Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 26 September 2024
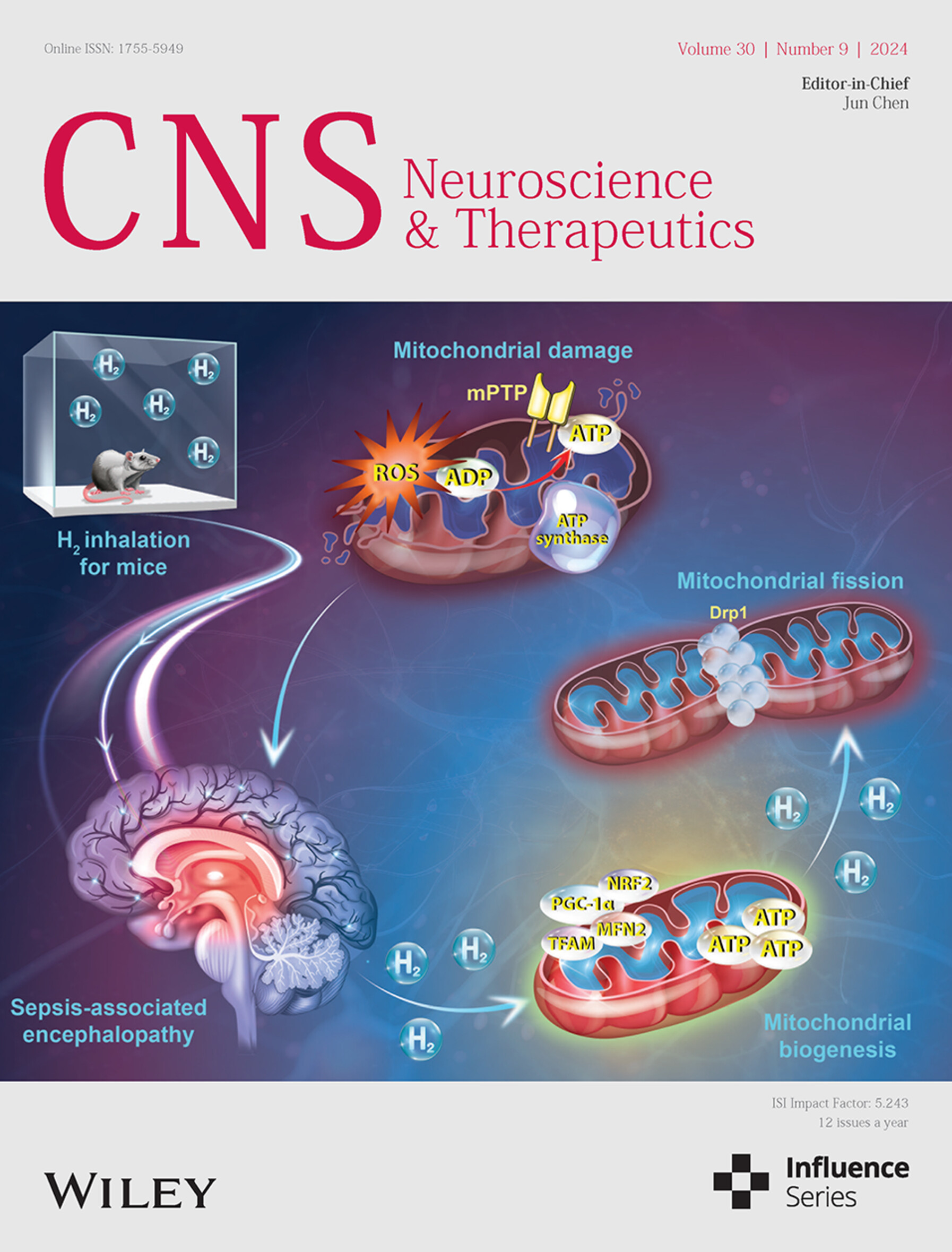
The cover image is based on the article High-concentration hydrogen inhalation mitigates sepsis-associated encephalopathy in mice by improving mitochondrial dynamics by Yan Cui et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70021.
Additional Cover
- First Published: 26 September 2024
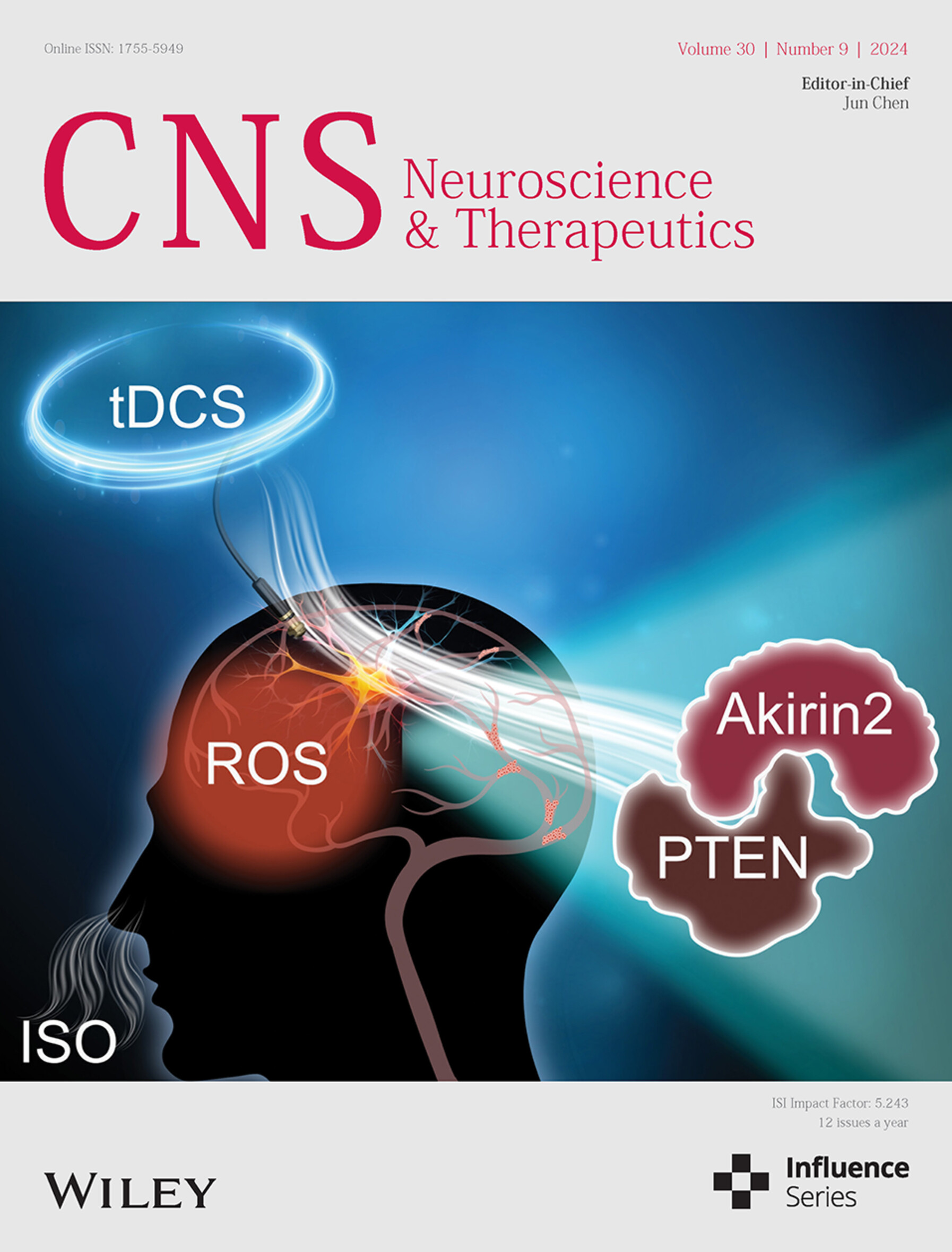
The cover image is based on the article Transcranial direct current stimulation enhances the protective effect of isoflurane preconditioning on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury: A new mechanism associated with the nuclear protein Akirin2 by Xiangyi Kong et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.70033.
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Immunotherapeutic advances in glioma management: The rise of vaccine-based approaches
- First Published: 30 August 2024
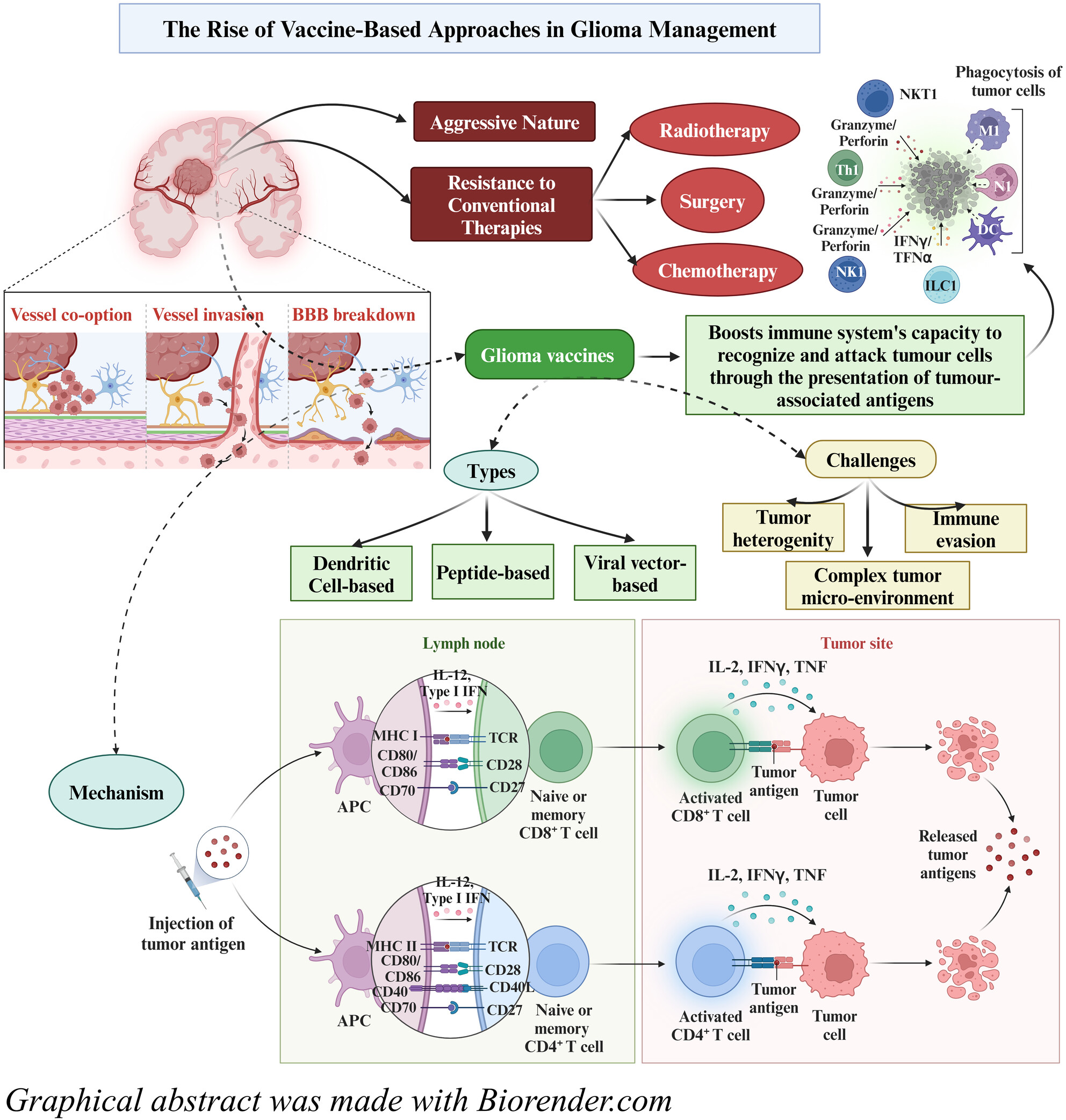
The complexity of gliomas, including challenges like blood–brain barrier (BBB) breakdown, tumor heterogeneity, and immune evasion, can be addressed through the development of glioma vaccines. These vaccines aim to enhance the immune system's ability to recognize and target tumor-associated antigens, leading to a more effective antitumor response. The various vaccine strategies—dendritic cell-based, peptide-based, and viral vector-based—are discussed, along with their potential in overcoming the limitations of traditional therapies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Association between plasma Netrin-1 levels and motor and nonmotor symptoms in Parkinson's disease
- First Published: 30 August 2024
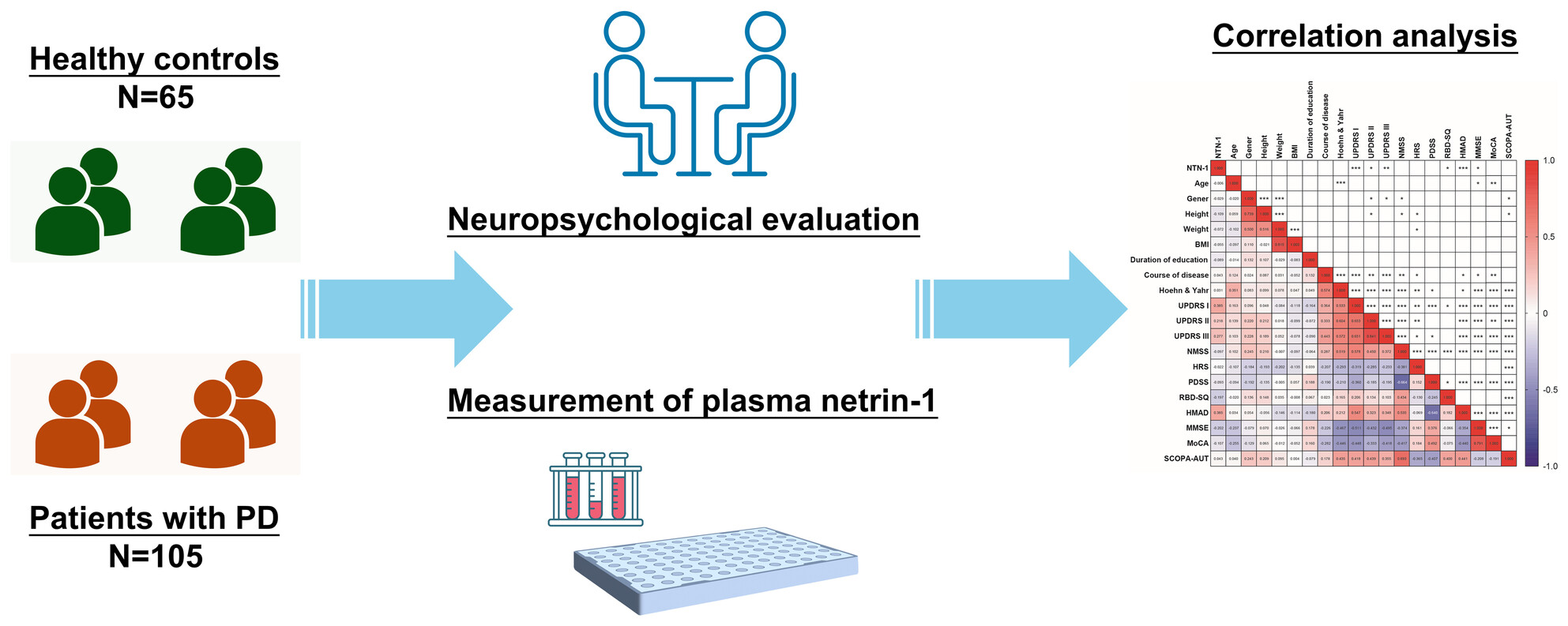
Parkinson's disease (PD) is characterized by neuron degeneration and diverse symptoms, posing diagnostic challenges. Plasma netrin-1 (NTN-1) emerges as a potential biomarker for early detection. A study with 105 PD patients and 65 controls shows lower NTN-1 levels in PD, correlating with symptom severity and demographic factors.
DNA damage induced PARP-1 overactivation confers paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain by regulating mitochondrial oxidative metabolism
- First Published: 30 August 2024
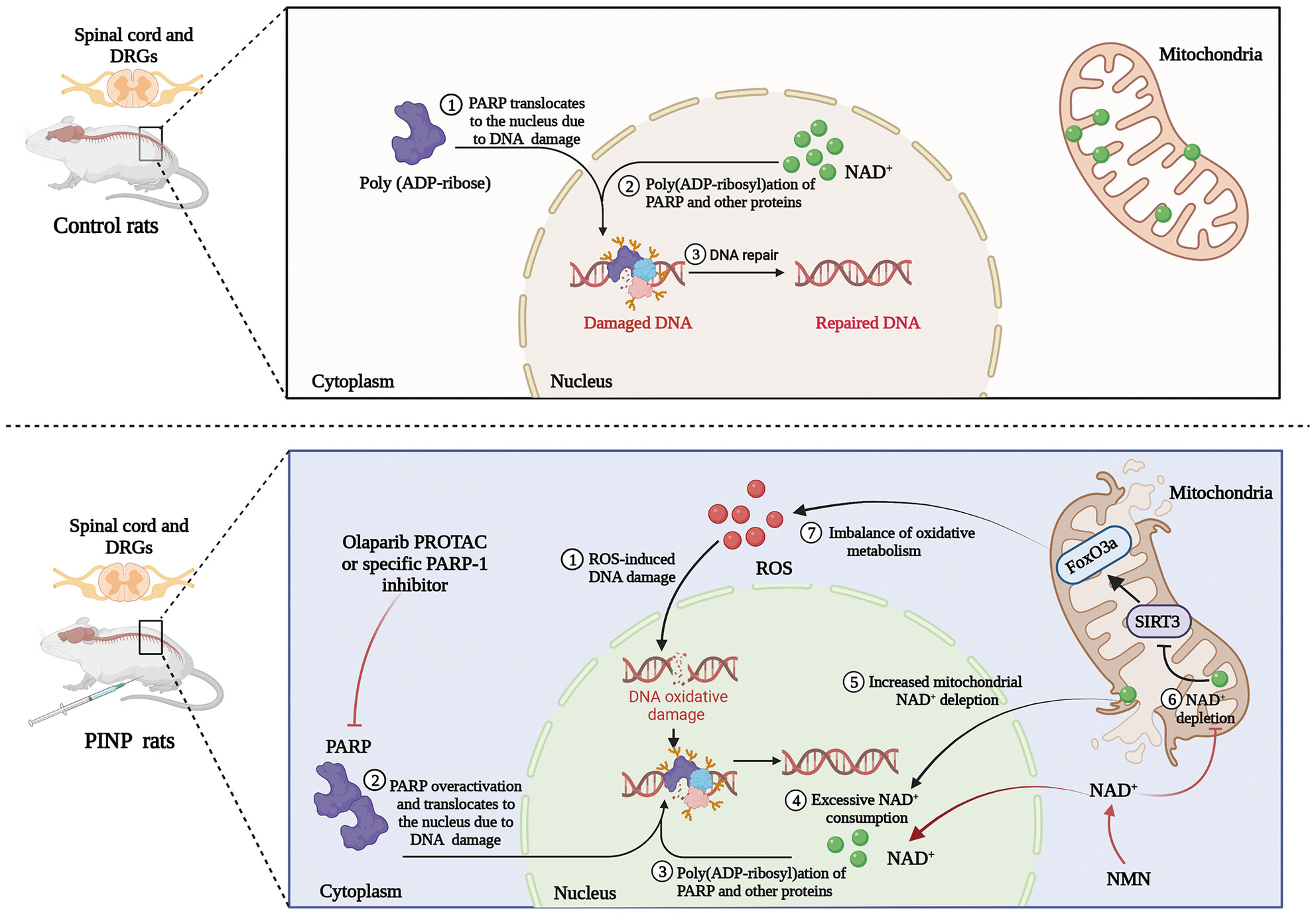
Induction of DNA oxidative damage, PARP-1 overactivation, and subsequent NAD+ depletion were proved to be crucial events in the pathogenesis of PINP. Specific inhibition of PARP-1 enhanced mitochondrial redox metabolism partly by upregulating the expression and deacetylase activity of SIRT3 in the PINP rats.
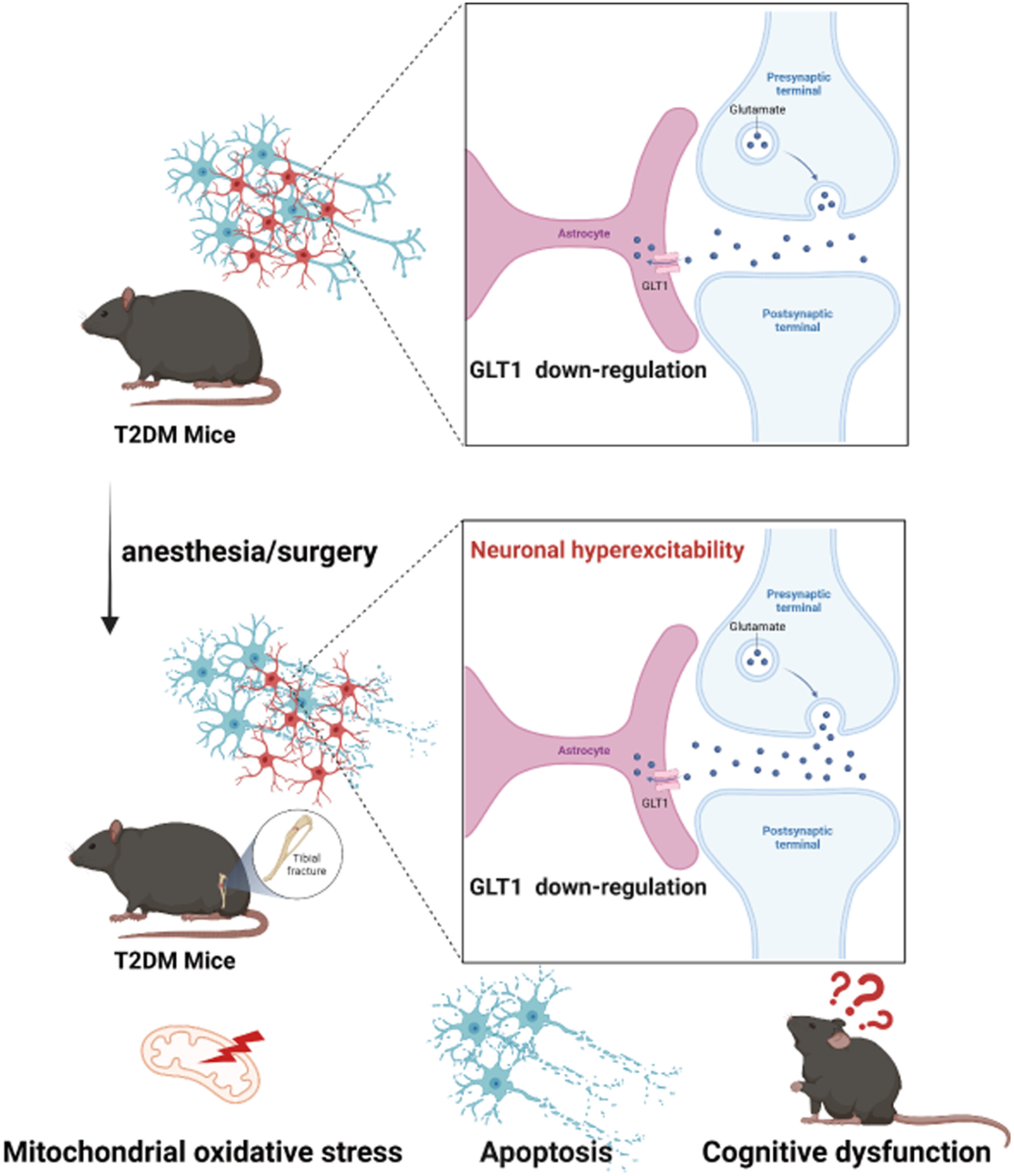
GLT-1 downregulation in hippocampal astrocytes induced by type 2 diabetes contributes to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in adult mice
- First Published: 01 September 2024
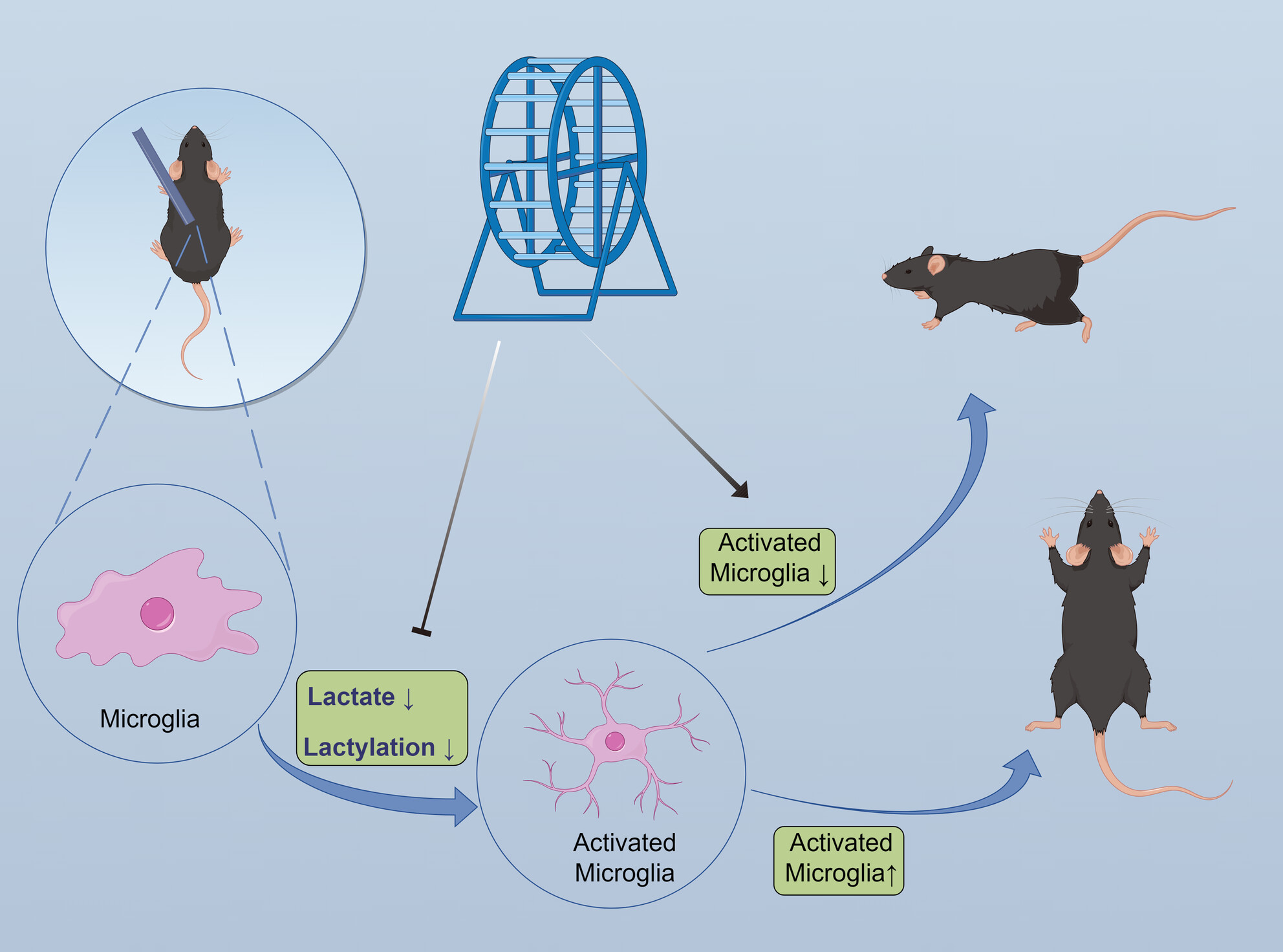
Single-cell RNA sequencing integrated with bulk RNA sequencing analysis reveals the protective effects of lactate-mediated lactylation of microglia-related proteins on spinal cord injury
- First Published: 01 September 2024
Sortilin is associated with progranulin deficiency and autism-like behaviors in valproic acid-induced autism rats
- First Published: 01 September 2024
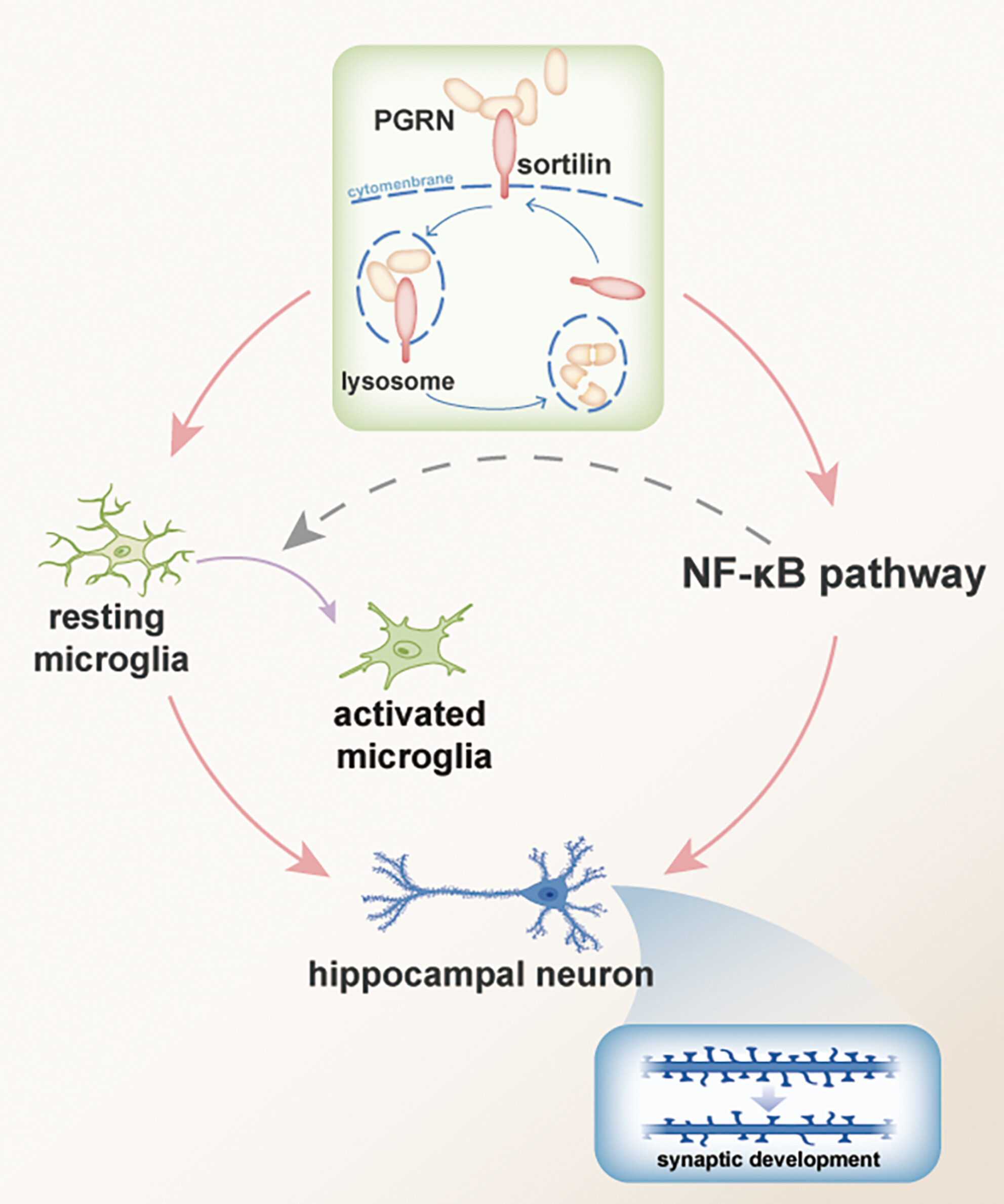
In hippocampal neurons of ASD rats, elevated sortilin levels are associated with increased delivery of PGRN to lysosomes, where the endocytosed PGRN is rapidly degraded. This high level of sortilin, coupled with low PGRN expression, could result in the activation of microglia and the NF-κB pathway. The activation of the NF-κB pathway might further promote microglial activation. Collectively, these factors contribute to synaptic loss and a reduction in dendritic spines in the hippocampus, leading to autism-like behaviors.
RNF122 promotes glioblastoma growth via the JAK2/STAT3/c-Myc signaling Axis
- First Published: 01 September 2024
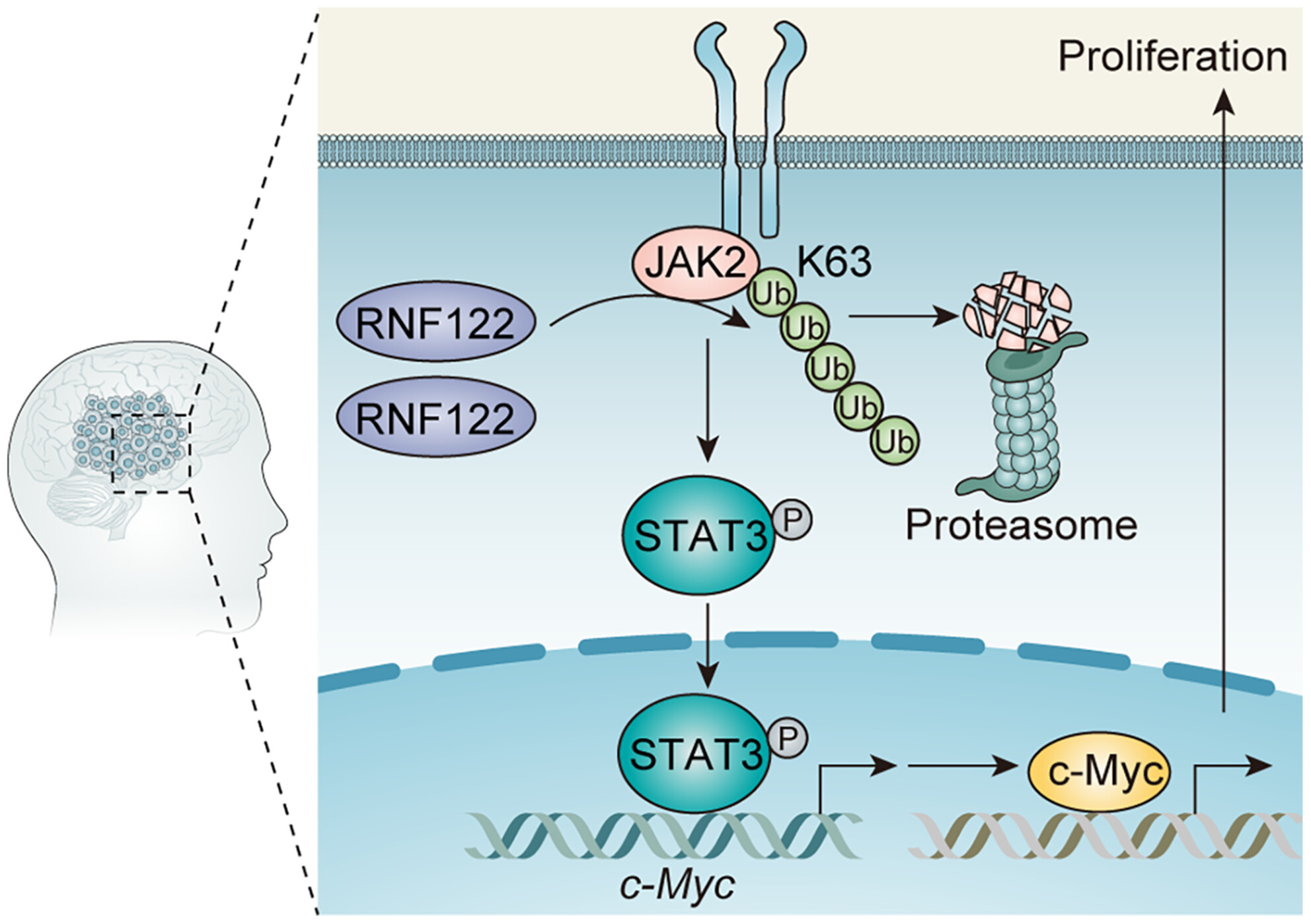
Schematic diagram of the mechanism. RNF122 catalyzes the non-degradative ubiquitination modification of K63 of JAK2 and further promotes the phosphorylation activation of JAK2. Phosphorylated JAK2 then activates its downstream protein STAT3. The phosphorylated STAT3 enters the nucleus and promotes the transcriptional activation and protein expression level of c-Myc. As a common oncogenic protein, c-Myc can further promote the malignant progression of glioblastoma.
Effect of ferric citrate on hippocampal iron accumulation and widespread molecular alterations associated with cognitive disorder in an ovariectomized mice model
- First Published: 09 September 2024
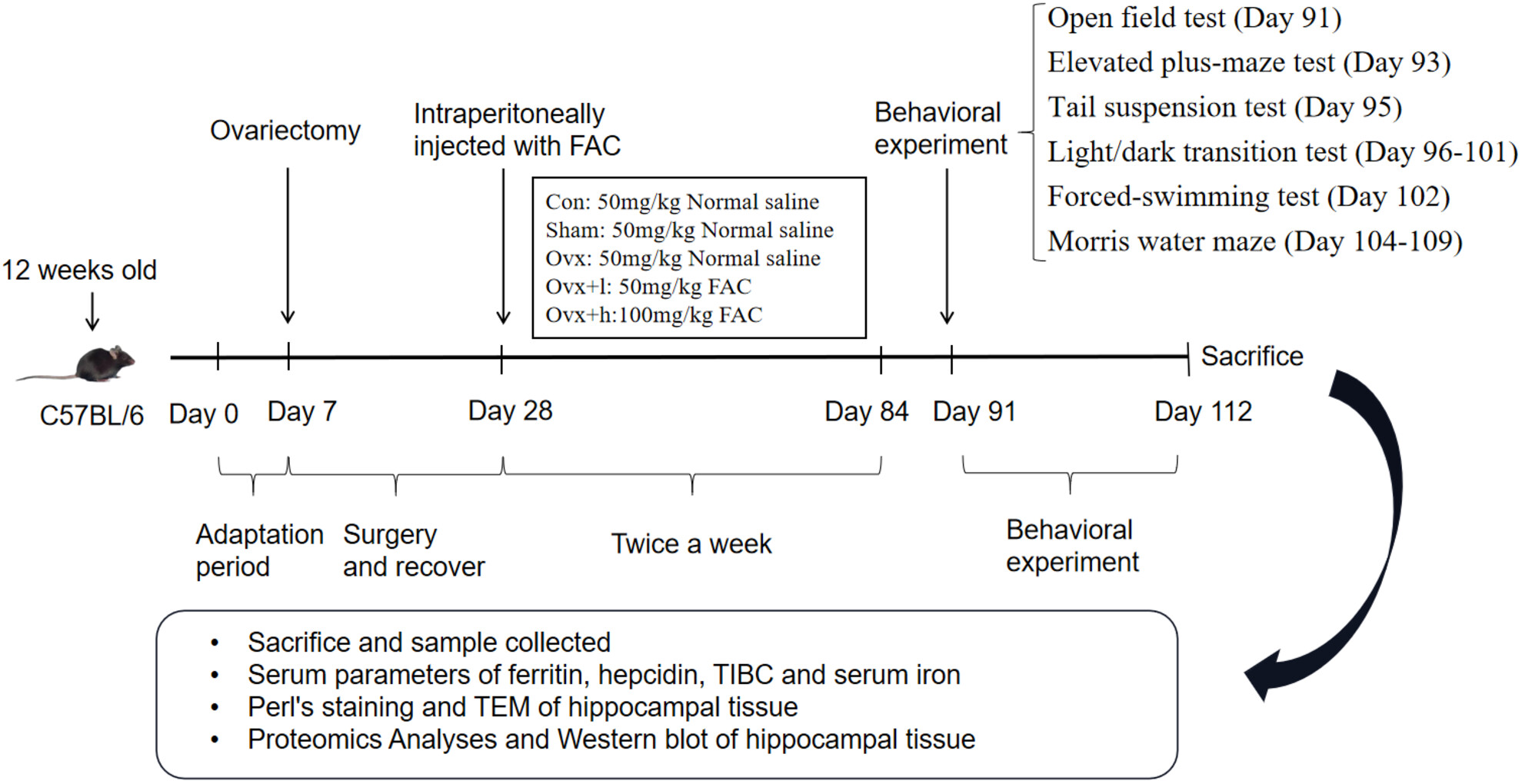
Iron accumulation mice model with ovariectomy could lead to the decline of movement and cognitive function. Iron accumulation could cause histopathological damage in the hippocampus of ovariectomized mice and, by disturbing hippocampus proteome, particularly the expression of hippocampal iron metabolism-related proteins, could further influence cognitive impairment in ovariectomized mice.
Remote ischemic preconditioning prevents high-altitude cerebral edema by enhancing glucose metabolic reprogramming
- First Published: 02 September 2024
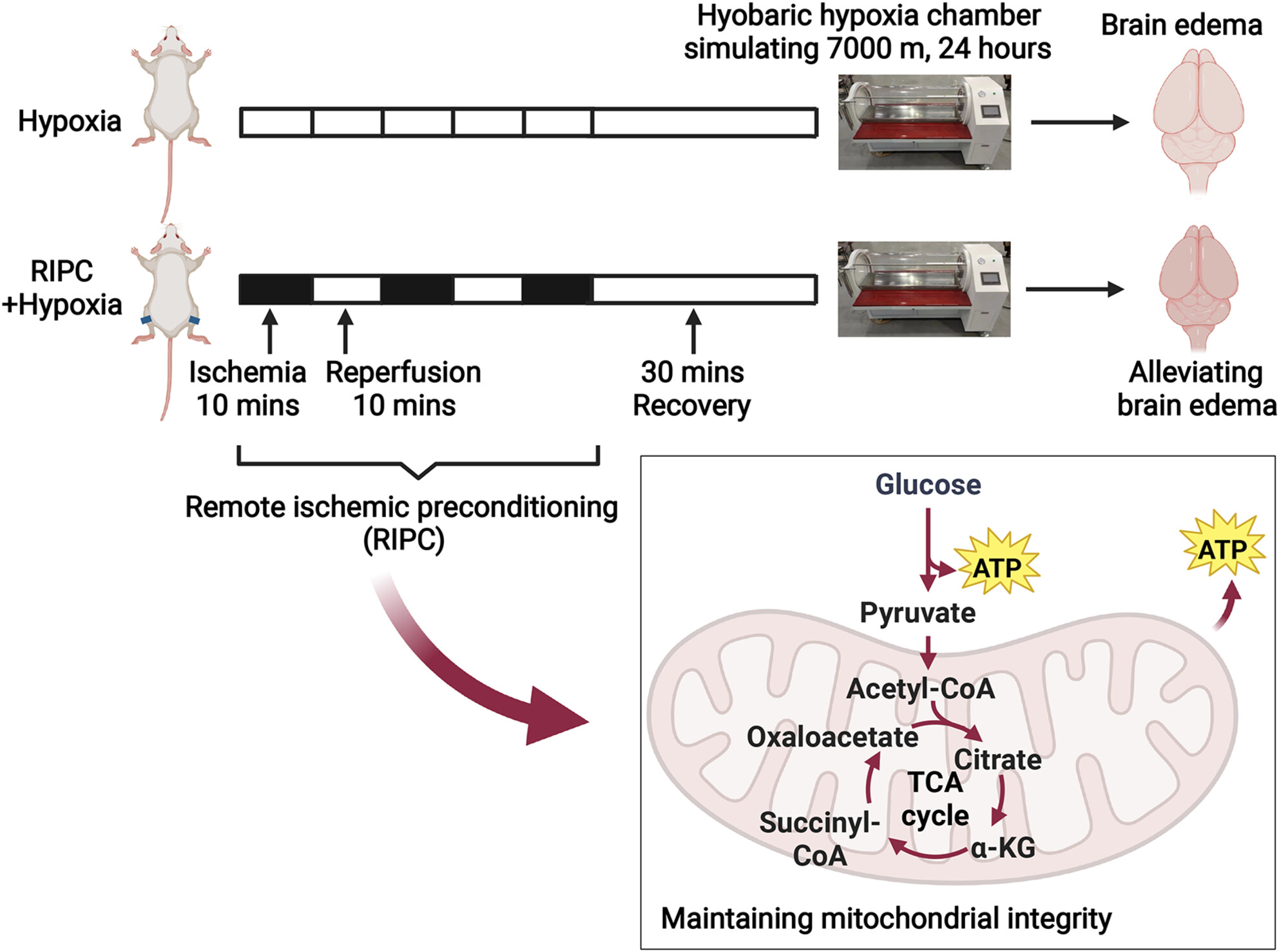
RIPC ameliorated brain edema induced by high-altitude hypoxia through stimulating glucose metabolism down to the TCA cycle to boost mitochondrial ATP production. This finding supports the potential of RIPC as a viable therapeutic approach for the prevention and treatment of HACE, targeting metabolic reprogramming. This figure was created with BioRender (https://www.biorender.com).
Luteolin as potential treatment for Huntington's disease: Insights from a transgenic mouse model
- First Published: 03 September 2024
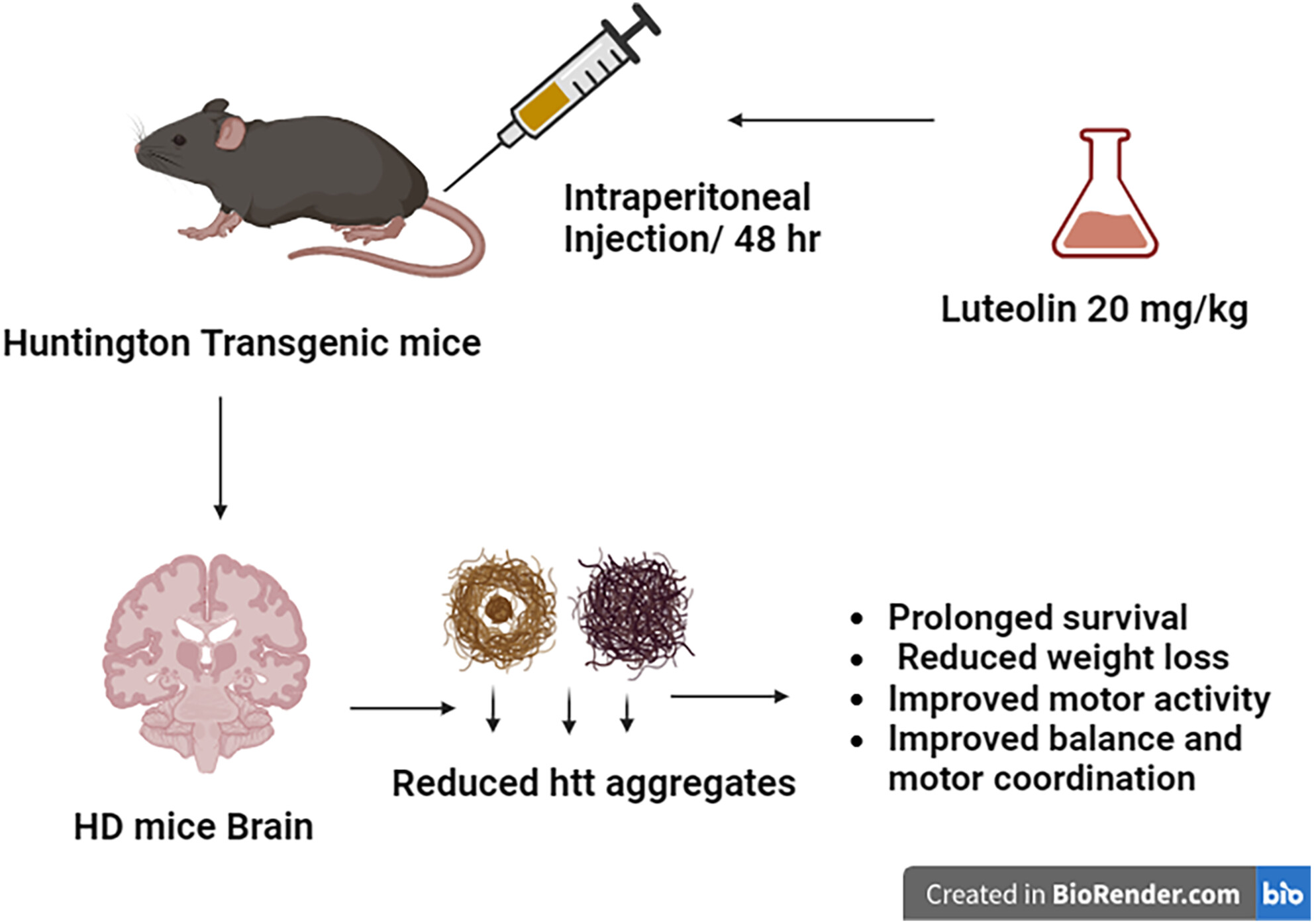
Huntington's disease (HD) is an inherited progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by motor dysfunction and premature mortality. Luteolin, a natural flavonoid with known antioxidant and neuroprotective properties, has shown promise in various neurodegenerative diseases. This study aimed to evaluate the potential benefits of luteolin treatment in a mouse model of (HD). To assess the effects of luteolin treatment, HD N171 82Q transgenic mice received luteolin administration, while another group received a vehicle treatment for comparison. The mice's body weight changes and survival rates were monitored throughout the study. Additionally, they underwent a series of motor function tests, including the rotarod test, balance beam test, and limb clasping test. Immunohistochemical staining and western blotting were utilized to assess the localization and expression of huntingtin aggregates, respectively. Findings revealed a significant protective effect of luteolin treatment against premature mortality and prevented weight loss in HD mice compared to the non-luteolin-treated group. Furthermore, the luteolin-treated mice exhibited enhanced motor coordination and balance and significantly reduced motor dysfunction-related manifestations, such as dystonic movements. Immunohistochemistry analysis and protein quantification demonstrated a decrease in the accumulation of huntingtin aggregates in the brain's cortex, hippocampus, and striatum of luteolin-treated mice compared to the vehicle-treated group. These findings collectively indicate that luteolin holds promise as a therapeutic agent for managing motor dysfunction, reducing huntingtin aggregations, and improving survival outcomes in individuals affected by Huntington's disease. The findings are of significance as currently, there are no approved therapeutic interventions that reverse HD pathology or slow down its progression.
Dynamic functional network connectivity and its association with lipid metabolism in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 20 September 2024

Alzheimer's disease is recognized to be associated with dysregulation of lipid metabolism and abnormal tempo-spatial patterns of dynamic functional network connectivity. The dynamic connectivity represented a better power in differentiating Alzheimer's disease patients from non-Alzheimer's disease subjects than static connectivity. Differential connectivity of strong-connected state between APOE-ε4 carriers and non-carriers mediated the relationship between Apolipoprotein E-ε4 genotype and cerebrospinal fluid and cognitive indicators.
Aberrant brain structural–functional connectivity coupling associated with cognitive dysfunction in different cerebral small vessel disease burdens
- First Published: 03 September 2024
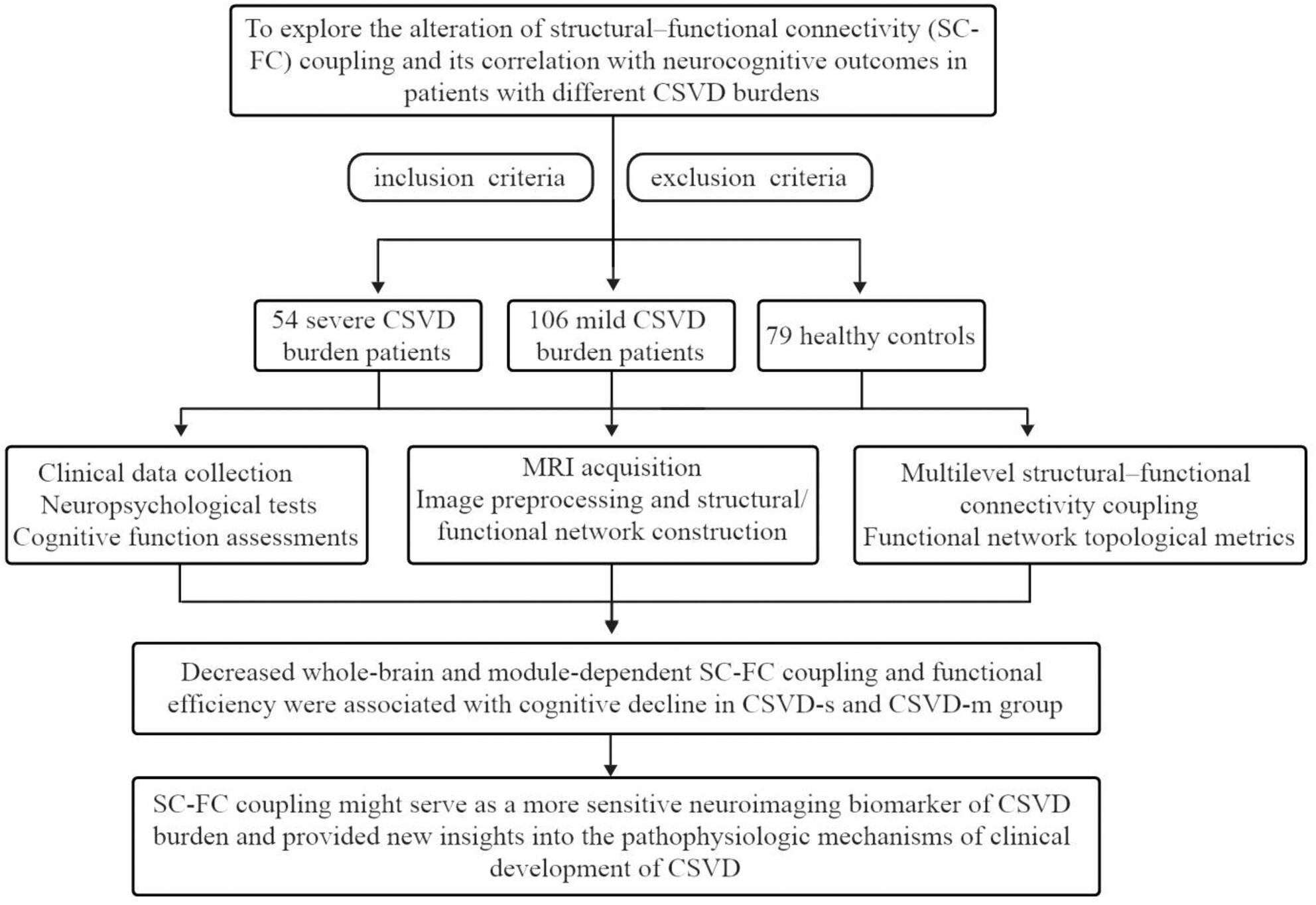
We reconstructed whole-brain structural connectivity (SC) and functional connectivity (FC) networks for severe cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) burden patients (CSVD-s), CSVD mild burden patients (CSVD-m), and healthy controls. The CSVD-s group showed considerably decreased SC-FC coupling in the limbic/subcortical module compared with the CSVD-m group, while there was no difference in SC-FC coupling between the CSVD-m and control groups.
REVIEW
Roles of osteocalcin in the central nervous system
- First Published: 09 September 2024
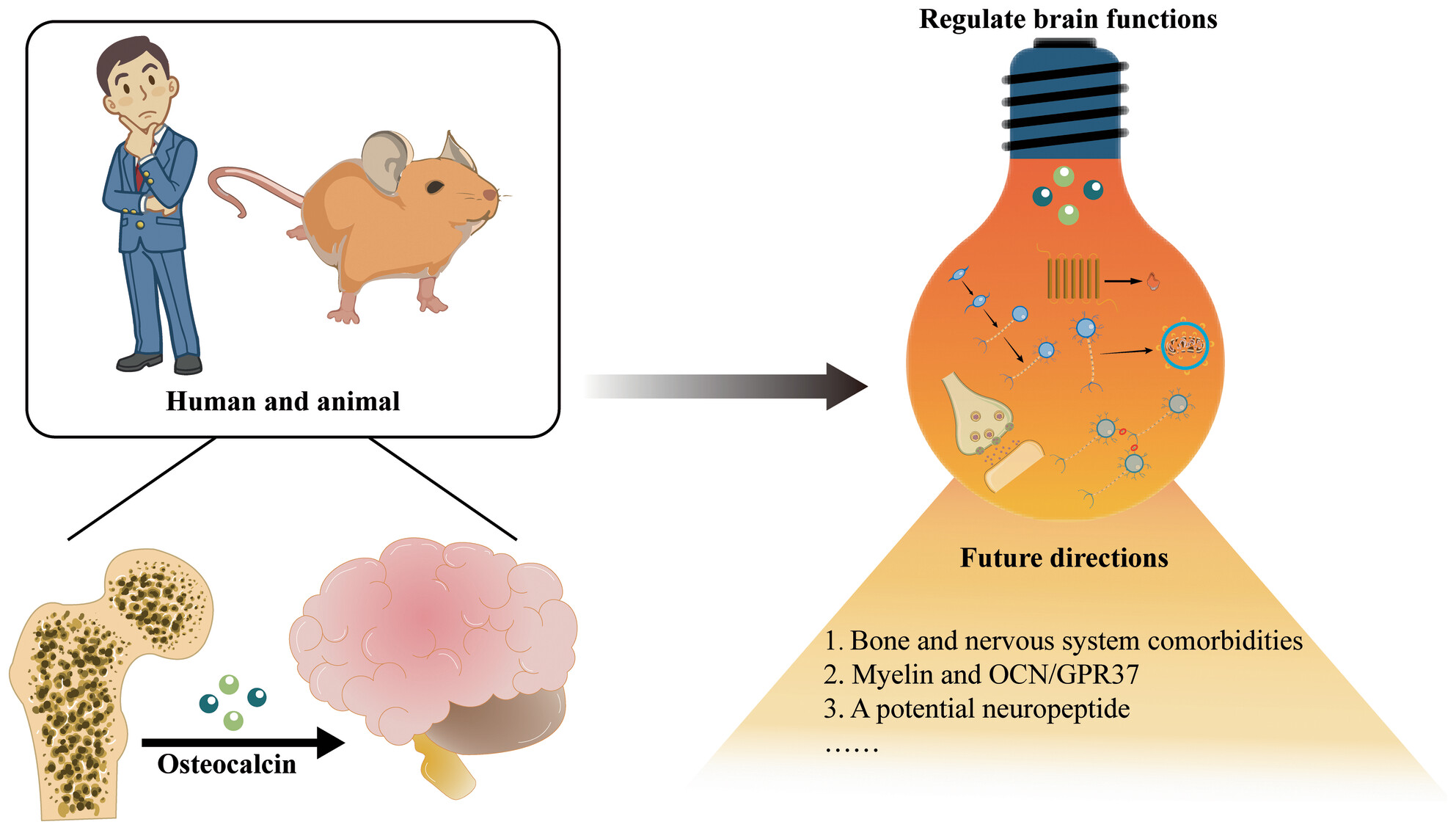
In the normal central nervous system, osteocalcin is involved in neuronal structure, neuroprotection, and the regulation of cognition and anxiety. Studies on osteocalcin-related abnormalities in the central nervous system are divided into animal model studies and human studies, depending on the subject. In humans, the link between osteocalcin and brain function is inconsistent. These conflicting data may be due to methodological inconsistencies. By reviewing the related literature on osteocalcin, some comorbidities of the bone and nervous system and future research directions related to osteocalcin are proposed.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
A novel strategy for spinal cord reconstruction via vascularized allogeneic spinal cord transplantation combine spinal cord fusion
- First Published: 23 September 2024

In this work, we proposed that vascularized allogeneic spinal cord transplantation (vASCT) might offer a new surgical approach for treating spinal cord injury. In the vASCT surgical model, the combination of polyethylene glycol with tacrolimus demonstrated the ability to reconstruct spinal cord continuity and restore hind limb motor function in beagles. The safety and efficacy of vASCT were verified by behavioral evaluation, electrophysiological examination and imaging examination.
CORRECTION
Correction to Targeting MS4A4A: A novel pathway to improve immunotherapy responses in glioblastoma
- First Published: 03 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Changes of NLRP3 in serum and cerebrospinal fluid of patients after moderate to severe traumatic brain injury and their predictive values for prognosis
- First Published: 20 September 2024
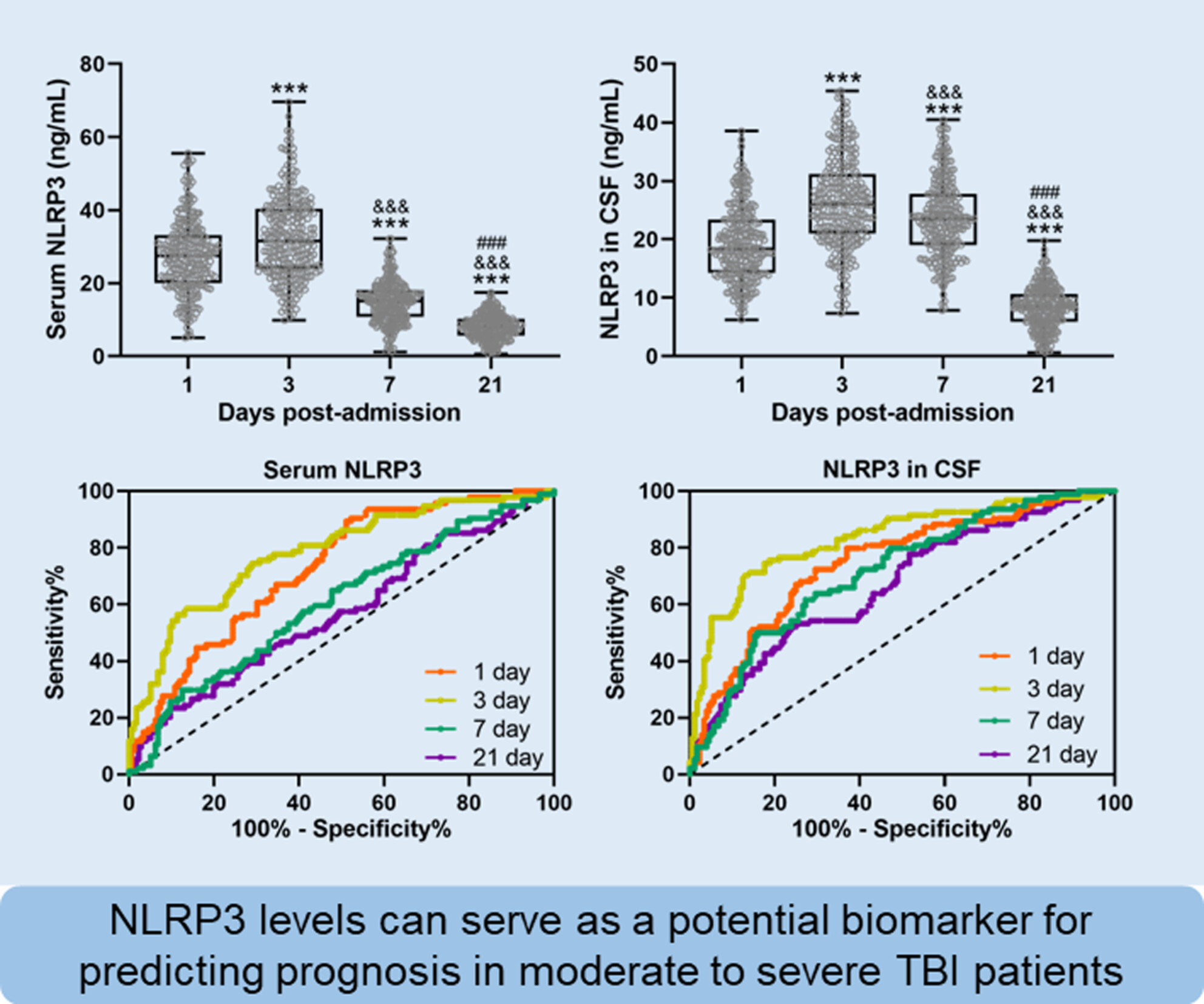
The study has provided that Levels of NLRP3, especially in the CSF on day 3 post-injury, could serve as a potential biomarker for predicting prognosis in moderate to severe TBI patients. Early measurement of NLRP3 levels could provide valuable insights into patient outcomes and guide therapeutic strategies.
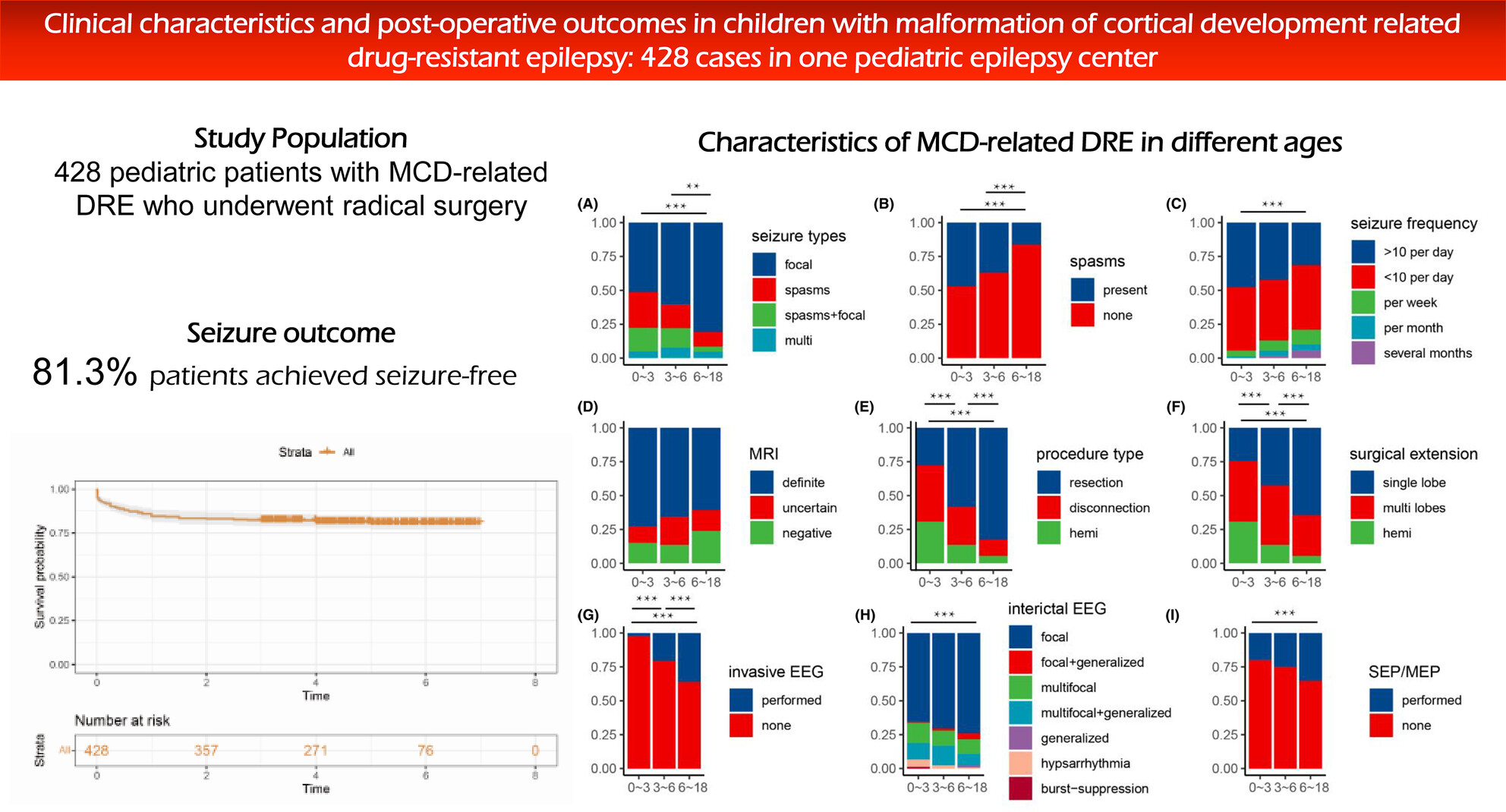
Clinical characteristics and post-operative outcomes in children with malformation of cortical development related drug-resistant epilepsy: 428 cases in one pediatric epilepsy center
- First Published: 04 September 2024
β-1,4-Galactosyltransferase 1 protects against cerebral ischemia injury in mice by suppressing ferroptosis via the TAZ/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway
- First Published: 04 September 2024
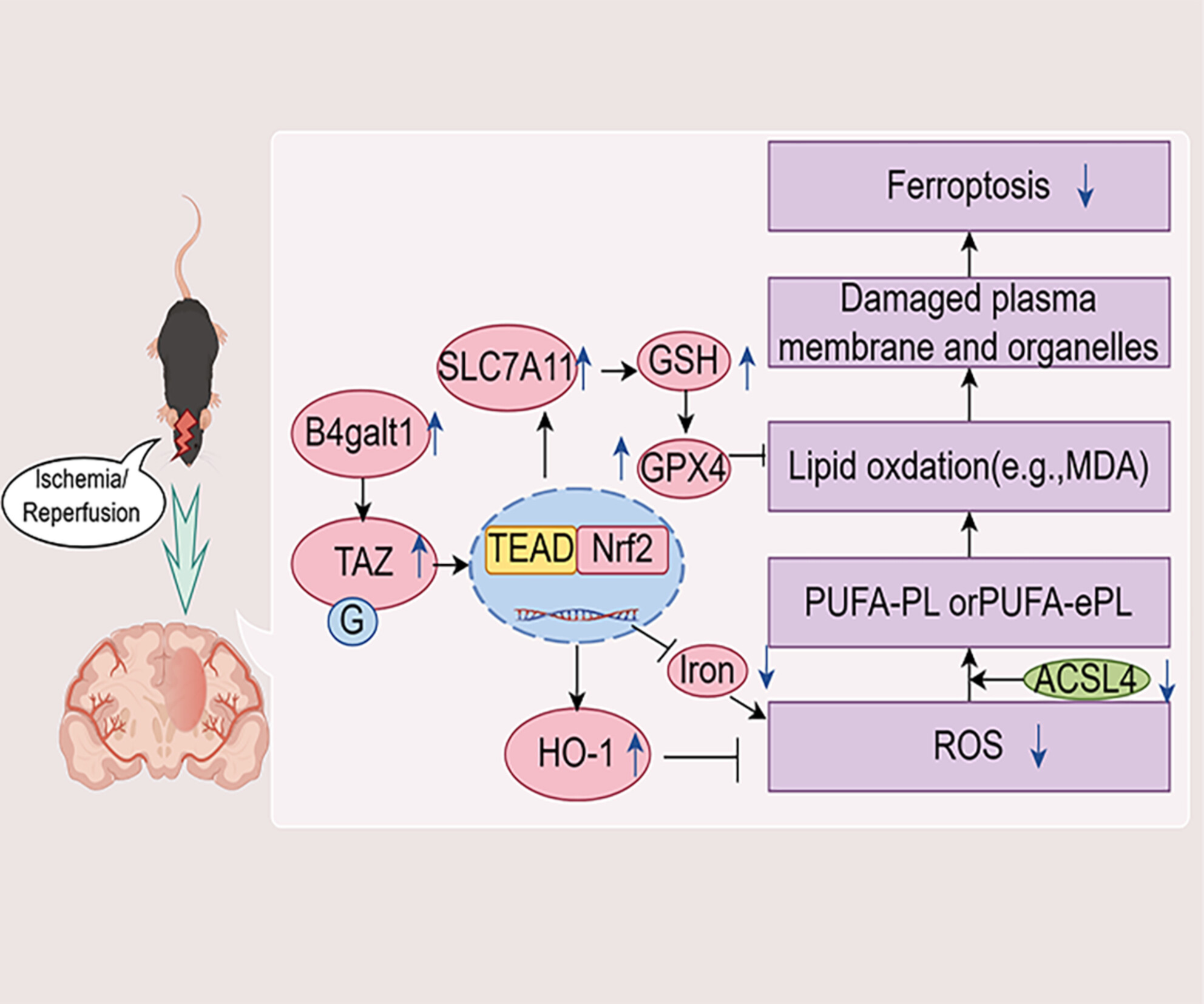
Ferroptosis occurs during cerebral ischemia/reperfusion, resulting in cerebral injury. Rh-B4galt1 exerts neuroprotective effects by regulating ischemia-induced ferroptosis, which is mainly dependent on the heightening of the TAZ/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway. Thus, B4galt1 may be considered a novel potential therapeutic target for ischemic stroke treatment.
Investigating the effects of Ginkgo biloba leaf extract on cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 05 September 2024
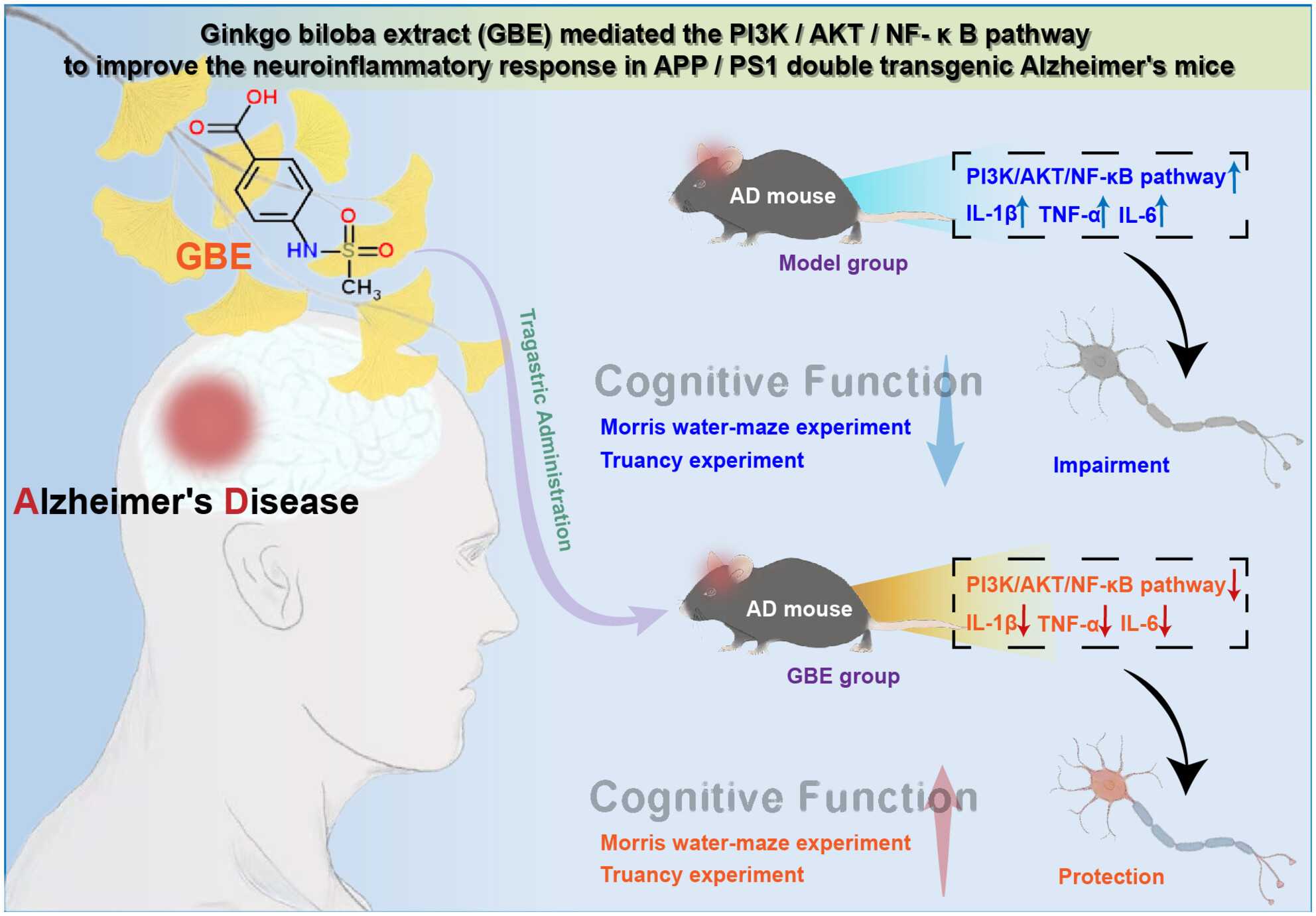
The Ginkgo biloba leaf extract (GBE) study demonstrates its promise as an Alzheimer's treatment, significantly improving cognitive function and neuronal morphology. The effects are mediated through modulation of the PI3K/AKT/NF-κB signaling pathway, which impacts inflammation and neuronal health, offering a potential new avenue for therapeutic intervention in neurodegenerative disorders.
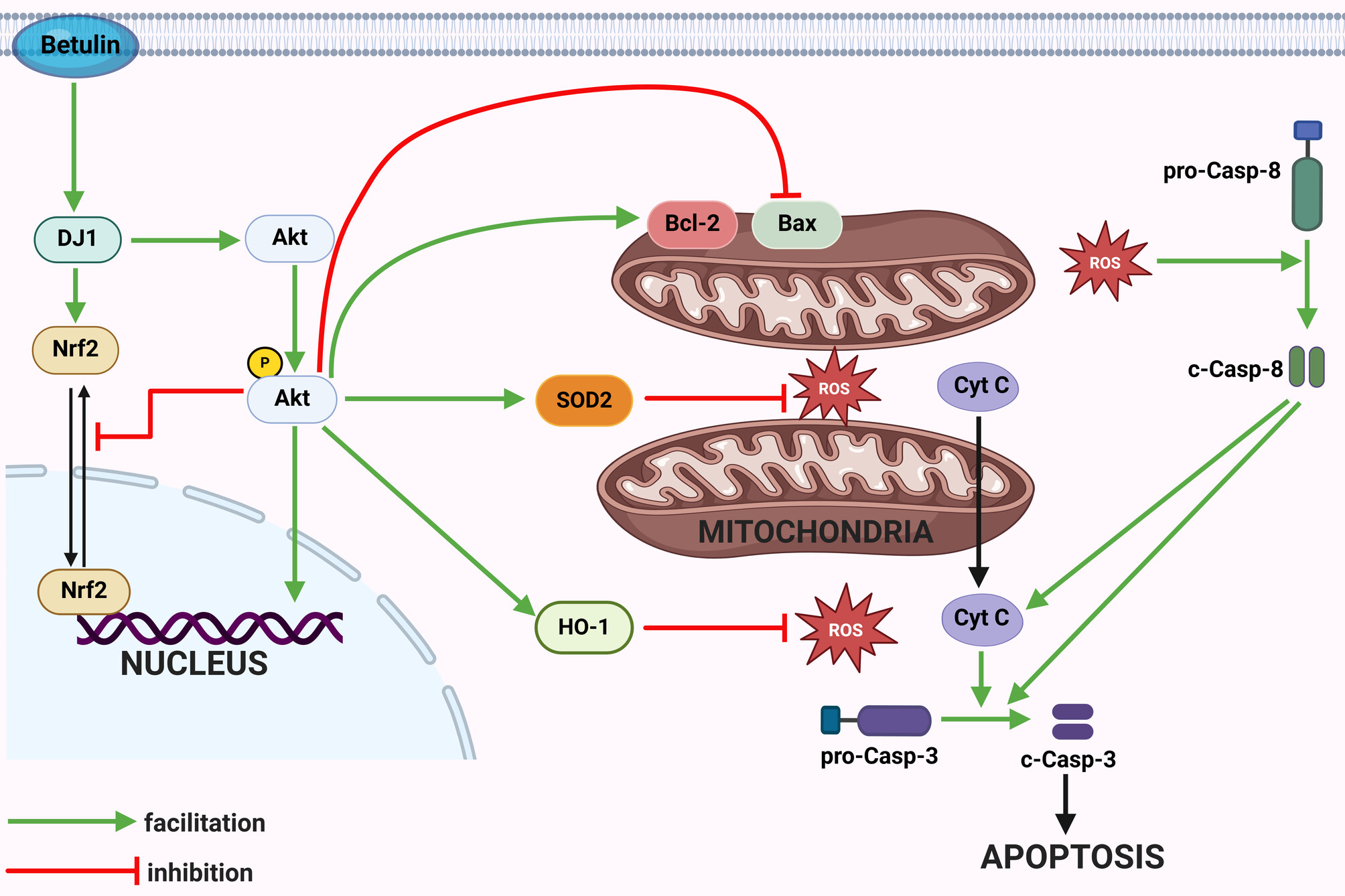
Betulin ameliorates neuronal apoptosis and oxidative injury via DJ-1/Akt/Nrf2 signaling pathway after subarachnoid hemorrhage
- First Published: 05 September 2024
Activation of Piezo1 by intracranial hypertension induced neuronal apoptosis via activating hippo pathway
- First Published: 27 September 2024
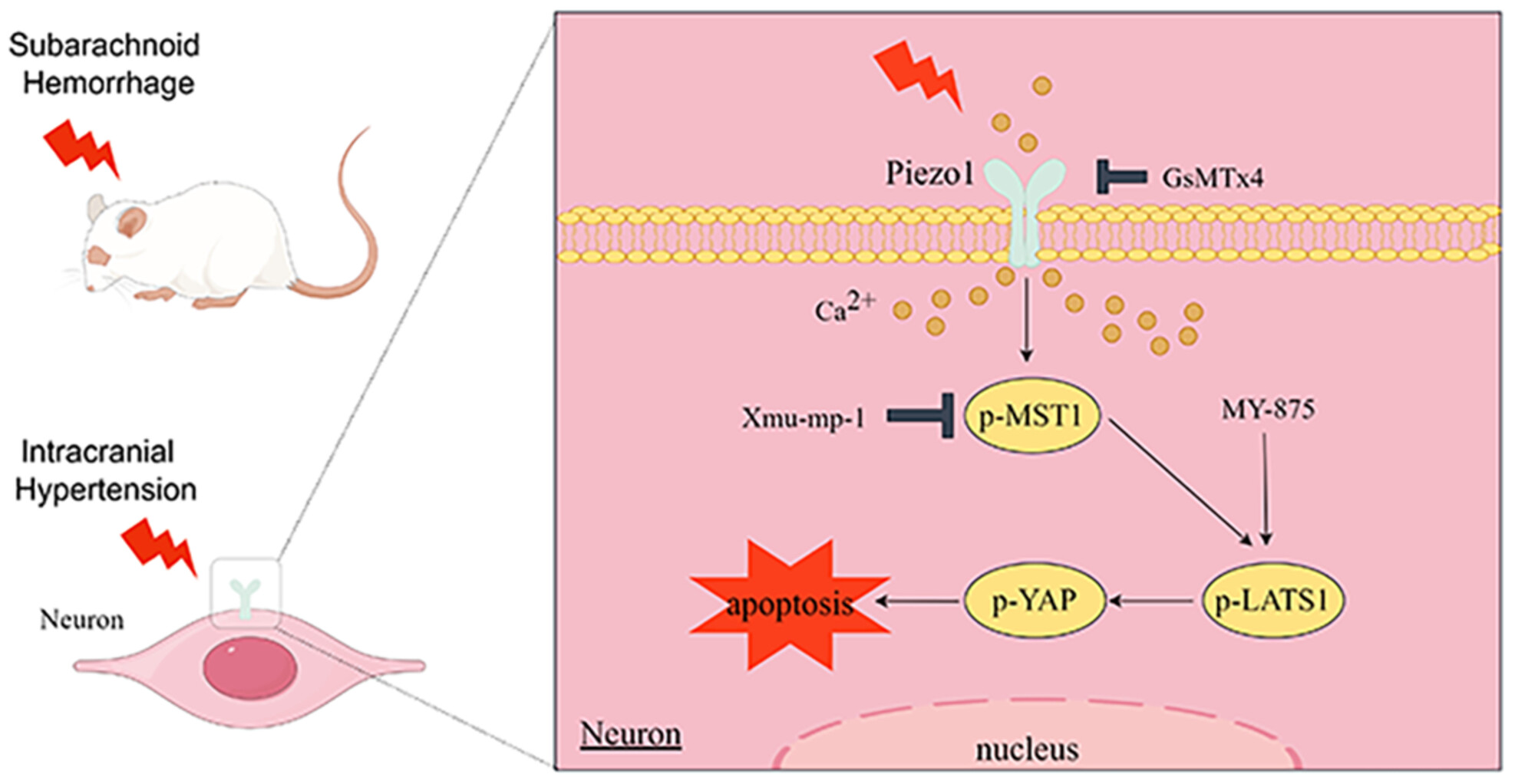
Here, we found that Piezo1 inhibition attenuated neuronal apoptosis and improved the outcome of neurological deficits in rats after subarachnoid hemorrhage. Activation of Piezo1 by intracranial hypertension induced neuronal apoptosis via activating the Hippo pathway in primary neurons. Furthermore, this study incorporated the variables of oxyhemoglobin and intracranial hypertension into the cultivation of neurons, resulting in a compounded impact on neuronal apoptosis.
Delineating structural and metabolic abnormalities in amygdala and hippocampal subfields for different seizure-onset patterns via stereotactic electroencephalography
- First Published: 09 September 2024
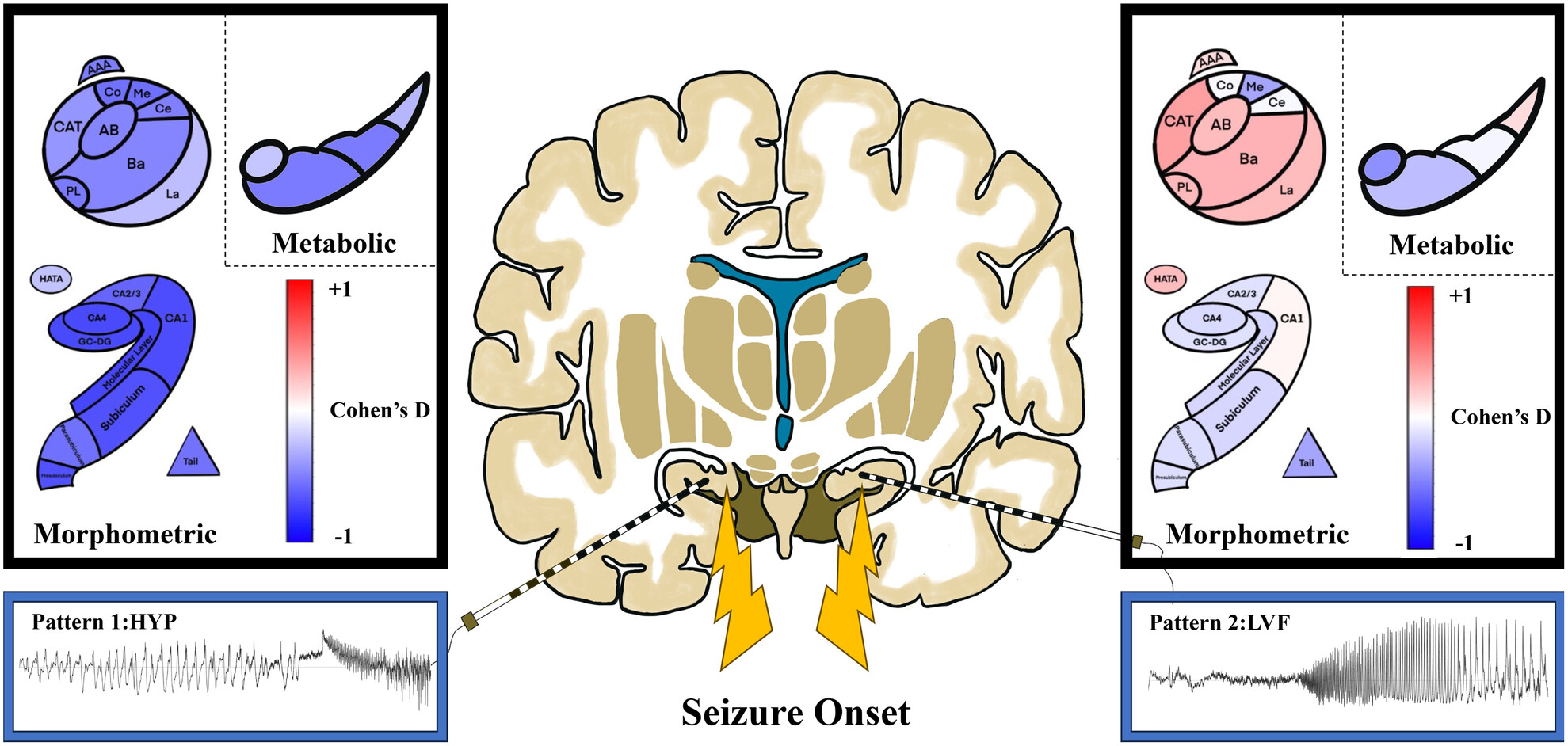
Hypersynchrony (HYP) and low-voltage fast (LVF) rhythm are the two most common forms of onset in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE). HYP onset often involve atrophy and hypometabolism of the ipsilateral hippocampus and amygdala, while LVF onset is mainly characterized by hypertrophy of the amygdala. Different SOPs also involve different pathology.
REVIEW
Advanced progress of vestibular compensation in vestibular neural networks
- First Published: 13 September 2024
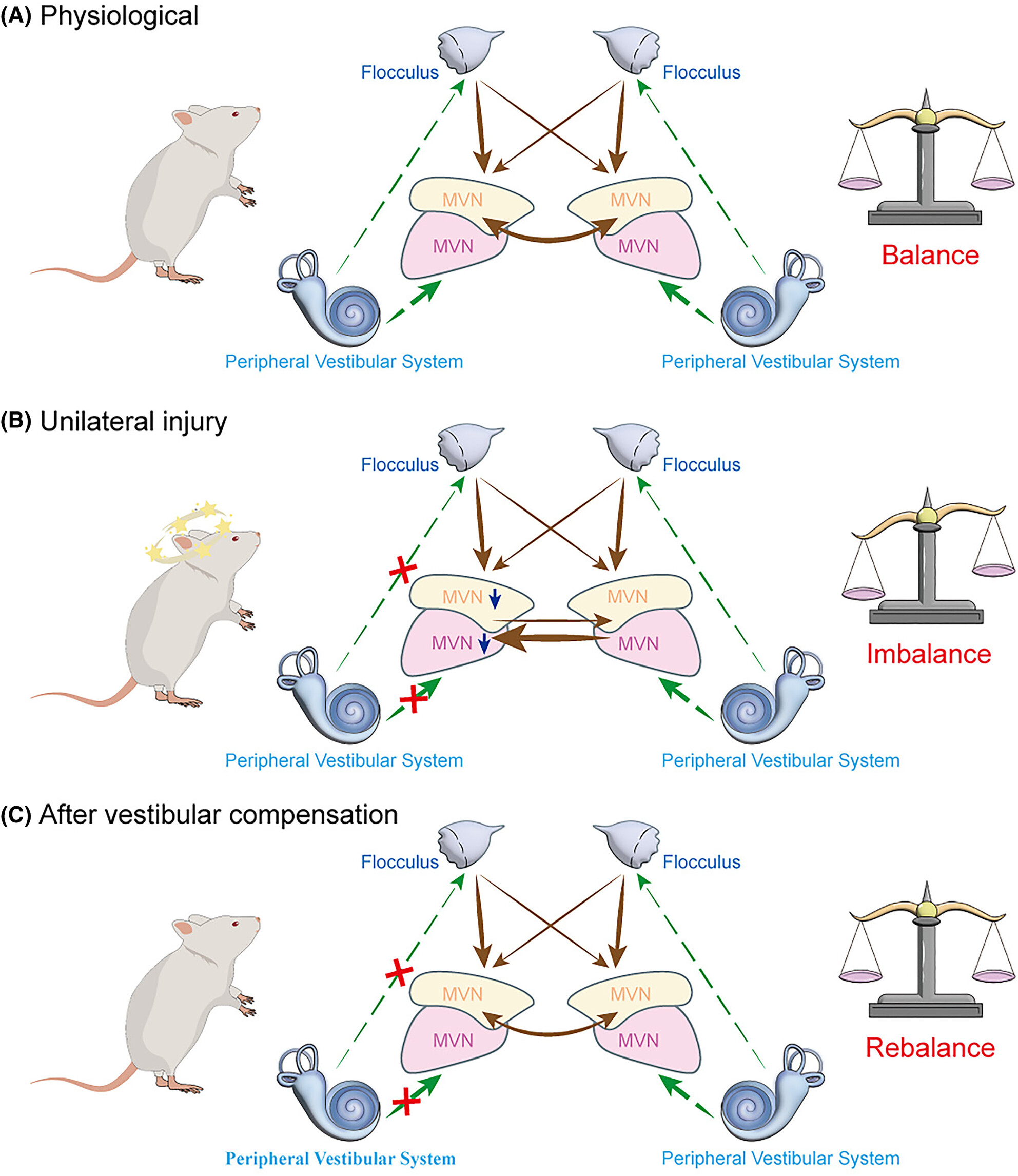
The mechanism of vestibular compensation.11 The MVN receive afferent signals from the peripheral vestibular system and other brain regions, such as the cerebellum, the neuronal activity is balanced between the bilateral vestibular nuclei. After the unilateral peripheral injury, this loss of afferent leads to down-regulation of neuronal activity in the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus, while up-regulation in the contralateral side. This imbalance is believed leading to the symptoms of vestibular disorders. CNS can partially rebalance the neural activity between bilateral MVN, and reverse the vestibular symptoms. In contrast to the ipsilateral side, the contralateral MVN neurons become more active, which might be due to the reduced inhibitory input from the ipsilateral vestibular nucleus. Besides the inhibitory commissural projections between the bilateral MVN, the cerebellum and other brain region inputs are also critical for vestibular compensation. Green dashed line with arrowheads: Excitatory transmission; Brown dashed line with arrowheads: Inhibitory transmission. CNS, Central nervous system; MVN, Medial Vestibular Nucleus.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
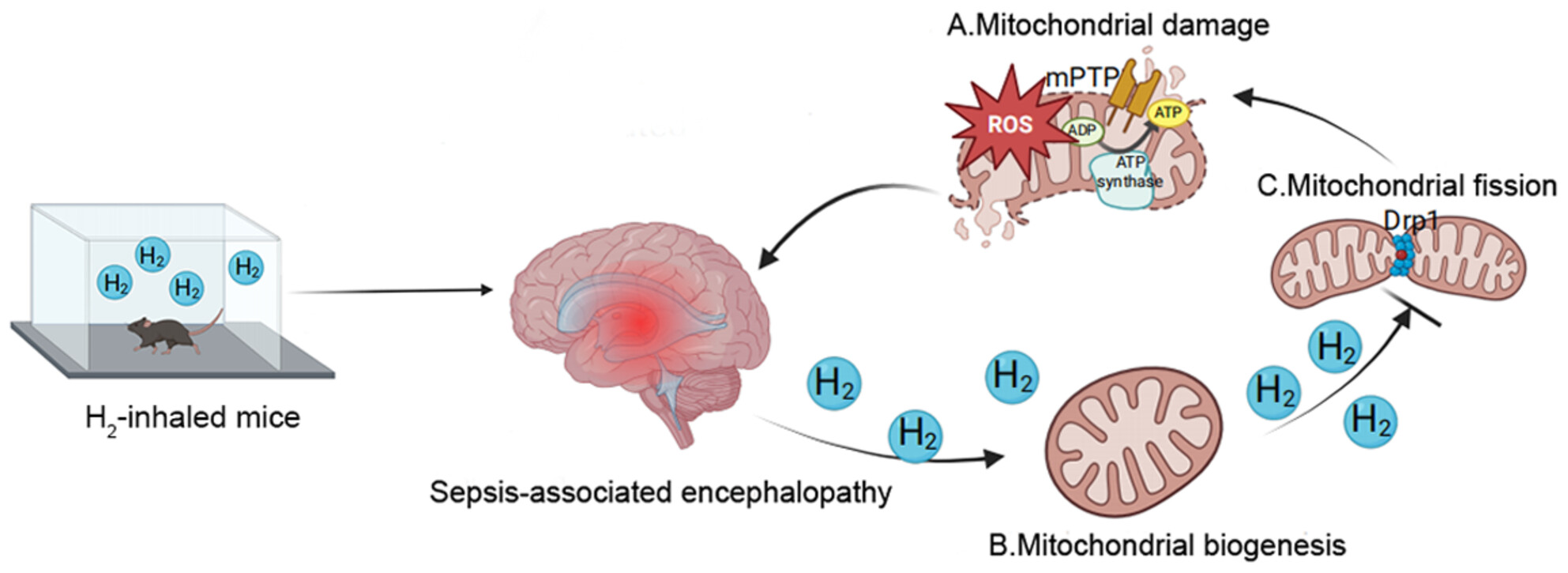
High-concentration hydrogen inhalation mitigates sepsis-associated encephalopathy in mice by improving mitochondrial dynamics
- First Published: 11 September 2024
Whether coagulation dysfunction influences the onset and progression of diabetic peripheral neuropathy: A multicenter study in middle-aged and aged patients with type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 11 September 2024

This multicenter study, which involved 1211 patients with type 2 diabetes, aimed to elucidate the correlation between coagulation function and the risk and severity of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). Among the coagulation parameters examined, fibrinogen was found to be independently associated with the risk (OR 1.172; p = 0.035) and severity of DPN (p < 0.05), and this finding was externally validated.
Neuroimaging analysis reveals distinct cerebral perfusion responses to fasting-postprandial metabolic switching in Alzheimer's disease patients
- First Published: 11 September 2024
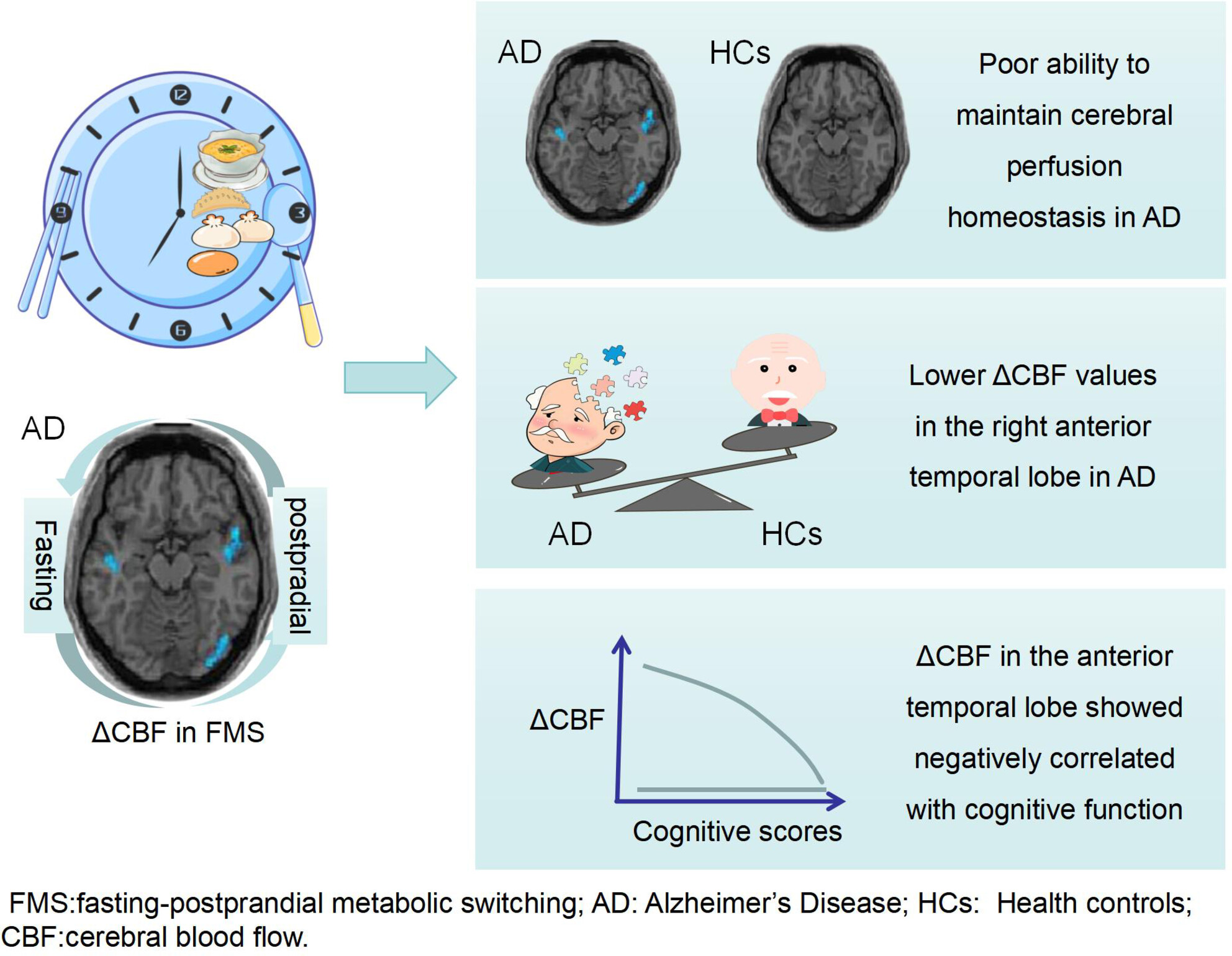
How could the cerebral perfusion response to fasting-postprandial metabolic switching in Alzheimer's Disease (AD)? Difference cerebral blood flow (ΔCBF) of arterial spin labeling imaging between fasting and postprandial states was used to reflect cerebral perfusion response to fasting-postprandial metabolic switching. AD participants had poor ability to maintain cerebral perfusion homeostasis; AD had lower ΔCBF values in the right anterior temporal lobe than mild cognitive impairment patients and healthy controls; ΔCBF in the anterior temporal lobe showed a negatively correlated with cognitive function in AD. ΔCBF in the anterior temporal lobe can be a potential radiological marker to reflect the cognitive function in fasting-postprandial metabolic switching in AD.
REVIEW
Cuproptosis: Mechanisms, biological significance, and advances in disease treatment—A systematic review
- First Published: 12 September 2024
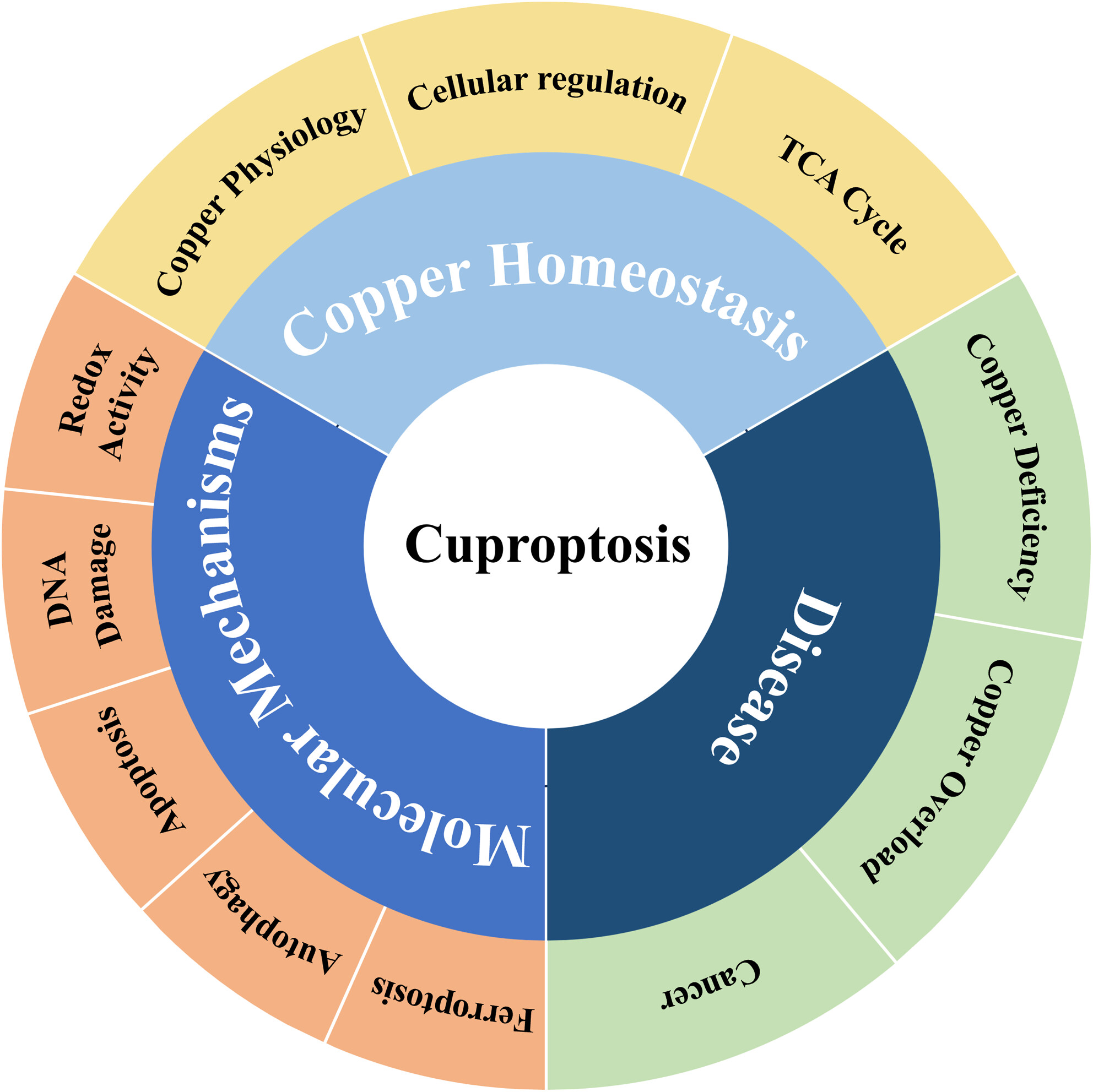
Copper is an essential trace element in the human body, participating in a variety of biological functions and metabolic processes. The homeostatic copper in the human body is regulated by the absorption, transportation, storage, and metabolism of copper. Dysregulation of copper metabolism is closely related to the occurrence and progression of various diseases. The cell death induced by copper overload is initiated by interaction between copper and acylated enzymes in the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, which then results in protein aggregation, loss of iron-sulfur cluster proteins, and cell death. Furthermore, we discuss the role of copper in regulating autophagy, the relationship between copper-dependent death and disease, and the potential role of copper in cancer treatment. We emphasize the necessity for further research into alternative pathways of copper-induced cell death, the detailed mechanisms of Cuproptosis, and biomarkers for copper poisoning. It proposes future research directions, including exploring the molecular mechanisms of Cuproptosis, developing new therapeutic strategies, and verifying their safety and efficacy in clinical trials.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Combined use of CLP290 and bumetanide alleviates neuropathic pain and its mechanism after spinal cord injury in rats
- First Published: 12 September 2024
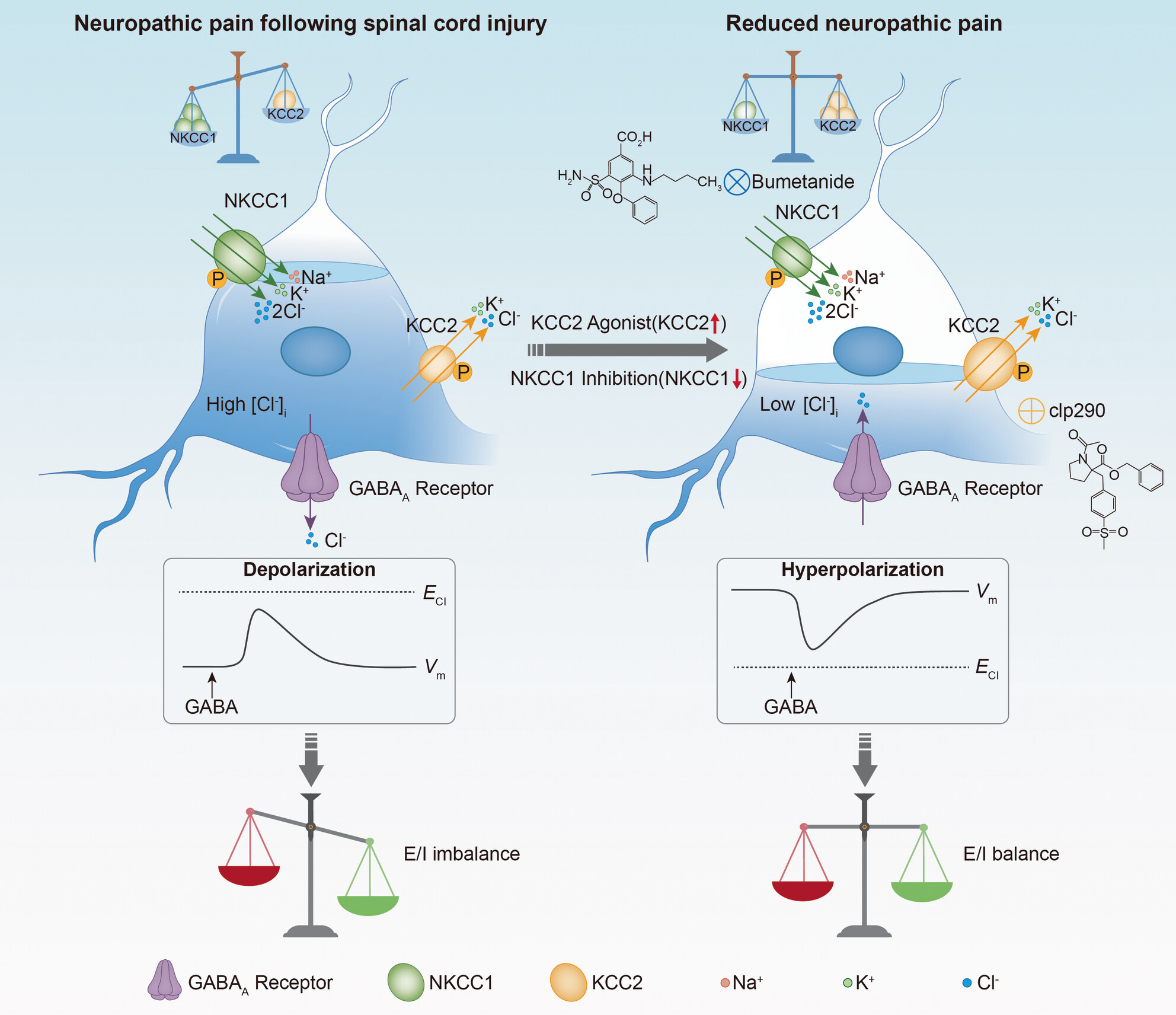
- Combined application of CLP290 and Bumetanide can effectively increase the ratio of KCC2/NKCC1, restore RDD levels, enhance GABAA receptor-mediated inhibitory function in the spinal cord, and relieve neuropathic pain in SCI.
- Bumetanide significantly improves neuropathic pain in the long term, whereas CLP290 demonstrates a notable short-term effect.
Autoimmune astrocytopathy double negative for AQP4-IgG and GFAP-IgG: Retrospective research of clinical practice, biomarkers, and pathology
- First Published: 15 September 2024
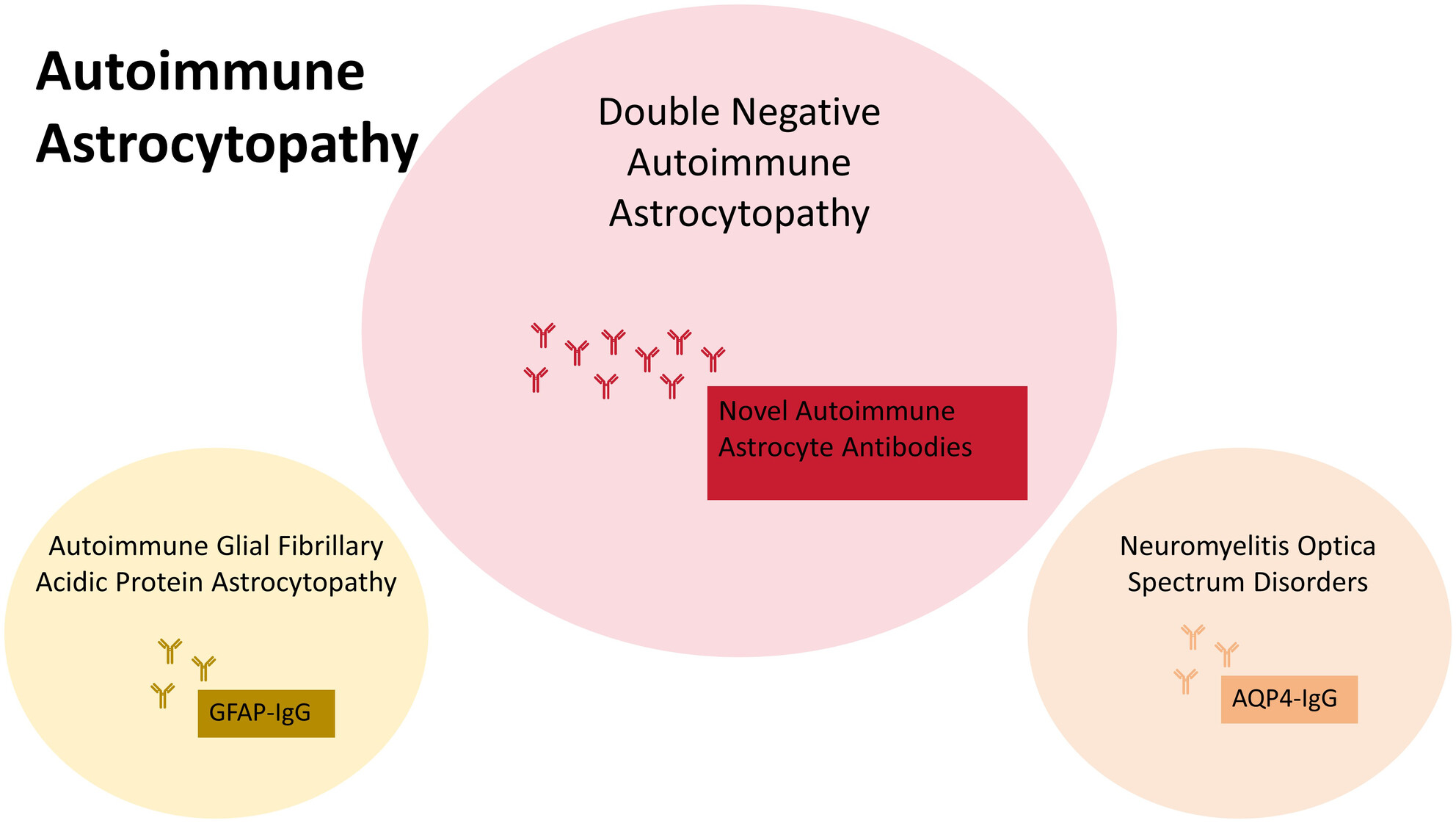
Current knowledge suggests that autoimmune astrocytopathy primarily involves antibodies targeting AQP4 and GFAP. This study aimed to investigate a novel type of autoimmune astrocytopathy that is negative for both AQP4-IgG and GFAP-IgG and explore its clinical manifestations, biomarkers, and pathology.
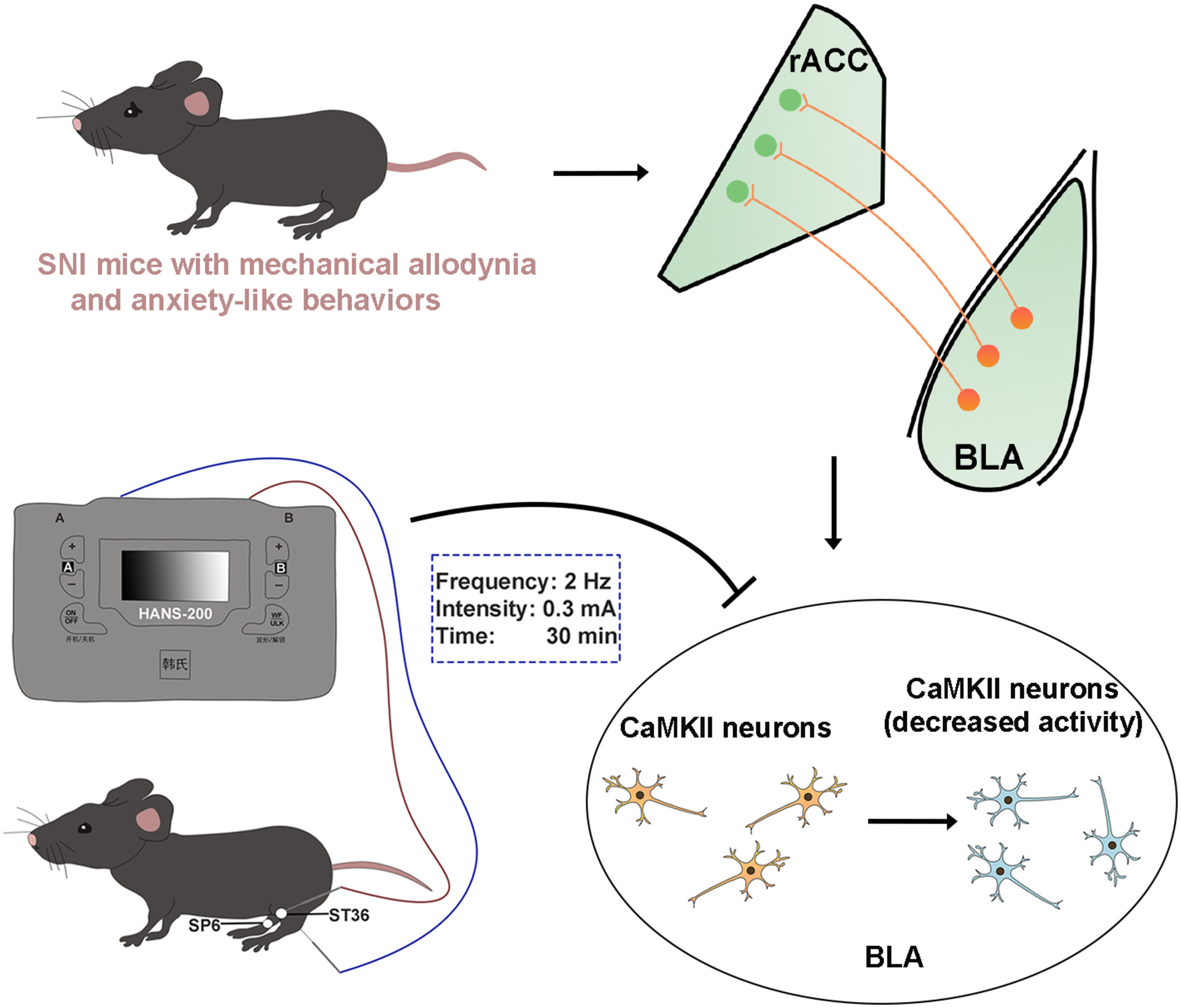
Involvement of basolateral amygdala-rostral anterior cingulate cortex in mechanical allodynia and anxiety-like behaviors and potential mechanisms of electroacupuncture
- First Published: 15 September 2024
A prediction model of dementia conversion for mild cognitive impairment by combining plasma pTau181 and structural imaging features
- First Published: 18 September 2024
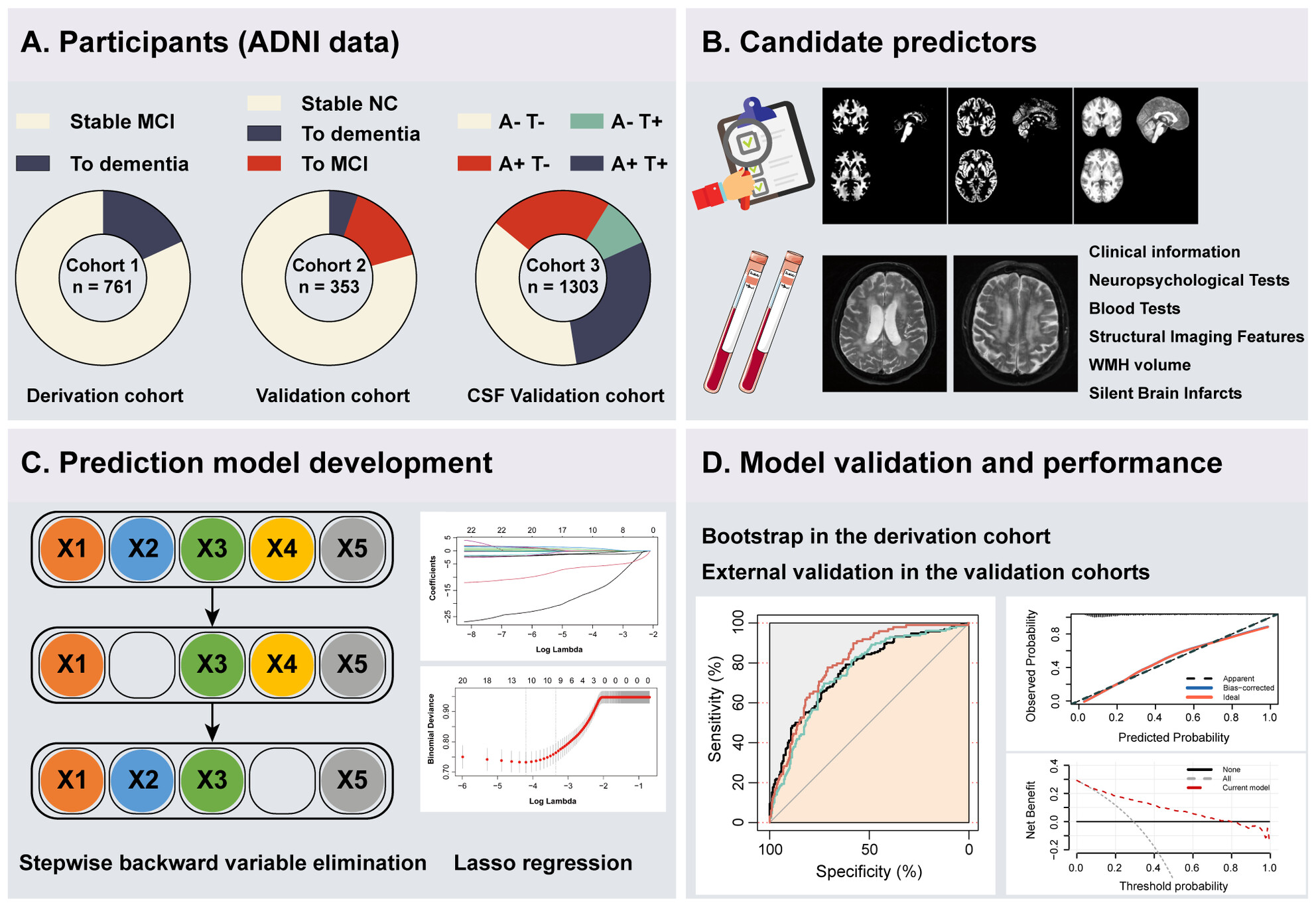
Based on predictors that are routinely available, we provided an accurate and convenient diagnostic tool that can predict the clinical progression of mild cognitive impairment patients and identify Alzheimer's disease specific pathological changes. This tool may contribute to more precise clinical treatment and better health care resource allocation.
Effects of β-sitosterol on anxiety in migraine-induced rats: The role of oxidative/nitrosative stress and mitochondrial function
- First Published: 20 September 2024
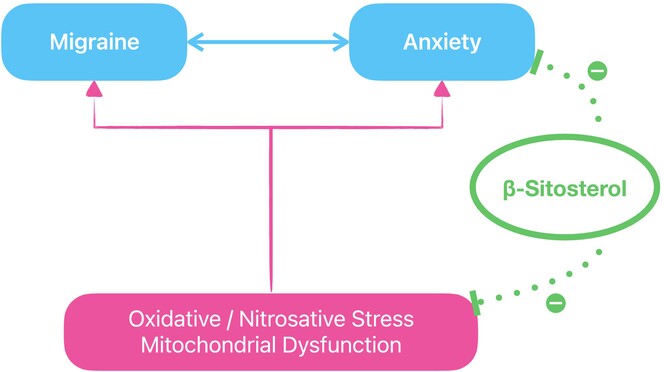
Anxiety often coexists with migraine, with both conditions sharing commonalities in oxidative/nitrosative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction contributing to their pathogenesis. In this study, we found β-sitosterol to reduce anxiety in migraine-induced rats, likely via its antioxidant and cellular metabolism enhancing effects.
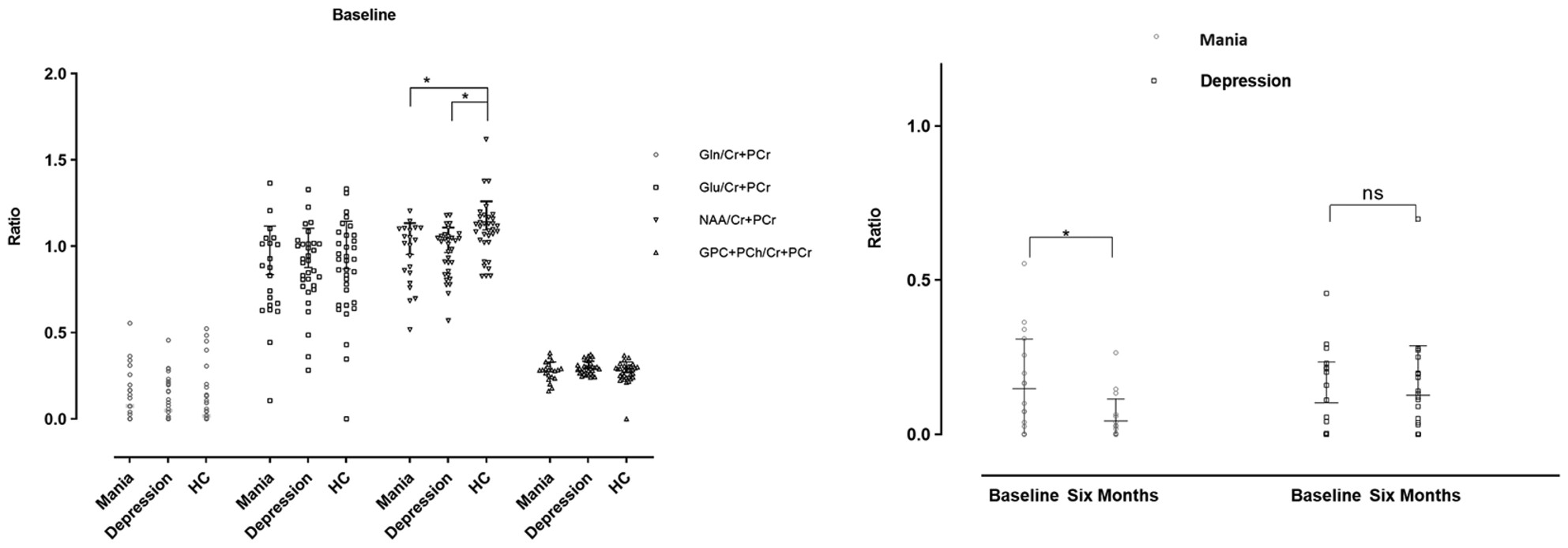
Changes in the medial prefrontal cortex metabolites after 6 months of medication therapy for patients with bipolar disorder: A 1H-MRS study
- First Published: 19 September 2024
REVIEW
Revisiting dezocine for opioid use disorder: A narrative review of its potential abuse liability
- First Published: 18 September 2024

Dezocine is a partial MOR agonist previously used clinically in the USA and currently in China. It has been proposed that dezocine be reintroduced to clinical use in the USA, as an analgesia and/or an additional tool to treat opioid use disorder. To consider the clinical reintroduction of dezocine knowing its abuse liability is important. In this review, we found no reports of abuse, dependence or overdose in the English literature, and a small number of cases of dependence in the Chinese literature. If it is less or non-addictive than other opioids, its short half-life would allow it to bridge to other medication assisted therapies, facilitate tapering of opioid use and perhaps be used as a rescue medication in those trying to reduce opioid use.
Modulating reward and aversion: Insights into addiction from the paraventricular nucleus
- First Published: 18 September 2024
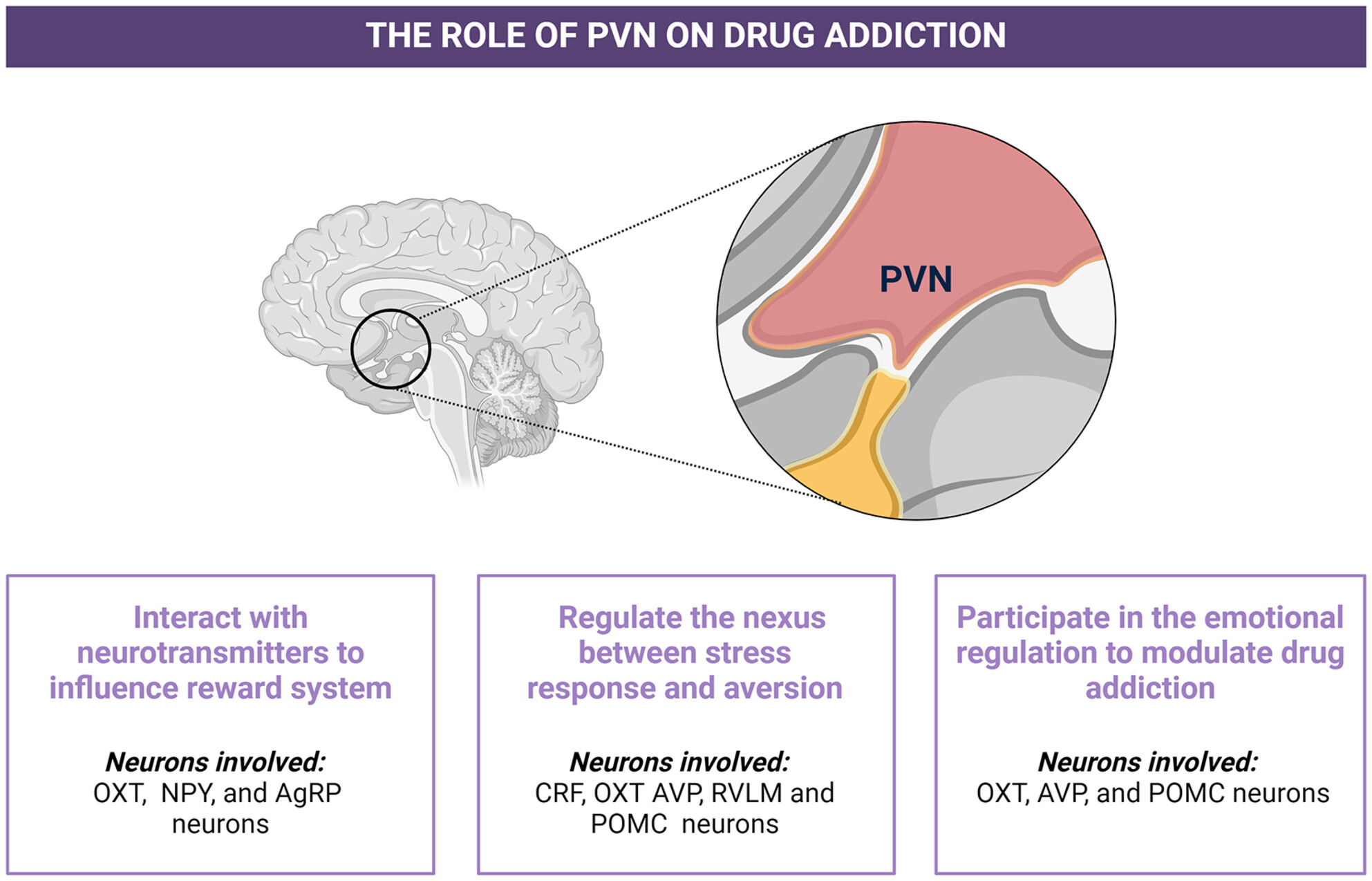
The paraventricular nucleus regulates drug addiction directly by modulating reward and aversion systems or indirectly by affecting stress response and emotional regulation. In this process, the corticotropin-releasing factor, oxytocin, arginine vasopressin, rostral ventrolateral medulla, neuropeptide Y, agouti-related peptide, and pro-opiomelanocortin neurons are involved in the modulation of drug addiction.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
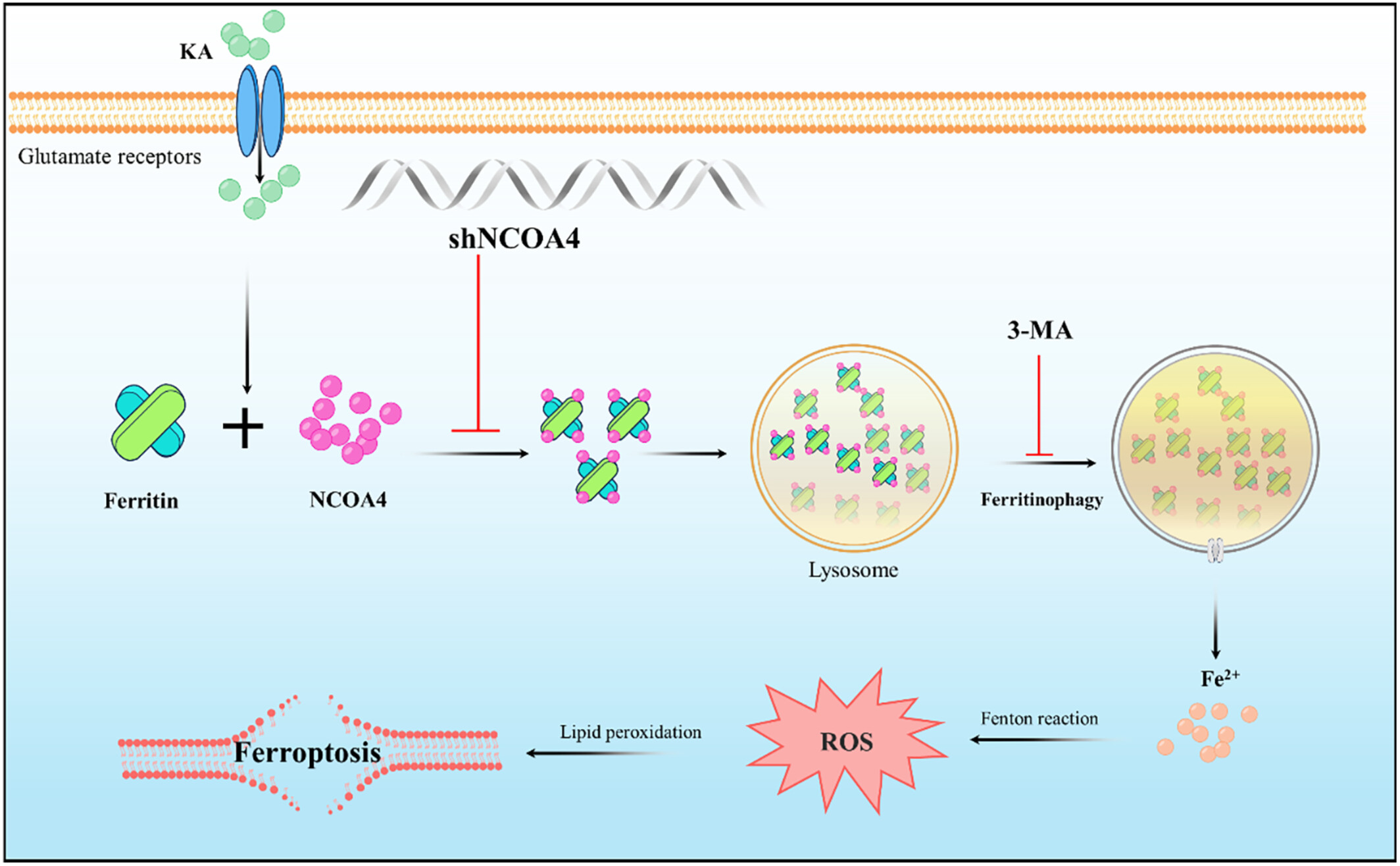
KA-mediated excitotoxicity induces neuronal ferroptosis through activation of ferritinophagy
- First Published: 22 September 2024
Early screening of post-stroke fall risk: A simultaneous multimodal fNIRs-EMG study
- First Published: 24 September 2024
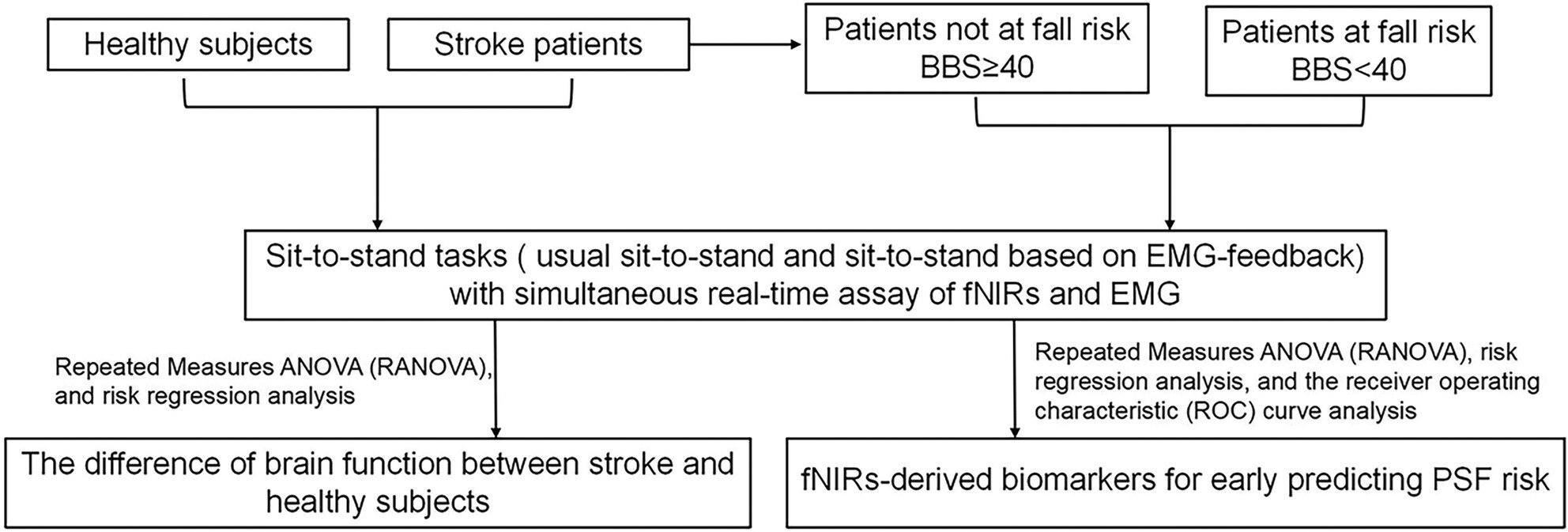
This study provided novel evidence that fNIR-derived biomarkers could early predict PSF risk that can be widely used in clinical practice. Meanwhile, this study demonstrated that the higher brain activation and inability to increase the brain functional connectivity in stroke patients during difficult task indicated the inefficient use of brain resources.
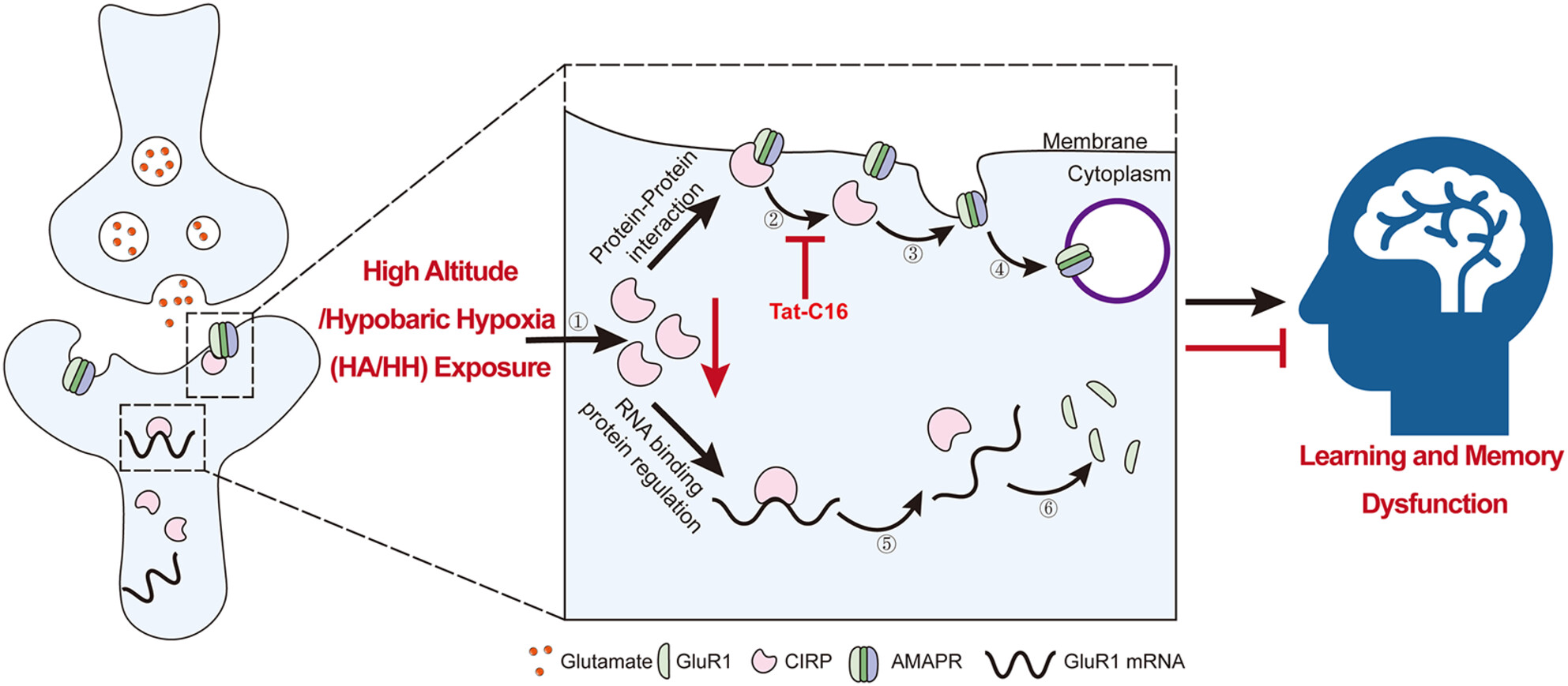
Decreased cold-inducible RNA-binding protein (CIRP) binding to GluRl on neuronal membranes mediates memory impairment resulting from prolonged hypobaric hypoxia exposure
- First Published: 24 September 2024
A hypothalamus-lateral periaqueductal gray GABAergic neural projection facilitates arousal following sevoflurane anesthesia in mice
- First Published: 24 September 2024
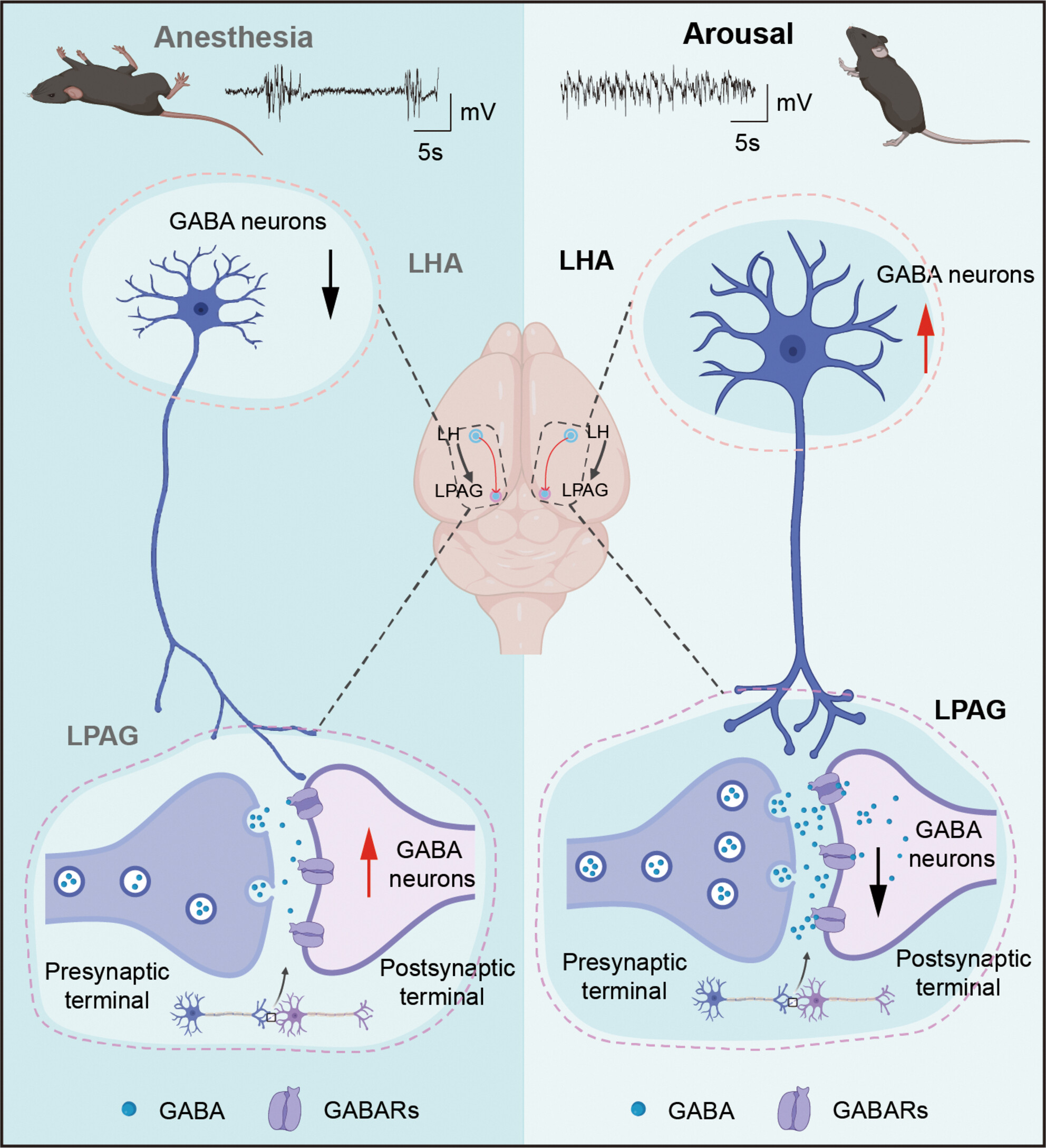
In this study, we revealed an inhibitory projection from LHAGABA to LPAG facilitates arousal from sevoflurane, suggesting a complex control of wakefulness through intimate interactions between long-range connections. These findings enhance our understanding of the mechanisms of consciousness shift and potentially facilitate the development of studies involving the GABAergic system.
Expression of microRNA induced by postoperative delirium-like behavior is associated with long-term default mode network disruption: Sequencing and a secondary analysis of resting-state fMRI data
- First Published: 24 September 2024
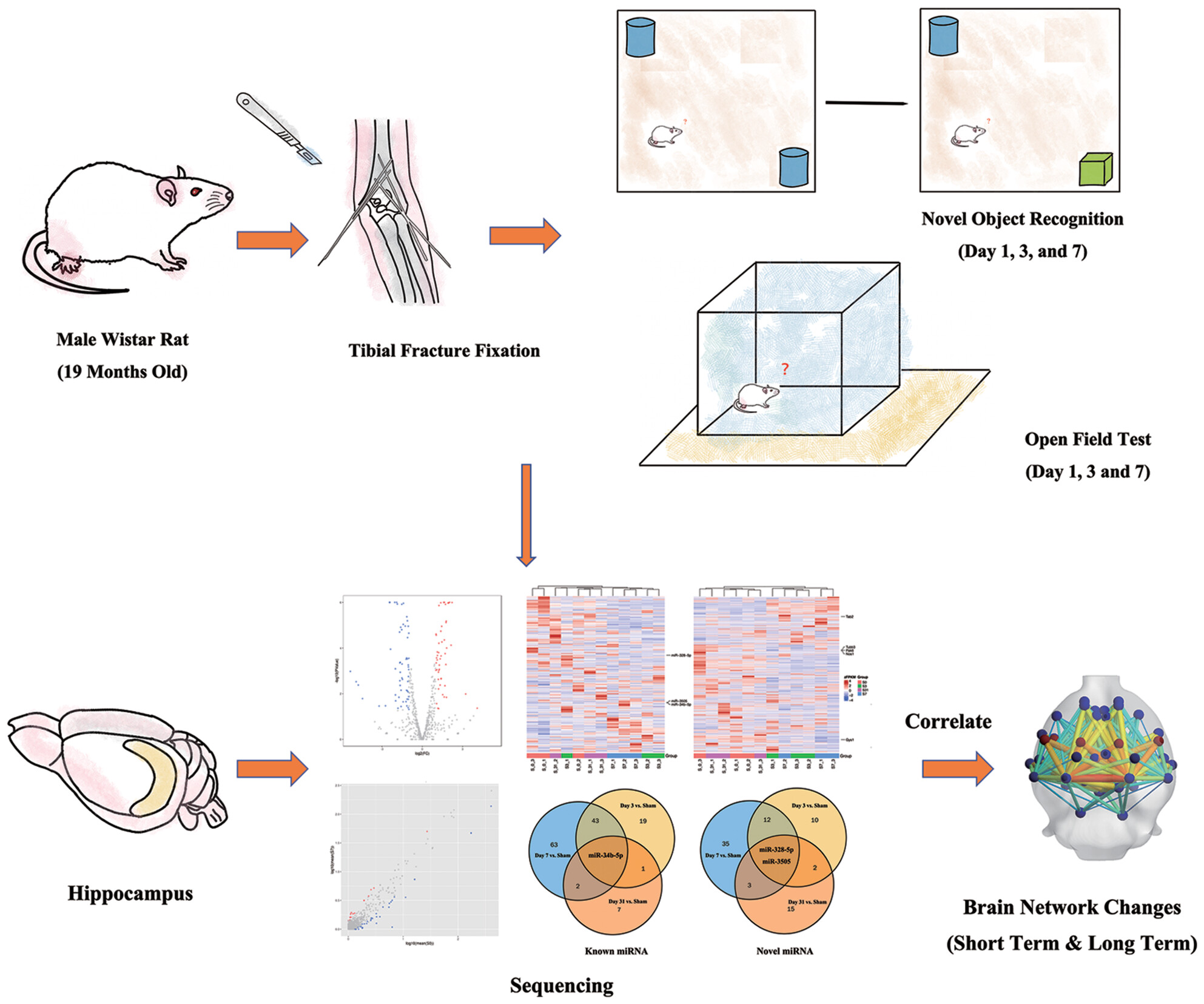
In this research we focused on the objective changes behind default mode network disruption induced by delirium-like behavior in aged rat induced by isoflurane anesthesia and tibia fracture fixation surgery. The study not only pointed out long-term changes in miRNA and target gene, but also improves interpretability and reproducibility of resting state functional magnetic resonance imaging data analysis.
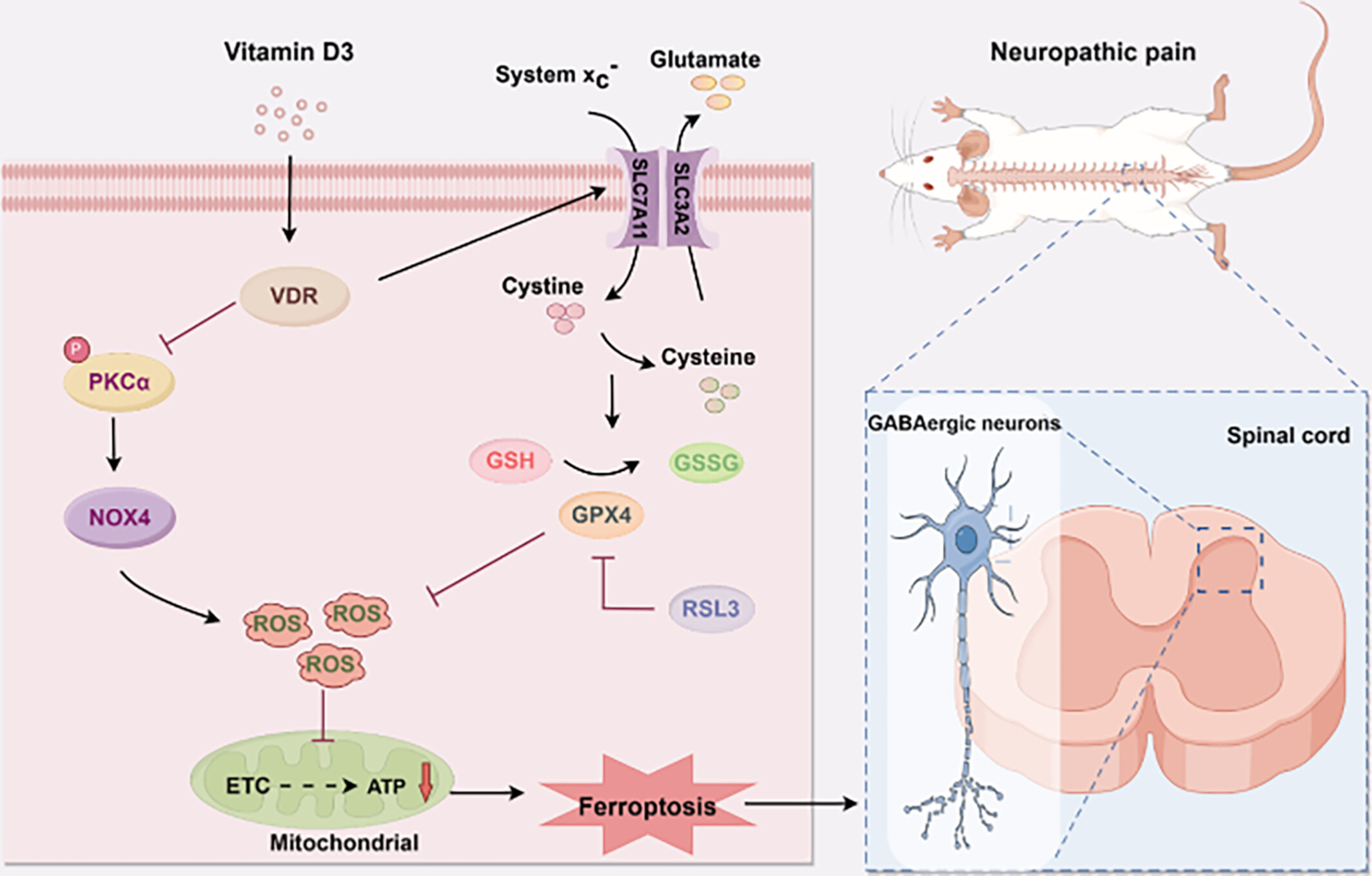
Vitamin D3 Attenuates Neuropathic Pain via Suppression of Mitochondria-Associated Ferroptosis by Inhibiting PKCα/NOX4 Signaling Pathway
- First Published: 27 September 2024
CORRECTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Feasibility and effectiveness of transcutaneous auricular vagus nerve stimulation (taVNS) in awake mice
- First Published: 11 September 2024
Physical exercise-induced circAnks1b upregulation promotes protective endoplasmic reticulum stress and suppresses apoptosis via miR-130b-5p/Pak2 signaling in an ischemic stroke model
- First Published: 27 September 2024
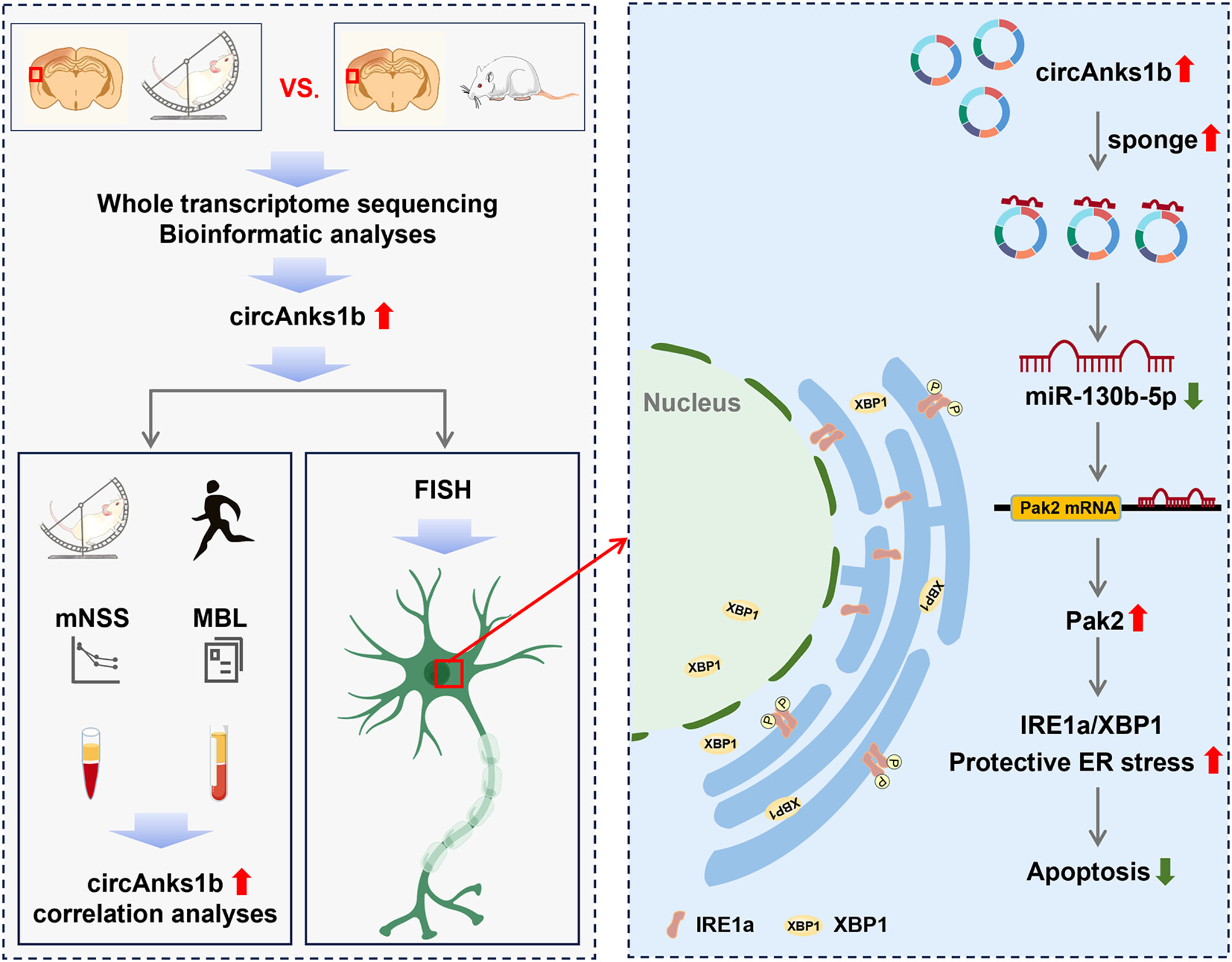
Experimental hypothesis: CircAnks1b is upregulated by physical exercise in neurons of peri-infarct cortex. CircAnks1b competitively binds to miR-130b-5p, thereby mitigating miR-130b-5p-mediated suppression of Pak2 mRNA expression. Ensuing Pak2 expression increases IRE1a/XBP1 signaling pathway activity, which promotes protective ER stress in neurons and reduces apoptosis. High plasma circAnks1b expression also predicts superior neurological recovery in IS patients.