Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Front Cover
- First Published: 02 August 2024
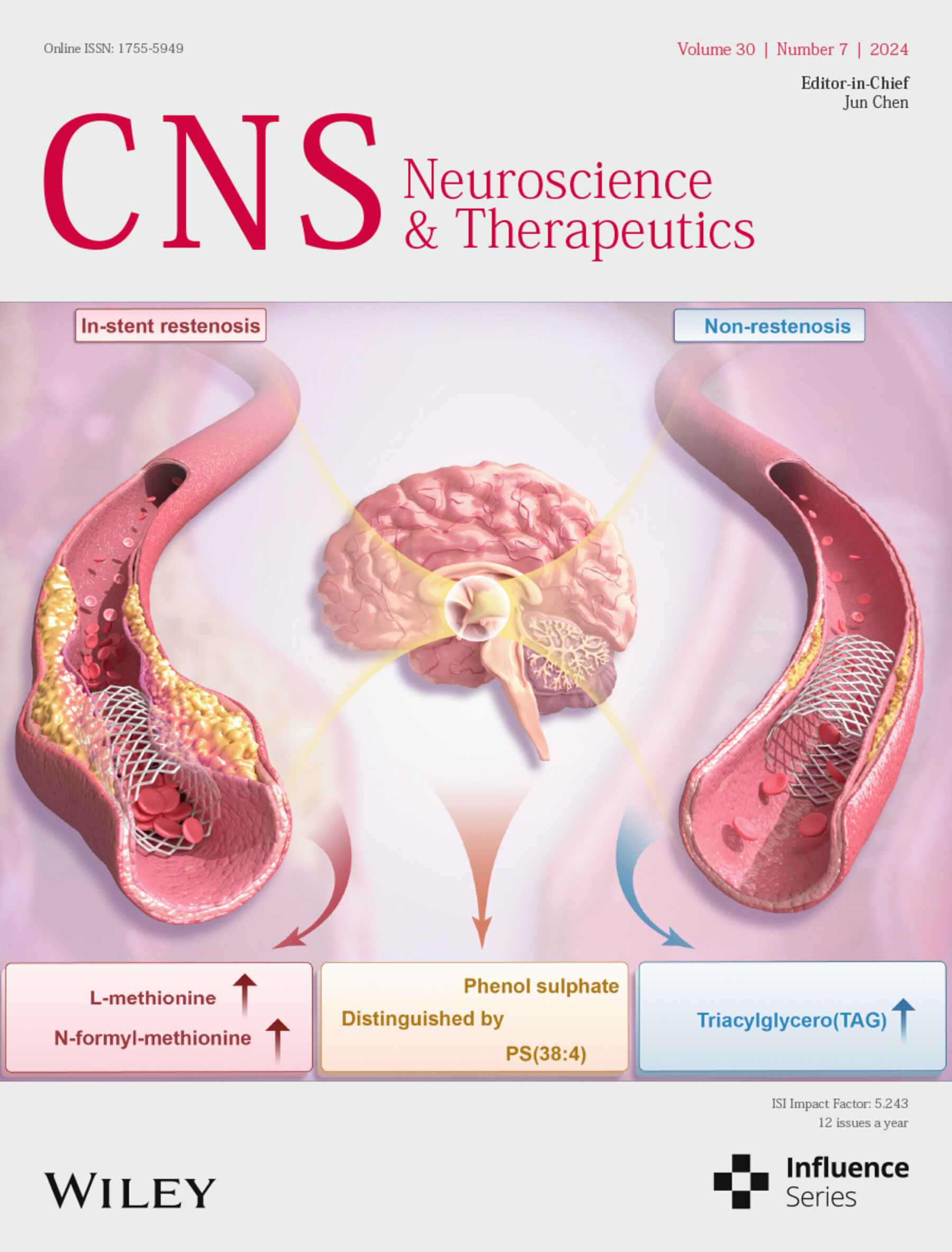
Cover image: The cover image is based on the article Alterations of Metabolome and Lipidome in Patients with In-Stent Restenosis by Ziqi Xu et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.14832.
Additional Cover
- First Published: 02 August 2024

The cover image is based on the article Exploring Functional and Structural Connectivity Disruptions in Spinocerebellar Ataxia Type 3: Insights from Gradient Analysis by Xingang Wang et al., https://doi.org/10.1111/cns.14842.
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL COMMENTARY
Building evidence on safety of endovascular thrombectomy for patients under anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists
- First Published: 03 July 2024
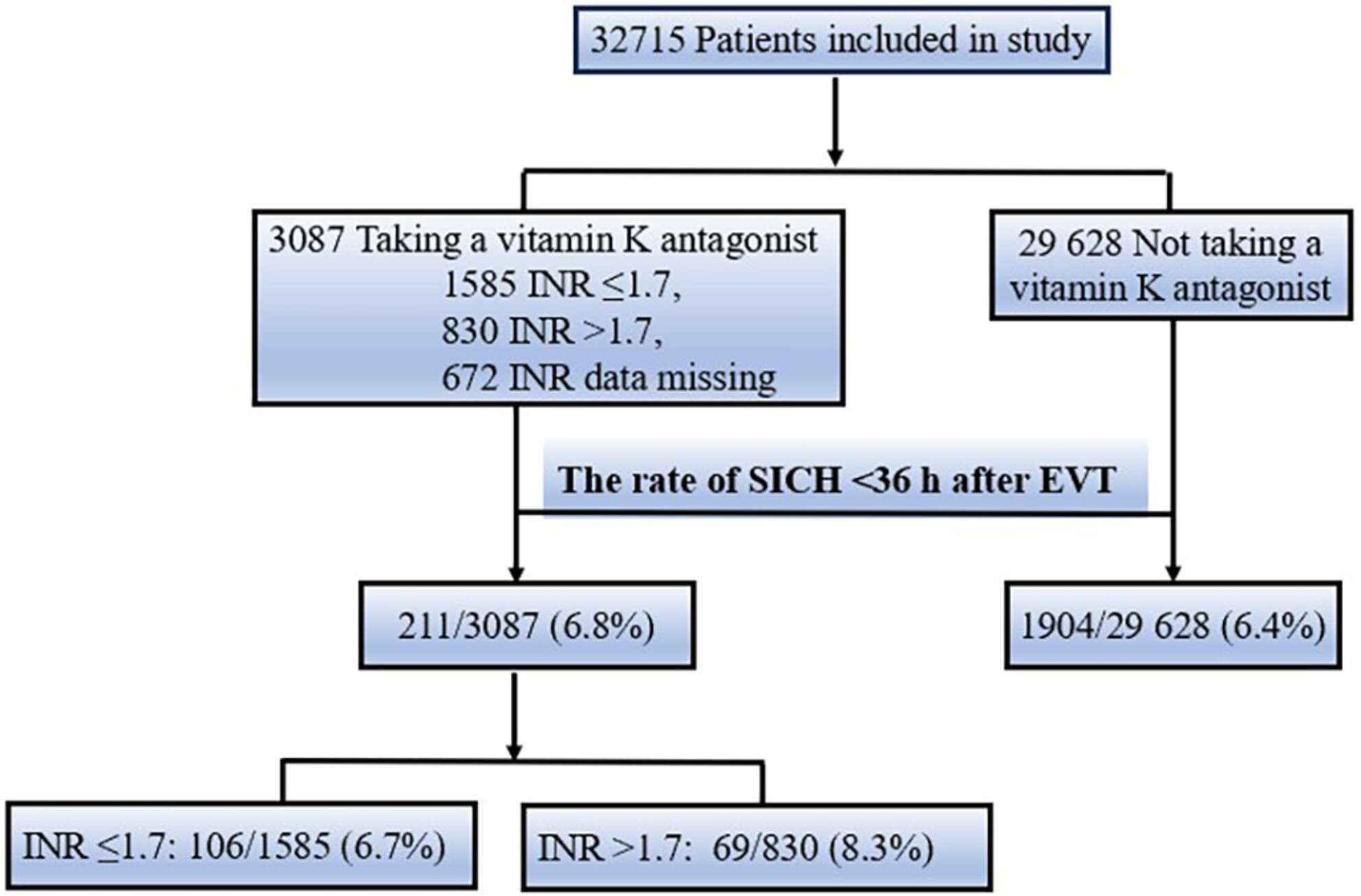
In this study, a total of 32,715 patients with acute ischemic stroke undergoing endovascular thrombectomy (EVT) were included. In total, 29,628 patients (90.6%) were not taking a vitamin K antagonist (VKA) prior to stroke, and 3087 patients (9.4%) were taking a VKA. The incidence of symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage (sICH) among the VKA group is 6.8%, which is comparable to those non-VKA users with an incidence of 6.4%. Then, the international normalized ratio (INR) was dichotomized as ≤1.7 and >1.7 to assess the risk of sICH in each subgroup. Among 830 patients taking a VKA with an INR greater than 1.7, the incidence of sICH was 8.3%, which is significantly higher than those not taking a VKA (6.4%). Meanwhile, those with an INR of 1.7 or lower (n = 1585) had no significant difference of the risk of sICH (6.7%).
REVIEWS
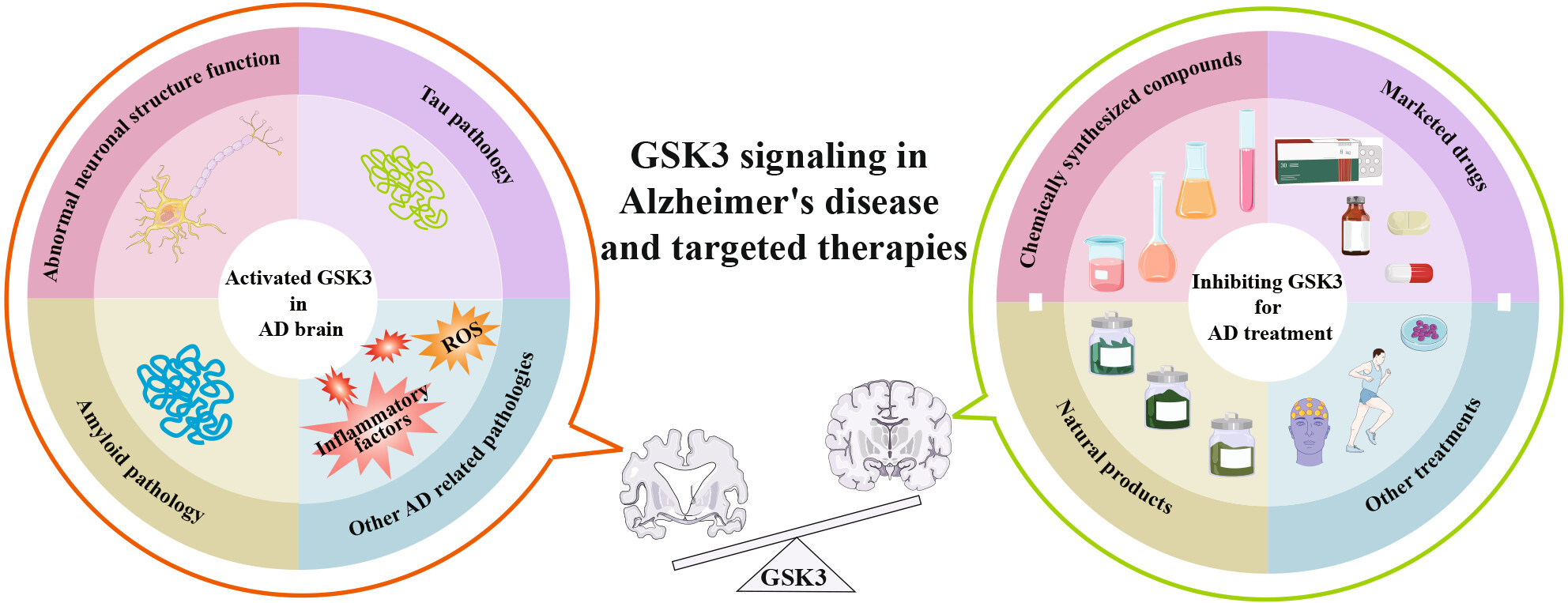
GSK3: A potential target and pending issues for treatment of Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 01 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Neuroimaging and clinical features of bilateral Wallerian degeneration of middle cerebellar peduncles subsequent to pontine infarction
- First Published: 01 July 2024
Wallerian degeneration (WD) of bilateral middle cerebellar peduncles (MCPs) following pontine infarction is a rare secondary neurodegenerative disorder. WD of bilateral (MCPs) does not seem to be a marker for a bad outcome in general. The radiological features in MRI included hyperintense T2WI signals, hyperintense FLAIR signals, high DWI signal intensity, and low ADC signal intensity.
Perioperative stroke deteriorates white matter integrity by enhancing cytotoxic CD8+ T-cell activation
- First Published: 07 July 2024
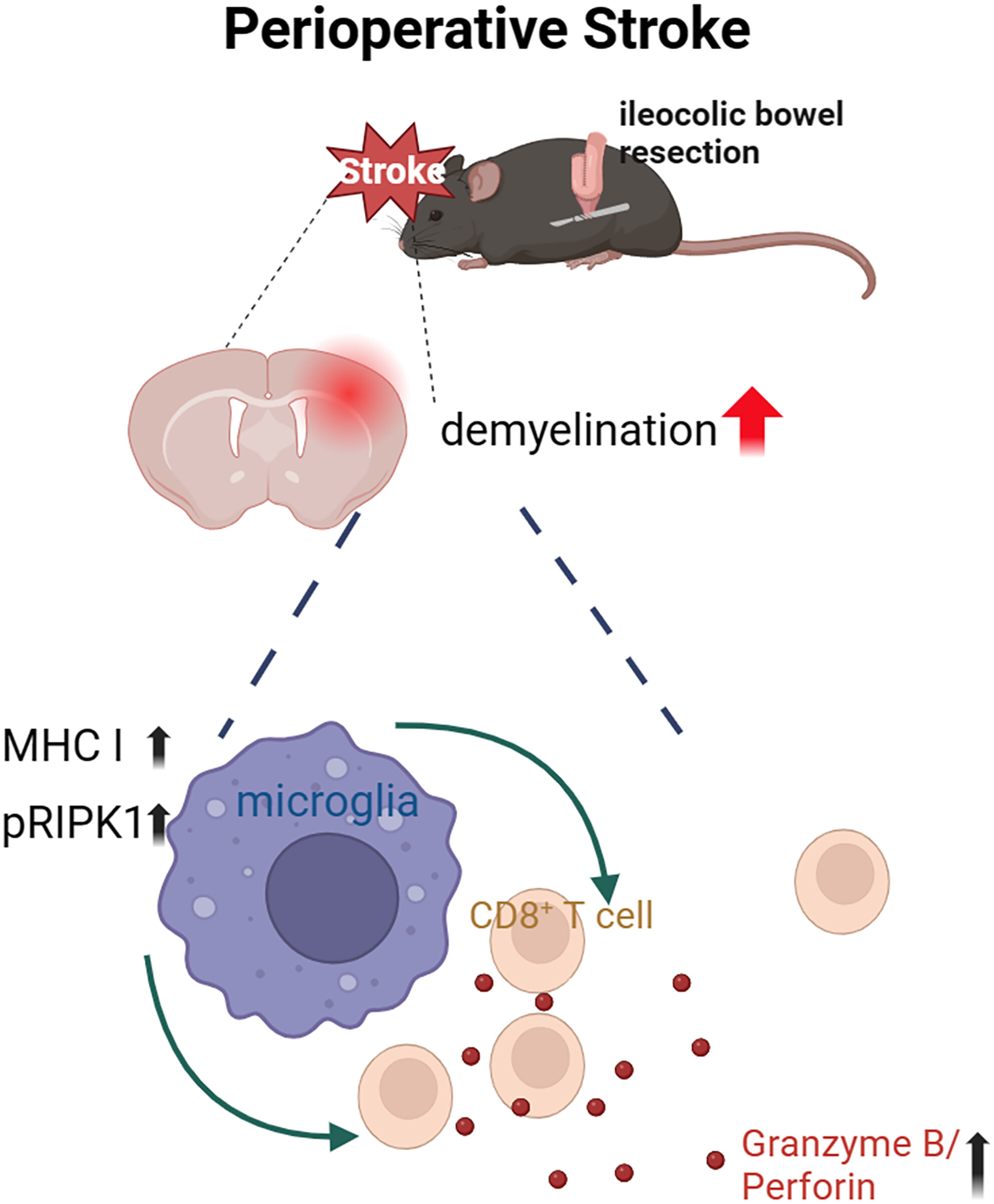
Perioperative stroke (PIS) exacerbates post-stroke demyelination and worsens neurological functions by promoting infiltration of CD8+ T cells and microglia necroptosis in experimental animal models. Pharmacological blockage or genetic deletion of receptor-interacting protein kinase 1 activity could partly reverse demyelination injury, suggesting a novel therapeutic target for the PIS treatment.
Optic nerve compression associated with visual cortex functional alteration in dysthyroid optic neuropathy: A combined orbital and brain imaging study
- First Published: 01 July 2024
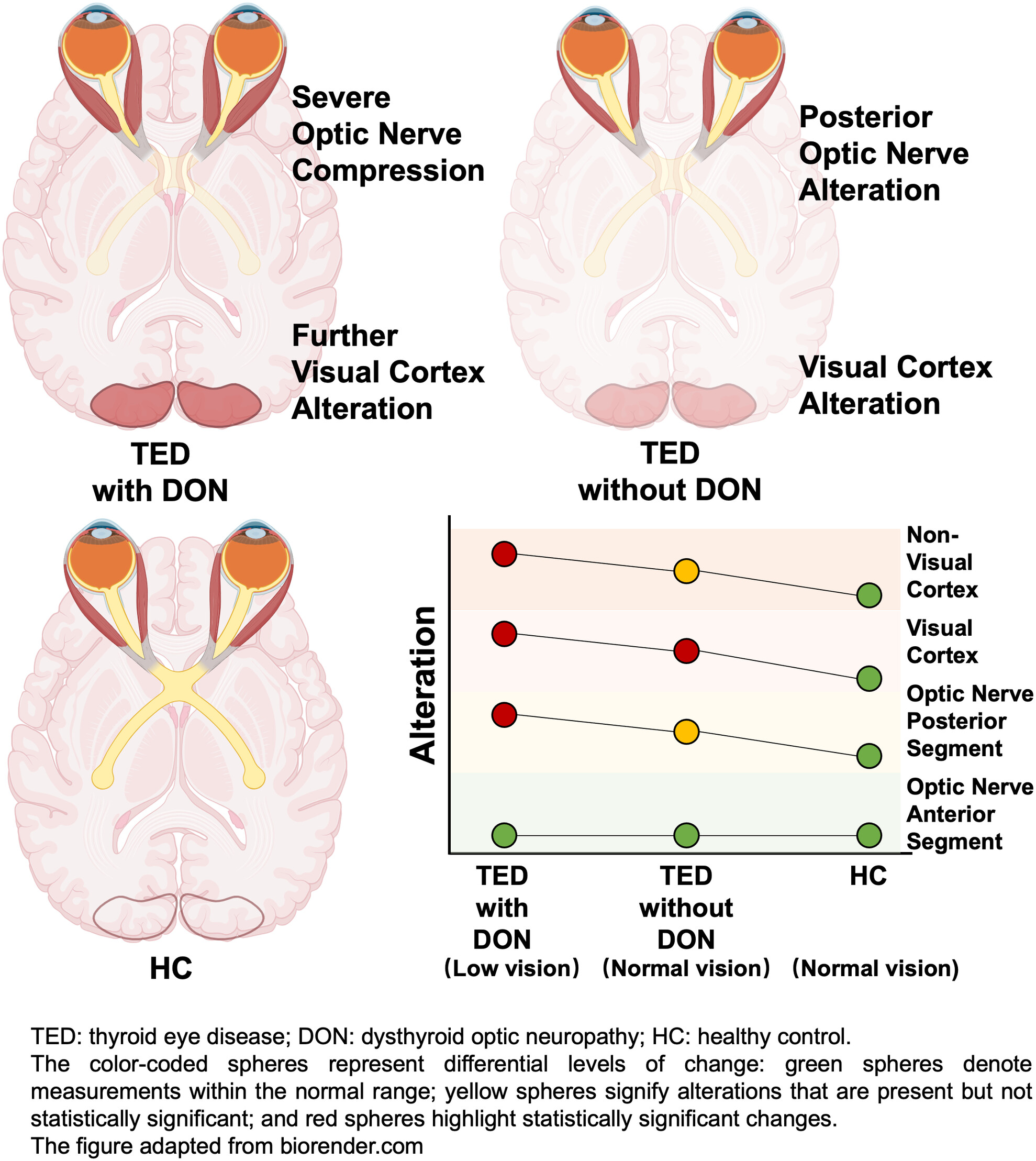
Changes of in the visual cortex were observed before the progression to dysthyroid optic neuropathy (DON). With the onset of DON, significant intraorbital optic nerve compression was noted, accompanied by further alterations in the visual cortex and other brain regions. This provides novel explanations of visual pathway alterations in DON.
The clinical and predictive value of 18F-FDG PET/CT metabolic patterns in a clinical Chinese cohort with autoimmune encephalitis
- First Published: 01 July 2024
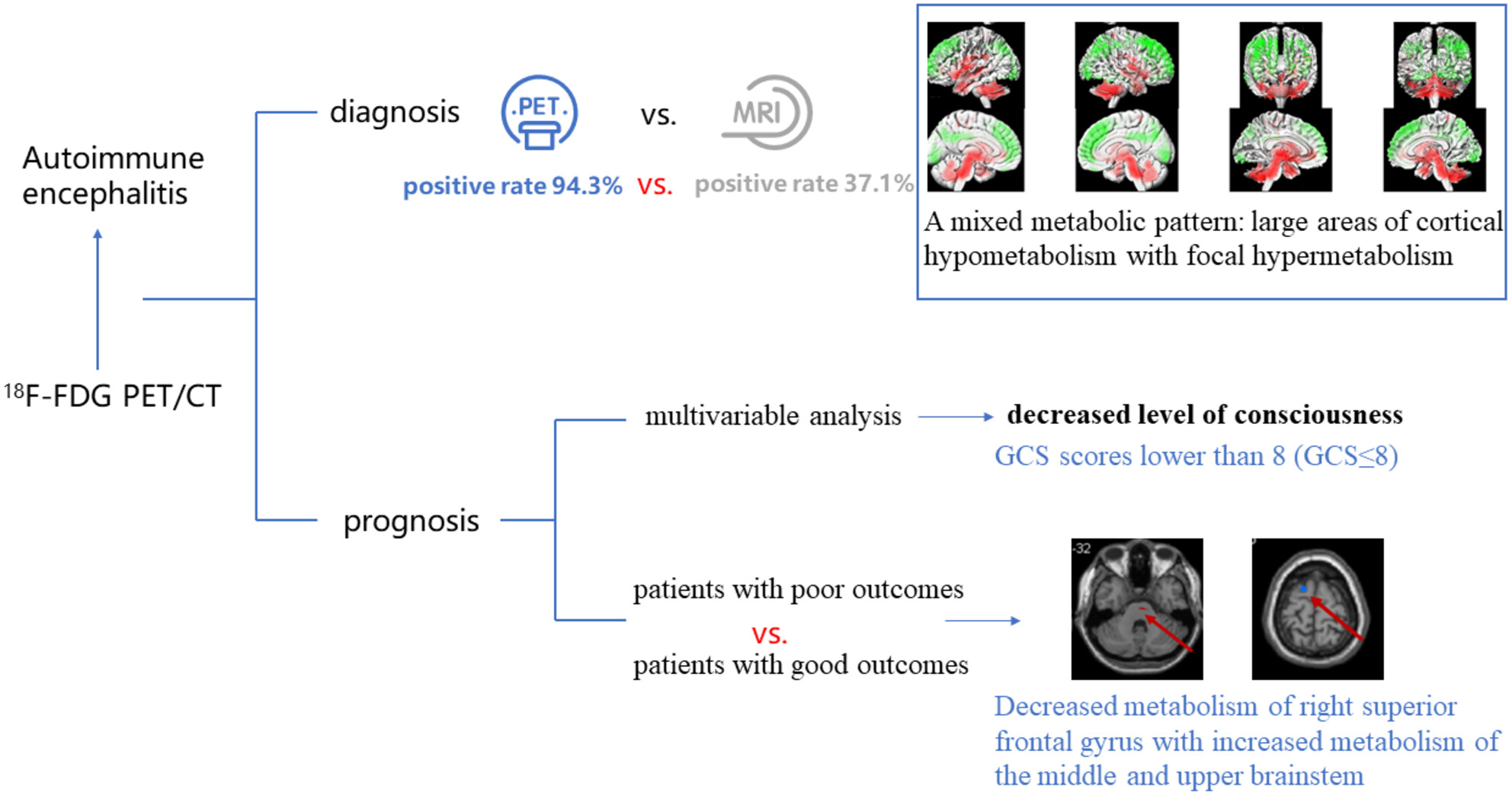
The present study investigates diagnostic and predictive role of 18F-FDG PET/CT in patients with autoimmune encephalitis (AE) as a whole group. Our findings suggest that 18F-FDG PET/CT is more sensitive than MRI in the early diagnosis of AE. A mixed metabolic pattern, characterized by large areas of cortical hypometabolism with focal hypermetabolism is a general metabolic pattern. Decreased metabolism of right superior frontal gyrus with increased metabolism of the middle and upper brainstem may predict poor long-term prognosis of AE.
Multicenter integration analysis of TRP channels revealed potential mechanisms of immunosuppressive microenvironment activation and identified a machine learning-derived signature for improving outcomes in gliomas
- First Published: 01 July 2024
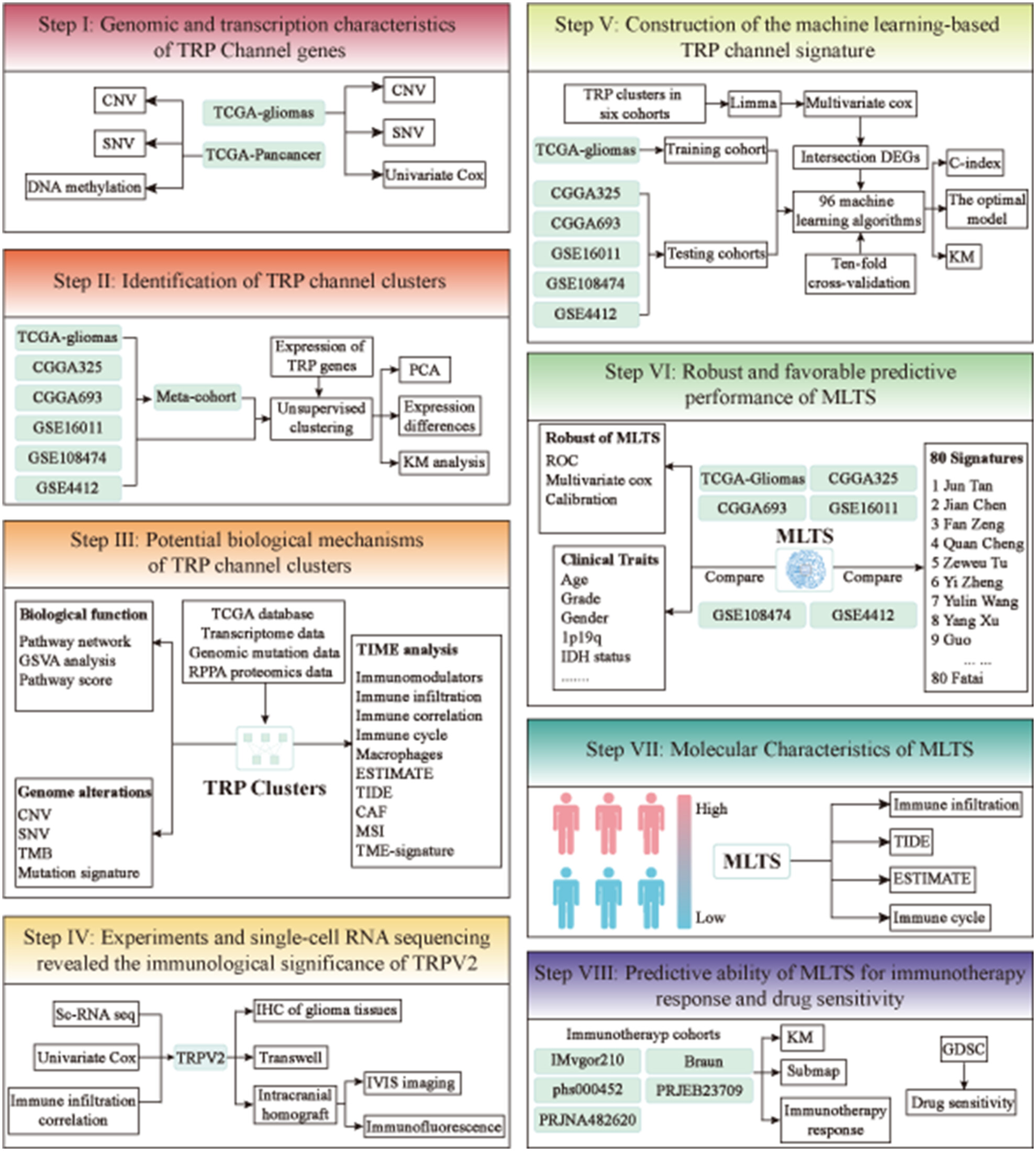
To identify novel TRP channel gene clusters and describe their characteristics, we conducted an unsupervised clustering algorithm. Based on eight independent glioma cohorts and ten machine learning algorithms, a TRP-related signature was constructed named MLTS. It provides a well-developed and robust model to predict prognosis and immunotherapy response in gliomas.
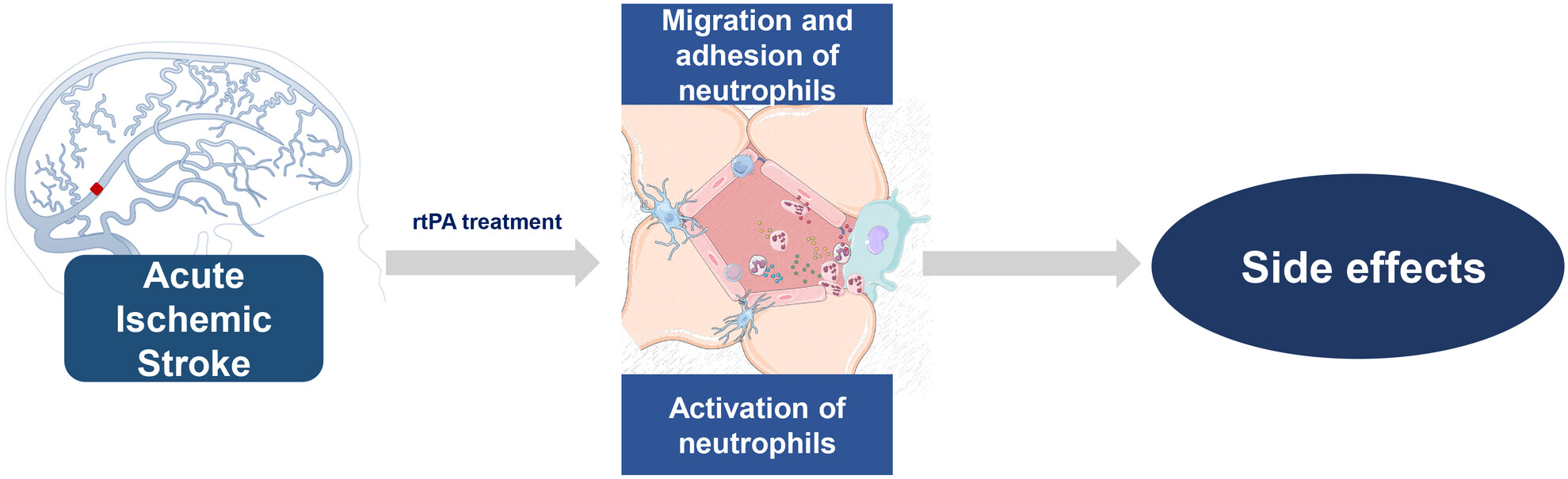
Neutrophil migration participates in the side effect of recombinant human tissue plasminogen activator
- First Published: 02 July 2024
Alterations in metabolome and lipidome in patients with in-stent restenosis
- First Published: 15 July 2024
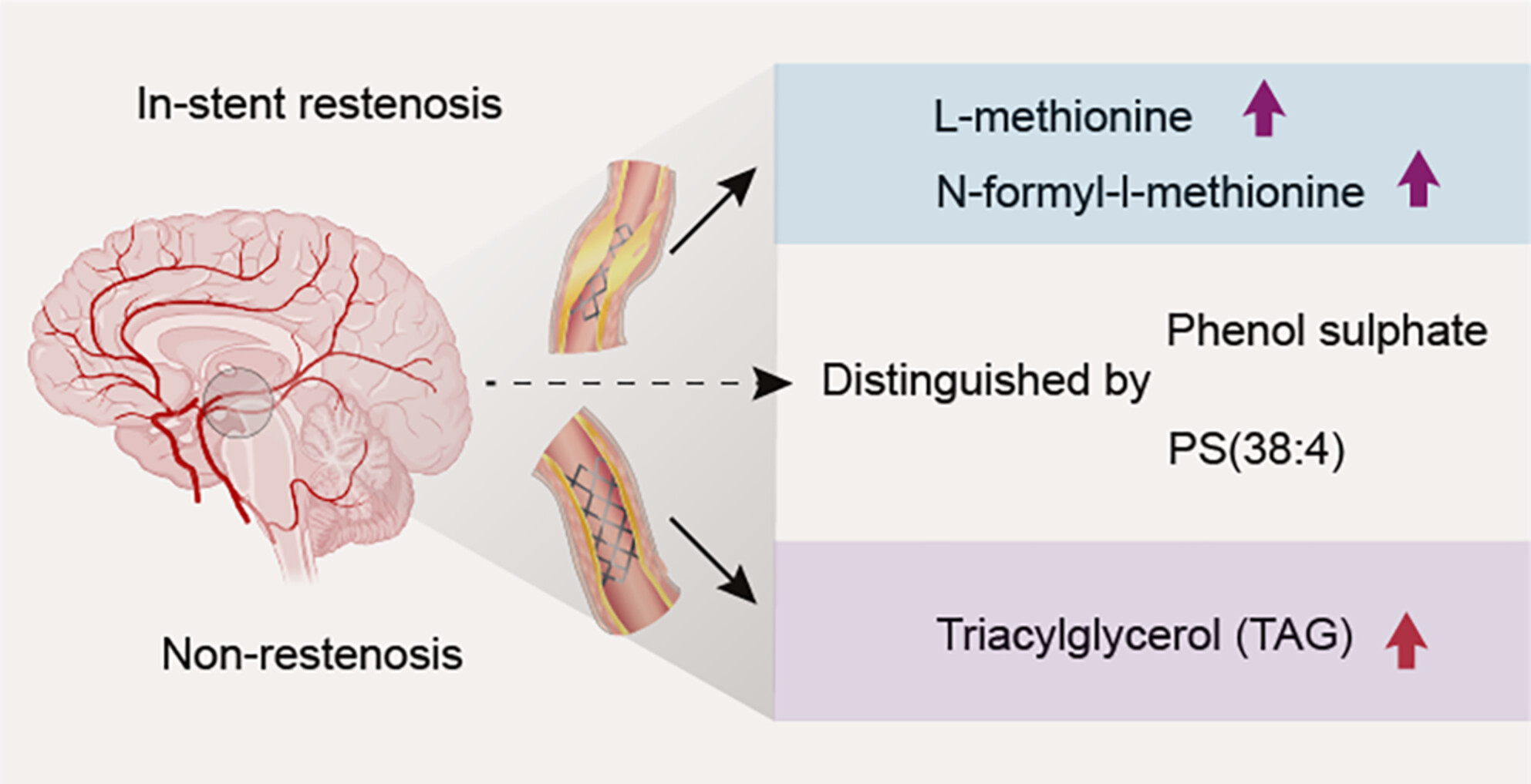
Metabolomic and lipidomic analysis showed that patients who developed in-stent restenosis (ISR) had significantly increased expression of L-methionine and N-formyl-l-methionine, and significantly decreased expression of triacylglycerol in their serum. Phenol sulfate and PS(38:4) may be potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of ISR.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
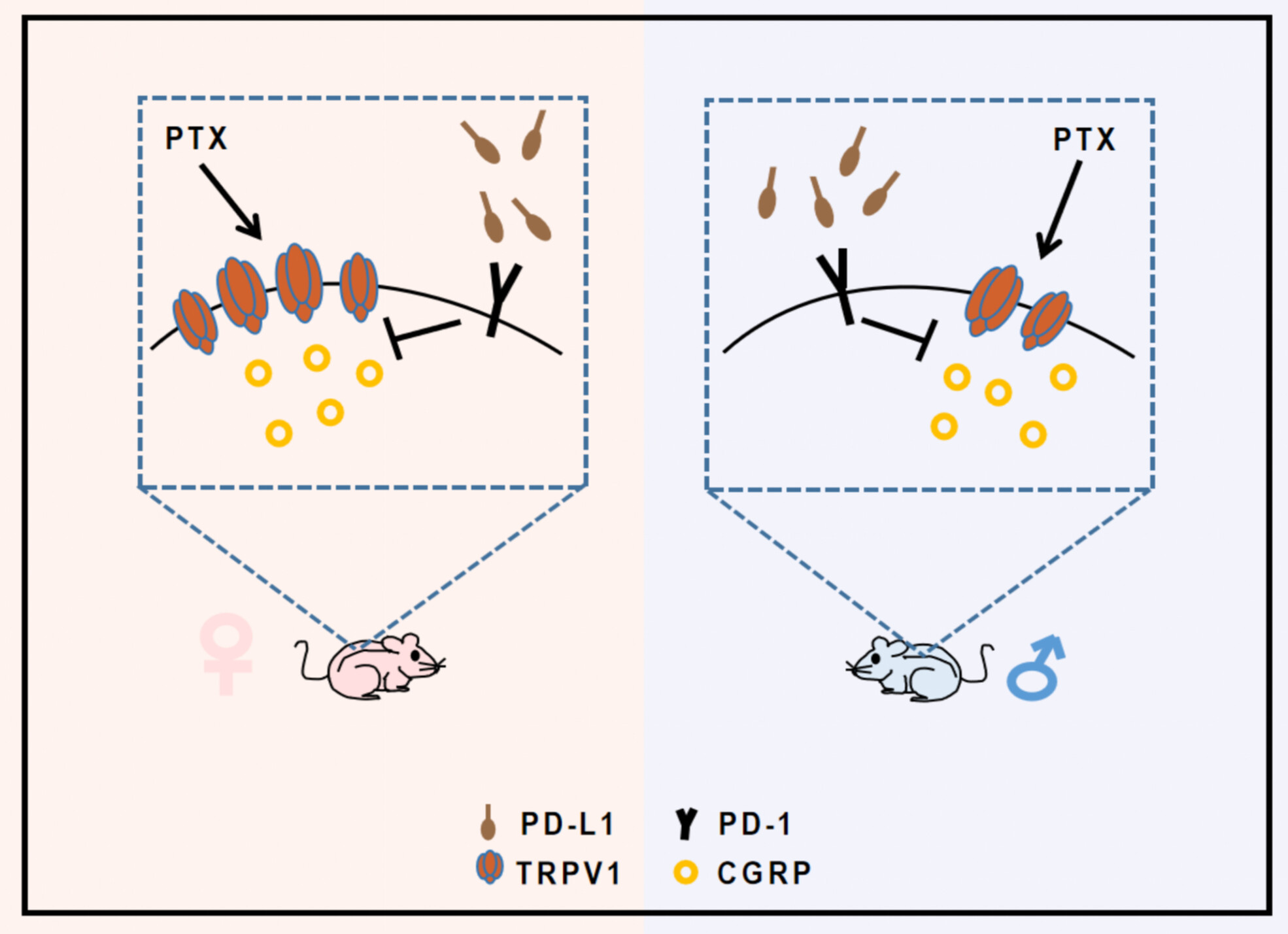
Sex differences in PD-L1-induced analgesia in paclitaxel-induced peripheral neuropathy mice depend on TRPV1-based inhibition of CGRP
- First Published: 03 July 2024
HCN channels in the lateral habenula regulate pain and comorbid depressive-like behaviors in mice
- First Published: 03 July 2024
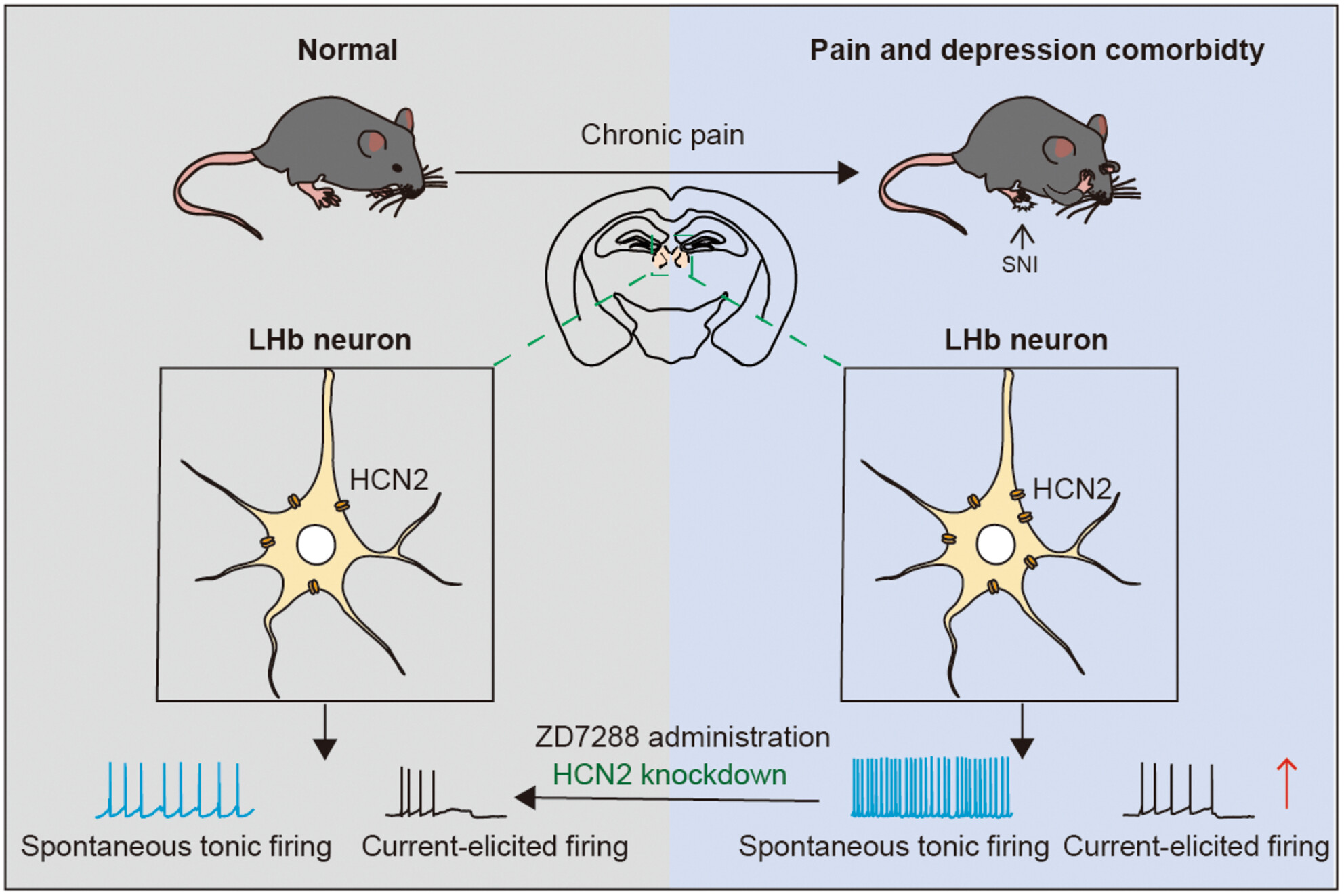
Increased LHb neuronal excitability, which potentially resulted from enhanced function of HCN channels and increased expression of HCN2 isoforms, is crucial for the development of CADS in chronic pain. Either bilateral microinjection of ZD7288 into the LHb to inhibit HCN channels or the specific knockdown of HCN2 channels could obviously decrease the LHb neuronal excitability and produce significant analgesic and antidepressant effects.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
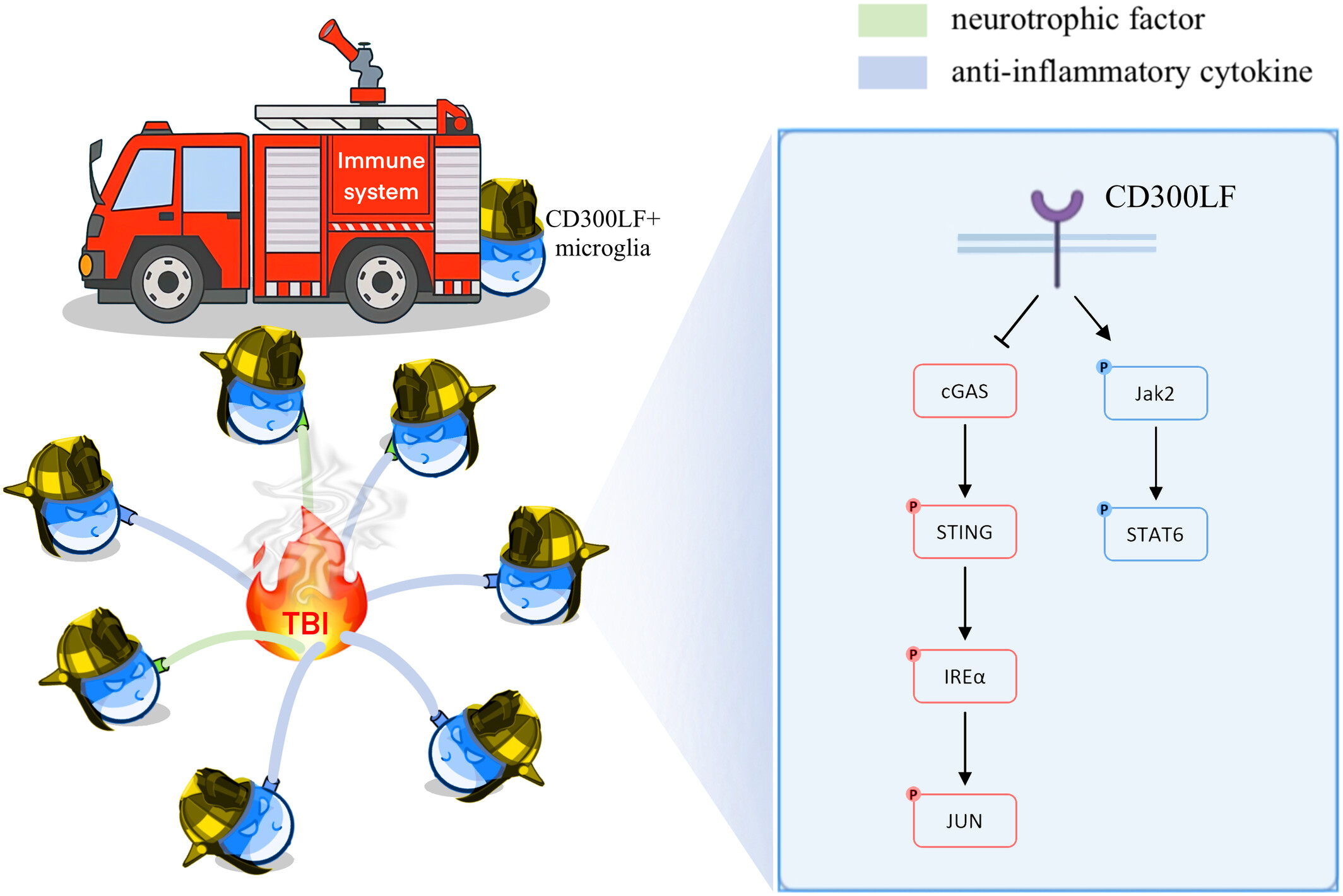
CD300LF+ microglia impede the neuroinflammation following traumatic brain injury by inhibiting STING pathway
- First Published: 04 July 2024
CORRECTION
Correction to Exosomes as a therapeutic tool to promote neurorestoration and cognitive function in neurological conditions: Achieve two ends with a single effort. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 May;30(5):e14752. doi: 10.1111/cns.14752
- First Published: 03 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Causal relationship and shared genes between air pollutants and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: A large-scale genetic analysis
- First Published: 05 July 2024
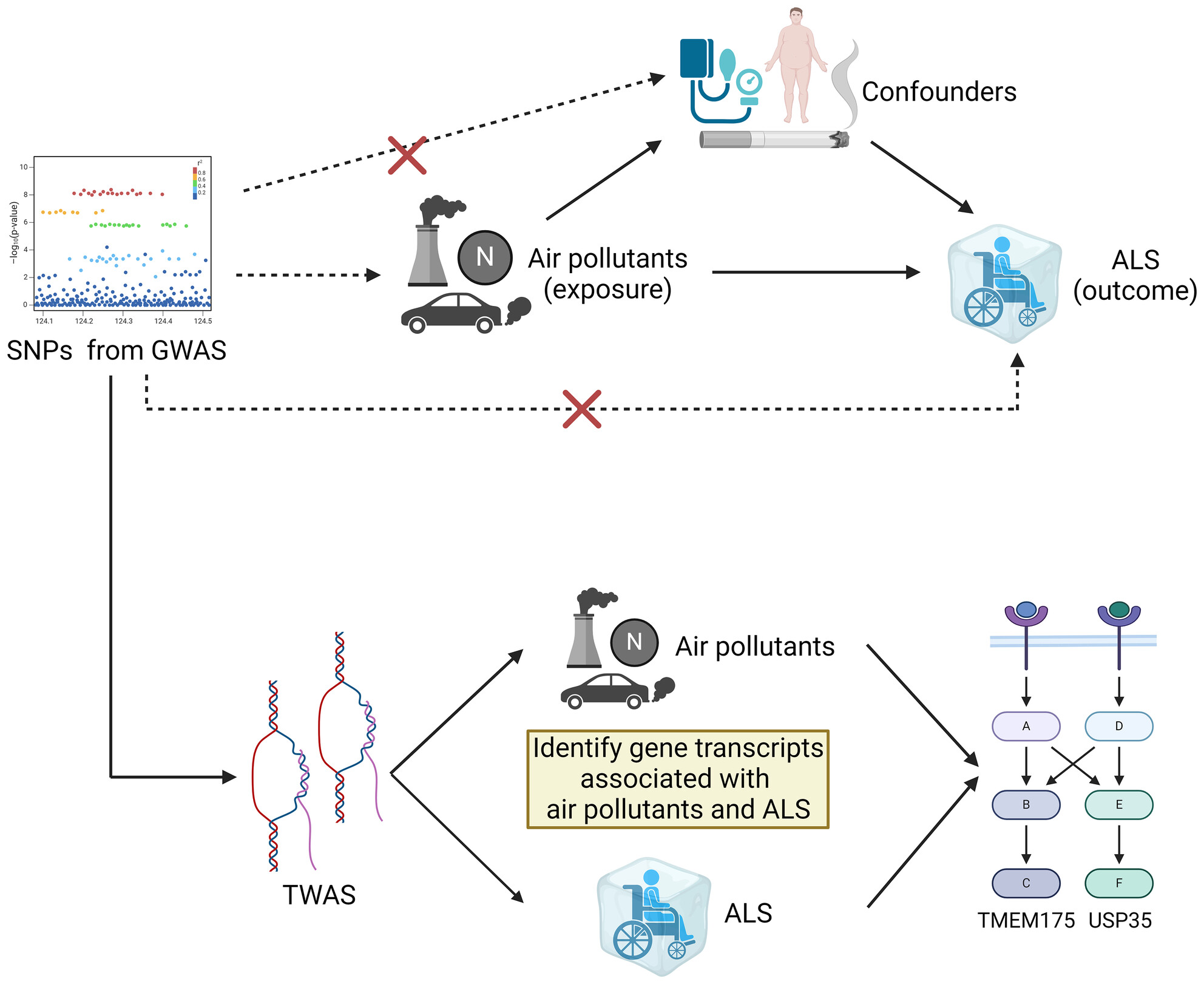
Causality between PM2.5 and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis has been identified via two-sample Mendelian randomization for the first time, with single nucleotide polymorphisms from genome-wide association study serving as instrumental variables. C9orf72 turned out to be the top gene in the transcriptome-wide association analysis. The figure was created by Biorender.com.
Therapeutic application of nicotinamide: As a potential target for inhibiting fibrotic scar formation following spinal cord injury
- First Published: 07 July 2024
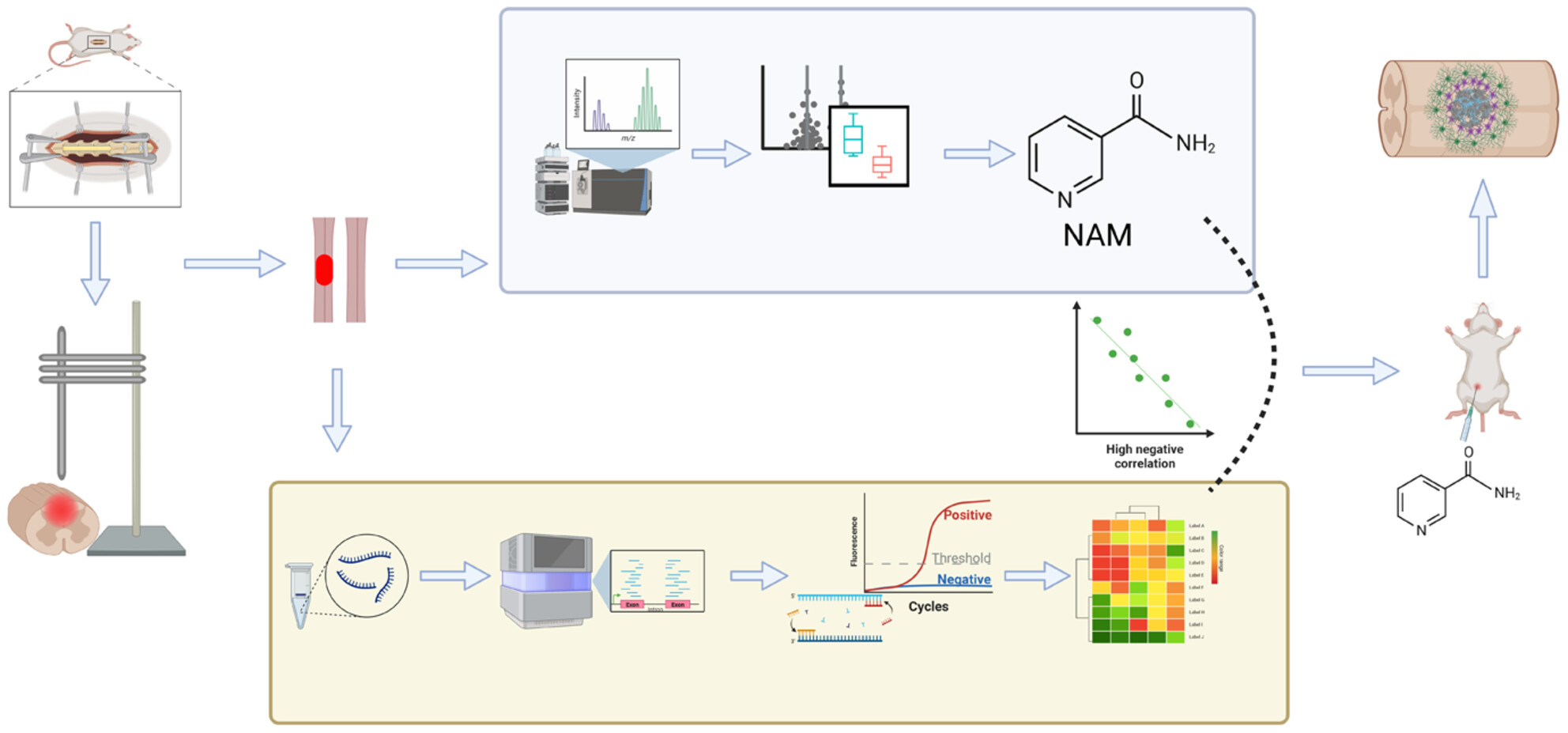
A novel functional metabolomics strategy was developed to establish relationships between changes in gene expression and metabolic phenotypes, which identified nicotinamide as a potential functional metabolite that suppressed fibrotic scar formation by suppressing the TGFβ/SMADs pathway in mice after SCI.
GV-971 attenuates the progression of neuromyelitis optica in murine models and reverses alterations in gut microbiota and associated peripheral abnormalities
- First Published: 07 July 2024
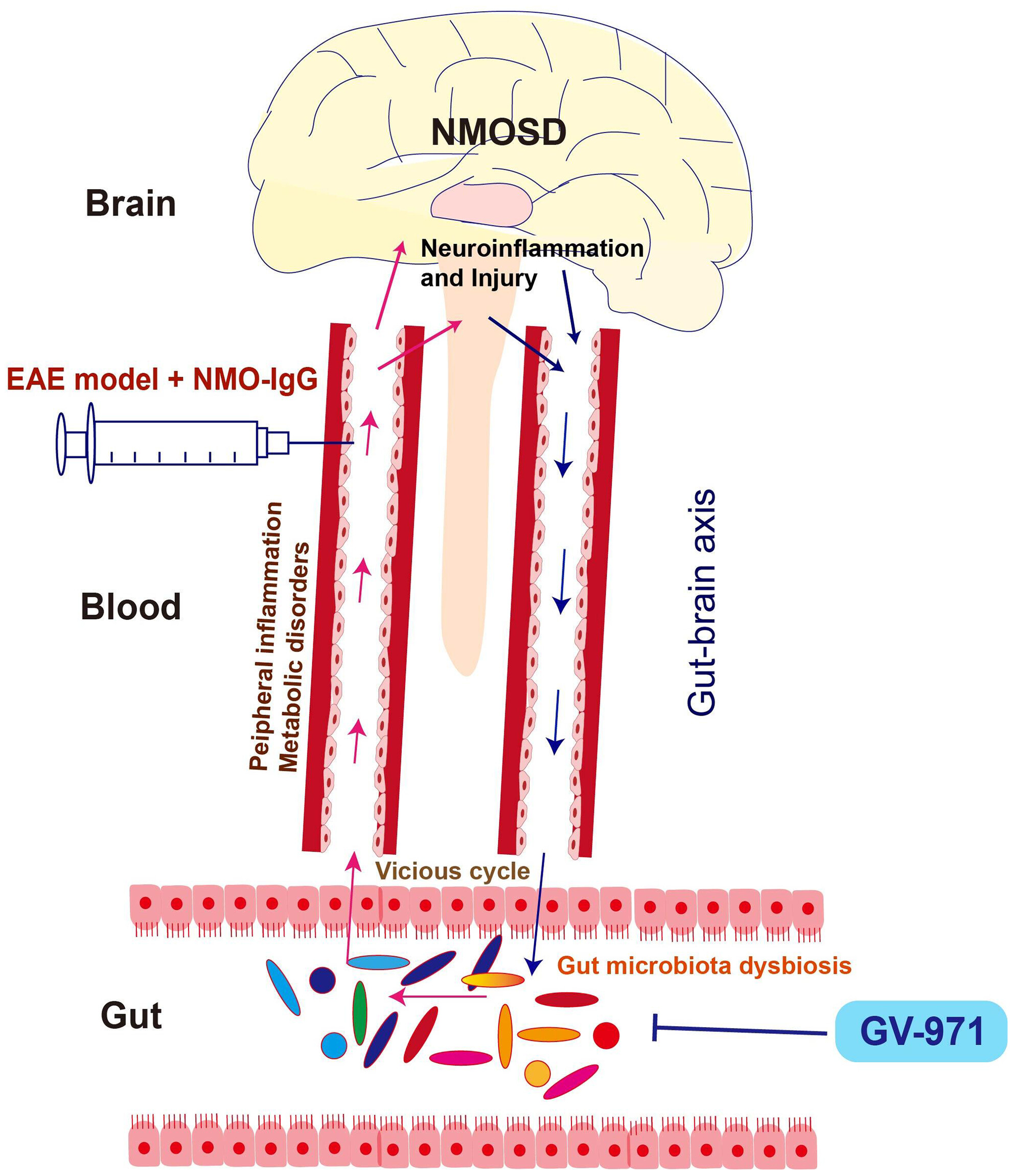
The NMOSD model demonstrated substantial neuroinflammation and neural injury, accompanied by imbalances in gut microbiota, peripheral inflammation, and metabolic disorders, suggesting a potentially vicious cycle that exacerbates disease pathogenesis. Notably, GV-971 effectively reduces neuroinflammation and injury, and restores gut microbiota composition, as well as ameliorates peripheral inflammation and metabolic disorders.
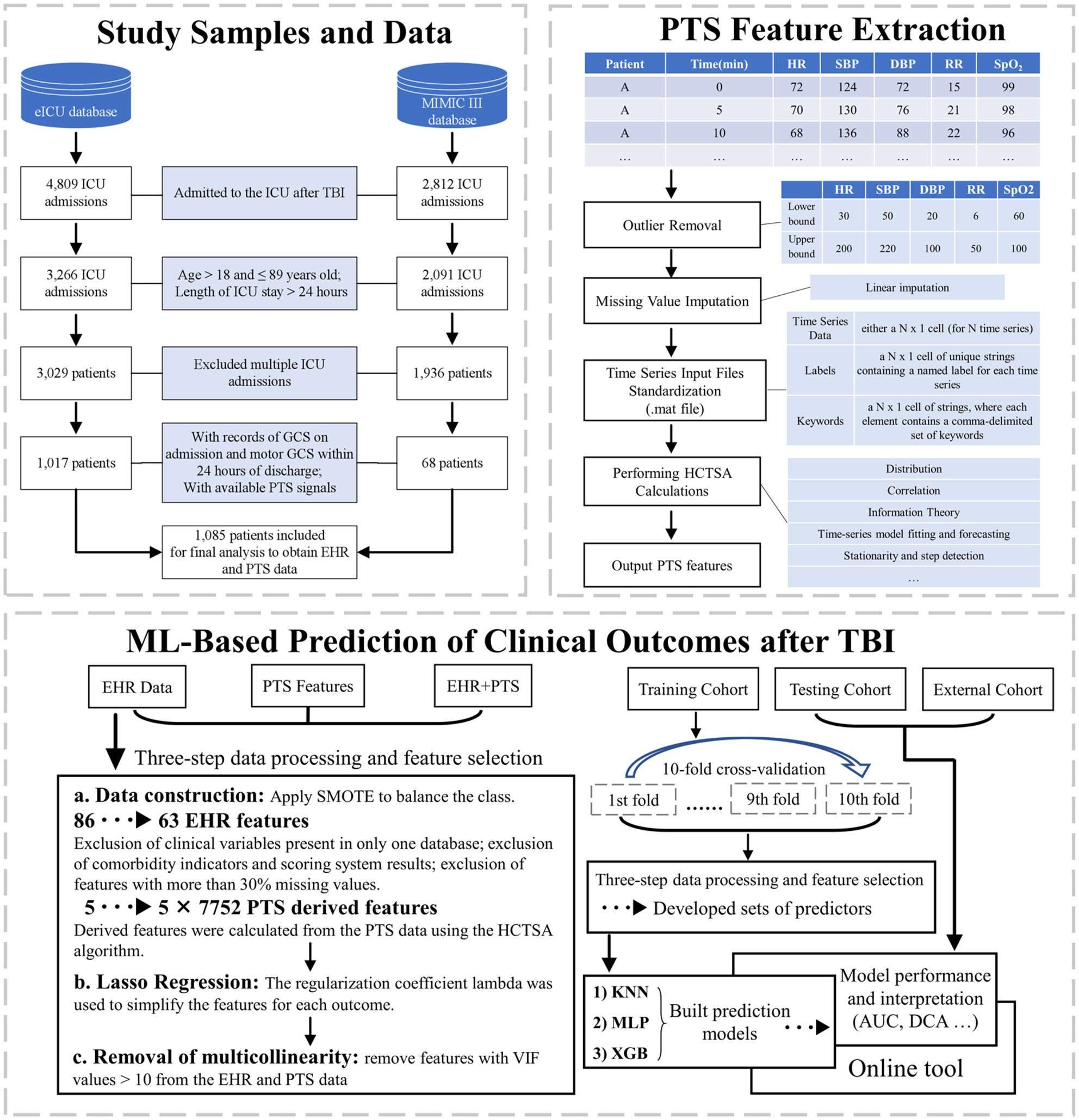
Machine learning-based prediction of clinical outcomes after traumatic brain injury: Hidden information of early physiological time series
- First Published: 07 July 2024
BHBA attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent neuroinflammation via the gut–brain axis in a mouse model of heat stress
- First Published: 07 July 2024
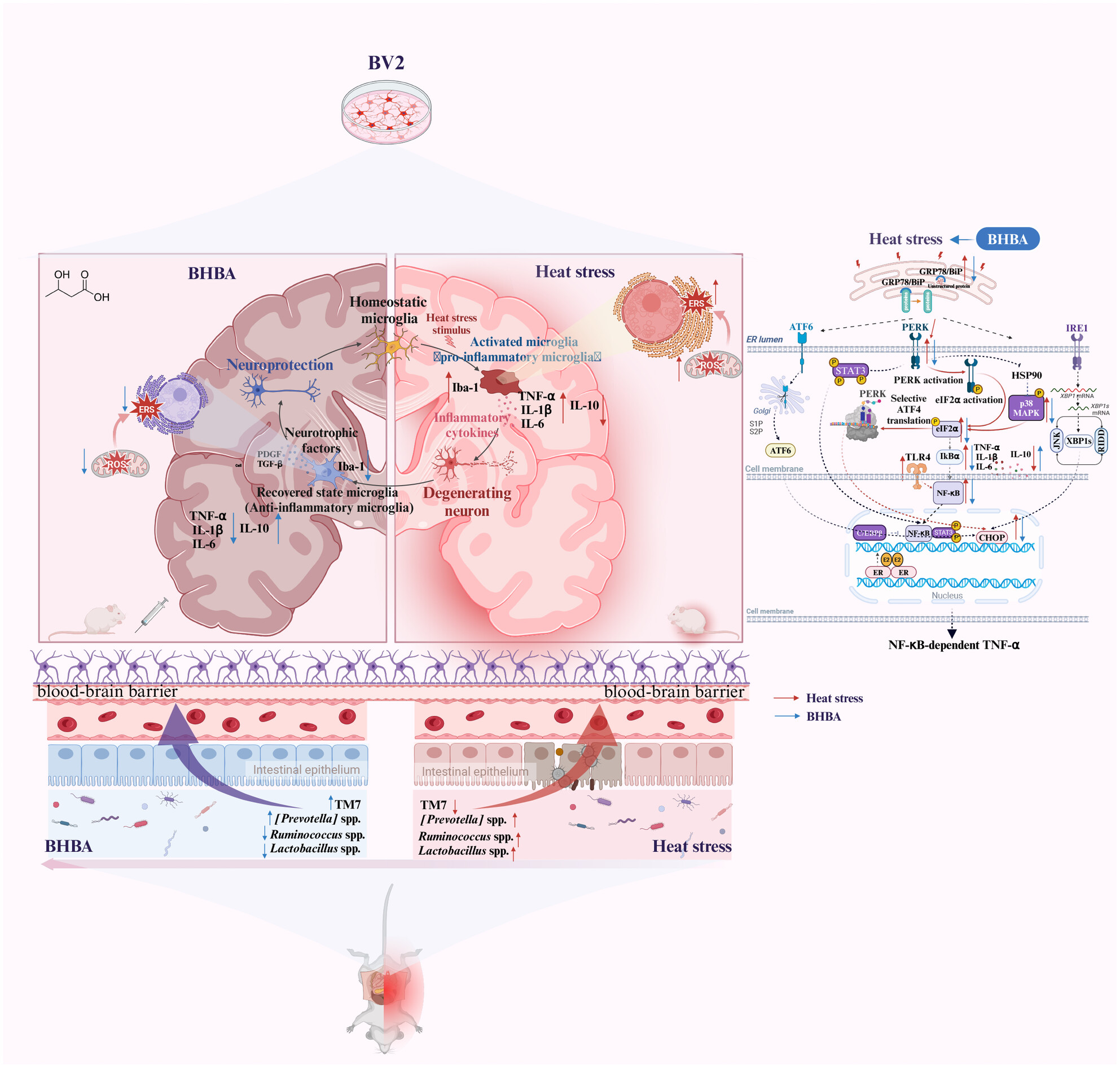
Heat stress affects the gut microbiota (TM7, Lactobacillus spp., Ruminococcus spp., and [Prevotella] spp.), which in turn acts on the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP, TLR4/NF-κB, and TLR4/p38MAPK signaling pathways to induce endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) and ERS-dependent neuroinflammation, whereas β-Hydroxybutyric acid exerts a potential therapeutic role in HS-induced neuroinflammation in mice via the gut–brain axis.
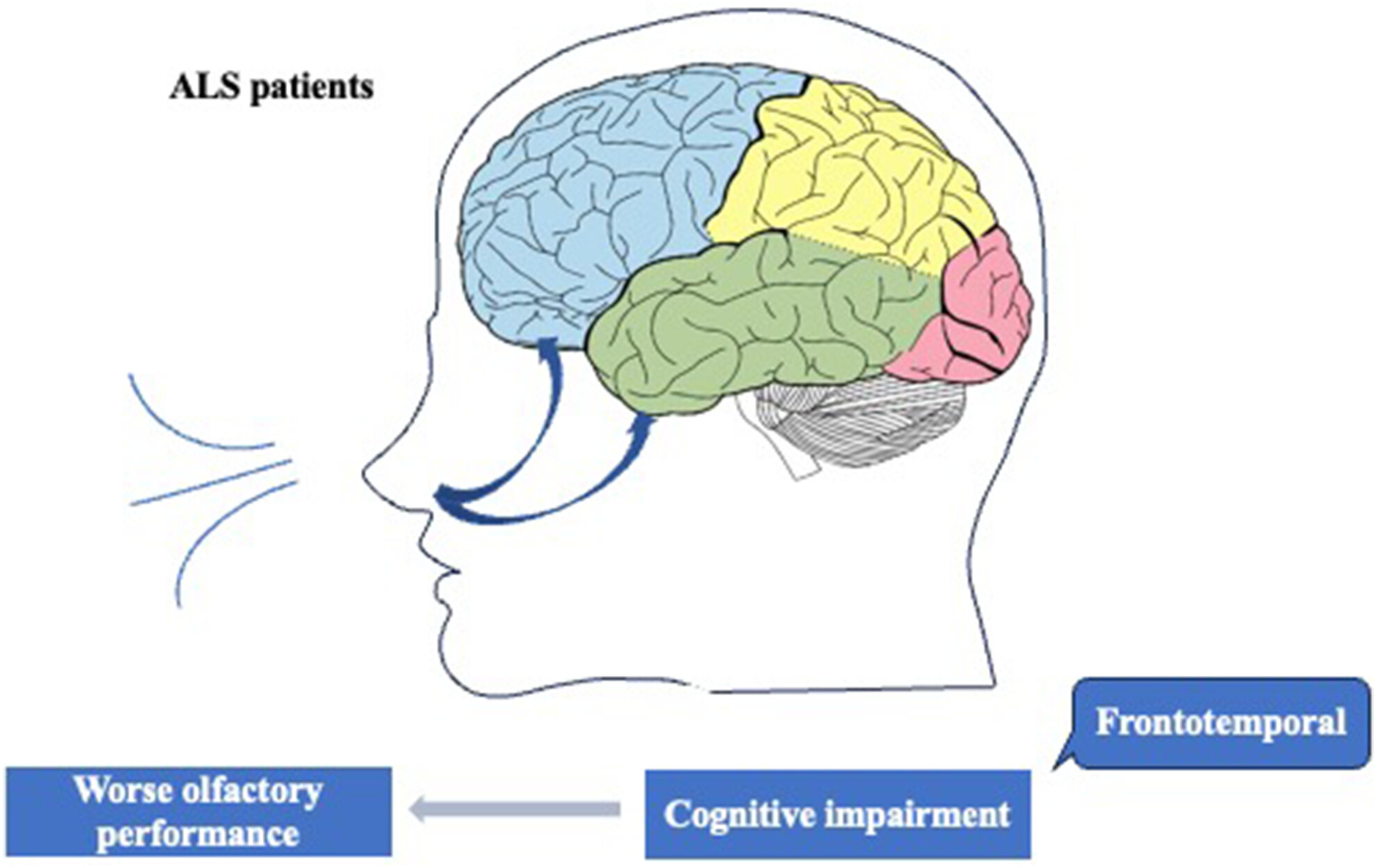
Smell loss is associated with cognitive impairment in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients
- First Published: 08 July 2024
CORRECTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
High body mass index is associated with elevated risk of perioperative ischemic stroke in patients who underwent noncardiac surgery: A retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 10 July 2024
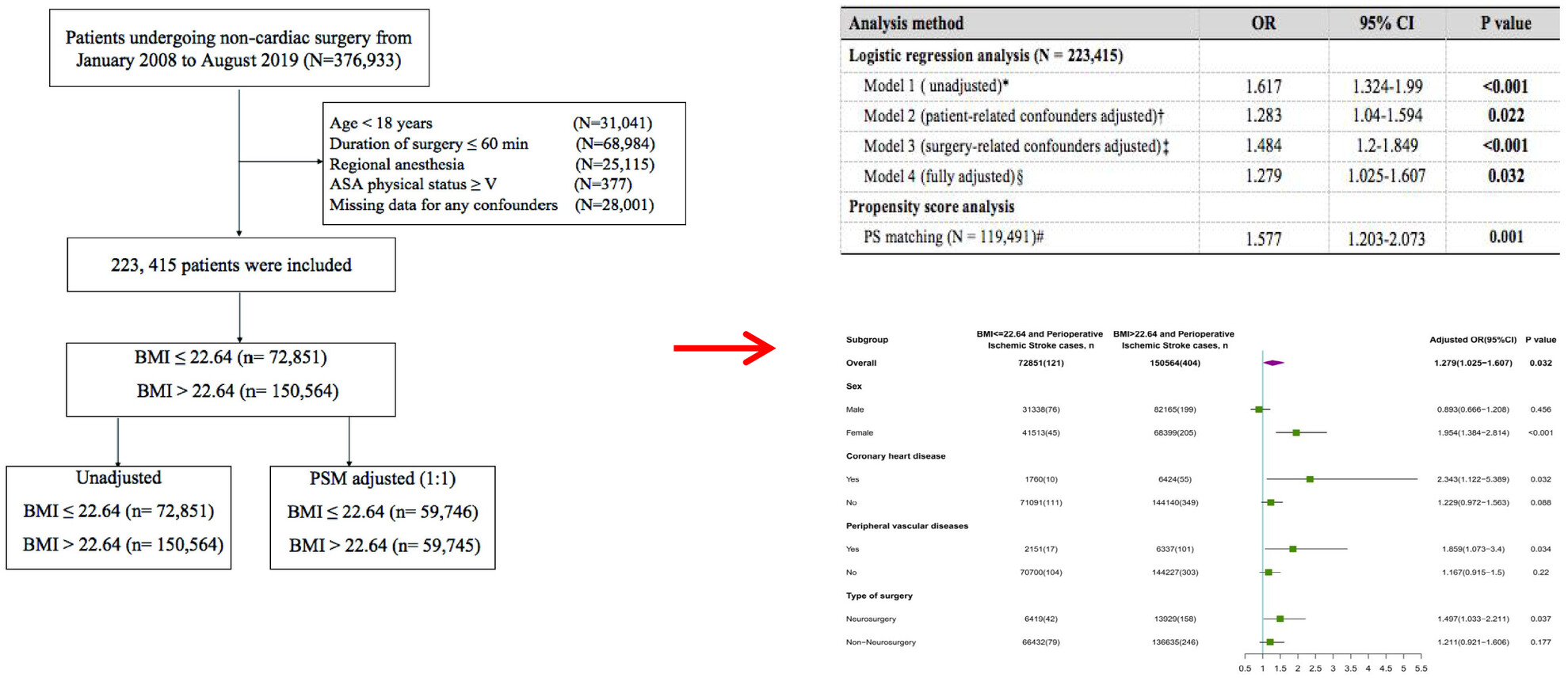
BMI >22.64 kg/m2 emerges as a substantial and independent risk factor for perioperative ischemic stroke. A more stringent perioperative weight management approach is recommended, particularly for specific subgroups such as female patients, those with coronary heart disease and peripheral vascular disease, and individuals scheduled for neurosurgery.
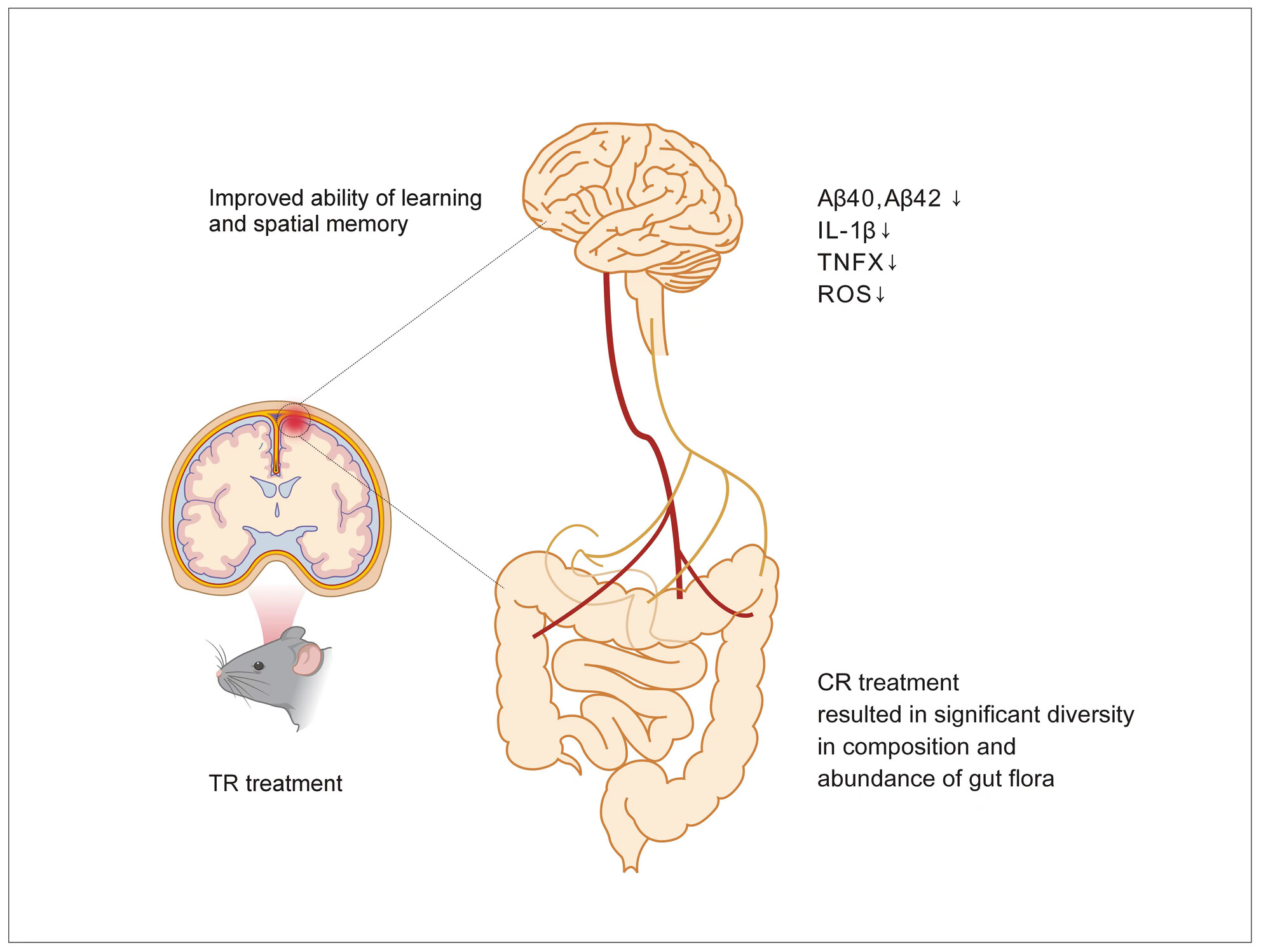
Caloric restriction leading to attenuation of experimental Alzheimer's disease results from alterations in gut microbiome
- First Published: 11 July 2024
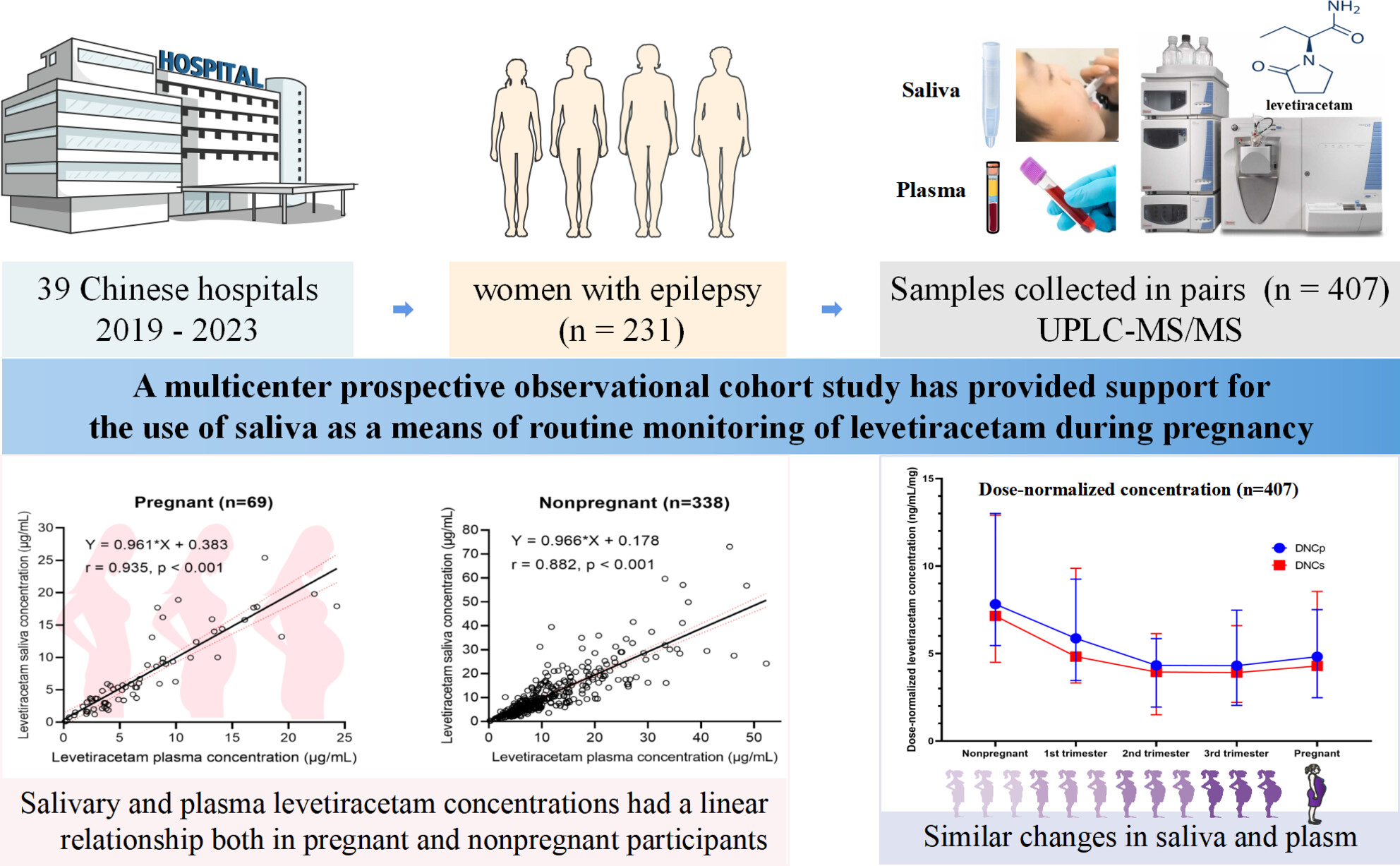
Monitoring levetiracetam concentration in saliva during pregnancy is stable and feasible
- First Published: 11 July 2024
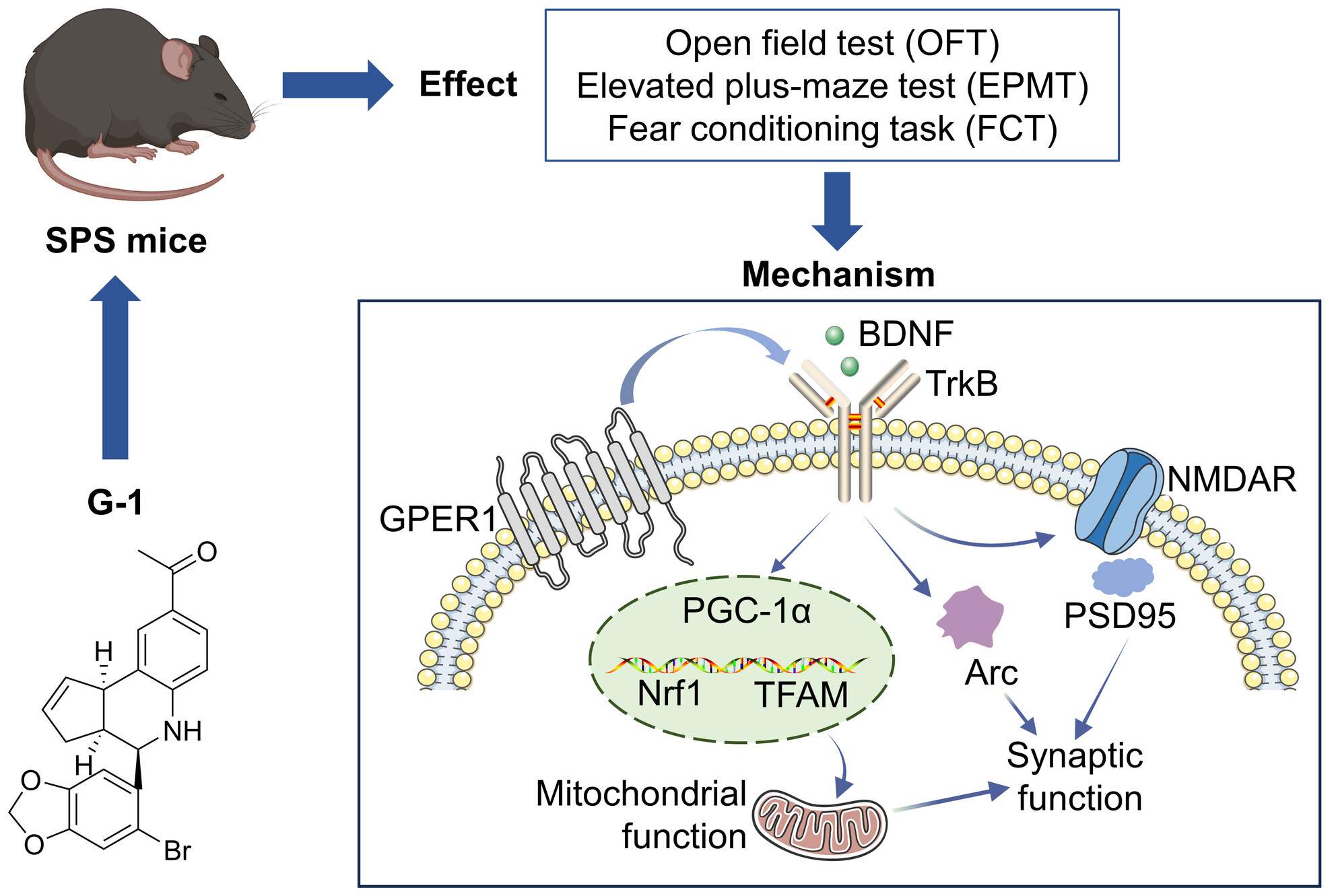
Activation of GPER1 by G1 prevents PTSD-like behaviors in mice: Illustrating the mechanisms from BDNF/TrkB to mitochondria and synaptic connection
- First Published: 11 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Targeting MS4A4A: A novel pathway to improve immunotherapy responses in glioblastoma
- First Published: 12 July 2024
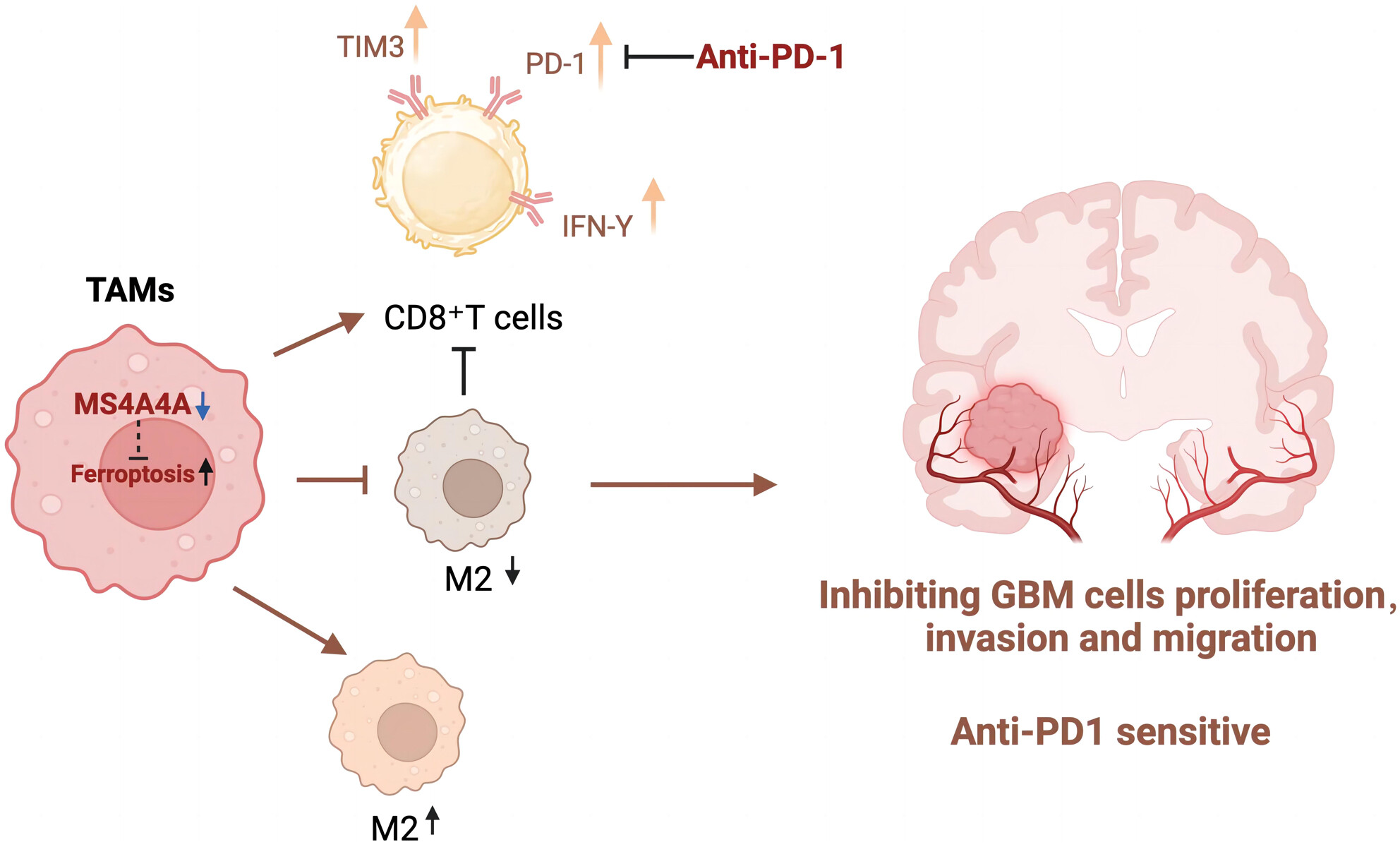
This study employs single-cell transcriptomic analysis to identify subgroups of glioblastoma-associated macrophages. Spatial transcriptomic analysis reveals the spatial distribution of macrophages within glioblastoma tissue. In vitro experiments demonstrate that inhibition of MS4A4A reduces the immunosuppressive function of M2-type macrophages. In vivo experiments confirm that inhibition of MS4A4A enhances the response of glioblastoma to PD-1 immunotherapy. This study provides new theoretical bases and molecular therapeutic targets for the diagnosis and treatment of glioblastoma.
REVIEW
Application of artificial intelligence-based magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis of cerebral small vessel disease
- First Published: 24 July 2024

Recent advancements in artificial intelligence, particularly deep learning, have revolutionized the detection and evaluation of cerebral small vessel disease (CSVD) through magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This study demonstrates how deep learning can extract high-dimensional imaging features, improving the quantitative assessment of CSVD, and leading to earlier diagnosis and better patient outcomes.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
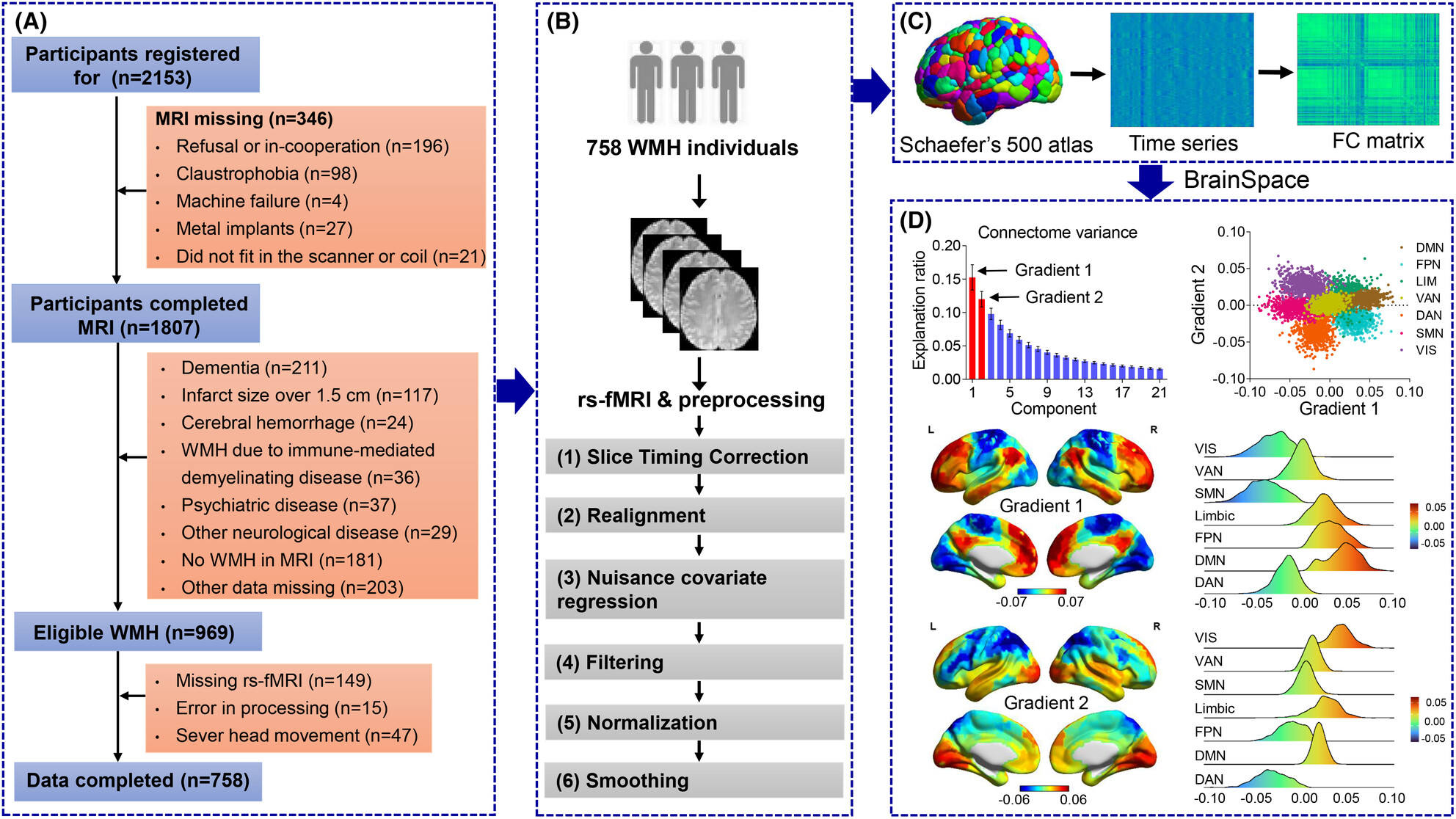
Connectome gradient dysfunction contributes to white matter hyperintensity-related cognitive decline
- First Published: 12 July 2024
Spectrum of psychiatric adverse reactions to cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6 inhibitors: A pharmacovigilance analysis of the FDA adverse event reporting system
- First Published: 15 July 2024
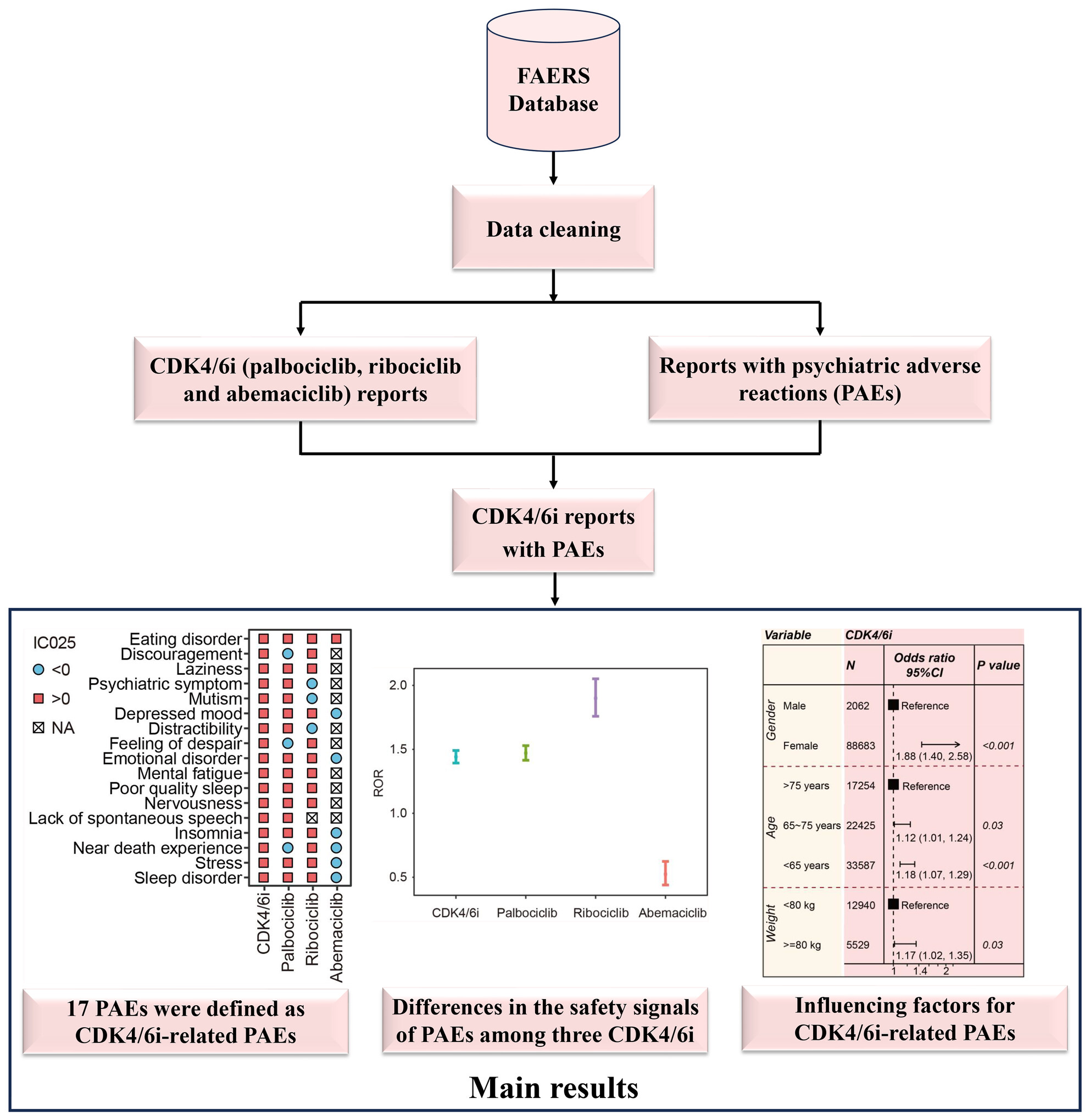
This is a pharmacovigilance study to comprehensively assess the correlation between cyclin-dependent kinases 4/6 inhibitors (CDK4/6i) and psychiatric adverse events (PAEs). Our study identified 17 categories of PAEs highly associated with CDK4/6i through disproportionality analysis, and revealed differences in the profiles of PAEs among three CDK4/6i.
Therapeutic effects of exendin-4 on spinal cord injury via restoring autophagy function and decreasing necroptosis in neuron
- First Published: 14 July 2024
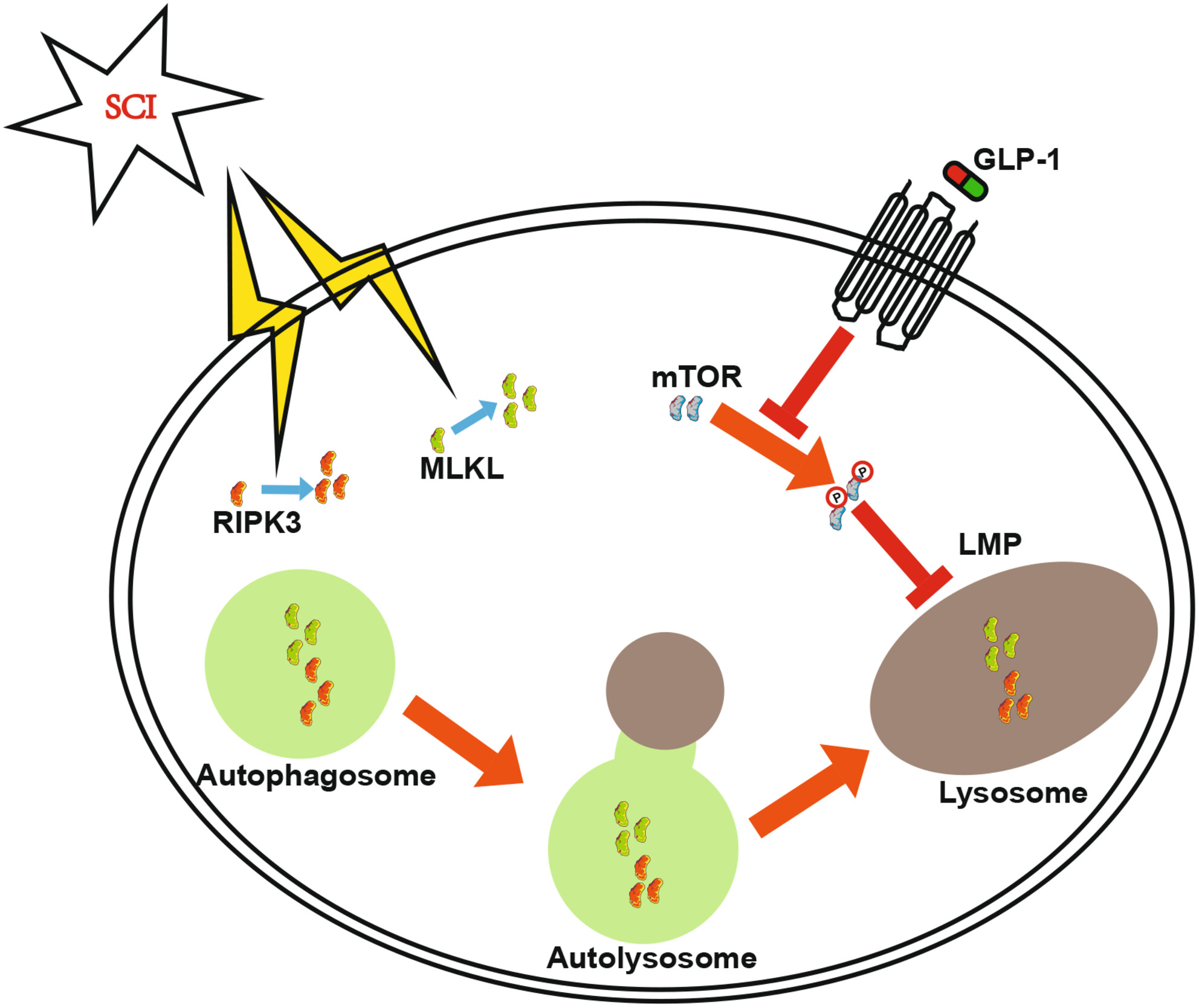
This study showed that the expression of necroptosis-related proteins increased after spinal cord injury (SCI). Exendin-4 (EX-4) played a therapeutic role via promoting the recovery of lysosome function and autophagy flux and accelerating the degradation of necroptosis-related proteins by inhibiting the phosphorylation level of mTOR in neurons. This finding may provide a new therapeutic target in clinical treatment after SCI.
REVIEW
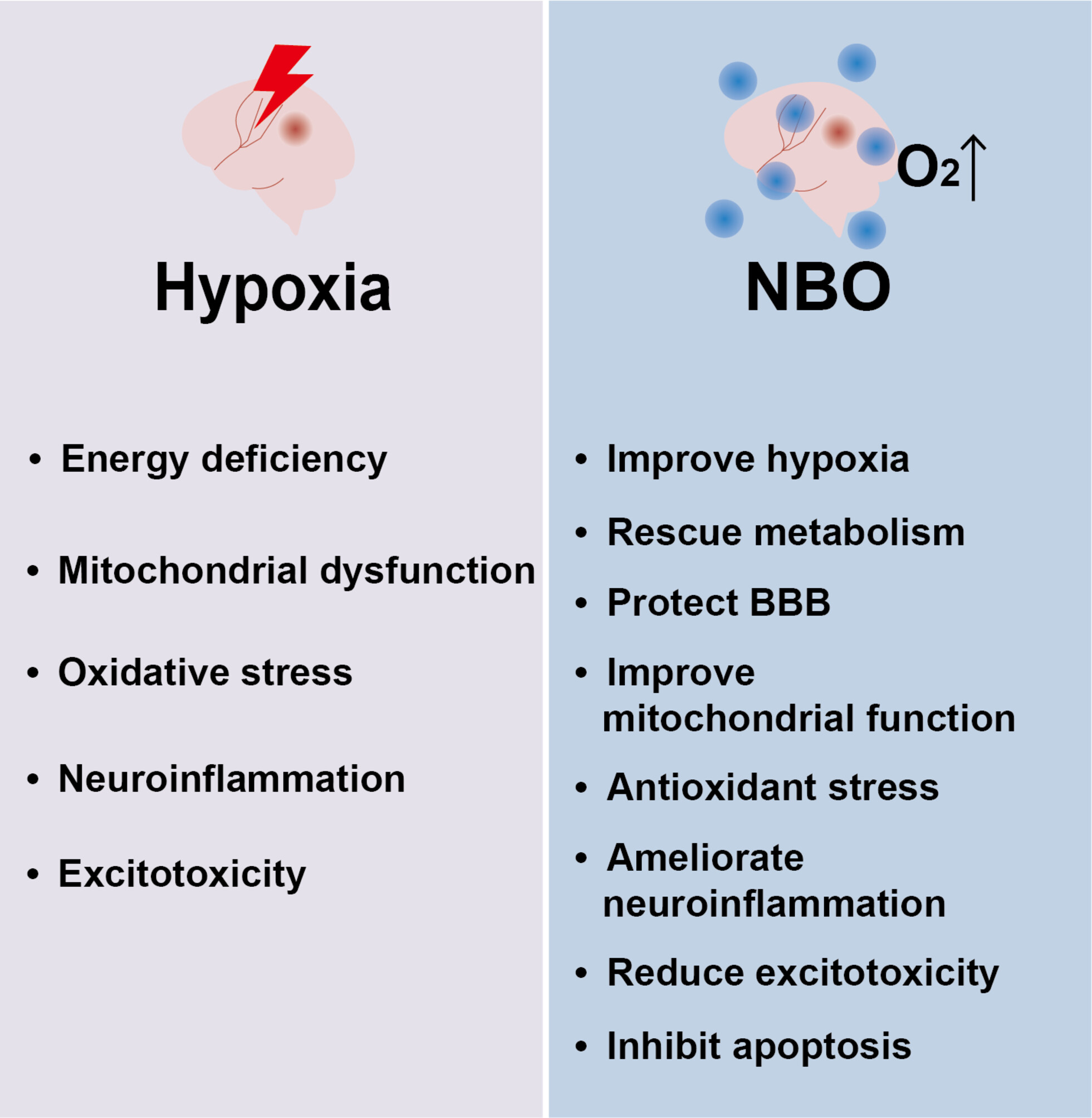
The neuroprotective effects of normobaric oxygen therapy after stroke
- First Published: 15 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
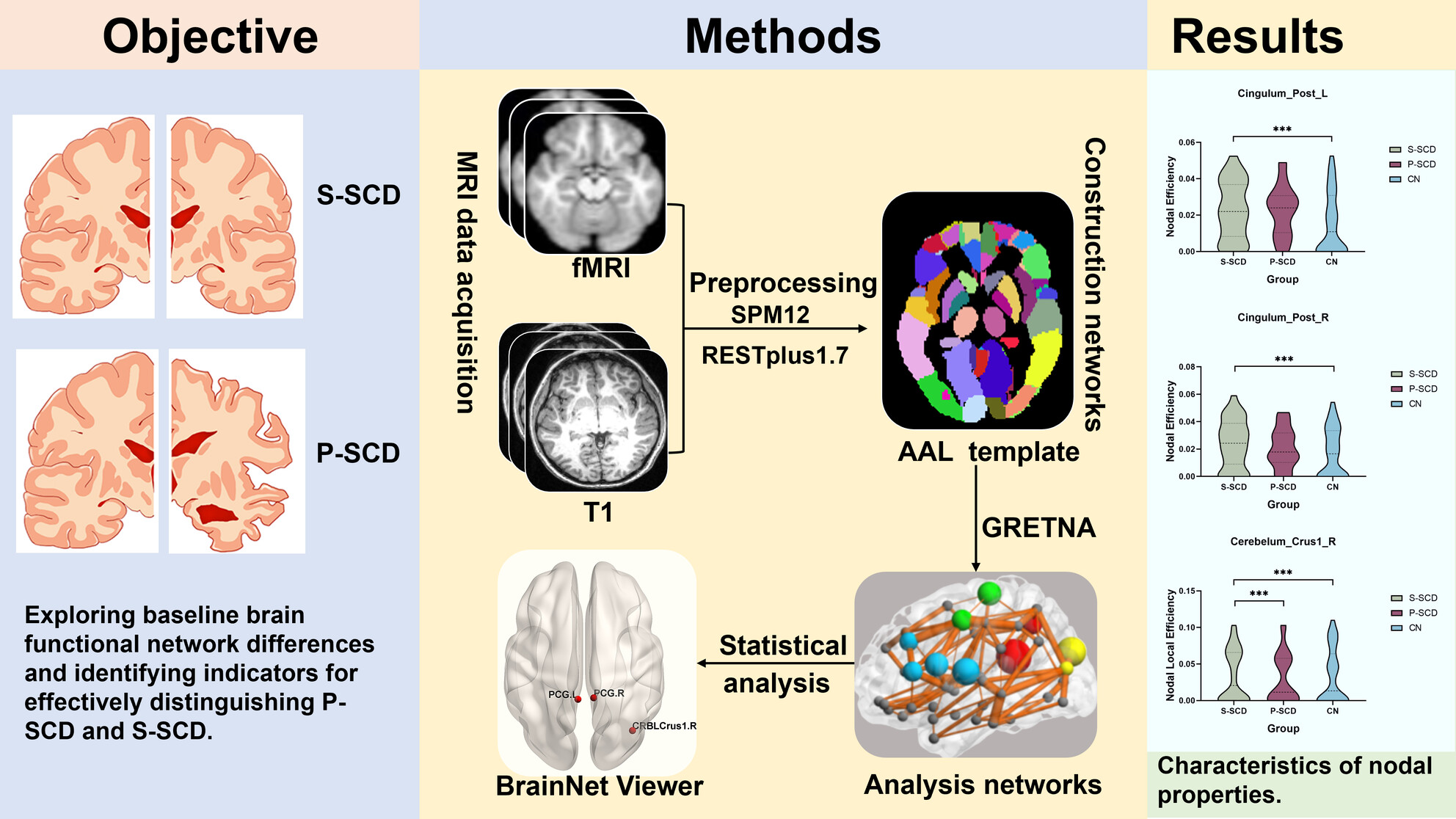
Prediction of disease progression in individuals with subjective cognitive decline using brain network analysis
- First Published: 15 July 2024
REVIEW
The unfolded protein response machinery in glioblastoma genesis, chemoresistance and as a druggable target
- First Published: 17 July 2024
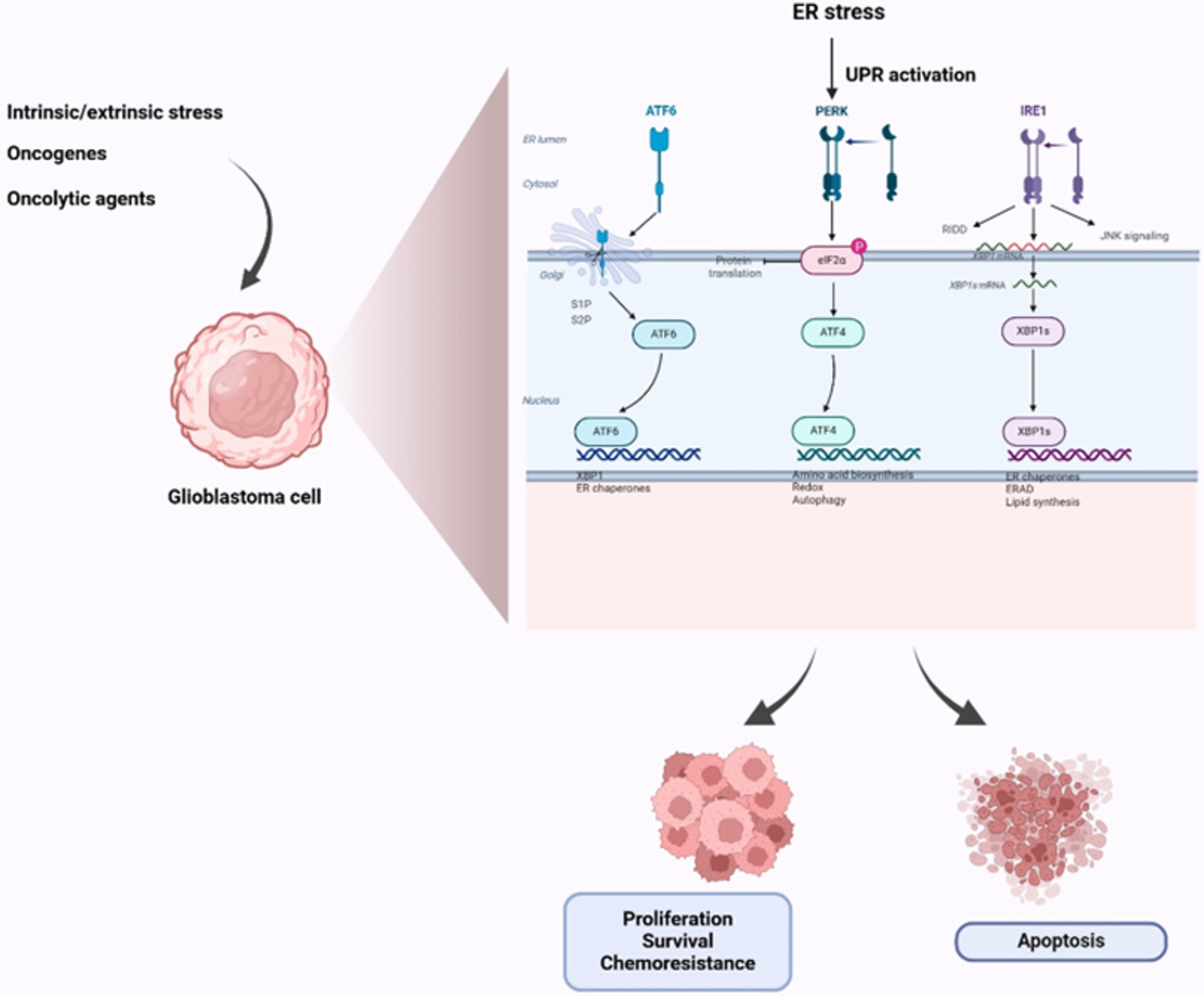
The Unfolded protein response is suggested as a therapeutic target for glioblastoma. The unfolded protein response is activated in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress in glioblastoma cells. Its three arms IRE1, PERK, and ATF6 activate their downstream pathways furthering tumor cell survival, proliferation and the development of chemoresistance. Furthermore, targeting the UPR arms induces apoptosis in glioblastomacells. Adapted from "UPR signaling (ATF6, PERK, IRE1)", by BioRender.com(2024). Retrieved from https://app.biorender.com/biorender-templates.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
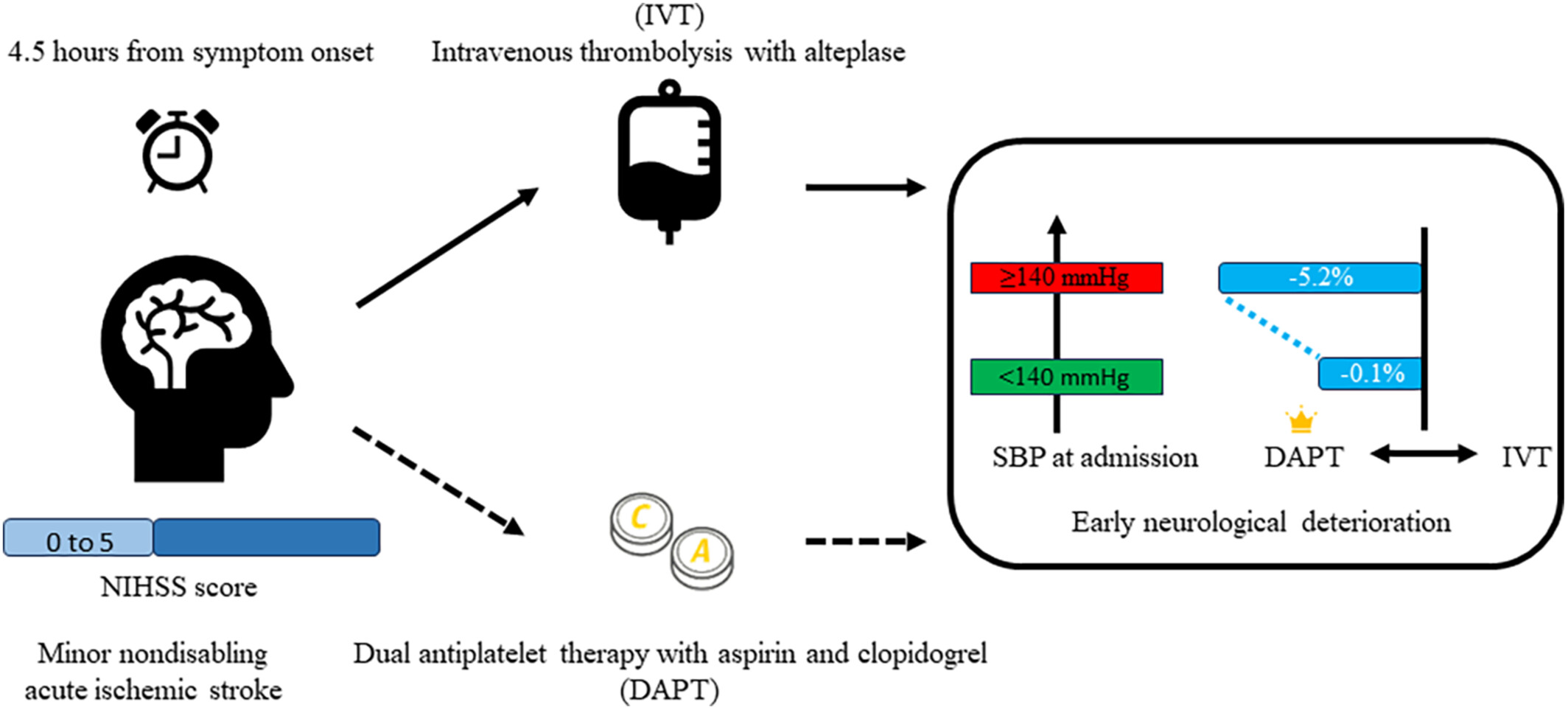
Systolic blood pressure and early neurological deterioration in minor stroke: A post hoc analysis of ARAMIS trial
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Amyloid-β but not tau accumulation is strongly associated with longitudinal cognitive decline
- First Published: 16 July 2024
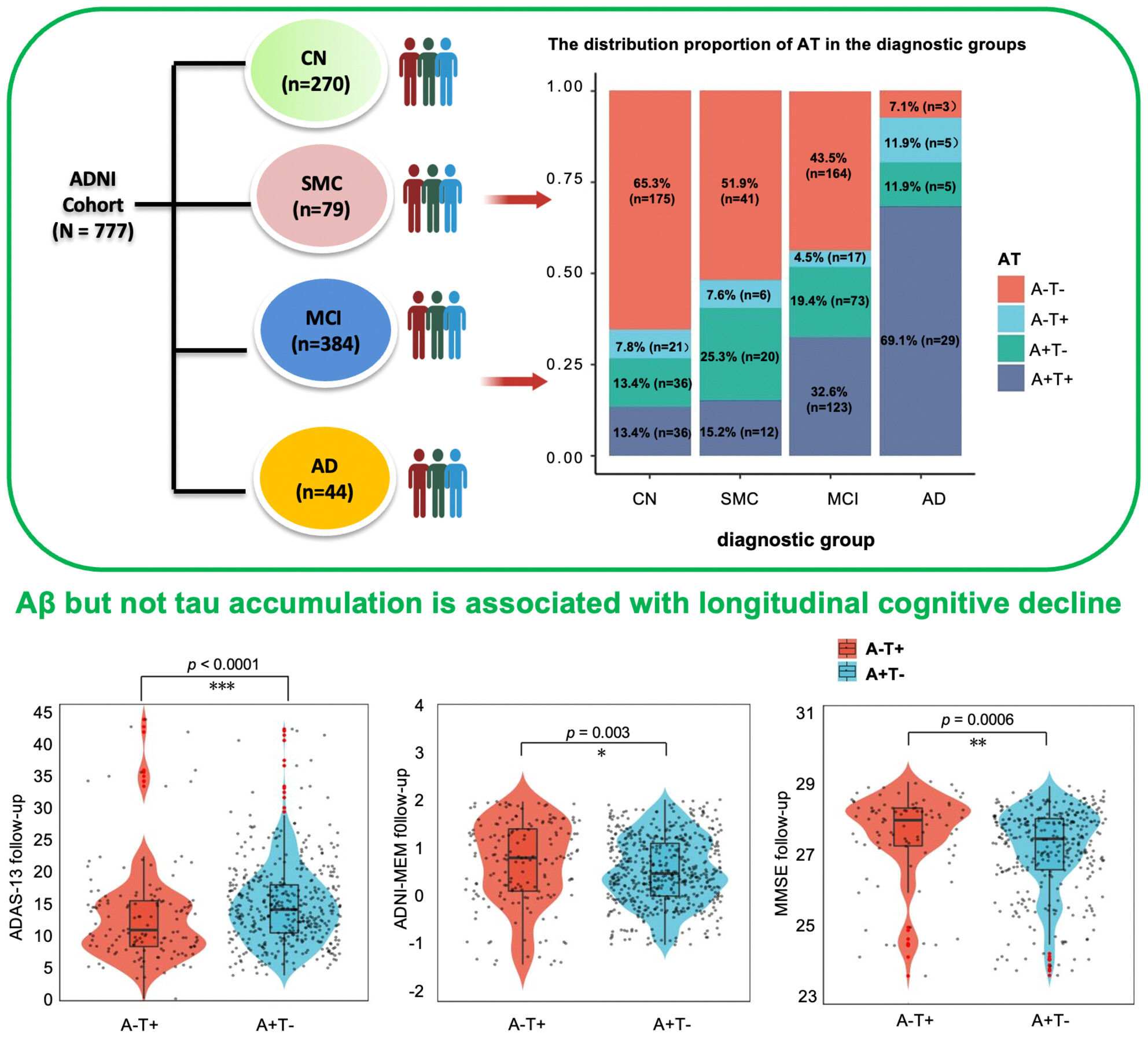
Aβ-PET and CSF p-tau181 were related to cognitive decline across the AD clinical spectrum, both as potential predictors for dementia progression. Aβ-PET (A + T− subjects) was an independent reliable predictor of longitudinal cognitive decline rather than tau pathology (A − T+ subjects), indicating tau accumulation was not closely correlated with future cognitive impairment without being driven by Aβ deposition. Stronger predictive value of Aβ pathology (A+ alone) than tau accumulation (T+ alone) for longitudinal cognitive decline in APOE ε4 carriers.
Novel diagnostic and prognostic approach for rapidly progressive dementias: Indicators based on amyloid/tau/neurodegeneration (ATN) framework
- First Published: 16 July 2024

The current study demonstrated for the first time that: (1) Indicators based on the ATN framework using CSF biomarkers had better diagnostic and prognostic power for RPDs, especially for autoantibodies-negative AE subjects. (2) Indicators based on the ATN framework using serum biomarkers still showed diagnostic value, which provides efficient clinical information for early recognition of treatment-responsive causes of RPDs.
CORRECTION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Common functional mechanisms underlying dynamic brain network changes across five general anesthetics: A rat fMRI study
- First Published: 16 July 2024
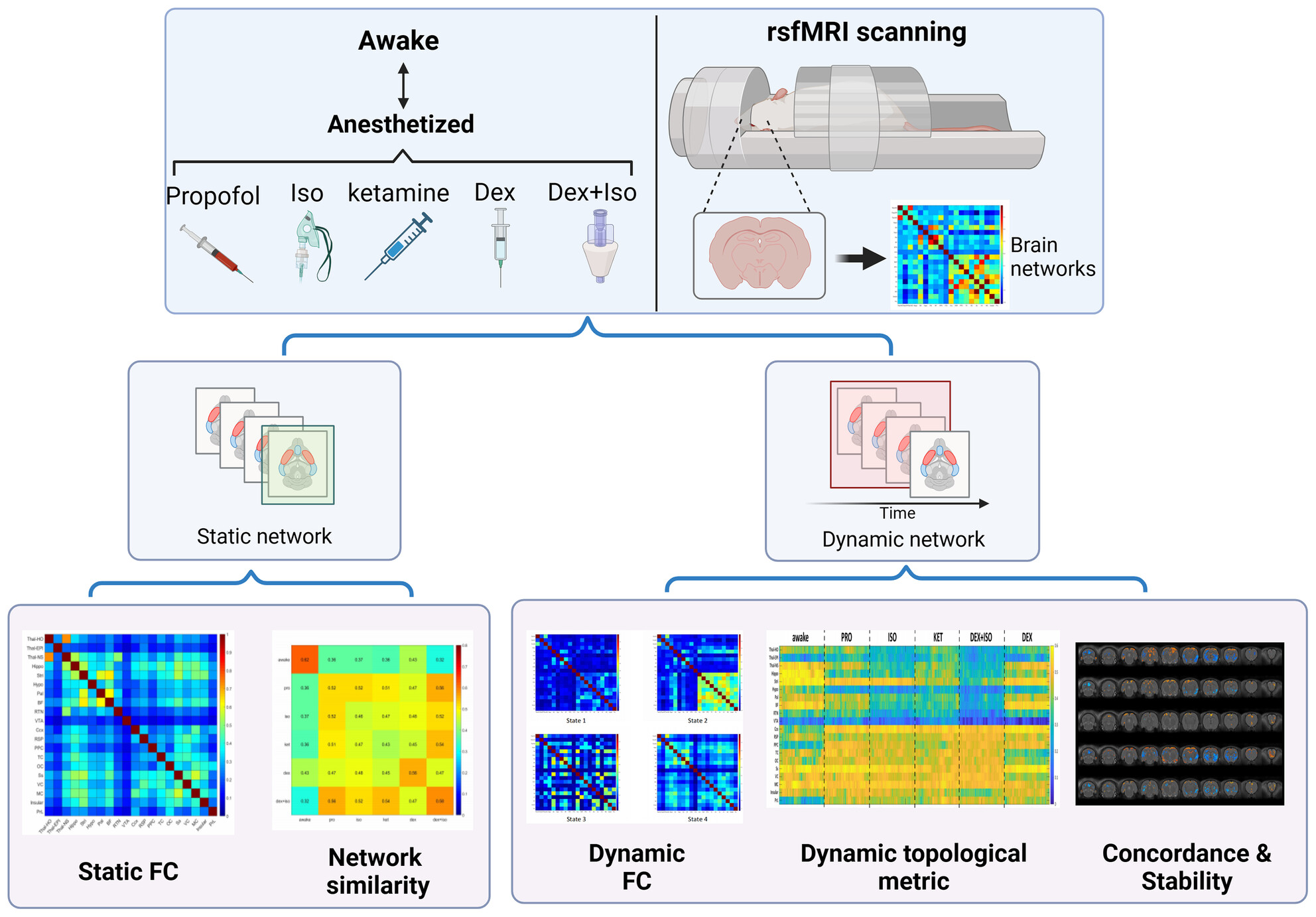
We found that the disruption of functional connectivity between subcortical and cortical regions by general anesthesia is a shared functional mechanism of various anesthetics. Moreover, the increased network and functional properties of higher-order and unimodal cortical regions imply that the information flow required for consciousness is impaired within and between cortical and subcortical regions.
Exploring functional and structural connectivity disruptions in spinocerebellar ataxia type 3: Insights from gradient analysis
- First Published: 16 July 2024
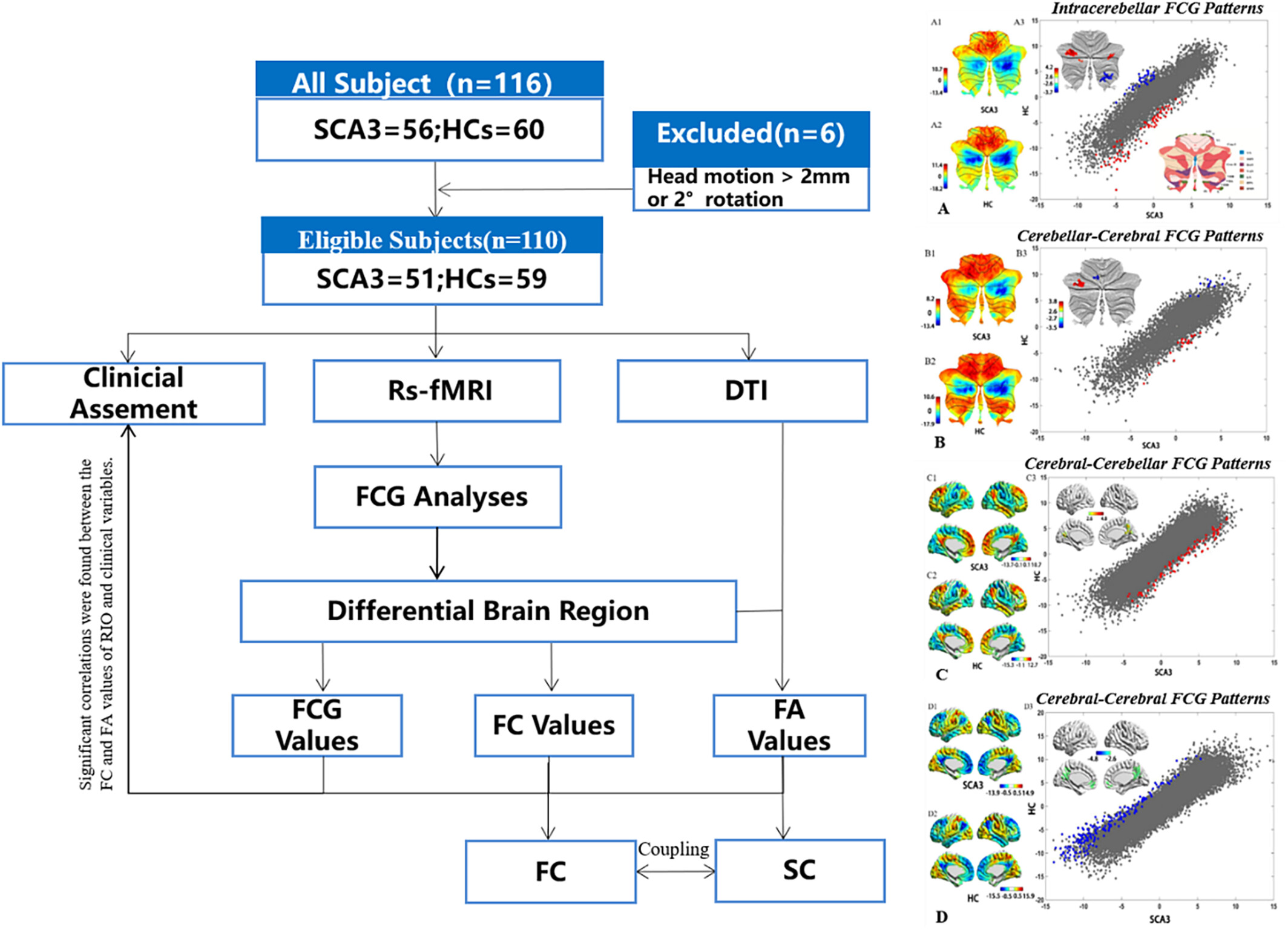
The experiment adhered to rigorous scientific methodologies and protocols, conducting the operational process with utmost attention to detail. FCG Values: functional connectivity gradient values; FC Values: functional connectivity values; FA Values: fractional anisotropy values; FC: functional connectivity; SC: structural connectivity. Four distinct gradient construction patterns and their corresponding inter-group differential brain region were identified (A.B.C.D).
PV and SST neurons in the anterior cingulate cortex regulate social disorders in adulthood induced by sensory abnormalities in childhood
- First Published: 22 July 2024
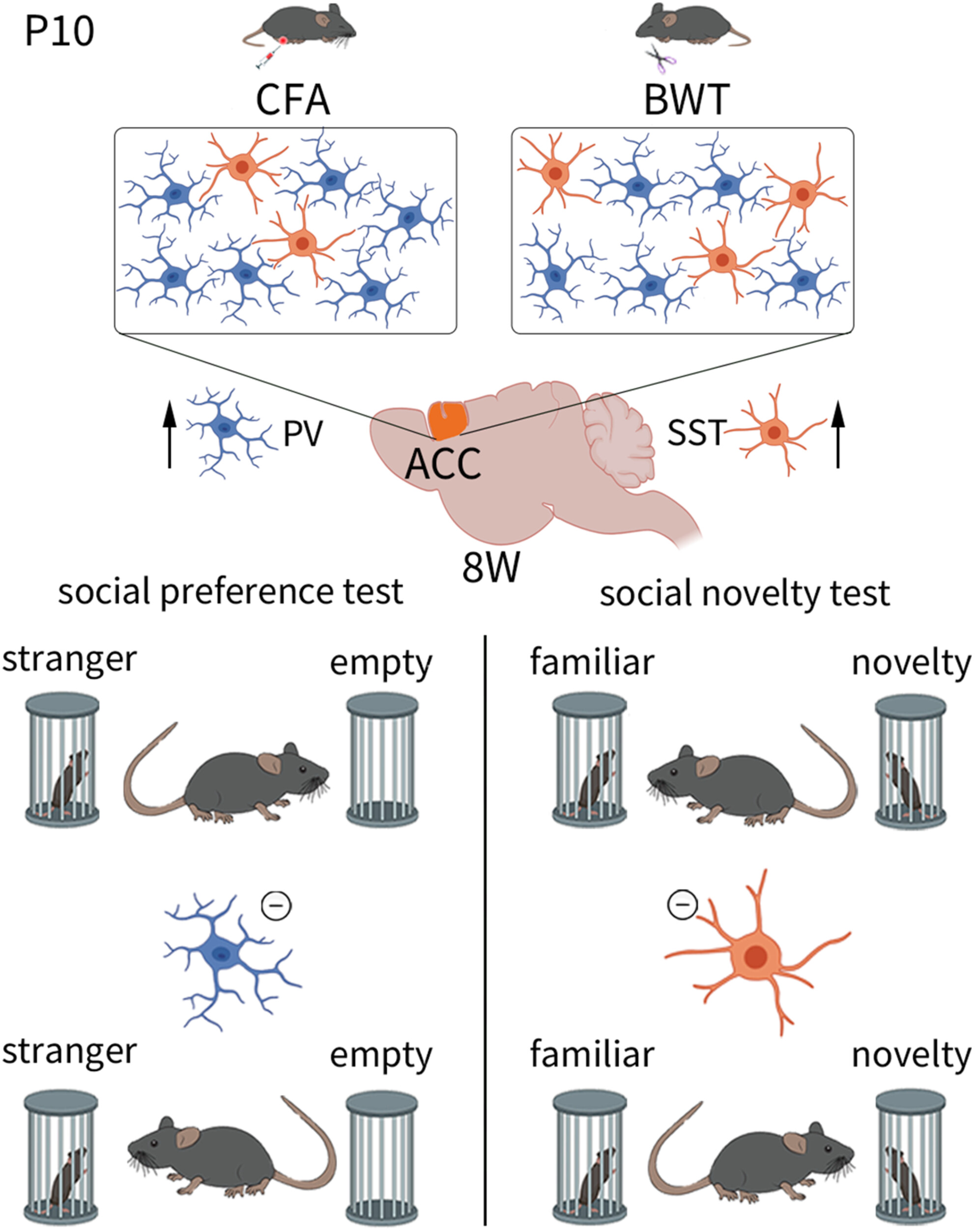
Inflammatory pain in childhood leads to social preference disorders, while BWT in childhood leads to social novelty disorders in adult mice. Inflammatory pain and BWT in childhood caused an increase in the number of PV and SST neurons, respectively, in adult mice ACC. Inhibiting PV neurons in ACC improved social preference disorders in adult mice that experienced inflammatory pain during childhood. Inhibiting SST neurons in ACC improved social novelty disorders in adult mice that experienced BWT in childhood. PV and SST neurons of the ACC may play a critical role in regulating social disorders induced by sensory abnormalities in childhood.
REVIEW
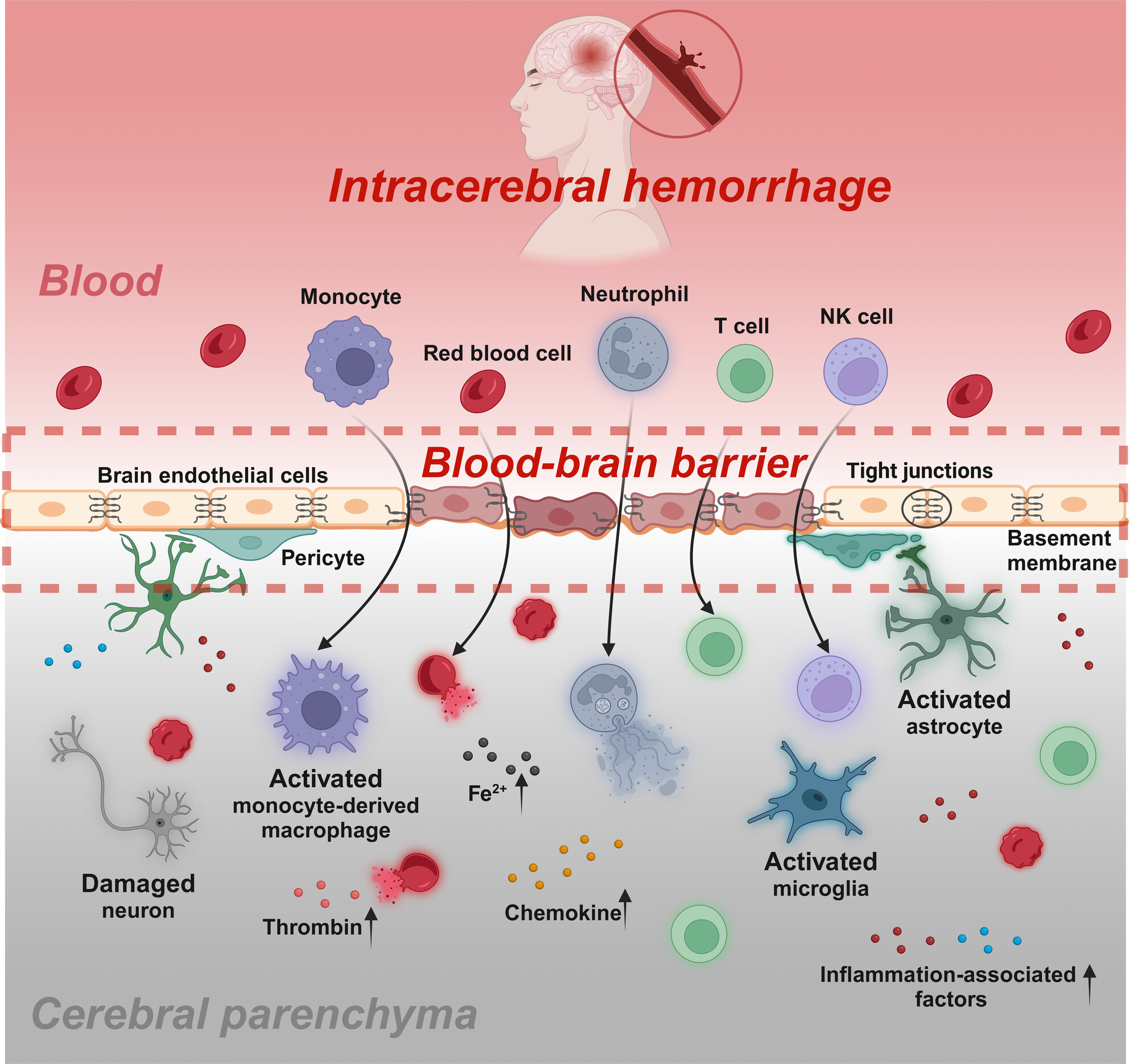
Immune-mediated disruption of the blood–brain barrier after intracerebral hemorrhage: Insights and potential therapeutic targets
- First Published: 21 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
NDC80/HEC1 promotes macrophage polarization and predicts glioma prognosis via single-cell RNA-seq and in vitro experiment
- First Published: 17 July 2024
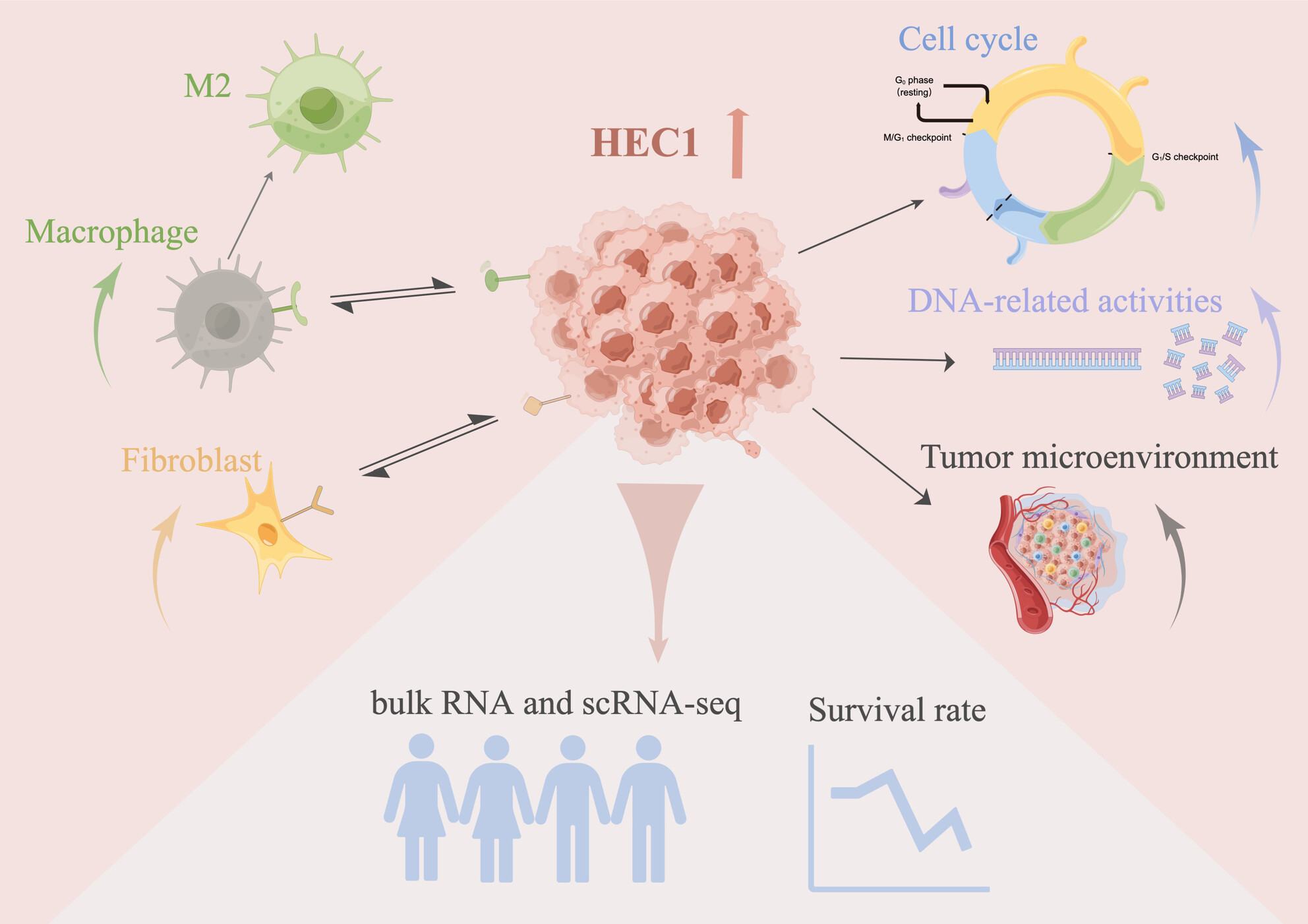
In summary, this study has revealed the role of NDC80/HEC1 in the process of glioma development and in the tumor microenvironment of glioma. The immunosuppressive property and role of HEC1 make it attractive to be used as novel prognostic biomarkers or effective therapeutic targets. Immunofluorescence of glioma tissue microarrays showed positive correlation of HEC1 expression with the malignancy degrees of glioma and a lower probability of patients with high HEC1 expression. In particular, HEC1 promotes development of glioma through the regulation of cell proliferation, cell cycle, DNA repair, and TME formation, possibly through transcriptional activation of E2F8. Moreover, tumor cells exhibiting HEC1 expression could shape the TME by interacting with macrophage and cancer-associated fibroblasts. Coculture confirmed that glioma cells devied-HEC1 promote macrophage migration and transform into M2. Our results provide further insight into the application of HEC1 in glioma (by Figdraw).
Ketogenic diet therapy leads to antiseizure medication reduction in children and adults with drug-resistant epilepsy
- First Published: 17 July 2024
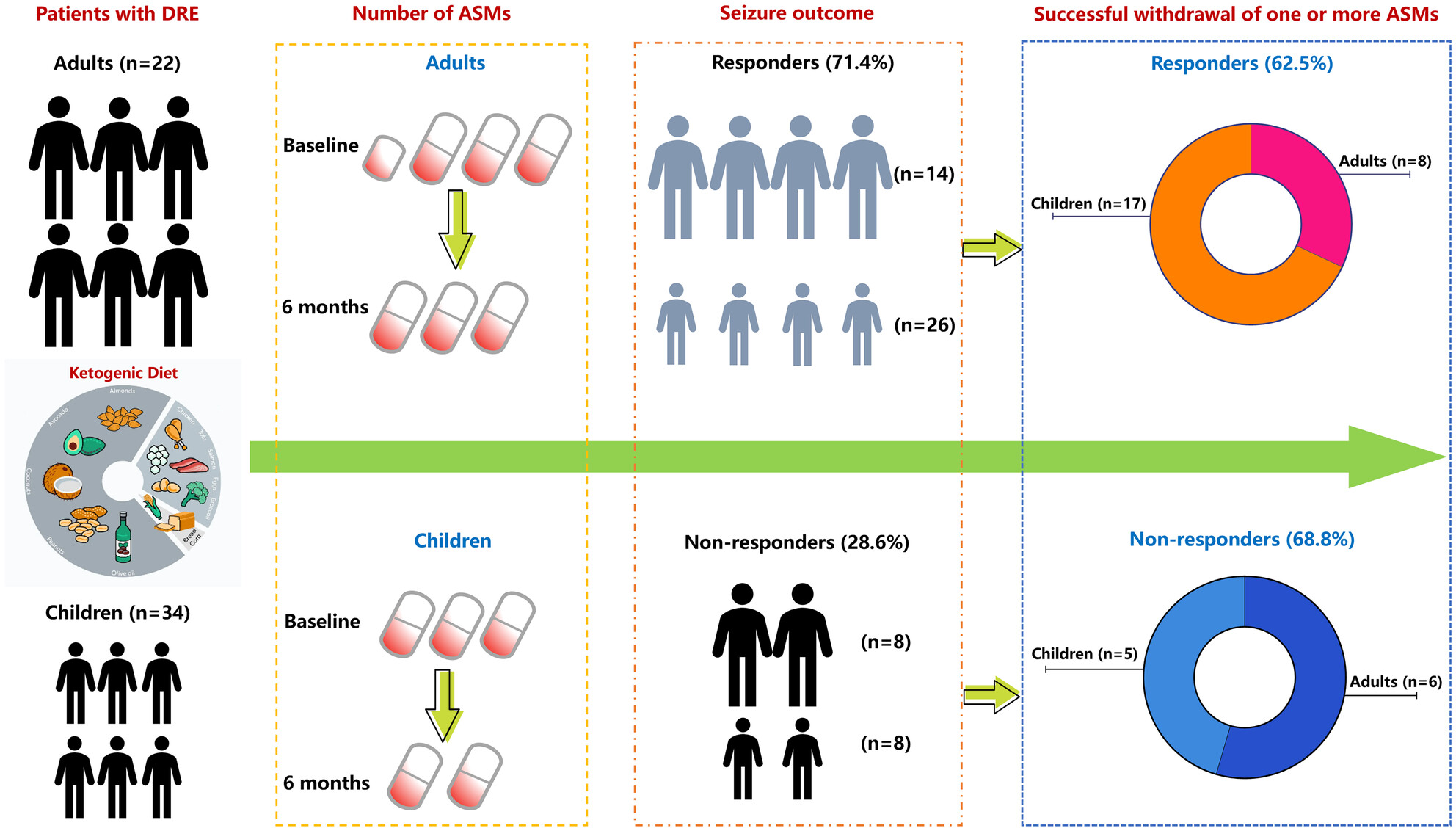
This study provides further evidence supporting safety of anti-seizure medications reduction or withdrawal during ketogenic diet therapy in both adult and children patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Additionally, it highlights that early anti-seizure medication reduction does not impact long-term outcomes of ketogenic diet therapy.
A predictive model combining connectomics and entropy biomarkers to discriminate long-term vagus nerve stimulation efficacy for pediatric patients with drug-resistant epilepsy
- First Published: 17 July 2024
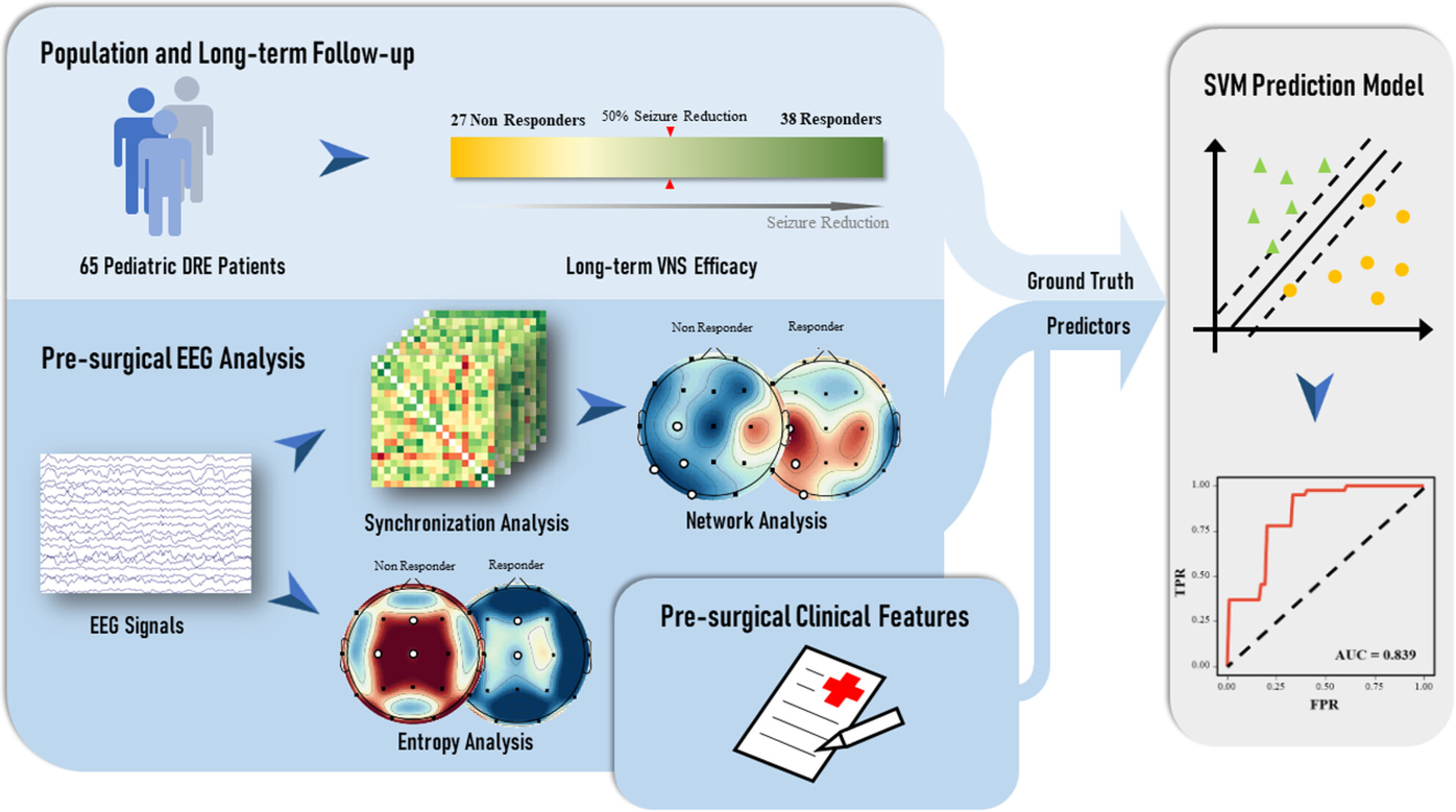
The long-term efficacy of VNS was assessed among 65 pediatric patients. Presurgical EEG analysis shows that VNS responders exhibit higher nodal efficiency in parietal-occipital EEG α activity and lower entropy in central-frontal EEG θ activity. The SVM model with clinical and EEG features for VNS efficacy shows high accuracy.
Propofol improves sleep deprivation-induced sleep structural and cognitive deficits via upregulating the BMAL1 expression and suppressing microglial M1 polarization
- First Published: 17 July 2024
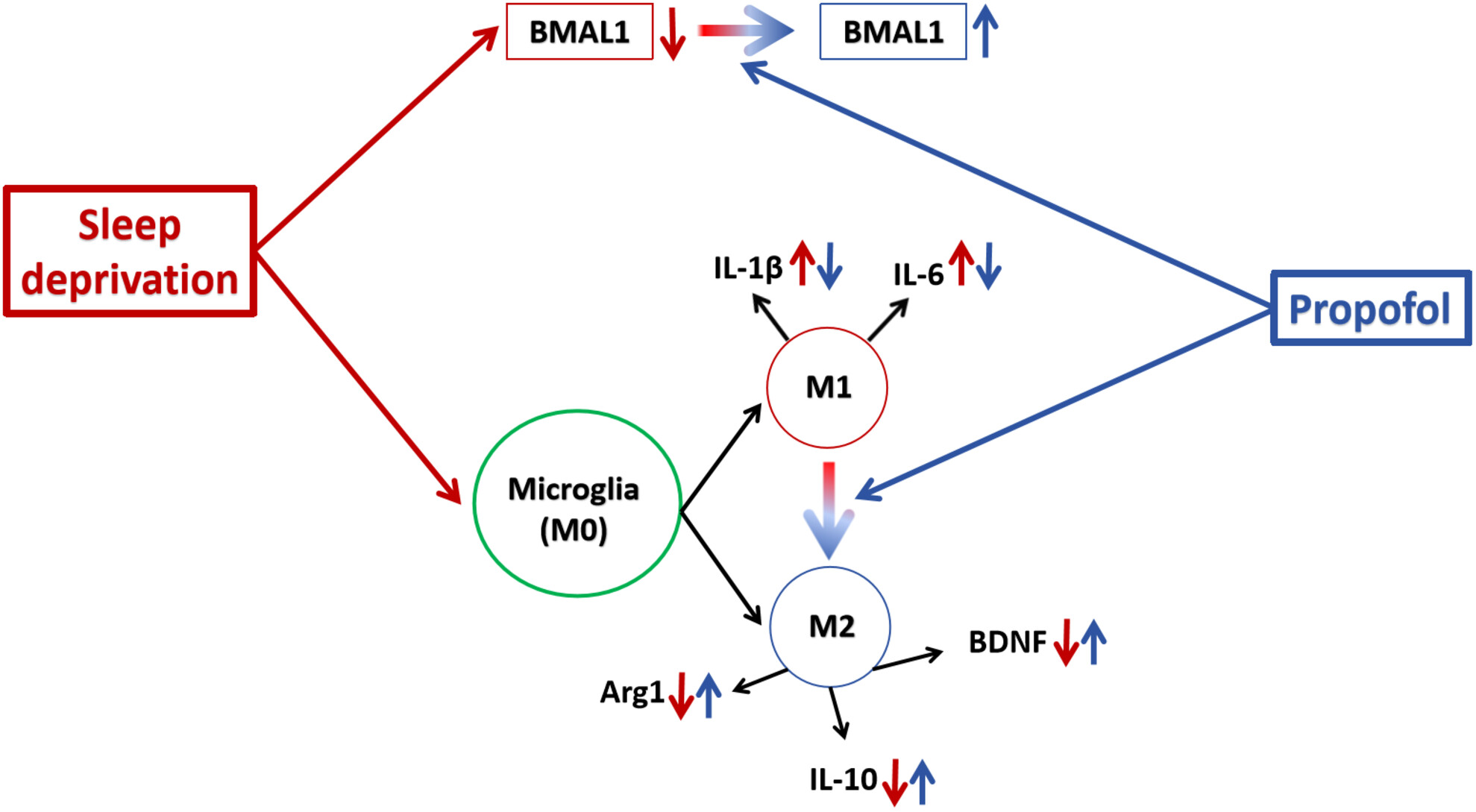
Acute sleep deprivation leads to cognitive deficits and disturbances in sleep structure, which are associated with microglia activation. Propofol works by inhibiting microglia, promoting the conversion of M1 to M2, reducing neuroinflammation, improving sleep quality, and reversing the cognitive deficits caused by sleep deprivation.
REVIEW
The neuroinflammatory role of microglia in Alzheimer's disease and their associated therapeutic targets
- First Published: 19 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Gray matter volume alterations in de novo Parkinson's disease: A mediational role in the interplay between sleep quality and anxiety
- First Published: 19 July 2024
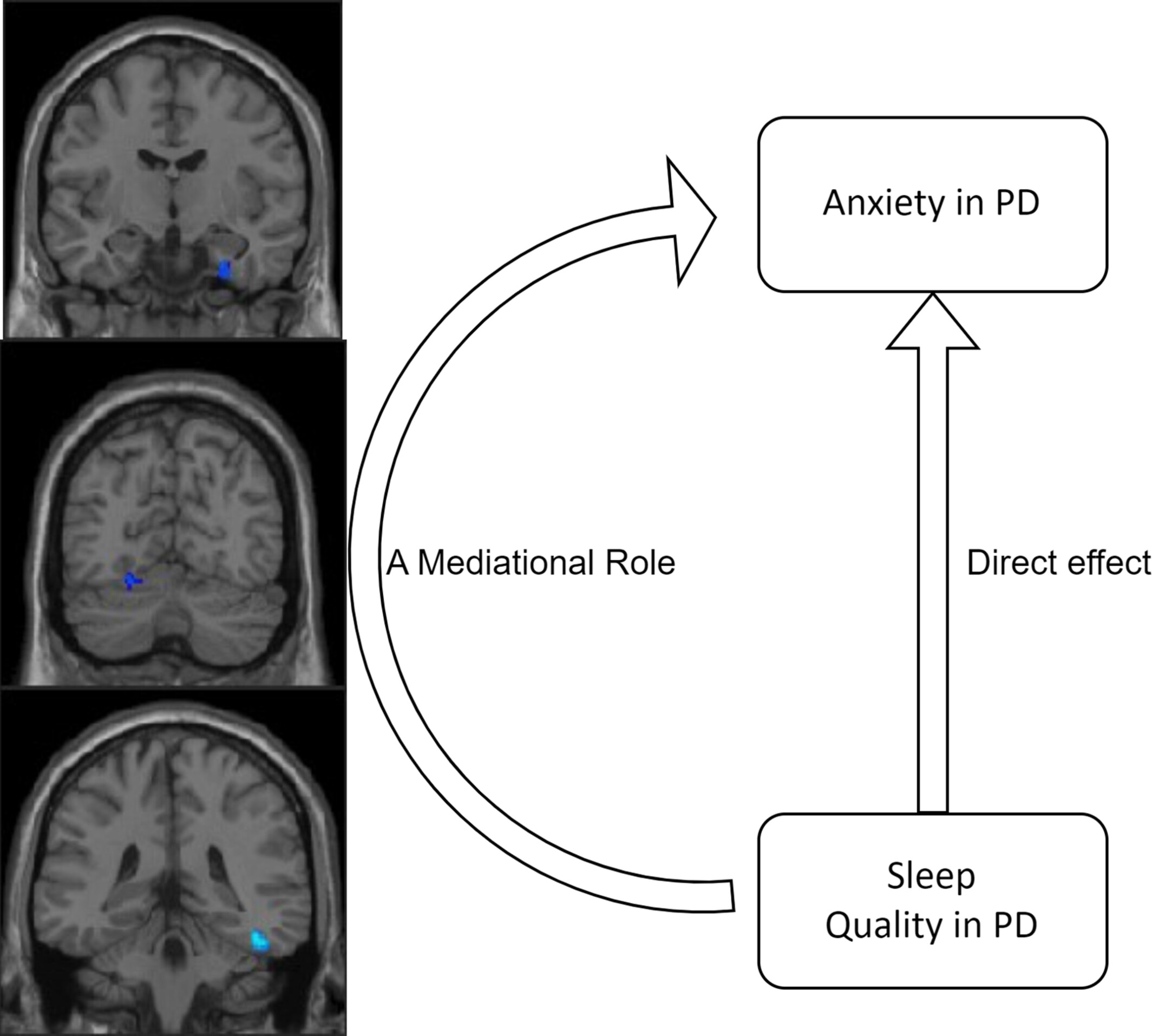
Compared to HCs and NA-PD patients, A-PD patients exhibited significantly reduced GMV in the fusiform gyrus and right inferior temporal gyrus. Our findings indicate that compromised sleep quality, under the pathological conditions of PD, may exacerbate the reduction in GMV within these regions, impairing the recognition of emotional facial expressions and thereby intensifying anxiety symptoms.
Neural substrates of predicting anhedonia symptoms in major depressive disorder via connectome-based modeling
- First Published: 22 July 2024
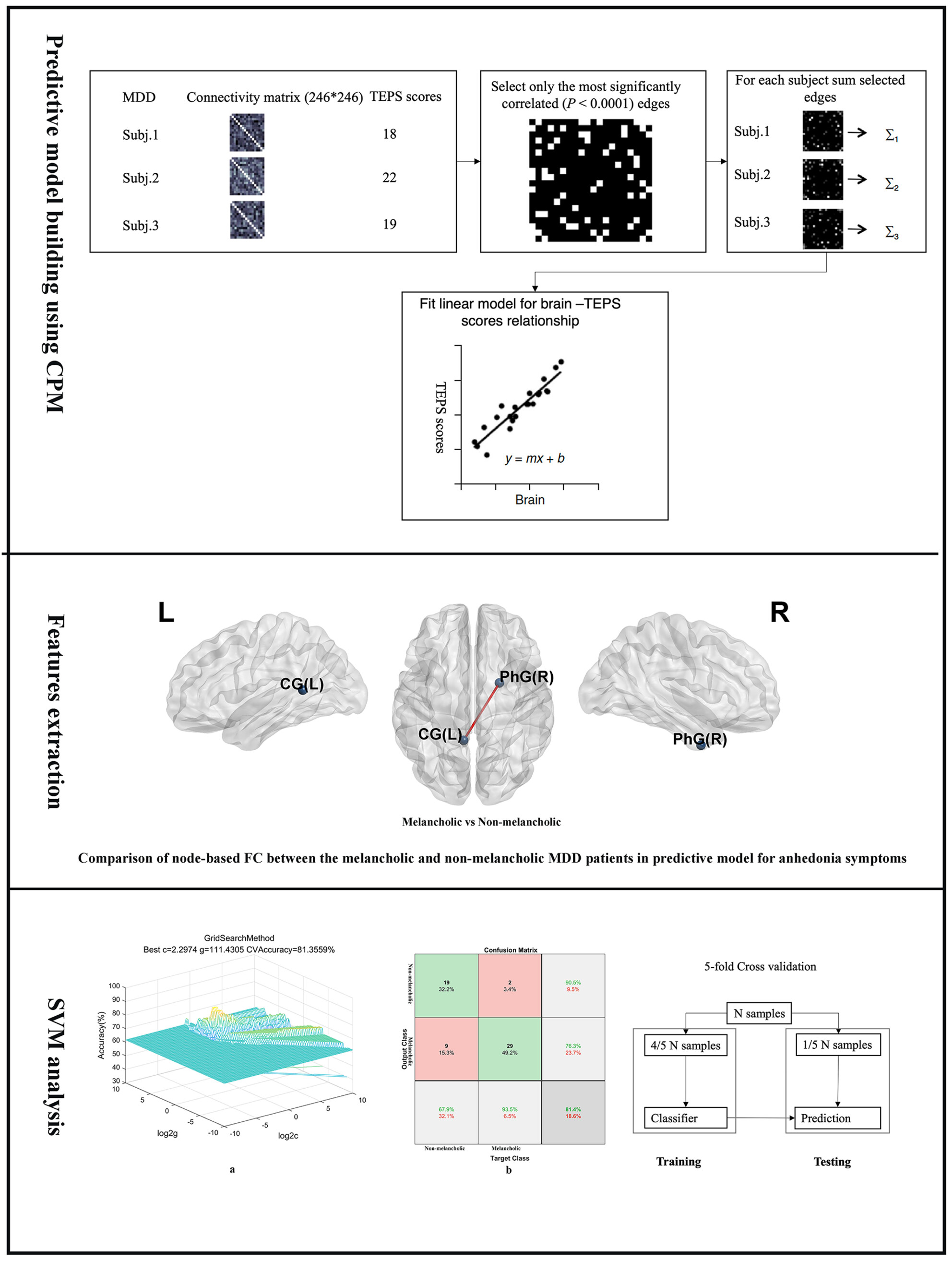
Our study aimed to identify a predictive model for anhedonia symptoms using connectome-based predictive modeling (CPM) in major depressive disorder (MDD). The abnormal functional connectivity patterns between the default mode network and the limbic network in the predictive networks serve as potential neurobiological markers to distinguish between melancholic and non-melancholic MDD. These findings revealed distinct neural substrates for anhedonia symptoms in melancholic and non-melancholic MDD.
REVIEW
Mechanism of ferroptosis regulating ischemic stroke and pharmacologically inhibiting ferroptosis in treatment of ischemic stroke
- First Published: 23 July 2024
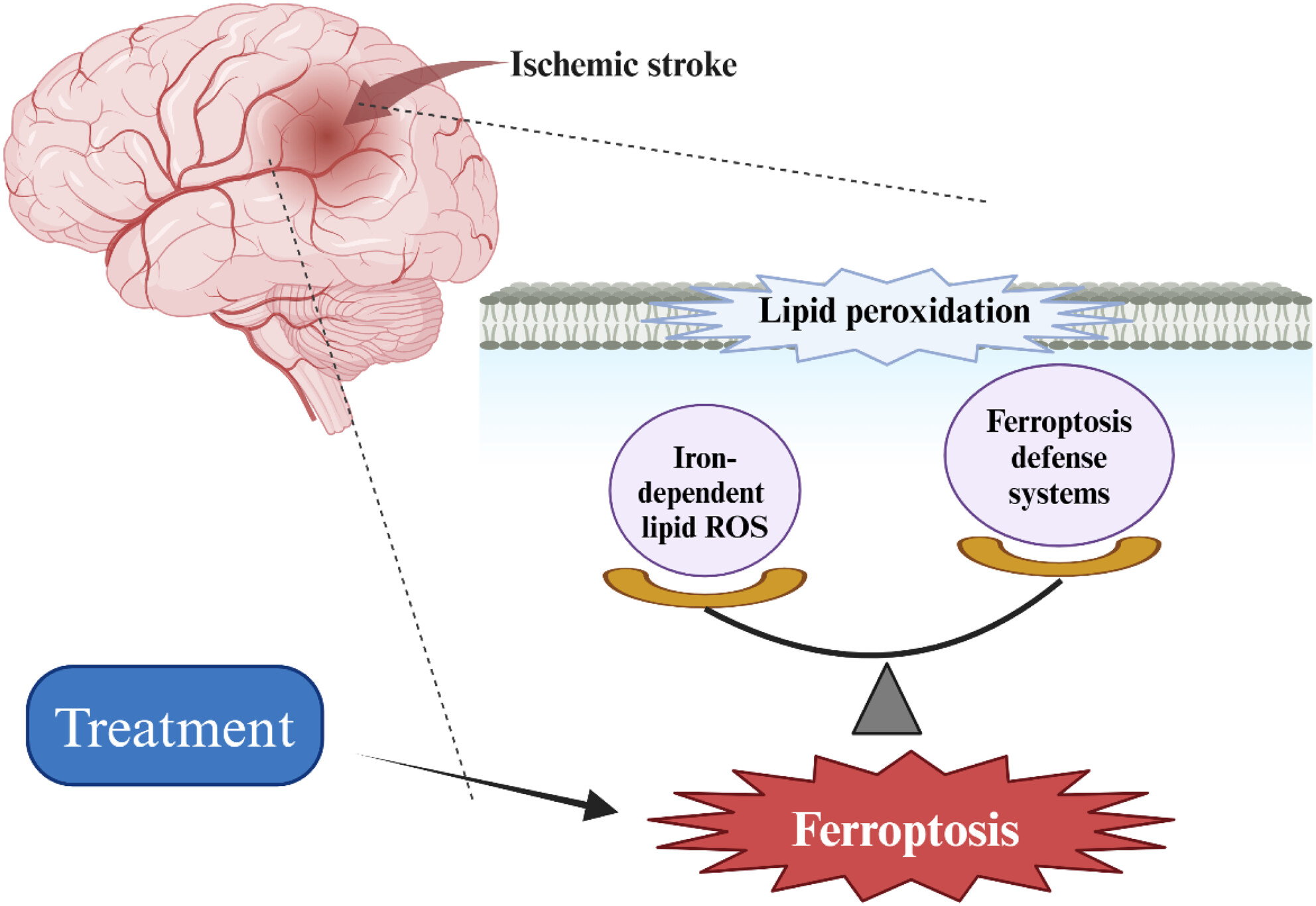
Ferroptosis plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of cerebral infarction, where the delicate balance between pro- and anti-ferroptotic factors critically influences the outcomes of an ischemic stroke. Our review aims to comprehensively elucidate the underlying mechanisms of ferroptosis and explore therapeutic strategies targeting ferroptosis in ischemic stroke.
CORRECTION
Correction to “Role of brain renin–angiotensin system in depression: A new perspective”
- First Published: 23 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
LncRNA H19 knockdown promotes neuropathologic and functional recovery via the Nrf2/HO-1 axis after traumatic brain injury
- First Published: 25 July 2024
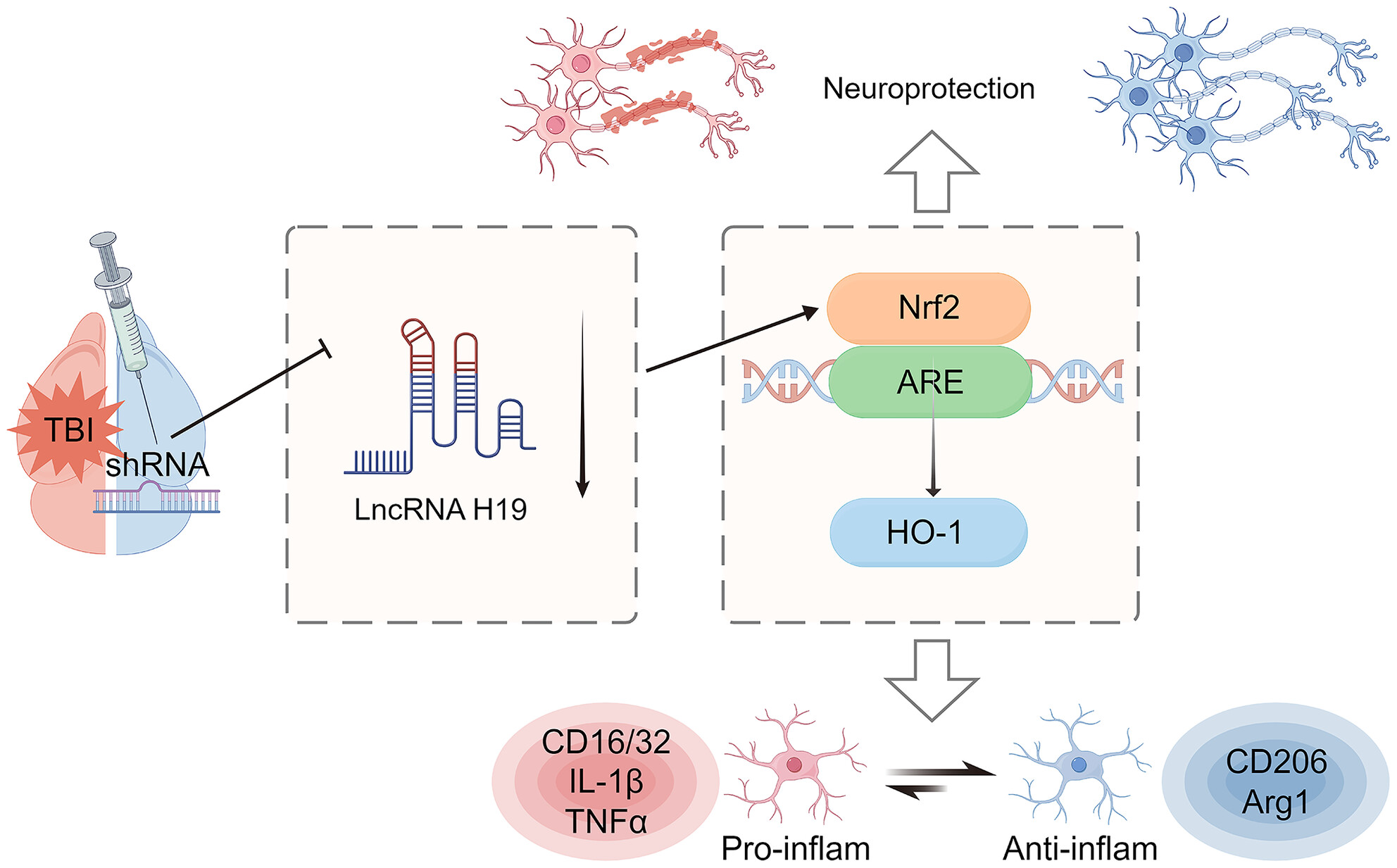
Knockdown of the lncRNA H19 significantly promotes recovery from traumatic brain injury (TBI) in mice, as evidenced by reduced neuroinflammation, attenuated tissue damage including gray and white matter, and improved neurological function. This neuroprotective effect was significantly mediated by activation of the Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway, revealing a potential target for therapeutic strategies for TBI.
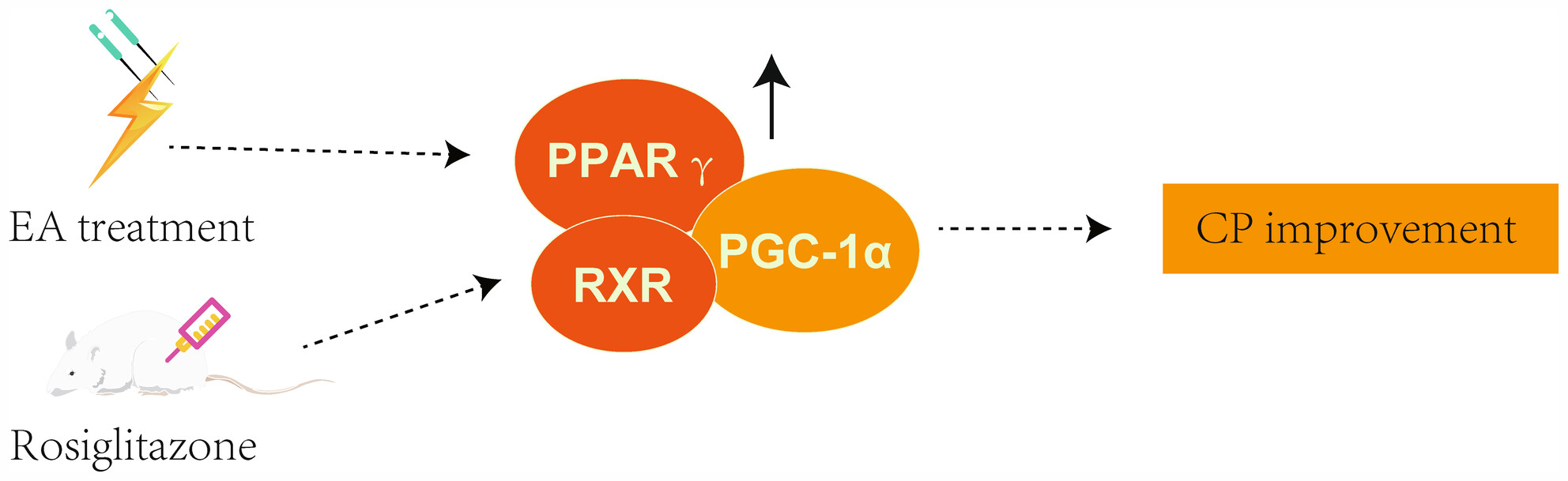
Electroacupuncture activates the peroxisome proliferators-activated receptor pathway to improve the phenotype of cerebral palsy
- First Published: 25 July 2024
METTL14-mediated upregulation of lncRNA HOTAIR represses PP1α expression by promoting H3K4me1 demethylation in oxycodone-treated mice
- First Published: 24 July 2024
REVIEW
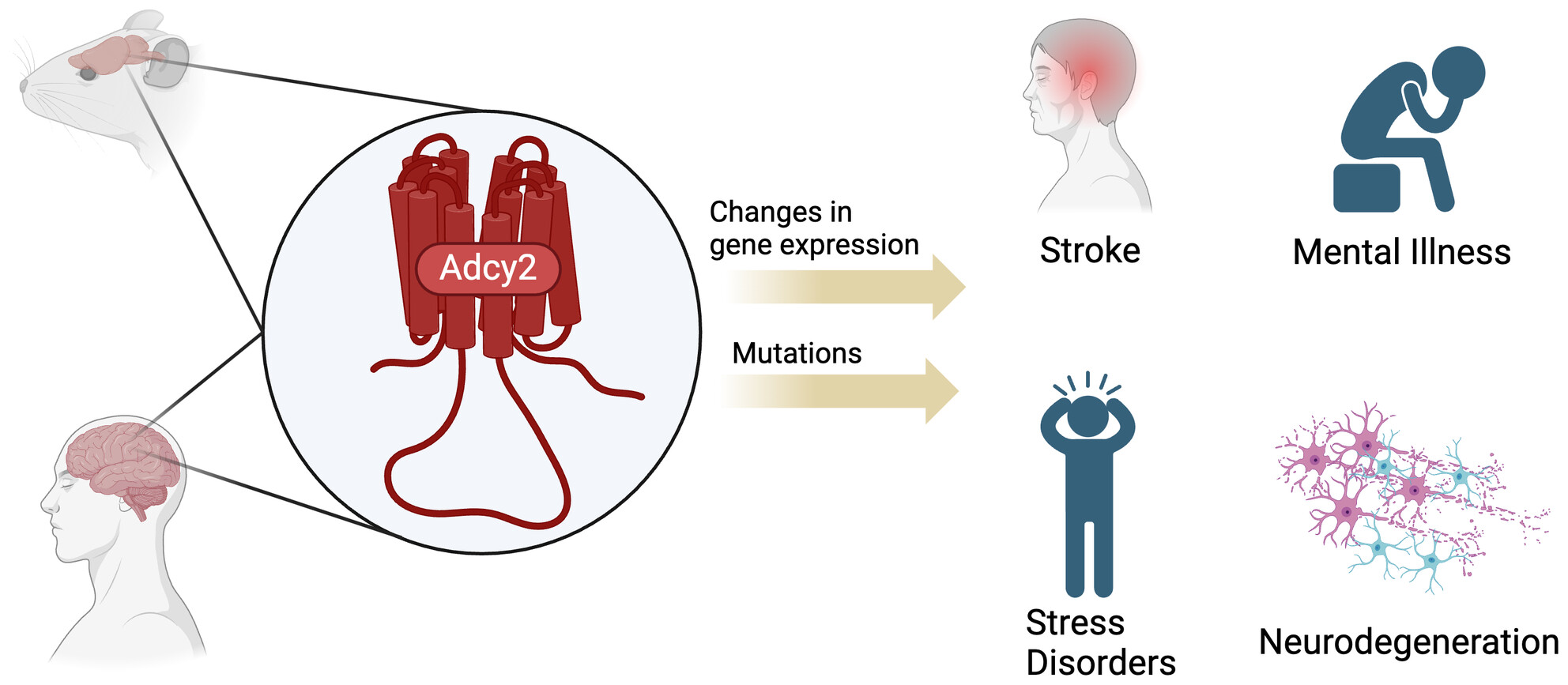
Adenylyl cyclase 2 expression and function in neurological diseases
- First Published: 28 July 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
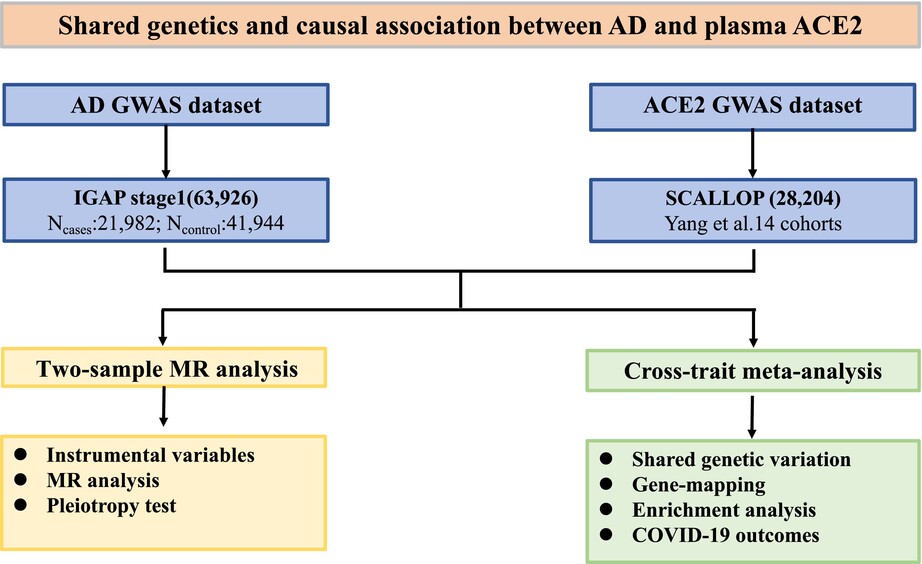
Shared genetics and causal association between plasma levels of SARS-CoV-2 entry receptor ACE2 and Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 26 July 2024
P7C3 suppresses astrocytic senescence to protect dopaminergic neurons: Implication in the mouse model of Parkinson’s disease
- First Published: 26 July 2024
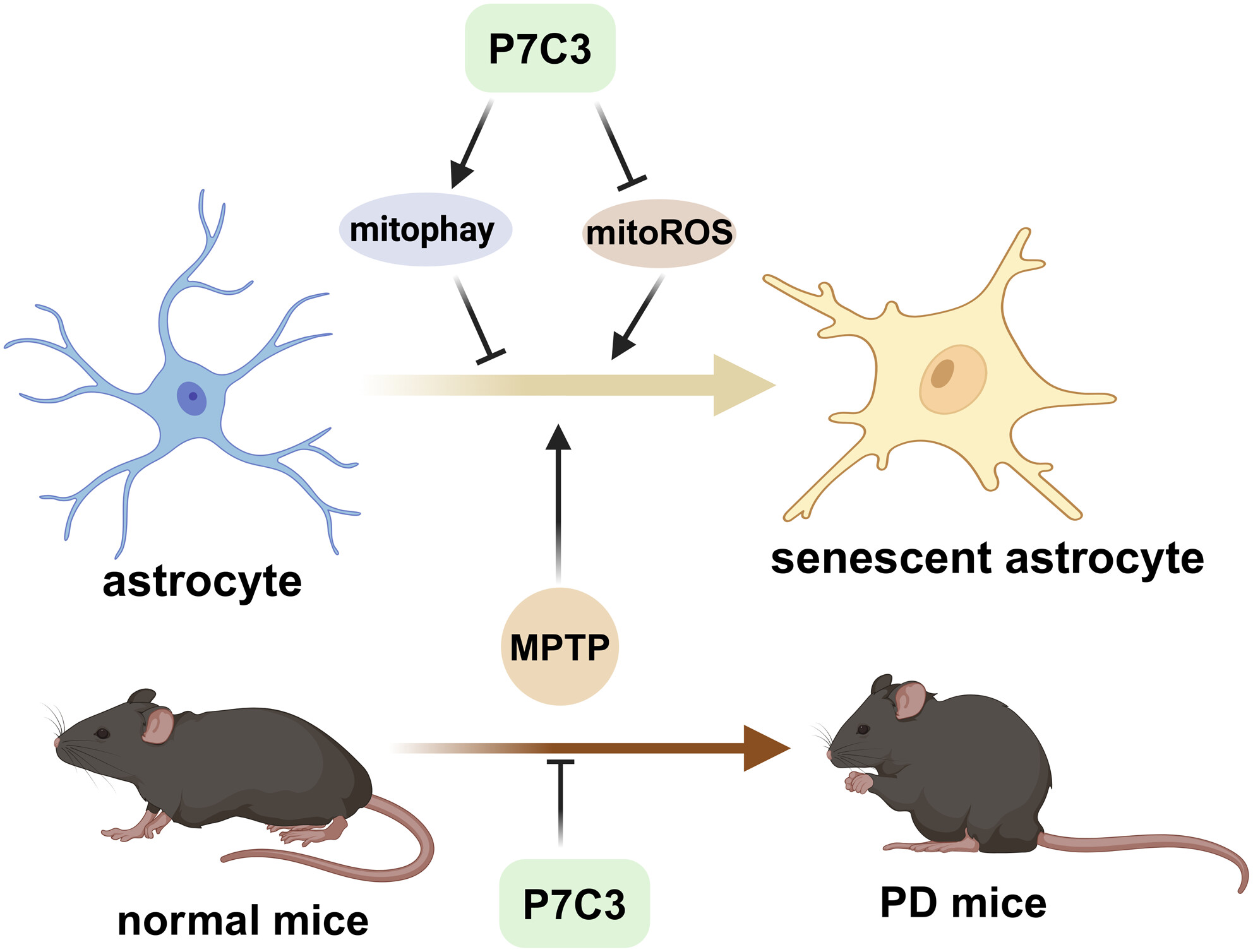
When astrocytes are exposed to neurotoxins (MPTP or rotenone), they undergo senescence and release excessive SASP factors such as IL-6, IL-1β, CXCL10, and MMP9. These SASP factors can harm nearby dopaminergic neurons. However, with the P7C3 treatment, senescent astrocytes could promote NRF2 nuclear translocation, leading to an increase in SIRT3 expression. This, in turn, further promotes mitophagy and inhibits mitoROS production, ultimately protecting dopaminergic neurons from damage.
Exploring brain asymmetry in early-stage Parkinson's disease through functional and structural MRI
- First Published: 26 July 2024
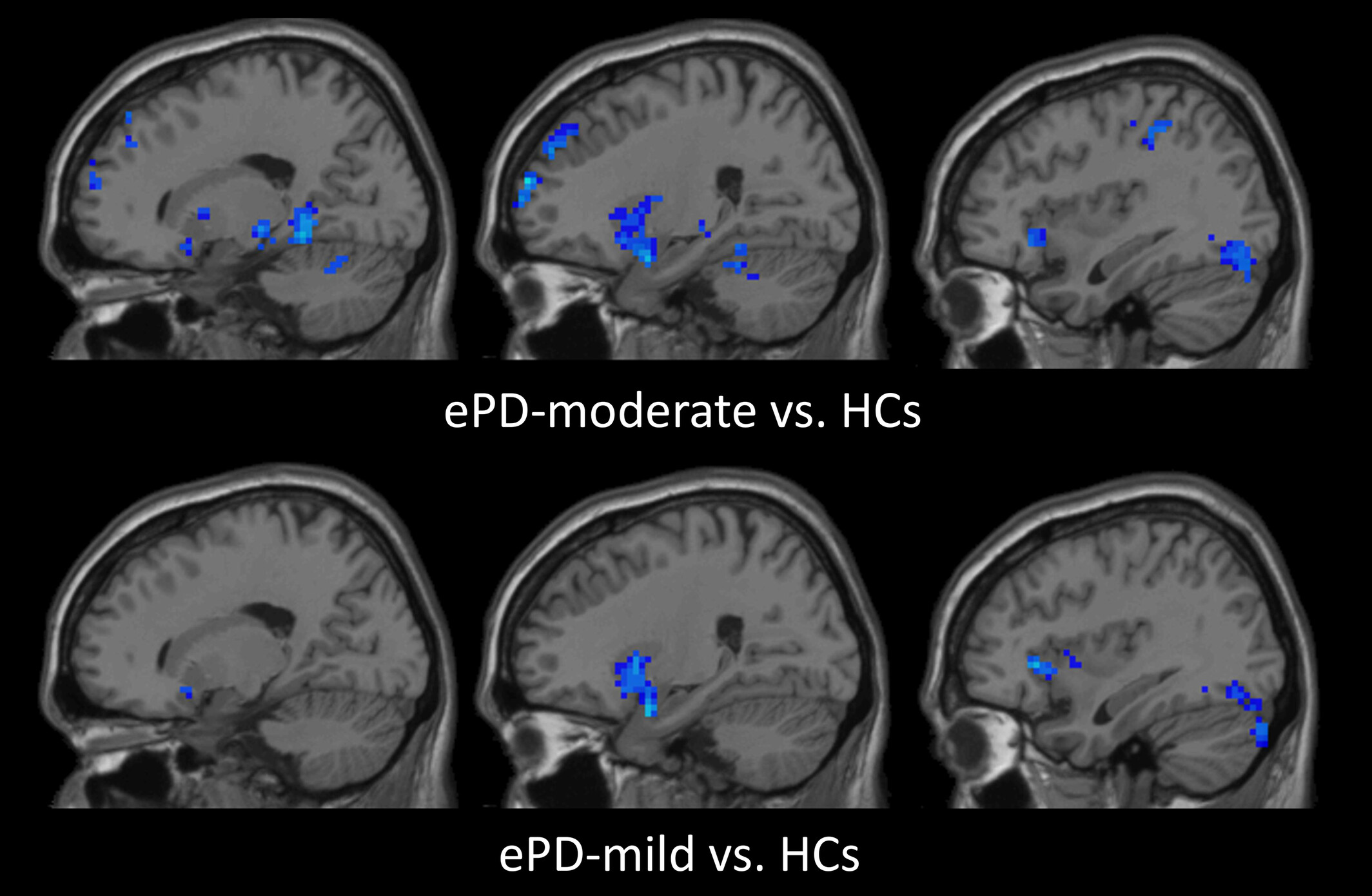
This graphical abstract depicts evolving brain functional asymmetry in early-stage Parkinson's disease (ePD). Comparing ePD mild and moderate groups with controls reveals increasing asymmetry akin to Lewy body spread from lower to higher brain regions. This insight offers a novel perspective on PD neuropathology and a potential progression biomarker.
Melatonin attenuates scopolamine-induced cognitive dysfunction through SIRT1/IRE1α/XBP1 pathway
- First Published: 26 July 2024
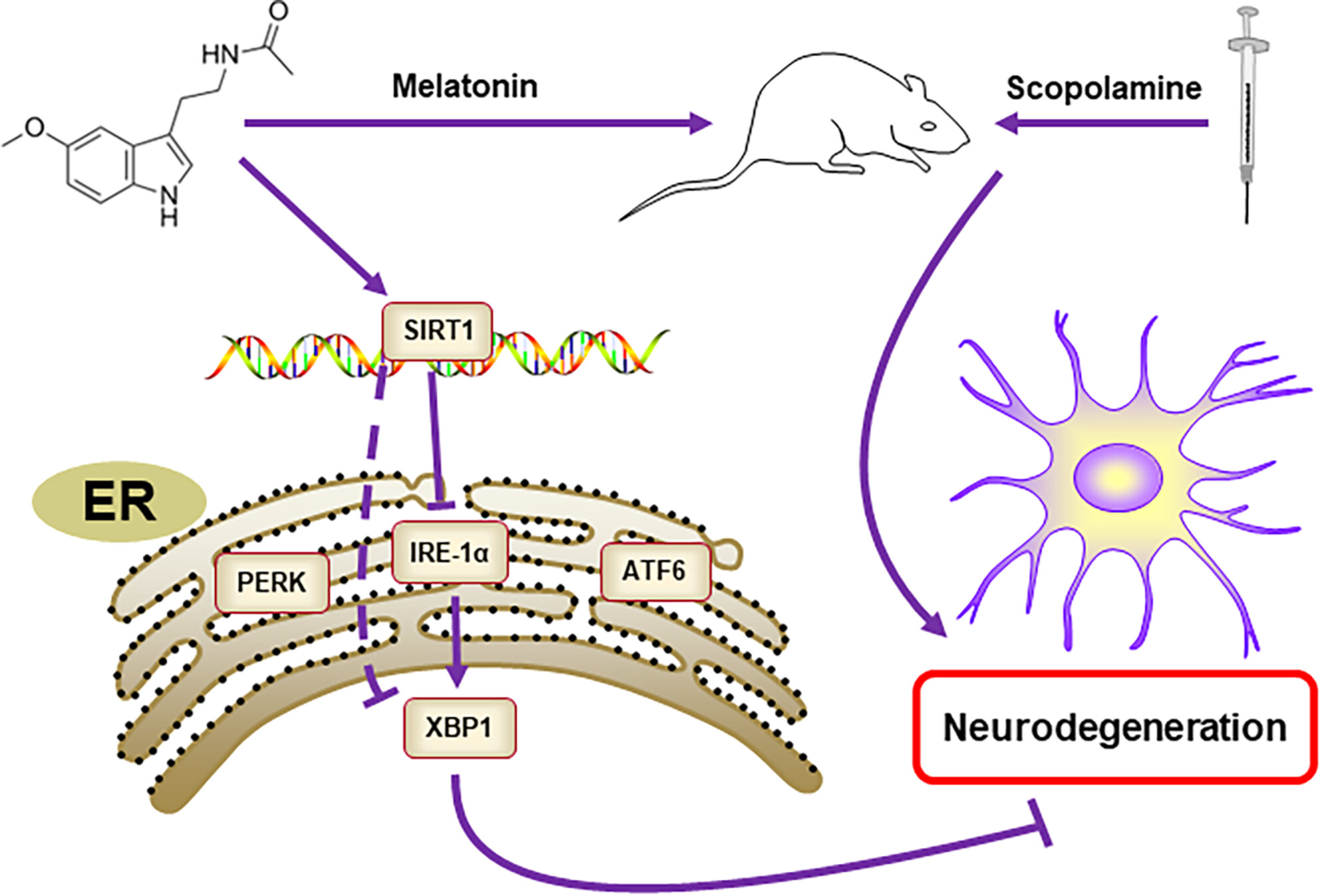
Melatonin is a hormone produced in the pineal gland, for adjusting the circadian rhythm of a vertebrate, particularly a mammal. In this study, it may ameliorate SCOP-induced cognitive dysfunction through SIRT1/IRE1α/XBP1 pathway. SIRT1 might be the key target of melatonin in the treatment of dementia.
The p75 neurotrophin receptor attenuates secondary thalamic damage after cortical infarction by promoting angiogenesis
- First Published: 28 July 2024
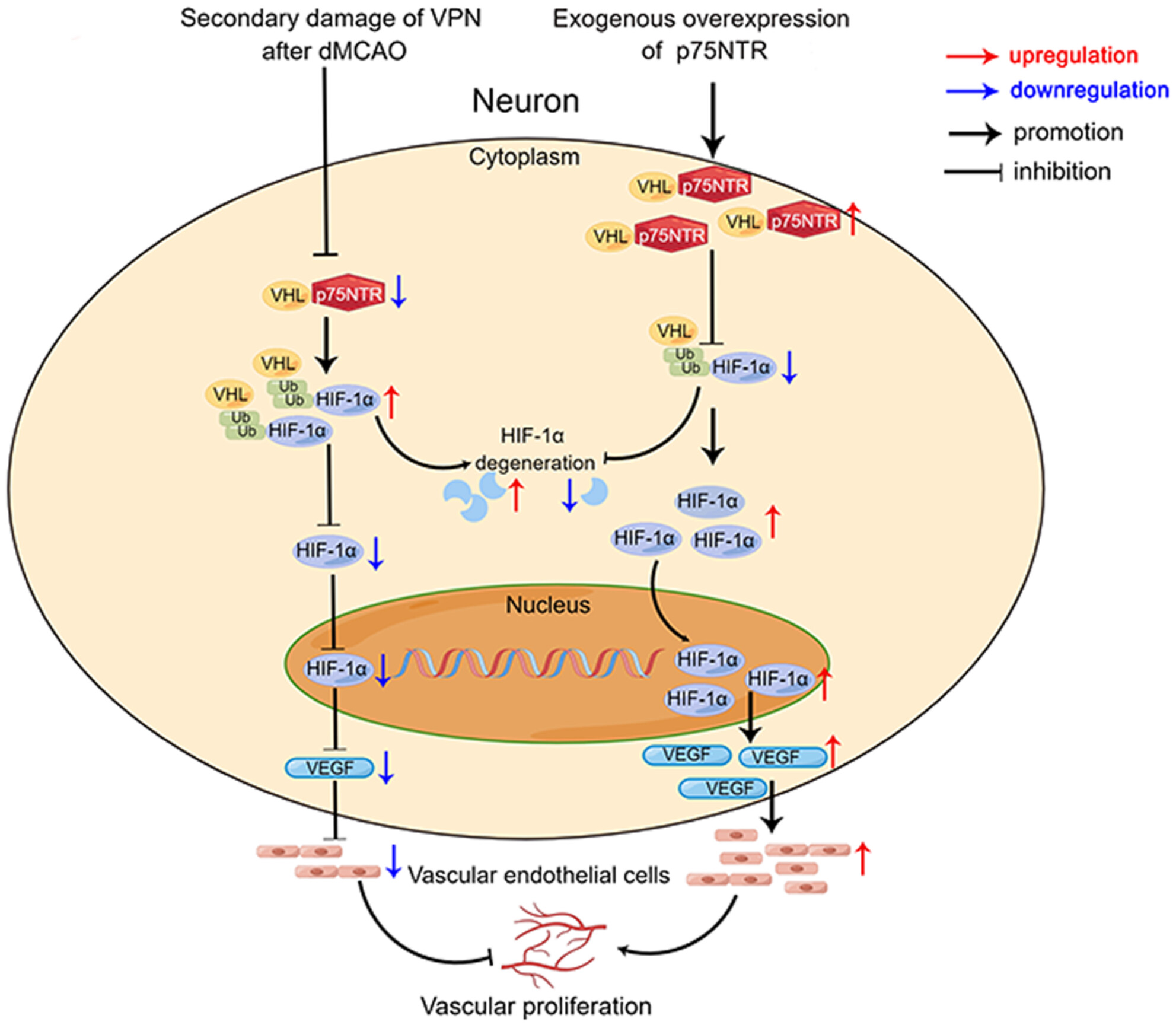
The expression of p75NTR and the interaction of p75NTR-VHL were decreased in the ipsilateral VPN after dMCAO, which in turn, increased the VHL-HIF-1α interaction, promoted the degradation of HIF-1α via ubiquitin proteasome pathway, downregulated the expression of VEGF and inhibited angiogenesis, ultimately leading to secondary thalamic damage. Instead, neuronal-targeted p75NTR overexpression enhanced the interaction of p75NTR-VHL and upregulated the expression of HIF-1α and VEGF in the ipsilateral VPN through inhibiting HIF-1α ubiquitination degradation mediated by VHL, which facilitates angiogenesis and increases CBF, consequently alleviating secondary thalamic damage after dMCAO.
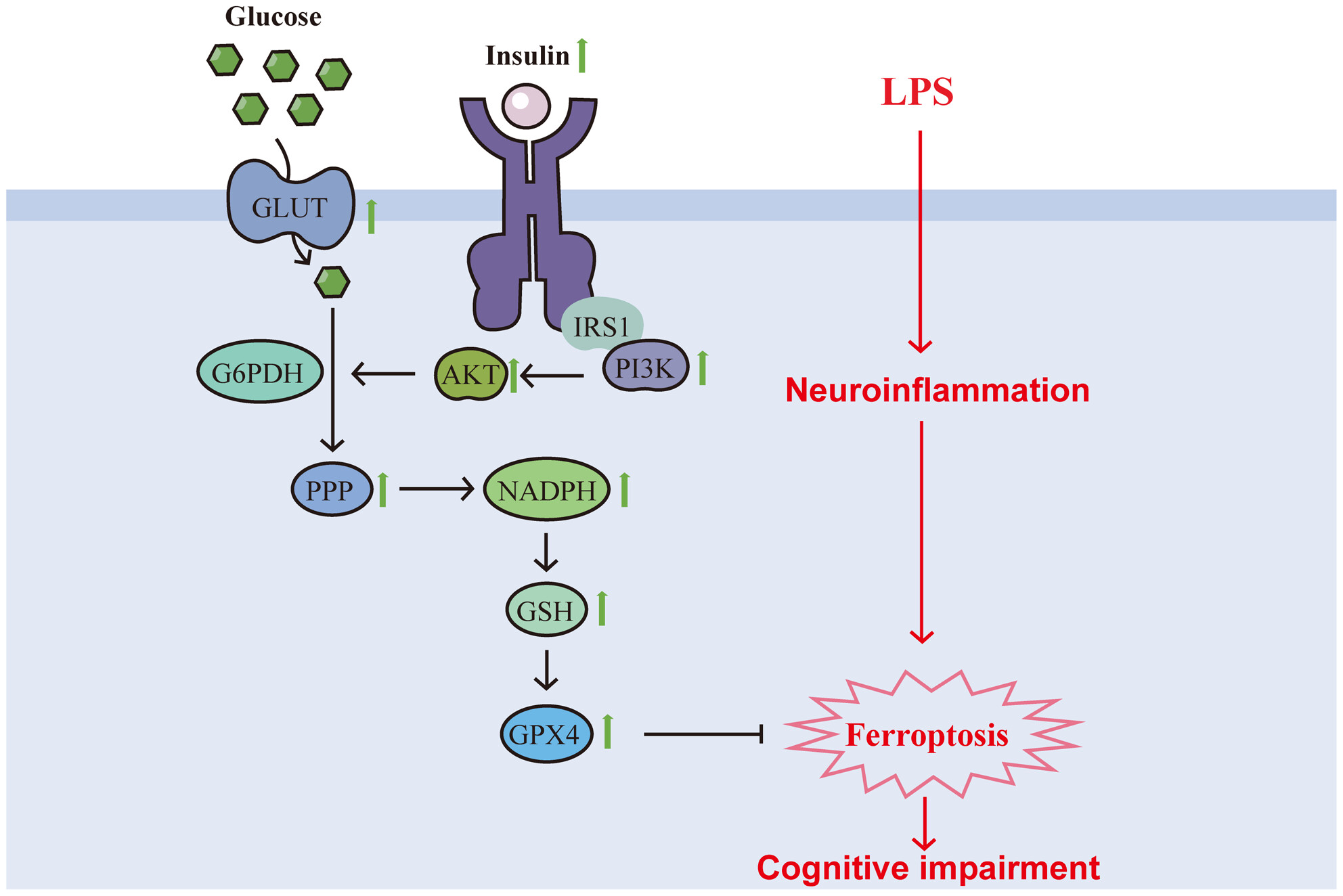
Insulin attenuates LPS-induced cognitive impairment and ferroptosis through regulation of glucose metabolism in hippocampus
- First Published: 28 July 2024
Effectiveness and mechanisms of combined use of antioxidant nutrients in protecting against oxidative stress-induced neuronal loss and related neurological deficits
- First Published: 28 July 2024
Comprehensive immune modulation mechanisms of Angong Niuhuang Wan in ischemic stroke: Insights from mass cytometry analysis
- First Published: 29 July 2024
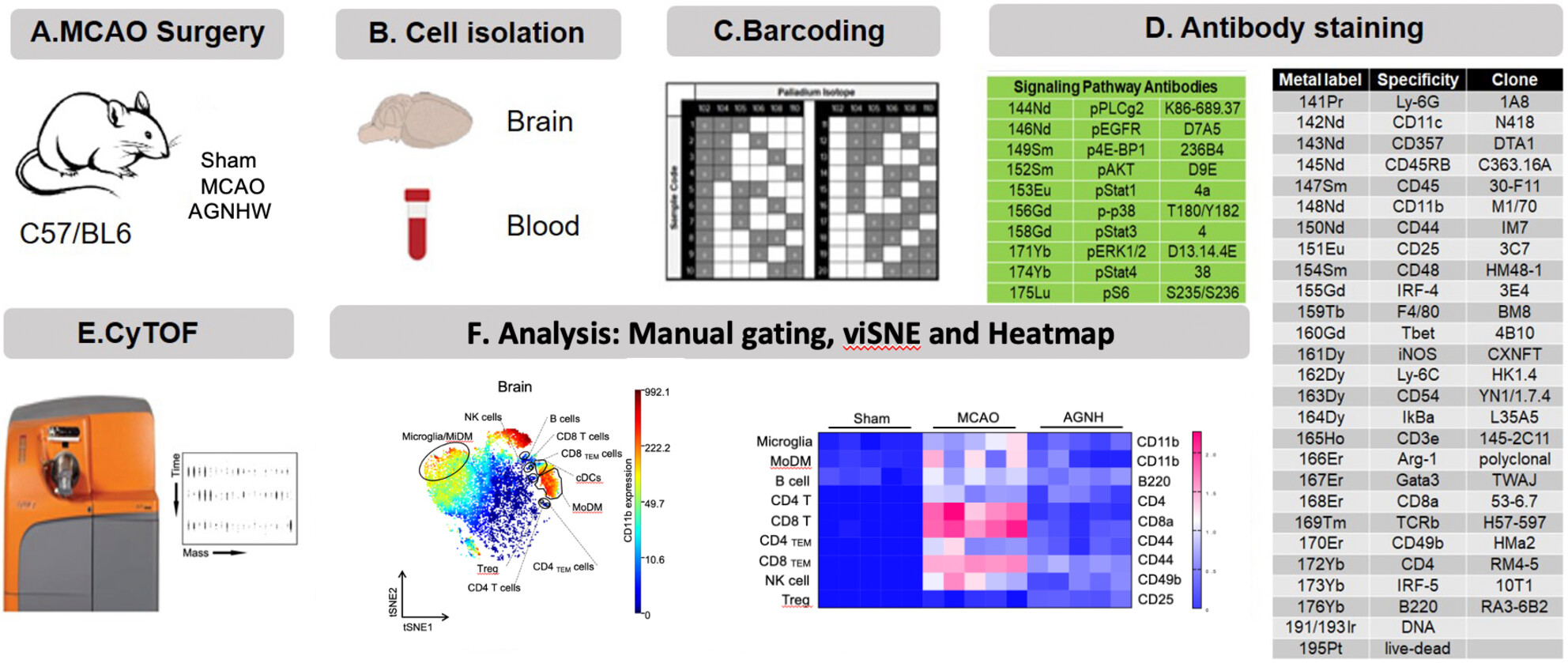
By employing the advanced CyTOF technique, we conducted an in-depth analysis to uncover the protective mechanisms of AGNHW. Leveraging the precision of CyTOF, our study provides a comprehensive understanding of AGNHW's therapeutic potential in ischemic stroke. It emphasizes its dual action, affecting both the cerebral and systemic aspects, and its nuanced modulation of cellular and molecular dynamics.
Identifying biomarkers related to motor function in chronic stroke: A fNIRS and TMS study
- First Published: 28 July 2024
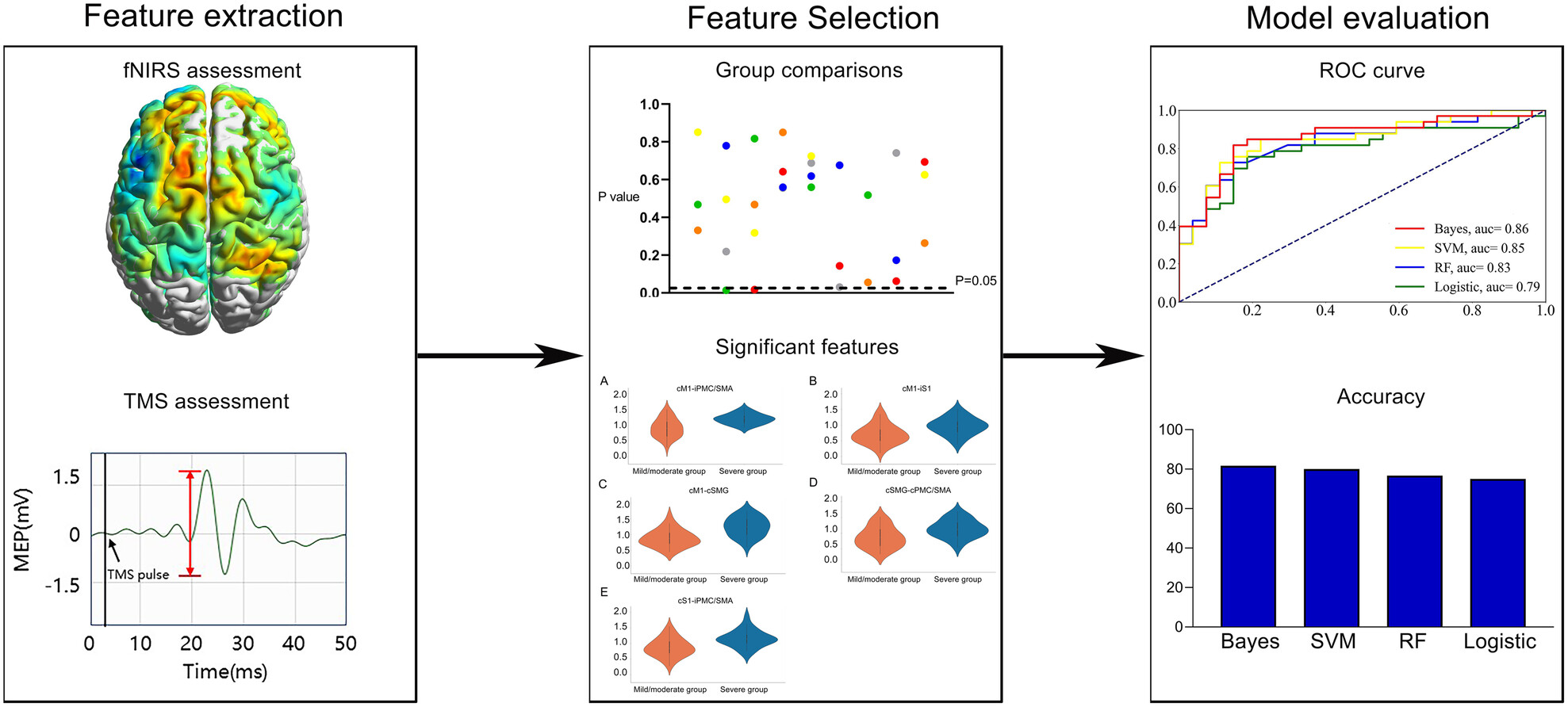
Content of the study. First, functional near-infrared spectroscopy and transcranial magnetic stimulation assessments were conducted, followed by feature extraction. Subsequently, independent t-tests and chi-squared tests were applied to reduce the feature dimensionality, and machine learning models were developed with the retained features. Finally, the performance of the models was evaluated by the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve and accuracy. Bayesian models effectively distinguished subgroups and identified the premotor cortex–primary motor cortex connection as highly contributory.