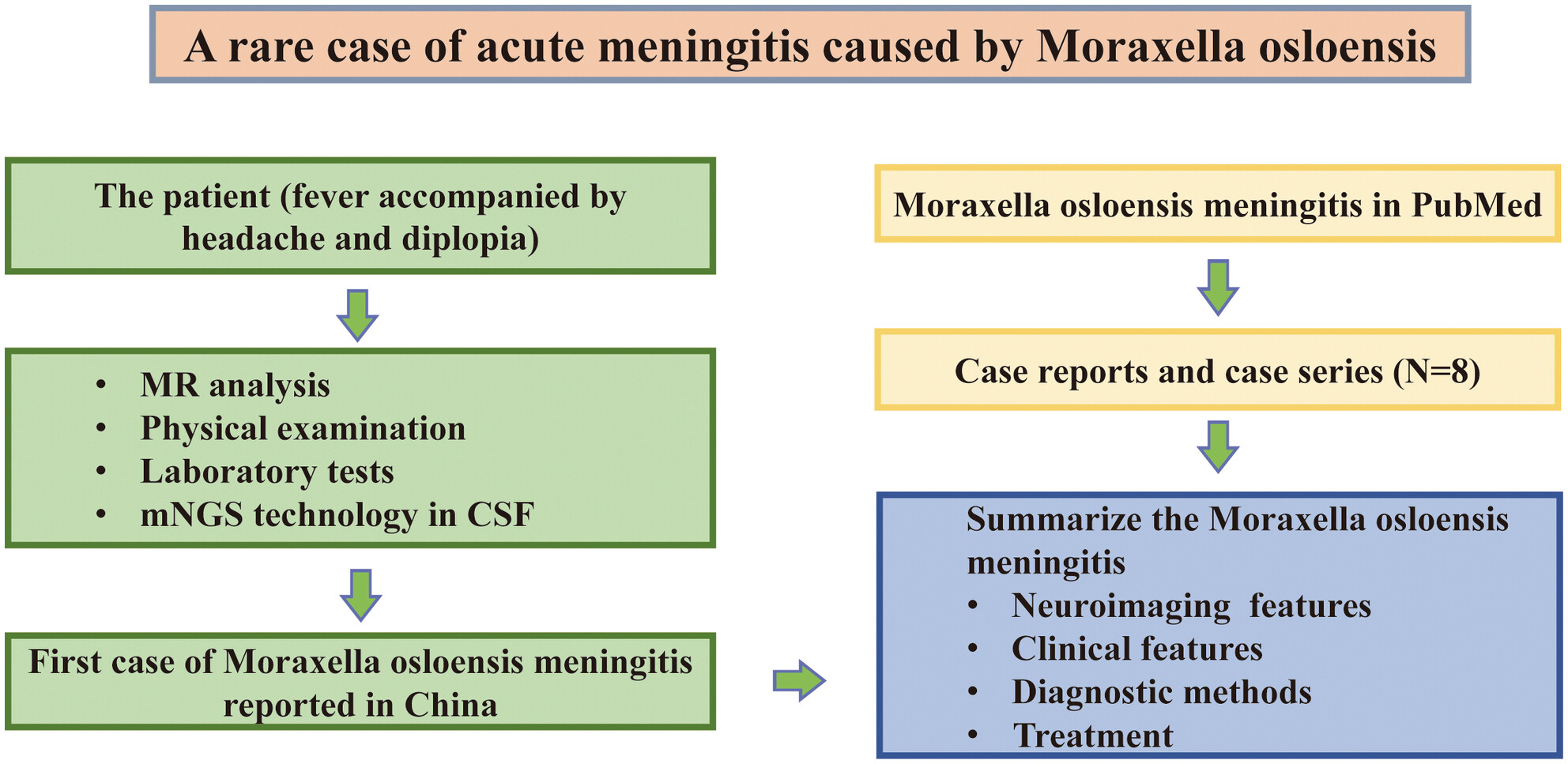
Meningitis caused by Moraxella osloensis is rare and easily misdiagnosed clinically. Here, we report the first case of meningitis caused by M. osloensis in China by taking advantage of the metagenomic next-generation sequencing technology in cerebrospinal fluid for pathogen screening. In addition, we extend the neurological signs, clinical symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment of this rare disease.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
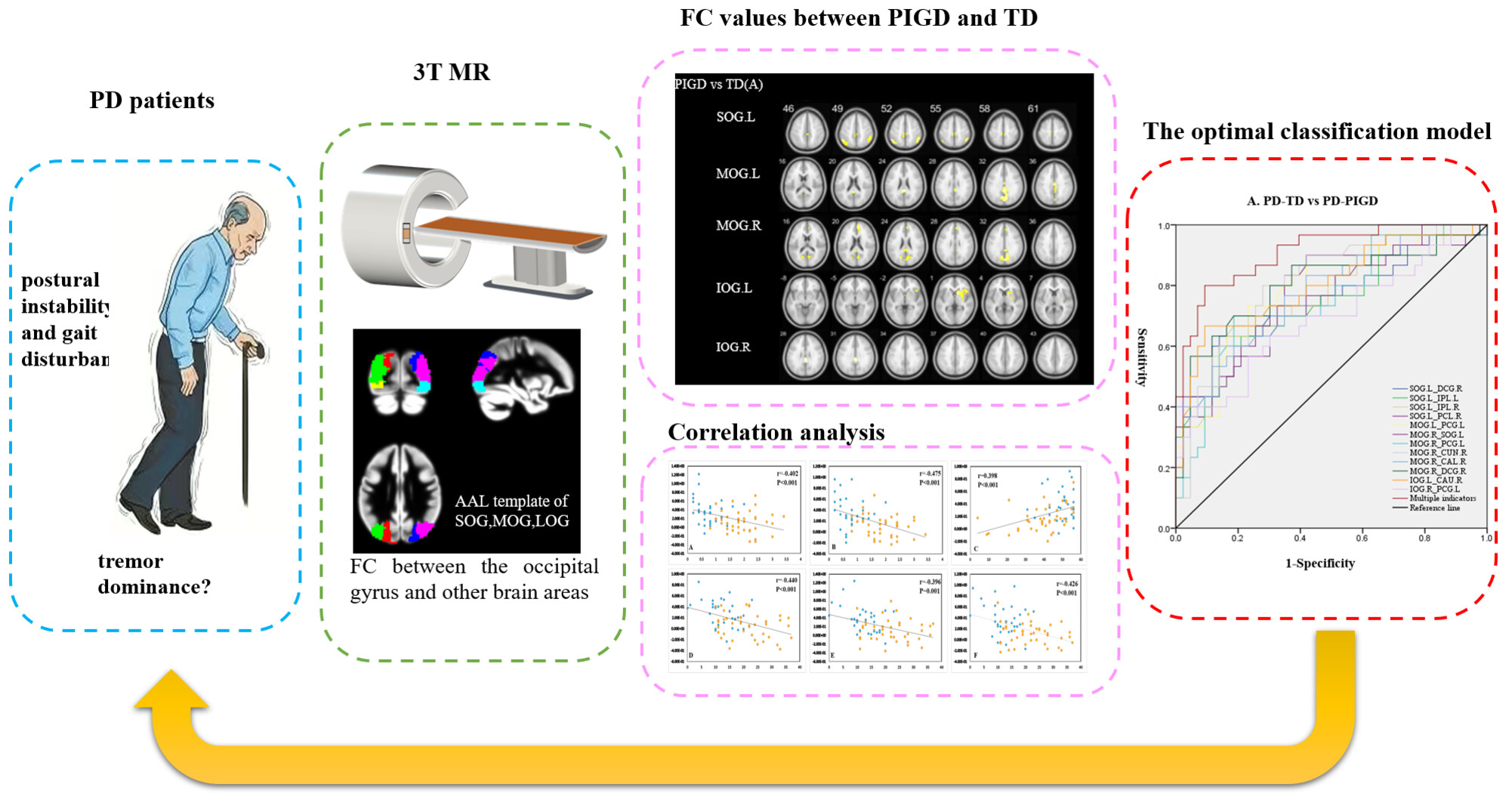
Resting-state functional connectivity of the occipital cortex in different subtypes of Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 26 August 2024
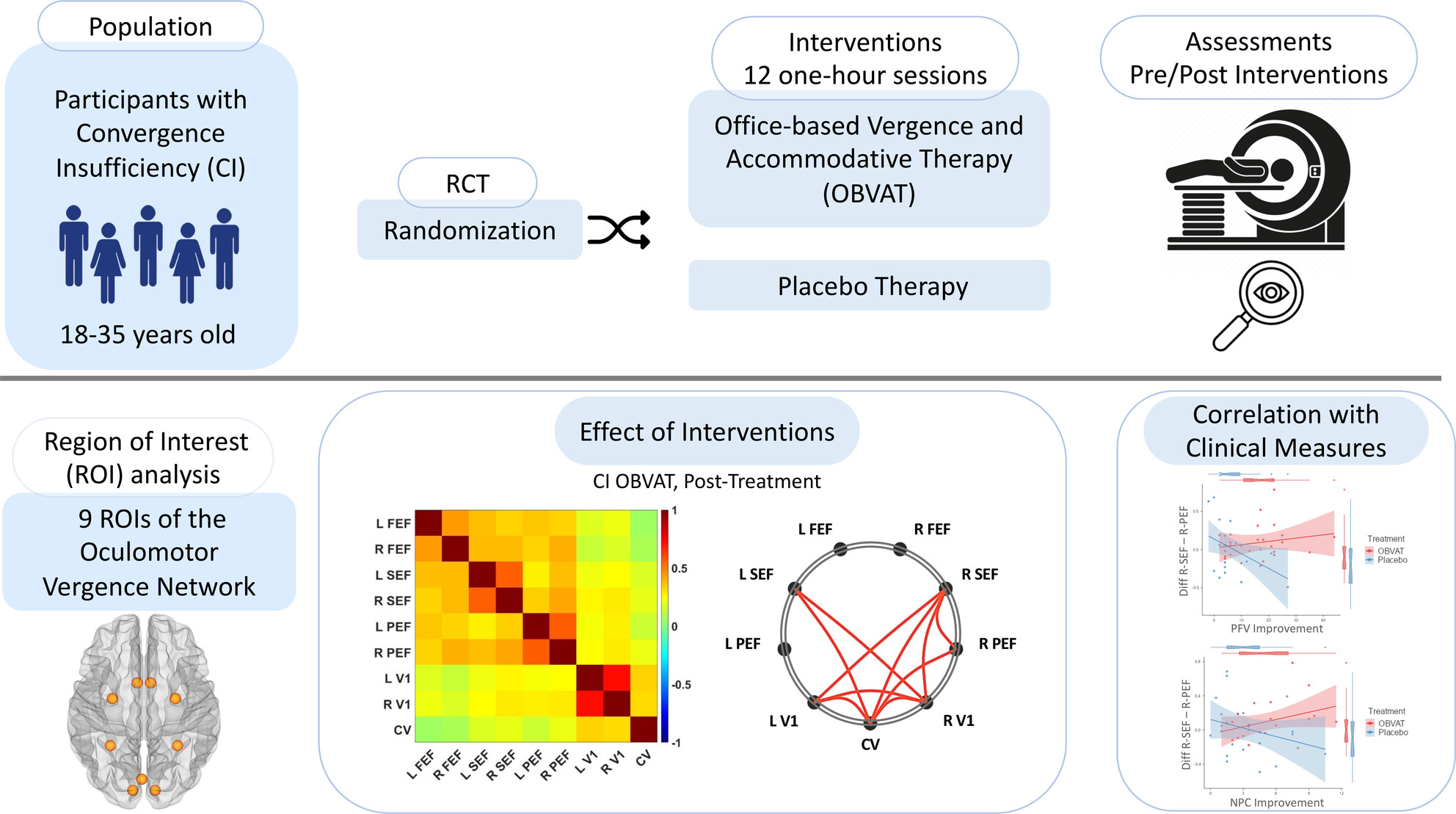
From convergence insufficiency to functional reorganization: A longitudinal randomized controlled trial of treatment-induced connectivity plasticity
- First Published: 26 August 2024